Professor+Kwang-Hyun+Cho
-
 Connecting the Dots to Find New Treatments for Breast Cancer
Systems biologists uncovered new ways of cancer cell reprogramming to treat drug-resistant cancers
Scientists at KAIST believe they may have found a way to reverse an aggressive, treatment-resistant type of breast cancer into a less dangerous kind that responds well to treatment. The study involved the use of mathematical models to untangle the complex genetic and molecular interactions that occur in the two types of breast cancer, but could be extended to find ways for treating many others. The study’s findings were published in the journal Cancer Research.
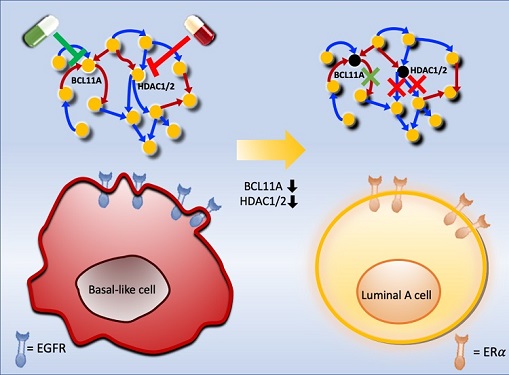
Basal-like tumours are the most aggressive type of breast cancer, with the worst prognosis. Chemotherapy is the only available treatment option, but patients experience high recurrence rates. On the other hand, luminal-A breast cancer responds well to drugs that specifically target a receptor on their cell surfaces, called estrogen receptor alpha (ERα).
KAIST systems biologist Kwang-Hyun Cho and colleagues analyzed the complex molecular and genetic interactions of basal-like and luminal-A breast cancers to find out if there might be a way to switch the former to the latter and give patients a better chance to respond to treatment.
To do this, they accessed large amounts of cancer and patient data to understand which genes and molecules are involved in the two types. They then input this data into a mathematical model that represents genes, proteins and molecules as dots and the interactions between them as lines. The model can be used to conduct simulations and see how interactions change when certain genes are turned on or off.
“There have been a tremendous number of studies trying to find therapeutic targets for treating basal-like breast cancer patients,” says Cho. “But clinical trials have failed due to the complex and dynamic nature of cancer. To overcome this issue, we looked at breast cancer cells as a complex network system and implemented a systems biological approach to unravel the underlying mechanisms that would allow us to reprogram basal-like into luminal-A breast cancer cells.”
Using this approach, followed by experimental validation on real breast cancer cells, the team found that turning off two key gene regulators, called BCL11A and HDAC1/2, switched a basal-like cancer signalling pathway into a different one used by luminal-A cancer cells. The switch reprograms the cancer cells and makes them more responsive to drugs that target ERα receptors. However, further tests will be needed to confirm that this also works in animal models and eventually humans.
“Our study demonstrates that the systems biological approach can be useful for identifying novel therapeutic targets,” says Cho.
The researchers are now expanding its breast cancer network model to include all breast cancer subtypes. Their ultimate aim is to identify more drug targets and to understand the mechanisms that could drive drug-resistant cells to turn into drug-sensitive ones.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Ministry of Science and ICT, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, and the KAIST Grand Challenge 30 Project.
-Publication Sea R. Choi, Chae Young Hwang, Jonghoon Lee, and Kwang-Hyun Cho, “Network Analysis Identifies Regulators of Basal-like Breast Cancer Reprogramming and Endocrine TherapyVulnerability,” Cancer Research, November 30. (doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0621)
-ProfileProfessor Kwang-Hyun ChoLaboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired EngineeringDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.07 View 7007
Connecting the Dots to Find New Treatments for Breast Cancer
Systems biologists uncovered new ways of cancer cell reprogramming to treat drug-resistant cancers
Scientists at KAIST believe they may have found a way to reverse an aggressive, treatment-resistant type of breast cancer into a less dangerous kind that responds well to treatment. The study involved the use of mathematical models to untangle the complex genetic and molecular interactions that occur in the two types of breast cancer, but could be extended to find ways for treating many others. The study’s findings were published in the journal Cancer Research.
Basal-like tumours are the most aggressive type of breast cancer, with the worst prognosis. Chemotherapy is the only available treatment option, but patients experience high recurrence rates. On the other hand, luminal-A breast cancer responds well to drugs that specifically target a receptor on their cell surfaces, called estrogen receptor alpha (ERα).
KAIST systems biologist Kwang-Hyun Cho and colleagues analyzed the complex molecular and genetic interactions of basal-like and luminal-A breast cancers to find out if there might be a way to switch the former to the latter and give patients a better chance to respond to treatment.
To do this, they accessed large amounts of cancer and patient data to understand which genes and molecules are involved in the two types. They then input this data into a mathematical model that represents genes, proteins and molecules as dots and the interactions between them as lines. The model can be used to conduct simulations and see how interactions change when certain genes are turned on or off.
“There have been a tremendous number of studies trying to find therapeutic targets for treating basal-like breast cancer patients,” says Cho. “But clinical trials have failed due to the complex and dynamic nature of cancer. To overcome this issue, we looked at breast cancer cells as a complex network system and implemented a systems biological approach to unravel the underlying mechanisms that would allow us to reprogram basal-like into luminal-A breast cancer cells.”
Using this approach, followed by experimental validation on real breast cancer cells, the team found that turning off two key gene regulators, called BCL11A and HDAC1/2, switched a basal-like cancer signalling pathway into a different one used by luminal-A cancer cells. The switch reprograms the cancer cells and makes them more responsive to drugs that target ERα receptors. However, further tests will be needed to confirm that this also works in animal models and eventually humans.
“Our study demonstrates that the systems biological approach can be useful for identifying novel therapeutic targets,” says Cho.
The researchers are now expanding its breast cancer network model to include all breast cancer subtypes. Their ultimate aim is to identify more drug targets and to understand the mechanisms that could drive drug-resistant cells to turn into drug-sensitive ones.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Ministry of Science and ICT, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute, and the KAIST Grand Challenge 30 Project.
-Publication Sea R. Choi, Chae Young Hwang, Jonghoon Lee, and Kwang-Hyun Cho, “Network Analysis Identifies Regulators of Basal-like Breast Cancer Reprogramming and Endocrine TherapyVulnerability,” Cancer Research, November 30. (doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0621)
-ProfileProfessor Kwang-Hyun ChoLaboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired EngineeringDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.07 View 7007 -
 Simulations Open a New Way to Reverse Cell Aging
Turning off a newly identified enzyme could reverse a natural aging process in cells.
Research findings by a KAIST team provide insight into the complex mechanism of cellular senescence and present a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing age-related diseases associated with the accumulation of senescent cells.
Simulations that model molecular interactions have identified an enzyme that could be targeted to reverse a natural aging process called cellular senescence. The findings were validated with laboratory experiments on skin cells and skin equivalent tissues, and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Our research opens the door for a new generation that perceives aging as a reversible biological phenomenon,” says Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), who led the research with colleagues from KAIST and Amorepacific Corporation in Korea.
Cells respond to a variety of factors, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, and shortening of the telomeres capping the ends of chromosomes, by entering a stable and persistent exit from the cell cycle. This process, called cellular senescence, is important, as it prevents damaged cells from proliferating and turning into cancer cells. But it is also a natural process that contributes to aging and age-related diseases. Recent research has shown that cellular senescence can be reversed. But the laboratory approaches used thus far also impair tissue regeneration or have the potential to trigger malignant transformations.
Professor Cho and his colleagues used an innovative strategy to identify molecules that could be targeted for reversing cellular senescence. The team pooled together information from the literature and databases about the molecular processes involved in cellular senescence. To this, they added results from their own research on the molecular processes involved in the proliferation, quiescence (a non-dividing cell that can re-enter the cell cycle) and senescence of skin fibroblasts, a cell type well known for repairing wounds. Using algorithms, they developed a model that simulates the interactions between these molecules. Their analyses allowed them to predict which molecules could be targeted to reverse cell senescence.
They then investigated one of the molecules, an enzyme called PDK1, in incubated senescent skin fibroblasts and three-dimensional skin equivalent tissue models. They found that blocking PDK1 led to the inhibition of two downstream signalling molecules, which in turn restored the cells’ ability to enter back into the cell cycle. Notably, the cells retained their capacity to regenerate wounded skin without proliferating in a way that could lead to malignant transformation.
The scientists recommend investigations are next done in organs and organisms to determine the full effect of PDK1 inhibition. Since the gene that codes for PDK1 is overexpressed in some cancers, the scientists expect that inhibiting it will have both anti-aging and anti-cancer effects.
-Profile
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
Laboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired Engineering
http://sbie.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.26 View 10949
Simulations Open a New Way to Reverse Cell Aging
Turning off a newly identified enzyme could reverse a natural aging process in cells.
Research findings by a KAIST team provide insight into the complex mechanism of cellular senescence and present a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing age-related diseases associated with the accumulation of senescent cells.
Simulations that model molecular interactions have identified an enzyme that could be targeted to reverse a natural aging process called cellular senescence. The findings were validated with laboratory experiments on skin cells and skin equivalent tissues, and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Our research opens the door for a new generation that perceives aging as a reversible biological phenomenon,” says Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), who led the research with colleagues from KAIST and Amorepacific Corporation in Korea.
Cells respond to a variety of factors, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, and shortening of the telomeres capping the ends of chromosomes, by entering a stable and persistent exit from the cell cycle. This process, called cellular senescence, is important, as it prevents damaged cells from proliferating and turning into cancer cells. But it is also a natural process that contributes to aging and age-related diseases. Recent research has shown that cellular senescence can be reversed. But the laboratory approaches used thus far also impair tissue regeneration or have the potential to trigger malignant transformations.
Professor Cho and his colleagues used an innovative strategy to identify molecules that could be targeted for reversing cellular senescence. The team pooled together information from the literature and databases about the molecular processes involved in cellular senescence. To this, they added results from their own research on the molecular processes involved in the proliferation, quiescence (a non-dividing cell that can re-enter the cell cycle) and senescence of skin fibroblasts, a cell type well known for repairing wounds. Using algorithms, they developed a model that simulates the interactions between these molecules. Their analyses allowed them to predict which molecules could be targeted to reverse cell senescence.
They then investigated one of the molecules, an enzyme called PDK1, in incubated senescent skin fibroblasts and three-dimensional skin equivalent tissue models. They found that blocking PDK1 led to the inhibition of two downstream signalling molecules, which in turn restored the cells’ ability to enter back into the cell cycle. Notably, the cells retained their capacity to regenerate wounded skin without proliferating in a way that could lead to malignant transformation.
The scientists recommend investigations are next done in organs and organisms to determine the full effect of PDK1 inhibition. Since the gene that codes for PDK1 is overexpressed in some cancers, the scientists expect that inhibiting it will have both anti-aging and anti-cancer effects.
-Profile
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
Laboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired Engineering
http://sbie.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.26 View 10949