research
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee demonstrates the transfer printing of a large number of micro-sized inorganic semiconductor chips via the selective modulation of micro-vacuum force.
MicroLEDs are a light source for next-generation displays that utilize inorganic LED chips with a size of less than 100 μm. MicroLEDs have attracted a great deal of attention due to their superior electrical/optical properties, reliability, and stability compared to conventional displays such as LCD, OLED, and QD. To commercialize microLEDs, transfer printing technology is essential for rearranging microLED dies from a growth substrate onto the final substrate with a desired layout and precise alignment. However, previous transfer methods still have many challenges such as the need for additional adhesives, misalignment, low transfer yield, and chip damage.
Professor Lee’s research team has developed a micro-vacuum assisted selective transfer printing (µVAST) technology to transfer a large number of microLED chips by adjusting the micro-vacuum suction force.
The key technology relies on a laser-induced etching (LIE) method for forming 20 μm-sized micro-hole arrays with a high aspect ratio on glass substrates at fabrication speed of up to 7,000 holes per second. The LIE-drilled glass is connected to the vacuum channels, controlling the micro-vacuum force at desired hole arrays to selectively pick up and release the microLEDs. The micro-vacuum assisted transfer printing accomplishes a higher adhesion switchability compared to previous transfer methods, enabling the assembly of micro-sized semiconductors with various heterogeneous materials, sizes, shapes, and thicknesses onto arbitrary substrates with high transfer yields.
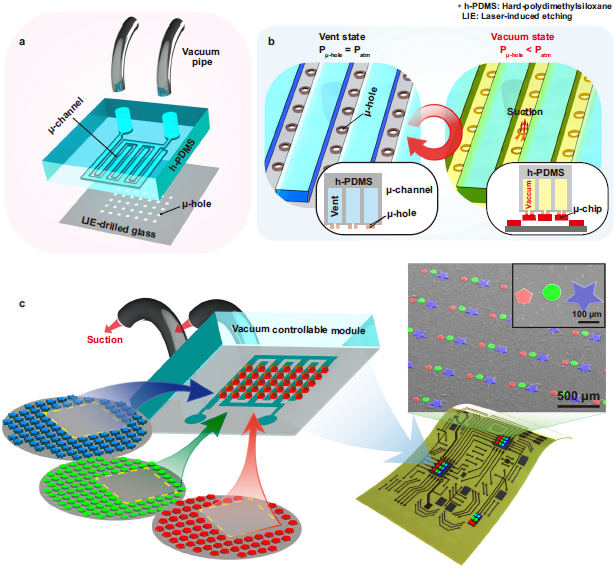
< Figure 01. Concept of micro-vacuum assisted selective transfer printing (μVAST). >
Professor Keon Jae Lee said, “The micro-vacuum assisted transfer provides an interesting tool for large-scale, selective integration of microscale high-performance inorganic semiconductors. Currently, we are investigating the transfer printing of commercial microLED chips with an ejector system for commercializing next-generation displays (Large screen TVs, flexible/stretchable devices) and wearable phototherapy patches.”
This result titled “Universal selective transfer printing via micro-vacuum force” was published in Nature Communications on November 26th, 2023. (DOI: 10.1038/S41467-023-43342-8)
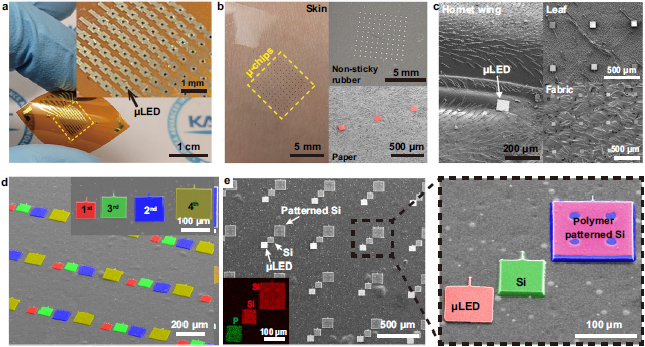
< Figure 02. Universal transfer printing of thin-film semiconductors via μVAST. >
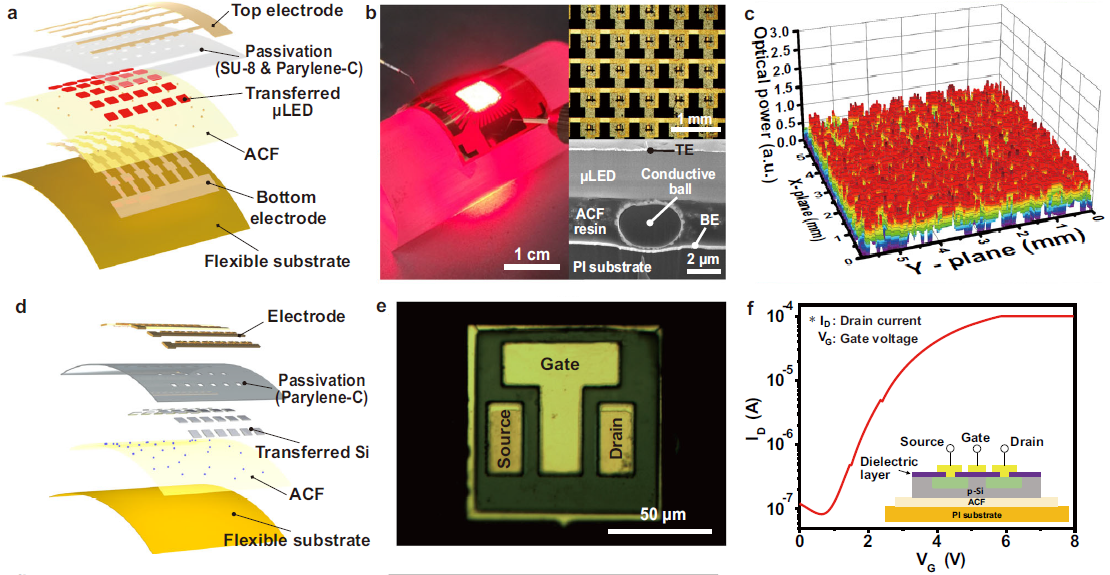
< Figure 03. Flexible devices fabricated by μVAST. >
Title: Entire process including LIE and µVAST
Vimeo link: https://vimeo.com/894430416?share=copy
-
event KAIST’s RAIBO2 becomes the World’s First Robo-dog to Successfully Complete a Full-course Marathon
KAIST's quadrupedal walking robot "RAIBO", which can run seamlessly on sandy beaches, has now evolved into "RAIBO2"and achieved the groundbreaking milestone by becomeing the world's first quadrupedal robot to successfully complete a full-course marathon in an official event. < Photo 1. A group photo of RAIBO2 and the team after completing the full-course marathon > KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of November that Professor Je Min Hwangbo's research team of t
2024-11-17 -
research KAIST Unveils New Possibilities for Treating Intractable Brain Tumors
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Heung Kyu Lee, KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, and Dr. Keun Bon Ku > Immunotherapy, which enhances the immune system's T cell response to eliminate cancer cells, has emerged as a key approach in cancer treatment. However, in the case of glioblastoma, an aggressive and treatment-resistant brain tumor, numerous clinical trials have failed to confirm their efficacy. Korean researchers have recently analyzed the mechanisms that cause T cell exhaus
2024-11-15 -
event KAIST’s Beach-Roaming Quadrupedal Robot “RAIBO” to Run a Marathon!
“RAIBO”, KAIST’s four-legged robot featuring remarkable agility even on challenging terrains like sandy beaches, is now set to be the first in the world to complete a full marathon. < Photo 1. A group photo of the research team of Professor Je Min Hwangbo (second from the right in the front row) of the Department of Mechanical Engineering who participated in the marathon event at 2024 Geumsan Insam Festival last September > On the 17th of November, KAIST (represen
2024-11-15 -
research KAIST Researchers Suggest an Extraordinary Alternative to Petroleum-based PET - Bacteria!
< (From left) Dr. Cindy Pricilia, Ph.D. Candidate Cheon Woo Moon, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee > Currently, the world is suffering from environmental problems caused by plastic waste. The KAIST research team has succeeded in producing a microbial-based plastic that is biodegradable and can replace existing PET bottles, making it a hot topic. Our university announced on the 7th of November that the research team of Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Ch
2024-11-08 -
research KAIST Researchers Introduce New and Improved, Next-Generation Perovskite Solar Cell
- KAIST-Yonsei university researchers developed innovative dipole technology to maximize near-infrared photon harvesting efficiency - Overcoming the shortcoming of existing perovskite solar cells that cannot utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy - Development of next-generation solar cell technology with high efficiency and high stability that can absorb near-infrared light beyond the existing visible light range with a perovskite-dipole-organic semiconductor hybrid structure &l
2024-10-31