research

(Professor Song, Ph.D. candidates Kim, and Lim (from left))
A KAIST research team led by Professor Hyunjoon Song of the Department of Chemistry developed a metal oxide nanocatalyst that converts carbon dioxide to 99% pure methane. This technology directly uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into methane, which is more efficient in terms of energy storage capacity, compared to the conventional way of storing the electricity produced by solar cells in batteries. The research team used cheap catalytic materials to significantly enhance the reaction efficiency and selectivity of the chemical energy storage method.
This research was conducted as a joint research project with Professor Ki Min Nam at Mokpo National University with co-first authors Dr. Kyung-Lyul Bae and Ph.D. candidates Jinmo Kim and Chan Kyu Lim. The study was published in Nature Communications on November 7.
Although there is growing interest in sunlight as an energy resource, its usage has been limited to daytime and the power output varies with the weather. If sunlight could be directly converted to chemical energy, such as fuel, the limitations of energy storage and its usage could be overcome. In particular, the usage of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide, a main cause of the greenhouse effect in our atmosphere, is of great interest since both energy and environmental issues can be addressed. However, the stability of carbon dioxide made it difficult to convert it to other molecules. Thus, there was a need for a catalyst with enhanced efficiency and selectivity.
Professor Song’s team synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles, often used in sun cream. The nanoparticles were then bound to copper oxide as single particles, forming a colloidal form of zinc oxide-copper oxide nanoparticles. Zinc oxides produce high energy electrons using light, and this energy is used to convert carbon dioxide into methane. Further, zinc oxide can also produce electrons with light and transfer the electrons to copper oxide. Similar to the principles of photosynthesis in leaves, the electron transfer reaction could be maintained for a long time. As a consequence, although the reaction was conducted in aqueous solution, methane of 99% purity could be obtained from carbon dioxide.
Conventional heterogeneous photocatalysts were in solid powder form with irregular structures and were not dispersed in water. Professor Song’s team used a nanochemical synthesis method to control the structure of the catalyst particles to be regular and maintained over a large surface area. This led to increasing carbon dioxide conversion activity by hundreds of fold in solution compared to existing catalysts.
Professor Song said, “A long time will be needed for the commercialization of the direct conversion reaction of carbon dioxide using sunlight. However, the precise control of catalyst structures at nanoscale would enhance the efficiency of photocatalyst reactions.” He continued, “Applying this method to various phtocatalysts will maximize the catalysts performance.”
(Figure 1. Scheme for carbon dioxide conversion reaction using nano photocatalyst in aqueous solution)
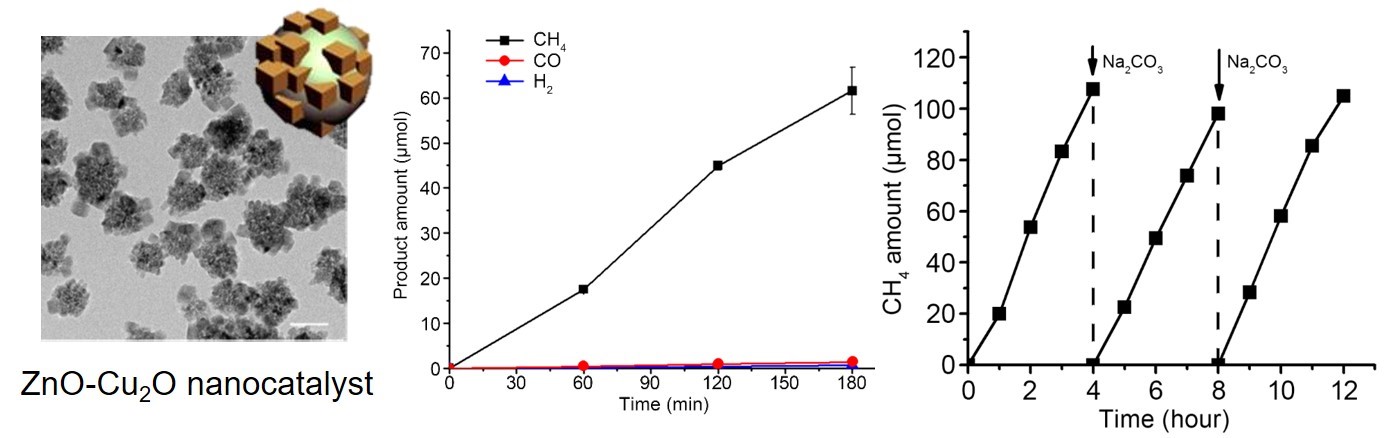
(Figure 2. Structure, photocatalytic CO2 conversion, and stability of ZnO-Cu2O nanocatalyst )
-
research A Hole in One for Holographic Display
(Professor YongKeun Park) Researchers have designed an ultrathin display that can project dynamic, multi-coloured, 3D holographic images, according to a study published in Nature Communications. The system’s critical component is a thin film of titanium filled with tiny holes that precisely correspond with each pixel in a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel. This film acts as a ‘photon sieve’ – each pinhole diffracts light emerging from them widely, resulting in a
2019-04-18 -
research Unravelling Inherent Electrocatalysis to Improve the Performance of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
(Figure 1. Electrode structure for the precise evaluation of the metal nanoparticles’ electrochemical catalytic characteristics at a high temperature.) A KAIST team presented an ideal electrode design to enhance the performance of high-temperature fuel cells. The new analytical platform with advanced nanoscale patterning method quantitatively revealed the electrochemical value of metal nanoparticles dispersed on the oxide electrode, thus leading to electrode design directions that c
2019-03-28 -
research New Catalyst for Synthesizing Chiral Molecules Selectively
(from left: Dr. Yoonsu Park and Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry) Molecules in nature often have “twin” molecules that look identical. In particular, the twin molecules that look like mirror images to each other are called enantiomers. However, even though they have the same type and number of elements, these twin molecules exhibit completely different properties. Professor Sukbok Chang and Dr. Yoonsu Park from the Department of Chemistry
2019-03-05 -
research New LSB with Theoretical Capacity over 90%
(Professor Hee-Tak Kim and Hyunwon Chu) A KAIST research team has developed a lithium sulfur battery (LSB) that realizes 92% of the theoretical capacity and an areal capacity of 4mAh/cm2. LSBs are gaining a great deal of attention as an alternative for lithium ion batteries (LIBs) because they have a theoretical energy density up to six to seven times higher than that of LIBs, and can be manufactured in a more cost-effective way. However, LSBs face the obstacle of
2019-02-11 -
research Noninvasive Light-Sensitive Recombinase for Deep Brain Genetic Manipulation
A KAIST team presented a noninvasive light-sensitive photoactivatable recombinase suitable for genetic manipulation in vivo. The highly light-sensitive property of photoactivatable Flp recombinase will be ideal for controlling genetic manipulation in deep mouse brain regions by illumination with a noninvasive light-emitting diode. This easy-to-use optogenetic module made by Professor Won Do Heo and his team will provide a side-effect free and expandable genetic manipulation tool for neurosci
2019-01-22