research
Dr. Jun-Yeop, Yeo and the research team led by Professor Seung-Hwan, Ko (both of the Department of Mechanical Engineering) successfully developed a process enabling the location-determinable, ultra high speed synthesis of nanomaterials using concentrated laser beams.
The result of the research effort was published as the frontispiece in the July 9th issue of Advanced Functional Materials, a world renowned material science and engineering academic journal.
Application of the technology reduced the time needed to process nanomaterial synthesis from a few hours to a mere five minutes. In addition, unlike conventional nanomaterial synthesis processes, it is simple enough to enable mass production and commercialization.
Conventional processes require the high temperatures of 900~1,000 °C and the use of toxic or explosive vapors. Complex processes such as separation after synthesis and patterning are needed for application in electronic devices. The multi-step, expensive, environmentally unfriendly characteristics of nanomaterial synthesis served as road blocks to its mass production and commercialization.
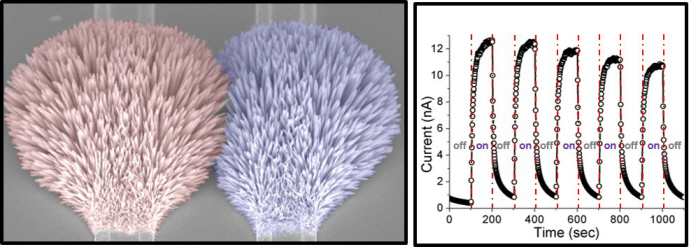
Exposing the precursor to concentrated continuous laser beam (green wavelength) resulted in the synthesis of nanowires in the desired location; the first instance in the world to accomplish this feat. The technology, according to the research team, makes possible the production, integration and patterning of nanomaterials using a single process. Applicable to various surfaces and substrates, nanowires have been successfully synthesized on flexible plastic substrates and controlled patterning on the surface of 3-dimensional structures.
Dr. Yeo commented that the research effort has “yielded the creation of a nanomaterial synthesis process capable of synthesis, integration, pattern, and material production using light energy” and has “reduced the synthesis process time of nanomaterial to one tenths of the conventional process.” Dr. Yeo continues to devise steps to commercialize the new multifunctional electronic material and methods for mass production.
The research effort, led by Dr. Yeo and Professor Ko, received contribution from Professor Hyung-Jin Sung (KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering), Seok-Joon Hong, a Ph.D. candidate, Hyun-Wook Kang, also a Ph.D. candidate, Professor Costas Grigoropoulos of UC Berkeley, and Dr. Dae Ho Lee. In addition, the team received support from the National Research Foundation, Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Global Frontier Program, and KAIST EEWS.
Picture I: Synthesized nanomaterials produced at a desirable location by laser beams
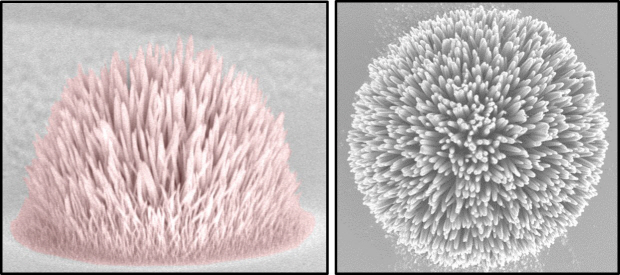
Picture 2: Synthesized nanomaterials built on the 3D structure by using the developed technology
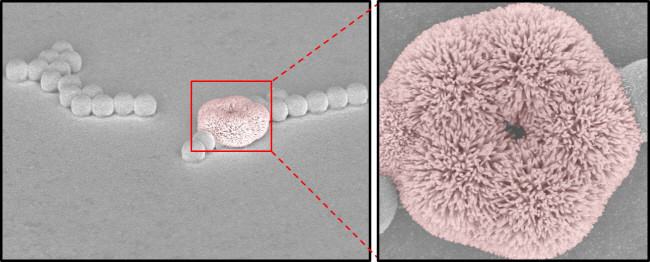
Picture 3: Functional electric circuit made with synthesized nanomaterials
Picture 4: Cover page of July 9th issue of Advanced Functional Materials

-
research A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries. A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the
2020-12-07 -
event Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano. Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journ
2020-10-06 -
research Energy Storage Using Oxygen to Boost Battery Performance
Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air. Professor Jeung Ku Kang’s team synthesized and preserved the sub-nanometric particles of atomic cluster sizes at high mass loadings within metal-organic frameworks (MOF) by controlling the behavior of reactants at the molecular level. This new strategy ensures high performance for lithium-oxygen batteries, acclaimed as a next-generation energy storage
2020-06-15 -
research Recyclable Nano-Fiber Filtered Face Masks a Boon for Supply Fiasco
Wearing a face mask is a common sight in Korea during the COVID-19 outbreak. Due to the overwhelming demand, last week the government started to ration two masks per person per week, as a drastic measure to address the supply fiasco. The face masks most commonly used are disposable ones, originally made for filtering out up to 94 or 95 percent of fine dust, referred to as N94 or N95 masks. A KAIST research team announced that they have developed a nano-filter that maintains excellent filteri
2020-03-17 -
people Professor Il-Doo Kim Named Scientist of the Year by the Journalists
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was named the 2019 Scientist of the Year by Korean science journalists. The award was conferred at the 2019 Science Press Night ceremony of the Korea Science Journalists Association (KSJA) on November 29. Professor Kim focuses on developing nanofiber gas sensors for diagnosing diseases in advance by analyzing exhaled biomarkers with electrospinning technology. His outstanding research was praised and selected as on
2019-12-17