Biophotonics+Laboratory
-
 KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
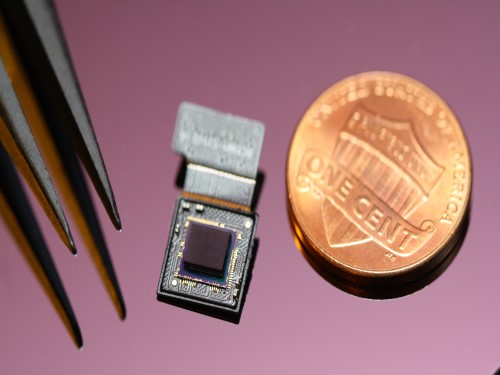
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
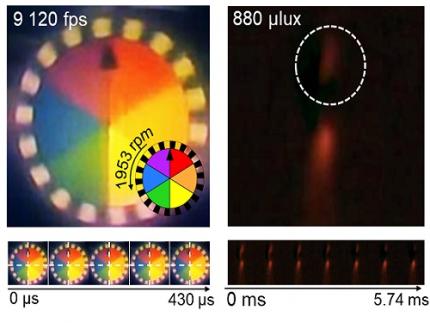
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 7363
KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 7363 -
 Ultrafast, on-Chip PCR Could Speed Up Diagnoses during Pandemics
A rapid point-of-care diagnostic plasmofluidic chip can deliver result in only 8 minutes
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been the gold standard for diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the PCR portion of the test requires bulky, expensive machines and takes about an hour to complete, making it difficult to quickly diagnose someone at a testing site. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a plasmofluidic chip that can perform PCR in only about 8 minutes, which could speed up diagnoses during current and future pandemics.
The rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 and other highly contagious viral diseases is important for timely medical care, quarantining and contact tracing. Currently, RT-PCR uses enzymes to reverse transcribe tiny amounts of viral RNA to DNA, and then amplifies the DNA so that it can be detected by a fluorescent probe. It is the most sensitive and reliable diagnostic method.
But because the PCR portion of the test requires 30-40 cycles of heating and cooling in special machines, it takes about an hour to perform, and samples must typically be sent away to a lab, meaning that a patient usually has to wait a day or two to receive their diagnosis.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his colleagues wanted to develop a plasmofluidic PCR chip that could quickly heat and cool miniscule volumes of liquids, allowing accurate point-of-care diagnoses in a fraction of the time. The research was reported in ACS Nano on May 19.
The researchers devised a postage stamp-sized polydimethylsiloxane chip with a microchamber array for the PCR reactions. When a drop of a sample is added to the chip, a vacuum pulls the liquid into the microchambers, which are positioned above glass nanopillars with gold nanoislands. Any microbubbles, which could interfere with the PCR reaction, diffuse out through an air-permeable wall. When a white LED is turned on beneath the chip, the gold nanoislands on the nanopillars quickly convert light to heat, and then rapidly cool when the light is switched off.
The researchers tested the device on a piece of DNA containing a SARS-CoV-2 gene, accomplishing 40 heating and cooling cycles and fluorescence detection in only 5 minutes, with an additional 3 minutes for sample loading. The amplification efficiency was 91%, whereas a comparable conventional PCR process has an efficiency of 98%. With the reverse transcriptase step added prior to sample loading, the entire testing time with the new method could take 10-13 minutes, as opposed to about an hour for typical RT-PCR testing. The new device could provide many opportunities for rapid point-of-care diagnostics during a pandemic, the researchers say.
-Publication
Ultrafast and Real-Time Nanoplasmonic On-Chip Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid and Quantitative Molecular Diagnostics
ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02154)
-Professor
Ki-Hun Jeong
Biophotonics Laboratory
https://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineeinrg
KAIST
2021.06.08 View 12526
Ultrafast, on-Chip PCR Could Speed Up Diagnoses during Pandemics
A rapid point-of-care diagnostic plasmofluidic chip can deliver result in only 8 minutes
Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) has been the gold standard for diagnosis during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the PCR portion of the test requires bulky, expensive machines and takes about an hour to complete, making it difficult to quickly diagnose someone at a testing site. Now, researchers at KAIST have developed a plasmofluidic chip that can perform PCR in only about 8 minutes, which could speed up diagnoses during current and future pandemics.
The rapid diagnosis of COVID-19 and other highly contagious viral diseases is important for timely medical care, quarantining and contact tracing. Currently, RT-PCR uses enzymes to reverse transcribe tiny amounts of viral RNA to DNA, and then amplifies the DNA so that it can be detected by a fluorescent probe. It is the most sensitive and reliable diagnostic method.
But because the PCR portion of the test requires 30-40 cycles of heating and cooling in special machines, it takes about an hour to perform, and samples must typically be sent away to a lab, meaning that a patient usually has to wait a day or two to receive their diagnosis.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his colleagues wanted to develop a plasmofluidic PCR chip that could quickly heat and cool miniscule volumes of liquids, allowing accurate point-of-care diagnoses in a fraction of the time. The research was reported in ACS Nano on May 19.
The researchers devised a postage stamp-sized polydimethylsiloxane chip with a microchamber array for the PCR reactions. When a drop of a sample is added to the chip, a vacuum pulls the liquid into the microchambers, which are positioned above glass nanopillars with gold nanoislands. Any microbubbles, which could interfere with the PCR reaction, diffuse out through an air-permeable wall. When a white LED is turned on beneath the chip, the gold nanoislands on the nanopillars quickly convert light to heat, and then rapidly cool when the light is switched off.
The researchers tested the device on a piece of DNA containing a SARS-CoV-2 gene, accomplishing 40 heating and cooling cycles and fluorescence detection in only 5 minutes, with an additional 3 minutes for sample loading. The amplification efficiency was 91%, whereas a comparable conventional PCR process has an efficiency of 98%. With the reverse transcriptase step added prior to sample loading, the entire testing time with the new method could take 10-13 minutes, as opposed to about an hour for typical RT-PCR testing. The new device could provide many opportunities for rapid point-of-care diagnostics during a pandemic, the researchers say.
-Publication
Ultrafast and Real-Time Nanoplasmonic On-Chip Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid and Quantitative Molecular Diagnostics
ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c02154)
-Professor
Ki-Hun Jeong
Biophotonics Laboratory
https://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineeinrg
KAIST
2021.06.08 View 12526 -
 Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 20580
Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 20580