research(3)
New metamaterial has been developed, exhibiting hundreds of times greater strength than pure metals.
Professor Seung Min, Han and Yoo Sung, Jeong (Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS)) and Professor Seok Woo, Jeon (Department of Material Science and Engineering) have developed a composite nanomaterial. The nanomaterial consists of graphene inserted in copper and nickel and exhibits strengths 500 times and 180 times, respectively, greater than that of pure metals. The result of the research was published on the July 2nd online edition in Nature Communications journal.
Graphene displays strengths 200 times greater than that of steel, is stretchable, and is flexible. The U.S. Army Armaments Research, Development and Engineering Center developed a graphene-metal nanomaterial but failed to drastically improve the strength of the material.
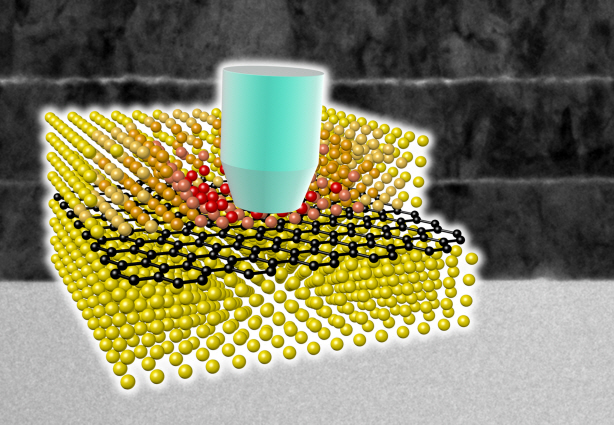
To maximize the strength increased by the addition of graphene, the KAIST research team created a layered structure of metal and graphene. Using CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition), the team grew a single layer of graphene on a metal deposited substrate and then deposited another metal layer. They repeated this process to produce a metal-graphene multilayer composite material, utilizing a single layer of graphene. Micro-compression tests within Transmission Electronic Microscope and Molecular Dynamics simulations effectively showed the strength enhancing effect and the dislocation movement in grain boundaries of graphene on an atomic level.
The mechanical characteristics of the graphene layer within the metal-graphene composite material successfully blocked the dislocations and cracks from external damage from traveling inwards. Therefore the composite material displayed strength beyond conventional metal-metal multilayer materials. The copper-graphene multilayer material with an interplanar distance of 70nm exhibited 500 times greater (1.5GPa) strength than pure copper. Nickel-graphene multilayer material with an interplanar distance of 100nm showed 180 times greater (4.0GPa) strength than pure nickel.
It was found that there is a clear relationship between the interplanar distance and the strength of the multilayer material. A smaller interplanar distance made the dislocation movement more difficult and therefore increased the strength of the material. Professor Han, who led the research, commented, “the result is astounding as 0.00004% in weight of graphene increased the strength of the materials by hundreds of times” and “improvements based on this success, especially mass production with roll-to-roll process or metal sintering process in the production of ultra-high strength, lightweight parts for automobile and spacecraft, may become possible.” In addition, Professor Han mentioned that “the new material can be applied to coating materials for nuclear reactor construction or other structural materials requiring high reliability.”
The research project received support from National Research Foundation, Global Frontier Program, KAIST EEWS-KINC Program and KISTI Supercomputer and was a collaborative effort with KISTI (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information), KBSI (Korea Basic Science Institute), Stanford University, and Columbia University.
A schematic diagram shows the structure of metal-graphene multi-layers. The metal-graphene multi-layered composite materials, containing a single-layered graphene, block the dislocation movement of graphene layers, resulting in a greater strength in the materials.
-
policy KAIST and the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis Agree to Cooperate
KAIST signed a cooperation agreement with the International Institute for Applied Systems Analysis (IIASA) on October 29, 2014 at the president’s office. Established in 1972 and based in Austria as a non-governmental research organization, IIASA is an international scientific institute that conducts policy-oriented research into global problems such as climate change, energy security, or population aging. IIASA examines such issues and devises strategies for cooperative action unc
2014-11-05 -
people Rechargeable Lithium Sulfur Battery for Greater Battery Capacity
Professor Do Kyung Kim from the Department of Material Science and Engineering and Professor Jang Wook Choi from the Graduate School of EEWS have been featured in the lead story of the renowned nanoscience journal Advanced Materials for their research on the lithium sulfur battery. This new type of battery developed by Professor Kim is expected to have a longer life battery life and [higher] energy density than currently commercial batteries. With ample energy density up to 2100Wh/kg—a
2013-12-11 -
people(2) Technology Developed for Flexible, Foldable & Rechargeable Battery
Flexible, Foldable & Rechargeable Battery The research group of professors Jang-Wook Choi & Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of EEWS and Taek-Soo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST has developed technology for flexible and foldable batteries which are rechargeable using solar energy. The research result was published in the online issue of Nano Letters on November 5. Trial versions of flexible and wearable electronics are being developed and introduc
2013-11-21