research
Flexible electronics have been touted as the next generation in electronics in various areas, ranging from consumer electronics to bio-integrated medical devices. In spite of their merits, insufficient performance of organic materials arising from inherent material properties and processing limitations in scalability have posed big challenges to developing all-in-one flexible electronics systems in which display, processor, memory, and energy devices are integrated. The high temperature processes, essential for high performance electronic devices, have severely restricted the development of flexible electronics because of the fundamental thermal instabilities of polymer materials.
A research team headed by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST provides an easier methodology to realize high performance flexible electronics by using the Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off (ILLO).
The ILLO process involves depositing a laser-reactive exfoliation layer on rigid substrates, and then fabricating ultrathin inorganic electronic devices, e.g., high density crossbar memristive memory on top of the exfoliation layer. By laser irradiation through the back of the substrate, only the ultrathin inorganic device layers are exfoliated from the substrate as a result of the reaction between laser and exfoliation layer, and then subsequently transferred onto any kind of receiver substrate such as plastic, paper, and even fabric.
This ILLO process can enable not only nanoscale processes for high density flexible devices but also the high temperature process that was previously difficult to achieve on plastic substrates. The transferred device successfully demonstrates fully-functional random access memory operation on flexible substrates even under severe bending.
Professor Lee said, “By selecting an optimized set of inorganic exfoliation layer and substrate, a nanoscale process at a high temperature of over 1000 °C can be utilized for high performance flexible electronics. The ILLO process can be applied to diverse flexible electronics, such as driving circuits for displays and inorganic-based energy devices such as battery, solar cell, and self-powered devices that require high temperature processes.”
The team’s results were published in the November issue of Wiley’s journal, ‘ Advanced Materials, ’ as a cover article entitled “ Flexible Crossbar-Structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substrates via Inorganic-Based Laser Lift-Off.”
( http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201402472/abstract )
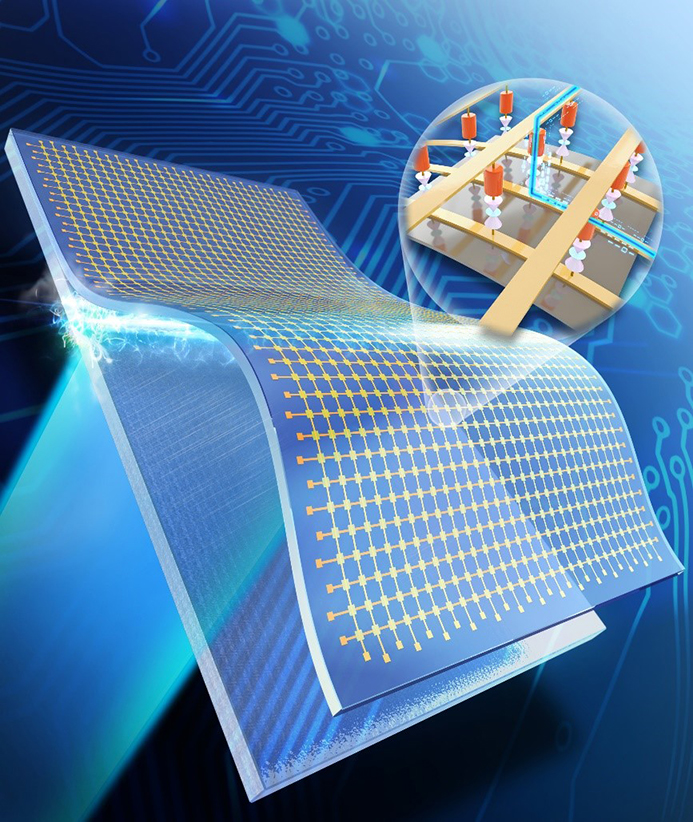
This schematic picture shows the flexible crossbar memory developed via the ILLO process.
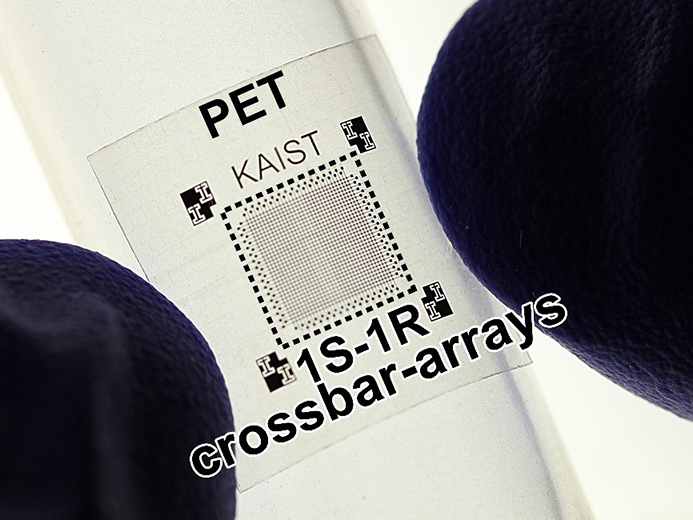
This photo shows the flexible RRAM device on a plastic substrate.
-
research KAIST Team Develops an Insect-Mimicking Semiconductor to Detect Motion
The recent development of an “intelligent sensor” semiconductor that mimics the optic nerve of insects while operating at ultra-high speeds and low power offers extensive expandability into various innovative technologies. This technology is expected to be applied to various fields including transportation, safety, and security systems, contributing to both industry and society. On February 19, a KAIST research team led by Professor Kyung Min Kim from the Department of Materials S
2024-02-29 -
research Novel Material Properties of Hybrid Perovskite Nanostructures for Next-generation Non-linear Electronic Devices
(from left: Juho Lee, Dr. Muhammad Ejaz Khan and Professor Yong-Hoon Kim) A KAIST research team reported a novel non-linear device with the founding property coming from perovskite nanowires. They showed that hybrid perovskite-derived, inorganic-framework nanowires can acquire semi-metallicity, and proposed negative differential resistance (NDR) devices with excellent NDR characteristics that resulted from a novel quantum-hybridization NDR mechanism, implying the potential of perovskite nano
2019-02-22 -
research Hierarchical Porous Titanium Nitride Synthesized by Multiscale Phase Separation for LSBs
(from left: Professor Jinwoo Lee and PhD candidate Won-Gwang Lim) A KAIST research team developed ultra-stable, high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs) by using hierarchical porous titanium nitride as a sulfur host, and achieved superior cycle stability and high rate performance for LSBs. The control of large amounts of energy is required for use in an electric vehicle or smart grid system. In this sense, the development of next-generation secondary batteries is in high
2019-01-28 -
research Highly Scalable Process to Obtain Stable 2D Nanosheet Dispersion
(Professor Do Hyun Kim and his team) A KAIST team developed technology that allows the mass production of two-dimensional (2D) nanomaterial dispersion by utilizing the characteristic shearing force of hydraulic power. The 2D nanosheet dispersion can be directly applied to solution-based processes to manufacture devices for electronics as well as energy storage and conversion. It is expected to be used in these devices with improved performance. There have been numero
2018-12-19 -
research Characteristics of Submesoscale Geophysical Turbulence Reported
A KAIST research team has reported some of unique characteristics and driving forces behind submesoscale geophysical turbulence. Using big data analysis on ocean surface currents and chlorophyll concentrations observed using coastal radars and satellites has brought better understanding of oceanic processes in space and time scales of O(1) kilometer and O(1) hour. The outcomes of this work will lead to improved tracking of water-borne materials and performance in global and regional climate
2018-12-13