ICA
-
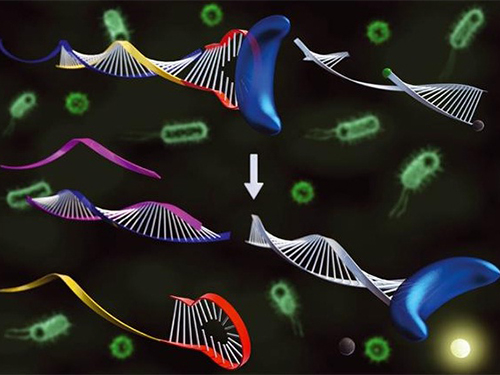 Affordable Genetic Diagnostic Technique for Target DNA Analysis Developed
Professor Hyun-Gyu Park of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a technique to analyze various target DNAs using an aptamer, a DNA fragment that can recognize and bind to a specific protein or enzyme. This technique will allow the development of affordable genetic diagnoses for new bacteria or virus, such as Middle Ease Respiratory Syndrome (MERS). The research findings were published in the June issue of Chemical Communications, issued by the Royal Society of Chemistry in the United Kingdom. The paper was selected as a lead article of the journal.
The existing genetic diagnosis technique, based on molecular beacon probes, requires a new beacon probe whenever a target DNA mutates. As a result, it was costly to analyze various target DNA fragments. To address this problem, Professor Park’s team designed an aptamer that binds and deactivates DNA polymerase. The technique was used in reverse, so that the aptemer did not bind to the polymerase, maintaining its activated state, only if the target DNA was present. These probes are called TagMan probes.
The controlled activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase enables nucleic acid to elongate or dwindle, making it possible to measure fluorescence signals coming from TaqMan probes. This same probe can be used to detect various target DNAs, leading to the development of a new and sensitive genetic diagnostic technique.
Unlike the existing molecular beacon probe technique which requires a new probe for every target DNA, this new technique uses the same fluorescent TaqMan probe, which is cheaper and easier to detect a number of different target nucleic acid fragments. The application of this technique will make the process of identifying and detecting foreign DNAs from pathogens such as virus and bacteria more affordable and simple.
Professor Park said, “This technique will enable us to develop simpler diagnostic kits for new pathogens, such as MERS, allowing a faster response to various diseases. Our technology can also be applied widely in the field of genetic diagnostics.”
Picture: A schematic image of target nucleic acid extracted through the activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase
2015.07.31 View 10538
Affordable Genetic Diagnostic Technique for Target DNA Analysis Developed
Professor Hyun-Gyu Park of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a technique to analyze various target DNAs using an aptamer, a DNA fragment that can recognize and bind to a specific protein or enzyme. This technique will allow the development of affordable genetic diagnoses for new bacteria or virus, such as Middle Ease Respiratory Syndrome (MERS). The research findings were published in the June issue of Chemical Communications, issued by the Royal Society of Chemistry in the United Kingdom. The paper was selected as a lead article of the journal.
The existing genetic diagnosis technique, based on molecular beacon probes, requires a new beacon probe whenever a target DNA mutates. As a result, it was costly to analyze various target DNA fragments. To address this problem, Professor Park’s team designed an aptamer that binds and deactivates DNA polymerase. The technique was used in reverse, so that the aptemer did not bind to the polymerase, maintaining its activated state, only if the target DNA was present. These probes are called TagMan probes.
The controlled activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase enables nucleic acid to elongate or dwindle, making it possible to measure fluorescence signals coming from TaqMan probes. This same probe can be used to detect various target DNAs, leading to the development of a new and sensitive genetic diagnostic technique.
Unlike the existing molecular beacon probe technique which requires a new probe for every target DNA, this new technique uses the same fluorescent TaqMan probe, which is cheaper and easier to detect a number of different target nucleic acid fragments. The application of this technique will make the process of identifying and detecting foreign DNAs from pathogens such as virus and bacteria more affordable and simple.
Professor Park said, “This technique will enable us to develop simpler diagnostic kits for new pathogens, such as MERS, allowing a faster response to various diseases. Our technology can also be applied widely in the field of genetic diagnostics.”
Picture: A schematic image of target nucleic acid extracted through the activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase
2015.07.31 View 10538 -
 KAIST Agrees to Cooperate with Three Hospitals in the Delivery of Emergency Medical Services
KAIST signed an agreement with three major hospitals in Korea, the National Police Hospital, Seoul National University Hospital in Bundang, and the Armed Forces Capital Hospital, to respond to national emergency situations such as the outbreak of epidemic diseases.
The signing ceremony for the agreement took place on July 27, 2015, at the JW Marriott Hotel in Seoul.
Under the agreement, the four institutions will cooperate in conducting research in basic medical science to develop treatments and vaccines, building a system to deliver emergency medical services including the establishment of preventive measures against epidemics, and providing emergency medical assistance to under-developed countries.
This agreement was initiated by the Institute of Disaster Studies at KAIST.
President Steve Kang of KAIST said, “Korean society has recently experienced the importance of building a network of medical intuitions and research universities to handle national emergency situations when Middle East Respiratory Syndrome hits the nation hard. We need to prepare for epidemics and biological disasters, and this agreement is the first step towards serving such need.”
From the left to the right in the picture are: President Hong-Soon Lee of the National Police Hospital, President Steve Kang of KAIST, President Myung-Chul Lee of the Armed Forces Capital Hospital, and President Ho-Sung Han of Seoul National University Hospital in Bundang.
2015.07.31 View 5250
KAIST Agrees to Cooperate with Three Hospitals in the Delivery of Emergency Medical Services
KAIST signed an agreement with three major hospitals in Korea, the National Police Hospital, Seoul National University Hospital in Bundang, and the Armed Forces Capital Hospital, to respond to national emergency situations such as the outbreak of epidemic diseases.
The signing ceremony for the agreement took place on July 27, 2015, at the JW Marriott Hotel in Seoul.
Under the agreement, the four institutions will cooperate in conducting research in basic medical science to develop treatments and vaccines, building a system to deliver emergency medical services including the establishment of preventive measures against epidemics, and providing emergency medical assistance to under-developed countries.
This agreement was initiated by the Institute of Disaster Studies at KAIST.
President Steve Kang of KAIST said, “Korean society has recently experienced the importance of building a network of medical intuitions and research universities to handle national emergency situations when Middle East Respiratory Syndrome hits the nation hard. We need to prepare for epidemics and biological disasters, and this agreement is the first step towards serving such need.”
From the left to the right in the picture are: President Hong-Soon Lee of the National Police Hospital, President Steve Kang of KAIST, President Myung-Chul Lee of the Armed Forces Capital Hospital, and President Ho-Sung Han of Seoul National University Hospital in Bundang.
2015.07.31 View 5250 -
 International Undergraduate Conference ICISTS-KAIST 2015 and ICISTS-KAIST Public Colloquium Held on August 3, 2015 at KAIST
The ICISTS-KAIST 2015, an international conference organized by a student organization called the International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST, was held from August 3rd to 7th at the KAIST campus and ICC Hotel in Daejeon. This year’s conference theme was “Shaping the Future.” Over 300 undergraduate students from more than 20 countries joined the event. The conference offered opportunities to explore emerging issues in science and technology, particularly in the fields of robotics, medicine, and science communication.
Vitalic Buterin, a rising scientist who received the 2014 World Technology Award for his development of the Ethereum Project, and Alan Irwin, a renowned scholar in science communication at the Copenhagen Business School in Denmark, were invited as keynote speakers. The list of other speakers included Stefan Lorenz Sorgner, the Director and Co-founder of the Beyond Humanism Network; Wendell Wallach, a scholar at Yale University's Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics; and Hideto Nakajima, a professor at the Department of History, Philosophy and Social Studies of Science and Technology at Tokyo Institute of Technology.
As part of the ICISTS-KAIST 2015, ICISTS also hosted a public colloquium on August 5, 2015 at the Science Hall in Daejeon National Science Museum. Ko San, the Director of TIDE Institute; Hyo-Joon Woo, the Chief Executive Officer of Fransen; and Dong-Il Jung, the Chief Executive Officer of iDrone participated as the speakers.
2015.07.29 View 7966
International Undergraduate Conference ICISTS-KAIST 2015 and ICISTS-KAIST Public Colloquium Held on August 3, 2015 at KAIST
The ICISTS-KAIST 2015, an international conference organized by a student organization called the International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST, was held from August 3rd to 7th at the KAIST campus and ICC Hotel in Daejeon. This year’s conference theme was “Shaping the Future.” Over 300 undergraduate students from more than 20 countries joined the event. The conference offered opportunities to explore emerging issues in science and technology, particularly in the fields of robotics, medicine, and science communication.
Vitalic Buterin, a rising scientist who received the 2014 World Technology Award for his development of the Ethereum Project, and Alan Irwin, a renowned scholar in science communication at the Copenhagen Business School in Denmark, were invited as keynote speakers. The list of other speakers included Stefan Lorenz Sorgner, the Director and Co-founder of the Beyond Humanism Network; Wendell Wallach, a scholar at Yale University's Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics; and Hideto Nakajima, a professor at the Department of History, Philosophy and Social Studies of Science and Technology at Tokyo Institute of Technology.
As part of the ICISTS-KAIST 2015, ICISTS also hosted a public colloquium on August 5, 2015 at the Science Hall in Daejeon National Science Museum. Ko San, the Director of TIDE Institute; Hyo-Joon Woo, the Chief Executive Officer of Fransen; and Dong-Il Jung, the Chief Executive Officer of iDrone participated as the speakers.
2015.07.29 View 7966 -
 KAIST Undergraduates Organize the Largest Interdisciplinary Conference in Asia
The largest interdisciplinary conference in Asia hosted by KAIST undergraduates for students around the world will be held in KAIST. The organizing committee of International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS) will hold the ICISTS-KAIST 2015 in KAIST and Hotel ICC from August 3-7, 2015, with around 300 Korean and international participants.
ICISTS-KAIST was established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for students to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology and society, regardless of their academic background.
This year’s theme is "Shaping the Future" and the topics for the conference are robotics, medicine, and science communication.
The keynote speakers are Vitalic Buterin, the winner of the World Technology Award in 2014 for the co-creation and invention of Ethereum and Alan Irwin, a well-known scholar of science, technology and society as well as the Dean of Research at the Copenhagen Business School in Denmark.
Other notable speakers include Adam Marcus, a professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory University School of Medicine; Stefan Lorenz Sorgner, the Director and co-founder of Beyond Humanism Network; Hideto Nakajima, a professor in the Department of History, Philosophy and Social Studies of Science and Technology at Tokyo Institute of Technology; Wendell Wallach, a lecturer at the Yale University Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics; Jinil Lee, a professor in the Division of Biological Science and Technology at Yonsei University; and Sangwook Kim, an editor of APCTP web journal Crossroads and a professor in the Department of Physics Education, Pusan National University.
Last year, more than 300 students from 50 different countries attended the ICISTS-KAIST 2014 as delegates to exchange their thoughts and ideas on science, technology, and society.
To register for the event, please visit www.icists.org.
2015.07.14 View 8551
KAIST Undergraduates Organize the Largest Interdisciplinary Conference in Asia
The largest interdisciplinary conference in Asia hosted by KAIST undergraduates for students around the world will be held in KAIST. The organizing committee of International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS) will hold the ICISTS-KAIST 2015 in KAIST and Hotel ICC from August 3-7, 2015, with around 300 Korean and international participants.
ICISTS-KAIST was established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for students to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology and society, regardless of their academic background.
This year’s theme is "Shaping the Future" and the topics for the conference are robotics, medicine, and science communication.
The keynote speakers are Vitalic Buterin, the winner of the World Technology Award in 2014 for the co-creation and invention of Ethereum and Alan Irwin, a well-known scholar of science, technology and society as well as the Dean of Research at the Copenhagen Business School in Denmark.
Other notable speakers include Adam Marcus, a professor of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Emory University School of Medicine; Stefan Lorenz Sorgner, the Director and co-founder of Beyond Humanism Network; Hideto Nakajima, a professor in the Department of History, Philosophy and Social Studies of Science and Technology at Tokyo Institute of Technology; Wendell Wallach, a lecturer at the Yale University Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics; Jinil Lee, a professor in the Division of Biological Science and Technology at Yonsei University; and Sangwook Kim, an editor of APCTP web journal Crossroads and a professor in the Department of Physics Education, Pusan National University.
Last year, more than 300 students from 50 different countries attended the ICISTS-KAIST 2014 as delegates to exchange their thoughts and ideas on science, technology, and society.
To register for the event, please visit www.icists.org.
2015.07.14 View 8551 -
 Professor Jae Kyu Lee Appointed the President of Association for Information Systems
Chair Professor Jae Kyu Lee of KAIST’s College of Business was appointed the President of Association for Information Systems (AIS) on July 1, 2015. Professor Lee will serve a one-year term, which will end in June 2016. With four thousand members researching information systems from 90 different nations, AIS is the largest academic society in the fields of information system and business process engineering.
Professor Lee has proposed his idea of “the Bright Internet” as the official vision of AIS. Employing this vision, AIS will create technology and systems, as well as sponsor international cooperation to solve fundamental issues of the Internet including concerns over hacking and cyber-related crimes.
The extent of damage from cyber-related crimes grows each year. Every day, 56 billion junk emails are sent to computers which are hacked and become “zombie” computers. The social cost of such crimes is estimated to be 400 billion US dollars annually.
Based on "the Bright Internet," AIS will build a preventative Internet security system by adopting ground rules that make attackers responsible for the damages from such crimes. The system will also modify technology and other systems to minimize privacy infringement while maintaining security. Finally, the Bright Internet proposes to adopt an international standard for this security system through collaboration with the International Telecommunications Union (ITU).
Professor Lee said, “The vision of the Bright Internet started from an awareness that we needed to resolve issues such as Internet addiction, indiscriminate media exposure, and verbal violence. This vision developed by the experts from all around the world will not only bring a revolution of a reliable Internet platform to a global scale but also reshape the Korean Internet platform.”
2015.07.02 View 8077
Professor Jae Kyu Lee Appointed the President of Association for Information Systems
Chair Professor Jae Kyu Lee of KAIST’s College of Business was appointed the President of Association for Information Systems (AIS) on July 1, 2015. Professor Lee will serve a one-year term, which will end in June 2016. With four thousand members researching information systems from 90 different nations, AIS is the largest academic society in the fields of information system and business process engineering.
Professor Lee has proposed his idea of “the Bright Internet” as the official vision of AIS. Employing this vision, AIS will create technology and systems, as well as sponsor international cooperation to solve fundamental issues of the Internet including concerns over hacking and cyber-related crimes.
The extent of damage from cyber-related crimes grows each year. Every day, 56 billion junk emails are sent to computers which are hacked and become “zombie” computers. The social cost of such crimes is estimated to be 400 billion US dollars annually.
Based on "the Bright Internet," AIS will build a preventative Internet security system by adopting ground rules that make attackers responsible for the damages from such crimes. The system will also modify technology and other systems to minimize privacy infringement while maintaining security. Finally, the Bright Internet proposes to adopt an international standard for this security system through collaboration with the International Telecommunications Union (ITU).
Professor Lee said, “The vision of the Bright Internet started from an awareness that we needed to resolve issues such as Internet addiction, indiscriminate media exposure, and verbal violence. This vision developed by the experts from all around the world will not only bring a revolution of a reliable Internet platform to a global scale but also reshape the Korean Internet platform.”
2015.07.02 View 8077 -
 KAIST Professor Sung-Ju Lee Appointed a Technical Program Chair of INFOCOM
Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the Department of Computer Science at KAIST has been appointed to serve as a technical program chair of IEEE INFOCOME. The computer communication conference, started in 1982, is influential in the research fields of the Internet, wireless, and data centers.
Professor Lee is the first Korean to serve as a program chair. He has been acknowledged for his work in network communications. In the 34th conference, which will be held next year, he will take part in selecting 650 experts in the field to become members and supervise the evaluation of around 1,600 papers.
Professor Lee is the leading researcher in the field of wireless mobile network systems. He is a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and served as the general chair of the 20th Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) SIGMOBILE Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing & Networking (MobiCom 2014). He is on the editorial boards of IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) and IEEE Internet of Things Journals.
Professor Lee said, “I hope to continue the traditions of the conference, as well as integrating research from various areas of network communication. I will strive to create a program with high technology transfer probability.”
The 34th IEEE INFOCOM will take place in San Francisco in April 2016.
2015.07.02 View 8904
KAIST Professor Sung-Ju Lee Appointed a Technical Program Chair of INFOCOM
Professor Sung-Ju Lee of the Department of Computer Science at KAIST has been appointed to serve as a technical program chair of IEEE INFOCOME. The computer communication conference, started in 1982, is influential in the research fields of the Internet, wireless, and data centers.
Professor Lee is the first Korean to serve as a program chair. He has been acknowledged for his work in network communications. In the 34th conference, which will be held next year, he will take part in selecting 650 experts in the field to become members and supervise the evaluation of around 1,600 papers.
Professor Lee is the leading researcher in the field of wireless mobile network systems. He is a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and served as the general chair of the 20th Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) SIGMOBILE Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing & Networking (MobiCom 2014). He is on the editorial boards of IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) and IEEE Internet of Things Journals.
Professor Lee said, “I hope to continue the traditions of the conference, as well as integrating research from various areas of network communication. I will strive to create a program with high technology transfer probability.”
The 34th IEEE INFOCOM will take place in San Francisco in April 2016.
2015.07.02 View 8904 -
 Professor Naehyuck Jang was Appointed Technical Program Chair of the Design Automation Conference
Professor Naehyuck Jang of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST was appointed as the technical program chair of the Design Automation Conference (DAC). He is the first Asian to serve the conference as the chair. At next year’s conference, he will select 150 program committee members and supervise the selection process of 1,000 papers.
Founded in 1964, DAC encompasses research related to automation of semiconductor processes, which usually involve billions of transistors. More than seven thousand people and 150 companies from all around the world participate, of which only the top 20% of the submitted papers are selected. It is the most prestigious conference in the field of semiconductor automation.
The Design Automation Conference also introduces optimization and automation of design processes of systems, hardware security, automobiles, and the Internet of things. Professor Jang specializes in low power system designs. As an ACM Distinguished Scientist, Professor Jang was elected as the chairman after contributing to this year’s program committee by reforming the process of selection of papers.
Professor Jang said, “This year’s conference represents a departure, where we move from the field of traditional semiconductors to the optimization of embedded system, the Internet of things, and security. He added that “we want to create a paper selection process that can propose the future of design automation.”
The 53rd annual DAC will take place at the Austin Convention Center in Texas in June 2016.
2015.07.02 View 7269
Professor Naehyuck Jang was Appointed Technical Program Chair of the Design Automation Conference
Professor Naehyuck Jang of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST was appointed as the technical program chair of the Design Automation Conference (DAC). He is the first Asian to serve the conference as the chair. At next year’s conference, he will select 150 program committee members and supervise the selection process of 1,000 papers.
Founded in 1964, DAC encompasses research related to automation of semiconductor processes, which usually involve billions of transistors. More than seven thousand people and 150 companies from all around the world participate, of which only the top 20% of the submitted papers are selected. It is the most prestigious conference in the field of semiconductor automation.
The Design Automation Conference also introduces optimization and automation of design processes of systems, hardware security, automobiles, and the Internet of things. Professor Jang specializes in low power system designs. As an ACM Distinguished Scientist, Professor Jang was elected as the chairman after contributing to this year’s program committee by reforming the process of selection of papers.
Professor Jang said, “This year’s conference represents a departure, where we move from the field of traditional semiconductors to the optimization of embedded system, the Internet of things, and security. He added that “we want to create a paper selection process that can propose the future of design automation.”
The 53rd annual DAC will take place at the Austin Convention Center in Texas in June 2016.
2015.07.02 View 7269 -
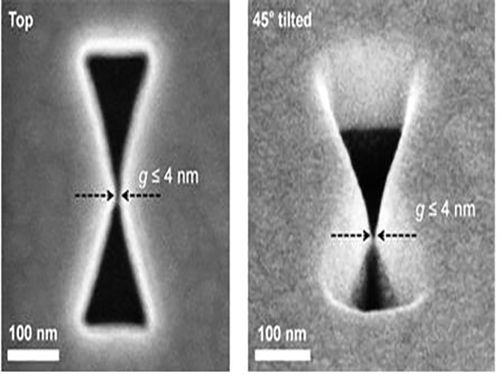 3D Plasmon Antenna Capable of Focusing Light into Few Nanometers
Professors Myung-Ki Kim and Yong-Hee Lee, both of the Physics Department at KAIST, and their research teams have developed a three dimensional (3D) gap-plasmon antenna which can focus light into a space a few nanometers wide. Their research findings were published in the June 10th issue of Nano Letters.
Focusing light into a point-like space is an active research field with many applications. However, concentrating light into a smaller space than its wavelength is often hindered by diffraction. To tackle this problem, many researchers have utilized the plasmonic phenomenon of a metal where light can be confined to a greater extent by overcoming the diffraction limit.
Many researchers have focused on developing a two dimensional (2D) plasmon antenna and were able to focus a light under 5 nanometers wide. However, this 2D antenna revealed a challenge: the light disperses to the opposite end regardless of how small its beam was focused. To solve this difficulty, a 3D structure had to be employed to maximize the light's intensity.
Adopting the proximal focused-ion-beam milling technology, the KAIST research team developed a 3D four nanometer wide gap-plasmon antenna. By squeezing the photons into a 3D nano space of 4 x 10 x 10 nm3 size, the researchers were able to increase the intensity of light by 400,000 times stronger than that of the incident light. Capitalizing on the enhanced intensity of light within the antenna, they intensified the second-harmonic signal and verified that the light was focused in the nano gap by scanning cathodoluminescent images.
The researchers anticipate that this technology will improve the speed of data transfer and processing up to the level of a terahertz (one trillion times per second) and to enlarge the storage volume per unit area on hard disks by 100 times. In addition, high definition images of submolecule size can be taken with actual light, instead of with an electron microscope, while improving the semiconductor process to a smaller size of few nanometers.
Professor Kim said, “A simple yet ingenious idea has shifted the research paradigm from 2D gap-plasmon antennas to 3D antennas. This technology will see numerous applications including in the field of information technology, data storage, imaging medical science, and semiconductor processes.”
The research was sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1: 3D Gap-Plasmon Antenna Structure and Simulation Results
Figure 2 – Constructed 3D Gap-Plasmon Antenna Structure
Figure 3 – Amplified Second Harmonic Signal Generation and Light Focused in the Nano Gap
2015.06.24 View 10538
3D Plasmon Antenna Capable of Focusing Light into Few Nanometers
Professors Myung-Ki Kim and Yong-Hee Lee, both of the Physics Department at KAIST, and their research teams have developed a three dimensional (3D) gap-plasmon antenna which can focus light into a space a few nanometers wide. Their research findings were published in the June 10th issue of Nano Letters.
Focusing light into a point-like space is an active research field with many applications. However, concentrating light into a smaller space than its wavelength is often hindered by diffraction. To tackle this problem, many researchers have utilized the plasmonic phenomenon of a metal where light can be confined to a greater extent by overcoming the diffraction limit.
Many researchers have focused on developing a two dimensional (2D) plasmon antenna and were able to focus a light under 5 nanometers wide. However, this 2D antenna revealed a challenge: the light disperses to the opposite end regardless of how small its beam was focused. To solve this difficulty, a 3D structure had to be employed to maximize the light's intensity.
Adopting the proximal focused-ion-beam milling technology, the KAIST research team developed a 3D four nanometer wide gap-plasmon antenna. By squeezing the photons into a 3D nano space of 4 x 10 x 10 nm3 size, the researchers were able to increase the intensity of light by 400,000 times stronger than that of the incident light. Capitalizing on the enhanced intensity of light within the antenna, they intensified the second-harmonic signal and verified that the light was focused in the nano gap by scanning cathodoluminescent images.
The researchers anticipate that this technology will improve the speed of data transfer and processing up to the level of a terahertz (one trillion times per second) and to enlarge the storage volume per unit area on hard disks by 100 times. In addition, high definition images of submolecule size can be taken with actual light, instead of with an electron microscope, while improving the semiconductor process to a smaller size of few nanometers.
Professor Kim said, “A simple yet ingenious idea has shifted the research paradigm from 2D gap-plasmon antennas to 3D antennas. This technology will see numerous applications including in the field of information technology, data storage, imaging medical science, and semiconductor processes.”
The research was sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1: 3D Gap-Plasmon Antenna Structure and Simulation Results
Figure 2 – Constructed 3D Gap-Plasmon Antenna Structure
Figure 3 – Amplified Second Harmonic Signal Generation and Light Focused in the Nano Gap
2015.06.24 View 10538 -
 Professor Kyoungsik Yu Receives the Young IT Engineer Award from IEEE and IEIE of Korea
Professor Kyoungsik Yu of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering is the recipient of this year’s Young IT (Information Technology) Engineer Award that was co-hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea (IEIE), and Haedong Science Culture Foundation in Korea. The award was presented on June 22, 2015 at The Ramada Plaza Jeju Hotel on Jeju Island, Korea.
The Young IT Engineer Award is given to emerging scientists who have made significant contributions to the advancement of technology, society, environment, and creative education.
Professor Yu's main research interests are IT, energy, and imaging through miniaturization and integration of optoelectronic devices. His contribution to academic and technological development is reflected in his publication of more than 100 papers in international journals and conferences, which were cited over 2,200 times.
Professor Yu said, “I’m honored to receive this award and am encouraged by it. I also find the award meaningful because the United Nations has designated this year as the “International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies,” the field I have been involved in as a researcher.”
In addition to Korea, the IEEE has jointly hosted and presented this award to researchers in countries such as Chile, Ecuador, Peru, Singapore, and Italy.
2015.06.22 View 12406
Professor Kyoungsik Yu Receives the Young IT Engineer Award from IEEE and IEIE of Korea
Professor Kyoungsik Yu of KAIST’s Department of Electrical Engineering is the recipient of this year’s Young IT (Information Technology) Engineer Award that was co-hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), the Institute of Electronics Engineers of Korea (IEIE), and Haedong Science Culture Foundation in Korea. The award was presented on June 22, 2015 at The Ramada Plaza Jeju Hotel on Jeju Island, Korea.
The Young IT Engineer Award is given to emerging scientists who have made significant contributions to the advancement of technology, society, environment, and creative education.
Professor Yu's main research interests are IT, energy, and imaging through miniaturization and integration of optoelectronic devices. His contribution to academic and technological development is reflected in his publication of more than 100 papers in international journals and conferences, which were cited over 2,200 times.
Professor Yu said, “I’m honored to receive this award and am encouraged by it. I also find the award meaningful because the United Nations has designated this year as the “International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies,” the field I have been involved in as a researcher.”
In addition to Korea, the IEEE has jointly hosted and presented this award to researchers in countries such as Chile, Ecuador, Peru, Singapore, and Italy.
2015.06.22 View 12406 -
 Professor Jeong-Guon Ih Is Appointed the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics
Professor Jeong-Guon Ih of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been elected to serve as the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics (ICA) from June 2015 to the end of 2016. The appointment was made at the meeting of the ICA Board held on June 1, 2015, in Maastricht, the Netherlands.
Professor Ih currently also chairs the Asia-Pacific Acoustics Commission.
Instituted in 1951, the ICA is an academic society that promotes international development and collaboration in all fields of acoustics including research, advancement, education, and standardization. It has a membership of 44 national acoustical societies worldwide and four observer countries.
2015.06.17 View 7309
Professor Jeong-Guon Ih Is Appointed the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics
Professor Jeong-Guon Ih of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been elected to serve as the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics (ICA) from June 2015 to the end of 2016. The appointment was made at the meeting of the ICA Board held on June 1, 2015, in Maastricht, the Netherlands.
Professor Ih currently also chairs the Asia-Pacific Acoustics Commission.
Instituted in 1951, the ICA is an academic society that promotes international development and collaboration in all fields of acoustics including research, advancement, education, and standardization. It has a membership of 44 national acoustical societies worldwide and four observer countries.
2015.06.17 View 7309 -
 KAIST and Sejong City Goverment Agree to Establish a Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST and the government of Sejong City will cooperate to establish a graduate school of medical science and engineering. On June 11, 2015, President Steve Kang of KAIST and Mayor Choon-Hee Lee of Sejong City signed a memorandum of understanding at the city hall of Sejong to establish the school.
Under the agreement, the two organizations will work out details to establish the graduate school in Sejong on such issues as administrative assistance, financial support, curriculum development, and the creation of an environment conducive to the growth of medical science.
President Kang said, “Once this graduate school is established, KAIST will be able to offer Korea and the world top-notch researchers in the field of medical science. I have high hopes that the school will produce high-impact research breakthroughs and lead in the advancement of interdisciplinary studies in biotechnology.”
In the picture below, President Steve Kang of KAIST (third from the left) holds the signed memorandum of understanding with Mayor Choon-Hee Lee of Sejong (fourth from the left).
2015.06.16 View 7041
KAIST and Sejong City Goverment Agree to Establish a Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST and the government of Sejong City will cooperate to establish a graduate school of medical science and engineering. On June 11, 2015, President Steve Kang of KAIST and Mayor Choon-Hee Lee of Sejong City signed a memorandum of understanding at the city hall of Sejong to establish the school.
Under the agreement, the two organizations will work out details to establish the graduate school in Sejong on such issues as administrative assistance, financial support, curriculum development, and the creation of an environment conducive to the growth of medical science.
President Kang said, “Once this graduate school is established, KAIST will be able to offer Korea and the world top-notch researchers in the field of medical science. I have high hopes that the school will produce high-impact research breakthroughs and lead in the advancement of interdisciplinary studies in biotechnology.”
In the picture below, President Steve Kang of KAIST (third from the left) holds the signed memorandum of understanding with Mayor Choon-Hee Lee of Sejong (fourth from the left).
2015.06.16 View 7041 -
 KAIST Team Develops Flexible PRAM
Phase change random access memory (PRAM) is one of the strongest candidates for next-generation nonvolatile memory for flexible and wearable electronics. In order to be used as a core memory for flexible devices, the most important issue is reducing high operating current. The effective solution is to decrease cell size in sub-micron region as in commercialized conventional PRAM. However, the scaling to nano-dimension on flexible substrates is extremely difficult due to soft nature and photolithographic limits on plastics, thus practical flexible PRAM has not been realized yet.
Recently, a team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed the first flexible PRAM enabled by self-assembled block copolymer (BCP) silica nanostructures with an ultralow current operation (below one quarter of conventional PRAM without BCP) on plastic substrates. BCP is the mixture of two different polymer materials, which can easily create self-ordered arrays of sub-20 nm features through simple spin-coating and plasma treatments. BCP silica nanostructures successfully lowered the contact area by localizing the volume change of phase-change materials and thus resulted in significant power reduction. Furthermore, the ultrathin silicon-based diodes were integrated with phase-change memories (PCM) to suppress the inter-cell interference, which demonstrated random access capability for flexible and wearable electronics. Their work was published in the March issue of ACS Nano: "Flexible One Diode-One Phase Change Memory Array Enabled by Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
Another way to achieve ultralow-powered PRAM is to utilize self-structured conductive filaments (CF) instead of the resistor-type conventional heater. The self-structured CF nanoheater originated from unipolar memristor can generate strong heat toward phase-change materials due to high current density through the nanofilament. This ground-breaking methodology shows that sub-10 nm filament heater, without using expensive and non-compatible nanolithography, achieved nanoscale switching volume of phase change materials, resulted in the PCM writing current of below 20 uA, the lowest value among top-down PCM devices. This achievement was published in the June online issue of ACS Nano: "Self-Structured Conductive Filament Nanoheater for Chalcogenide Phase Transition." In addition, due to self-structured low-power technology compatible to plastics, the research team has recently succeeded in fabricating a flexible PRAM on wearable substrates.
Professor Lee said, "The demonstration of low power PRAM on plastics is one of the most important issues for next-generation wearable and flexible non-volatile memory. Our innovative and simple methodology represents the strong potential for commercializing flexible PRAM."
In addition, he wrote a review paper regarding the nanotechnology-based electronic devices in the June online issue of Advanced Materials entitled "Performance Enhancement of Electronic and Energy Devices via Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
Picture Caption:
Low-power nonvolatile PRAM for flexible and wearable memories enabled by (a) self-assembled BCP silica nanostructures and (b) self-structured conductive filament nanoheater.
2015.06.15 View 15471
KAIST Team Develops Flexible PRAM
Phase change random access memory (PRAM) is one of the strongest candidates for next-generation nonvolatile memory for flexible and wearable electronics. In order to be used as a core memory for flexible devices, the most important issue is reducing high operating current. The effective solution is to decrease cell size in sub-micron region as in commercialized conventional PRAM. However, the scaling to nano-dimension on flexible substrates is extremely difficult due to soft nature and photolithographic limits on plastics, thus practical flexible PRAM has not been realized yet.
Recently, a team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed the first flexible PRAM enabled by self-assembled block copolymer (BCP) silica nanostructures with an ultralow current operation (below one quarter of conventional PRAM without BCP) on plastic substrates. BCP is the mixture of two different polymer materials, which can easily create self-ordered arrays of sub-20 nm features through simple spin-coating and plasma treatments. BCP silica nanostructures successfully lowered the contact area by localizing the volume change of phase-change materials and thus resulted in significant power reduction. Furthermore, the ultrathin silicon-based diodes were integrated with phase-change memories (PCM) to suppress the inter-cell interference, which demonstrated random access capability for flexible and wearable electronics. Their work was published in the March issue of ACS Nano: "Flexible One Diode-One Phase Change Memory Array Enabled by Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
Another way to achieve ultralow-powered PRAM is to utilize self-structured conductive filaments (CF) instead of the resistor-type conventional heater. The self-structured CF nanoheater originated from unipolar memristor can generate strong heat toward phase-change materials due to high current density through the nanofilament. This ground-breaking methodology shows that sub-10 nm filament heater, without using expensive and non-compatible nanolithography, achieved nanoscale switching volume of phase change materials, resulted in the PCM writing current of below 20 uA, the lowest value among top-down PCM devices. This achievement was published in the June online issue of ACS Nano: "Self-Structured Conductive Filament Nanoheater for Chalcogenide Phase Transition." In addition, due to self-structured low-power technology compatible to plastics, the research team has recently succeeded in fabricating a flexible PRAM on wearable substrates.
Professor Lee said, "The demonstration of low power PRAM on plastics is one of the most important issues for next-generation wearable and flexible non-volatile memory. Our innovative and simple methodology represents the strong potential for commercializing flexible PRAM."
In addition, he wrote a review paper regarding the nanotechnology-based electronic devices in the June online issue of Advanced Materials entitled "Performance Enhancement of Electronic and Energy Devices via Block Copolymer Self-Assembly."
Picture Caption:
Low-power nonvolatile PRAM for flexible and wearable memories enabled by (a) self-assembled BCP silica nanostructures and (b) self-structured conductive filament nanoheater.
2015.06.15 View 15471