research
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee (http://fand.kaist.ac.kr) of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed a hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvesting device called a nanogenerator.
Flexible electronics have come into the market and are enabling new technologies like flexible displays in mobile phone, wearable electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoTs). However, is the degree of flexibility enough for most applications? For many flexible devices, elasticity is a very important issue. For example, wearable/biomedical devices and electronic skins (e-skins) should stretch to conform to arbitrarily curved surfaces and moving body parts such as joints, diaphragms, and tendons. They must be able to withstand the repeated and prolonged mechanical stresses of stretching. In particular, the development of elastic energy devices is regarded as critical to establish power supplies in stretchable applications. Although several researchers have explored diverse stretchable electronics, due to the absence of the appropriate device structures and correspondingly electrodes, researchers have not developed ultra-stretchable and fully-reversible energy conversion devices properly.
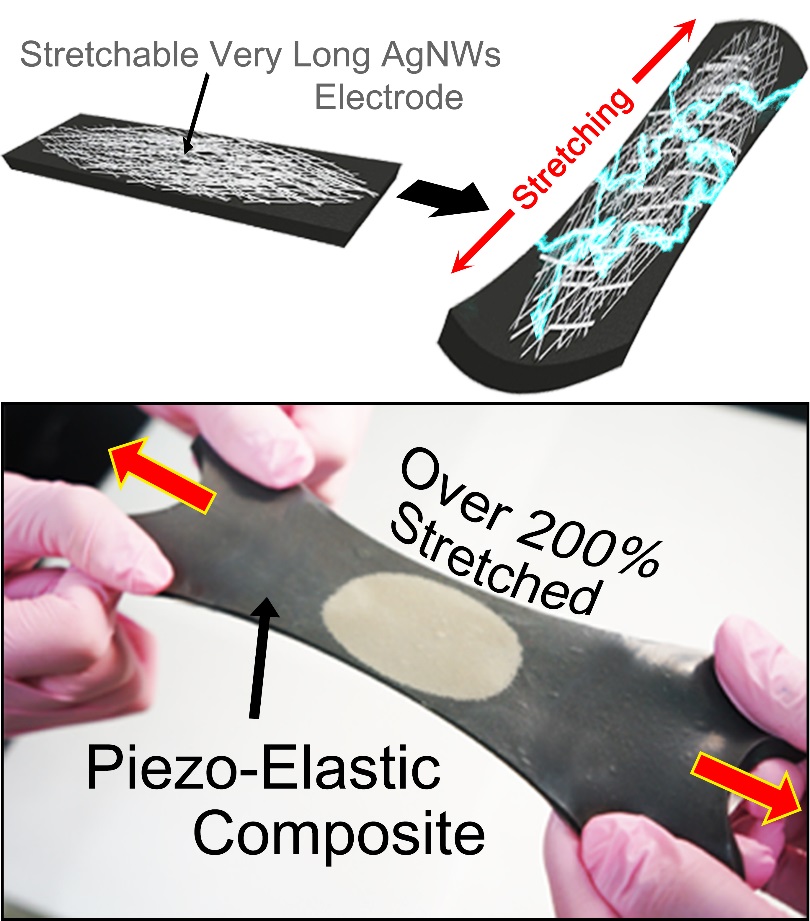
Recently, researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) have collaborated and demonstrated a facile methodology to obtain a high-performance and hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator (SEG) using very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes. Their stretchable piezoelectric generator can harvest mechanical energy to produce high power output (~4 V) with large elasticity (~250%) and excellent durability (over 104 cycles). These noteworthy results were achieved by the non-destructive stress- relaxation ability of the unique electrodes as well as the good piezoelectricity of the device components. The new SEG can be applied to a wide-variety of wearable energy-harvesters to transduce biomechanical-stretching energy from the body (or machines) to electrical energy.
Professor Lee said, “This exciting approach introduces an ultra-stretchable piezoelectric generator. It can open avenues for power supplies in universal wearable and biomedical applications as well as self-powered ultra-stretchable electronics.”
This result was published online in the March issue of Advanced Materials, which is entitled “A Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester.”
YouTube Link: “A hyper-stretchable energy harvester”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBByFvPVRiU&feature=youtu.be
Figure: Top row: Schematics of hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator enabled by very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes.
Bottom row: The SEG energy harvester stretched by human hands over 200% strain.
-
research Sturdy Fabric-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Takes Us One Step Closer to Wearable Electronics
KAIST researchers presented a highly flexible but sturdy wearable piezoelectric harvester using the simple and easy fabrication process of hot pressing and tape casting. This energy harvester, which has record high interfacial adhesion strength, will take us one step closer to being able to manufacture embedded wearable electronics. A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong said that the novelty of this result lies in its simplicity, applicability, durability, and its new characterization
2020-09-17 -
research Novel Material Properties of Hybrid Perovskite Nanostructures for Next-generation Non-linear Electronic Devices
(from left: Juho Lee, Dr. Muhammad Ejaz Khan and Professor Yong-Hoon Kim) A KAIST research team reported a novel non-linear device with the founding property coming from perovskite nanowires. They showed that hybrid perovskite-derived, inorganic-framework nanowires can acquire semi-metallicity, and proposed negative differential resistance (NDR) devices with excellent NDR characteristics that resulted from a novel quantum-hybridization NDR mechanism, implying the potential of perovskite nano
2019-02-22 -
research Hierarchical Porous Titanium Nitride Synthesized by Multiscale Phase Separation for LSBs
(from left: Professor Jinwoo Lee and PhD candidate Won-Gwang Lim) A KAIST research team developed ultra-stable, high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs) by using hierarchical porous titanium nitride as a sulfur host, and achieved superior cycle stability and high rate performance for LSBs. The control of large amounts of energy is required for use in an electric vehicle or smart grid system. In this sense, the development of next-generation secondary batteries is in high
2019-01-28 -
research Highly Scalable Process to Obtain Stable 2D Nanosheet Dispersion
(Professor Do Hyun Kim and his team) A KAIST team developed technology that allows the mass production of two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterial dispersion by utilizing the characteristic shearing force of hydraulic power. The 2D nanosheet dispersion can be directly applied to solution-based processes to manufacture devices for electronics as well as energy storage and conversion. It is expected to be used in these devices with improved performance. There have been numero
2018-12-19 -
research Characteristics of Submesoscale Geophysical Turbulence Reported
A KAIST research team has reported some of unique characteristics and driving forces behind submesoscale geophysical turbulence. Using big data analysis on ocean surface currents and chlorophyll concentrations observed using coastal radars and satellites has brought better understanding of oceanic processes in space and time scales of O(1) kilometer and O(1) hour. The outcomes of this work will lead to improved tracking of water-borne materials and performance in global and regional climate
2018-12-13