Department+of+Chemical+and+Biomolecular+Engineering
-
 Quantum Dot Film Can Withstand High Temperatures and Humidity
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Doh Chang Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was able to fabricate a siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot film, which exhibits stable emission intensity over one month even at high temperatures and humidity.
The results of this study were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on November 29, 2016. The research article is entitled “Quantum Dot/Siloxane Composite Film Exceptionally Stable against Oxidation under Heat and Moisture.” (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b10681)
Quantum dots (QDs), light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for next-generation displays, are tiny particles or nanocrystals of semiconducting materials. Their emission wavelength can easily be adjusted by changing their sizes, which are just a few nanometers. A wide spectrum of their colors can also achieve ultra-high definition displays.
Due to these characteristics, QDs are coated on a film as a polymer resin in dispersed form, or they are spread on an LED light source. They are thus considered to be crucial for next generation displays.
Despite their exceptional optical properties, however, QDs are easily oxidized in a high temperature and high humidity environment, and, as a result, this greatly deteriorates their luminescence quality (quantum efficiency). Therefore, they are encapsulated in an extra thin layer to block oxygen and moisture.
QD displays in the current market have a film inserted to separate them from LEDs, which create heat. The high unit cost of this protective layer, however, increases the overall cost of displays, lowering their price competitiveness in the market.
For a solution, the research team applied the sol-gel condensation reaction of silane precursors with QDs. This technology uses the reactions of chemical substances to synthesize ceramics or glass at a low temperature.
The team applied QDs in a heat resistant siloxane polymer by employing this technology. The siloxane resin acted as a cup holding the QDs and also blocked heat and moisture. Thus, their performance can be maintained without an extra protective film.
QDs are evenly dispersed into the resin from a chemical process to fabricate a QD embedded film and retained the high quality luminescence not only at a high temperature of 85°C and in a high humidity of 85%, but also in a high acid and high base environment. Remarkably though, the luminescence actually increased in the high humidity environment.
If this technology is used, the overall price of displays will decrease by producing a stable QD film without an extra protective barrier. In the future, the QD film can be directly applied to a blue LED light source. As a result, it will be possible to develop a QD display that can reduce the amount of QDs needed and improve its performance.
Professor Bae said, “We have proposed a way to make quantum dots overcome their limitations and have wide applications as they are being developed for next-generation displays. Our technology will make significant contributions to the display industry in the country.”
He also added, “In the future, we plan to cooperate with companies both in and out of the country to improve the performance of quantum dots and concentrate on their commercialization.”
The research team is currently applying for related patents both in and out of the country. The team is also plan ning to transfer the patents to Sol Ip Technology Inc., a company founded at KAIST, to start the commercialization.
Picture 1:
Siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot (QD) films showing performance stability in boiling water
Picture 2 and 3:
So-gel condensation reaction in silane precursors between Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTS) and diphenylsilanediol (DPSD). The inset shows photographs of a QD-oligosiloxane resin under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
Free radical addition reactions among carbon double bonds of methacryl functional groups and oleic acids. The inset shows photographs of a QD-silox film under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
2017.02.24 View 9475
Quantum Dot Film Can Withstand High Temperatures and Humidity
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Doh Chang Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was able to fabricate a siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot film, which exhibits stable emission intensity over one month even at high temperatures and humidity.
The results of this study were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS) on November 29, 2016. The research article is entitled “Quantum Dot/Siloxane Composite Film Exceptionally Stable against Oxidation under Heat and Moisture.” (DOI: 10.1021/jacs.6b10681)
Quantum dots (QDs), light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for next-generation displays, are tiny particles or nanocrystals of semiconducting materials. Their emission wavelength can easily be adjusted by changing their sizes, which are just a few nanometers. A wide spectrum of their colors can also achieve ultra-high definition displays.
Due to these characteristics, QDs are coated on a film as a polymer resin in dispersed form, or they are spread on an LED light source. They are thus considered to be crucial for next generation displays.
Despite their exceptional optical properties, however, QDs are easily oxidized in a high temperature and high humidity environment, and, as a result, this greatly deteriorates their luminescence quality (quantum efficiency). Therefore, they are encapsulated in an extra thin layer to block oxygen and moisture.
QD displays in the current market have a film inserted to separate them from LEDs, which create heat. The high unit cost of this protective layer, however, increases the overall cost of displays, lowering their price competitiveness in the market.
For a solution, the research team applied the sol-gel condensation reaction of silane precursors with QDs. This technology uses the reactions of chemical substances to synthesize ceramics or glass at a low temperature.
The team applied QDs in a heat resistant siloxane polymer by employing this technology. The siloxane resin acted as a cup holding the QDs and also blocked heat and moisture. Thus, their performance can be maintained without an extra protective film.
QDs are evenly dispersed into the resin from a chemical process to fabricate a QD embedded film and retained the high quality luminescence not only at a high temperature of 85°C and in a high humidity of 85%, but also in a high acid and high base environment. Remarkably though, the luminescence actually increased in the high humidity environment.
If this technology is used, the overall price of displays will decrease by producing a stable QD film without an extra protective barrier. In the future, the QD film can be directly applied to a blue LED light source. As a result, it will be possible to develop a QD display that can reduce the amount of QDs needed and improve its performance.
Professor Bae said, “We have proposed a way to make quantum dots overcome their limitations and have wide applications as they are being developed for next-generation displays. Our technology will make significant contributions to the display industry in the country.”
He also added, “In the future, we plan to cooperate with companies both in and out of the country to improve the performance of quantum dots and concentrate on their commercialization.”
The research team is currently applying for related patents both in and out of the country. The team is also plan ning to transfer the patents to Sol Ip Technology Inc., a company founded at KAIST, to start the commercialization.
Picture 1:
Siloxane-encapsulated quantum dot (QD) films showing performance stability in boiling water
Picture 2 and 3:
So-gel condensation reaction in silane precursors between Methacryloxypropyltrimethoxysilane (MPTS) and diphenylsilanediol (DPSD). The inset shows photographs of a QD-oligosiloxane resin under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
Free radical addition reactions among carbon double bonds of methacryl functional groups and oleic acids. The inset shows photographs of a QD-silox film under room light (left) and a UV lamp (λ = 365 nm) (right).
2017.02.24 View 9475 -
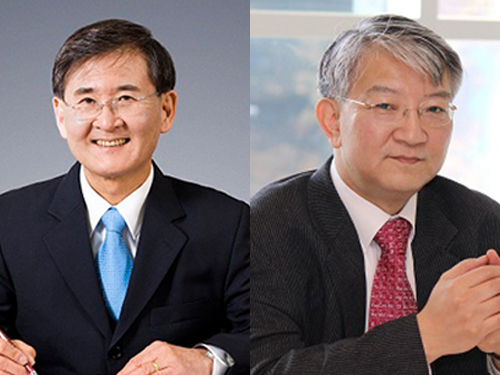 KAIST to Participate in the 2017 Davos Forum
(President Sung-Mo Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
KAIST representatives will join high profile, multi-stakeholder dialogues with global leaders across the world to discuss higher education, science, and technological innovation.
KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will participate in the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Annual Meeting on January 17-20, 2017, in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
To be held under the theme “Responsive and Responsible Leadership,” the Annual Meeting will offer global leaders from government, business, academia, and civil society a highly interactive platform to address some of the most pressing issues facing the world today, from climate change, economic inequality, to the Fourth Industrial Revolution and its impact on future employment.
On January 18, President Kang will participate in the Global University Leaders Forum, a community of top 26 universities invited from around the world, and will discuss the relevance of higher education in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He will also share KAIST’s experiences in developing innovative initiatives to bring future-oriented and creative values into its educational and research programs.
On January 19, at the Global Future Council on Production, President Kang will speak about new technologies taking place in traditional production and distribution systems as introduced by the emergence of rapidly evolving technological advancements, and present KAIST’s endeavors to transform those changes into opportunities.
With an eminent group of scientists, including the Director of the US National Science Foundation France A. Córdova and the Editor-in-Chief Philip Campbell of Nature at the Global Science Outlook session, on January 20, President Kang will discuss key challenges for the global science agenda in the year ahead and examine the role of science in formulating public discussions and polices that will have great impact on society and the lives of people.
Currently, Professor Lee is the founding Co-Chair of the WEF’s Global Future Council, an interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking on the future. On January 20, he will share his insights at an independent session entitled “World Changing Technology: Biotech and Neurotech,” briefing the audience on the current state of research, development, and commercialization in these fields, as well as explaining how they will contribute to coping with the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Professor Lee said, “In recent years, we have seen the world become ever more complex, interconnected, and realigned as it is deeply affected by this unprecedented technological innovations, collectively driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution. One pillar of such innovation will take place in biotechnology and neuroscience, which will help us design solutions to many of global problems such as environment, pandemic diseases, aging, healthcare, and previously intractable illnesses.”
President Kang added, “This year’s Davos meeting will focus on the need to foster leadership at the national, regional, and global level to respond collectively with credible actions to issues of major concern for the sustainable and equitable growth, social inclusion, and human development. KAIST has always been a crucial player in these collaborative efforts, and I am happy to share our insights at the upcoming event.”
2017.01.17 View 8531
KAIST to Participate in the 2017 Davos Forum
(President Sung-Mo Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
KAIST representatives will join high profile, multi-stakeholder dialogues with global leaders across the world to discuss higher education, science, and technological innovation.
KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will participate in the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) Annual Meeting on January 17-20, 2017, in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
To be held under the theme “Responsive and Responsible Leadership,” the Annual Meeting will offer global leaders from government, business, academia, and civil society a highly interactive platform to address some of the most pressing issues facing the world today, from climate change, economic inequality, to the Fourth Industrial Revolution and its impact on future employment.
On January 18, President Kang will participate in the Global University Leaders Forum, a community of top 26 universities invited from around the world, and will discuss the relevance of higher education in the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He will also share KAIST’s experiences in developing innovative initiatives to bring future-oriented and creative values into its educational and research programs.
On January 19, at the Global Future Council on Production, President Kang will speak about new technologies taking place in traditional production and distribution systems as introduced by the emergence of rapidly evolving technological advancements, and present KAIST’s endeavors to transform those changes into opportunities.
With an eminent group of scientists, including the Director of the US National Science Foundation France A. Córdova and the Editor-in-Chief Philip Campbell of Nature at the Global Science Outlook session, on January 20, President Kang will discuss key challenges for the global science agenda in the year ahead and examine the role of science in formulating public discussions and polices that will have great impact on society and the lives of people.
Currently, Professor Lee is the founding Co-Chair of the WEF’s Global Future Council, an interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking on the future. On January 20, he will share his insights at an independent session entitled “World Changing Technology: Biotech and Neurotech,” briefing the audience on the current state of research, development, and commercialization in these fields, as well as explaining how they will contribute to coping with the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
Professor Lee said, “In recent years, we have seen the world become ever more complex, interconnected, and realigned as it is deeply affected by this unprecedented technological innovations, collectively driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution. One pillar of such innovation will take place in biotechnology and neuroscience, which will help us design solutions to many of global problems such as environment, pandemic diseases, aging, healthcare, and previously intractable illnesses.”
President Kang added, “This year’s Davos meeting will focus on the need to foster leadership at the national, regional, and global level to respond collectively with credible actions to issues of major concern for the sustainable and equitable growth, social inclusion, and human development. KAIST has always been a crucial player in these collaborative efforts, and I am happy to share our insights at the upcoming event.”
2017.01.17 View 8531 -
 The World Economic Forum Invites KAIST to 2014 Davos Forum
President Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee have been invited by the World Economic Forum (WEF) to attend its annual meeting slated for January 22-25, 2014 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
The president will also join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to be held during the annual meeting. The GULF consists of leading research universities throughout the world, at which President Kang will address agenda related to higher education and research.
From September 11th to 13th, KAIST was invited to the WEF’s 2013 Summer Davos Forum held in Dalian, China. The Summer Davos Forum is recognized as a barometer of the world economy, and KAIST hosted three sessions there.
In a session titled “Smart Regulations,” Professor Sang Yup Lee hosted presentations and discussions under the topic of “How regulation models can strengthen technical innovation and expansion.” President Steve Kang, Peter Sands, CEO of Standard Chartered Bank Group, Mark Weinberger, CEO of Ernest & Young, and Peter Terium, CEO of RWE, participated in the discussions.
The KAIST delegates also presented and participated in a session titled “From Trade Center to Innovative Hub” to discuss how to lead innovations in Asia, as well as “Marine Resources: Finding New Frontier” to address issues of how to develop and manage oceanic resources for potential growth.
President Kang said, “The World Economic Forum allows us to introduce the results of our innovative and creative research to global leaders and to demonstrate that our global position continues to grow.”
The WEF has been hosting Summer Davos Forum in China since 2007. About 1,500 participants from over 90 countries joined in this year’s summer forum under the theme of “Innovation: Inevitable Mainstream.” New strategies for innovations and solutions for global threats were suggested through presentations and discussions in 125 sessions.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an independent, international, and non-profit organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. It is committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and government leaders to shape global, regional and industry agenda.
Among the meetings and forums organized by the WEF, its annual meeting held each January in Davos, a.k.a. the Davos Forum, has been the best known gathering. The Davos Forum brings together some 2,500 top business leaders, international political leaders, selected intellectuals and journalists to discuss the most pressing issues facing the world including health and environment.
2013.11.07 View 10178
The World Economic Forum Invites KAIST to 2014 Davos Forum
President Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee have been invited by the World Economic Forum (WEF) to attend its annual meeting slated for January 22-25, 2014 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
The president will also join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to be held during the annual meeting. The GULF consists of leading research universities throughout the world, at which President Kang will address agenda related to higher education and research.
From September 11th to 13th, KAIST was invited to the WEF’s 2013 Summer Davos Forum held in Dalian, China. The Summer Davos Forum is recognized as a barometer of the world economy, and KAIST hosted three sessions there.
In a session titled “Smart Regulations,” Professor Sang Yup Lee hosted presentations and discussions under the topic of “How regulation models can strengthen technical innovation and expansion.” President Steve Kang, Peter Sands, CEO of Standard Chartered Bank Group, Mark Weinberger, CEO of Ernest & Young, and Peter Terium, CEO of RWE, participated in the discussions.
The KAIST delegates also presented and participated in a session titled “From Trade Center to Innovative Hub” to discuss how to lead innovations in Asia, as well as “Marine Resources: Finding New Frontier” to address issues of how to develop and manage oceanic resources for potential growth.
President Kang said, “The World Economic Forum allows us to introduce the results of our innovative and creative research to global leaders and to demonstrate that our global position continues to grow.”
The WEF has been hosting Summer Davos Forum in China since 2007. About 1,500 participants from over 90 countries joined in this year’s summer forum under the theme of “Innovation: Inevitable Mainstream.” New strategies for innovations and solutions for global threats were suggested through presentations and discussions in 125 sessions.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an independent, international, and non-profit organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. It is committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and government leaders to shape global, regional and industry agenda.
Among the meetings and forums organized by the WEF, its annual meeting held each January in Davos, a.k.a. the Davos Forum, has been the best known gathering. The Davos Forum brings together some 2,500 top business leaders, international political leaders, selected intellectuals and journalists to discuss the most pressing issues facing the world including health and environment.
2013.11.07 View 10178