research
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
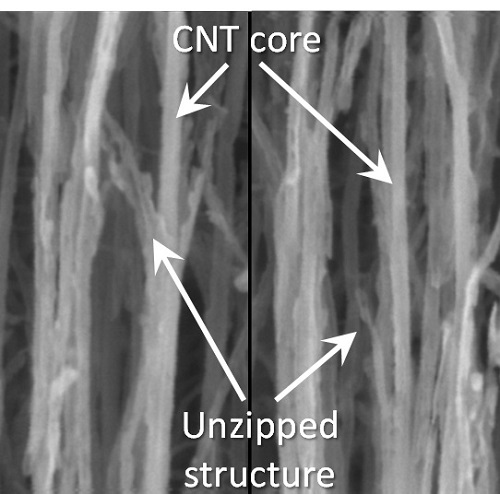
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
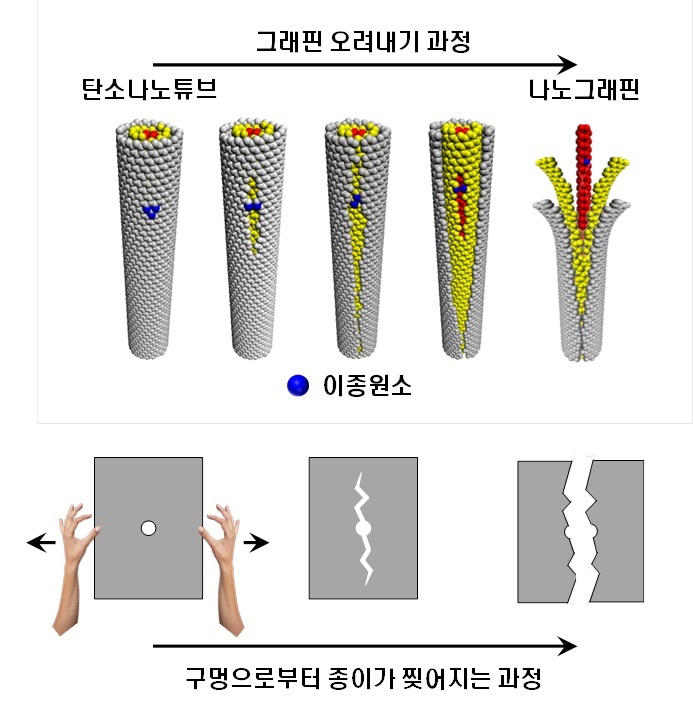
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
-
research A Hole in One for Holographic Display
(Professor YongKeun Park) Researchers have designed an ultrathin display that can project dynamic, multi-coloured, 3D holographic images, according to a study published in Nature Communications. The system’s critical component is a thin film of titanium filled with tiny holes that precisely correspond with each pixel in a liquid crystal display (LCD) panel. This film acts as a ‘photon sieve’ – each pinhole diffracts light emerging from them widely, resulting in a
2019-04-18 -
research Unravelling Inherent Electrocatalysis to Improve the Performance of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
(Figure 1. Electrode structure for the precise evaluation of the metal nanoparticles’ electrochemical catalytic characteristics at a high temperature.) A KAIST team presented an ideal electrode design to enhance the performance of high-temperature fuel cells. The new analytical platform with advanced nanoscale patterning method quantitatively revealed the electrochemical value of metal nanoparticles dispersed on the oxide electrode, thus leading to electrode design directions that c
2019-03-28 -
research New Catalyst for Synthesizing Chiral Molecules Selectively
(from left: Dr. Yoonsu Park and Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry) Molecules in nature often have “twin” molecules that look identical. In particular, the twin molecules that look like mirror images to each other are called enantiomers. However, even though they have the same type and number of elements, these twin molecules exhibit completely different properties. Professor Sukbok Chang and Dr. Yoonsu Park from the Department of Chemistry
2019-03-05 -
research New LSB with Theoretical Capacity over 90%
(Professor Hee-Tak Kim and Hyunwon Chu) A KAIST research team has developed a lithium sulfur battery (LSB) that realizes 92% of the theoretical capacity and an areal capacity of 4mAh/cm2. LSBs are gaining a great deal of attention as an alternative for lithium ion batteries (LIBs) because they have a theoretical energy density up to six to seven times higher than that of LIBs, and can be manufactured in a more cost-effective way. However, LSBs face the obstacle of
2019-02-11 -
research Noninvasive Light-Sensitive Recombinase for Deep Brain Genetic Manipulation
A KAIST team presented a noninvasive light-sensitive photoactivatable recombinase suitable for genetic manipulation in vivo. The highly light-sensitive property of photoactivatable Flp recombinase will be ideal for controlling genetic manipulation in deep mouse brain regions by illumination with a noninvasive light-emitting diode. This easy-to-use optogenetic module made by Professor Won Do Heo and his team will provide a side-effect free and expandable genetic manipulation tool for neurosci
2019-01-22