Neutron+Scattering+and+Nanoscale+Materials+Lab
-
 The thermal fluctuation and elasticity of cell membranes, lipid vesicles, interacting with pore-forming peptides were reported by a research team at KAIST.
A research team from KAIST, consisted of Sung-Min Choi, Professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering Department, and Ji-Hwan Lee, a doctoral student in the Department, published a paper on the “thermal fluctuation and elasticity of lipid vesicles interacting with pore-forming peptides.” The paper was carried by Physical Review Letters, an internationally renowned peer-review journal on physics on July 16, 2010.
Cell membranes, which consist of lipid bilayers, play important roles in cells as barriers to maintain concentrations and matrices to host membrane proteins. During cellular processes such as cell fission and fusion, the cell membranes undergo various morphological changes governed by the interplay between protein and lipid membranes. There have been many theoretical and experimental approaches to understand cellular processes driven by protein-lipid membrane interactions. However, it is not fully established how the membrane elastic properties, which play an important role in membrane deformation, are affected by the protein-membrane interactions.
Antimicrobial peptides are one of the most common examples of proteins that modify membrane morphology. While the pore-forming mechanisms of antimicrobial peptides in lipid bilayers have been widely investigated, there have been only a few attempts to understand the mechanisms in terms of membrane elastic properties. In particular, the effects of pore formation on the membrane fluctuation and elastic properties, which provide key information to understand the mechanism of antimicrobial peptide activity, have not been reported yet. The research team reports the thermal fluctuation and elasticity of lipid vesicles interacting with pore-forming peptides, which were measured by neutron spin-echo spectroscopy.
The results of this study are expected to pay an important role in understanding the elastic behavior and morphological changes of cell membranes induced by protein-membrane interactions, and may provide new insights for developing new theoretical models for membrane fluctuations which include the membrane mediated interaction between protein patches.
(a) (b)
Figure
(a) Schematics for bound melittin and pores in lipid bilayers
(b) P NMR signal ratio (with/without Mn2+) of DOPC LUV-melittin vs P/L at 30˚C. The dashed line is a guide for eyes.
2010.07.23 View 11386
The thermal fluctuation and elasticity of cell membranes, lipid vesicles, interacting with pore-forming peptides were reported by a research team at KAIST.
A research team from KAIST, consisted of Sung-Min Choi, Professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering Department, and Ji-Hwan Lee, a doctoral student in the Department, published a paper on the “thermal fluctuation and elasticity of lipid vesicles interacting with pore-forming peptides.” The paper was carried by Physical Review Letters, an internationally renowned peer-review journal on physics on July 16, 2010.
Cell membranes, which consist of lipid bilayers, play important roles in cells as barriers to maintain concentrations and matrices to host membrane proteins. During cellular processes such as cell fission and fusion, the cell membranes undergo various morphological changes governed by the interplay between protein and lipid membranes. There have been many theoretical and experimental approaches to understand cellular processes driven by protein-lipid membrane interactions. However, it is not fully established how the membrane elastic properties, which play an important role in membrane deformation, are affected by the protein-membrane interactions.
Antimicrobial peptides are one of the most common examples of proteins that modify membrane morphology. While the pore-forming mechanisms of antimicrobial peptides in lipid bilayers have been widely investigated, there have been only a few attempts to understand the mechanisms in terms of membrane elastic properties. In particular, the effects of pore formation on the membrane fluctuation and elastic properties, which provide key information to understand the mechanism of antimicrobial peptide activity, have not been reported yet. The research team reports the thermal fluctuation and elasticity of lipid vesicles interacting with pore-forming peptides, which were measured by neutron spin-echo spectroscopy.
The results of this study are expected to pay an important role in understanding the elastic behavior and morphological changes of cell membranes induced by protein-membrane interactions, and may provide new insights for developing new theoretical models for membrane fluctuations which include the membrane mediated interaction between protein patches.
(a) (b)
Figure
(a) Schematics for bound melittin and pores in lipid bilayers
(b) P NMR signal ratio (with/without Mn2+) of DOPC LUV-melittin vs P/L at 30˚C. The dashed line is a guide for eyes.
2010.07.23 View 11386 -
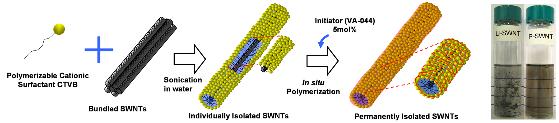 Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
A research team headed by Seong-Min Choi, a professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST, has developed technologies to stably disperse carbon nanotube particles in aqueous solutions and organic solvents, essential for industrial applications of carbon nanotube, and discovered the dispersion characteristics of carbon nanotube. The research outputs have been published by ‘Advanced materials’ (19, 929, 2007), the most distinguished journal in Material Science field, and introduced as Research Highlight at the May 7th edition of ‘Heart Cut’ by the American Chemical Society (ACS).
A number of processes for industrial applications of carbon nanotube require the dispersion of carbon nanotube in aqueous solutions or organic solvents, and thus far, surfactant particles or DNAs have been used to disperse carbon nanotube particles. However, they have shortcomings of easy destruction of dispersion. In order to overcome such shortcomings, Prof. Choi’s team produced carbon nanotube particle-dispersed aqueous solutions by using surfactant particles and then polymerized surfactant particles absorbed to the surfaces of carbon nanotube in situ to develop carbon nanotube with hydrophile and safe surfaces. The functional carbon nanotube so obtained shows features of easy dispersion in aqueous solutions and organic solvents even after being processed, such as freeze drying, therefore, is expected to significantly contribute to the development of application technologies of carbon nanotubes. Tae-Hwan Kim and Chang-Woo Doh, both doctoral students, played key roles in the researches carried out under the auspices of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) as a nuclear power R&D project, and the relevant technologies were filed for patent applications.
Figures: Carbon nanotube before polymerization (left), carbon nanotube polymerized with surfactant particles (right)
2007.05.14 View 13255
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
A research team headed by Seong-Min Choi, a professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST, has developed technologies to stably disperse carbon nanotube particles in aqueous solutions and organic solvents, essential for industrial applications of carbon nanotube, and discovered the dispersion characteristics of carbon nanotube. The research outputs have been published by ‘Advanced materials’ (19, 929, 2007), the most distinguished journal in Material Science field, and introduced as Research Highlight at the May 7th edition of ‘Heart Cut’ by the American Chemical Society (ACS).
A number of processes for industrial applications of carbon nanotube require the dispersion of carbon nanotube in aqueous solutions or organic solvents, and thus far, surfactant particles or DNAs have been used to disperse carbon nanotube particles. However, they have shortcomings of easy destruction of dispersion. In order to overcome such shortcomings, Prof. Choi’s team produced carbon nanotube particle-dispersed aqueous solutions by using surfactant particles and then polymerized surfactant particles absorbed to the surfaces of carbon nanotube in situ to develop carbon nanotube with hydrophile and safe surfaces. The functional carbon nanotube so obtained shows features of easy dispersion in aqueous solutions and organic solvents even after being processed, such as freeze drying, therefore, is expected to significantly contribute to the development of application technologies of carbon nanotubes. Tae-Hwan Kim and Chang-Woo Doh, both doctoral students, played key roles in the researches carried out under the auspices of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) as a nuclear power R&D project, and the relevant technologies were filed for patent applications.
Figures: Carbon nanotube before polymerization (left), carbon nanotube polymerized with surfactant particles (right)
2007.05.14 View 13255