AR
-
 The 2014 Wearable Computer Competition Takes Place at KAIST
“This is a smart wig for patients who are reluctant to go outdoors because their hair is falling out from cancer treatment.”
A graduate student from Sungkyunkwan University, Jee-Hoon Lee enthusiastically explains his project at the KAIST KI Building where the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition was held. He said, “The sensor embedded inside the wig monitors the heart rate and the body temperature, and during an emergency, the device warns the patient about the situation. The product emphasizes two aspects; it notifies the patient in emergency situations, and it encourages patients to perform outdoor activities by enhancing their looks.”
The the tenth anniversary meeting of the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition took place at the KAIST campus on November 13-14, 2014.
A wearable computer is a mobile device designed to be put on the body or clothes so that a user can comfortably use it while walking. Recently, these devices that are able to support versatile internet-based services through smartphones are receiving a great deal of attention.
Wearable devices have been employed in two categorizes: health checks and information-entertainment. In this year’s competition, six healthcare products and nine information-entertainment products were exhibited.
Among these products, participants favored a smart helmet for motorcycle drivers. The driver can see through a rear camera with a navigation screen of the smartphone and text messages through the screen installed in the front glass of the helmet. Another product included a uniform that can control presentation slides by means of motion detection and voice recognition technology. Yet another popular device offered an insole to guide travelers to their destination with the help of motion sensors.
The chairman of the competition, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST said, “Wearable devices such as smart watches, glasses, and clothes are gaining interest these days. Through this event, people will have a chance to look at the creativity of our students through the display of their wearable devices. In turn, these devices will advance computer technology.”
The third annual wearable computer workshop on convergence technology of wearable computers followed the competition. In the workshop, experts from leading information technology companies such as Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, and KT Corporation addressed the convergence technology of wearable computers and trends in the field.
2014.11.19 View 9493
The 2014 Wearable Computer Competition Takes Place at KAIST
“This is a smart wig for patients who are reluctant to go outdoors because their hair is falling out from cancer treatment.”
A graduate student from Sungkyunkwan University, Jee-Hoon Lee enthusiastically explains his project at the KAIST KI Building where the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition was held. He said, “The sensor embedded inside the wig monitors the heart rate and the body temperature, and during an emergency, the device warns the patient about the situation. The product emphasizes two aspects; it notifies the patient in emergency situations, and it encourages patients to perform outdoor activities by enhancing their looks.”
The the tenth anniversary meeting of the 2014 Wearable Computer Competition took place at the KAIST campus on November 13-14, 2014.
A wearable computer is a mobile device designed to be put on the body or clothes so that a user can comfortably use it while walking. Recently, these devices that are able to support versatile internet-based services through smartphones are receiving a great deal of attention.
Wearable devices have been employed in two categorizes: health checks and information-entertainment. In this year’s competition, six healthcare products and nine information-entertainment products were exhibited.
Among these products, participants favored a smart helmet for motorcycle drivers. The driver can see through a rear camera with a navigation screen of the smartphone and text messages through the screen installed in the front glass of the helmet. Another product included a uniform that can control presentation slides by means of motion detection and voice recognition technology. Yet another popular device offered an insole to guide travelers to their destination with the help of motion sensors.
The chairman of the competition, Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST said, “Wearable devices such as smart watches, glasses, and clothes are gaining interest these days. Through this event, people will have a chance to look at the creativity of our students through the display of their wearable devices. In turn, these devices will advance computer technology.”
The third annual wearable computer workshop on convergence technology of wearable computers followed the competition. In the workshop, experts from leading information technology companies such as Samsung Electronics, LG Electronics, and KT Corporation addressed the convergence technology of wearable computers and trends in the field.
2014.11.19 View 9493 -
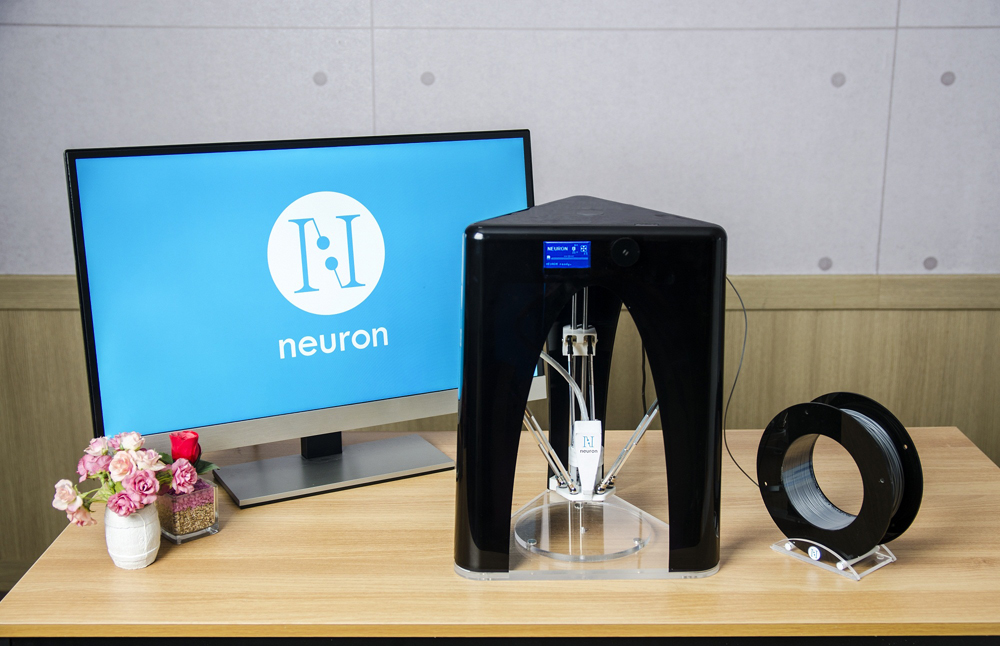 3D Printer Developed by KAIST Undergraduate Students
More than 100 Pre-orders Prior to Product Launch Made
KAIST undergraduate students received more than 100 pre-orders before the launch for 3D printers they developed and became a hot topic of interest.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations (Head Hong-Kyu Lee) had a launch party at Daejeon Riviera Hotel on 17 November 2014 for “Commercial Delta 3D Printer” developed by KAIST undergraduate students inviting around 50 businesses, buyers and representatives of 3D Printing Industry Association.
“3D Printer” uses blueprints of products such as toys, mug cups and chairs to make 3D objects and is thought to be revolutionary technology in manufacturing industry. The interest has grown as recent printers could print even fruits and cosmetics.
The printing structure of 3D printer can be divided roughly into horizontal Mendel method and Delta method. KAIST students focused on the Delta method to give a differentiated product from 90% of commercial products that use Mendel method.
First, the students focused on lowering the cost of unit price by using self-developed components. The carriage (transport machine) of the product is replaced by self-developed components instead of bearing to reduce the noise and the linking method was changed to beads from loop guide to increase the completeness of the printed product. Also, an auto-levelling is loaded to ensure the nozzle and the bed is parallel and hence increasing convenience for the users. Further, the printer, designed by a product designer in Germany, is linked to a smartphone application for blueprints.
A student in the development team, Seokhyeon Seo (Department of Computer Science, 3rd Year Undergraduate) said, “The biggest merits of the product are lowering the price to a 1/3 by using self-developed components and reducing the noise.” He continued, “By using a smartphone application, anyone can easily design the product. So it is applicable to use for education or at home”
In the exhibit, “3D Printing Korea 2014,” in Coex, Seoul the printer had a preview demonstration, and received more than 100 pre-orders from educational and business training institutions. Further, buyers from Canada and the US requested opening agencies in their countries.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations Head Hong-Kyu Lee said, “3D printing is an innovative technology that could bring the 3rd industrial revolution.” He continued, “It is still early days but the demand will increase exponentially.”
This project was a research project of KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations led by a development team consisting of 4 undergraduate students of KAIST, one student from University of Oxford and one German product designer.
Students in the picture below are Won-Hoi Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering), Sung-Hyun Cho (Department of Mechanical Engineering), and Suk-Hyun Seo (Department of Computer Science) from left to right.
2014.11.19 View 10105
3D Printer Developed by KAIST Undergraduate Students
More than 100 Pre-orders Prior to Product Launch Made
KAIST undergraduate students received more than 100 pre-orders before the launch for 3D printers they developed and became a hot topic of interest.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations (Head Hong-Kyu Lee) had a launch party at Daejeon Riviera Hotel on 17 November 2014 for “Commercial Delta 3D Printer” developed by KAIST undergraduate students inviting around 50 businesses, buyers and representatives of 3D Printing Industry Association.
“3D Printer” uses blueprints of products such as toys, mug cups and chairs to make 3D objects and is thought to be revolutionary technology in manufacturing industry. The interest has grown as recent printers could print even fruits and cosmetics.
The printing structure of 3D printer can be divided roughly into horizontal Mendel method and Delta method. KAIST students focused on the Delta method to give a differentiated product from 90% of commercial products that use Mendel method.
First, the students focused on lowering the cost of unit price by using self-developed components. The carriage (transport machine) of the product is replaced by self-developed components instead of bearing to reduce the noise and the linking method was changed to beads from loop guide to increase the completeness of the printed product. Also, an auto-levelling is loaded to ensure the nozzle and the bed is parallel and hence increasing convenience for the users. Further, the printer, designed by a product designer in Germany, is linked to a smartphone application for blueprints.
A student in the development team, Seokhyeon Seo (Department of Computer Science, 3rd Year Undergraduate) said, “The biggest merits of the product are lowering the price to a 1/3 by using self-developed components and reducing the noise.” He continued, “By using a smartphone application, anyone can easily design the product. So it is applicable to use for education or at home”
In the exhibit, “3D Printing Korea 2014,” in Coex, Seoul the printer had a preview demonstration, and received more than 100 pre-orders from educational and business training institutions. Further, buyers from Canada and the US requested opening agencies in their countries.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations Head Hong-Kyu Lee said, “3D printing is an innovative technology that could bring the 3rd industrial revolution.” He continued, “It is still early days but the demand will increase exponentially.”
This project was a research project of KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations led by a development team consisting of 4 undergraduate students of KAIST, one student from University of Oxford and one German product designer.
Students in the picture below are Won-Hoi Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering), Sung-Hyun Cho (Department of Mechanical Engineering), and Suk-Hyun Seo (Department of Computer Science) from left to right.
2014.11.19 View 10105 -
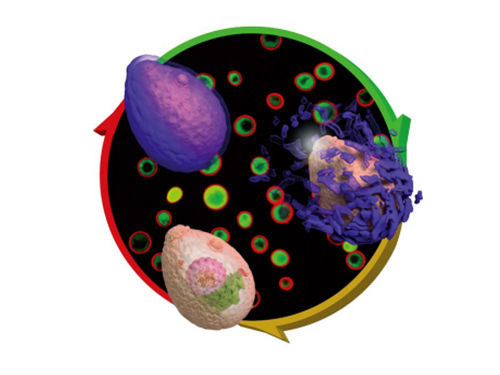 Eggshell-like Cell Encapsulation and Degradation Technology Developed
Some bacteria form endospores on cell walls to protect their DNA in case of nutrient deficiency. When an endospore meets a suitable environment for survival, the cell can revert to the original state from which it can reproduce.
The technique that can artificially control such phenomenon was developed by an international team of researchers. At first, a cell is wrapped and preserved like an egg. When the cell is needed, the technique allows the endospore to decompose while it is alive. Future applications for this technique include cell-based biosensor, cell therapy, and biocatalyst processes.
Professors Insung Choi and Younghoon Lee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST as well as and Professor Frank Caruso from the University of Melbourne developed this technique which permits a cell to stay alive by coating it with film on a nanometer scale and then to be decomposed while it is alive.
The research finding was published in the November 10th issue of Angewandte Chemie International Edition as the lead article.
Cell encapsulation allows researchers to capture a cell in a tight capsule while it is alive. It is highly recognized in cell-based applications where the control of cell stability and cell-division is the biggest issue.
Traditional cell encapsulation methods utilized organic film or inorganic capsules that are made of organic film moldings. Although these films tightly closed around the cell, because they were not easily decomposable, it was difficult to apply the method.
The research team succeeded in encapsulating each cell in a metal-polyphenol film by mixing tannic acid and iron ion solution with yeast cells.
Usually extracted from oak barks or grape peels, tannic acid is a natural substance. It forms a metal-polyphenol film within ten seconds when it meets iron ions due to its high affinity with cells. Cells encapsulated with this film presented high survival rates. Since the film forms quickly in a simple manner, it was possible to obtain large amount of encapsulated cells.
The research team also found that the metal-polyphenol film was stable in neutral pH, but is easily degradable under a weak acidic condition. Using this property, they were able to control cell division by restoring the cell to its pre-encapsulated state at a desired moment.
Protecting the cell from the external environment like an egg shell, the metal-polyphenol film protected the cell against foreign conditions such as lytic enzymes, extended exposure to UV radiation, and silver nanoparticles. The research indicated that the encapsulated cells had a high survival rate even under extreme environments.
Professor Lee said that “not only the cells remain alive during the encapsulation stage, but also they can be protected under extreme environment.” He added, “This is an advanced cell encapsulation technology that allows controlling cell-division of those cells through responsive shell degradation on-demand.”
Professor Choi commented, “Although the cell encapsulation technology is still in its infancy, as the technology matures the application of cell-manipulation technology will be actualized.” He highlighted that “it will serve as a breakthrough to problems faced by cell-based applications.”
Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research was led by two Master’s candidates, Ji Hun Park and Kyung Hwan Kim, under the joint guidance of research professors from KAIST and the University of Melbourne.
Figure 1: Lead article of Angewandte Chemie
Background: Shows a live native yeast (in green) encapsulated in a metal-polyphenol film (in red) illustrating the vitality of the yeast
Front: A native yeast at each encapsulation stage
Pictured on the bottom left is a cell prior to encapsulation. Following the red arrow, the native yeast is in purple to show metal-polyphenol film formed around the cell. The cell after the green arrow is a visualization of the degradation of the film in weak acidic condition.
Figure 2: A mimetic diagram of cell encapsulation with a metal-polyphenol film
Top: A native yeast before encapsulation
Middle: A native yeast encapsulated with Tannic Acid-Fe (III) Nanoshell – cell-division of the encapsulated cell is controlled by pH and the shell is protected against silver nanoparticle, lytic enzyme, and UV-C
Bottom: Shell degradation on-demand depending on pH
2014.11.18 View 9626
Eggshell-like Cell Encapsulation and Degradation Technology Developed
Some bacteria form endospores on cell walls to protect their DNA in case of nutrient deficiency. When an endospore meets a suitable environment for survival, the cell can revert to the original state from which it can reproduce.
The technique that can artificially control such phenomenon was developed by an international team of researchers. At first, a cell is wrapped and preserved like an egg. When the cell is needed, the technique allows the endospore to decompose while it is alive. Future applications for this technique include cell-based biosensor, cell therapy, and biocatalyst processes.
Professors Insung Choi and Younghoon Lee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST as well as and Professor Frank Caruso from the University of Melbourne developed this technique which permits a cell to stay alive by coating it with film on a nanometer scale and then to be decomposed while it is alive.
The research finding was published in the November 10th issue of Angewandte Chemie International Edition as the lead article.
Cell encapsulation allows researchers to capture a cell in a tight capsule while it is alive. It is highly recognized in cell-based applications where the control of cell stability and cell-division is the biggest issue.
Traditional cell encapsulation methods utilized organic film or inorganic capsules that are made of organic film moldings. Although these films tightly closed around the cell, because they were not easily decomposable, it was difficult to apply the method.
The research team succeeded in encapsulating each cell in a metal-polyphenol film by mixing tannic acid and iron ion solution with yeast cells.
Usually extracted from oak barks or grape peels, tannic acid is a natural substance. It forms a metal-polyphenol film within ten seconds when it meets iron ions due to its high affinity with cells. Cells encapsulated with this film presented high survival rates. Since the film forms quickly in a simple manner, it was possible to obtain large amount of encapsulated cells.
The research team also found that the metal-polyphenol film was stable in neutral pH, but is easily degradable under a weak acidic condition. Using this property, they were able to control cell division by restoring the cell to its pre-encapsulated state at a desired moment.
Protecting the cell from the external environment like an egg shell, the metal-polyphenol film protected the cell against foreign conditions such as lytic enzymes, extended exposure to UV radiation, and silver nanoparticles. The research indicated that the encapsulated cells had a high survival rate even under extreme environments.
Professor Lee said that “not only the cells remain alive during the encapsulation stage, but also they can be protected under extreme environment.” He added, “This is an advanced cell encapsulation technology that allows controlling cell-division of those cells through responsive shell degradation on-demand.”
Professor Choi commented, “Although the cell encapsulation technology is still in its infancy, as the technology matures the application of cell-manipulation technology will be actualized.” He highlighted that “it will serve as a breakthrough to problems faced by cell-based applications.”
Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research was led by two Master’s candidates, Ji Hun Park and Kyung Hwan Kim, under the joint guidance of research professors from KAIST and the University of Melbourne.
Figure 1: Lead article of Angewandte Chemie
Background: Shows a live native yeast (in green) encapsulated in a metal-polyphenol film (in red) illustrating the vitality of the yeast
Front: A native yeast at each encapsulation stage
Pictured on the bottom left is a cell prior to encapsulation. Following the red arrow, the native yeast is in purple to show metal-polyphenol film formed around the cell. The cell after the green arrow is a visualization of the degradation of the film in weak acidic condition.
Figure 2: A mimetic diagram of cell encapsulation with a metal-polyphenol film
Top: A native yeast before encapsulation
Middle: A native yeast encapsulated with Tannic Acid-Fe (III) Nanoshell – cell-division of the encapsulated cell is controlled by pH and the shell is protected against silver nanoparticle, lytic enzyme, and UV-C
Bottom: Shell degradation on-demand depending on pH
2014.11.18 View 9626 -
 The Website of the KAIST Industrial Design Department Receives a Design Award
The 10th QS-Apple Higher Education Conference and Exhibition took place on November 11-13, 2014 in Taipei, Taiwan. The conference was hosted by Quacquarelli Symonds, a British company specializing in education, which publishes annually its world university rankings. Apple stands for Asia Pacific Professional Leaders in Education.
The QS-Apple conference supports the internationalization of Asia Pacific universities by providing opportunities for networking, exchanging best practices, and discussing recent developments in higher education. During the conference, the organizers presented the Creative Awards for best international education promotional designs in four categories: Website Pages, Video, Print Advertisement, and International Student Recruitment Brochures.
KAIST’s Industrial Design Department received the Best Website Pages Award for their website in recognition of high levels of user convenience and satisfaction as well as English language services. A total of 39 universities in the Asia and Pacific region competed in this category, and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore came in second place, followed by Hong Kong Baptist University in third.
2014.11.13 View 8146
The Website of the KAIST Industrial Design Department Receives a Design Award
The 10th QS-Apple Higher Education Conference and Exhibition took place on November 11-13, 2014 in Taipei, Taiwan. The conference was hosted by Quacquarelli Symonds, a British company specializing in education, which publishes annually its world university rankings. Apple stands for Asia Pacific Professional Leaders in Education.
The QS-Apple conference supports the internationalization of Asia Pacific universities by providing opportunities for networking, exchanging best practices, and discussing recent developments in higher education. During the conference, the organizers presented the Creative Awards for best international education promotional designs in four categories: Website Pages, Video, Print Advertisement, and International Student Recruitment Brochures.
KAIST’s Industrial Design Department received the Best Website Pages Award for their website in recognition of high levels of user convenience and satisfaction as well as English language services. A total of 39 universities in the Asia and Pacific region competed in this category, and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore came in second place, followed by Hong Kong Baptist University in third.
2014.11.13 View 8146 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 10486
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 10486 -
 A KAIST Student Team Wins the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest
A KAIST team consisted of students from the Departments of Industrial Design and Computer Science participated in the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest and received 1st Prize in the category of People’s Choice.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST) is an international forum to promote innovations in human-computer interfaces, which takes place annually and is sponsored by ACM Special Interest Groups on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) and Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH). The ACM UIST conference brings together professionals in the fields of graphical and web-user interfaces, tangible and ubiquitous computing, virtual and augmented reality, multimedia, and input and output devices.
The Student Innovation Contest has been held during the UIST conference since 2009 to innovate new interactions on state-of-the-art hardware. The participating students were given with the hardware platform to build on—this year, it was Kinoma Create, a JavaScript-powered construction kit that allows makers, professional product designers, and web developers to create personal projects, consumer electronics, and "Internet of Things" prototypes. Contestants demonstrated their creations on household interfaces, and two winners in each of three categories -- Most Creative, Most Useful, and the People’s Choice -- were awarded.
Utilizing Kinoma Create, which came with a built-in touchscreen, WiFi, Bluetooth, a front-facing sensor connector, and a 50-pin rear sensor dock, the KAIST team developed a “smart mop,” transforming the irksome task of cleaning into a fun game. The smart mop identifies target dirt and shows its location on the display built in the rod of a mop. If the user turns on a game mode, then winning scores are gained wherever the target dirt is cleaned.
The People’s Choice award was decided by conference attendees, and they voted the smart mop as their most favorite project.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, who advised the students, said, "A total of 24 teams from such prestigious universities as Carnegie Mellon University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and the University of Tokyo joined the contest, and we are pleased with the good results. Many people, in fact, praised the integration of creativity and technical excellence our have shown through the smart mop.”
Team KAIST: pictured from right to left, Sun-Jun Kim, Se-Jin Kim, and Han-Jong Kim
The Smart Mop can clean the floor and offer users a fun game.
2014.11.12 View 10245
A KAIST Student Team Wins the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest
A KAIST team consisted of students from the Departments of Industrial Design and Computer Science participated in the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest and received 1st Prize in the category of People’s Choice.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST) is an international forum to promote innovations in human-computer interfaces, which takes place annually and is sponsored by ACM Special Interest Groups on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) and Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH). The ACM UIST conference brings together professionals in the fields of graphical and web-user interfaces, tangible and ubiquitous computing, virtual and augmented reality, multimedia, and input and output devices.
The Student Innovation Contest has been held during the UIST conference since 2009 to innovate new interactions on state-of-the-art hardware. The participating students were given with the hardware platform to build on—this year, it was Kinoma Create, a JavaScript-powered construction kit that allows makers, professional product designers, and web developers to create personal projects, consumer electronics, and "Internet of Things" prototypes. Contestants demonstrated their creations on household interfaces, and two winners in each of three categories -- Most Creative, Most Useful, and the People’s Choice -- were awarded.
Utilizing Kinoma Create, which came with a built-in touchscreen, WiFi, Bluetooth, a front-facing sensor connector, and a 50-pin rear sensor dock, the KAIST team developed a “smart mop,” transforming the irksome task of cleaning into a fun game. The smart mop identifies target dirt and shows its location on the display built in the rod of a mop. If the user turns on a game mode, then winning scores are gained wherever the target dirt is cleaned.
The People’s Choice award was decided by conference attendees, and they voted the smart mop as their most favorite project.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, who advised the students, said, "A total of 24 teams from such prestigious universities as Carnegie Mellon University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and the University of Tokyo joined the contest, and we are pleased with the good results. Many people, in fact, praised the integration of creativity and technical excellence our have shown through the smart mop.”
Team KAIST: pictured from right to left, Sun-Jun Kim, Se-Jin Kim, and Han-Jong Kim
The Smart Mop can clean the floor and offer users a fun game.
2014.11.12 View 10245 -
 Professor Sung-Yong Kim Receives the Young Scientist Award
Professor Sung-Yong Kim of the Department of Ocean Systems Engineering at KAIST received the Young Scientist Award for 2014 conferred by the Korean Society of Oceanography (KSO). The award was presented at the KSO’s fall conference that took place on November 6, 2014 at the campus of the Naval Academy of the Republic of Korea in Jinhae.
Professor Kim has been recognized for his outstanding research in coastal oceanography and environmental fluid mechanics. His research papers are frequently published in prestigious journals such as the Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans by the American Geophysical Union.
2014.11.11 View 7124
Professor Sung-Yong Kim Receives the Young Scientist Award
Professor Sung-Yong Kim of the Department of Ocean Systems Engineering at KAIST received the Young Scientist Award for 2014 conferred by the Korean Society of Oceanography (KSO). The award was presented at the KSO’s fall conference that took place on November 6, 2014 at the campus of the Naval Academy of the Republic of Korea in Jinhae.
Professor Kim has been recognized for his outstanding research in coastal oceanography and environmental fluid mechanics. His research papers are frequently published in prestigious journals such as the Journal of Geophysical Research-Oceans by the American Geophysical Union.
2014.11.11 View 7124 -
 The 2014 SoC Robot Competition Took Place
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his research team hosted a competition for miniature robots with artificial intelligence at KINTEX in Ilsan, Korea, on October 23-26, 2014.
The competition, called the 2014 SoC Robot War, showed the latest developments of semiconductor and robot technology through the robots’ presentations of the Korean martial art, Taekwondo, and hurdles race. SoC is a system on ship, an integrated circuit that holds all components of a computer or other electronic systems in a single chip. SoC robots are equipped with an artificial intelligence system, and therefore, can recognize things on their own or respond automatically to environmental changes. SoC robots are developed with the integration of semiconductor technology and robotics engineering.
Marking the thirteenth competition this year since its inception, the Robot War featured two competitions between HURO and Taekwon Robots. Under the HURO competition, participating robots were required to run a hurdle race, pass through barricades, and cross a bridge. The winning team received an award from the president of the Republic of Korea. Robots participating in the Taekwon Robot competition performed some of the main movements of Taekwondo such as front and side kicks and fist techniques. The winning team received an award from the prime minster of the Republic of Korea.
A total of 105 teams with 530 students and researchers from different universities across the country participated in preliminaries, and 30 teams qualified for the final competition.
2014.10.27 View 7837
The 2014 SoC Robot Competition Took Place
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and his research team hosted a competition for miniature robots with artificial intelligence at KINTEX in Ilsan, Korea, on October 23-26, 2014.
The competition, called the 2014 SoC Robot War, showed the latest developments of semiconductor and robot technology through the robots’ presentations of the Korean martial art, Taekwondo, and hurdles race. SoC is a system on ship, an integrated circuit that holds all components of a computer or other electronic systems in a single chip. SoC robots are equipped with an artificial intelligence system, and therefore, can recognize things on their own or respond automatically to environmental changes. SoC robots are developed with the integration of semiconductor technology and robotics engineering.
Marking the thirteenth competition this year since its inception, the Robot War featured two competitions between HURO and Taekwon Robots. Under the HURO competition, participating robots were required to run a hurdle race, pass through barricades, and cross a bridge. The winning team received an award from the president of the Republic of Korea. Robots participating in the Taekwon Robot competition performed some of the main movements of Taekwondo such as front and side kicks and fist techniques. The winning team received an award from the prime minster of the Republic of Korea.
A total of 105 teams with 530 students and researchers from different universities across the country participated in preliminaries, and 30 teams qualified for the final competition.
2014.10.27 View 7837 -
 The KAIST Institute for Disaster Studies (KIDS) Opens
About 60 professors from across different departments at KAIST teamed up to make Korean society safer and more secure.
The professors voluntarily created the KAIST Institute for Disaster Studies (KIDS) that will implement the following responsibilities:
- Conduct research on disaster prevention and reduction
- Develop policy on safety and preventive measures for the public
- Establish resilience engineering programs at the university
- Create a platform for social media and machine-based information management
- Develop robot-based search and rescue mission programs
- Conduct disaster risk assessments and develop disaster-recovery plans
- Establish virtual reality programs for training and education
An opening ceremony for the institute took place on campus on October 22, 2014. President Steve Kang of KAIST, Young Jin, a National Assemblyman of the Republic of Korea, Myung-Ja Kim, a former Minister of the Environment of the Republic of Korea, Professor Hee-Kyung Park of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at KAIST, and other dignitaries attended the ceremony.
Professor Park, the Director of KIDS, said, “In recent years, our society has seen many tragic accidents that claimed hundreds of lives. This prompted us to examine the fundamental cause of accidents and forced us to review our current public safety policies and measures. As a result, we were able to identify many reasons, among others, technological problems in public facilities and structures, lack of social policies and systems to protect public safety, and human error.”
He further explained the need for KIDS as follows:
“In order to understand the cause of disasters and prepare remedies, such as how disasters happen, how to respond to them, and what to do for recovery, we need to have a comprehensive approach to the issues from the various perspective of social policy, science, and engineering. KIDS has been created to meet these needs.”
Following the opening ceremony, a seminar was held on the topic of “KIDS’s Mission and Its Role.”
2014.10.24 View 7246
The KAIST Institute for Disaster Studies (KIDS) Opens
About 60 professors from across different departments at KAIST teamed up to make Korean society safer and more secure.
The professors voluntarily created the KAIST Institute for Disaster Studies (KIDS) that will implement the following responsibilities:
- Conduct research on disaster prevention and reduction
- Develop policy on safety and preventive measures for the public
- Establish resilience engineering programs at the university
- Create a platform for social media and machine-based information management
- Develop robot-based search and rescue mission programs
- Conduct disaster risk assessments and develop disaster-recovery plans
- Establish virtual reality programs for training and education
An opening ceremony for the institute took place on campus on October 22, 2014. President Steve Kang of KAIST, Young Jin, a National Assemblyman of the Republic of Korea, Myung-Ja Kim, a former Minister of the Environment of the Republic of Korea, Professor Hee-Kyung Park of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering at KAIST, and other dignitaries attended the ceremony.
Professor Park, the Director of KIDS, said, “In recent years, our society has seen many tragic accidents that claimed hundreds of lives. This prompted us to examine the fundamental cause of accidents and forced us to review our current public safety policies and measures. As a result, we were able to identify many reasons, among others, technological problems in public facilities and structures, lack of social policies and systems to protect public safety, and human error.”
He further explained the need for KIDS as follows:
“In order to understand the cause of disasters and prepare remedies, such as how disasters happen, how to respond to them, and what to do for recovery, we need to have a comprehensive approach to the issues from the various perspective of social policy, science, and engineering. KIDS has been created to meet these needs.”
Following the opening ceremony, a seminar was held on the topic of “KIDS’s Mission and Its Role.”
2014.10.24 View 7246 -
 KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries Celebrate 20 Years of Cooperation
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) celebrated the twentieth anniversary of their university-industry cooperation in shipbuilding and ocean technology research. Established in 1995, the cooperation has remained steadfast for two decades, even times when Korea suffered gravely from its financial crisis in late 1990s.
A ceremony to commemorate the cooperation took place at the Mechanical Engineering Building on October 17, 2014. About thirty distinguished guests including the Head of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Choong-Sik Bae, and the chief engineer of SHI Marine Research Institute, Dr. Jong-Soo Seo, participated in the ceremony.
The cooperation programs included appointing advisory professors for technological support, implementing business-based academic courses, offering university-industry wide open lectures, opening regular courses for auditing, and finding possible joint researches. Through this cooperation, Samsung has secured technologies needed for industry, and KAIST has produced students who have real-world experience in industrial fields.
Twenty years of cooperation has produced shining results by running various programs such as technological advice, special lectures, small-scale research projects, consignment research projects, and courses for research and design personnel.
For example, what started as a small-scale research project with USD 4,800 in funding, the LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) related research has grown into a large-scale research project with a total of USD 2.85 million in funding. As a result, they developed a secondary barrier for LNG carriers which was recognized by Lloyd‘s Register. Their research eventually lowered ship manufacturing costs tremendously.
In 2003, the cooperation project received the presidential citation from the University-Industry Cooperation Competition organized by the Federation of Korean Industries.
KAIST and SHI planned to increase their cooperation to make it Korea’s leading university-industry cooperation program.
Professor Bae said, “Our programs to focus on solving industrial problems have turned out quite successful.” He emphasized that “for this reason, the cooperation even continued during the Asian financial crisis in 1997.”
He added, “By expanding the current cooperation, we aim to make it an exemplary program that contributes to Korea’s shipbuilding and ocean plant industries.”
2014.10.21 View 9088
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries Celebrate 20 Years of Cooperation
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) celebrated the twentieth anniversary of their university-industry cooperation in shipbuilding and ocean technology research. Established in 1995, the cooperation has remained steadfast for two decades, even times when Korea suffered gravely from its financial crisis in late 1990s.
A ceremony to commemorate the cooperation took place at the Mechanical Engineering Building on October 17, 2014. About thirty distinguished guests including the Head of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Choong-Sik Bae, and the chief engineer of SHI Marine Research Institute, Dr. Jong-Soo Seo, participated in the ceremony.
The cooperation programs included appointing advisory professors for technological support, implementing business-based academic courses, offering university-industry wide open lectures, opening regular courses for auditing, and finding possible joint researches. Through this cooperation, Samsung has secured technologies needed for industry, and KAIST has produced students who have real-world experience in industrial fields.
Twenty years of cooperation has produced shining results by running various programs such as technological advice, special lectures, small-scale research projects, consignment research projects, and courses for research and design personnel.
For example, what started as a small-scale research project with USD 4,800 in funding, the LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) related research has grown into a large-scale research project with a total of USD 2.85 million in funding. As a result, they developed a secondary barrier for LNG carriers which was recognized by Lloyd‘s Register. Their research eventually lowered ship manufacturing costs tremendously.
In 2003, the cooperation project received the presidential citation from the University-Industry Cooperation Competition organized by the Federation of Korean Industries.
KAIST and SHI planned to increase their cooperation to make it Korea’s leading university-industry cooperation program.
Professor Bae said, “Our programs to focus on solving industrial problems have turned out quite successful.” He emphasized that “for this reason, the cooperation even continued during the Asian financial crisis in 1997.”
He added, “By expanding the current cooperation, we aim to make it an exemplary program that contributes to Korea’s shipbuilding and ocean plant industries.”
2014.10.21 View 9088 -
 Wuhan University, China, Appoints Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee as Honorary Professor
Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, has been appointed an honorary professor at Wuhan University in Hubei Province, China. This is the third time that Professor Lee has received an honorary professorship from Chinese academic institutions. The Chinese Academy of Sciences appointed him an honorary professor in 2012, and Shanghai Jia Tong University asked him to serve as an advisory professor in 2013, respectively.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
Wuhan University is a comprehensive and key national university selected by the Chinese government as a major recipient of state funding for research. It is also known as one of the most beautiful campuses in China.
2014.10.20 View 8597
Wuhan University, China, Appoints Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee as Honorary Professor
Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, has been appointed an honorary professor at Wuhan University in Hubei Province, China. This is the third time that Professor Lee has received an honorary professorship from Chinese academic institutions. The Chinese Academy of Sciences appointed him an honorary professor in 2012, and Shanghai Jia Tong University asked him to serve as an advisory professor in 2013, respectively.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
Wuhan University is a comprehensive and key national university selected by the Chinese government as a major recipient of state funding for research. It is also known as one of the most beautiful campuses in China.
2014.10.20 View 8597 -
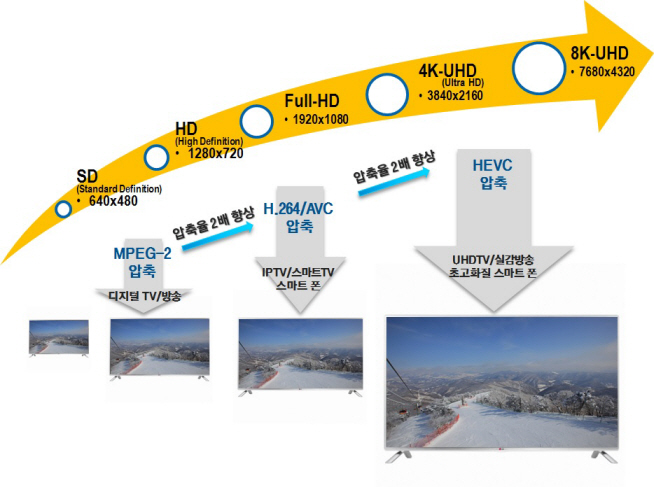 KAIST Registers an Internationally Recognized Standard Patent
A video compression technology, jointly developed by Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), and the Korean Broadcasting System (KBS), is registered internationally as the standard patent in the next-generation High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
HEVC (H.265) is an international technology standard that compresses large image data for Ultra High Definition (UHD) televisions and smartphones. It has the twice the compression efficiency as that of H.264/AVC which is most commonly used for processing full HD sources. This means that it is able to compress a video file to half the size while maintaining the same image quality.
Although the related market is at a nascent stage, HEVC technology has already been applied to the latest version of televisions and smartphones. Experts predict that the market will grow to USD 200 billion by 2016, and KAIST is expected to receive a royalty payment of USD 9.3 million from this patent.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC) established the HEVC standard in January 2013. Also, an international patent pool licensing corporation, MPEG LA announced the HEVC standard patent pool on September 29, 2014.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae, Dean of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) of KAIST, said, “This is an unprecedented case for Korea whereby a core technology developed by a university became an international standard, which has a vast impact on the market.”
President of KAIST, Steve Kang commented, “With its advanced technology, KAIST joined the HEVC standard patent pool as one of the 23 founding members along with Apple, Siemens, and NEC. This is a remarkable achievement.”
Picture 1: Improvements in video compression technology
Picture 2: Comparison of different screen resolutions
2014.10.09 View 11445
KAIST Registers an Internationally Recognized Standard Patent
A video compression technology, jointly developed by Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), and the Korean Broadcasting System (KBS), is registered internationally as the standard patent in the next-generation High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
HEVC (H.265) is an international technology standard that compresses large image data for Ultra High Definition (UHD) televisions and smartphones. It has the twice the compression efficiency as that of H.264/AVC which is most commonly used for processing full HD sources. This means that it is able to compress a video file to half the size while maintaining the same image quality.
Although the related market is at a nascent stage, HEVC technology has already been applied to the latest version of televisions and smartphones. Experts predict that the market will grow to USD 200 billion by 2016, and KAIST is expected to receive a royalty payment of USD 9.3 million from this patent.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC) established the HEVC standard in January 2013. Also, an international patent pool licensing corporation, MPEG LA announced the HEVC standard patent pool on September 29, 2014.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae, Dean of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) of KAIST, said, “This is an unprecedented case for Korea whereby a core technology developed by a university became an international standard, which has a vast impact on the market.”
President of KAIST, Steve Kang commented, “With its advanced technology, KAIST joined the HEVC standard patent pool as one of the 23 founding members along with Apple, Siemens, and NEC. This is a remarkable achievement.”
Picture 1: Improvements in video compression technology
Picture 2: Comparison of different screen resolutions
2014.10.09 View 11445