people
- Project aims to enable humanoids to interact with people and their environment
June 1, 2009-- A Drexel University-led research team late last week unveiled the newest, most central member of its collaboration with a team of Korean researchers: Jaemi, a humanoid (HUBO). Jaemi HUBO embodies efforts to advance humanoid development and enhance the concept of human-robotic interaction. The project"s goal is to enable humanoids to interact with their environment, and enhancement plans include enabling the humanoid to move over rugged terrain, in unstructured environments and to interact socially with humans and handle objects.
The five-year project, funded through the National Science Foundation (NSF) Partnership for International Research and Education (PIRE) program, seeks transformative models to catalyze discovery through international research collaboration and train U.S. students and junior researchers to effectively think and work in global teams.
"The field of robotics is among the top 10 technology areas considered engines for economic growth. Korea understands this and is aggressively pursuing robotics. To stay competitive, the U.S. must do the same," said Mark Suskin, acting deputy director of NSF"s Office of International Science and Engineering. "NSF"s PIRE program and this robotics collaboration in particular, enable the U.S. to capitalize on research in other countries and remain competitive."
The PIRE research team is composed of researchers at The University of Pennsylvania, Colby College, Bryn Mawr College and Virginia Tech in the United States; and Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), Korea University and Seoul National University in Korea.
The team obtained a version of KAIST"s HUBO humanoid, which it named Jaemi HUBO and decided to house it at Drexel University. KAIST HUBO lab has become a model of cutting advance humanoid research by relatively small teams working on tight budgets.
KAIST excels in humanoid leg and body design, biped gait (walking, running, kicking), balance (modeling and control system design), and hardware integration. U.S. robotics researchers tend to enjoy an edge in locomotion over rugged, unstructured terrain; manipulation/grasping; cognition, perception and human-robot interaction; and vision (image, understanding, navigation).
This collaboration of American and Korean researchers will seek to draw on the expertise of each researcher and take Jaemi HUBO to the next level of development--that is, to improve Jaemi"s capabilities to navigate and manipulate objects and interact with people in unstructured environments. Such capabilities demand information technologies like cognition, perception and networking areas. Targeted enhancement features include a capability to move over rugged terrain and in unstructured environments and to handle objects and interact socially with humans.
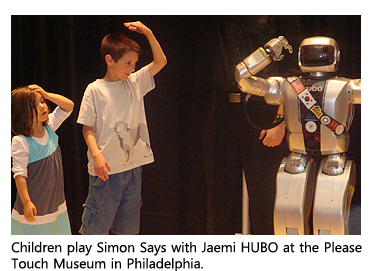
Jaemi HUBO will also educate the American public, particularly young people, about the science of robotics. This education process began at the Please Touch Museum in Philadelphia on May 28, 2009, when Jaemi HUBO was unveiled and introduced to a crowded audience of children and a few adults. Neither male nor female,Jaemi connected with the children, boys and girls alike. Guided by a Drexel University graduate student, Jamei moved, spoke, danced, shook hands and lead the children in a game of Simon Says. Such access to Jaemi HUBO starkly contrasts with that afforded by other high-profile humanoids that are often protected trade secrets, largely inaccessible to the public.
Museum curators are pleased to have had Jaemi visit and entertain kids during the weekend. "At the Please Touch Museum, we promote learning through a variety of senses," said J. Willard Whitson,the museum"s vice president for exhibits and education. "A humanoid not only embodies our goal of building layers of knowledge in young people, but Jaemi helps all of us celebrate the playful side of technology."
Jaemi HUBO is now at its permanent home at Drexel University, from which travel and guest appearances may be arranged by appointment. Journalists interested in meeting and interviewing Jaemi HUBO and other research team members are encouraged to contact Lisa-Joy Zgorski at lisajoy@nsf.gov. (Press Release of U.S. National Science Foundation)
-
people Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineer
2016-06-27 -
people Two Undergraduate KAIST Students Publish a Book on Health Management
Joonho Suh of the Aerospace Engineering Department and Jiho Suh of the Mechanical Engineering Department are both brothers and undergraduates at KAIST. The Suh brothers, who are three years apart, have recently published a self-help book in English on staying healthy entitled “A Scientific Approach to Building Muscle: Mass Effect.” The book introduces techniques to build muscles, adapting them from an engineering concept called "Active Torque Control (ACT)," the management o
2015-10-26 -
people Seven Graduates of KAIST S+ Convergence AMP Publish a Book, “The First Penguinâ€
Seven graduates of KAIST’s S+ Convergence Advanced Management Program (KAMP) have published a book containing their business success stories, The First Penguin, hoping that in telling their story, they will inspire readers who want to become entrepreneurs. The book is available only in Korean. The title of the book refers to a penguin that enters the water first when other penguins hesitate to dive into the ocean, symbolizing the need to make the first move. The book reflects the experien
2015-05-26 -
people Professor Shim Featured with His Drone System in IEEE Spectrum
The IEEE Spectrum, a technology and science magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), featured an article of KAIST’s autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) entitled “South Korea Prepares for Drone vs. Drone Combat,” posted on April 1, 2015. The article introduces the anti-drone defense system being developed by Professor “David” Hyunchul Shim of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST. With the goal of developi
2015-04-02 -
people Interactions Features KAIST's Human-Computer Interaction Lab
Interactions, a bi-monthly magazine published by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), the largest educational and scientific computing society in the world, featured an article introducing Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) Lab at KAIST in the March/April 2015 issue (http://interactions.acm.org/archive/toc/march-april-2015). Established in 2002, the HCI Lab (http://hcil.kaist.ac.kr/) is run by Professor Geehyuk Lee of the Computer Science Department at KAIST. The lab conducts various
2015-03-02