research
Figure 1
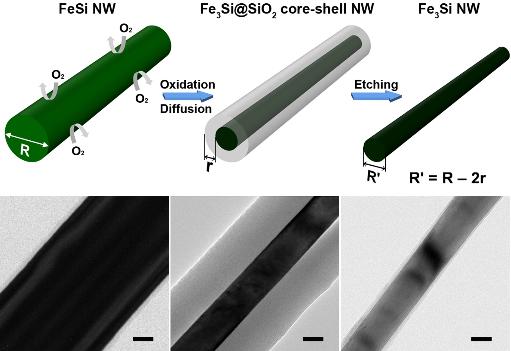
Schematic illustration of NW crystal transformation process. FeSi is converted to Fe3Si by high-temperature thermal annealing in diluted O2 condition and subsequent wet etching by 5% HF.
Figure 2
Low-resolution TEM images of FeSi; Fe3Si@SiO2 core—shell; Fe3Si NW after shell-etching; and Scale bars are 20 nm
Professor Bongsoo Kim of the Department of Chemistry, KAIST, and his research team succeeded to fabricate Heusler alloy Fe3Si nanowires by a diffusion-driven crystal structure transformation method from paramagnetic FeSi nanowires. This methodology is also applied to Co2Si nanowires in order to obtain metal-rich nanowires (Co) as another evidence of the structural transformation process. The newly developed nanowire crystal transformation method, Professor Kim said, would be valuable as a general method to fabricate metal-rich silicide nanowires that are otherwise difficult to synthesize.
Metal silicide nanowires are potentially useful in a wide array of fields including nao-optics, information technology, biosensors, and medicine. Chemical synthesis of these nanowires, however, is challenging due to the complex phase behavior of silicides.
The metal silicide nanowires are grown on a silicon substrate covered with a thin layer of silicon oxide via a simple chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process using single or multiple source precursors. Alternatively, the nanowires can be grown on the thin silicon oxide film via a chemical vapor transport (CVT) process using solid metal silicide precursors.
The CVT-based method has been highly effective for the syntheses of metal silicide NWs, but changing the composition of metal silicide NWs in a wider range, especially achieving a composition of a metal to silicon, has been quite difficult.
Thus, developing efficient and reliable synthetic methods to adjust flexibly the elemental compositions in metal silicide NWs can be valuable for the fabrication of practical spintronic and neonelectronic devices.
Professor Kim expliained, “The key concept underlying this work is metal-enrichment of metal silicide NWs by thermal diffusion. This conversion method could prove highly valuable, since novel metal-rich silicide NWs that are difficult to synthesize but possess interesting physical properties can be fabricated from other metal silicide NWs.”
The research result was published in Nanao Letters, a leading peer-reviewed journal, and posted online in early August 2010.
- No Data