University+of+Tokyo
-
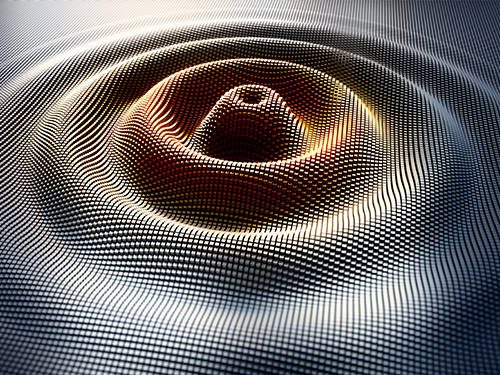 Scientists Observe the Elusive Kondo Screening Cloud
Scientists ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon
An international research group of Professor Heung-Sun Sim has ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. This research, published in Nature on March 11, opens a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement. According to the research, the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This spin-spin interaction mediated by the Kondo cloud is unique since both its strength and sign (two spins favor either parallel or anti-parallel configuration) are electrically tunable, while conventional schemes cannot reverse the sign.
This phenomenon, which is important for many physical phenomena such as dilute magnetic impurities and spin glasses, is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed.
Magnetism arises from a property of electrons known as spin, meaning that they have angular momentum aligned in one of either two directions, conventionally known as up and down. However, due to a phenomenon known as the Kondo effect, the spins of conduction electrons—the electrons that flow freely in a material—become entangled with a localized magnetic impurity, and effectively screen it. The strength of this spin coupling, calibrated as a temperature, is known as the Kondo temperature.
The size of the cloud is another important parameter for a material containing multiple magnetic impurities because the spins in the cloud couple with one another and mediate the coupling between magnetic impurities when the clouds overlap. This happens in various materials such as Kondo lattices, spin glasses, and high temperature superconductors.
Although the Kondo effect for a single magnetic impurity is now a text-book subject in many-body physics, detection of its key object, the Kondo cloud and its length, has remained elusive despite many attempts during the past five decades. Experiments using nuclear magnetic resonance or scanning tunneling microscopy, two common methods for understanding the structure of matter, have either shown no signature of the cloud, or demonstrated a signature only at a very short distance, less than 1 nanometer, so much shorter than the predicted cloud size, which was in the micron range.
In the present study, the authors observed a Kondo screening cloud formed by an impurity defined as a localized electron spin in a quantum dot—a type of “artificial atom”—coupled to quasi-one-dimensional conduction electrons, and then used an interferometer to measure changes in the Kondo temperature, allowing them to investigate the presence of a cloud at the interferometer end.
Essentially, they slightly perturbed the conduction electrons at a location away from the quantum dot using an electrostatic gate. The wave of conducting electrons scattered by this perturbation returned back to the quantum dot and interfered with itself. This is similar to how a wave on a water surface being scattered by a wall forms a stripe pattern. The Kondo cloud is a quantum mechanical object which acts to preserve the wave nature of electrons inside the cloud.
Even though there is no direct electrostatic influence of the perturbation on the quantum dot, this interference modifies the Kondo signature measured by electron conductance through the quantum dot if the perturbation is present inside the cloud. In the study, the researchers found that the length as well as the shape of the cloud is universally scaled by the inverse of the Kondo temperature, and that the cloud’s size and shape were in good agreement with theoretical calculations.
Professor Sim at the Department of Physics proposed the method for detecting the Kondo cloud in the co-research with the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science, the City University of Hong Kong, the University of Tokyo, and Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
Professor Sim said, “The observed spin cloud is a micrometer-size object that has quantum mechanical wave nature and entanglement. This is why the spin cloud has not been observed despite a long search. It is remarkable in a fundamental and technical point of view that such a large quantum object can now be created, controlled, and detected.
Dr. Michihisa Yamamoto of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science also said, “It is very satisfying to have been able to obtain real space image of the Kondo cloud, as it is a real breakthrough for understanding various systems containing multiple magnetic impurities. The size of the Kondo cloud in semiconductors was found to be much larger than the typical size of semiconductor devices.”
Publication:
Borzenets et al. (2020) Observation of the Kondo screening cloud. Nature, 579. pp.210-213. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2058-6
Profile:
Heung-Sun Sim, PhD
Professor
hssim@kaist.ac.kr
https://qet.kaist.ac.kr/
Quantum Electron Correlation & Transport Theory Group (QECT Lab)
https://qc.kaist.ac.kr/index.php/group1/
Center for Quantum Coherence In COndensed Matter
Department of Physics
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2020.03.13 View 18001
Scientists Observe the Elusive Kondo Screening Cloud
Scientists ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon
An international research group of Professor Heung-Sun Sim has ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. This research, published in Nature on March 11, opens a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement. According to the research, the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This spin-spin interaction mediated by the Kondo cloud is unique since both its strength and sign (two spins favor either parallel or anti-parallel configuration) are electrically tunable, while conventional schemes cannot reverse the sign.
This phenomenon, which is important for many physical phenomena such as dilute magnetic impurities and spin glasses, is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed.
Magnetism arises from a property of electrons known as spin, meaning that they have angular momentum aligned in one of either two directions, conventionally known as up and down. However, due to a phenomenon known as the Kondo effect, the spins of conduction electrons—the electrons that flow freely in a material—become entangled with a localized magnetic impurity, and effectively screen it. The strength of this spin coupling, calibrated as a temperature, is known as the Kondo temperature.
The size of the cloud is another important parameter for a material containing multiple magnetic impurities because the spins in the cloud couple with one another and mediate the coupling between magnetic impurities when the clouds overlap. This happens in various materials such as Kondo lattices, spin glasses, and high temperature superconductors.
Although the Kondo effect for a single magnetic impurity is now a text-book subject in many-body physics, detection of its key object, the Kondo cloud and its length, has remained elusive despite many attempts during the past five decades. Experiments using nuclear magnetic resonance or scanning tunneling microscopy, two common methods for understanding the structure of matter, have either shown no signature of the cloud, or demonstrated a signature only at a very short distance, less than 1 nanometer, so much shorter than the predicted cloud size, which was in the micron range.
In the present study, the authors observed a Kondo screening cloud formed by an impurity defined as a localized electron spin in a quantum dot—a type of “artificial atom”—coupled to quasi-one-dimensional conduction electrons, and then used an interferometer to measure changes in the Kondo temperature, allowing them to investigate the presence of a cloud at the interferometer end.
Essentially, they slightly perturbed the conduction electrons at a location away from the quantum dot using an electrostatic gate. The wave of conducting electrons scattered by this perturbation returned back to the quantum dot and interfered with itself. This is similar to how a wave on a water surface being scattered by a wall forms a stripe pattern. The Kondo cloud is a quantum mechanical object which acts to preserve the wave nature of electrons inside the cloud.
Even though there is no direct electrostatic influence of the perturbation on the quantum dot, this interference modifies the Kondo signature measured by electron conductance through the quantum dot if the perturbation is present inside the cloud. In the study, the researchers found that the length as well as the shape of the cloud is universally scaled by the inverse of the Kondo temperature, and that the cloud’s size and shape were in good agreement with theoretical calculations.
Professor Sim at the Department of Physics proposed the method for detecting the Kondo cloud in the co-research with the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science, the City University of Hong Kong, the University of Tokyo, and Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
Professor Sim said, “The observed spin cloud is a micrometer-size object that has quantum mechanical wave nature and entanglement. This is why the spin cloud has not been observed despite a long search. It is remarkable in a fundamental and technical point of view that such a large quantum object can now be created, controlled, and detected.
Dr. Michihisa Yamamoto of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science also said, “It is very satisfying to have been able to obtain real space image of the Kondo cloud, as it is a real breakthrough for understanding various systems containing multiple magnetic impurities. The size of the Kondo cloud in semiconductors was found to be much larger than the typical size of semiconductor devices.”
Publication:
Borzenets et al. (2020) Observation of the Kondo screening cloud. Nature, 579. pp.210-213. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2058-6
Profile:
Heung-Sun Sim, PhD
Professor
hssim@kaist.ac.kr
https://qet.kaist.ac.kr/
Quantum Electron Correlation & Transport Theory Group (QECT Lab)
https://qc.kaist.ac.kr/index.php/group1/
Center for Quantum Coherence In COndensed Matter
Department of Physics
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2020.03.13 View 18001 -
 KAIST to Participate in the Summer Davos Forum
KAIST will participate in the 2017 Summer Davos Forum in Dalian, China from June 27 to 29. The Summer Davos Forum with the official title “Annual Meeting of New Champions” is an annual international meeting co-hosted by China and the World Economic Forum (WEF) to address global issues which has been held since 2007.
Focusing on this year’s theme ‘Achieving Inclusive Growth in the Fourth Industrial Revolution,’ science and technology experts from 90 different countries will participate in various sessions to present on and discuss pending global innovative issues. KAIST is to be the only Korean university to run ‘IdeasLab,’ in which researchers will introduce current research trends and discuss ideas with global leaders. This is the sixth year for KAIST to run IdeasLab.
This year’s IdeasLab has the theme ‘Materials of the Future,’ and will include presentations and discussions on materials developed at KAIST which could lead the Fourth Industrial Revolution. President Sung-Chul Shin, the chairman of the session, will first introduce the current status of KAIST and IdeasLab, followed by a presentation of cutting-edge integrated research findings by KAIST professors.
President Shin will also participate in various sessions organized by the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) as discussion leader. President Shin is the only Korean member of GULF, a community comprised of the presidents of the world’s top 27 universities. Other members include the presidents of the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge in the U.K., MIT, Harvard, Stanford, and Columbia Universities in the US, and the University of Tokyo in Japan.
Further, President Shin will participate in a strategy session for inclusive growth in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and a meeting with the WEF directors.
The Dean of KAIST Institutes, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department, who has been invited to the Davos Forum and Summer Davos Forum for the last 15 years, is to present in the ‘Future of Life: Medicine’ session to introduce advancements in traditional medicine through systems biology such as his research on microbiomes (gut microbes).
Professor Lee, as the chair of the Global Future Council on Biotechnology at the WEF, and committee member of the Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is to participate in various bio-sessions and the Fourth Industrial Revolution banquet session to lead the discussions.
President Shin said, “KAIST has been sharing global research findings with global leaders through IdeasLab at the Davos Forum for the past six years and it has always been well received.” He continued, “The forum will be the place for in-depth discussion on the technological changes that accompany the Fourth Industrial Revolution and human-centered development plan, as well as introducing innovative research and integrated research findings from KAIST.”
This year’s speakers include Li Keqiang, the current Premier of the State Council of China; Guo Ping, the rotating C.E.O. of Huawei; and Ya-Qin Zhang, the President of Baidu, a company leading technological innovation in various fields such as robotics and autonomous vehicles. Two thousand distinguished guests in politics, administration, finance, and academia from 90 countries are to participate in the meeting.
2017.06.21 View 10224
KAIST to Participate in the Summer Davos Forum
KAIST will participate in the 2017 Summer Davos Forum in Dalian, China from June 27 to 29. The Summer Davos Forum with the official title “Annual Meeting of New Champions” is an annual international meeting co-hosted by China and the World Economic Forum (WEF) to address global issues which has been held since 2007.
Focusing on this year’s theme ‘Achieving Inclusive Growth in the Fourth Industrial Revolution,’ science and technology experts from 90 different countries will participate in various sessions to present on and discuss pending global innovative issues. KAIST is to be the only Korean university to run ‘IdeasLab,’ in which researchers will introduce current research trends and discuss ideas with global leaders. This is the sixth year for KAIST to run IdeasLab.
This year’s IdeasLab has the theme ‘Materials of the Future,’ and will include presentations and discussions on materials developed at KAIST which could lead the Fourth Industrial Revolution. President Sung-Chul Shin, the chairman of the session, will first introduce the current status of KAIST and IdeasLab, followed by a presentation of cutting-edge integrated research findings by KAIST professors.
President Shin will also participate in various sessions organized by the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) as discussion leader. President Shin is the only Korean member of GULF, a community comprised of the presidents of the world’s top 27 universities. Other members include the presidents of the University of Oxford and the University of Cambridge in the U.K., MIT, Harvard, Stanford, and Columbia Universities in the US, and the University of Tokyo in Japan.
Further, President Shin will participate in a strategy session for inclusive growth in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and a meeting with the WEF directors.
The Dean of KAIST Institutes, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department, who has been invited to the Davos Forum and Summer Davos Forum for the last 15 years, is to present in the ‘Future of Life: Medicine’ session to introduce advancements in traditional medicine through systems biology such as his research on microbiomes (gut microbes).
Professor Lee, as the chair of the Global Future Council on Biotechnology at the WEF, and committee member of the Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is to participate in various bio-sessions and the Fourth Industrial Revolution banquet session to lead the discussions.
President Shin said, “KAIST has been sharing global research findings with global leaders through IdeasLab at the Davos Forum for the past six years and it has always been well received.” He continued, “The forum will be the place for in-depth discussion on the technological changes that accompany the Fourth Industrial Revolution and human-centered development plan, as well as introducing innovative research and integrated research findings from KAIST.”
This year’s speakers include Li Keqiang, the current Premier of the State Council of China; Guo Ping, the rotating C.E.O. of Huawei; and Ya-Qin Zhang, the President of Baidu, a company leading technological innovation in various fields such as robotics and autonomous vehicles. Two thousand distinguished guests in politics, administration, finance, and academia from 90 countries are to participate in the meeting.
2017.06.21 View 10224