PAC
-
 KAIST sends out Music and Bio-Signs of Professor Kwon Ji-yong, a.k.a. G-Dragon, into Space to Pulsate through Universe and Resonate among Stars
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th of April that it successfully promoted the world’s first ‘Space Sound Source Transmission Project’ based on media art at the KAIST Space Research Institute on April 9th through collaboration between Professor Jinjoon Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, a world-renowned media artist, and the global K-Pop artist, G-Dragon.
This project was proposed as part of the ‘AI Entertech Research Center’ being promoted by KAIST and Galaxy Corporation. It is a project to transmit the message and sound of G-Dragon (real name, Kwon Ji-yong), a singer/song writer affiliated with Galaxy Corporation and a visiting professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST, to space for the first time in the world.
This is a convergence project that combines science, technology, art, and popular music, and is a new form of ‘space culture content’ experiment that connects KAIST’s cutting-edge space technology, Professor Jinjoon Lee’s media art work, and G-Dragon’s voice and sound source containing his latest digital single, "HOME SWEET HOME".
< Photo 1. Professor Jinjoon Lee's Open Your Eyes Project "Iris"'s imagery projected on the 13m space antenna at the Space Research Institute >
This collaboration was planned with the theme of ‘emotional signals that expand the inner universe of humans to the outer universe.’ The image of G-Dragon’s iris was augmented through AI as a window into soul symbolizing his uniqueness and identity, and the new song “Home Sweet Home” was combined as an audio message containing the vibration of that emotion.
This was actually transmitted into space using a next-generation small satellite developed by KAIST Space Research Institute, completing a symbolic performance in which an individual’s inner universe is transmitted to outer space.
Professor Jinjoon Lee’s cinematic media art work “Iris” was unveiled at the site. This work was screened in the world’s first projection mapping method* on KAIST Space Research Institute’s 13m space antenna. This video was created using generative artificial intelligence (AI) technology based on the image of G-Dragon's iris, and combined with sound using the data of the sounds of Emile Bell rings – the bell that holds a thousand years of history, it presented an emotional art experience that transcends time and space.
*Projection Mapping: A technology that projects light and images onto actual structures to create visual changes, and is a method of expression that artistically reinterprets space.
This work is one of the major research achievements of KAIST TX Lab and Professor Lee based on new media technology based on biometric data such as iris, heartbeat, and brain waves.
Professor Jinjoon Lee said, "The iris is a symbol that reflects inner emotions and identity, so much so that it is called the 'mirror of the soul,' and this work sought to express 'the infinite universe seen from the inside of humanity' through G-Dragon's gaze."
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Jinjoon Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology and G-Dragon (Visiting Professor Kwon Ji-yong of the Department of Mechanical Engineering) >
He continued, "The universe is a realm of technology as well as a stage for imagination and emotion, and I look forward to an encounter with the unknown through a new attempt to speak of art in the language of science including AI and imagine science in the form of art." “G-Dragon’s voice and music have now begun their journey to space,” said Yong-ho Choi, Galaxy Corporation’s Chief Happiness Officer (CHO). “This project is an act of leaving music as a legacy for humanity, while also having an important meaning of attempting to communicate with space.” He added, “This is a pioneering step to introduce human culture to space, and it will remain as a monumental performance that opens a new chapter in the history of music comparable to the Beatles.”
Galaxy Corporation is leading the future entertainment technology industry through its collaboration with KAIST, and was recently selected as the only entertainment technology company in a private meeting with Microsoft CEO Nadella. In particular, it is promoting the globalization of AI entertainment technology, receiving praise as a “pioneer of imagination” for new forms of AI entertainment content, including the AI contents for the deceased.
< Photo 3. Photo of G-Dragon's Home Sweet Home being sent into the space via Professor Jinjoon Lee's Space Sound Source Transmission Project >
Through this project, KAIST Space Research Institute presented new possibilities for utilizing satellite technology, and showed a model for science to connect with society in a more popular way.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “KAIST is a place that always supports new imaginations and challenges,” and added, “We will continue to strive to continue creative research that no one has ever thought of, like this project that combines science, technology, and art.”
In the meantime, Galaxy Corporation, the agency of G-Dragon’s Professor Kwon Ji-yong, is an AI entertainment company that presents a new paradigm based on IP, media, tech, and entertainment convergence technology.
2025.04.10 View 4694
KAIST sends out Music and Bio-Signs of Professor Kwon Ji-yong, a.k.a. G-Dragon, into Space to Pulsate through Universe and Resonate among Stars
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th of April that it successfully promoted the world’s first ‘Space Sound Source Transmission Project’ based on media art at the KAIST Space Research Institute on April 9th through collaboration between Professor Jinjoon Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, a world-renowned media artist, and the global K-Pop artist, G-Dragon.
This project was proposed as part of the ‘AI Entertech Research Center’ being promoted by KAIST and Galaxy Corporation. It is a project to transmit the message and sound of G-Dragon (real name, Kwon Ji-yong), a singer/song writer affiliated with Galaxy Corporation and a visiting professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST, to space for the first time in the world.
This is a convergence project that combines science, technology, art, and popular music, and is a new form of ‘space culture content’ experiment that connects KAIST’s cutting-edge space technology, Professor Jinjoon Lee’s media art work, and G-Dragon’s voice and sound source containing his latest digital single, "HOME SWEET HOME".
< Photo 1. Professor Jinjoon Lee's Open Your Eyes Project "Iris"'s imagery projected on the 13m space antenna at the Space Research Institute >
This collaboration was planned with the theme of ‘emotional signals that expand the inner universe of humans to the outer universe.’ The image of G-Dragon’s iris was augmented through AI as a window into soul symbolizing his uniqueness and identity, and the new song “Home Sweet Home” was combined as an audio message containing the vibration of that emotion.
This was actually transmitted into space using a next-generation small satellite developed by KAIST Space Research Institute, completing a symbolic performance in which an individual’s inner universe is transmitted to outer space.
Professor Jinjoon Lee’s cinematic media art work “Iris” was unveiled at the site. This work was screened in the world’s first projection mapping method* on KAIST Space Research Institute’s 13m space antenna. This video was created using generative artificial intelligence (AI) technology based on the image of G-Dragon's iris, and combined with sound using the data of the sounds of Emile Bell rings – the bell that holds a thousand years of history, it presented an emotional art experience that transcends time and space.
*Projection Mapping: A technology that projects light and images onto actual structures to create visual changes, and is a method of expression that artistically reinterprets space.
This work is one of the major research achievements of KAIST TX Lab and Professor Lee based on new media technology based on biometric data such as iris, heartbeat, and brain waves.
Professor Jinjoon Lee said, "The iris is a symbol that reflects inner emotions and identity, so much so that it is called the 'mirror of the soul,' and this work sought to express 'the infinite universe seen from the inside of humanity' through G-Dragon's gaze."
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Jinjoon Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology and G-Dragon (Visiting Professor Kwon Ji-yong of the Department of Mechanical Engineering) >
He continued, "The universe is a realm of technology as well as a stage for imagination and emotion, and I look forward to an encounter with the unknown through a new attempt to speak of art in the language of science including AI and imagine science in the form of art." “G-Dragon’s voice and music have now begun their journey to space,” said Yong-ho Choi, Galaxy Corporation’s Chief Happiness Officer (CHO). “This project is an act of leaving music as a legacy for humanity, while also having an important meaning of attempting to communicate with space.” He added, “This is a pioneering step to introduce human culture to space, and it will remain as a monumental performance that opens a new chapter in the history of music comparable to the Beatles.”
Galaxy Corporation is leading the future entertainment technology industry through its collaboration with KAIST, and was recently selected as the only entertainment technology company in a private meeting with Microsoft CEO Nadella. In particular, it is promoting the globalization of AI entertainment technology, receiving praise as a “pioneer of imagination” for new forms of AI entertainment content, including the AI contents for the deceased.
< Photo 3. Photo of G-Dragon's Home Sweet Home being sent into the space via Professor Jinjoon Lee's Space Sound Source Transmission Project >
Through this project, KAIST Space Research Institute presented new possibilities for utilizing satellite technology, and showed a model for science to connect with society in a more popular way.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “KAIST is a place that always supports new imaginations and challenges,” and added, “We will continue to strive to continue creative research that no one has ever thought of, like this project that combines science, technology, and art.”
In the meantime, Galaxy Corporation, the agency of G-Dragon’s Professor Kwon Ji-yong, is an AI entertainment company that presents a new paradigm based on IP, media, tech, and entertainment convergence technology.
2025.04.10 View 4694 -
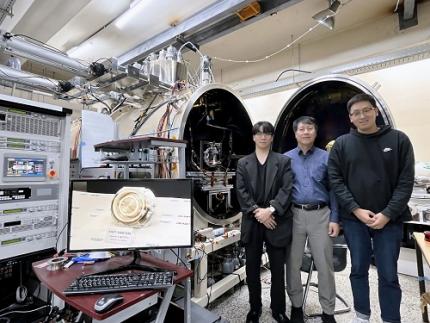 KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 6175
KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 6175 -
 KAIST Wins CES 2025 Innovation Award, Showcasing Innovative Technologies
KAIST will showcase innovative technologies at the world’s largest technology fair, the Consumer Electronics Show (CES 2025). In addition, KAIST startups VIRNECT Inc., Standard Energy Inc., A2US Inc., and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards.
< Image 1. 3D-Graphical Profile of CES 2025 KAIST Exhibition Booth >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 31st that it will operate a 140㎡ standalone booth at CES Eureka Park, which will be held in Las Vegas, USA from January 7th to 10th next year, to showcase KAIST's innovative technologies to global companies and investors.
KAIST startups VIRNECT, Standard Energy, A2US, and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards. ▴VIRNECT won the Innovation Award in the ‘Industrial Equipment and Machinery’ category for ‘VisionX’, an AI-based smart glass for industrial sites; ▴Standard Energy Co., Ltd. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Smart City’ category for developing the world’s first vanadium-ion battery; ▴A2US won the Innovation Award in the ‘Environment & Energy’ category for its portable air purifier that eliminates bacteria, odors, and fine dust in the air with just water droplets; ▴Panmnesia, Inc. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Computer Peripherals and Accessories’ category for its ‘CXL-based GPU Memory Expansion Kit’ that can drastically reduce the cost of building AI infrastructure.
< Image 2. (From left on the top row) VIRNECT, Standard Energy, (From left on the bottom row) A2US, Panmnesia, Inc. >
This exhibition will feature 15 startups that are standing out in cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, mobility, and sustainability. In particular, AI-based deep tech startups in various industries such as logistics, architecture, and medicine will take up half of the total, showcasing the companies’ innovative AI technologies.
Polyphenol Factory Co.,Ltd introduces ‘Grabity’, a hair loss shampoo launched domestically, which applies the patented ingredient ‘LiftMax 308™’ that forms an instantaneous protective layer on the hair during the shampooing process. A real-time demonstration will be held at this exhibition hall so that visitors can experience the effects of the ingredient directly, and plans to enter the global market starting with the launch on Amazon in the US in January 2025.
VIRNECT will present ‘VisionX’, a prototype that won the Innovation Award this time. The product provides a chatbot AI through an AI voice interface, and has a function that allows users to check the status of the equipment in real time through conversations with the AI and receive troubleshooting guidance through voice conversations, so users can experience it directly at the KAIST Hall.
‘Standard Energy’ plans to exhibit ‘Energy Tile’, an indoor ESS that utilizes the world’s first vanadium ion battery (hereinafter referred to as VIB). VIB is absolutely safe from fire and has high installation flexibility, so it can be applied to smart cities and AI data centers.
‘A2US’ is the only company in the world that has hydroxyl radical water production technology, and won the Innovation Award for its first product, an air purifier. In the future, it is expected to be widely commercialized in air and water purification, smart farms, food tech, and semiconductor cleaning using safe and environmentally friendly hydroxyl radical water.
Panmnesia, Inc. won the CES Innovation Award for its GPU memory expansion solution equipped with its CXL 3.1 IP. By connecting a memory expansion device using Panmnesia’s CXL IP, the GPU’s memory capacity can be expanded to the terabyte level. Following the Innovation Award for ‘CXL-equipped AI Accelerator’ at CES 2024 last year, it is the only company to have won the Innovation Award for its AI-oriented CXL solution for two consecutive years.
In addition, technologies from a total of 15 companies will be introduced, including ▴Omelet ▴NEXTWAVE ▴Planby Technologies ▴Cosmo Bee ▴ImpactAI ▴Roen Surgical ▴DIDEN Roboticss ▴Autopedia ▴OAQ ▴HydroXpand ▴BOOKEND ▴Sterri.
On the central stage of the KAIST Hall, KAIST students selected as CES Student Supporters will conduct interviews with participating companies and promote the companies' innovative technologies and solutions. On the 8th, from 5 PM to 7 PM, a KAIST NIGHT event will be held where pre-invited investors and participating companies can network.
Keon Jae Lee, the head of the Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “Through CES 2025, we will showcase innovative technologies and solutions from startups based on KAIST’s deep science and deep tech, and lead commercialization in cutting-edge technology fields such as AI, robotics, mobility, and environment/energy. KAIST plans to further promote technology commercialization by supporting the growth and marketing of innovative startups through the Institute of Technology Value Creation and by strengthening global networks and expanding cooperation opportunities.”
2024.12.31 View 6553
KAIST Wins CES 2025 Innovation Award, Showcasing Innovative Technologies
KAIST will showcase innovative technologies at the world’s largest technology fair, the Consumer Electronics Show (CES 2025). In addition, KAIST startups VIRNECT Inc., Standard Energy Inc., A2US Inc., and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards.
< Image 1. 3D-Graphical Profile of CES 2025 KAIST Exhibition Booth >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 31st that it will operate a 140㎡ standalone booth at CES Eureka Park, which will be held in Las Vegas, USA from January 7th to 10th next year, to showcase KAIST's innovative technologies to global companies and investors.
KAIST startups VIRNECT, Standard Energy, A2US, and Panmnesia, Inc. won the 2025 CES Innovation Awards. ▴VIRNECT won the Innovation Award in the ‘Industrial Equipment and Machinery’ category for ‘VisionX’, an AI-based smart glass for industrial sites; ▴Standard Energy Co., Ltd. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Smart City’ category for developing the world’s first vanadium-ion battery; ▴A2US won the Innovation Award in the ‘Environment & Energy’ category for its portable air purifier that eliminates bacteria, odors, and fine dust in the air with just water droplets; ▴Panmnesia, Inc. won the Innovation Award in the ‘Computer Peripherals and Accessories’ category for its ‘CXL-based GPU Memory Expansion Kit’ that can drastically reduce the cost of building AI infrastructure.
< Image 2. (From left on the top row) VIRNECT, Standard Energy, (From left on the bottom row) A2US, Panmnesia, Inc. >
This exhibition will feature 15 startups that are standing out in cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, mobility, and sustainability. In particular, AI-based deep tech startups in various industries such as logistics, architecture, and medicine will take up half of the total, showcasing the companies’ innovative AI technologies.
Polyphenol Factory Co.,Ltd introduces ‘Grabity’, a hair loss shampoo launched domestically, which applies the patented ingredient ‘LiftMax 308™’ that forms an instantaneous protective layer on the hair during the shampooing process. A real-time demonstration will be held at this exhibition hall so that visitors can experience the effects of the ingredient directly, and plans to enter the global market starting with the launch on Amazon in the US in January 2025.
VIRNECT will present ‘VisionX’, a prototype that won the Innovation Award this time. The product provides a chatbot AI through an AI voice interface, and has a function that allows users to check the status of the equipment in real time through conversations with the AI and receive troubleshooting guidance through voice conversations, so users can experience it directly at the KAIST Hall.
‘Standard Energy’ plans to exhibit ‘Energy Tile’, an indoor ESS that utilizes the world’s first vanadium ion battery (hereinafter referred to as VIB). VIB is absolutely safe from fire and has high installation flexibility, so it can be applied to smart cities and AI data centers.
‘A2US’ is the only company in the world that has hydroxyl radical water production technology, and won the Innovation Award for its first product, an air purifier. In the future, it is expected to be widely commercialized in air and water purification, smart farms, food tech, and semiconductor cleaning using safe and environmentally friendly hydroxyl radical water.
Panmnesia, Inc. won the CES Innovation Award for its GPU memory expansion solution equipped with its CXL 3.1 IP. By connecting a memory expansion device using Panmnesia’s CXL IP, the GPU’s memory capacity can be expanded to the terabyte level. Following the Innovation Award for ‘CXL-equipped AI Accelerator’ at CES 2024 last year, it is the only company to have won the Innovation Award for its AI-oriented CXL solution for two consecutive years.
In addition, technologies from a total of 15 companies will be introduced, including ▴Omelet ▴NEXTWAVE ▴Planby Technologies ▴Cosmo Bee ▴ImpactAI ▴Roen Surgical ▴DIDEN Roboticss ▴Autopedia ▴OAQ ▴HydroXpand ▴BOOKEND ▴Sterri.
On the central stage of the KAIST Hall, KAIST students selected as CES Student Supporters will conduct interviews with participating companies and promote the companies' innovative technologies and solutions. On the 8th, from 5 PM to 7 PM, a KAIST NIGHT event will be held where pre-invited investors and participating companies can network.
Keon Jae Lee, the head of the Institute of Technology Value Creation, said, “Through CES 2025, we will showcase innovative technologies and solutions from startups based on KAIST’s deep science and deep tech, and lead commercialization in cutting-edge technology fields such as AI, robotics, mobility, and environment/energy. KAIST plans to further promote technology commercialization by supporting the growth and marketing of innovative startups through the Institute of Technology Value Creation and by strengthening global networks and expanding cooperation opportunities.”
2024.12.31 View 6553 -
 KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 8152
KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 8152 -
 Genome Sequencing Unveils Mutational Impacts of Radiation on Mammalian Cells
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer and genetic disorders. Yet, our understanding of the quantitative and qualitative mutational impacts of ionizing radiation has been incomplete.
On the 14th, Professor Young Seok Ju and his research team from KAIST, in collaboration with Dr. Tae Gen Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science, and Professors Kyung Su Kim and Ji Hyun Chang from Seoul National University, unveiled a breakthrough. Their study, led by joint first authors Drs. Jeonghwan Youk, Hyun Woo Kwon, Joonoh Lim, Eunji Kim and Tae-Woo Kim, titled "Quantitative and qualitative mutational impact of ionizing radiation on normal cells," was published in Cell Genomics.
Employing meticulous techniques, the research team comprehensively analyzed the whole-genome sequences of cells pre- and post-radiation exposure, pinpointing radiation-induced DNA mutations. Experiments involving cells from different organs of humans and mice exposed to varying radiation doses revealed mutation patterns correlating with exposure levels. (Figure 1)
Notably, exposure to 1 Gray (Gy) of radiation resulted in on average 14 mutations in every post-exposure cell. (Figure 2) Unlike other carcinogens, radiation-induced mutations primarily comprised short base deletions and a set of structural variations including inversions, translocations, and various complex genomic rearrangements. (Figure 3) Interestingly, experiments subjecting cells to low radiation dose rate over 100 days demonstrated that mutation quantities, under equivalent total radiation doses, mirrored those of high-dose exposure.
"Through this study, we have clearly elucidated the effects of radiation on cells at the molecular level," said Prof. Ju at KAIST. "Now we understand better how radiation changes the DNA of our cells," he added.
Dr. Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science stated, "Based on this study, we will continue to research the effects of very low and very high doses of radiation on the human body," and further remarked, "We will advance the development of safe and effective radiation therapy techniques."
Professors Kim and Chang from Seoul National University College of Medicine expressed their views, saying, "Through this study, we believe we now have a tool to accurately understand the impact of radiation on human DNA," and added, "We hope that many subsequent studies will emerge using the research methodologies employed in this study."
This research represents a significant leap forward in radiation studies, made possible through collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary approaches. This pioneering research engaged scholars from diverse backgrounds, spanning from the Genetic Engineering Research Institute at Seoul National University, the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute in the UK, the Institute for Molecular Biotechnology in Austria (IMBA), and the Genome Insight Inc. (a KAIST spin-off start-up). This study was supported by various institutions including the National Research Foundation of Korea, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science (supported by Ministry of Science and ICT, the government of South Korea), the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), and the Korea University Anam Hospital Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science and Creativity, the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National R&D Program.
2024.02.15 View 9000
Genome Sequencing Unveils Mutational Impacts of Radiation on Mammalian Cells
Recent release of the waste water from Japan's Fukushima nuclear disaster stirred apprehension regarding the health implications of radiation exposure. Classified as a Group 1 carcinogen, ionizing radiation has long been associated with various cancers and genetic disorders, as evidenced by survivors and descendants of atomic bombings and the Chernobyl disaster. Despite much smaller amount, we remain consistently exposed to low levels of radiation in everyday life and medical procedures.
Radiation, whether in the form of high-energy particles or electromagnetic waves, is conventionally known to break our cellular DNA, leading to cancer and genetic disorders. Yet, our understanding of the quantitative and qualitative mutational impacts of ionizing radiation has been incomplete.
On the 14th, Professor Young Seok Ju and his research team from KAIST, in collaboration with Dr. Tae Gen Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science, and Professors Kyung Su Kim and Ji Hyun Chang from Seoul National University, unveiled a breakthrough. Their study, led by joint first authors Drs. Jeonghwan Youk, Hyun Woo Kwon, Joonoh Lim, Eunji Kim and Tae-Woo Kim, titled "Quantitative and qualitative mutational impact of ionizing radiation on normal cells," was published in Cell Genomics.
Employing meticulous techniques, the research team comprehensively analyzed the whole-genome sequences of cells pre- and post-radiation exposure, pinpointing radiation-induced DNA mutations. Experiments involving cells from different organs of humans and mice exposed to varying radiation doses revealed mutation patterns correlating with exposure levels. (Figure 1)
Notably, exposure to 1 Gray (Gy) of radiation resulted in on average 14 mutations in every post-exposure cell. (Figure 2) Unlike other carcinogens, radiation-induced mutations primarily comprised short base deletions and a set of structural variations including inversions, translocations, and various complex genomic rearrangements. (Figure 3) Interestingly, experiments subjecting cells to low radiation dose rate over 100 days demonstrated that mutation quantities, under equivalent total radiation doses, mirrored those of high-dose exposure.
"Through this study, we have clearly elucidated the effects of radiation on cells at the molecular level," said Prof. Ju at KAIST. "Now we understand better how radiation changes the DNA of our cells," he added.
Dr. Son from the Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science stated, "Based on this study, we will continue to research the effects of very low and very high doses of radiation on the human body," and further remarked, "We will advance the development of safe and effective radiation therapy techniques."
Professors Kim and Chang from Seoul National University College of Medicine expressed their views, saying, "Through this study, we believe we now have a tool to accurately understand the impact of radiation on human DNA," and added, "We hope that many subsequent studies will emerge using the research methodologies employed in this study."
This research represents a significant leap forward in radiation studies, made possible through collaborative efforts and interdisciplinary approaches. This pioneering research engaged scholars from diverse backgrounds, spanning from the Genetic Engineering Research Institute at Seoul National University, the Cambridge Stem Cell Institute in the UK, the Institute for Molecular Biotechnology in Austria (IMBA), and the Genome Insight Inc. (a KAIST spin-off start-up). This study was supported by various institutions including the National Research Foundation of Korea, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Science (supported by Ministry of Science and ICT, the government of South Korea), the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP), and the Korea University Anam Hospital Korea Foundation for the Advancement of Science and Creativity, the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National R&D Program.
2024.02.15 View 9000 -
 A KAIST Research Team Develops a Smart Color-Changing Flexible Battery with Ultra-high Efficiency
With the rapid growth of the smart and wearable electronic devices market, smart next-generation energy storage systems that have energy storage functions as well as additional color-changing properties are receiving a great deal of attention. However, existing electrochromic devices have low electrical conductivity, leading to low efficiency in electron and ion mobility, and low storage capacities. Such batteries have therefore been limited to use in flexible and wearable devices.
On August 21, a joint research team led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) and Professor Tae Gwang Yun from the Myongji University Department of Materials Science and Engineering announced the development of a smart electrochromic Zn-ion battery that can visually represent its charging and discharging processes using an electrochromic polymer anode incorporated with a “π-bridge spacer”, which increases electron and ion mobility efficiency.
Batteries topped with electrochromic properties are groundbreaking inventions that can visually represent their charged and discharged states using colors, and can be used as display devices that cut down energy consumption for indoor cooling by controlling solar absorbance. The research team successfully built a flexible and electrochromic smart Zn-ion battery that can maintain its excellent electrochromic and electrochemical properties, even under long-term exposure to the atmosphere and mechanical deformations.
< Figure 1. Electrochromic zinc ion battery whose anode is made of a polymer that turns dark blue when charged and transparent when discharged. >
To maximize the efficiency of electron and ion mobility, the team modelled and synthesized the first π-bridge spacer-incorporated polymer anode in the world. π-bonds can improve the mobility of electrons within a structure to speed up ion movement and maximize ion adsorption efficiency, which improves its energy storage capacity.
In anode-based batteries with a π-bridge spacer, the spacer provides room for quicker ion movement. This allows fast charging, an improved zinc-ion discharging capacity of 110 mAh/g, which is 40% greater than previously reported, and a 30% increase in electrochromic function that switches from dark blue to transparent when the device is charged/discharged. In addition, should the transparent flexible battery technology be applied to smart windows, they would display darker colors during the day while they absorb solar energy, and function as a futuristic energy storage technique that can block out UV radiation and replace curtains.
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the structure of the electrochromic polymer with π-π spacer and the operation of a smart flexible battery using this cathode material. >
< Figure 3. (A) Density Functional Theory (DFT) theory-based atomic and electronic structure analysis. (B) Comparison of rate characteristics for polymers with and without π-bridge spacers. (C) Electrochemical performance comparison graph with previously reported zinc ion batteries. The anode material, which has an electron donor-acceptor structure with a built-in π-bridge spacer, shows better electrochemical performance and electrochromic properties than existing zinc ion batteries and electrochromic devices. >
Professor Il-Doo Kim said, “We have developed a polymer incorporated with a π-bridge spacer and successfully built a smart Zn-ion battery with excellent electrochromic efficiency and high energy storage capacity.” He added, “This technique goes beyond the existing concept of batteries that are used simply as energy storage devices, and we expect this technology to be used as a futuristic energy storage system that accelerates innovation in smart batteries and wearable technologies.”
This research, co-first authored by the alums of KAIST Departments of Material Sciences of Engineering, Professor Tae Gwang Yun of Myongji University, Dr. Jiyoung Lee, a post-doctoral associate at Northwestern University, and Professor Han Seul Kim at Chungbuk National University, was published as an inside cover article for Advanced Materials on August 3 under the title, “A π-Bridge Spacer Embedded Electron Donor-Acceptor Polymer for Flexible Electrochromic Zn-Ion Batteries”.
< Figure 4. Advanced Materials Inside Cover (August Issue) >
This research was supported by the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT, the Nano and Material Technology Development Project under the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Successive Academic Generation Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Education, and the Alchemist Project under the Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy.
2023.09.01 View 9068
A KAIST Research Team Develops a Smart Color-Changing Flexible Battery with Ultra-high Efficiency
With the rapid growth of the smart and wearable electronic devices market, smart next-generation energy storage systems that have energy storage functions as well as additional color-changing properties are receiving a great deal of attention. However, existing electrochromic devices have low electrical conductivity, leading to low efficiency in electron and ion mobility, and low storage capacities. Such batteries have therefore been limited to use in flexible and wearable devices.
On August 21, a joint research team led by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering (DMSE) and Professor Tae Gwang Yun from the Myongji University Department of Materials Science and Engineering announced the development of a smart electrochromic Zn-ion battery that can visually represent its charging and discharging processes using an electrochromic polymer anode incorporated with a “π-bridge spacer”, which increases electron and ion mobility efficiency.
Batteries topped with electrochromic properties are groundbreaking inventions that can visually represent their charged and discharged states using colors, and can be used as display devices that cut down energy consumption for indoor cooling by controlling solar absorbance. The research team successfully built a flexible and electrochromic smart Zn-ion battery that can maintain its excellent electrochromic and electrochemical properties, even under long-term exposure to the atmosphere and mechanical deformations.
< Figure 1. Electrochromic zinc ion battery whose anode is made of a polymer that turns dark blue when charged and transparent when discharged. >
To maximize the efficiency of electron and ion mobility, the team modelled and synthesized the first π-bridge spacer-incorporated polymer anode in the world. π-bonds can improve the mobility of electrons within a structure to speed up ion movement and maximize ion adsorption efficiency, which improves its energy storage capacity.
In anode-based batteries with a π-bridge spacer, the spacer provides room for quicker ion movement. This allows fast charging, an improved zinc-ion discharging capacity of 110 mAh/g, which is 40% greater than previously reported, and a 30% increase in electrochromic function that switches from dark blue to transparent when the device is charged/discharged. In addition, should the transparent flexible battery technology be applied to smart windows, they would display darker colors during the day while they absorb solar energy, and function as a futuristic energy storage technique that can block out UV radiation and replace curtains.
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the structure of the electrochromic polymer with π-π spacer and the operation of a smart flexible battery using this cathode material. >
< Figure 3. (A) Density Functional Theory (DFT) theory-based atomic and electronic structure analysis. (B) Comparison of rate characteristics for polymers with and without π-bridge spacers. (C) Electrochemical performance comparison graph with previously reported zinc ion batteries. The anode material, which has an electron donor-acceptor structure with a built-in π-bridge spacer, shows better electrochemical performance and electrochromic properties than existing zinc ion batteries and electrochromic devices. >
Professor Il-Doo Kim said, “We have developed a polymer incorporated with a π-bridge spacer and successfully built a smart Zn-ion battery with excellent electrochromic efficiency and high energy storage capacity.” He added, “This technique goes beyond the existing concept of batteries that are used simply as energy storage devices, and we expect this technology to be used as a futuristic energy storage system that accelerates innovation in smart batteries and wearable technologies.”
This research, co-first authored by the alums of KAIST Departments of Material Sciences of Engineering, Professor Tae Gwang Yun of Myongji University, Dr. Jiyoung Lee, a post-doctoral associate at Northwestern University, and Professor Han Seul Kim at Chungbuk National University, was published as an inside cover article for Advanced Materials on August 3 under the title, “A π-Bridge Spacer Embedded Electron Donor-Acceptor Polymer for Flexible Electrochromic Zn-Ion Batteries”.
< Figure 4. Advanced Materials Inside Cover (August Issue) >
This research was supported by the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT, the Nano and Material Technology Development Project under the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Successive Academic Generation Development Project under the Korean Ministry of Education, and the Alchemist Project under the Korean Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy.
2023.09.01 View 9068 -
 2023 Global Entrepreneurship Summer School in Silicon Valley Successfully Concluded
< 2023 Silicon Valley Global Entrepreneurship Summer School Participants >
The 2023 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS) was successfully held. Co-hosted by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) (Director Man-Sung Yim) and the Startup KAIST (Director Hyeonmin Bae), the 2023 KAIST GESS was the second one of the summer programs, repeating the Silicon Valley global entrepreneurship bootcamp of 2022 (2022 GESC), based on industry-academia collaboration. This program was designed to provide students with the opportunity to visit Silicon Valley, the global hub of entrepreneurship, and personally experience the Silicon Valley culture while developing human networks that would serve as a foundation for their overseas startup development.
A total of 20 participants were selected earlier this year, including potential KAISTian entrepreneurs and early-stage entrepreneurs from KAIST within one year of incorporation. In particular, a number of foreign students of various nationalities such as Vietnam, Azerbaijan, Honduras, Indonesia, Philippines, and Kazakhstan, increased significantly, demonstrating the enthusiasm for entrepreneurship across national boundaries along with the program's growing international status. This year's event was also open to 20 Impact MBA and Social Entrepreneur (SE) students from KAIST's College of Business for the Silicon Valley program.
For the past two months, the participants have trained on business model development and pitching at KAIST's main campus in Daejeon. From June 21st to the 30th, they visited the campuses of leading universities, such as, Stanford University, UC Santa Cruz, and UC Berkeley, as well as KOTRA Silicon Valley Trade Center (Manager Hyoung il Kim), and local alumni companies and Apple company to experience the global technology startups. The start-ups by KAIST alums including B Garage (CEO Aiden Kim), ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim), Medic Life Sciences (CEO Kyuho Han), and VESSL AI (CEO Jaeman Ahn) participated in the program and gave lectures and company tours to inspire the participants to have passion to take on the entrepreneurial endeavors and challenges.
On the last day, the participants gave presentations on their team’s business items in front of local venture capitalists in Silicon Valley. After receiving continuous coaching from Silicon Valley's professional accelerators through remote video conferencing and face-to-face mentoring for the last two months, the participants developed their business models and presented their creative and innovative ideas, revealing their potential as future global entrepreneurs. At the final competition, Team Sparky that developed “Snoove” won the first prize. Snoove is a scientifically-proven mattress accessory that applies mild vibration to the mattress to aid users in achieving better sleep, a method previously used to soothe infants.
< GESS Pitching Day Presentation >
Kevin Choi from the Team Sparky said, "Seeing and experiencing the realities of entrepreneurship in Silicon Valley, a global startup scene, made me think about the importance of unlearning, challenging, and failing to be a global entrepreneur who contributes to our society." Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President of the International Office, who organized the event added, "Through this experience, we expect KAIST students to grow to become global leaders who would create global values and enhance the international reputation of our university."
Meanwhile, the GSP and Startup KAIST commented that they will to continue to develop the KAIST GESS program to foster prospective entrepreneurs who can compete in the global market based on the success of this program.
2023.07.05 View 11823
2023 Global Entrepreneurship Summer School in Silicon Valley Successfully Concluded
< 2023 Silicon Valley Global Entrepreneurship Summer School Participants >
The 2023 KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS) was successfully held. Co-hosted by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) (Director Man-Sung Yim) and the Startup KAIST (Director Hyeonmin Bae), the 2023 KAIST GESS was the second one of the summer programs, repeating the Silicon Valley global entrepreneurship bootcamp of 2022 (2022 GESC), based on industry-academia collaboration. This program was designed to provide students with the opportunity to visit Silicon Valley, the global hub of entrepreneurship, and personally experience the Silicon Valley culture while developing human networks that would serve as a foundation for their overseas startup development.
A total of 20 participants were selected earlier this year, including potential KAISTian entrepreneurs and early-stage entrepreneurs from KAIST within one year of incorporation. In particular, a number of foreign students of various nationalities such as Vietnam, Azerbaijan, Honduras, Indonesia, Philippines, and Kazakhstan, increased significantly, demonstrating the enthusiasm for entrepreneurship across national boundaries along with the program's growing international status. This year's event was also open to 20 Impact MBA and Social Entrepreneur (SE) students from KAIST's College of Business for the Silicon Valley program.
For the past two months, the participants have trained on business model development and pitching at KAIST's main campus in Daejeon. From June 21st to the 30th, they visited the campuses of leading universities, such as, Stanford University, UC Santa Cruz, and UC Berkeley, as well as KOTRA Silicon Valley Trade Center (Manager Hyoung il Kim), and local alumni companies and Apple company to experience the global technology startups. The start-ups by KAIST alums including B Garage (CEO Aiden Kim), ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim), Medic Life Sciences (CEO Kyuho Han), and VESSL AI (CEO Jaeman Ahn) participated in the program and gave lectures and company tours to inspire the participants to have passion to take on the entrepreneurial endeavors and challenges.
On the last day, the participants gave presentations on their team’s business items in front of local venture capitalists in Silicon Valley. After receiving continuous coaching from Silicon Valley's professional accelerators through remote video conferencing and face-to-face mentoring for the last two months, the participants developed their business models and presented their creative and innovative ideas, revealing their potential as future global entrepreneurs. At the final competition, Team Sparky that developed “Snoove” won the first prize. Snoove is a scientifically-proven mattress accessory that applies mild vibration to the mattress to aid users in achieving better sleep, a method previously used to soothe infants.
< GESS Pitching Day Presentation >
Kevin Choi from the Team Sparky said, "Seeing and experiencing the realities of entrepreneurship in Silicon Valley, a global startup scene, made me think about the importance of unlearning, challenging, and failing to be a global entrepreneur who contributes to our society." Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President of the International Office, who organized the event added, "Through this experience, we expect KAIST students to grow to become global leaders who would create global values and enhance the international reputation of our university."
Meanwhile, the GSP and Startup KAIST commented that they will to continue to develop the KAIST GESS program to foster prospective entrepreneurs who can compete in the global market based on the success of this program.
2023.07.05 View 11823 -
 KAIST Civil Engineering Students named Runner-up at the 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific
A team of five students from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) were awarded second place in a premier urban design student competition hosted by the Urban Land Institute and Hines, 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific.
The competition, which was held for the first time in the Asia-Pacific region, is an internationally recognized event which typically attract hundreds of applicants.
Jonah Remigio, Sojung Noh, Estefania Rodriguez, Jihyun Kang, and Ayantu Teshome, who joined forces under the name of “Team Hashtag Development”, were supported by faculty advisors Dr. Albert Han and Dr. Youngchul Kim of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering to imagine a more sustainable and enriched way of living in the Jurong district of Singapore.
Their submission, titled “Proposal: The Nest”, analyzed the big data within Singapore, using the data to determine which real estate business strategies would best enhance the quality of living and economy of the region.
Their final design, "The Nest" utilized mixed-use zoning to integrate the site’s scenic waterfront with homes, medical innovation, and sustainable technology, altogether creating a place to innovate, inhabit, and immerse.
< The Nest by Team Hashtag Development (Jonah Remigio, Ayantu Teshome Mossisa, Estefania Ayelen Rodriguez del Puerto, Sojung Noh, Jihyun Kang) ©2023 Urban Land Institute >
Ultimately, the team was recognized for their hard work and determination, imprinting South Korea’s indelible footprint in the arena of international scholastic achievement as they were named to be one of the Finalists on April 13th.
< Members of Team Hashtag Development >
Team Hashtag Development gave a virtual presentation to a jury of six ULI members on April 20th along with the "Team The REAL" from the University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City of Vietnam and "Team Omusubi" from the Waseda University of Japan, the team that submitted the proposal "Jurong Urban Health Campus" which was announced to be the winner on the 31st of May, after the virtual briefing by the top three finalists.
2023.06.26 View 9382
KAIST Civil Engineering Students named Runner-up at the 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific
A team of five students from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) were awarded second place in a premier urban design student competition hosted by the Urban Land Institute and Hines, 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific.
The competition, which was held for the first time in the Asia-Pacific region, is an internationally recognized event which typically attract hundreds of applicants.
Jonah Remigio, Sojung Noh, Estefania Rodriguez, Jihyun Kang, and Ayantu Teshome, who joined forces under the name of “Team Hashtag Development”, were supported by faculty advisors Dr. Albert Han and Dr. Youngchul Kim of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering to imagine a more sustainable and enriched way of living in the Jurong district of Singapore.
Their submission, titled “Proposal: The Nest”, analyzed the big data within Singapore, using the data to determine which real estate business strategies would best enhance the quality of living and economy of the region.
Their final design, "The Nest" utilized mixed-use zoning to integrate the site’s scenic waterfront with homes, medical innovation, and sustainable technology, altogether creating a place to innovate, inhabit, and immerse.
< The Nest by Team Hashtag Development (Jonah Remigio, Ayantu Teshome Mossisa, Estefania Ayelen Rodriguez del Puerto, Sojung Noh, Jihyun Kang) ©2023 Urban Land Institute >
Ultimately, the team was recognized for their hard work and determination, imprinting South Korea’s indelible footprint in the arena of international scholastic achievement as they were named to be one of the Finalists on April 13th.
< Members of Team Hashtag Development >
Team Hashtag Development gave a virtual presentation to a jury of six ULI members on April 20th along with the "Team The REAL" from the University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City of Vietnam and "Team Omusubi" from the Waseda University of Japan, the team that submitted the proposal "Jurong Urban Health Campus" which was announced to be the winner on the 31st of May, after the virtual briefing by the top three finalists.
2023.06.26 View 9382 -
 UAE Space Program Leaders named to be the 1st of the honorees of KAIST Alumni Association's special recognition for graduates of foreign nationality
The KAIST Alumni Association (Chairman, Chil-Hee Chung) announced on the 12th that the winners of the 2023 KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award and International Alumni Award has been selected.
The KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award, which produced the first recipient in 1992, is an award given to alumni who have contributed to the development of the nation and society, or who have glorified the honor of their alma mater with outstanding academic achievements and social and/or communal contributions.
On a special note, this year, there has been an addition to the honors, “the KAIST Distinguished International Alumni Award” to honor and encourage overseas alumni who are making their marks in the international community that will boost positive recognition of KAIST in the global setting and will later become a bridge that will expedite Korea's international efforts in the future.
As of 2022, the number of international students who succeeded in earning KAIST degrees has exceeded 1,700, and they are actively doing their part back in their home countries as leaders in various fields in which they belong, spanning from science and technology, to politics, industry and other corners of the society.
(From left) Omran Sharaf, the Assistant Minister of UAE Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation for Advanced Science and Technology, Amer Al Sayegh the Director General of Space Project at MBRSC, and Mohammed Al Harmi the Director General of Administration at MBRSC (Photos provided by the courtesy of MBRSC)
To celebrate and honor their outstanding achievements, the KAIST Alumni Association selected a team of three alumni of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to receive the Distinguished International Alumni Award for the first time. The named honorees are Omran Sharaf, a master’s graduate from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, and Amer Al Sayegh and Mohammed Al Harmi, master’s graduates of the Department of Aerospace Engineering - all three of the class of 2013 in leading positions in the UAE space program to lead the advancement of the science and technology of the country.
Currently, the three alums are in directorship of the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) with Mr. Omran Sharaf, who has recently been appointed as the Assistant Minister in charge of Advanced Science and Technology at the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, being the Project Director of the Emirates Mars Mission of MBRSC and Mr. Amer Al Sayegh in the Director General position in charge of Space Project and Mr. Mohammed Al Harmi, the Director General of Administration, at MBRSC.
They received technology transfer from “SatRec I”, Korea's first satellite system exporter and KAIST alumni company, for about 10 years from 2006, while carrying out their master’s studies at the same time.
Afterwards, they returned to UAE to lead the Emirates Mars Mission, which is already showing tangible progress including the successful launch of the Mars probe "Amal" (ال امل, meaning ‘Hope’ in Arabic), which was the first in the Arab world and the fifth in the world to successfully enter into orbit around Mars, and the UAE’s first independently developed Earth observation satellite "KhalifaSat".
An official from the KAIST Alumni Association said, "We selected the Distinguished International Alumni after evaluating their industrious leadership in promoting various space industry strategies, ranging from the development of Mars probes and Earth observation satellites, as well as lunar exploration, asteroid exploration, and Mars residence plans."
(From left) Joo-Sun Choi, President & CEO of Samsung Display Co. Ltd., Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), Kyunghyun Cho, Professor of New York University (NYU)
Also, four of the Korean graduates, Joo-Sun Choi, the CEO of Samsung Display, Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), and Kyunghyun Cho, a Professor of New York University (NYU), were selected as the winners of the “Distinguished Alumni Award”.
Mr. Joo-Sun Choi (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1989, Ph.D. in 1995), the CEO of Samsung Display, led the successful development and mass-production of the world's first ultra-high-definition QD-OLED Displays, and preemptively transformed the structure of business of the industry and has been leading the way in technological innovation.
Mr. Jung Goo Cho (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D. in 1992), the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., developed wireless power technology for the first time in Korea in the early 2000s and applied it to semiconductor/display lines and led the wireless power charging technology in various fields, such as developing KAIST On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEV) and commercializing the world's first wireless charger for 11kW electric vehicles.
Mr. Jong Seung Park (Mechanical Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D., in 1991), The President of ADD is an expert with abundant science and technology knowledge and organizational management capabilities. He is contributing greatly to national defense and security through science and technology.
Mr. Kyunghyun Cho (Computer Science, B.S., in 2009), the Professor of Computer Science and Data Science at NYU, is a world-renowned expert in Artificial Intelligence (AI), advancing the concept of 'Neural Machine Translation' in the field of natural language processing, to make great contributions to AI translation technology and related industries.
Chairman Chil-Hee Chung, the 26th Chair of KAIST Alumni Association “As each year goes by, I feel that the influence of KAIST alumni goes beyond science and technology to affect our society as a whole.” He went on to say, “This year, as it was more meaningful to extend the award to honor the international members of our Alums, we look forward to seeing more of our alumni continuing their social and academic endeavors to play an active role in the global stage in taking on the global challenges.”
The Ceremony for KAIST Distinguished Alumni and International Alumni Award Honorees will be conducted at the Annual New Year’s Event of KAIST Alumni Association for 2023 to be held on Friday, January 13th, at the Grand InterContinental Seoul Parnas.
2023.01.12 View 16931
UAE Space Program Leaders named to be the 1st of the honorees of KAIST Alumni Association's special recognition for graduates of foreign nationality
The KAIST Alumni Association (Chairman, Chil-Hee Chung) announced on the 12th that the winners of the 2023 KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award and International Alumni Award has been selected.
The KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award, which produced the first recipient in 1992, is an award given to alumni who have contributed to the development of the nation and society, or who have glorified the honor of their alma mater with outstanding academic achievements and social and/or communal contributions.
On a special note, this year, there has been an addition to the honors, “the KAIST Distinguished International Alumni Award” to honor and encourage overseas alumni who are making their marks in the international community that will boost positive recognition of KAIST in the global setting and will later become a bridge that will expedite Korea's international efforts in the future.
As of 2022, the number of international students who succeeded in earning KAIST degrees has exceeded 1,700, and they are actively doing their part back in their home countries as leaders in various fields in which they belong, spanning from science and technology, to politics, industry and other corners of the society.
(From left) Omran Sharaf, the Assistant Minister of UAE Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation for Advanced Science and Technology, Amer Al Sayegh the Director General of Space Project at MBRSC, and Mohammed Al Harmi the Director General of Administration at MBRSC (Photos provided by the courtesy of MBRSC)
To celebrate and honor their outstanding achievements, the KAIST Alumni Association selected a team of three alumni of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to receive the Distinguished International Alumni Award for the first time. The named honorees are Omran Sharaf, a master’s graduate from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, and Amer Al Sayegh and Mohammed Al Harmi, master’s graduates of the Department of Aerospace Engineering - all three of the class of 2013 in leading positions in the UAE space program to lead the advancement of the science and technology of the country.
Currently, the three alums are in directorship of the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) with Mr. Omran Sharaf, who has recently been appointed as the Assistant Minister in charge of Advanced Science and Technology at the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, being the Project Director of the Emirates Mars Mission of MBRSC and Mr. Amer Al Sayegh in the Director General position in charge of Space Project and Mr. Mohammed Al Harmi, the Director General of Administration, at MBRSC.
They received technology transfer from “SatRec I”, Korea's first satellite system exporter and KAIST alumni company, for about 10 years from 2006, while carrying out their master’s studies at the same time.
Afterwards, they returned to UAE to lead the Emirates Mars Mission, which is already showing tangible progress including the successful launch of the Mars probe "Amal" (ال امل, meaning ‘Hope’ in Arabic), which was the first in the Arab world and the fifth in the world to successfully enter into orbit around Mars, and the UAE’s first independently developed Earth observation satellite "KhalifaSat".
An official from the KAIST Alumni Association said, "We selected the Distinguished International Alumni after evaluating their industrious leadership in promoting various space industry strategies, ranging from the development of Mars probes and Earth observation satellites, as well as lunar exploration, asteroid exploration, and Mars residence plans."
(From left) Joo-Sun Choi, President & CEO of Samsung Display Co. Ltd., Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), Kyunghyun Cho, Professor of New York University (NYU)
Also, four of the Korean graduates, Joo-Sun Choi, the CEO of Samsung Display, Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), and Kyunghyun Cho, a Professor of New York University (NYU), were selected as the winners of the “Distinguished Alumni Award”.
Mr. Joo-Sun Choi (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1989, Ph.D. in 1995), the CEO of Samsung Display, led the successful development and mass-production of the world's first ultra-high-definition QD-OLED Displays, and preemptively transformed the structure of business of the industry and has been leading the way in technological innovation.
Mr. Jung Goo Cho (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D. in 1992), the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., developed wireless power technology for the first time in Korea in the early 2000s and applied it to semiconductor/display lines and led the wireless power charging technology in various fields, such as developing KAIST On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEV) and commercializing the world's first wireless charger for 11kW electric vehicles.
Mr. Jong Seung Park (Mechanical Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D., in 1991), The President of ADD is an expert with abundant science and technology knowledge and organizational management capabilities. He is contributing greatly to national defense and security through science and technology.
Mr. Kyunghyun Cho (Computer Science, B.S., in 2009), the Professor of Computer Science and Data Science at NYU, is a world-renowned expert in Artificial Intelligence (AI), advancing the concept of 'Neural Machine Translation' in the field of natural language processing, to make great contributions to AI translation technology and related industries.
Chairman Chil-Hee Chung, the 26th Chair of KAIST Alumni Association “As each year goes by, I feel that the influence of KAIST alumni goes beyond science and technology to affect our society as a whole.” He went on to say, “This year, as it was more meaningful to extend the award to honor the international members of our Alums, we look forward to seeing more of our alumni continuing their social and academic endeavors to play an active role in the global stage in taking on the global challenges.”
The Ceremony for KAIST Distinguished Alumni and International Alumni Award Honorees will be conducted at the Annual New Year’s Event of KAIST Alumni Association for 2023 to be held on Friday, January 13th, at the Grand InterContinental Seoul Parnas.
2023.01.12 View 16931 -
 KAIST to showcase a pack of KAIST Start-ups at CES 2023
- KAIST is to run an Exclusive Booth at the Venetian Expo (Hall G) in Eureka Park, at CES 2023, to be held in Las Vegas from Thursday, January 5th through Sunday, the 8th.
- Twelve businesses recently put together by KAIST faculty, alumni, and the start-ups given legal usage of KAIST technologies will be showcased.
- Out of the participating start-ups, the products by Fluiz and Hills Robotics were selected as the “CES Innovation Award 2023 Honoree”, scoring top in their respective categories.
On January 3, KAIST announced that there will be a KAIST booth at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2023, the most influential tech event in the world, to be held in Las Vegas from January 3 to 8.
At this exclusive corner, KAIST will introduce the technologies of KAIST start-ups over the exhibition period.
KAIST first started holding its exclusive booth in CES 2019 with five start-up businesses, following up at CES 2020 with 12 start-ups and at CES 2022 with 10 start-ups. At CES 2023, which would be KAIST’s fourth conference, KAIST will be accompanying 12 businesses including start-ups by the faculty members, alumni, and technology transfer companies that just began their businesses with technologies from their research findings that stands a head above others.
To maximize the publicity opportunity, KAIST will support each company’s marketing strategies through cooperation with the Korea International Trade Association (KITA), and provide an opportunity for the school and each startup to create global identity and exhibit the excellence of their technologies at the convention.
The following companies will be at the KAIST Booth in Eureka Park:
The twelve startups mentioned above aim to achieve global technology commecialization in their respective fields of expertise spanning from eXtended Reality (XR) and gaming, to AI and robotics, vehicle and transport, mobile platform, smart city, autonomous driving, healthcare, internet of thing (IoT), through joint research and development, technology transfer and investment attraction from world’s leading institutions and enterprises.
In particular, Fluiz and Hills Robotics won the CES Innovation Award as 2023 Honorees and is expected to attain greater achievements in the future.
A staff member from the KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation said, “The KAIST Showcase for CES 2023 has prepared a new pitching space for each of the companies for their own IR efforts, and we hope that KAIST startups will actively and effectively market their products and technologies while they are at the convention. We hope it will help them utilize their time here to establish their name in presence here which will eventually serve as a good foothold for them and their predecessors to further global commercialization goals.”
2023.01.04 View 17580
KAIST to showcase a pack of KAIST Start-ups at CES 2023
- KAIST is to run an Exclusive Booth at the Venetian Expo (Hall G) in Eureka Park, at CES 2023, to be held in Las Vegas from Thursday, January 5th through Sunday, the 8th.
- Twelve businesses recently put together by KAIST faculty, alumni, and the start-ups given legal usage of KAIST technologies will be showcased.
- Out of the participating start-ups, the products by Fluiz and Hills Robotics were selected as the “CES Innovation Award 2023 Honoree”, scoring top in their respective categories.
On January 3, KAIST announced that there will be a KAIST booth at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2023, the most influential tech event in the world, to be held in Las Vegas from January 3 to 8.
At this exclusive corner, KAIST will introduce the technologies of KAIST start-ups over the exhibition period.
KAIST first started holding its exclusive booth in CES 2019 with five start-up businesses, following up at CES 2020 with 12 start-ups and at CES 2022 with 10 start-ups. At CES 2023, which would be KAIST’s fourth conference, KAIST will be accompanying 12 businesses including start-ups by the faculty members, alumni, and technology transfer companies that just began their businesses with technologies from their research findings that stands a head above others.
To maximize the publicity opportunity, KAIST will support each company’s marketing strategies through cooperation with the Korea International Trade Association (KITA), and provide an opportunity for the school and each startup to create global identity and exhibit the excellence of their technologies at the convention.
The following companies will be at the KAIST Booth in Eureka Park:
The twelve startups mentioned above aim to achieve global technology commecialization in their respective fields of expertise spanning from eXtended Reality (XR) and gaming, to AI and robotics, vehicle and transport, mobile platform, smart city, autonomous driving, healthcare, internet of thing (IoT), through joint research and development, technology transfer and investment attraction from world’s leading institutions and enterprises.
In particular, Fluiz and Hills Robotics won the CES Innovation Award as 2023 Honorees and is expected to attain greater achievements in the future.
A staff member from the KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation said, “The KAIST Showcase for CES 2023 has prepared a new pitching space for each of the companies for their own IR efforts, and we hope that KAIST startups will actively and effectively market their products and technologies while they are at the convention. We hope it will help them utilize their time here to establish their name in presence here which will eventually serve as a good foothold for them and their predecessors to further global commercialization goals.”
2023.01.04 View 17580 -
 KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 16466
KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 16466 -
 Eco-Friendly Micro-Supercapacitors Using Fallen Leaves
Green micro-supercapacitors on a single leaf could easily be applied in wearable electronics, smart houses, and IoTs
A KAIST research team has developed graphene-inorganic-hybrid micro-supercapacitors made of fallen leaves using femtosecond laser direct writing. The rapid development of wearable electronics requires breakthrough innovations in flexible energy storage devices in which micro-supercapacitors have drawn a great deal of interest due to their high power density, long lifetimes, and short charging times. Recently, there has been an enormous increase in waste batteries owing to the growing demand and the shortened replacement cycle in consumer electronics. The safety and environmental issues involved in the collection, recycling, and processing of such waste batteries are creating a number of challenges.
Forests cover about 30 percent of the Earth’s surface and produce a huge amount of fallen leaves. This naturally occurring biomass comes in large quantities and is completely biodegradable, which makes it an attractive sustainable resource. Nevertheless, if the fallen leaves are left neglected instead of being used efficiently, they can contribute to fire hazards, air pollution, and global warming.
To solve both problems at once, a research team led by Professor Young-Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Hana Yoon from the Korea Institute of Energy Research developed a novel technology that can create 3D porous graphene microelectrodes with high electrical conductivity by irradiating femtosecond laser pulses on the leaves in ambient air. This one-step fabrication does not require any additional materials or pre-treatment.
They showed that this technique could quickly and easily produce porous graphene electrodes at a low price, and demonstrated potential applications by fabricating graphene micro-supercapacitors to power an LED and an electronic watch. These results open up a new possibility for the mass production of flexible and green graphene-based electronic devices.
Professor Young-Jin Kim said, “Leaves create forest biomass that comes in unmanageable quantities, so using them for next-generation energy storage devices makes it possible for us to reuse waste resources, thereby establishing a virtuous cycle.”
This research was published in Advanced Functional Materials last month and was sponsored by the Ministry of Agriculture Food and Rural Affairs, the Korea Forest Service, and the Korea Institute of Energy Research.
-Publication
Truong-Son Dinh Le, Yeong A. Lee, Han Ku Nam, Kyu Yeon Jang, Dongwook Yang, Byunggi Kim, Kanghoon Yim, Seung Woo Kim, Hana Yoon, and Young-jin Kim, “Green Flexible Graphene-Inorganic-Hybrid Micro-Supercapacitors Made of Fallen Leaves Enabled by Ultrafast Laser Pulses," December 05, 2021, Advanced Functional Materials (doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202107768)
-ProfileProfessor Young-Jin KimUltra-Precision Metrology and Manufacturing (UPM2) LaboratoryDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.27 View 13948
Eco-Friendly Micro-Supercapacitors Using Fallen Leaves
Green micro-supercapacitors on a single leaf could easily be applied in wearable electronics, smart houses, and IoTs
A KAIST research team has developed graphene-inorganic-hybrid micro-supercapacitors made of fallen leaves using femtosecond laser direct writing. The rapid development of wearable electronics requires breakthrough innovations in flexible energy storage devices in which micro-supercapacitors have drawn a great deal of interest due to their high power density, long lifetimes, and short charging times. Recently, there has been an enormous increase in waste batteries owing to the growing demand and the shortened replacement cycle in consumer electronics. The safety and environmental issues involved in the collection, recycling, and processing of such waste batteries are creating a number of challenges.
Forests cover about 30 percent of the Earth’s surface and produce a huge amount of fallen leaves. This naturally occurring biomass comes in large quantities and is completely biodegradable, which makes it an attractive sustainable resource. Nevertheless, if the fallen leaves are left neglected instead of being used efficiently, they can contribute to fire hazards, air pollution, and global warming.
To solve both problems at once, a research team led by Professor Young-Jin Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Hana Yoon from the Korea Institute of Energy Research developed a novel technology that can create 3D porous graphene microelectrodes with high electrical conductivity by irradiating femtosecond laser pulses on the leaves in ambient air. This one-step fabrication does not require any additional materials or pre-treatment.
They showed that this technique could quickly and easily produce porous graphene electrodes at a low price, and demonstrated potential applications by fabricating graphene micro-supercapacitors to power an LED and an electronic watch. These results open up a new possibility for the mass production of flexible and green graphene-based electronic devices.
Professor Young-Jin Kim said, “Leaves create forest biomass that comes in unmanageable quantities, so using them for next-generation energy storage devices makes it possible for us to reuse waste resources, thereby establishing a virtuous cycle.”
This research was published in Advanced Functional Materials last month and was sponsored by the Ministry of Agriculture Food and Rural Affairs, the Korea Forest Service, and the Korea Institute of Energy Research.
-Publication
Truong-Son Dinh Le, Yeong A. Lee, Han Ku Nam, Kyu Yeon Jang, Dongwook Yang, Byunggi Kim, Kanghoon Yim, Seung Woo Kim, Hana Yoon, and Young-jin Kim, “Green Flexible Graphene-Inorganic-Hybrid Micro-Supercapacitors Made of Fallen Leaves Enabled by Ultrafast Laser Pulses," December 05, 2021, Advanced Functional Materials (doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202107768)
-ProfileProfessor Young-Jin KimUltra-Precision Metrology and Manufacturing (UPM2) LaboratoryDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2022.01.27 View 13948