research
Published on May 29th Nature Scientific Reports online
Recently, a popular article demonstrated that an opaque glass becomes transparent as transparent tape is applied to the glass. The scientific principle is that light is less scattered as the rough surface of the opaque glass is filled by transparent tape, thereby making things behind the opaque glass look clearer.
Professor Yong-Keun Park from KAIST’s Department of Physics, in a joint research with MIT Spectroscopy Lab, has developed a technology to easily control light scattering using holography. Their results are published on Nature’s Scientific Reports May 29th online edition.
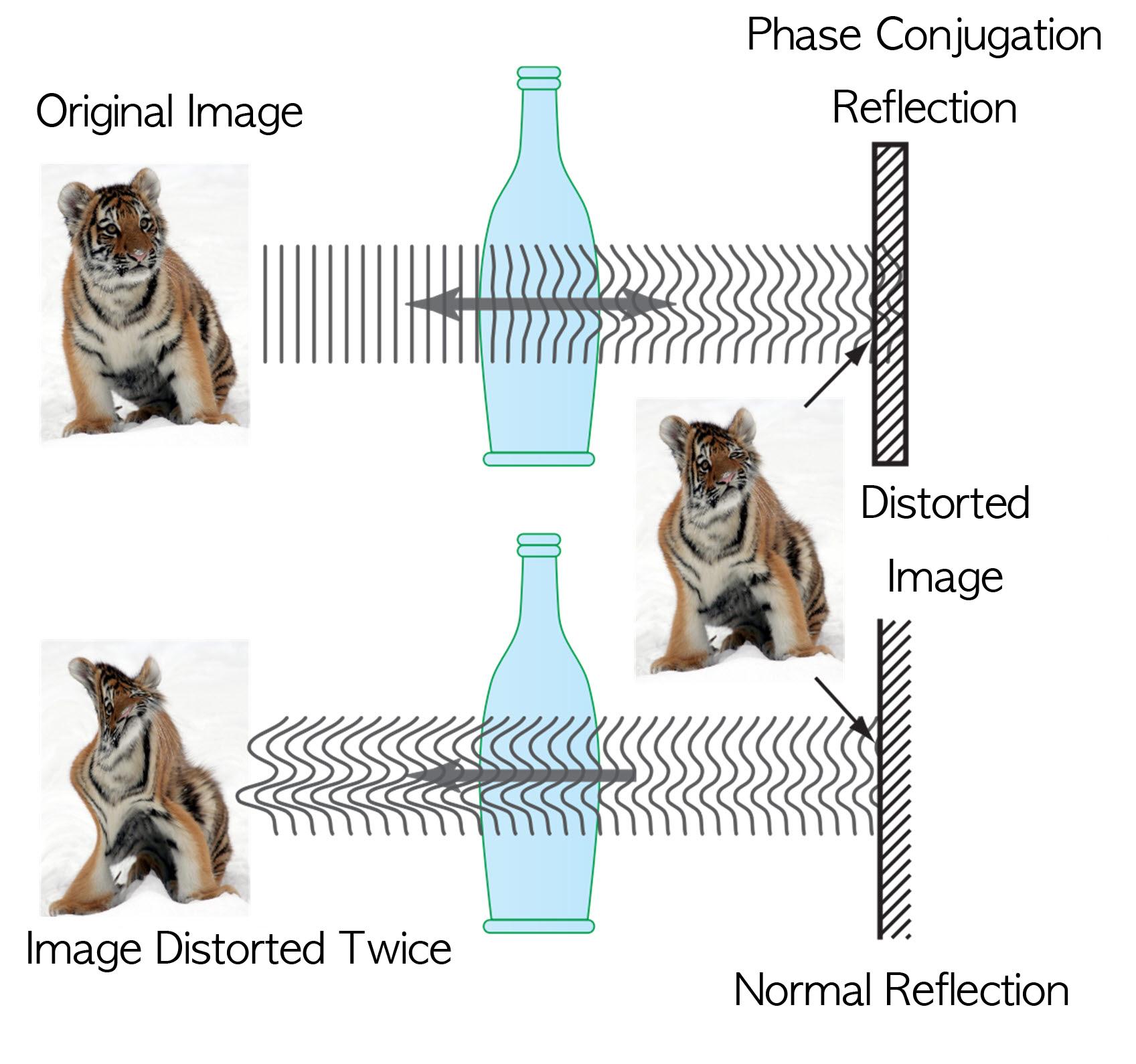
This technology allows us to see things behind visual obstructions such as cloud and smoke, or even human skin that is highly scattering, optically thick materials. The research team applied the holography technology that records both the direction and intensity of light, and controlled light scattering of obstacles lied between an observer and a target image. The team was able to retrieve the original image by recording the information of scattered light and reflecting the light precisely to the other side.
This phenomenon is known as “phase conjugation” in physics. Professor Park’s team applied phase conjugation and digital holography to observe two-dimensional image behind a highly scattering wall. “This technology will be utilized in many fields of physics, optics, nanotechnology, medical science, and even military science,” said Professor Park. “This is different from what is commonly known as penetrating camera or invisible clothes.” He nevertheless drew the line at over-interpreting the technology, “Currently, the significance is on the development of the technology itself that allows us to accurately control the scattering of light."
Figure I. Observed Images

Figure II. Light Scattering Control
-
research A KAIST research team develops a washable, transparent, and flexible OLED with MXene nanotechnology
Transparent and flexible displays, which have received a lot of attention in various fields including automobile displays, bio-healthcare, military, and fashion, are in fact known to break easily when experiencing small deformations. To solve this problem, active research is being conducted on many transparent and flexible conductive materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, silver nanowires, and conductive polymers. On June 13, a joint research team led by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from
2023-07-10 -
research KAIST Team Develops Semi-Transparent Solar Cells with Thermal Mirror Capability
A research team led by KAIST and Sungkyunkwan University professors has created semi-transparent perovskite solar cells that demonstrate high-power conversion efficiency and transmit visible light while blocking infrared light, making them great candidates for solar windows. Modern architects prefer to build exteriors designed with glass mainly from artistic or cost perspectives. Scientists, however, go one step further and see opportunities from its potential ability to harness solar energ
2016-08-02 -
research Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs. The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or
2016-06-07 -
people Transparent Glass Wall as a Touch Game Media
Professor Woo-hoon Lee - Selected as the “Highlight” at SIGGRAPH emerging technology conference - “An excellent example of the transparent display panel in everyday life” A joint research team led by KAIST Industrial Design Department’s Prof. Woo-hoon Lee and Computer Sciences Prof. Ki-hyuk Lee has developed a brand new concept game media “TransWall”, which utilizes both sides of the glass wall as the touch medium. TransWall has been ch
2013-09-19 -
research KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens
Source: IDTechEX, Feb. 28, 2011 KAIST paves the way to commercialize flexible display screens 28 Feb 2011 Transparent plastic and glass cloths, which have a limited thermal expansion needed for the production of flexible display screens and solar power cells, were developed by researchers at KAIST (Korea Advance Institute of Science & Technology). The research, led by KAIST"s Professor Byoung-Soo Bae, was funded by the Engineering Research Center under the initiative of the Minist
2011-03-01