Engineering
-
 Engineered E. coli Using Formic Acid and CO2 As a C1-Refinery Platform Strain
(Figure: Formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathways consisting of the reconstructed THF cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. This schematic diagram shows the formic acid and CO2 assimilation procedure through the pathway. Plasmids used in this study and the genetic engineering performed in this study are illustrated.)
A research group at KAIST has developed an engineered E. coli strain that converts formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produces cellular energy from formic acid through reconstructed one-carbon pathways. The strategy described in this study provides a new platform for producing value-added chemicals from one-carbon sources.
Formic acid is a carboxylic acid composed of one carbon. Formic acid was produced from CO2 by the chemical method. Recently, the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center has successfully developed a biological process that produces formic acid from carbon monoxide for the first time. Formic acid is in a liquid state when at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. In addition, it is chemically stable and less toxic, thus, easy to store and transport. Therefore, it can be used as an alternative carbon source in the microbial fermentation process. In order to produce value-added chemicals using formic acid, a metabolic pathway that converts formic acid into cellular molecules composed of multiple carbons is required. However, a metabolic pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid into cellular molecules has not been developed. This acted as an obstacle for the production of value-added chemicals using formic acid
A research group of Ph.D. student Junho Bang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. This study, entitled “Assimilation of Formic Acid and CO2 by Engineered Escherichia coli Equipped with Reconstructed One-Carbon Assimilation Pathways”, has been published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on September 18.
There has been increasing interest in utilizing formic acid as an alternative carbon source for the production of value-added chemicals. This research reports the development of an engineered E. coli strain that can convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produce cellular energy from formic acid through the reconstructed one-carbon pathways.
The metabolic pathway that efficiently converts formic acid and CO2 into pyruvate was constructed by the combined use of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. The tetrahydrofolate cycle was reconstructed by utilizing Methylobacterium extorquens formate-THF ligase, methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase, and methylene-THF dehydrogenase. The glycine cleavage reaction was reversed by knocking out the repressor gene (gcvR) and overexpressing the gcvTHP genes that encode enzymes related with the glycine cleavage reaction. Formic acid and CO2 conversion to pyruvate was increased via metabolic engineering of the E. coli strain equipped with the one-carbon assimilation pathway.
In addition, in order to reduce glucose consumption and increase formic acid consumption, Candida boidnii formate dehydrogenase was additionally introduced to construct a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid. This reduces glucose consumption and increases formic acid consumption.
The reconstructed one-carbon pathways can supply cellular molecules and cellular energies from the formic acid and CO2. Thus, the engineered E. coli strain equipped with the formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathway and cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid showed cell growth from formic acid and CO2 without glucose. Cell growth was monitored and 13C isotope analysis was performed to confirm E. coli growth from the formic acid and CO2. It was found that the engineered E. coli strain sustained cell growth from the formic acid and CO2 without glucose.
Professor Lee said, “To construct the C1-refinery system, a platform strain that can convert one-carbon materials to higher carbon materials needs to be developed. In this report, a one-carbon pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate was developed and a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid was introduced. This resulted in an engineered E. coli strain that can efficiently utilize formic acid as a carbon source while glucose consumption was reduced. The reconstructed one-carbon pathways in this research will be useful for the construction of the C1-refinery system.”
This work was supported by the C1 Gas Refinery Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2016M3D3A1A01913250). For further information: Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, Tel: +82-42-350-3930)
2018.09.18 View 5909
Engineered E. coli Using Formic Acid and CO2 As a C1-Refinery Platform Strain
(Figure: Formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathways consisting of the reconstructed THF cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. This schematic diagram shows the formic acid and CO2 assimilation procedure through the pathway. Plasmids used in this study and the genetic engineering performed in this study are illustrated.)
A research group at KAIST has developed an engineered E. coli strain that converts formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produces cellular energy from formic acid through reconstructed one-carbon pathways. The strategy described in this study provides a new platform for producing value-added chemicals from one-carbon sources.
Formic acid is a carboxylic acid composed of one carbon. Formic acid was produced from CO2 by the chemical method. Recently, the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center has successfully developed a biological process that produces formic acid from carbon monoxide for the first time. Formic acid is in a liquid state when at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. In addition, it is chemically stable and less toxic, thus, easy to store and transport. Therefore, it can be used as an alternative carbon source in the microbial fermentation process. In order to produce value-added chemicals using formic acid, a metabolic pathway that converts formic acid into cellular molecules composed of multiple carbons is required. However, a metabolic pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid into cellular molecules has not been developed. This acted as an obstacle for the production of value-added chemicals using formic acid
A research group of Ph.D. student Junho Bang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. This study, entitled “Assimilation of Formic Acid and CO2 by Engineered Escherichia coli Equipped with Reconstructed One-Carbon Assimilation Pathways”, has been published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on September 18.
There has been increasing interest in utilizing formic acid as an alternative carbon source for the production of value-added chemicals. This research reports the development of an engineered E. coli strain that can convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate and produce cellular energy from formic acid through the reconstructed one-carbon pathways.
The metabolic pathway that efficiently converts formic acid and CO2 into pyruvate was constructed by the combined use of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage reaction. The tetrahydrofolate cycle was reconstructed by utilizing Methylobacterium extorquens formate-THF ligase, methenyl-THF cyclohydrolase, and methylene-THF dehydrogenase. The glycine cleavage reaction was reversed by knocking out the repressor gene (gcvR) and overexpressing the gcvTHP genes that encode enzymes related with the glycine cleavage reaction. Formic acid and CO2 conversion to pyruvate was increased via metabolic engineering of the E. coli strain equipped with the one-carbon assimilation pathway.
In addition, in order to reduce glucose consumption and increase formic acid consumption, Candida boidnii formate dehydrogenase was additionally introduced to construct a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid. This reduces glucose consumption and increases formic acid consumption.
The reconstructed one-carbon pathways can supply cellular molecules and cellular energies from the formic acid and CO2. Thus, the engineered E. coli strain equipped with the formic acid and CO2 assimilation pathway and cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid showed cell growth from formic acid and CO2 without glucose. Cell growth was monitored and 13C isotope analysis was performed to confirm E. coli growth from the formic acid and CO2. It was found that the engineered E. coli strain sustained cell growth from the formic acid and CO2 without glucose.
Professor Lee said, “To construct the C1-refinery system, a platform strain that can convert one-carbon materials to higher carbon materials needs to be developed. In this report, a one-carbon pathway that can efficiently convert formic acid and CO2 to pyruvate was developed and a cellular energy producing pathway from formic acid was introduced. This resulted in an engineered E. coli strain that can efficiently utilize formic acid as a carbon source while glucose consumption was reduced. The reconstructed one-carbon pathways in this research will be useful for the construction of the C1-refinery system.”
This work was supported by the C1 Gas Refinery Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2016M3D3A1A01913250). For further information: Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST (leesy@kaist.ac.kr, Tel: +82-42-350-3930)
2018.09.18 View 5909 -
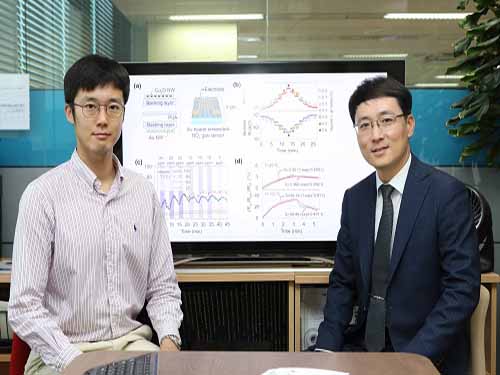 Transfering Nanowires onto a Flexible Substrate
(from left: PhD Min-Ho Seo and Professor Jun-Bo Yoon)
Boasting excellent physical and chemical properties, nanowires (NWs) are suitable for fabricating flexible electronics; therefore, technology to transfer well-aligned wires plays a crucial role in enhancing performance of the devices. A KAIST research team succeeded in developing NW-transfer technology that is expected to enhance the existing chemical reaction-based NW fabrication technology that has this far showed low performance in applicability and productivity.
NWs, one of the most well-known nanomaterials, have the structural advantage of being small and lightweight. Hence, NW-transfer technology has drawn attention because it can fabricate high-performance, flexible nanodevices with high simplicity and throughput.
A conventional nanowire-fabrication method generally has an irregularity issue since it mixes chemically synthesized nanowires in a solution and randomly distributes the NWs onto flexible substrates. Hence, numerous nanofabrication processes have emerged, and one of them is master-mold-based, which enables the fabrication of highly ordered NW arrays embedded onto substrates in a simple and cost-effective manner, but its employment is limited to only some materials because of its chemistry-based NW-transfer mechanism, which is complex and time consuming. For the successful transfer, it requires that adequate chemicals controlling the chemical interfacial adhesion between the master mold, NWs, and flexible substrate be present.
Here, Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his team from the School of Electrical Engineering introduced a material-independent mechanical-interlocking-based nanowire-transfer (MINT) method to fabricate ultralong and fully aligned NWs on a large flexible substrate in a highly robust manner.
This method involves sequentially forming a nanosacrificial layer and NWs on a nanograting substrate that becomes the master mold for the transfer, then weakening the structure of the nanosacrificial layer through a dry etching process. The nanosacrificial layer very weakly holds the nanowires on the master mold. Therefore, when using a flexible substrate material, the nanowires are very easily transferred from the master mold to the substrate, just like a piece of tape lifting dust off a carpet.
This technology uses common physical vapor deposition and does not rely on NW materials, making it easy to fabricate NWs onto the flexible substrates.
Using this technology, the team was able to fabricate a variety of metal and metal-oxide NWs, including gold, platinum, and copper – all perfectly aligned on a flexible substrate. They also confirmed that it can be applied to creating stable and applicable devices in everyday life by successfully applying it to flexible heaters and gas sensors.
PhD Min-Ho Seo who led this research said, “We have successfully aligned various metals and semiconductor NWs with excellent physical properties onto flexible substrates and applied them to fabricated devices. As a platform-technology, it will contribute to developing high-performing and stable electronic devices.”
This research was published in ACS Nano on May 24.
Figure 1. Photograph of the fabricated wafer-scale fully aligned and ultralong Au nanowire array on a flexible substrate
2018.09.17 View 5613
Transfering Nanowires onto a Flexible Substrate
(from left: PhD Min-Ho Seo and Professor Jun-Bo Yoon)
Boasting excellent physical and chemical properties, nanowires (NWs) are suitable for fabricating flexible electronics; therefore, technology to transfer well-aligned wires plays a crucial role in enhancing performance of the devices. A KAIST research team succeeded in developing NW-transfer technology that is expected to enhance the existing chemical reaction-based NW fabrication technology that has this far showed low performance in applicability and productivity.
NWs, one of the most well-known nanomaterials, have the structural advantage of being small and lightweight. Hence, NW-transfer technology has drawn attention because it can fabricate high-performance, flexible nanodevices with high simplicity and throughput.
A conventional nanowire-fabrication method generally has an irregularity issue since it mixes chemically synthesized nanowires in a solution and randomly distributes the NWs onto flexible substrates. Hence, numerous nanofabrication processes have emerged, and one of them is master-mold-based, which enables the fabrication of highly ordered NW arrays embedded onto substrates in a simple and cost-effective manner, but its employment is limited to only some materials because of its chemistry-based NW-transfer mechanism, which is complex and time consuming. For the successful transfer, it requires that adequate chemicals controlling the chemical interfacial adhesion between the master mold, NWs, and flexible substrate be present.
Here, Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his team from the School of Electrical Engineering introduced a material-independent mechanical-interlocking-based nanowire-transfer (MINT) method to fabricate ultralong and fully aligned NWs on a large flexible substrate in a highly robust manner.
This method involves sequentially forming a nanosacrificial layer and NWs on a nanograting substrate that becomes the master mold for the transfer, then weakening the structure of the nanosacrificial layer through a dry etching process. The nanosacrificial layer very weakly holds the nanowires on the master mold. Therefore, when using a flexible substrate material, the nanowires are very easily transferred from the master mold to the substrate, just like a piece of tape lifting dust off a carpet.
This technology uses common physical vapor deposition and does not rely on NW materials, making it easy to fabricate NWs onto the flexible substrates.
Using this technology, the team was able to fabricate a variety of metal and metal-oxide NWs, including gold, platinum, and copper – all perfectly aligned on a flexible substrate. They also confirmed that it can be applied to creating stable and applicable devices in everyday life by successfully applying it to flexible heaters and gas sensors.
PhD Min-Ho Seo who led this research said, “We have successfully aligned various metals and semiconductor NWs with excellent physical properties onto flexible substrates and applied them to fabricated devices. As a platform-technology, it will contribute to developing high-performing and stable electronic devices.”
This research was published in ACS Nano on May 24.
Figure 1. Photograph of the fabricated wafer-scale fully aligned and ultralong Au nanowire array on a flexible substrate
2018.09.17 View 5613 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 6227
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 6227 -
 Electron Heating in Weakly Ionized Collisional Plasmas
(from left: Professor Wonho Choe and Research Professor Sanghoo Park)
A KAIST research team successfully identified the underlying principles behind electron heating, which is one of the most important phenomena in plasmas. As the electric heating determines wide range of physical and chemical properties of plasmas, this outcome will allow relevant industries to extend and effectively customize a range of plasma characteristics for their specific needs.
Plasma, frequently called the fourth state of matter, can be mostly formed by artificially energizing gases in standard temperature (25°C) and pressure (1 atm) range. Among the many types of plasma, atmospheric-pressure plasmas have been gaining a great deal of attention due to their unique features and applicability in various scientific and industrial fields.
Because plasma characteristics strongly depends on gas pressure in the sub-atmospheric to atmospheric pressure range, characterizing the plasma at different pressures is a prerequisite for understanding the fundamental principles of plasmas and for their industrial applications.
In that sense, information on the spatio-temporal evolution in the electron density and temperature is very important because various physical and chemical reactions within a plasma arise from electrons. Hence, electron heating has been an interesting topic in the field of plasma.
Because collisions between free electrons and neutral gases are frequent under atmospheric-pressure conditions, there are physical limits to measuring the electron density and temperature in plasmas using conventional diagnostic tools, thus the principles behind free electron heating could not be experimentally revealed.
Moreover, lacking information on a key parameter of electron heating and its controlling methods is troublesome and limit improving the reactivity and applicability of such plasmas.
To address these issues, Professor Wonho Choe and his team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering employed neutral bremsstrahlung-based electron diagnostics in order to accurately examine the electron density and temperature in target plasmas. In addition, a novel imaging diagnostics for two dimensional distribution of electron information was developed.
Using the diagnostic technique they developed, the team measured the nanosecond-resolved electron temperature in weakly ionized collisional plasmas, and they succeeded in revealing the spatiotemporal distribution and the fundamental principle involved in the electron heating process.
The team successfully revealed the fundamental principle of the electron heating process under atmospheric to sub-atmospheric pressure (0.25-1atm) conditions through conducting the experiment on the spatiotemporal evolution of electron temperature.
Their findings of the underlying research data on free electrons in weakly ionized collisional plasmas will contribute to enhancing the field of plasma science and their commercial applications.
Professor Choe said, “The results of this study provide a clear picture of electron heating in weakly ionized plasmas under conditions where collisions between free electrons and neutral particles are frequent. We hope this study will be informative and helpful in utilizing and commercializing atmospheric-pressure plasma sources in the near future.”
Articles related to this research, led by Research Professor Sanghoo Park, were published in Scientific Reports on May 14 and July 5.
Figure 1. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of the electron heating structure. Spatiotemporal evolution of 514.5-nm continuum radiation,Te, Ar I emission
Figure 2. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of electron heating. Spatiotemporal evolution of neutral bremsstrahlung at 514.5 nm
2018.09.10 View 6106
Electron Heating in Weakly Ionized Collisional Plasmas
(from left: Professor Wonho Choe and Research Professor Sanghoo Park)
A KAIST research team successfully identified the underlying principles behind electron heating, which is one of the most important phenomena in plasmas. As the electric heating determines wide range of physical and chemical properties of plasmas, this outcome will allow relevant industries to extend and effectively customize a range of plasma characteristics for their specific needs.
Plasma, frequently called the fourth state of matter, can be mostly formed by artificially energizing gases in standard temperature (25°C) and pressure (1 atm) range. Among the many types of plasma, atmospheric-pressure plasmas have been gaining a great deal of attention due to their unique features and applicability in various scientific and industrial fields.
Because plasma characteristics strongly depends on gas pressure in the sub-atmospheric to atmospheric pressure range, characterizing the plasma at different pressures is a prerequisite for understanding the fundamental principles of plasmas and for their industrial applications.
In that sense, information on the spatio-temporal evolution in the electron density and temperature is very important because various physical and chemical reactions within a plasma arise from electrons. Hence, electron heating has been an interesting topic in the field of plasma.
Because collisions between free electrons and neutral gases are frequent under atmospheric-pressure conditions, there are physical limits to measuring the electron density and temperature in plasmas using conventional diagnostic tools, thus the principles behind free electron heating could not be experimentally revealed.
Moreover, lacking information on a key parameter of electron heating and its controlling methods is troublesome and limit improving the reactivity and applicability of such plasmas.
To address these issues, Professor Wonho Choe and his team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering employed neutral bremsstrahlung-based electron diagnostics in order to accurately examine the electron density and temperature in target plasmas. In addition, a novel imaging diagnostics for two dimensional distribution of electron information was developed.
Using the diagnostic technique they developed, the team measured the nanosecond-resolved electron temperature in weakly ionized collisional plasmas, and they succeeded in revealing the spatiotemporal distribution and the fundamental principle involved in the electron heating process.
The team successfully revealed the fundamental principle of the electron heating process under atmospheric to sub-atmospheric pressure (0.25-1atm) conditions through conducting the experiment on the spatiotemporal evolution of electron temperature.
Their findings of the underlying research data on free electrons in weakly ionized collisional plasmas will contribute to enhancing the field of plasma science and their commercial applications.
Professor Choe said, “The results of this study provide a clear picture of electron heating in weakly ionized plasmas under conditions where collisions between free electrons and neutral particles are frequent. We hope this study will be informative and helpful in utilizing and commercializing atmospheric-pressure plasma sources in the near future.”
Articles related to this research, led by Research Professor Sanghoo Park, were published in Scientific Reports on May 14 and July 5.
Figure 1. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of the electron heating structure. Spatiotemporal evolution of 514.5-nm continuum radiation,Te, Ar I emission
Figure 2. Nanosecond-resolved visualization of electron heating. Spatiotemporal evolution of neutral bremsstrahlung at 514.5 nm
2018.09.10 View 6106 -
 NEREC Summer Program Keeps Fellows Thinking, Engaged in Nuclear Nonproliferation
Nuclear technology is more than just technology. It is the fruit of the most advanced science and technology. It also requires high standards of policymaking and global cooperation for benefiting the technology.
As part of the fifth annual Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) Summer Fellows Program at KAIST, 24 students from 15 countries participated in six-week intensive education and training program. NEREC is the only university-based center dedicated to nuclear nonproliferation education and research established in 2014.
The program, which provides multidisciplinary lectures and seminars on nuclear technology and policy as well as international relations, was designed to nurture global nuclear technology experts well equipped in three areas: in-depth knowledge of technology, applicability gained from sound policy building, and negotiating for international cooperation. It now has grown into the most popular summer program at KAIST.
During the program from July 6 to August 18, participants were able to engage in enriching and stimulating learning experiences in tandem with policies and technology for the utilization and provision of peaceful and safe nuclear technology.
Participating fellows also had to conduct a group research project on a given topic. This year, they explored nuclear nonproliferation issues in relation to nuclear exports and brainstormed some recommendations for current policy. They presented their outcomes at the 2018 NEREC Conference on Nuclear Nonproliferation. After intensive lecture sessions and group research work, the fellows went off to key policy think-tanks, nuclear research institutes, and research power facilities in Korea, Japan, and China.
“NEREC emphasizes nuclear nonproliferation issues related to civilian nuclear power and the associated nuclear fuel cycle development from the point of technology users. I am very glad that the number of participants are increasing year by year,” said the Director of NEREC Man-Sung Yim, a professor in the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering.
Participants’ majors vary from nuclear engineering to international relations to economics. The fellows divided into two groups of graduate and undergraduate courses. They expressed their deep satisfactory in the multidisciplinary lectures by scholars from KAIST, Seoul National University, and Korea National Defense University.
Many participants reported that they learned a lot, not only about policy and international relations but on the research they are conducting and what the key issues will be in dealing for producing meaningful research work.
Moad Aldbissi from the KTH Royal Institute of Technology is one of the students who shared the same view. He said, “Coming from a technical background in nuclear engineering, I managed to learn a lot about nuclear policy and international relations. The importance of integrating the technical and political fields became even clearer.”
Most students concurred that they recognized how important it was to make international collaboration in this powerful field for each country through this program.
“As an engineering student, I just approached this program like an empty glass in policy areas. While working with colleagues during the program, I came to understand how important it is to make cooperation in these fields for the better result of national development and international relations,” said Thanataon Pornphatdetaudom from the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
To Director Yim, this program is becoming well positioned to educate nuclear policy experts in a number of countries of strategic importance. He believes the continuous supply of these experts will contribute to promoting global nuclear nonproliferation and the peaceful use of nuclear energy while the use of nuclear technology continues.
2018.09.04 View 8882
NEREC Summer Program Keeps Fellows Thinking, Engaged in Nuclear Nonproliferation
Nuclear technology is more than just technology. It is the fruit of the most advanced science and technology. It also requires high standards of policymaking and global cooperation for benefiting the technology.
As part of the fifth annual Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) Summer Fellows Program at KAIST, 24 students from 15 countries participated in six-week intensive education and training program. NEREC is the only university-based center dedicated to nuclear nonproliferation education and research established in 2014.
The program, which provides multidisciplinary lectures and seminars on nuclear technology and policy as well as international relations, was designed to nurture global nuclear technology experts well equipped in three areas: in-depth knowledge of technology, applicability gained from sound policy building, and negotiating for international cooperation. It now has grown into the most popular summer program at KAIST.
During the program from July 6 to August 18, participants were able to engage in enriching and stimulating learning experiences in tandem with policies and technology for the utilization and provision of peaceful and safe nuclear technology.
Participating fellows also had to conduct a group research project on a given topic. This year, they explored nuclear nonproliferation issues in relation to nuclear exports and brainstormed some recommendations for current policy. They presented their outcomes at the 2018 NEREC Conference on Nuclear Nonproliferation. After intensive lecture sessions and group research work, the fellows went off to key policy think-tanks, nuclear research institutes, and research power facilities in Korea, Japan, and China.
“NEREC emphasizes nuclear nonproliferation issues related to civilian nuclear power and the associated nuclear fuel cycle development from the point of technology users. I am very glad that the number of participants are increasing year by year,” said the Director of NEREC Man-Sung Yim, a professor in the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering.
Participants’ majors vary from nuclear engineering to international relations to economics. The fellows divided into two groups of graduate and undergraduate courses. They expressed their deep satisfactory in the multidisciplinary lectures by scholars from KAIST, Seoul National University, and Korea National Defense University.
Many participants reported that they learned a lot, not only about policy and international relations but on the research they are conducting and what the key issues will be in dealing for producing meaningful research work.
Moad Aldbissi from the KTH Royal Institute of Technology is one of the students who shared the same view. He said, “Coming from a technical background in nuclear engineering, I managed to learn a lot about nuclear policy and international relations. The importance of integrating the technical and political fields became even clearer.”
Most students concurred that they recognized how important it was to make international collaboration in this powerful field for each country through this program.
“As an engineering student, I just approached this program like an empty glass in policy areas. While working with colleagues during the program, I came to understand how important it is to make cooperation in these fields for the better result of national development and international relations,” said Thanataon Pornphatdetaudom from the Tokyo Institute of Technology.
To Director Yim, this program is becoming well positioned to educate nuclear policy experts in a number of countries of strategic importance. He believes the continuous supply of these experts will contribute to promoting global nuclear nonproliferation and the peaceful use of nuclear energy while the use of nuclear technology continues.
2018.09.04 View 8882 -
 Potential Drug to Cure Ciliopathies
(from left: Professor Joon Kim and PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim)
Ciliopathies are rare disorders involving functional and structural abnormalities of cilia. Although they are rare, they may reach 1 in 1,000 births. Unfortunately, there are no small-molecule drugs for treating ciliary defects. A KAIST research team conducted successful research that introduces a potential treatment that will be a foundation for developing drugs to treat the disease as well as a platform for developing small-molecule drugs for similar genetic disorders.
It was found that mutations in genes required for the formation or function of primary cilia cause ciliopathies and they result in cerebellar disorders, kidney dysfunction, and retinal degeneration.
Primary cilia are cell organelles playing a crucial role in the human body. They participate in intercellular signal transduction during embryonic development and allow retinal photoreceptor cells to function.
Currently, there are no approved drugs available for treating most ciliopathies. In fact, this is the case for most of the rare genetic disorders involving functional abnormalities through genetic mutation, and gene therapy is usually the only treatment available.
To tackle this issue, a team led by Professor Joon Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and Ho Jeong Kwon from Yonsei University constructed a cell that mimics a gene-mutated CEP290, one of the main causes of ciliopathies, through genome editing. They then used cell-based compound library screening to obtain a natural small-molecule compound capable of relieving defects in ciliogenesis, the production of cilia.
The CEP290 protein forms a complex with a ciliopathy protein called NPHP5 to support the function of the ciliary transition zone. In cases where the CEP290 protein is not formed due to a genetic mutation, NPHP5 will not function normally. Here, the compound was confirmed to partially restore the function of the complex by normalizing the function of NPHP5.
The team also identified that the compound is capable of retarding retinal degeneration by injecting the compound into animal models.
As a result, they discovered a lead compound for developing medication to treat ciliopathy patients involving retinal degeneration. Hence, the findings imply that chemical compounds that target other proteins interacting with the disease protein can mitigate shortages of a disease protein in recessive genetic disorders.
PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim stated, “This study shows how genetic disorders caused by genetic mutation can be treated with small-molecule drugs.”
Professor Kim said, “Since the efficacy of the candidate drug has been verified through animal testing, a follow-up study will also be conducted to demonstrate the effect on humans.”
This research was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation on July 23.
Figure 1. Identification of compounds that rescue ciliogenesis defects caused by CEP290 knockout
Figure 2. Eupatilin injection ameliorates M-opsin trafficking and electrophysiological response of cone photoreceptors in rd16 mice
2018.08.30 View 7378
Potential Drug to Cure Ciliopathies
(from left: Professor Joon Kim and PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim)
Ciliopathies are rare disorders involving functional and structural abnormalities of cilia. Although they are rare, they may reach 1 in 1,000 births. Unfortunately, there are no small-molecule drugs for treating ciliary defects. A KAIST research team conducted successful research that introduces a potential treatment that will be a foundation for developing drugs to treat the disease as well as a platform for developing small-molecule drugs for similar genetic disorders.
It was found that mutations in genes required for the formation or function of primary cilia cause ciliopathies and they result in cerebellar disorders, kidney dysfunction, and retinal degeneration.
Primary cilia are cell organelles playing a crucial role in the human body. They participate in intercellular signal transduction during embryonic development and allow retinal photoreceptor cells to function.
Currently, there are no approved drugs available for treating most ciliopathies. In fact, this is the case for most of the rare genetic disorders involving functional abnormalities through genetic mutation, and gene therapy is usually the only treatment available.
To tackle this issue, a team led by Professor Joon Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and Ho Jeong Kwon from Yonsei University constructed a cell that mimics a gene-mutated CEP290, one of the main causes of ciliopathies, through genome editing. They then used cell-based compound library screening to obtain a natural small-molecule compound capable of relieving defects in ciliogenesis, the production of cilia.
The CEP290 protein forms a complex with a ciliopathy protein called NPHP5 to support the function of the ciliary transition zone. In cases where the CEP290 protein is not formed due to a genetic mutation, NPHP5 will not function normally. Here, the compound was confirmed to partially restore the function of the complex by normalizing the function of NPHP5.
The team also identified that the compound is capable of retarding retinal degeneration by injecting the compound into animal models.
As a result, they discovered a lead compound for developing medication to treat ciliopathy patients involving retinal degeneration. Hence, the findings imply that chemical compounds that target other proteins interacting with the disease protein can mitigate shortages of a disease protein in recessive genetic disorders.
PhD candidate Yong Joon Kim stated, “This study shows how genetic disorders caused by genetic mutation can be treated with small-molecule drugs.”
Professor Kim said, “Since the efficacy of the candidate drug has been verified through animal testing, a follow-up study will also be conducted to demonstrate the effect on humans.”
This research was published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation on July 23.
Figure 1. Identification of compounds that rescue ciliogenesis defects caused by CEP290 knockout
Figure 2. Eupatilin injection ameliorates M-opsin trafficking and electrophysiological response of cone photoreceptors in rd16 mice
2018.08.30 View 7378 -
 Rh Ensemble Catalyst for Effective Automobile Exhaust Treatment
(from left: Professor Hyunjoo Lee and PhD candidate Hojin Jeong)
A KAIST research team has developed a fully dispersed Rh ensemble catalyst (ENS) that shows better performance than commercial diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). This newly developed ENSs could improve low-temperature automobile exhaust treatment.
Precious metals have been used for various heterogeneous reactions, but it is crucial to maximize efficiency of catalysts due to their high cost. Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received much attention because it is possible for all of the metal atoms to be used for reactions, yet they do not show catalytic activity for reactions that require ensemble sites.
Meanwhile, hydrocarbons, such as propylene (C3H6) and propane (C3H8) are typical automobile exhaust gas pollutants and must be converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) before they are released as exhaust. Since the hydrocarbon oxidation reaction proceeds only during carbon-carbon (C-C) or carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond cleavage, it is essential to secure the metal ensemble site for the catalytic reaction. Therefore, precious metal catalysts with high dispersion and ensemble sites are greatly needed.
To solve this issue, Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH developed an Rh ensemble catalyst with 100% dispersion, and applied it to automobile after-treatment. Having a 100% dispersion means that every metal atom is used for the reaction since it is exposed on the surface.
SACs also have 100% dispersion, but the difference is that ENSs have the unique advantage of having an ensemble site with two or more atoms.
As a result of the experiment, the ENSs showed excellent catalytic performance in CO, NO, propylene, and propane oxidation at low temperatures. This complements the disadvantage of nanoparticle catalyst (NPs) that perform catalysis poorly at low temperatures due to low metal dispersion, or SACs without hydrocarbon oxidation.
In particular, the ENSs have superior low-temperature activity even better than commercial DOC, hence they are expected to be applied to automobile exhaust treatment.
Professor Lee said, “I believe that the ENSs have given academic contribution for proposing a new concept of metal catalysts, differentiating from conventional SACs and NPs. At the same time, they are of great value in the industry of exhaust treatment catalysts.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Hojin Jeong, was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 5.
Figure 1. Concept of Rh ensemble catalyst for automobile exhaust treatment
Figure 2. Structure and performance comparison of single-atom catalyst and ensemble catalyst
Figure 3. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images for SAC, ENS, and NP, respectively (green, Eh; red, Ce)
2018.08.29 View 6446
Rh Ensemble Catalyst for Effective Automobile Exhaust Treatment
(from left: Professor Hyunjoo Lee and PhD candidate Hojin Jeong)
A KAIST research team has developed a fully dispersed Rh ensemble catalyst (ENS) that shows better performance than commercial diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). This newly developed ENSs could improve low-temperature automobile exhaust treatment.
Precious metals have been used for various heterogeneous reactions, but it is crucial to maximize efficiency of catalysts due to their high cost. Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received much attention because it is possible for all of the metal atoms to be used for reactions, yet they do not show catalytic activity for reactions that require ensemble sites.
Meanwhile, hydrocarbons, such as propylene (C3H6) and propane (C3H8) are typical automobile exhaust gas pollutants and must be converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) before they are released as exhaust. Since the hydrocarbon oxidation reaction proceeds only during carbon-carbon (C-C) or carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond cleavage, it is essential to secure the metal ensemble site for the catalytic reaction. Therefore, precious metal catalysts with high dispersion and ensemble sites are greatly needed.
To solve this issue, Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH developed an Rh ensemble catalyst with 100% dispersion, and applied it to automobile after-treatment. Having a 100% dispersion means that every metal atom is used for the reaction since it is exposed on the surface.
SACs also have 100% dispersion, but the difference is that ENSs have the unique advantage of having an ensemble site with two or more atoms.
As a result of the experiment, the ENSs showed excellent catalytic performance in CO, NO, propylene, and propane oxidation at low temperatures. This complements the disadvantage of nanoparticle catalyst (NPs) that perform catalysis poorly at low temperatures due to low metal dispersion, or SACs without hydrocarbon oxidation.
In particular, the ENSs have superior low-temperature activity even better than commercial DOC, hence they are expected to be applied to automobile exhaust treatment.
Professor Lee said, “I believe that the ENSs have given academic contribution for proposing a new concept of metal catalysts, differentiating from conventional SACs and NPs. At the same time, they are of great value in the industry of exhaust treatment catalysts.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Hojin Jeong, was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 5.
Figure 1. Concept of Rh ensemble catalyst for automobile exhaust treatment
Figure 2. Structure and performance comparison of single-atom catalyst and ensemble catalyst
Figure 3. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images for SAC, ENS, and NP, respectively (green, Eh; red, Ce)
2018.08.29 View 6446 -
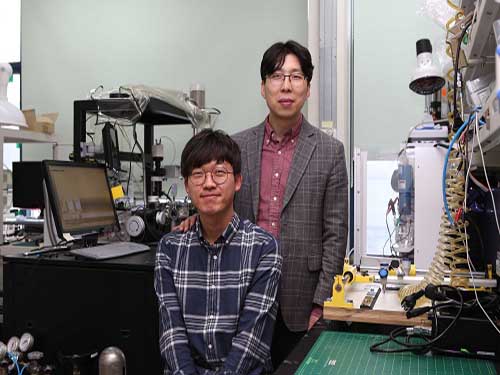 Levitating 2D Semiconductor for Better Performance
(from top: Professor Yeon Sik Jung and PhD candidate Soomin Yim)
Atomically thin 2D semiconductors have been drawing attention for their superior physical properties over silicon semiconductors; nevertheless, they are not the most appealing materials due to their structural instability and costly manufacturing process. To shed some light on these limitations, a KAIST research team suspended a 2D semiconductor on a dome-shaped nanostructure to produce a highly efficient semiconductor at a low cost.
2D semiconducting materials have emerged as alternatives for silicon-based semiconductors because of their inherent flexibility, high transparency, and excellent carrier transport properties, which are the important characteristics for flexible electronics.
Despite their outstanding physical and chemical properties, they are oversensitive to their environment due to their extremely thin nature. Hence, any irregularities in the supporting surface can affect the properties of 2D semiconductors and make it more difficult to produce reliable and well performing devices. In particular, it can result in serious degradation of charge-carrier mobility or light-emission yield.
To solve this problem, there have been continued efforts to fundamentally block the substrate effects. One way is to suspend a 2D semiconductor; however, this method will degrade mechanical durability due to the absence of a supporter underneath the 2D semiconducting materials.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and his team came up with a new strategy based on the insertion of high-density topographic patterns as a nanogap-containing supporter between 2D materials and the substrate in order to mitigate their contact and to block the substrate-induced unwanted effects.
More than 90% of the dome-shaped supporter is simply an empty space because of its nanometer scale size. Placing a 2D semiconductor on this structure creates a similar effect to levitating the layer. Hence, this method secures the mechanical durability of the device while minimizing the undesired effects from the substrate. By applying this method to the 2D semiconductor, the charge-carrier mobility was more than doubled, showing a significant improvement of the performance of the 2D semiconductor.
Additionally, the team reduced the price of manufacturing the semiconductor. In general, constructing an ultra-fine dome structure on a surface generally involves costly equipment to create individual patterns on the surface. However, the team employed a method of self-assembling nanopatterns in which molecules assemble themselves to form a nanostructure. This method led to reducing production costs and showed good compatibility with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Professor Jung said, “This research can be applied to improve devices using various 2D semiconducting materials as well as devices using graphene, a metallic 2D material. It will be useful in a broad range of applications, such as the material for the high speed transistor channels for next-generation flexible displays or for the active layer in light detectors.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Soomin Yim, was published in Nano Letters in April.
Figure 1. Image of a 2D semiconductor using dome structures
2018.08.28 View 5925
Levitating 2D Semiconductor for Better Performance
(from top: Professor Yeon Sik Jung and PhD candidate Soomin Yim)
Atomically thin 2D semiconductors have been drawing attention for their superior physical properties over silicon semiconductors; nevertheless, they are not the most appealing materials due to their structural instability and costly manufacturing process. To shed some light on these limitations, a KAIST research team suspended a 2D semiconductor on a dome-shaped nanostructure to produce a highly efficient semiconductor at a low cost.
2D semiconducting materials have emerged as alternatives for silicon-based semiconductors because of their inherent flexibility, high transparency, and excellent carrier transport properties, which are the important characteristics for flexible electronics.
Despite their outstanding physical and chemical properties, they are oversensitive to their environment due to their extremely thin nature. Hence, any irregularities in the supporting surface can affect the properties of 2D semiconductors and make it more difficult to produce reliable and well performing devices. In particular, it can result in serious degradation of charge-carrier mobility or light-emission yield.
To solve this problem, there have been continued efforts to fundamentally block the substrate effects. One way is to suspend a 2D semiconductor; however, this method will degrade mechanical durability due to the absence of a supporter underneath the 2D semiconducting materials.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and his team came up with a new strategy based on the insertion of high-density topographic patterns as a nanogap-containing supporter between 2D materials and the substrate in order to mitigate their contact and to block the substrate-induced unwanted effects.
More than 90% of the dome-shaped supporter is simply an empty space because of its nanometer scale size. Placing a 2D semiconductor on this structure creates a similar effect to levitating the layer. Hence, this method secures the mechanical durability of the device while minimizing the undesired effects from the substrate. By applying this method to the 2D semiconductor, the charge-carrier mobility was more than doubled, showing a significant improvement of the performance of the 2D semiconductor.
Additionally, the team reduced the price of manufacturing the semiconductor. In general, constructing an ultra-fine dome structure on a surface generally involves costly equipment to create individual patterns on the surface. However, the team employed a method of self-assembling nanopatterns in which molecules assemble themselves to form a nanostructure. This method led to reducing production costs and showed good compatibility with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Professor Jung said, “This research can be applied to improve devices using various 2D semiconducting materials as well as devices using graphene, a metallic 2D material. It will be useful in a broad range of applications, such as the material for the high speed transistor channels for next-generation flexible displays or for the active layer in light detectors.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Soomin Yim, was published in Nano Letters in April.
Figure 1. Image of a 2D semiconductor using dome structures
2018.08.28 View 5925 -
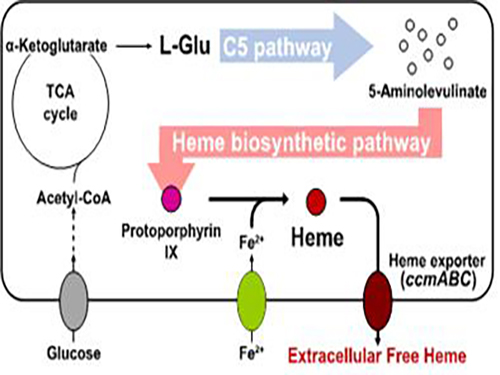 Metabolic Engineering of E. coli for the Secretory Production of Free Haem
Researchers of KAIST have defined a novel strategy for the secretory production of free haem using engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains. They utilized the C5 pathway, the optimized downstream pathways, and the haem exporter to construct a recombinant micro-organism producing extracellular haem using fed-batch fermentation. This is the first report to extracellularly produce haem using engineered E. coli.
This strategy will expedite the efficient production of free haem to serve as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent and an important prosthetic group of multiple hemoproteins for medical uses. This study, led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, was published in Nature Catalysis on Aug. 28.
Haem, an organometallic compound complexed with a ferrous ion, is an essential molecule delivering oxygen in the blood of many animals. It is also a key component of electron transport chains responsible for the respiration of aerobic organisms including diverse bacteria. It is now being widely applied as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent in the healthcare and dietary supplement industries. The demand for haem and the need for the efficient production of this compound continue to grow.
Many previous researchers have attempted to produce free haem using engineered E. coli. However, none of the studies was successful in producing free haem extracellularly, requiring an additional step to extract the accumulated haem from cells for subsequent uses. The secretion of haem in the form of haem peptides or proteins also requires an extraction step to isolate the free haem from the secreted products. Thus, the secretory production of free haem is an important task for the economical production of haem that is suitable for human consumption.
Although some researchers could produce intracellular haem using recombinant E. coli strains, its final titer was extremely low, resulting from the use of sub-optimal metabolic pathways. Furthermore, the addition of the precursors L-glycine and succinate was deemed undesirable for massive industrial production. Thus, it is necessary to construct an optimized haem biosynthetic pathway to enable the efficient production of haem and examine the consequent secretion of free haem.
To address this issue, the KAIST team used multiple strategies to produce extracellular free haem by enhancing its biosynthesis in E. coli. First, the capacities of the C4 and C5 pathways to produce aminolevulinate (ALA) without feeding precursors were examined. After confirming the superior performance of the C5 pathway over the C4 pathway, the metabolic genes of the C5 pathway and downstream pathways for haem biosynthesis were overexpressed. Then, the metabolic pathways were optimized by adjusting the expression levels of the relevant genes and disrupting the putative haem degradation enzyme encoded by the yfeX gene.
Consequently, the resulting engineered strain secreted a significant amount of haem to the medium. Subsequent optimization of the cultivation conditions and the supplementation of nitrogen sources further increased both the titer of the total free haem and the amount of free haem secreted to the medium. Finally, the overexpression of the ccmABC genes encoding the haem exporter further enhanced the production and secretion of haem, producing the highest titer of haem both intracellularly and extracellularly from glucose.
Professor Lee said, “The eco-friendly and sustainable chemical industry is a key global agenda every nation faces. We are conducting research to bio-synthesize high concentrations, high yields, and high productivity in natural products. This novel technology will serve as an opportunity to advance the biochemical industry moving forward.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea. Further Contact: Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea ( leesy@kaist.ac.kr+82-42-350-3930).
2018.08.28 View 5311
Metabolic Engineering of E. coli for the Secretory Production of Free Haem
Researchers of KAIST have defined a novel strategy for the secretory production of free haem using engineered Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains. They utilized the C5 pathway, the optimized downstream pathways, and the haem exporter to construct a recombinant micro-organism producing extracellular haem using fed-batch fermentation. This is the first report to extracellularly produce haem using engineered E. coli.
This strategy will expedite the efficient production of free haem to serve as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent and an important prosthetic group of multiple hemoproteins for medical uses. This study, led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, was published in Nature Catalysis on Aug. 28.
Haem, an organometallic compound complexed with a ferrous ion, is an essential molecule delivering oxygen in the blood of many animals. It is also a key component of electron transport chains responsible for the respiration of aerobic organisms including diverse bacteria. It is now being widely applied as a bioavailable iron-supplying agent in the healthcare and dietary supplement industries. The demand for haem and the need for the efficient production of this compound continue to grow.
Many previous researchers have attempted to produce free haem using engineered E. coli. However, none of the studies was successful in producing free haem extracellularly, requiring an additional step to extract the accumulated haem from cells for subsequent uses. The secretion of haem in the form of haem peptides or proteins also requires an extraction step to isolate the free haem from the secreted products. Thus, the secretory production of free haem is an important task for the economical production of haem that is suitable for human consumption.
Although some researchers could produce intracellular haem using recombinant E. coli strains, its final titer was extremely low, resulting from the use of sub-optimal metabolic pathways. Furthermore, the addition of the precursors L-glycine and succinate was deemed undesirable for massive industrial production. Thus, it is necessary to construct an optimized haem biosynthetic pathway to enable the efficient production of haem and examine the consequent secretion of free haem.
To address this issue, the KAIST team used multiple strategies to produce extracellular free haem by enhancing its biosynthesis in E. coli. First, the capacities of the C4 and C5 pathways to produce aminolevulinate (ALA) without feeding precursors were examined. After confirming the superior performance of the C5 pathway over the C4 pathway, the metabolic genes of the C5 pathway and downstream pathways for haem biosynthesis were overexpressed. Then, the metabolic pathways were optimized by adjusting the expression levels of the relevant genes and disrupting the putative haem degradation enzyme encoded by the yfeX gene.
Consequently, the resulting engineered strain secreted a significant amount of haem to the medium. Subsequent optimization of the cultivation conditions and the supplementation of nitrogen sources further increased both the titer of the total free haem and the amount of free haem secreted to the medium. Finally, the overexpression of the ccmABC genes encoding the haem exporter further enhanced the production and secretion of haem, producing the highest titer of haem both intracellularly and extracellularly from glucose.
Professor Lee said, “The eco-friendly and sustainable chemical industry is a key global agenda every nation faces. We are conducting research to bio-synthesize high concentrations, high yields, and high productivity in natural products. This novel technology will serve as an opportunity to advance the biochemical industry moving forward.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea. Further Contact: Dr. Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor, KAIST, Daejeon, Korea ( leesy@kaist.ac.kr+82-42-350-3930).
2018.08.28 View 5311 -
 Robotic Herding of a Flock of Birds Using Drones
A joint team from KAIST, Caltech, and Imperial College London, presents a drone with a new algorithm to shepherd birds safely away from airports
Researchers made a new algorithm for enabling a single robotic unmanned aerial vehicle to herd a flock of birds away from a designated airspace. This novel approach allows a single autonomous quadrotor drone to herd an entire flock of birds away without breaking their formation.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim at KAIST in collaboration with Professor Soon-Jo Chung of Caltech and Professor Aditya Paranjape of Imperial College London investigated the problem of diverting a flock of birds away from a prescribed area, such as an airport, using a robotic UVA. A novel boundary control strategy called the m-waypoint algorithm was introduced for enabling a single pursuer UAV to safely herd the flock without fragmenting it.
The team developed the herding algorithm on the basis of macroscopic properties of the flocking model and the response of the flock. They tested their robotic autonomous drone by successfully shepherding an entire flock of birds out of a designated airspace near KAIST’s campus in Daejeon, South Korea. This study is published in IEEE Transactions on Robotics.
“It is quite interesting, and even awe-inspiring, to monitor how birds react to threats and collectively behave against threatening objects through the flock. We made careful observations of flock dynamics and interactions between flocks and the pursuer. This allowed us to create a new herding algorithm for ideal flight paths for incoming drones to move the flock away from a protected airspace,” said Professor Shim, who leads the Unmanned Systems Research Group at KAIST.
Bird strikes can threaten the safety of airplanes and their passengers. Korean civil aircraft suffered more than 1,000 bird strikes between 2011 and 2016. In the US, 142,000 bird strikes destroyed 62 civilian airplanes, injured 279 people, and killed 25 between 1990 and 2013. In the UK in 2016, there were 1,835 confirmed bird strikes, about eight for every 10,000 flights. Bird and other wildlife collisions with aircraft cause well over 1.2 billion USD in damages to the aviation industry worldwide annually. In the worst case, Canadian geese knocked out both engines of a US Airway jet in January 2009. The flight had to make an emergency landing on the Hudson River.
Airports and researchers have continued to reduce the risk of bird strikes through a variety of methods. They scare birds away using predators such as falcons or loud noises from small cannons or guns. Some airports try to prevent birds from coming by ridding the surrounding areas of crops that birds eat and hide in.
However, birds are smart. “I was amazed with the birds’ capability to interact with flying objects. We thought that only birds of prey have a strong sense of maneuvering with the prey. But our observation of hundreds of migratory birds such as egrets and loons led us to reach the hypothesis that they all have similar levels of maneuvering with the flying objects. It will be very interesting to collaborate with ornithologists to study further with birds’ behaviors with aerial objects,” said Professor Shim. “Airports are trying to transform into smart airports. This algorithm will help improve safety for the aviation industry. In addition, this will also help control avian influenza that plagues farms nationwide every year,” he stressed.
For this study, two drones were deployed. One drone performed various types of maneuvers around the flocks as a pursuer of herding drone, while a surveillance drone hovered at a high altitude with a camera pointing down for recording the trajectories of the pursuer drone and the birds.
During the experiments on egrets, the birds made frequent visits to a hunting area nearby and a large number of egrets were found to return to their nests at sunset. During the time, the team attempted to fly the herding drone in various directions with respect to the flock.
The drone approached the flock from the side. When the birds noticed the drone, they diverted from their original paths and flew at a 45˚ angle to their right. When the birds noticed the drone while it was still far away, they adjusted their paths horizontally and made smaller changes in the vertical direction. In the second round of the experiment on loons, the drone flew almost parallel to the flight path of a flock of birds, starting from an initial position located just off the nominal flight path. The birds had a nominal flight speed that was considerably higher than that of the drone so the interaction took place over a relatively short period of time.
Professor Shim said, “I think we just completed the first step of the research. For the next step, more systems will be developed and integrated for bird detection, ranging, and automatic deployment of drones.” “Professor Chung at Caltech is a KAIST graduate. And his first student was Professor Paranjape who now teaches at Imperial. It is pretty interesting that this research was made by a KAIST faculty member, an alumnus, and his student on three different continents,” he said.
(Figure A. Case 1: drone approaches the herd with sufficient distance to induce horizontal deviation)
(Figure B. Case 2: drone approaches the herd abruptly to cause vertical deviation)
2018.08.23 View 8873
Robotic Herding of a Flock of Birds Using Drones
A joint team from KAIST, Caltech, and Imperial College London, presents a drone with a new algorithm to shepherd birds safely away from airports
Researchers made a new algorithm for enabling a single robotic unmanned aerial vehicle to herd a flock of birds away from a designated airspace. This novel approach allows a single autonomous quadrotor drone to herd an entire flock of birds away without breaking their formation.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim at KAIST in collaboration with Professor Soon-Jo Chung of Caltech and Professor Aditya Paranjape of Imperial College London investigated the problem of diverting a flock of birds away from a prescribed area, such as an airport, using a robotic UVA. A novel boundary control strategy called the m-waypoint algorithm was introduced for enabling a single pursuer UAV to safely herd the flock without fragmenting it.
The team developed the herding algorithm on the basis of macroscopic properties of the flocking model and the response of the flock. They tested their robotic autonomous drone by successfully shepherding an entire flock of birds out of a designated airspace near KAIST’s campus in Daejeon, South Korea. This study is published in IEEE Transactions on Robotics.
“It is quite interesting, and even awe-inspiring, to monitor how birds react to threats and collectively behave against threatening objects through the flock. We made careful observations of flock dynamics and interactions between flocks and the pursuer. This allowed us to create a new herding algorithm for ideal flight paths for incoming drones to move the flock away from a protected airspace,” said Professor Shim, who leads the Unmanned Systems Research Group at KAIST.
Bird strikes can threaten the safety of airplanes and their passengers. Korean civil aircraft suffered more than 1,000 bird strikes between 2011 and 2016. In the US, 142,000 bird strikes destroyed 62 civilian airplanes, injured 279 people, and killed 25 between 1990 and 2013. In the UK in 2016, there were 1,835 confirmed bird strikes, about eight for every 10,000 flights. Bird and other wildlife collisions with aircraft cause well over 1.2 billion USD in damages to the aviation industry worldwide annually. In the worst case, Canadian geese knocked out both engines of a US Airway jet in January 2009. The flight had to make an emergency landing on the Hudson River.
Airports and researchers have continued to reduce the risk of bird strikes through a variety of methods. They scare birds away using predators such as falcons or loud noises from small cannons or guns. Some airports try to prevent birds from coming by ridding the surrounding areas of crops that birds eat and hide in.
However, birds are smart. “I was amazed with the birds’ capability to interact with flying objects. We thought that only birds of prey have a strong sense of maneuvering with the prey. But our observation of hundreds of migratory birds such as egrets and loons led us to reach the hypothesis that they all have similar levels of maneuvering with the flying objects. It will be very interesting to collaborate with ornithologists to study further with birds’ behaviors with aerial objects,” said Professor Shim. “Airports are trying to transform into smart airports. This algorithm will help improve safety for the aviation industry. In addition, this will also help control avian influenza that plagues farms nationwide every year,” he stressed.
For this study, two drones were deployed. One drone performed various types of maneuvers around the flocks as a pursuer of herding drone, while a surveillance drone hovered at a high altitude with a camera pointing down for recording the trajectories of the pursuer drone and the birds.
During the experiments on egrets, the birds made frequent visits to a hunting area nearby and a large number of egrets were found to return to their nests at sunset. During the time, the team attempted to fly the herding drone in various directions with respect to the flock.
The drone approached the flock from the side. When the birds noticed the drone, they diverted from their original paths and flew at a 45˚ angle to their right. When the birds noticed the drone while it was still far away, they adjusted their paths horizontally and made smaller changes in the vertical direction. In the second round of the experiment on loons, the drone flew almost parallel to the flight path of a flock of birds, starting from an initial position located just off the nominal flight path. The birds had a nominal flight speed that was considerably higher than that of the drone so the interaction took place over a relatively short period of time.
Professor Shim said, “I think we just completed the first step of the research. For the next step, more systems will be developed and integrated for bird detection, ranging, and automatic deployment of drones.” “Professor Chung at Caltech is a KAIST graduate. And his first student was Professor Paranjape who now teaches at Imperial. It is pretty interesting that this research was made by a KAIST faculty member, an alumnus, and his student on three different continents,” he said.
(Figure A. Case 1: drone approaches the herd with sufficient distance to induce horizontal deviation)
(Figure B. Case 2: drone approaches the herd abruptly to cause vertical deviation)
2018.08.23 View 8873 -
 The MSE/CBE Int'l Workshop Explores Big Ideas in Emerging Materials
(KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin with scholars participated in the workshop)
The MSE/CBE International Workshop brought together editors from key academic journals in multidisciplinary materials science and scholars from leading universities at KAIST on Aug. 7.
The workshop hosted ten distinguished speakers in the fields of nanostructures for next-generation emerging applications, chemical and bio-engineering, and materials innovation for functional applications. They explored opportunities and challenges for reinventing novel materials that will solve complex problems.
(From left: Professor Buriak, Professor Swager and Professor Il-Doo Kim)
Speakers included: Chief Editor of Nature Materials Vincent Dusastre; Editor-in- Chief of ACS NANO and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss; Jillian M. Buriak, Editor-in-Chief of Chemistry of Materials; Associate Editor of Macromolecules and professor at MIT Timothy M. Swager; Coordinating Editor of Acta Materialia and Head of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at MIT Christopher A. Schuh; Editor-in-Chief of Biotechnology Journal and Metabolic Engineering and Distinguished Professor at KAIST Sang-Yup Lee; Associate Editor of Energy Storage Materials and professor at KAIST Sang Ouk Kim; Professor Jeffrey C. Grossman at MIT; Professor Zhenan Bao at Stanford University; and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee, head of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST.
Interdisciplinary materials research holds the key to building technological competitiveness in many industrial sectors extending from energy, environment, and health care to medicine and beyond. It has also been the bedrock of KAIST’s scholarship and research innovation. More than 200 faculty members in the field of materials science produce about 800 SCI papers every year. The two departments of materials science and chemical biomolecular engineering are leading KAIST’s global reputation, as they were both ranked 13th and 14th in the QS World University Ranking by Subject this year.
(Professor Il-Doo Kim fromt he Department of Materials Science Engineering)
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science Engineering has been the chair of this workshop from 2016. In hosting the second one this year, he said that he hopes this year’s workshop will inspire many materials scientists to have big ideas and work to make those big ideas get noticed in order to have a real impact.
(KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin, who is a physicist specializing in materials physics, expressed his keen interest in the workshop, saying innovative materials made of unthinkable and noble combinations will be the key factor in determining the competitiveness of new technology and new industries. He lauded international collaborations for making new materials and the scholarly passion to evaluate the materials’ characteristics that made this significant progress possible.
Dr. Vincent Dusastre, chief editor of Nature Materials, presented recent trends in materials for energy. He described how the rational design and improvement of materials’ properties can lead to energy alternatives which will compete with existing technologies. He pointed out that given the dramatic fundamental and practical breakthroughs that are taking place in the realization of solar cells with high energy-conversion efficiency, the improvement of batteries for electric vehicles and the grid is also a major challenge. He stressed, “Key advances in sustainable approaches beyond Li-ion batteries and control of redox processes are also greatly needed.”
Meanwhile, ACS NANO Editor-in-Chief Paul S. Weiss spoke on the importance of heterogeneity in the structure and function of molecules and nanoscale assemblies. He stressed that such extensiveness of multi-interdisciplinary research will accelerate a greater impact as indicated when the fields of neuroscience and microbiome converged with nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Editor-in-Chief of Chemistry of Materials Professor Jillian M. Buriak from the University of Alberta described how predictive models and machine learning can replace time consuming empirical device production and screening. By understanding and pinpointing the frustrating bottlenecks in the design of stable and efficient organic photovoltaics, much faster throughput can be obtained to enable a more direct pathway to stability, efficiency, and finally commercialization.
2018.08.13 View 10970
The MSE/CBE Int'l Workshop Explores Big Ideas in Emerging Materials
(KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin with scholars participated in the workshop)
The MSE/CBE International Workshop brought together editors from key academic journals in multidisciplinary materials science and scholars from leading universities at KAIST on Aug. 7.
The workshop hosted ten distinguished speakers in the fields of nanostructures for next-generation emerging applications, chemical and bio-engineering, and materials innovation for functional applications. They explored opportunities and challenges for reinventing novel materials that will solve complex problems.
(From left: Professor Buriak, Professor Swager and Professor Il-Doo Kim)
Speakers included: Chief Editor of Nature Materials Vincent Dusastre; Editor-in- Chief of ACS NANO and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss; Jillian M. Buriak, Editor-in-Chief of Chemistry of Materials; Associate Editor of Macromolecules and professor at MIT Timothy M. Swager; Coordinating Editor of Acta Materialia and Head of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at MIT Christopher A. Schuh; Editor-in-Chief of Biotechnology Journal and Metabolic Engineering and Distinguished Professor at KAIST Sang-Yup Lee; Associate Editor of Energy Storage Materials and professor at KAIST Sang Ouk Kim; Professor Jeffrey C. Grossman at MIT; Professor Zhenan Bao at Stanford University; and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee, head of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST.
Interdisciplinary materials research holds the key to building technological competitiveness in many industrial sectors extending from energy, environment, and health care to medicine and beyond. It has also been the bedrock of KAIST’s scholarship and research innovation. More than 200 faculty members in the field of materials science produce about 800 SCI papers every year. The two departments of materials science and chemical biomolecular engineering are leading KAIST’s global reputation, as they were both ranked 13th and 14th in the QS World University Ranking by Subject this year.
(Professor Il-Doo Kim fromt he Department of Materials Science Engineering)
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science Engineering has been the chair of this workshop from 2016. In hosting the second one this year, he said that he hopes this year’s workshop will inspire many materials scientists to have big ideas and work to make those big ideas get noticed in order to have a real impact.
(KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin, who is a physicist specializing in materials physics, expressed his keen interest in the workshop, saying innovative materials made of unthinkable and noble combinations will be the key factor in determining the competitiveness of new technology and new industries. He lauded international collaborations for making new materials and the scholarly passion to evaluate the materials’ characteristics that made this significant progress possible.
Dr. Vincent Dusastre, chief editor of Nature Materials, presented recent trends in materials for energy. He described how the rational design and improvement of materials’ properties can lead to energy alternatives which will compete with existing technologies. He pointed out that given the dramatic fundamental and practical breakthroughs that are taking place in the realization of solar cells with high energy-conversion efficiency, the improvement of batteries for electric vehicles and the grid is also a major challenge. He stressed, “Key advances in sustainable approaches beyond Li-ion batteries and control of redox processes are also greatly needed.”
Meanwhile, ACS NANO Editor-in-Chief Paul S. Weiss spoke on the importance of heterogeneity in the structure and function of molecules and nanoscale assemblies. He stressed that such extensiveness of multi-interdisciplinary research will accelerate a greater impact as indicated when the fields of neuroscience and microbiome converged with nanoscience and nanotechnology.
Editor-in-Chief of Chemistry of Materials Professor Jillian M. Buriak from the University of Alberta described how predictive models and machine learning can replace time consuming empirical device production and screening. By understanding and pinpointing the frustrating bottlenecks in the design of stable and efficient organic photovoltaics, much faster throughput can be obtained to enable a more direct pathway to stability, efficiency, and finally commercialization.
2018.08.13 View 10970 -
 A Breakthrough for Understanding Glioblastoma: Origin Cells for Deadly Brain Tumors Identified
Figure 1. The pattern of GBM genesis is similar to that of firework. The bottom canon represents the first occurrence of the SVZ mutated cell.
A new study by KAIST researchers identified where the mutation causing glioblastoma starts. According to the study, neural stem cells away from the tumor mass are the cells of origin that contain mutation drivers for glioblastoma, one of the most aggressive brain tumor. This breakthrough research, reported in Nature on August 1, gives insights for understanding why glioblastomas almost always grow back, even after surgery, and suggests novel ways to treat glioblastoma, which was previously thought to be incurable.
Like most cancers, glioblastoma is treated with surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, then radiation and chemotherapy. However, it almost always returns in less than a year and its median survival time is only 15 months. Precision therapeutic approaches targeting tumors themselves didn’t lead to any breakthroughs.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering described direct genetic evidence through the deep sequencing of all triple-matched samples: normal SVZ tissue away from the tumor mass, tumor tissue, and normal cortical tissue. The research team studied 28 patients with glioblastomas and other types of brain tumors who underwent supra-total resection or other surgical resections of tumors, providing access to normal subventricular zone (SVZ) tissue (where neural stem cells are located) away from the tumor mass. The researchers used various deep and single cell sequencing technologies to conduct comparative DNA analysis on the samples from the patient’s SVZ tissue and tumors.
They reported that normal SVZ tissue away from the tumor in 56.3% of patients with glioblastoma already contained low-level glioblastoma driver mutations that were observed at high levels in their matching tumors. Furthermore, the research team generated a genome edited mouse carrying glioblastoma mutations in the SVZ and showed that neural stem cells with mutations migrate from the SVZ lead to the development of glioblastomas in distant brain regions. (See the image below)
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Seok-Gu Kang of the Brain Tumor Center at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “It’s easier to understand when we compare it to fireworks. Every flare flying around sky can be likened to cancer cells even though the fireworks are triggered on the ground. We found the trigger.” The identification of this mutation pathway of glioblastomas will lead to a new paradigm for therapeutic strategies. He added, “Now, we can focus on interrupting the recurrence and evolution of glioblastomas.”
Professor Lee has investigated mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup, SoVarGen. “All technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
Figure 2. Genetic analysis of tumor-free SVZ tissue and matching tumor tissue from GBM patients.
Figure 3. Glioma progression in genome edited mice carrying GBM mutations in the SVZ
2018.08.02 View 11505
A Breakthrough for Understanding Glioblastoma: Origin Cells for Deadly Brain Tumors Identified
Figure 1. The pattern of GBM genesis is similar to that of firework. The bottom canon represents the first occurrence of the SVZ mutated cell.
A new study by KAIST researchers identified where the mutation causing glioblastoma starts. According to the study, neural stem cells away from the tumor mass are the cells of origin that contain mutation drivers for glioblastoma, one of the most aggressive brain tumor. This breakthrough research, reported in Nature on August 1, gives insights for understanding why glioblastomas almost always grow back, even after surgery, and suggests novel ways to treat glioblastoma, which was previously thought to be incurable.
Like most cancers, glioblastoma is treated with surgery to remove as much of the tumor as possible, then radiation and chemotherapy. However, it almost always returns in less than a year and its median survival time is only 15 months. Precision therapeutic approaches targeting tumors themselves didn’t lead to any breakthroughs.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering described direct genetic evidence through the deep sequencing of all triple-matched samples: normal SVZ tissue away from the tumor mass, tumor tissue, and normal cortical tissue. The research team studied 28 patients with glioblastomas and other types of brain tumors who underwent supra-total resection or other surgical resections of tumors, providing access to normal subventricular zone (SVZ) tissue (where neural stem cells are located) away from the tumor mass. The researchers used various deep and single cell sequencing technologies to conduct comparative DNA analysis on the samples from the patient’s SVZ tissue and tumors.
They reported that normal SVZ tissue away from the tumor in 56.3% of patients with glioblastoma already contained low-level glioblastoma driver mutations that were observed at high levels in their matching tumors. Furthermore, the research team generated a genome edited mouse carrying glioblastoma mutations in the SVZ and showed that neural stem cells with mutations migrate from the SVZ lead to the development of glioblastomas in distant brain regions. (See the image below)
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Seok-Gu Kang of the Brain Tumor Center at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “It’s easier to understand when we compare it to fireworks. Every flare flying around sky can be likened to cancer cells even though the fireworks are triggered on the ground. We found the trigger.” The identification of this mutation pathway of glioblastomas will lead to a new paradigm for therapeutic strategies. He added, “Now, we can focus on interrupting the recurrence and evolution of glioblastomas.”
Professor Lee has investigated mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup, SoVarGen. “All technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
Figure 2. Genetic analysis of tumor-free SVZ tissue and matching tumor tissue from GBM patients.
Figure 3. Glioma progression in genome edited mice carrying GBM mutations in the SVZ
2018.08.02 View 11505