research
Therapy developed to induce Angiogenesis of Retina
View : 10444
Date : 2013-10-12
Writer : ed_news
- Junyeop Lee, Graduate School of Medical Sciences and Engineering
- Research results expected to be applied for treatment of diabetic retinopathy
A major clue to treatment of retinovascular disease, which causes blindness, has been found. The key to protection of the retinal nerve is the angiogenic protein that promotes healthy retinal vessel growth around the retina, which usually does not receive blood supply readily. This research offers a beginning to the possible improvement of therapy for diabetic retinopathy1 and retinopathy of prematurity2. Also important to the research is the fact that the ophthalmology specialist researcher, currently undergoing professional training, provided the results.
KAIST Graduate School of Medical Sciences and Engineering’s Junyeop Lee is the opthalmology specialist, who carried out the research under supervision by academic advisers Gyuyeong Go and Wookjun Yoo. The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning as well as the National Research Foundation of Korea have funded his research. The research results have been published as a cover paper on ‘Science Translational Medicine’ on 18th August. This journal is a sister publication of Science, which is prestigious in the field of translational medicine that ties the basic science with clinical medicine. (Thesis title: Angiopoietin-1 Guides Directional Angiogenesis Through Integrin αvβ5 Signaling for Recovery of Ischemic Retinopathy)
The traditional treatment of diabetic retinopathy includes laser photocoagulation to destroy the retinal tissues or antibody therapeutics, which prevents vessel proliferation and blood leaking. The advantage of antibody therapeutics3 is that it retains the retinal nerves, however, it is not the fundamental solution but merely a temporary one, which requires repeated treatments.
The research team identified that Angiopoietin-14 protein, known as essential for growth and stabilization of vessels, also plays an important role in retinal vessel growth. The protein protects the retinal nerves, as well as provides improvement for retinal ischemia5 that is the root cause of vision loss due to retinal hemorrhages. It is expected to become a key to finding fundamental treatment method – by providing sufficient blood supply to the retina, thereby preserving the retinal nerve functions.
The results show that administration of Angiopoietin-1 to retinopathy mouse model promotes growth of healthy vessel growth, further preventing abnormal vessel growth, retinal hemorrhage and vision loss due to retinal ischemia.
Junyeop Lee said, “This research has identified that Angiopoietin-1 is an important factor in retinal vessel generation and stabilization. The paradigm will shift from traditional treatment method, which prevents vessel growth, to a new method that generates healthy vessels and strengthens vessel functions.”
- Research results expected to be applied for treatment of diabetic retinopathy
A major clue to treatment of retinovascular disease, which causes blindness, has been found. The key to protection of the retinal nerve is the angiogenic protein that promotes healthy retinal vessel growth around the retina, which usually does not receive blood supply readily. This research offers a beginning to the possible improvement of therapy for diabetic retinopathy1 and retinopathy of prematurity2. Also important to the research is the fact that the ophthalmology specialist researcher, currently undergoing professional training, provided the results.
KAIST Graduate School of Medical Sciences and Engineering’s Junyeop Lee is the opthalmology specialist, who carried out the research under supervision by academic advisers Gyuyeong Go and Wookjun Yoo. The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning as well as the National Research Foundation of Korea have funded his research. The research results have been published as a cover paper on ‘Science Translational Medicine’ on 18th August. This journal is a sister publication of Science, which is prestigious in the field of translational medicine that ties the basic science with clinical medicine. (Thesis title: Angiopoietin-1 Guides Directional Angiogenesis Through Integrin αvβ5 Signaling for Recovery of Ischemic Retinopathy)
The traditional treatment of diabetic retinopathy includes laser photocoagulation to destroy the retinal tissues or antibody therapeutics, which prevents vessel proliferation and blood leaking. The advantage of antibody therapeutics3 is that it retains the retinal nerves, however, it is not the fundamental solution but merely a temporary one, which requires repeated treatments.
The research team identified that Angiopoietin-14 protein, known as essential for growth and stabilization of vessels, also plays an important role in retinal vessel growth. The protein protects the retinal nerves, as well as provides improvement for retinal ischemia5 that is the root cause of vision loss due to retinal hemorrhages. It is expected to become a key to finding fundamental treatment method – by providing sufficient blood supply to the retina, thereby preserving the retinal nerve functions.
The results show that administration of Angiopoietin-1 to retinopathy mouse model promotes growth of healthy vessel growth, further preventing abnormal vessel growth, retinal hemorrhage and vision loss due to retinal ischemia.
Junyeop Lee said, “This research has identified that Angiopoietin-1 is an important factor in retinal vessel generation and stabilization. The paradigm will shift from traditional treatment method, which prevents vessel growth, to a new method that generates healthy vessels and strengthens vessel functions.”
1 Diabetic retinopathy: This retinovascular disease is a diabetic complication caused by insufficient blood supply. It is the major causes of blindness in adults.
2 Retinopathy of prematurity: The retinal vascular disease that occurs in premature infants with incomplete retinal vascular development. It is also the most common cause of blindness in children.
3 Antibody Therapeutics: Antibody developed to selectively inhibit abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage. Typical antibody therapeutics is Avastin and Lucentis, which hinder vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
4 Angiopoietin-1: A critical growth factor that induces the production of healthy blood vessels and maintains the stability of the created vessel.
5 Retinal ischemia: State of ailment where retinal tissue blood supply is not sufficient.
2 Retinopathy of prematurity: The retinal vascular disease that occurs in premature infants with incomplete retinal vascular development. It is also the most common cause of blindness in children.
3 Antibody Therapeutics: Antibody developed to selectively inhibit abnormal blood vessel growth and leakage. Typical antibody therapeutics is Avastin and Lucentis, which hinder vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
4 Angiopoietin-1: A critical growth factor that induces the production of healthy blood vessels and maintains the stability of the created vessel.
5 Retinal ischemia: State of ailment where retinal tissue blood supply is not sufficient.
Figure 1. Retinopathy mouse models show that, in comparison to the control group, the VEGF-Trap treatment and Angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) treatment groups significantly suppresses the pathological vascular proliferation. In addition, the Ang 1 group show vessel growth toward the central avascular area (region of retinal ischemia), which is not observed in VEGF-Trap treatment.
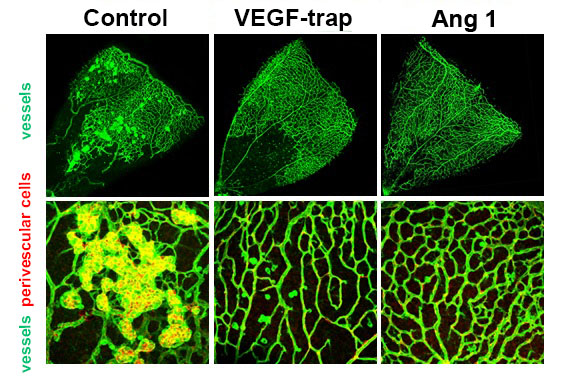
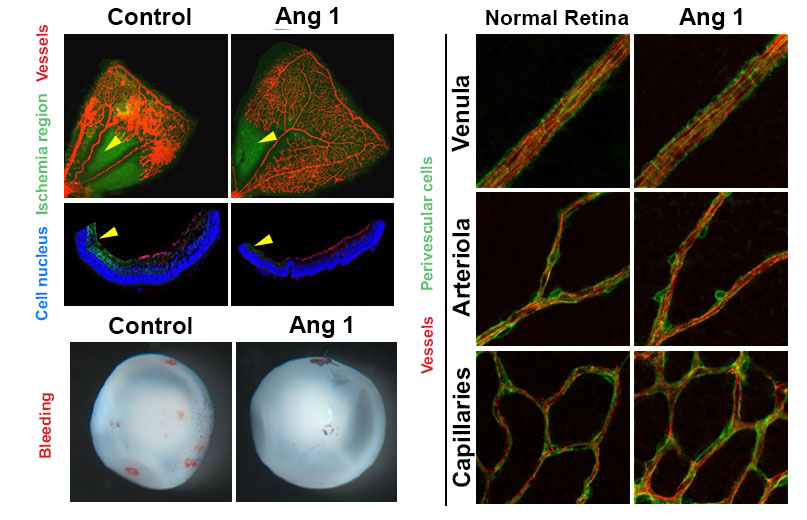
Figure 2. Reduced retinal ischemia, retinal bleeding and blood vessel normalization by Angiopoietin-1. Retinal ischemic region (arrow) and retinal bleeding significantly reduced in the Angiopoietin-1 (Ang1) treatment model in comparison to control group (left). The newly generated vessels in Ang 1 model are structurally supported by perivascular cells as normal retinal vessels do (right).