AT
-
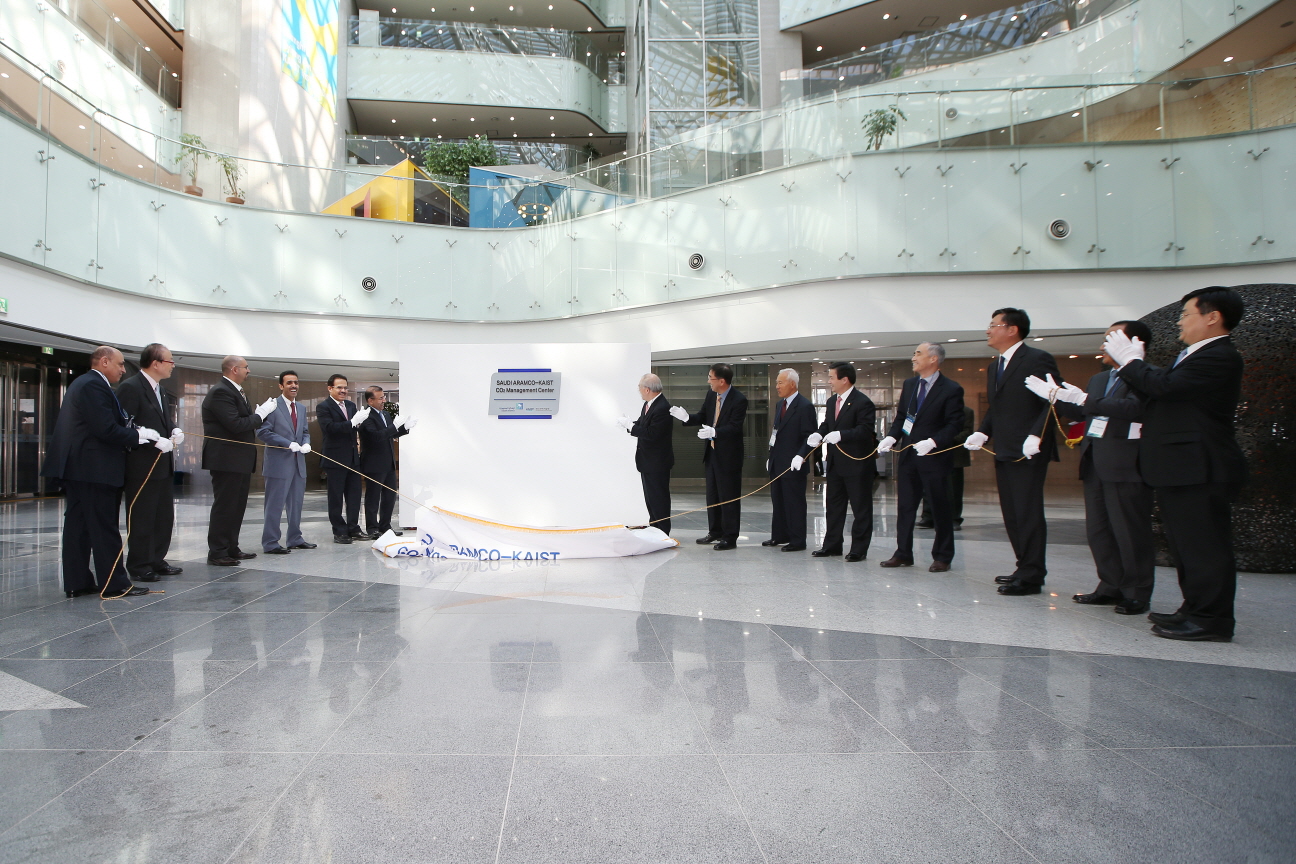 Launched the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed on February 20, 2013 the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement (the Agreement) on joint collaborations in research and development of carbon management between the two entities.
The Agreement was subsequently concluded upon the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between KAIST and Saudi Aramco, dated January 7th, 2013. In the Agreement, the two organizations specified terms and conditions necessary to conduct joint research projects and stipulated governing body for the operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a national oil company for Saudi Arabia, entered into the MOU, in which the two parties shared a common interest in addressing the issue of CO2 capture, CO2storage, CO2 avoidance using efficiency improvements, and converting CO2 into useful chemicals and other materials, and agreed to “create a major research center for CO2” in Korea.
As envisioned by the MOU and its subsequent agreement, KAIST and Saudi Aramco decided to operate an interim office of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST campus in Daejeon, Korea, pending the establishment of the research center. The full-fledged, independent research facility will be built at a location and during a period to be agreed between the two parties.
Following the signing of the Agreement, there was a celebration event taken place, including a signboard hanging ceremony for the interim research office. A 10-member delegation from Saudi Aramco, which was headed by Vice President of Engineering Services Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Dr. Nam-Pyo Suh, former president of KAIST, Vice President of Research at KAIST Kyung-Wook Paik, and senior representatives from Korean oil and petrochemical companies such as S-Oil, Lotte Chemicals, SK Innovation, and STX attended the event.
Kyung-Wook Paik, Vice President of Research at KAIST, said,
“In order to help find solutions to carbon management, KAIST and Saudi Aramco will facilitate to exchange each party’s complementary technical expertise, gain insight into new research fields, and have access to key sources of talent, while promoting innovation for technology solutions and contributing to the lifelong learning agenda of both organizations.”
Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Vice President of Engineering Services at Saudi Aramco, added that “As a world-leading oil and gas company, Saudi Aramco’s mission is to promote the continued use of safe, environmentally-friendly petroleum products with a vision to becoming a global leader in research and technology. Building a strong and cooperative relationship with KAIST in our endeavor to search for alternative ways to better utilization of fossil fuels will expedite the creation of opportunities to make the world environmentally safer and sustainable.”
KAIST and Saudi Aramco will each chip in a maximum of USD 5 million annually for the establishment and operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center during the initial term of the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement, which starts in 2013 and continues through 2018.
2013.03.19 View 14137
Launched the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed on February 20, 2013 the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement (the Agreement) on joint collaborations in research and development of carbon management between the two entities.
The Agreement was subsequently concluded upon the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between KAIST and Saudi Aramco, dated January 7th, 2013. In the Agreement, the two organizations specified terms and conditions necessary to conduct joint research projects and stipulated governing body for the operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a national oil company for Saudi Arabia, entered into the MOU, in which the two parties shared a common interest in addressing the issue of CO2 capture, CO2storage, CO2 avoidance using efficiency improvements, and converting CO2 into useful chemicals and other materials, and agreed to “create a major research center for CO2” in Korea.
As envisioned by the MOU and its subsequent agreement, KAIST and Saudi Aramco decided to operate an interim office of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST campus in Daejeon, Korea, pending the establishment of the research center. The full-fledged, independent research facility will be built at a location and during a period to be agreed between the two parties.
Following the signing of the Agreement, there was a celebration event taken place, including a signboard hanging ceremony for the interim research office. A 10-member delegation from Saudi Aramco, which was headed by Vice President of Engineering Services Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Dr. Nam-Pyo Suh, former president of KAIST, Vice President of Research at KAIST Kyung-Wook Paik, and senior representatives from Korean oil and petrochemical companies such as S-Oil, Lotte Chemicals, SK Innovation, and STX attended the event.
Kyung-Wook Paik, Vice President of Research at KAIST, said,
“In order to help find solutions to carbon management, KAIST and Saudi Aramco will facilitate to exchange each party’s complementary technical expertise, gain insight into new research fields, and have access to key sources of talent, while promoting innovation for technology solutions and contributing to the lifelong learning agenda of both organizations.”
Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Vice President of Engineering Services at Saudi Aramco, added that “As a world-leading oil and gas company, Saudi Aramco’s mission is to promote the continued use of safe, environmentally-friendly petroleum products with a vision to becoming a global leader in research and technology. Building a strong and cooperative relationship with KAIST in our endeavor to search for alternative ways to better utilization of fossil fuels will expedite the creation of opportunities to make the world environmentally safer and sustainable.”
KAIST and Saudi Aramco will each chip in a maximum of USD 5 million annually for the establishment and operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center during the initial term of the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement, which starts in 2013 and continues through 2018.
2013.03.19 View 14137 -
 An efficient strategy for developing microbial cell factories by employing synthetic small regulatory RNAs
A new metabolic engineering tool that allows fine control of gene expression level by employing synthetic small regulatory RNAs was developed to efficiently construct microbial cell factories producing desired chemicals and materials
Biotechnologists have been working hard to address the climate change and limited fossil resource issues through the development of sustainable processes for the production of chemicals, fuels and materials from renewable non-food biomass. One promising sustainable technology is the use of microbial cell factories for the efficient production of desired chemicals and materials. When microorganisms are isolated from nature, the performance in producing our desired product is rather poor. That is why metabolic engineering is performed to improve the metabolic and cellular characteristics to achieve enhanced production of desired product at high yield and productivity. Since the performance of microbial cell factory is very important in lowering the overall production cost of the bioprocess, many different strategies and tools have been developed for the metabolic engineering of microorganisms.
One of the big challenges in metabolic engineering is to find the best platform organism and to find those genes to be engineered so as to maximize the production efficiency of the desired chemical. Even Escherichia coli, the most widely utilized simple microorganism, has thousands of genes, the expression of which is highly regulated and interconnected to finely control cellular and metabolic activities. Thus, the complexity of cellular genetic interactions is beyond our intuition and thus it is very difficult to find effective target genes to engineer. Together with gene amplification strategy, gene knockout strategy has been an essential tool in metabolic engineering to redirect the pathway fluxes toward our desired product formation. However, experiment to engineer many genes can be rather difficult due to the time and effort required; for example, gene deletion experiment can take a few weeks depending on the microorganisms. Furthermore, as certain genes are essential or play important roles for the survival of a microorganism, gene knockout experiments cannot be performed. Even worse, there are many different microbial strains one can employ. There are more than 50 different E. coli strains that metabolic engineer can consider to use. Since gene knockout experiment is hard-coded (that is, one should repeat the gene knockout experiments for each strain), the result cannot be easily transferred from one strain to another.
A paper published in Nature Biotechnology online today addresses this issue and suggests a new strategy for identifying gene targets to be knocked out or knocked down through the use of synthetic small RNA. A Korean research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), a prestigeous science and engineering university in Korea reported that synthetic small RNA can be employed for finely controlling the expression levels of multiple genes at the translation level. Already well-known for their systems metabolic engineering strategies, Professor Lee’s team added one more strategy to efficiently develop microbial cell factories for the production of chemicals and materials.
Gene expression works like this: the hard-coded blueprint (DNA) is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA), and the coding information in mRNA is read to produce protein by ribosomes. Conventional genetic engineering approaches have often targeted modification of the blueprint itself (DNA) to alter organism’s physiological characteristics. Again, engineering the blueprint itself takes much time and effort, and in addition, the results obtained cannot be transferred to another organism without repeating the whole set of experiments. This is why Professor Lee and his colleagues aimed at controlling the gene expression level at the translation stage through the use of synthetic small RNA. They created novel RNAs that can regulate the translation of multiple messenger RNAs (mRNA), and consequently varying the expression levels of multiple genes at the same time. Briefly, synthetic regulatory RNAs interrupt gene expression process from DNA to protein by destroying the messenger RNAs to different yet controllable extents. The advantages of taking this strategy of employing synthetic small regulatory RNAs include simple, easy and high-throughput identification of gene knockout or knockdown targets, fine control of gene expression levels, transferability to many different host strains, and possibility of identifying those gene targets that are essential.
As proof-of-concept demonstration of the usefulness of this strategy, Professor Lee and his colleagues applied it to develop engineered E. coli strains capable of producing an aromatic amino acid tyrosine, which is used for stress symptom relief, food supplements, and precursor for many drugs. They examined a large number of genes in multiple E. coli strains, and developed a highly efficient tyrosine producer. Also, they were able to show that this strategy can be employed to an already metabolically engineered E. coli strain for further improvement by demonstrating the development of highly efficient producer of cadaverine, an important platform chemical for nylon in the chemical industry.
This new strategy, being simple yet very powerful for systems metabolic engineering, is thus expected to facilitate the efficient development of microbial cell factories capable of producing chemicals, fuels and materials from renewable biomass.
Source: Dokyun Na, Seung Min Yoo, Hannah Chung, Hyegwon Park, Jin Hwan Park, and Sang Yup Lee, “Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using synthetic small regulatory RNAs”, Nature Biotechnology, doi:10.1038/nbt.2461 (2013)
2013.03.19 View 10282
An efficient strategy for developing microbial cell factories by employing synthetic small regulatory RNAs
A new metabolic engineering tool that allows fine control of gene expression level by employing synthetic small regulatory RNAs was developed to efficiently construct microbial cell factories producing desired chemicals and materials
Biotechnologists have been working hard to address the climate change and limited fossil resource issues through the development of sustainable processes for the production of chemicals, fuels and materials from renewable non-food biomass. One promising sustainable technology is the use of microbial cell factories for the efficient production of desired chemicals and materials. When microorganisms are isolated from nature, the performance in producing our desired product is rather poor. That is why metabolic engineering is performed to improve the metabolic and cellular characteristics to achieve enhanced production of desired product at high yield and productivity. Since the performance of microbial cell factory is very important in lowering the overall production cost of the bioprocess, many different strategies and tools have been developed for the metabolic engineering of microorganisms.
One of the big challenges in metabolic engineering is to find the best platform organism and to find those genes to be engineered so as to maximize the production efficiency of the desired chemical. Even Escherichia coli, the most widely utilized simple microorganism, has thousands of genes, the expression of which is highly regulated and interconnected to finely control cellular and metabolic activities. Thus, the complexity of cellular genetic interactions is beyond our intuition and thus it is very difficult to find effective target genes to engineer. Together with gene amplification strategy, gene knockout strategy has been an essential tool in metabolic engineering to redirect the pathway fluxes toward our desired product formation. However, experiment to engineer many genes can be rather difficult due to the time and effort required; for example, gene deletion experiment can take a few weeks depending on the microorganisms. Furthermore, as certain genes are essential or play important roles for the survival of a microorganism, gene knockout experiments cannot be performed. Even worse, there are many different microbial strains one can employ. There are more than 50 different E. coli strains that metabolic engineer can consider to use. Since gene knockout experiment is hard-coded (that is, one should repeat the gene knockout experiments for each strain), the result cannot be easily transferred from one strain to another.
A paper published in Nature Biotechnology online today addresses this issue and suggests a new strategy for identifying gene targets to be knocked out or knocked down through the use of synthetic small RNA. A Korean research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), a prestigeous science and engineering university in Korea reported that synthetic small RNA can be employed for finely controlling the expression levels of multiple genes at the translation level. Already well-known for their systems metabolic engineering strategies, Professor Lee’s team added one more strategy to efficiently develop microbial cell factories for the production of chemicals and materials.
Gene expression works like this: the hard-coded blueprint (DNA) is transcribed into messenger RNA (mRNA), and the coding information in mRNA is read to produce protein by ribosomes. Conventional genetic engineering approaches have often targeted modification of the blueprint itself (DNA) to alter organism’s physiological characteristics. Again, engineering the blueprint itself takes much time and effort, and in addition, the results obtained cannot be transferred to another organism without repeating the whole set of experiments. This is why Professor Lee and his colleagues aimed at controlling the gene expression level at the translation stage through the use of synthetic small RNA. They created novel RNAs that can regulate the translation of multiple messenger RNAs (mRNA), and consequently varying the expression levels of multiple genes at the same time. Briefly, synthetic regulatory RNAs interrupt gene expression process from DNA to protein by destroying the messenger RNAs to different yet controllable extents. The advantages of taking this strategy of employing synthetic small regulatory RNAs include simple, easy and high-throughput identification of gene knockout or knockdown targets, fine control of gene expression levels, transferability to many different host strains, and possibility of identifying those gene targets that are essential.
As proof-of-concept demonstration of the usefulness of this strategy, Professor Lee and his colleagues applied it to develop engineered E. coli strains capable of producing an aromatic amino acid tyrosine, which is used for stress symptom relief, food supplements, and precursor for many drugs. They examined a large number of genes in multiple E. coli strains, and developed a highly efficient tyrosine producer. Also, they were able to show that this strategy can be employed to an already metabolically engineered E. coli strain for further improvement by demonstrating the development of highly efficient producer of cadaverine, an important platform chemical for nylon in the chemical industry.
This new strategy, being simple yet very powerful for systems metabolic engineering, is thus expected to facilitate the efficient development of microbial cell factories capable of producing chemicals, fuels and materials from renewable biomass.
Source: Dokyun Na, Seung Min Yoo, Hannah Chung, Hyegwon Park, Jin Hwan Park, and Sang Yup Lee, “Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using synthetic small regulatory RNAs”, Nature Biotechnology, doi:10.1038/nbt.2461 (2013)
2013.03.19 View 10282 -
 KAIST Inaugurates Its 15th President
President Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang praised what KAIST has achieved as a powerful engine for the economic and industrial advancement of Korea over the past 41 years, while pledging to continue its endeavor “to go above and beyond its present accomplishments.”
KAIST inaugurated its 15th president, Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang, on February 27, 2013, in a ceremony at the auditorium of its main campus in Daejeon, South Korea. President Kang delivered his inauguration speech to 1,000 distinguished guests from government and public offices and the nation’s science community, including Chairman Myung Oh of the KAIST Board of Trustees, Former Presidents of KAIST Soon-Dal Choi and Chang-Sun Hong, Former National Assembly Member Yong-Kyung Lee, and members of the university.
In his speech, President Kang recalled that he had formed a strong bond with KAIST over many years, before assuming the presidency and extolled the university’s contribution to Korea’s current economic prowess. Referring to the “growing pains” that KAIST has experienced amid its successes, he vowed to unify the university community to take another leap forward:
We must ease the pain through trust and consideration for one another and join in unity to take steps toward the brighter tomorrow of KAIST. I humbly seek your help and pledge to put forth my utmost effort as a servant and leader.
Speaking of KAIST’s importance to the Korean nation, President Kang said, “Korea, as a nation lacking a deep pool of natural resources, must find innovative ways to compete globally to ensure the prosperity and well-being of its people.” He emphasized KAIST’s role as a catalyst to “lead the nation toward the frontiers of science and technology with fervor and responsibility.”
In order to become a global leader in higher learning and contribute to the advancement of science and technology in Korea and beyond, President Kang said that KAIST must do well in five areas with letters matching those of its own acronym: Knowledge creation, Advancement on all fronts, Integrity, Sustainability, and Trust.
In knowledge creation, the president pointed out the necessity of collaboration, student-centered and faculty-led research programs, and interdisciplinary research. For advancement on all fronts, he proposed redrafting KAIST’s future blueprint by consulting with all of its constituents and the Board of Trustees to improve the overall efficiency of the university.
President Kang added that KAIST should uphold integrity in all research publications, financial management, and human relations to withstand unforeseen challenges and problems and that is should seek sustainable value for education and research, not becoming overly driven by short-term research goals. Last, he said that KAIST must be an institution trusted by the public and KAIST faculty, students, and staff. This culture of trust can be made possible, he added, when the members of the university do their best to create an environment of understanding and caring for each other.
President Kang concluded his remarks by promising that he would always open his door and welcome anyone for visits, discussions, and sharing. Known as “Captain Smooth” for the well-rounded, warm, yet decisive leadership style that he showed during his chancellorship at the University of California, Merced, President Kang now pledges to guide KAIST to become better and stronger in the next four years. For a full transcript of the speech, download the PDF file below.
2013.03.13 View 8032
KAIST Inaugurates Its 15th President
President Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang praised what KAIST has achieved as a powerful engine for the economic and industrial advancement of Korea over the past 41 years, while pledging to continue its endeavor “to go above and beyond its present accomplishments.”
KAIST inaugurated its 15th president, Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang, on February 27, 2013, in a ceremony at the auditorium of its main campus in Daejeon, South Korea. President Kang delivered his inauguration speech to 1,000 distinguished guests from government and public offices and the nation’s science community, including Chairman Myung Oh of the KAIST Board of Trustees, Former Presidents of KAIST Soon-Dal Choi and Chang-Sun Hong, Former National Assembly Member Yong-Kyung Lee, and members of the university.
In his speech, President Kang recalled that he had formed a strong bond with KAIST over many years, before assuming the presidency and extolled the university’s contribution to Korea’s current economic prowess. Referring to the “growing pains” that KAIST has experienced amid its successes, he vowed to unify the university community to take another leap forward:
We must ease the pain through trust and consideration for one another and join in unity to take steps toward the brighter tomorrow of KAIST. I humbly seek your help and pledge to put forth my utmost effort as a servant and leader.
Speaking of KAIST’s importance to the Korean nation, President Kang said, “Korea, as a nation lacking a deep pool of natural resources, must find innovative ways to compete globally to ensure the prosperity and well-being of its people.” He emphasized KAIST’s role as a catalyst to “lead the nation toward the frontiers of science and technology with fervor and responsibility.”
In order to become a global leader in higher learning and contribute to the advancement of science and technology in Korea and beyond, President Kang said that KAIST must do well in five areas with letters matching those of its own acronym: Knowledge creation, Advancement on all fronts, Integrity, Sustainability, and Trust.
In knowledge creation, the president pointed out the necessity of collaboration, student-centered and faculty-led research programs, and interdisciplinary research. For advancement on all fronts, he proposed redrafting KAIST’s future blueprint by consulting with all of its constituents and the Board of Trustees to improve the overall efficiency of the university.
President Kang added that KAIST should uphold integrity in all research publications, financial management, and human relations to withstand unforeseen challenges and problems and that is should seek sustainable value for education and research, not becoming overly driven by short-term research goals. Last, he said that KAIST must be an institution trusted by the public and KAIST faculty, students, and staff. This culture of trust can be made possible, he added, when the members of the university do their best to create an environment of understanding and caring for each other.
President Kang concluded his remarks by promising that he would always open his door and welcome anyone for visits, discussions, and sharing. Known as “Captain Smooth” for the well-rounded, warm, yet decisive leadership style that he showed during his chancellorship at the University of California, Merced, President Kang now pledges to guide KAIST to become better and stronger in the next four years. For a full transcript of the speech, download the PDF file below.
2013.03.13 View 8032 -
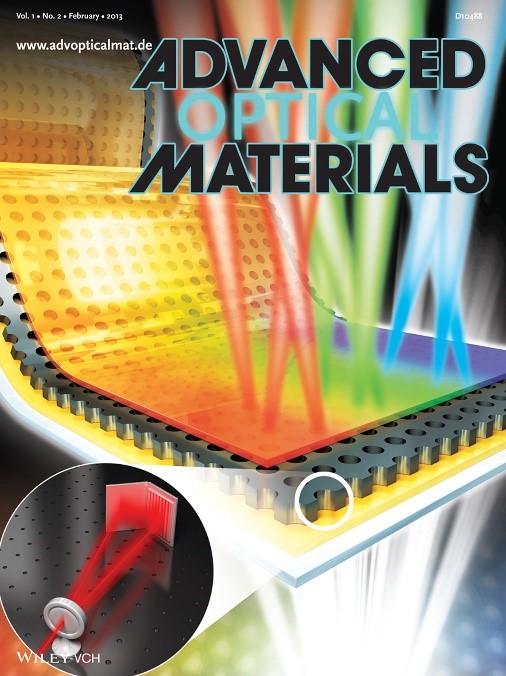 New Technology Will Enable the Commercialization of Plasmon Displays
-- Enhancements in the penetration ratios of color filters are expected by applying nano-surface plasmon effects. --
-- Color filter technology will be applicable to large-area OLED and LCD. --
The fabrication technology to commercialize display color filters using plasmon effects has been discovered.
A joint research team headed by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the Department of Electrical Engineering of the Korea Advanced Institute for Science and Technology and Prof. Byeong-Kwon Ju from the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University has developed the technology to design and produce a display color filter by applying nano-surface plasmon effects.
Color filters are core components used to express colors in CMOS image sensors found in LCD/OLED displays or digital cameras. The current color filters have penetration ratios of 20~30%, but the objective of the joint research team is to raise this penetration ratio by over 40% to facilitate the mass production of energy-efficient plasmonic displays.
Currently available plasmonic color filters are limited to applications on micrometer scales. However, outcomes of the newest research extend the size of the applications up to 2.5 cm by using laser interference lithography. The academic and industrial sectors agree that it is now possible to mass-produce displays using plasmonic color filters.
The researchers built a nanohole array to large scale by using laser interference lithography, a technology that forms nanostructures with laser light interferences. They also suggested a new manufacturing process that can optimize the features of color filters while compensating for defects arising from the fabrication stages.
The new manufacturing process of applying laser interference lithography is expected to overcome the shortcomings of traditional color filters by simplifying production and, enabling them to be produced at lower costs.
“There were limitations to industrial applications of plasmon effect due to production costs, time, and yields,” explained Yun Seon Do, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Electrical Engineering of KAIST. “The new technology can reduce fabrication time and cost to the extent that it would be advisable to replace dye-based and pigment-based color filter technology."
“This research can be applied to large-scale displays, such as TV screens, by using laser-interference lithography,” said Jung-Ho Park, a Ph. D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University. “The research outcome is expected to be widely applied in advanced nano-manufacturing processes as it does not restrict the types of circuit boards."
The research outcome, led by doctoral candidates Do and Park, appeared on the front cover of the second issue of Advanced Optical Materials, a highly regarded academic journal in the field of nanotechnologies, and the team has applied for six related patents.
2013.03.13 View 9108
New Technology Will Enable the Commercialization of Plasmon Displays
-- Enhancements in the penetration ratios of color filters are expected by applying nano-surface plasmon effects. --
-- Color filter technology will be applicable to large-area OLED and LCD. --
The fabrication technology to commercialize display color filters using plasmon effects has been discovered.
A joint research team headed by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the Department of Electrical Engineering of the Korea Advanced Institute for Science and Technology and Prof. Byeong-Kwon Ju from the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University has developed the technology to design and produce a display color filter by applying nano-surface plasmon effects.
Color filters are core components used to express colors in CMOS image sensors found in LCD/OLED displays or digital cameras. The current color filters have penetration ratios of 20~30%, but the objective of the joint research team is to raise this penetration ratio by over 40% to facilitate the mass production of energy-efficient plasmonic displays.
Currently available plasmonic color filters are limited to applications on micrometer scales. However, outcomes of the newest research extend the size of the applications up to 2.5 cm by using laser interference lithography. The academic and industrial sectors agree that it is now possible to mass-produce displays using plasmonic color filters.
The researchers built a nanohole array to large scale by using laser interference lithography, a technology that forms nanostructures with laser light interferences. They also suggested a new manufacturing process that can optimize the features of color filters while compensating for defects arising from the fabrication stages.
The new manufacturing process of applying laser interference lithography is expected to overcome the shortcomings of traditional color filters by simplifying production and, enabling them to be produced at lower costs.
“There were limitations to industrial applications of plasmon effect due to production costs, time, and yields,” explained Yun Seon Do, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Electrical Engineering of KAIST. “The new technology can reduce fabrication time and cost to the extent that it would be advisable to replace dye-based and pigment-based color filter technology."
“This research can be applied to large-scale displays, such as TV screens, by using laser-interference lithography,” said Jung-Ho Park, a Ph. D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University. “The research outcome is expected to be widely applied in advanced nano-manufacturing processes as it does not restrict the types of circuit boards."
The research outcome, led by doctoral candidates Do and Park, appeared on the front cover of the second issue of Advanced Optical Materials, a highly regarded academic journal in the field of nanotechnologies, and the team has applied for six related patents.
2013.03.13 View 9108 -
 Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 11290
Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 11290 -
 A Substance with Amazingly Improved Efficiency of Capturing Carbon Dioxides Developed
From left to right: Prof.Ali Coskun, Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Yousung Jung
- Selectivity of CO2 increased by 300 times in comparison to nitrogen, published in Nature Communications-
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s joint research team led by Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, Prof. Ali Coskun, and Prof. Yousung Jung has developed the world"s most efficient CO2 absorbent that has 300 times higher carbon dioxide selectivity in comparison to nitrogen.
Recently, the importance of CCS* technology, which is about capturing, storing and treating carbon dioxides, has begun to emerge world-widely as a practical alternative for the response to climate change.
* CCS : Carbon Capture and sequestration
Current carbon dioxide capturing technologies are wet capturing using liquid absorbent, dry capturing using solid absorbent and separation-membrane capturing using a thin membrane like a film.
For the places like power plant and forge, where the emission of carbon dioxides is huge, the main task is to maintain the capturing efficiency under extremely hot and humid conditions.
The previously studied dry absorbents, such as MOF or zeolite, had the disadvantages of instability in moist conditions and expensive cost for synthesis.
On the other hand, the research team"s newly discovered dry absorbent, named ‘Azo-COP’, can be synthesized without any expensive catalysts so the production cost is very low. It is also stable under hot and humid conditions.
COP is a structure consisting of simple organic molecules combined into porous polymer and is the first dry carbon dioxide capturing material developed by this research team.
The research team introduced an additional functional group called "Azo" to the substance, so that it can selectively capture carbon dioxides among the mixture of gas.
Azo-COP, which includes ‘Azo’ functional group, is manufactured easily by using common synthesis methods, and impurities are removed simply by using cheap solvents like water and acetone instead of expensive catalysts. As a result, the manufacturing cost has lowered drastically.
Especially, Azo-COP is combined with carbon dioxides by weak attraction force rather than chemical attraction so the recycling energy cost for the absorbent can be reduced innovatively, and it is expected to be used for capturing substances other than carbon dioxides in various areas as it is stable under extreme conditions even under 350 degrees Celsius.
This research is supported by Korea Carbon Capture&Sequestration R&D Center(Head: Sangdo Park) and KAIST EEWS planning group.
Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Ali Coskun said that “when Azo-COP is used for separation of CO2 and N2, the capturing efficiency has increased by hundred times.” He continued “This substance does not need any catalysts and has great chemical characteristics like water stability and structure stability so is expected to be used in various fields including carbon dioxides capturing”
Meanwhile, this research is published in ‘Nature’s stablemate ‘Nature Communications’ on 15th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 12448
A Substance with Amazingly Improved Efficiency of Capturing Carbon Dioxides Developed
From left to right: Prof.Ali Coskun, Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Yousung Jung
- Selectivity of CO2 increased by 300 times in comparison to nitrogen, published in Nature Communications-
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s joint research team led by Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, Prof. Ali Coskun, and Prof. Yousung Jung has developed the world"s most efficient CO2 absorbent that has 300 times higher carbon dioxide selectivity in comparison to nitrogen.
Recently, the importance of CCS* technology, which is about capturing, storing and treating carbon dioxides, has begun to emerge world-widely as a practical alternative for the response to climate change.
* CCS : Carbon Capture and sequestration
Current carbon dioxide capturing technologies are wet capturing using liquid absorbent, dry capturing using solid absorbent and separation-membrane capturing using a thin membrane like a film.
For the places like power plant and forge, where the emission of carbon dioxides is huge, the main task is to maintain the capturing efficiency under extremely hot and humid conditions.
The previously studied dry absorbents, such as MOF or zeolite, had the disadvantages of instability in moist conditions and expensive cost for synthesis.
On the other hand, the research team"s newly discovered dry absorbent, named ‘Azo-COP’, can be synthesized without any expensive catalysts so the production cost is very low. It is also stable under hot and humid conditions.
COP is a structure consisting of simple organic molecules combined into porous polymer and is the first dry carbon dioxide capturing material developed by this research team.
The research team introduced an additional functional group called "Azo" to the substance, so that it can selectively capture carbon dioxides among the mixture of gas.
Azo-COP, which includes ‘Azo’ functional group, is manufactured easily by using common synthesis methods, and impurities are removed simply by using cheap solvents like water and acetone instead of expensive catalysts. As a result, the manufacturing cost has lowered drastically.
Especially, Azo-COP is combined with carbon dioxides by weak attraction force rather than chemical attraction so the recycling energy cost for the absorbent can be reduced innovatively, and it is expected to be used for capturing substances other than carbon dioxides in various areas as it is stable under extreme conditions even under 350 degrees Celsius.
This research is supported by Korea Carbon Capture&Sequestration R&D Center(Head: Sangdo Park) and KAIST EEWS planning group.
Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz and Prof. Ali Coskun said that “when Azo-COP is used for separation of CO2 and N2, the capturing efficiency has increased by hundred times.” He continued “This substance does not need any catalysts and has great chemical characteristics like water stability and structure stability so is expected to be used in various fields including carbon dioxides capturing”
Meanwhile, this research is published in ‘Nature’s stablemate ‘Nature Communications’ on 15th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 12448 -
 Online Article on President Sung-Mo 'Steve' Kang by California Council on Science and Technology (CCST)
The California Council on Science and Technology (CCST), an independent, not-for-profit organization established by the mandate of California Legislature in 1988, is designed to offer expert advice to the California state government and recommend solutions to science and technology-related policy issues.
Over the past three years, President Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang has served as a member of CCST Council, an assembly of corporate CEOs, academicians, scientists, and scholars of the highest distinction.
On February 21, 2013, CCST posted on its website the announcement of Council Member Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang as President of KAIST along with his personal comments on his move to KAIST and its presidency. For the online article, please visit: http://www.ccst.us/news/2013/0221KAIST.php
2013.02.23 View 8326
Online Article on President Sung-Mo 'Steve' Kang by California Council on Science and Technology (CCST)
The California Council on Science and Technology (CCST), an independent, not-for-profit organization established by the mandate of California Legislature in 1988, is designed to offer expert advice to the California state government and recommend solutions to science and technology-related policy issues.
Over the past three years, President Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang has served as a member of CCST Council, an assembly of corporate CEOs, academicians, scientists, and scholars of the highest distinction.
On February 21, 2013, CCST posted on its website the announcement of Council Member Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang as President of KAIST along with his personal comments on his move to KAIST and its presidency. For the online article, please visit: http://www.ccst.us/news/2013/0221KAIST.php
2013.02.23 View 8326 -
 New BioFactory Technique Developed using sRNAs
Professor Sang Yup Lee
- published on the online edition of Nature Biotechnology. “Expected as a new strategy for the bio industry that may replace the chemical industry.”-
KAIST Chemical & Biomolecular engineering department’s Professor Sang Yup Lee and his team has developed a new technology that utilizes the synthetic small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) to implement the BioFactory in a larger scale with more effectiveness.
* BioFactory: Microbial-based production system which creates the desired compound in mass by manipulating the genes of the cell.
In order to solve the problems of modern society, such as environmental pollution caused by the exhaustion of fossil fuels and usage of petrochemical products, an eco-friendly and sustainable bio industry is on the rise. BioFactory development technology has especially attracted the attention world-wide, with its ability to produce bio-energy, pharmaceuticals, eco-friendly materials and more.
For the development of an excellent BioFactory, selection for the gene that produces the desired compounds must be accompanied by finding the microorganism with high production efficiency; however, the previous research method had a complicated and time-consuming problem of having to manipulate the genes of the microorganism one by one.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team, including Dr. Dokyun Na and Dr. Seung Min Yoo, has produced the synthetic sRNAs and utilized it to overcome the technical limitations mentioned above.
In particular, unlike the existing method, this technology using synthetic sRNAs exhibits no strain specificity which can dramatically shorten the experiment that used to take months to just a few days.
The research team applied the synthetic small regulatory RNA technology to the production of the tyrosine*, which is used as the precursor of the medicinal compound, and cadaverine**, widely utilized in a variety of petrochemical products, and has succeeded developing BioFactory with the world’s highest yield rate (21.9g /L, 12.6g / L each).
*tyrosine: amino acid known to control stress and improve concentration
**cadaverine: base material used in many petrochemical products, such as polyurethane
Professor Sang Yup Lee highlighted the significance of this research: “it is expected the synthetic small regulatory RNA technology will stimulate the BioFactory development and also serve as a catalyst which can make the chemical industry, currently represented by its petroleum energy, transform into bio industry.”
The study was carried out with the support of Global Frontier Project (Intelligent Bio-Systems Design and Synthesis Research Unit (Chief Seon Chang Kim)) and the findings have been published on January 20th in the online edition of the worldwide journal Nature Biotechnology.
2013.02.21 View 11375
New BioFactory Technique Developed using sRNAs
Professor Sang Yup Lee
- published on the online edition of Nature Biotechnology. “Expected as a new strategy for the bio industry that may replace the chemical industry.”-
KAIST Chemical & Biomolecular engineering department’s Professor Sang Yup Lee and his team has developed a new technology that utilizes the synthetic small regulatory RNAs (sRNAs) to implement the BioFactory in a larger scale with more effectiveness.
* BioFactory: Microbial-based production system which creates the desired compound in mass by manipulating the genes of the cell.
In order to solve the problems of modern society, such as environmental pollution caused by the exhaustion of fossil fuels and usage of petrochemical products, an eco-friendly and sustainable bio industry is on the rise. BioFactory development technology has especially attracted the attention world-wide, with its ability to produce bio-energy, pharmaceuticals, eco-friendly materials and more.
For the development of an excellent BioFactory, selection for the gene that produces the desired compounds must be accompanied by finding the microorganism with high production efficiency; however, the previous research method had a complicated and time-consuming problem of having to manipulate the genes of the microorganism one by one.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team, including Dr. Dokyun Na and Dr. Seung Min Yoo, has produced the synthetic sRNAs and utilized it to overcome the technical limitations mentioned above.
In particular, unlike the existing method, this technology using synthetic sRNAs exhibits no strain specificity which can dramatically shorten the experiment that used to take months to just a few days.
The research team applied the synthetic small regulatory RNA technology to the production of the tyrosine*, which is used as the precursor of the medicinal compound, and cadaverine**, widely utilized in a variety of petrochemical products, and has succeeded developing BioFactory with the world’s highest yield rate (21.9g /L, 12.6g / L each).
*tyrosine: amino acid known to control stress and improve concentration
**cadaverine: base material used in many petrochemical products, such as polyurethane
Professor Sang Yup Lee highlighted the significance of this research: “it is expected the synthetic small regulatory RNA technology will stimulate the BioFactory development and also serve as a catalyst which can make the chemical industry, currently represented by its petroleum energy, transform into bio industry.”
The study was carried out with the support of Global Frontier Project (Intelligent Bio-Systems Design and Synthesis Research Unit (Chief Seon Chang Kim)) and the findings have been published on January 20th in the online edition of the worldwide journal Nature Biotechnology.
2013.02.21 View 11375 -
 Professor Shin In Shik First in Asia to receive Excellent Dissertation Award from IEEE RTSS
The research team lead by Professor Shin In Shik (Department of Computer Science) received the Excellent Dissertation Awardy in the IEEE RTSS out of 157 dissertations.
It is the first time a Professor under an institute in the Asia region received the Award in the RTSS field during its 33 year history.
Professor Shin had already received an Excellent Dissertation Award as a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Pennsylvania. Thus Professor Shin became the first and only scientist to receive the Award twice.
Professor Shin has successfully defined the scheduling method of the multicore processor which was regarded as the problem in the field of RTSS for the past decade.
Professor Shin has suggested new criteria for sorting real time tasks in parallel thereby suggesting a new scheduling method that surpasses current scheduling methods. The results are anticipated to provide new perspectives in the field of RTSS using multicore processors.
2013.01.22 View 8548
Professor Shin In Shik First in Asia to receive Excellent Dissertation Award from IEEE RTSS
The research team lead by Professor Shin In Shik (Department of Computer Science) received the Excellent Dissertation Awardy in the IEEE RTSS out of 157 dissertations.
It is the first time a Professor under an institute in the Asia region received the Award in the RTSS field during its 33 year history.
Professor Shin had already received an Excellent Dissertation Award as a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Pennsylvania. Thus Professor Shin became the first and only scientist to receive the Award twice.
Professor Shin has successfully defined the scheduling method of the multicore processor which was regarded as the problem in the field of RTSS for the past decade.
Professor Shin has suggested new criteria for sorting real time tasks in parallel thereby suggesting a new scheduling method that surpasses current scheduling methods. The results are anticipated to provide new perspectives in the field of RTSS using multicore processors.
2013.01.22 View 8548 -
 KAIST OLEV (On-Line Electric Vehicle) to begin operation!
An On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) that can charge during travel will be put into service for the first time in the world on normal roads.
From July of this year 2 OLEV buses will undergo trial operations in the city of Gumi.
The trial route spans 24km from Gumi station and the region of In-Dong and the establishment of the route is expected to be of a 4.8billion Won scale. The start of the infrastructure construction will start on February and operation will start in July.
KAIST had held sessions in October of last year to local governments and had a follow up OLEV suitability evaluation to those local governments expressing interest.
The city of Gumi was elected due to its good electrical infrastructure and an administrative willingness to match.
The OLEV developed by KAIST is an environmentally friendly vehicle that allows the transfer of electrical power using magnetic fields imbedded in the roads.
Ordinary electric vehicles require frequent visits to replenish their power which gives the OLEV a comparative advantage as it can charge while on the road. The ability to charge whilst on the road means that the OLEV requires a smaller battery than the ordinary electrical vehicle resulting in lower prices and weight.
The OLEV development commenced at KAIST in 2009 and in 2010 most of the core technologies required to realize the OLEV was developed and verified. Finally in 2012 steps were taken that will allow the commercialization of the OLEV.
And in October of last year KAIST OLEV accomplished 75% power transfer efficiency that allowed a system that can be commercialized.
The KAIST OLEV was named top 50 inventions in 2010 by Time Magazine.
2013.01.22 View 11139
KAIST OLEV (On-Line Electric Vehicle) to begin operation!
An On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) that can charge during travel will be put into service for the first time in the world on normal roads.
From July of this year 2 OLEV buses will undergo trial operations in the city of Gumi.
The trial route spans 24km from Gumi station and the region of In-Dong and the establishment of the route is expected to be of a 4.8billion Won scale. The start of the infrastructure construction will start on February and operation will start in July.
KAIST had held sessions in October of last year to local governments and had a follow up OLEV suitability evaluation to those local governments expressing interest.
The city of Gumi was elected due to its good electrical infrastructure and an administrative willingness to match.
The OLEV developed by KAIST is an environmentally friendly vehicle that allows the transfer of electrical power using magnetic fields imbedded in the roads.
Ordinary electric vehicles require frequent visits to replenish their power which gives the OLEV a comparative advantage as it can charge while on the road. The ability to charge whilst on the road means that the OLEV requires a smaller battery than the ordinary electrical vehicle resulting in lower prices and weight.
The OLEV development commenced at KAIST in 2009 and in 2010 most of the core technologies required to realize the OLEV was developed and verified. Finally in 2012 steps were taken that will allow the commercialization of the OLEV.
And in October of last year KAIST OLEV accomplished 75% power transfer efficiency that allowed a system that can be commercialized.
The KAIST OLEV was named top 50 inventions in 2010 by Time Magazine.
2013.01.22 View 11139 -
 Professor Lee Jeong Yong Receives 2012 'KAISTian of the Year' Award
Professor Lee Jeong Yong (Department of Material Science and Engineering) received the 2012 ‘KAISTian of the Year’ Award.
Professor Lee had successfully developed a technique that allowed the observation and analysis of liquid in atomic scale.
The technique is expected to have great impact on nano-material synthesis in solution, explaining electrode and electrolyte reaction, liquid and catalysis reaction research, and etc. and was therefore named as the best experimental accomplishment in KAIST in 2012.
Professor Lee and his team’s finding has been published in the April edition of Science magazine and has had attracted the attention of the world. In addition, BBC News, and Science & Environment reported on the findings as their respective top articles.
The optical microscope is incapable of atomic scale observation and the electron microscopes are capable but because of the vacuum state all liquids undergo evaporation making it impossible to observe liquids in an atomic scale.
Professor Lee’s team wrapped the liquid with a layer of grapheme to prevent evaporation and successfully observed real time the platinum growth process in solution.
Professor Lee’s findings were introduced as an example of exemplar research case in the Presidential address for ‘Science Day’ in April.
2013.01.22 View 9375
Professor Lee Jeong Yong Receives 2012 'KAISTian of the Year' Award
Professor Lee Jeong Yong (Department of Material Science and Engineering) received the 2012 ‘KAISTian of the Year’ Award.
Professor Lee had successfully developed a technique that allowed the observation and analysis of liquid in atomic scale.
The technique is expected to have great impact on nano-material synthesis in solution, explaining electrode and electrolyte reaction, liquid and catalysis reaction research, and etc. and was therefore named as the best experimental accomplishment in KAIST in 2012.
Professor Lee and his team’s finding has been published in the April edition of Science magazine and has had attracted the attention of the world. In addition, BBC News, and Science & Environment reported on the findings as their respective top articles.
The optical microscope is incapable of atomic scale observation and the electron microscopes are capable but because of the vacuum state all liquids undergo evaporation making it impossible to observe liquids in an atomic scale.
Professor Lee’s team wrapped the liquid with a layer of grapheme to prevent evaporation and successfully observed real time the platinum growth process in solution.
Professor Lee’s findings were introduced as an example of exemplar research case in the Presidential address for ‘Science Day’ in April.
2013.01.22 View 9375 -
 KAIST Alumni Association Selects 'Proud Alums'
KAIST Alumni Association selected ‘Proud Alums’ who have contributed to the development of Korea and society and brought honor to KAIST.
The Alums selected were: CEO of Hyundai Heavy Industry Lee Jae Seong, Vice President of SK Hynix Park Sang Hoon, President of Samsung Display Kim Ki Nam, Director of Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science Kang Dae Lim, and President of Dawonsys Park Sun Soon.
Lee Jae Song (Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, M.S. 3rd) has led Hyundai Heavy Industries through innovation and had contributed in the development of Korea and oversaw the growth of Hyundai Heavy Industries to number 1 in Shipbuilding.
Park Sang Hoon (Biological and Chemical Engineering, M.S. 5th) has led SK Hynix in the fields of energy, chemical and biological medicine and oversaw the development of world class R&D and production technologies to aid the development of Korea.
Kim Ki Nam (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 9th) has led the development of innovative semiconductor technologies thereby helping strengthening the competitiveness of Korean semiconductor industry.
Kang Dae Lim (Mechanical Engineering, Ph.D. 1994 graduate) has helped in the development of Korean science and technology by leading the field of measurement standardization as Chairman of International Measurement Confederation and Chairman of Korea Association of Standards & Testing Organizations.
Park Sun Soon (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 12th) has succeeded in advancing the field of electronics by pioneering the field of creative technology.
2013.01.22 View 9997
KAIST Alumni Association Selects 'Proud Alums'
KAIST Alumni Association selected ‘Proud Alums’ who have contributed to the development of Korea and society and brought honor to KAIST.
The Alums selected were: CEO of Hyundai Heavy Industry Lee Jae Seong, Vice President of SK Hynix Park Sang Hoon, President of Samsung Display Kim Ki Nam, Director of Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science Kang Dae Lim, and President of Dawonsys Park Sun Soon.
Lee Jae Song (Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, M.S. 3rd) has led Hyundai Heavy Industries through innovation and had contributed in the development of Korea and oversaw the growth of Hyundai Heavy Industries to number 1 in Shipbuilding.
Park Sang Hoon (Biological and Chemical Engineering, M.S. 5th) has led SK Hynix in the fields of energy, chemical and biological medicine and oversaw the development of world class R&D and production technologies to aid the development of Korea.
Kim Ki Nam (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 9th) has led the development of innovative semiconductor technologies thereby helping strengthening the competitiveness of Korean semiconductor industry.
Kang Dae Lim (Mechanical Engineering, Ph.D. 1994 graduate) has helped in the development of Korean science and technology by leading the field of measurement standardization as Chairman of International Measurement Confederation and Chairman of Korea Association of Standards & Testing Organizations.
Park Sun Soon (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 12th) has succeeded in advancing the field of electronics by pioneering the field of creative technology.
2013.01.22 View 9997