college+of+e
-
 Engineered C. glutamicum Strain Capable of Producing High-Level Glutaric Acid from Glucose
An engineered C. glutamicum strain that can produce the world’s highest titer of glutaric acid was developed by employing systems metabolic engineering strategies
A metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid without byproducts from glucose. This new strategy will be useful for developing engineered micro-organisms for the bio-based production of value-added chemicals.
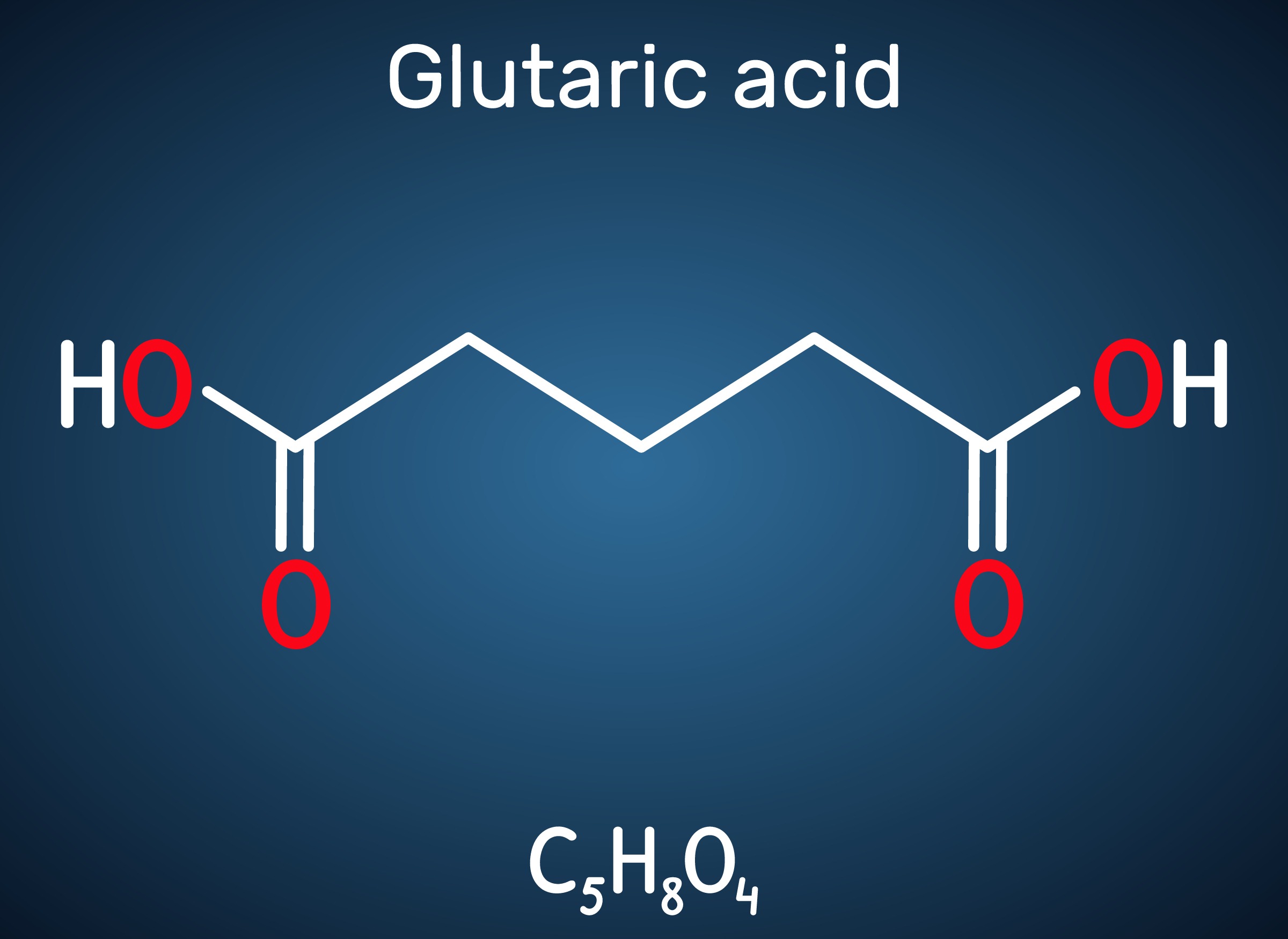
Glutaric acid, also known as pentanedioic acid, is a carboxylic acid that is widely used for various applications including the production of polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, glutaric anhydride, 1,5-pentanediol, and 5-hydroxyvaleric acid. Glutaric acid has been produced using various petroleum-based chemical methods, relying on non-renewable and toxic starting materials. Thus, various approaches have been taken to biologically produce glutaric acid from renewable resources. Previously, the development of the first glutaric acid producing Escherichia coli by introducing Pseudomonas putida genes was reported by a research group from KAIST, but the titer was low. Glutaric acid production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum has also been reported in several studies, but further improvements in glutaric acid production seemed possible since C. glutamicum has the capability of producing more than 130 g/L of L-lysine.
A research group comprised of Taehee Han, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. Their research paper “Glutaric acid production by systems metabolic engineering of an L-lysine-overproducing Corynebacterium glutamicum” was published online in PNAS on November 16, 2020.
This research reports the development of a metabolically engineered C. glutamicum strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid, starting from an L-lysine overproducer. The following novel strategies and approaches to achieve high-level glutaric acid production were employed. First, metabolic pathways in C. glutamicum were reconstituted for glutaric acid production by introducing P. putida genes. Then, multi-omics analyses including genome, transcriptome, and fluxome were conducted to understand the phenotype of the L-lysine overproducer strain. In addition to systematic understanding of the host strain, gene manipulation targets were predicted by omics analyses and applied for engineering C. glutamicum, which resulted in the development of an engineered strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid. Furthermore, the new glutaric acid exporter was discovered for the first time, which was used to further increase glutaric acid production through enhancing product excretion. Last but not least, culture conditions were optimized for high-level glutaric acid production. As a result, the final engineered strain was able to produce 105.3 g/L glutaric acid, the highest titer ever reported, in 69 hours by fed-batch fermentation.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is meaningful that we were able to develop a highly efficient glutaric acid producer capable of producing glutaric acid at the world’s highest titer without any byproducts from renewable carbon sources. This will further accelerate the bio-based production of valuable chemicals in pharmaceutical/medical/chemical industries.” This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.17 View 6228
Engineered C. glutamicum Strain Capable of Producing High-Level Glutaric Acid from Glucose
An engineered C. glutamicum strain that can produce the world’s highest titer of glutaric acid was developed by employing systems metabolic engineering strategies
A metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid without byproducts from glucose. This new strategy will be useful for developing engineered micro-organisms for the bio-based production of value-added chemicals.
Glutaric acid, also known as pentanedioic acid, is a carboxylic acid that is widely used for various applications including the production of polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, glutaric anhydride, 1,5-pentanediol, and 5-hydroxyvaleric acid. Glutaric acid has been produced using various petroleum-based chemical methods, relying on non-renewable and toxic starting materials. Thus, various approaches have been taken to biologically produce glutaric acid from renewable resources. Previously, the development of the first glutaric acid producing Escherichia coli by introducing Pseudomonas putida genes was reported by a research group from KAIST, but the titer was low. Glutaric acid production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum has also been reported in several studies, but further improvements in glutaric acid production seemed possible since C. glutamicum has the capability of producing more than 130 g/L of L-lysine.
A research group comprised of Taehee Han, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. Their research paper “Glutaric acid production by systems metabolic engineering of an L-lysine-overproducing Corynebacterium glutamicum” was published online in PNAS on November 16, 2020.
This research reports the development of a metabolically engineered C. glutamicum strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid, starting from an L-lysine overproducer. The following novel strategies and approaches to achieve high-level glutaric acid production were employed. First, metabolic pathways in C. glutamicum were reconstituted for glutaric acid production by introducing P. putida genes. Then, multi-omics analyses including genome, transcriptome, and fluxome were conducted to understand the phenotype of the L-lysine overproducer strain. In addition to systematic understanding of the host strain, gene manipulation targets were predicted by omics analyses and applied for engineering C. glutamicum, which resulted in the development of an engineered strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid. Furthermore, the new glutaric acid exporter was discovered for the first time, which was used to further increase glutaric acid production through enhancing product excretion. Last but not least, culture conditions were optimized for high-level glutaric acid production. As a result, the final engineered strain was able to produce 105.3 g/L glutaric acid, the highest titer ever reported, in 69 hours by fed-batch fermentation.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is meaningful that we were able to develop a highly efficient glutaric acid producer capable of producing glutaric acid at the world’s highest titer without any byproducts from renewable carbon sources. This will further accelerate the bio-based production of valuable chemicals in pharmaceutical/medical/chemical industries.” This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.17 View 6228 -
 To Talk or Not to Talk: Smart Speaker Determines Optimal Timing to Talk
A KAIST research team has developed a new context-awareness technology that enables AI assistants to determine when to talk to their users based on user circumstances. This technology can contribute to developing advanced AI assistants that can offer pre-emptive services such as reminding users to take medication on time or modifying schedules based on the actual progress of planned tasks.
Unlike conventional AI assistants that used to act passively upon users’ commands, today’s AI assistants are evolving to provide more proactive services through self-reasoning of user circumstances. This opens up new opportunities for AI assistants to better support users in their daily lives. However, if AI assistants do not talk at the right time, they could rather interrupt their users instead of helping them.
The right time for talking is more difficult for AI assistants to determine than it appears. This is because the context can differ depending on the state of the user or the surrounding environment.
A group of researchers led by Professor Uichin Lee from the KAIST School of Computing identified key contextual factors in user circumstances that determine when the AI assistant should start, stop, or resume engaging in voice services in smart home environments. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT) in September.
The group conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Jae-Gil Lee’s group in the KAIST School of Computing, Professor Sangsu Lee’s group in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, and Professor Auk Kim’s group at Kangwon National University.
After developing smart speakers equipped with AI assistant function for experimental use, the researchers installed them in the rooms of 40 students who live in double-occupancy campus dormitories and collected a total of 3,500 in-situ user response data records over a period of a week.
The smart speakers repeatedly asked the students a question, “Is now a good time to talk?” at random intervals or whenever a student’s movement was detected. Students answered with either “yes” or “no” and then explained why, describing what they had been doing before being questioned by the smart speakers.
Data analysis revealed that 47% of user responses were “no” indicating they did not want to be interrupted. The research team then created 19 home activity categories to cross-analyze the key contextual factors that determine opportune moments for AI assistants to talk, and classified these factors into ‘personal,’ ‘movement,’ and ‘social’ factors respectively.
Personal factors, for instance, include:
1. the degree of concentration on or engagement in activities,
2. the degree urgency and busyness,
3. the state of user’s mental or physical condition, and
4. the state of being able to talk or listen while multitasking.
While users were busy concentrating on studying, tired, or drying hair, they found it difficult to engage in conversational interactions with the smart speakers.
Some representative movement factors include departure, entrance, and physical activity transitions. Interestingly, in movement scenarios, the team found that the communication range was an important factor. Departure is an outbound movement from the smart speaker, and entrance is an inbound movement. Users were much more available during inbound movement scenarios as opposed to outbound movement scenarios.
In general, smart speakers are located in a shared place at home, such as a living room, where multiple family members gather at the same time. In Professor Lee’s group’s experiment, almost half of the in-situ user responses were collected when both roommates were present. The group found social presence also influenced interruptibility. Roommates often wanted to minimize possible interpersonal conflicts, such as disturbing their roommates' sleep or work.
Narae Cha, the lead author of this study, explained, “By considering personal, movement, and social factors, we can envision a smart speaker that can intelligently manage the timing of conversations with users.”
She believes that this work lays the foundation for the future of AI assistants, adding, “Multi-modal sensory data can be used for context sensing, and this context information will help smart speakers proactively determine when it is a good time to start, stop, or resume conversations with their users.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Cha, N, et al. (2020) “Hello There! Is Now a Good Time to Talk?”: Opportune Moments for Proactive Interactions with Smart Speakers. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), Vol. 4, No. 3, Article No. 74, pp. 1-28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1145/3411810
Link to Introductory Video:
https://youtu.be/AA8CTi2hEf0
Profile:
Uichin Lee
Associate Professor
uclee@kaist.ac.kr
http://ic.kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Computing Lab.
School of Computing
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.05 View 10214
To Talk or Not to Talk: Smart Speaker Determines Optimal Timing to Talk
A KAIST research team has developed a new context-awareness technology that enables AI assistants to determine when to talk to their users based on user circumstances. This technology can contribute to developing advanced AI assistants that can offer pre-emptive services such as reminding users to take medication on time or modifying schedules based on the actual progress of planned tasks.
Unlike conventional AI assistants that used to act passively upon users’ commands, today’s AI assistants are evolving to provide more proactive services through self-reasoning of user circumstances. This opens up new opportunities for AI assistants to better support users in their daily lives. However, if AI assistants do not talk at the right time, they could rather interrupt their users instead of helping them.
The right time for talking is more difficult for AI assistants to determine than it appears. This is because the context can differ depending on the state of the user or the surrounding environment.
A group of researchers led by Professor Uichin Lee from the KAIST School of Computing identified key contextual factors in user circumstances that determine when the AI assistant should start, stop, or resume engaging in voice services in smart home environments. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT) in September.
The group conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Jae-Gil Lee’s group in the KAIST School of Computing, Professor Sangsu Lee’s group in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, and Professor Auk Kim’s group at Kangwon National University.
After developing smart speakers equipped with AI assistant function for experimental use, the researchers installed them in the rooms of 40 students who live in double-occupancy campus dormitories and collected a total of 3,500 in-situ user response data records over a period of a week.
The smart speakers repeatedly asked the students a question, “Is now a good time to talk?” at random intervals or whenever a student’s movement was detected. Students answered with either “yes” or “no” and then explained why, describing what they had been doing before being questioned by the smart speakers.
Data analysis revealed that 47% of user responses were “no” indicating they did not want to be interrupted. The research team then created 19 home activity categories to cross-analyze the key contextual factors that determine opportune moments for AI assistants to talk, and classified these factors into ‘personal,’ ‘movement,’ and ‘social’ factors respectively.
Personal factors, for instance, include:
1. the degree of concentration on or engagement in activities,
2. the degree urgency and busyness,
3. the state of user’s mental or physical condition, and
4. the state of being able to talk or listen while multitasking.
While users were busy concentrating on studying, tired, or drying hair, they found it difficult to engage in conversational interactions with the smart speakers.
Some representative movement factors include departure, entrance, and physical activity transitions. Interestingly, in movement scenarios, the team found that the communication range was an important factor. Departure is an outbound movement from the smart speaker, and entrance is an inbound movement. Users were much more available during inbound movement scenarios as opposed to outbound movement scenarios.
In general, smart speakers are located in a shared place at home, such as a living room, where multiple family members gather at the same time. In Professor Lee’s group’s experiment, almost half of the in-situ user responses were collected when both roommates were present. The group found social presence also influenced interruptibility. Roommates often wanted to minimize possible interpersonal conflicts, such as disturbing their roommates' sleep or work.
Narae Cha, the lead author of this study, explained, “By considering personal, movement, and social factors, we can envision a smart speaker that can intelligently manage the timing of conversations with users.”
She believes that this work lays the foundation for the future of AI assistants, adding, “Multi-modal sensory data can be used for context sensing, and this context information will help smart speakers proactively determine when it is a good time to start, stop, or resume conversations with their users.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Cha, N, et al. (2020) “Hello There! Is Now a Good Time to Talk?”: Opportune Moments for Proactive Interactions with Smart Speakers. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), Vol. 4, No. 3, Article No. 74, pp. 1-28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1145/3411810
Link to Introductory Video:
https://youtu.be/AA8CTi2hEf0
Profile:
Uichin Lee
Associate Professor
uclee@kaist.ac.kr
http://ic.kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Computing Lab.
School of Computing
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.05 View 10214 -
 Chemical Scissors Snip 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenides into Nanoribbon
New ‘nanoribbon’ catalyst should slash cost of hydrogen production for clean fuels
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative – and an innovative way to produce them using chemical ‘scissors’ – that could make hydrogen production more economical.
The research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering published their work in Nature Communications.
Hydrogen is likely to play a key role in the clean transition away from fossil fuels and other processes that produce greenhouse gas emissions. There is a raft of transportation sectors such as long-haul shipping and aviation that are difficult to electrify and so will require cleanly produced hydrogen as a fuel or as a feedstock for other carbon-neutral synthetic fuels. Likewise, fertilizer production and the steel sector are unlikely to be “de-carbonized” without cheap and clean hydrogen.
The problem is that the cheapest methods by far of producing hydrogen gas is currently from natural gas, a process that itself produces the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide–which defeats the purpose.
Alternative techniques of hydrogen production, such as electrolysis using an electric current between two electrodes plunged into water to overcome the chemical bonds holding water together, thereby splitting it into its constituent elements, oxygen and hydrogen are very well established. But one of the factors contributing to the high cost, beyond being extremely energy-intensive, is the need for the very expensive precious and relatively rare metal platinum. The platinum is used as a catalyst–a substance that kicks off or speeds up a chemical reaction–in the hydrogen production process.
As a result, researchers have long been on the hunt for a substitution for platinum -- another catalyst that is abundant in the earth and thus much cheaper.
Transition metal dichalcogenides, or TMDs, in a nanomaterial form, have for some time been considered a good candidate as a catalyst replacement for platinum. These are substances composed of one atom of a transition metal (the elements in the middle part of the periodic table) and two atoms of a chalcogen element (the elements in the third-to-last column in the periodic table, specifically sulfur, selenium and tellurium).
What makes TMDs a good bet as a platinum replacement is not just that they are much more abundant, but also their electrons are structured in a way that gives the electrodes a boost.
In addition, a TMD that is a nanomaterial is essentially a two-dimensional super-thin sheet only a few atoms thick, just like graphene. The ultrathin nature of a 2-D TMD nanosheet allows for a great many more TMD molecules to be exposed during the catalysis process than would be the case in a block of the stuff, thus kicking off and speeding up the hydrogen-making chemical reaction that much more.
However, even here the TMD molecules are only reactive at the four edges of a nanosheet. In the flat interior, not much is going on. In order to increase the chemical reaction rate in the production of hydrogen, the nanosheet would need to be cut into very thin – almost one-dimensional strips, thereby creating many edges.
In response, the research team developed what are in essence a pair of chemical scissors that can snip TMD into tiny strips.
“Up to now, the only substances that anyone has been able to turn into these ‘nano-ribbons’ are graphene and phosphorene,” said Sang Professor Kim, one of the researchers involved in devising the process.
“But they’re both made up of just one element, so it’s pretty straightforward. Figuring out how to do it for TMD, which is made of two elements was going to be much harder.”
The ‘scissors’ involve a two-step process involving first inserting lithium ions into the layered structure of the TMD sheets, and then using ultrasound to cause a spontaneous ‘unzipping’ in straight lines.
“It works sort of like how when you split a plank of plywood: it breaks easily in one direction along the grain,” Professor Kim continued. “It’s actually really simple.”
The researchers then tried it with various types of TMDs, including those made of molybdenum, selenium, sulfur, tellurium and tungsten. All worked just as well, with a catalytic efficiency as effective as platinum’s.
Because of the simplicity of the procedure, this method should be able to be used not just in the large-scale production of TMD nanoribbons, but also to make similar nanoribbons from other multi-elemental 2D materials for purposes beyond just hydrogen production.
-ProfileProfessor Sang Ouk KimSoft Nanomaterials Laboratory (http://snml.kaist.ac.kr)Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.29 View 6897
Chemical Scissors Snip 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenides into Nanoribbon
New ‘nanoribbon’ catalyst should slash cost of hydrogen production for clean fuels
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative – and an innovative way to produce them using chemical ‘scissors’ – that could make hydrogen production more economical.
The research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering published their work in Nature Communications.
Hydrogen is likely to play a key role in the clean transition away from fossil fuels and other processes that produce greenhouse gas emissions. There is a raft of transportation sectors such as long-haul shipping and aviation that are difficult to electrify and so will require cleanly produced hydrogen as a fuel or as a feedstock for other carbon-neutral synthetic fuels. Likewise, fertilizer production and the steel sector are unlikely to be “de-carbonized” without cheap and clean hydrogen.
The problem is that the cheapest methods by far of producing hydrogen gas is currently from natural gas, a process that itself produces the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide–which defeats the purpose.
Alternative techniques of hydrogen production, such as electrolysis using an electric current between two electrodes plunged into water to overcome the chemical bonds holding water together, thereby splitting it into its constituent elements, oxygen and hydrogen are very well established. But one of the factors contributing to the high cost, beyond being extremely energy-intensive, is the need for the very expensive precious and relatively rare metal platinum. The platinum is used as a catalyst–a substance that kicks off or speeds up a chemical reaction–in the hydrogen production process.
As a result, researchers have long been on the hunt for a substitution for platinum -- another catalyst that is abundant in the earth and thus much cheaper.
Transition metal dichalcogenides, or TMDs, in a nanomaterial form, have for some time been considered a good candidate as a catalyst replacement for platinum. These are substances composed of one atom of a transition metal (the elements in the middle part of the periodic table) and two atoms of a chalcogen element (the elements in the third-to-last column in the periodic table, specifically sulfur, selenium and tellurium).
What makes TMDs a good bet as a platinum replacement is not just that they are much more abundant, but also their electrons are structured in a way that gives the electrodes a boost.
In addition, a TMD that is a nanomaterial is essentially a two-dimensional super-thin sheet only a few atoms thick, just like graphene. The ultrathin nature of a 2-D TMD nanosheet allows for a great many more TMD molecules to be exposed during the catalysis process than would be the case in a block of the stuff, thus kicking off and speeding up the hydrogen-making chemical reaction that much more.
However, even here the TMD molecules are only reactive at the four edges of a nanosheet. In the flat interior, not much is going on. In order to increase the chemical reaction rate in the production of hydrogen, the nanosheet would need to be cut into very thin – almost one-dimensional strips, thereby creating many edges.
In response, the research team developed what are in essence a pair of chemical scissors that can snip TMD into tiny strips.
“Up to now, the only substances that anyone has been able to turn into these ‘nano-ribbons’ are graphene and phosphorene,” said Sang Professor Kim, one of the researchers involved in devising the process.
“But they’re both made up of just one element, so it’s pretty straightforward. Figuring out how to do it for TMD, which is made of two elements was going to be much harder.”
The ‘scissors’ involve a two-step process involving first inserting lithium ions into the layered structure of the TMD sheets, and then using ultrasound to cause a spontaneous ‘unzipping’ in straight lines.
“It works sort of like how when you split a plank of plywood: it breaks easily in one direction along the grain,” Professor Kim continued. “It’s actually really simple.”
The researchers then tried it with various types of TMDs, including those made of molybdenum, selenium, sulfur, tellurium and tungsten. All worked just as well, with a catalytic efficiency as effective as platinum’s.
Because of the simplicity of the procedure, this method should be able to be used not just in the large-scale production of TMD nanoribbons, but also to make similar nanoribbons from other multi-elemental 2D materials for purposes beyond just hydrogen production.
-ProfileProfessor Sang Ouk KimSoft Nanomaterials Laboratory (http://snml.kaist.ac.kr)Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.29 View 6897 -
 KAIST Showcases Healthcare Technologies at K-Hospital Fair 2020
KAIST Pavilion showcased its innovative medical and healthcare technologies and their advanced applications at the K-Hospital Fair 2020. Five KAIST research groups who teamed up for the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project participated in the fair held in Seoul last week.
The K-Hospital Fair is a yearly event organized by the Korean Hospital Association to present the latest research and practical innovations to help the medical industry better serve the patients. This year, 120 healthcare organizations participated in the fair and operated 320 booths.
At the fair, a research group led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering demonstrated the manufacturing process of orthogonal nanofibers used to develop their ‘recyclable nano-fiber filtered face mask’ introduced in March of this year. This mask has garnered immense international attention for maintaining its sturdy frame and filtering function even after being washed more than 20 times. Professor Kim is now extending his facilities for the mass production of this mask at his start-up company. While awaiting final approval from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety to bring his product into the market, Professor Kim is developing other mask variations such as eco-friendly biodegradable masks and transparent masks to aid the hearing-impaired who rely on lip reading to communicate.
The team working under Professor Wonho Choe from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering presented two low-temperature plasma sterilizers for medical use, co-developed with Plasmapp, a start-up company founded by a KAIST alumnus. Their sterilizers are the first ones that can sterilize medical devices by diffusing hydrogen peroxide vapor into the pouch. They rapidly sterilize medical instruments and materials in just seven minutes without leaving toxic residue, while reducing sterilization time and costs by 90%.
Professor Hyung-Soon Park and his researchers from the Department of Mechanical Engineering introduced a smart protective suit ventilation system that features high cooling capacity and a slimmed-down design. For comfortable use, the suit is equipped with a technique that monitors its inner temperature and humidity and automatically controls its inner circulation accordingly. The group also presented a new system that helps a person in a contaminated suit undress without coming into contact with the contaminated outer part of the suit.
Professor Jong Chul Ye's group from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated AI software that can quickly diagnose an infectious disease based on chest X-ray imaging. The technique compares the differences in the severity of pneumonia in individual patients to distinguish whether their conditions fall under viral pneumonia including COVID-19, bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, other diseases, or normal conditions. The AI software visualizes the basis of its reasoning for each of the suspected diseases and provides them as information that can be utilized by medical personnel.
Finally, researchers of Professor Ki-Hun Jeong’s team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated their ultra-high-speed sub-miniature molecular diagnostic system for the on-site diagnosis of diseases. The existing Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) diagnostic usually takes from 30 minutes to an hour to provide results, but their new technique using an LED light source can present results within just three minutes and it is expected to be used actively for on-site diagnosis.
Professor Choongsik Bae, the Director of the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project, said, “KAIST will build a healthy relationship amongst researchers, enterprises, and hospitals to contribute to the end of COVID-19 and build a new paradigm of Korean disease prevention and control.”
KAIST launched the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative in July with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea. This unit was created to overcome the pandemic crisis by using science and technology, and to contribute to economic development by creating a new antiviral drug industry. The unit is comprised of 464 KAIST members including professors, researchers, and students as well as 503 professionals from enterprises, hospitals, and research centers.
(END)
2020.10.26 View 11892
KAIST Showcases Healthcare Technologies at K-Hospital Fair 2020
KAIST Pavilion showcased its innovative medical and healthcare technologies and their advanced applications at the K-Hospital Fair 2020. Five KAIST research groups who teamed up for the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project participated in the fair held in Seoul last week.
The K-Hospital Fair is a yearly event organized by the Korean Hospital Association to present the latest research and practical innovations to help the medical industry better serve the patients. This year, 120 healthcare organizations participated in the fair and operated 320 booths.
At the fair, a research group led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering demonstrated the manufacturing process of orthogonal nanofibers used to develop their ‘recyclable nano-fiber filtered face mask’ introduced in March of this year. This mask has garnered immense international attention for maintaining its sturdy frame and filtering function even after being washed more than 20 times. Professor Kim is now extending his facilities for the mass production of this mask at his start-up company. While awaiting final approval from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety to bring his product into the market, Professor Kim is developing other mask variations such as eco-friendly biodegradable masks and transparent masks to aid the hearing-impaired who rely on lip reading to communicate.
The team working under Professor Wonho Choe from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering presented two low-temperature plasma sterilizers for medical use, co-developed with Plasmapp, a start-up company founded by a KAIST alumnus. Their sterilizers are the first ones that can sterilize medical devices by diffusing hydrogen peroxide vapor into the pouch. They rapidly sterilize medical instruments and materials in just seven minutes without leaving toxic residue, while reducing sterilization time and costs by 90%.
Professor Hyung-Soon Park and his researchers from the Department of Mechanical Engineering introduced a smart protective suit ventilation system that features high cooling capacity and a slimmed-down design. For comfortable use, the suit is equipped with a technique that monitors its inner temperature and humidity and automatically controls its inner circulation accordingly. The group also presented a new system that helps a person in a contaminated suit undress without coming into contact with the contaminated outer part of the suit.
Professor Jong Chul Ye's group from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated AI software that can quickly diagnose an infectious disease based on chest X-ray imaging. The technique compares the differences in the severity of pneumonia in individual patients to distinguish whether their conditions fall under viral pneumonia including COVID-19, bacterial pneumonia, tuberculosis, other diseases, or normal conditions. The AI software visualizes the basis of its reasoning for each of the suspected diseases and provides them as information that can be utilized by medical personnel.
Finally, researchers of Professor Ki-Hun Jeong’s team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering demonstrated their ultra-high-speed sub-miniature molecular diagnostic system for the on-site diagnosis of diseases. The existing Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) diagnostic usually takes from 30 minutes to an hour to provide results, but their new technique using an LED light source can present results within just three minutes and it is expected to be used actively for on-site diagnosis.
Professor Choongsik Bae, the Director of the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project, said, “KAIST will build a healthy relationship amongst researchers, enterprises, and hospitals to contribute to the end of COVID-19 and build a new paradigm of Korean disease prevention and control.”
KAIST launched the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative in July with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea. This unit was created to overcome the pandemic crisis by using science and technology, and to contribute to economic development by creating a new antiviral drug industry. The unit is comprised of 464 KAIST members including professors, researchers, and students as well as 503 professionals from enterprises, hospitals, and research centers.
(END)
2020.10.26 View 11892 -
 Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 9148
Taesik Gong Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Taesik Gong from the School of Computing was named a 2020 Google PhD Fellow in the field of machine learning.
The Google PhD Fellowship Program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Gong is one of two Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 53 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Gong’s research on condition-independent mobile sensing powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He has published and presented his work through many conferences including ACM SenSys and ACM UbiComp, and has worked at Microsoft Research Asia and Nokia Bell Labs as a research intern. Gong was also the winner of the NAVER PhD Fellowship Award in 2018.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 9148 -
 Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 9444
Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 9444 -
 Slippery When Wet: Fish and Seaweed Inspire Ships to Reduce Fluid Friction
Faster ships could be on the horizon after KAIST scientists develop a slippery surface inspired by fish and seaweed to reduce the hull's drag through the water.
Long-distance cargo ships lose a significant amount of energy due to fluid friction. Looking to the drag reduction mechanisms employed by aquatic life can provide inspiration on how to improve efficiency.
Fish and seaweed secrete a layer of mucus to create a slippery surface, reducing their friction as they travel through water. A potential way to mimic this is by creating lubricant-infused surfaces covered with cavities. As the cavities are continuously filled with the lubricant, a layer is formed over the surface.
Though this method has previously been shown to work, reducing drag by up to 18%, the underlying physics is not fully understood. KAIST researchers in collaboration with a team of researchers from POSTECH conducted simulations of this process to help explain the effects, and their findings were published in the journal Physics of Fluids on September 15.
The group looked at the average speed of a cargo ship with realistic material properties and simulated how it behaves under various lubrication setups. Specifically, they monitored the effects of the open area of the lubricant-filled cavities, as well as the thickness of the cavity lids.
They found that for larger open areas, the lubricant spreads more than it does with smaller open areas, leading to a slipperier surface. On the other hand, the lid thickness does not have much of an effect on the slip, though a thicker lid does create a thicker lubricant buildup layer.
Professor Emeritus Hyung Jin Sung from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering who led this study said, “Our investigation of the hydrodynamics of a lubricant layer and how it results in drag reduction with a slippery surface in a basic configuration has provided significant insight into the benefits of a lubricant-infused surface.”
Now that they have worked on optimizing the lubricant secretion design, the authors hope it can be implemented in real-life marine vehicles.
“If the present design parameters are adopted, the drag reduction rate will increase significantly,” Professor Sung added.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Source:
Materials provided by American Institute of Physics.
Publication:
Kim, Seung Joong, et al. (2020). A lubricant-infused slip surface for drag reduction. Physics of Fluids. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0018460
Profile:
Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Emeritus
hyungjin@kaist.ac.kr
http://flow.kaist.ac.kr/index.php
Flow Control Lab. (FCL)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.10.12 View 6219
Slippery When Wet: Fish and Seaweed Inspire Ships to Reduce Fluid Friction
Faster ships could be on the horizon after KAIST scientists develop a slippery surface inspired by fish and seaweed to reduce the hull's drag through the water.
Long-distance cargo ships lose a significant amount of energy due to fluid friction. Looking to the drag reduction mechanisms employed by aquatic life can provide inspiration on how to improve efficiency.
Fish and seaweed secrete a layer of mucus to create a slippery surface, reducing their friction as they travel through water. A potential way to mimic this is by creating lubricant-infused surfaces covered with cavities. As the cavities are continuously filled with the lubricant, a layer is formed over the surface.
Though this method has previously been shown to work, reducing drag by up to 18%, the underlying physics is not fully understood. KAIST researchers in collaboration with a team of researchers from POSTECH conducted simulations of this process to help explain the effects, and their findings were published in the journal Physics of Fluids on September 15.
The group looked at the average speed of a cargo ship with realistic material properties and simulated how it behaves under various lubrication setups. Specifically, they monitored the effects of the open area of the lubricant-filled cavities, as well as the thickness of the cavity lids.
They found that for larger open areas, the lubricant spreads more than it does with smaller open areas, leading to a slipperier surface. On the other hand, the lid thickness does not have much of an effect on the slip, though a thicker lid does create a thicker lubricant buildup layer.
Professor Emeritus Hyung Jin Sung from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering who led this study said, “Our investigation of the hydrodynamics of a lubricant layer and how it results in drag reduction with a slippery surface in a basic configuration has provided significant insight into the benefits of a lubricant-infused surface.”
Now that they have worked on optimizing the lubricant secretion design, the authors hope it can be implemented in real-life marine vehicles.
“If the present design parameters are adopted, the drag reduction rate will increase significantly,” Professor Sung added.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Source:
Materials provided by American Institute of Physics.
Publication:
Kim, Seung Joong, et al. (2020). A lubricant-infused slip surface for drag reduction. Physics of Fluids. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0018460
Profile:
Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Emeritus
hyungjin@kaist.ac.kr
http://flow.kaist.ac.kr/index.php
Flow Control Lab. (FCL)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.10.12 View 6219 -
 Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 12316
Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 12316 -
 E. coli Engineered to Grow on CO₂ and Formic Acid as Sole Carbon Sources
- An E. coli strain that can grow to a relatively high cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid was developed by employing metabolic engineering. -
Most biorefinery processes have relied on the use of biomass as a raw material for the production of chemicals and materials. Even though the use of CO₂ as a carbon source in biorefineries is desirable, it has not been possible to make common microbial strains such as E. coli grow on CO₂.
Now, a metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed a strategy to grow an E. coli strain to higher cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid. Formic acid is a one carbon carboxylic acid, and can be easily produced from CO₂ using a variety of methods. Since it is easier to store and transport than CO₂, formic acid can be considered a good liquid-form alternative of CO₂.
With support from the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center and the Ministry of Science and ICT, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stepped up their work to develop an engineered E. coli strain capable of growing up to 11-fold higher cell density than those previously reported, using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources. This work was published in Nature Microbiology on September 28.
Despite the recent reports by several research groups on the development of E. coli strains capable of growing on CO₂ and formic acid, the maximum cell growth remained too low (optical density of around 1) and thus the production of chemicals from CO₂ and formic acid has been far from realized.
The team previously reported the reconstruction of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage pathway to construct an engineered E. coli strain that can sustain growth on CO₂ and formic acid. To further enhance the growth, the research team introduced the previously designed synthetic CO₂ and formic acid assimilation pathway, and two formate dehydrogenases.
Metabolic fluxes were also fine-tuned, the gluconeogenic flux enhanced, and the levels of cytochrome bo3 and bd-I ubiquinol oxidase for ATP generation were optimized. This engineered E. coli strain was able to grow to a relatively high OD600 of 7~11, showing promise as a platform strain growing solely on CO₂ and formic acid.
Professor Lee said, “We engineered E. coli that can grow to a higher cell density only using CO₂ and formic acid. We think that this is an important step forward, but this is not the end. The engineered strain we developed still needs further engineering so that it can grow faster to a much higher density.”
Professor Lee’s team is continuing to develop such a strain. “In the future, we would be delighted to see the production of chemicals from an engineered E. coli strain using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources,” he added.
-Profile:Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Leehttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.09.29 View 9547
E. coli Engineered to Grow on CO₂ and Formic Acid as Sole Carbon Sources
- An E. coli strain that can grow to a relatively high cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid was developed by employing metabolic engineering. -
Most biorefinery processes have relied on the use of biomass as a raw material for the production of chemicals and materials. Even though the use of CO₂ as a carbon source in biorefineries is desirable, it has not been possible to make common microbial strains such as E. coli grow on CO₂.
Now, a metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed a strategy to grow an E. coli strain to higher cell density solely on CO₂ and formic acid. Formic acid is a one carbon carboxylic acid, and can be easily produced from CO₂ using a variety of methods. Since it is easier to store and transport than CO₂, formic acid can be considered a good liquid-form alternative of CO₂.
With support from the C1 Gas Refinery R&D Center and the Ministry of Science and ICT, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee stepped up their work to develop an engineered E. coli strain capable of growing up to 11-fold higher cell density than those previously reported, using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources. This work was published in Nature Microbiology on September 28.
Despite the recent reports by several research groups on the development of E. coli strains capable of growing on CO₂ and formic acid, the maximum cell growth remained too low (optical density of around 1) and thus the production of chemicals from CO₂ and formic acid has been far from realized.
The team previously reported the reconstruction of the tetrahydrofolate cycle and reverse glycine cleavage pathway to construct an engineered E. coli strain that can sustain growth on CO₂ and formic acid. To further enhance the growth, the research team introduced the previously designed synthetic CO₂ and formic acid assimilation pathway, and two formate dehydrogenases.
Metabolic fluxes were also fine-tuned, the gluconeogenic flux enhanced, and the levels of cytochrome bo3 and bd-I ubiquinol oxidase for ATP generation were optimized. This engineered E. coli strain was able to grow to a relatively high OD600 of 7~11, showing promise as a platform strain growing solely on CO₂ and formic acid.
Professor Lee said, “We engineered E. coli that can grow to a higher cell density only using CO₂ and formic acid. We think that this is an important step forward, but this is not the end. The engineered strain we developed still needs further engineering so that it can grow faster to a much higher density.”
Professor Lee’s team is continuing to develop such a strain. “In the future, we would be delighted to see the production of chemicals from an engineered E. coli strain using CO₂ and formic acid as sole carbon sources,” he added.
-Profile:Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Leehttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.09.29 View 9547 -
 Deep Learning Helps Explore the Structural and Strategic Bases of Autism
Psychiatrists typically diagnose autism spectrum disorders (ASD) by observing a person’s behavior and by leaning on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), widely considered the “bible” of mental health diagnosis.
However, there are substantial differences amongst individuals on the spectrum and a great deal remains unknown by science about the causes of autism, or even what autism is. As a result, an accurate diagnosis of ASD and a prognosis prediction for patients can be extremely difficult.
But what if artificial intelligence (AI) could help? Deep learning, a type of AI, deploys artificial neural networks based on the human brain to recognize patterns in a way that is akin to, and in some cases can surpass, human ability. The technique, or rather suite of techniques, has enjoyed remarkable success in recent years in fields as diverse as voice recognition, translation, autonomous vehicles, and drug discovery.
A group of researchers from KAIST in collaboration with the Yonsei University College of Medicine has applied these deep learning techniques to autism diagnosis. Their findings were published on August 14 in the journal IEEE Access.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of brains of people known to have autism have been used by researchers and clinicians to try to identify structures of the brain they believed were associated with ASD. These researchers have achieved considerable success in identifying abnormal grey and white matter volume and irregularities in cerebral cortex activation and connections as being associated with the condition.
These findings have subsequently been deployed in studies attempting more consistent diagnoses of patients than has been achieved via psychiatrist observations during counseling sessions. While such studies have reported high levels of diagnostic accuracy, the number of participants in these studies has been small, often under 50, and diagnostic performance drops markedly when applied to large sample sizes or on datasets that include people from a wide variety of populations and locations.
“There was something as to what defines autism that human researchers and clinicians must have been overlooking,” said Keun-Ah Cheon, one of the two corresponding authors and a professor in Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry at Severance Hospital of the Yonsei University College of Medicine.
“And humans poring over thousands of MRI scans won’t be able to pick up on what we’ve been missing,” she continued. “But we thought AI might be able to.”
So the team applied five different categories of deep learning models to an open-source dataset of more than 1,000 MRI scans from the Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE) initiative, which has collected brain imaging data from laboratories around the world, and to a smaller, but higher-resolution MRI image dataset (84 images) taken from the Child Psychiatric Clinic at Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine. In both cases, the researchers used both structural MRIs (examining the anatomy of the brain) and functional MRIs (examining brain activity in different regions).
The models allowed the team to explore the structural bases of ASD brain region by brain region, focusing in particular on many structures below the cerebral cortex, including the basal ganglia, which are involved in motor function (movement) as well as learning and memory.
Crucially, these specific types of deep learning models also offered up possible explanations of how the AI had come up with its rationale for these findings.
“Understanding the way that the AI has classified these brain structures and dynamics is extremely important,” said Sang Wan Lee, the other corresponding author and an associate professor at KAIST. “It’s no good if a doctor can tell a patient that the computer says they have autism, but not be able to say why the computer knows that.”
The deep learning models were also able to describe how much a particular aspect contributed to ASD, an analysis tool that can assist psychiatric physicians during the diagnosis process to identify the severity of the autism.
“Doctors should be able to use this to offer a personalized diagnosis for patients, including a prognosis of how the condition could develop,” Lee said.
“Artificial intelligence is not going to put psychiatrists out of a job,” he explained. “But using AI as a tool should enable doctors to better understand and diagnose complex disorders than they could do on their own.”
-ProfileProfessor Sang Wan LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringLaboratory for Brain and Machine Intelligence https://aibrain.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
2020.09.23 View 9769
Deep Learning Helps Explore the Structural and Strategic Bases of Autism
Psychiatrists typically diagnose autism spectrum disorders (ASD) by observing a person’s behavior and by leaning on the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), widely considered the “bible” of mental health diagnosis.
However, there are substantial differences amongst individuals on the spectrum and a great deal remains unknown by science about the causes of autism, or even what autism is. As a result, an accurate diagnosis of ASD and a prognosis prediction for patients can be extremely difficult.
But what if artificial intelligence (AI) could help? Deep learning, a type of AI, deploys artificial neural networks based on the human brain to recognize patterns in a way that is akin to, and in some cases can surpass, human ability. The technique, or rather suite of techniques, has enjoyed remarkable success in recent years in fields as diverse as voice recognition, translation, autonomous vehicles, and drug discovery.
A group of researchers from KAIST in collaboration with the Yonsei University College of Medicine has applied these deep learning techniques to autism diagnosis. Their findings were published on August 14 in the journal IEEE Access.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of brains of people known to have autism have been used by researchers and clinicians to try to identify structures of the brain they believed were associated with ASD. These researchers have achieved considerable success in identifying abnormal grey and white matter volume and irregularities in cerebral cortex activation and connections as being associated with the condition.
These findings have subsequently been deployed in studies attempting more consistent diagnoses of patients than has been achieved via psychiatrist observations during counseling sessions. While such studies have reported high levels of diagnostic accuracy, the number of participants in these studies has been small, often under 50, and diagnostic performance drops markedly when applied to large sample sizes or on datasets that include people from a wide variety of populations and locations.
“There was something as to what defines autism that human researchers and clinicians must have been overlooking,” said Keun-Ah Cheon, one of the two corresponding authors and a professor in Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry at Severance Hospital of the Yonsei University College of Medicine.
“And humans poring over thousands of MRI scans won’t be able to pick up on what we’ve been missing,” she continued. “But we thought AI might be able to.”
So the team applied five different categories of deep learning models to an open-source dataset of more than 1,000 MRI scans from the Autism Brain Imaging Data Exchange (ABIDE) initiative, which has collected brain imaging data from laboratories around the world, and to a smaller, but higher-resolution MRI image dataset (84 images) taken from the Child Psychiatric Clinic at Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine. In both cases, the researchers used both structural MRIs (examining the anatomy of the brain) and functional MRIs (examining brain activity in different regions).
The models allowed the team to explore the structural bases of ASD brain region by brain region, focusing in particular on many structures below the cerebral cortex, including the basal ganglia, which are involved in motor function (movement) as well as learning and memory.
Crucially, these specific types of deep learning models also offered up possible explanations of how the AI had come up with its rationale for these findings.
“Understanding the way that the AI has classified these brain structures and dynamics is extremely important,” said Sang Wan Lee, the other corresponding author and an associate professor at KAIST. “It’s no good if a doctor can tell a patient that the computer says they have autism, but not be able to say why the computer knows that.”
The deep learning models were also able to describe how much a particular aspect contributed to ASD, an analysis tool that can assist psychiatric physicians during the diagnosis process to identify the severity of the autism.
“Doctors should be able to use this to offer a personalized diagnosis for patients, including a prognosis of how the condition could develop,” Lee said.
“Artificial intelligence is not going to put psychiatrists out of a job,” he explained. “But using AI as a tool should enable doctors to better understand and diagnose complex disorders than they could do on their own.”
-ProfileProfessor Sang Wan LeeDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringLaboratory for Brain and Machine Intelligence https://aibrain.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
2020.09.23 View 9769 -
 Sturdy Fabric-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Takes Us One Step Closer to Wearable Electronics
KAIST researchers presented a highly flexible but sturdy wearable piezoelectric harvester using the simple and easy fabrication process of hot pressing and tape casting. This energy harvester, which has record high interfacial adhesion strength, will take us one step closer to being able to manufacture embedded wearable electronics.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong said that the novelty of this result lies in its simplicity, applicability, durability, and its new characterization of wearable electronic devices.
Wearable devices are increasingly being used in a wide array of applications from small electronics to embedded devices such as sensors, actuators, displays, and energy harvesters.
Despite their many advantages, high costs and complex fabrication processes remained challenges for reaching commercialization. In addition, their durability was frequently questioned. To address these issues, Professor Hong’s team developed a new fabrication process and analysis technology for testing the mechanical properties of affordable wearable devices.
For this process, the research team used a hot pressing and tape casting procedure to connect the fabric structures of polyester and a polymer film. Hot pressing has usually been used when making batteries and fuel cells due to its high adhesiveness. Above all, the process takes only two to three minutes.
The newly developed fabrication process will enable the direct application of a device into general garments using hot pressing just as graphic patches can be attached to garments using a heat press.
In particular, when the polymer film is hot pressed onto a fabric below its crystallization temperature, it transforms into an amorphous state. In this state, it compactly attaches to the concave surface of the fabric and infiltrates into the gaps between the transverse wefts and longitudinal warps. These features result in high interfacial adhesion strength. For this reason, hot pressing has the potential to reduce the cost of fabrication through the direct application of fabric-based wearable devices to common garments.
In addition to the conventional durability test of bending cycles, the newly introduced surface and interfacial cutting analysis system proved the high mechanical durability of the fabric-based wearable device by measuring the high interfacial adhesion strength between the fabric and the polymer film. Professor Hong said the study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of wearable devices using fabrics and polymers.
He added that his team first used the surface and interfacial cutting analysis system (SAICAS) in the field of wearable electronics to test the mechanical properties of polymer-based wearable devices. Their surface and interfacial cutting analysis system is more precise than conventional methods (peel test, tape test, and microstretch test) because it qualitatively and quantitatively measures the adhesion strength.
Professor Hong explained, “This study could enable the commercialization of highly durable wearable devices based on the analysis of their interfacial adhesion strength. Our study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of other devices using fabrics and polymers. We look forward to fabric-based wearable electronics hitting the market very soon.”
The results of this study were registered as a domestic patent in Korea last year, and published in Nano Energy this month. This study has been conducted through collaboration with Professor Yong Min Lee in the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST, Professor Kwangsoo No in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Seunghwa Ryu in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST.
This study was supported by the High-Risk High-Return Project and the Global Singularity Research Project at KAIST, the National Research Foundation, and the Ministry of Science and ICT in Korea.
-Publication:
Jaegyu Kim, Seoungwoo Byun, Sangryun Lee, Jeongjae Ryu, Seongwoo Cho, Chungik Oh, Hongjun Kim, Kwangsoo No, Seunghwa Ryu, Yong Min Lee, Seungbum Hong*, Nano Energy 75 (2020), 104992.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104992
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.09.17 View 11873
Sturdy Fabric-Based Piezoelectric Energy Harvester Takes Us One Step Closer to Wearable Electronics
KAIST researchers presented a highly flexible but sturdy wearable piezoelectric harvester using the simple and easy fabrication process of hot pressing and tape casting. This energy harvester, which has record high interfacial adhesion strength, will take us one step closer to being able to manufacture embedded wearable electronics.
A research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong said that the novelty of this result lies in its simplicity, applicability, durability, and its new characterization of wearable electronic devices.
Wearable devices are increasingly being used in a wide array of applications from small electronics to embedded devices such as sensors, actuators, displays, and energy harvesters.
Despite their many advantages, high costs and complex fabrication processes remained challenges for reaching commercialization. In addition, their durability was frequently questioned. To address these issues, Professor Hong’s team developed a new fabrication process and analysis technology for testing the mechanical properties of affordable wearable devices.
For this process, the research team used a hot pressing and tape casting procedure to connect the fabric structures of polyester and a polymer film. Hot pressing has usually been used when making batteries and fuel cells due to its high adhesiveness. Above all, the process takes only two to three minutes.
The newly developed fabrication process will enable the direct application of a device into general garments using hot pressing just as graphic patches can be attached to garments using a heat press.
In particular, when the polymer film is hot pressed onto a fabric below its crystallization temperature, it transforms into an amorphous state. In this state, it compactly attaches to the concave surface of the fabric and infiltrates into the gaps between the transverse wefts and longitudinal warps. These features result in high interfacial adhesion strength. For this reason, hot pressing has the potential to reduce the cost of fabrication through the direct application of fabric-based wearable devices to common garments.
In addition to the conventional durability test of bending cycles, the newly introduced surface and interfacial cutting analysis system proved the high mechanical durability of the fabric-based wearable device by measuring the high interfacial adhesion strength between the fabric and the polymer film. Professor Hong said the study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of wearable devices using fabrics and polymers.
He added that his team first used the surface and interfacial cutting analysis system (SAICAS) in the field of wearable electronics to test the mechanical properties of polymer-based wearable devices. Their surface and interfacial cutting analysis system is more precise than conventional methods (peel test, tape test, and microstretch test) because it qualitatively and quantitatively measures the adhesion strength.
Professor Hong explained, “This study could enable the commercialization of highly durable wearable devices based on the analysis of their interfacial adhesion strength. Our study lays a new foundation for the manufacturing process and analysis of other devices using fabrics and polymers. We look forward to fabric-based wearable electronics hitting the market very soon.”
The results of this study were registered as a domestic patent in Korea last year, and published in Nano Energy this month. This study has been conducted through collaboration with Professor Yong Min Lee in the Department of Energy Science and Engineering at DGIST, Professor Kwangsoo No in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, and Professor Seunghwa Ryu in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST.
This study was supported by the High-Risk High-Return Project and the Global Singularity Research Project at KAIST, the National Research Foundation, and the Ministry of Science and ICT in Korea.
-Publication:
Jaegyu Kim, Seoungwoo Byun, Sangryun Lee, Jeongjae Ryu, Seongwoo Cho, Chungik Oh, Hongjun Kim, Kwangsoo No, Seunghwa Ryu, Yong Min Lee, Seungbum Hong*, Nano Energy 75 (2020), 104992.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104992
-Profile: Professor Seungbum Hong
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.09.17 View 11873 -
 Advanced NVMe Controller Technology for Next Generation Memory Devices
KAIST researchers advanced non-volatile memory express (NVMe) controller technology for next generation information storage devices, and made this new technology named ‘OpenExpress’ freely available to all universities and research institutes around the world to help reduce the research cost in related fields.
NVMe is a communication protocol made for high-performance storage devices based on a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCI-E) interface. NVMe has been developed to take the place of the Serial AT Attachment (SATA) protocol, which was developed to process data on hard disk drives (HDDs) and did not perform well in solid state drives (SSDs).
Unlike HDDs that use magnetic spinning disks, SSDs use semiconductor memory, allowing the rapid reading and writing of data. SSDs also generate less heat and noise, and are much more compact and lightweight.
Since data processing in SSDs using NVMe is up to six times faster than when SATA is used, NVMe has become the standard protocol for ultra-high speed and volume data processing, and is currently used in many flash-based information storage devices.
Studies on NVMe continue at both the academic and industrial levels, however, its poor accessibility is a drawback. Major information and communications technology (ICT) companies around the world expend astronomical costs to procure intellectual property (IP) related to hardware NVMe controllers, necessary for the use of NVMe. However, such IP is not publicly disclosed, making it difficult to be used by universities and research institutes for research purposes.
Although a small number of U.S. Silicon Valley startups provide parts of their independently developed IP for research, the cost of usage is around 34,000 USD per month. The costs skyrocket even further because each copy of single-use source code purchased for IP modification costs approximately 84,000 USD.
In order to address these issues, a group of researchers led by Professor Myoungsoo Jung from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a next generation NVMe controller technology that achieved parallel data input/output processing for SSDs in a fully hardware automated form.
The researchers presented their work at the 2020 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC ’20) in July, and released it as an open research framework named ‘OpenExpress.’
This NVMe controller technology developed by Professor Jung’s team comprises a wide range of basic hardware IP and key NVMe IP cores. To examine its actual performance, the team made an NVMe hardware controller prototype using OpenExpress, and designed all logics provided by OpenExpress to operate at high frequency.
The field-programmable gate array (FPGA) memory card prototype developed using OpenExpress demonstrated increased input/output data processing capacity per second, supporting up to 7 gigabit per second (GB/s) bandwidth. This makes it suitable for ultra-high speed and volume next generation memory device research.
In a test comparing various storage server loads on devices, the team’s FPGA also showed 76% higher bandwidth and 68% lower input/output delay compared to Intel’s new high performance SSD (Optane SSD), which is sufficient for many researchers studying systems employing future memory devices. Depending on user needs, silicon devices can be synthesized as well, which is expected to further enhance performance.
The NVMe controller technology of Professor Jung’s team can be freely used and modified under the OpenExpress open-source end-user agreement for non-commercial use by all universities and research institutes. This makes it extremely useful for research on next-generation memory compatible NVMe controllers and software stacks.
“With the product of this study being disclosed to the world, universities and research institutes can now use controllers that used to be exclusive for only the world’s biggest companies, at no cost,ˮ said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “This is a meaningful first step in research of information storage device systems such as high-speed and volume next generation memory.”
This work was supported by a grant from MemRay, a company specializing in next generation memory development and distribution.
More details about the study can be found at http://camelab.org.
Image credit: Professor Myoungsoo Jung, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
-Publication:
Myoungsoo Jung. (2020). OpenExpress: Fully Hardware Automated Open Research Framework for Future Fast NVMe Devices. Presented in the Proceedings of the 2020 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC ’20), Available online at https://www.usenix.org/system/files/atc20-jung.pdf
-Profile: Myoungsoo Jung
Associate Professor
m.jung@kaist.ac.kr
http://camelab.org
Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.09.04 View 9598
Advanced NVMe Controller Technology for Next Generation Memory Devices
KAIST researchers advanced non-volatile memory express (NVMe) controller technology for next generation information storage devices, and made this new technology named ‘OpenExpress’ freely available to all universities and research institutes around the world to help reduce the research cost in related fields.
NVMe is a communication protocol made for high-performance storage devices based on a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCI-E) interface. NVMe has been developed to take the place of the Serial AT Attachment (SATA) protocol, which was developed to process data on hard disk drives (HDDs) and did not perform well in solid state drives (SSDs).
Unlike HDDs that use magnetic spinning disks, SSDs use semiconductor memory, allowing the rapid reading and writing of data. SSDs also generate less heat and noise, and are much more compact and lightweight.
Since data processing in SSDs using NVMe is up to six times faster than when SATA is used, NVMe has become the standard protocol for ultra-high speed and volume data processing, and is currently used in many flash-based information storage devices.
Studies on NVMe continue at both the academic and industrial levels, however, its poor accessibility is a drawback. Major information and communications technology (ICT) companies around the world expend astronomical costs to procure intellectual property (IP) related to hardware NVMe controllers, necessary for the use of NVMe. However, such IP is not publicly disclosed, making it difficult to be used by universities and research institutes for research purposes.
Although a small number of U.S. Silicon Valley startups provide parts of their independently developed IP for research, the cost of usage is around 34,000 USD per month. The costs skyrocket even further because each copy of single-use source code purchased for IP modification costs approximately 84,000 USD.
In order to address these issues, a group of researchers led by Professor Myoungsoo Jung from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a next generation NVMe controller technology that achieved parallel data input/output processing for SSDs in a fully hardware automated form.
The researchers presented their work at the 2020 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC ’20) in July, and released it as an open research framework named ‘OpenExpress.’
This NVMe controller technology developed by Professor Jung’s team comprises a wide range of basic hardware IP and key NVMe IP cores. To examine its actual performance, the team made an NVMe hardware controller prototype using OpenExpress, and designed all logics provided by OpenExpress to operate at high frequency.
The field-programmable gate array (FPGA) memory card prototype developed using OpenExpress demonstrated increased input/output data processing capacity per second, supporting up to 7 gigabit per second (GB/s) bandwidth. This makes it suitable for ultra-high speed and volume next generation memory device research.
In a test comparing various storage server loads on devices, the team’s FPGA also showed 76% higher bandwidth and 68% lower input/output delay compared to Intel’s new high performance SSD (Optane SSD), which is sufficient for many researchers studying systems employing future memory devices. Depending on user needs, silicon devices can be synthesized as well, which is expected to further enhance performance.
The NVMe controller technology of Professor Jung’s team can be freely used and modified under the OpenExpress open-source end-user agreement for non-commercial use by all universities and research institutes. This makes it extremely useful for research on next-generation memory compatible NVMe controllers and software stacks.
“With the product of this study being disclosed to the world, universities and research institutes can now use controllers that used to be exclusive for only the world’s biggest companies, at no cost,ˮ said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “This is a meaningful first step in research of information storage device systems such as high-speed and volume next generation memory.”
This work was supported by a grant from MemRay, a company specializing in next generation memory development and distribution.
More details about the study can be found at http://camelab.org.
Image credit: Professor Myoungsoo Jung, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
-Publication:
Myoungsoo Jung. (2020). OpenExpress: Fully Hardware Automated Open Research Framework for Future Fast NVMe Devices. Presented in the Proceedings of the 2020 USENIX Annual Technical Conference (USENIX ATC ’20), Available online at https://www.usenix.org/system/files/atc20-jung.pdf
-Profile: Myoungsoo Jung
Associate Professor
m.jung@kaist.ac.kr
http://camelab.org
Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.09.04 View 9598