AT
-
 SPIE (The International Society for Optics and Photonics): Scattering Super-lens
The International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE), dedicated to advancing an interdisciplinary approach to the science and application of light, published online a short paper authored by a KAIST research team, Dr. Jung-Hoon Park and Professor YongKeun Park of Physics, introducing a new optical technology to observe sub-wavelength light by exploiting multiple light scattering in complex media.
For the article, please go to the link below:
SPIE: Nanotechnology
May 7th, 2014
"Scattering superlens" by Jung-Hoon Park and YongKeun Park
http://spie.org/x108298.xml
2014.05.14 View 7310
SPIE (The International Society for Optics and Photonics): Scattering Super-lens
The International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE), dedicated to advancing an interdisciplinary approach to the science and application of light, published online a short paper authored by a KAIST research team, Dr. Jung-Hoon Park and Professor YongKeun Park of Physics, introducing a new optical technology to observe sub-wavelength light by exploiting multiple light scattering in complex media.
For the article, please go to the link below:
SPIE: Nanotechnology
May 7th, 2014
"Scattering superlens" by Jung-Hoon Park and YongKeun Park
http://spie.org/x108298.xml
2014.05.14 View 7310 -
 Professor Jae-Kyu Lee Elected to Head the Association for Information Systems
Jae Kyu Lee, HHI (Hyundai Heavy Industries, Co., Ltd.) Chair Professor, College of Business at KAIST, has been elected to lead the world major academic society, Association for Information Systems (AIS), from July 2015 to June 2016. Professor Lee will be the first Korean to serve the organization as president. From July 2014 to June 2015, he will serve as president-elect.
Currently, Professor Lee is the Director of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability) Research Center at KAIST, focusing on research and development in finding solutions to critical issues facing humanity. He also played a pivotal role in the conclusion of a memorandum of understanding between HHI and KAIST in June 2013 to establish HHI-KAIST EEWS Research Center within the KAIST campus.
The AIS is the premier professional association for individuals and organizations who lead the research, teaching, practice, and study of information systems worldwide.
2014.05.14 View 10249
Professor Jae-Kyu Lee Elected to Head the Association for Information Systems
Jae Kyu Lee, HHI (Hyundai Heavy Industries, Co., Ltd.) Chair Professor, College of Business at KAIST, has been elected to lead the world major academic society, Association for Information Systems (AIS), from July 2015 to June 2016. Professor Lee will be the first Korean to serve the organization as president. From July 2014 to June 2015, he will serve as president-elect.
Currently, Professor Lee is the Director of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability) Research Center at KAIST, focusing on research and development in finding solutions to critical issues facing humanity. He also played a pivotal role in the conclusion of a memorandum of understanding between HHI and KAIST in June 2013 to establish HHI-KAIST EEWS Research Center within the KAIST campus.
The AIS is the premier professional association for individuals and organizations who lead the research, teaching, practice, and study of information systems worldwide.
2014.05.14 View 10249 -
 Yong-Joon Park, doctoral student, receives the Korea Dow Chemical Award 2014
Yong-Joon Park, a Ph.D. candidate of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, received the Korea Dow Chemical Award 2014, a prestigious recognition of the year’s best paper produced by students in the field of chemistry and materials science.
The award ceremony took place on April 18, 2014 at Ilsan Kintex, Republic of Korea.
The Korea Dow Chemical Award is annually given by Korea Dow Chemical and the Korean Chemical Society to outstanding papers produced by graduate and postdoc students. This year, a total of nine papers were selected out of 148 papers submitted.
The title of Park’s paper is “The Development of 3D Nano-structure-based New Concept Super-elastic Materials.” This material could be used in flexible electronic devices such as displays and wearable computers.
2014.05.03 View 8894
Yong-Joon Park, doctoral student, receives the Korea Dow Chemical Award 2014
Yong-Joon Park, a Ph.D. candidate of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, received the Korea Dow Chemical Award 2014, a prestigious recognition of the year’s best paper produced by students in the field of chemistry and materials science.
The award ceremony took place on April 18, 2014 at Ilsan Kintex, Republic of Korea.
The Korea Dow Chemical Award is annually given by Korea Dow Chemical and the Korean Chemical Society to outstanding papers produced by graduate and postdoc students. This year, a total of nine papers were selected out of 148 papers submitted.
The title of Park’s paper is “The Development of 3D Nano-structure-based New Concept Super-elastic Materials.” This material could be used in flexible electronic devices such as displays and wearable computers.
2014.05.03 View 8894 -
 KAIST ranked third in the top 100 universities under 50 years old
The Times Higher Education (THE) released on April 30, 2014 its annual ranking of 100 top universities whose history is under 50 years.
KAIST placed 3rd, holding the same spot from last year.
The (THE) 100 Under 50 ranking used 13 indicators across five factors to measure the performance of institutions: research, citations, teaching, international outlook, and industry income. The indicators included research volume and income, reputation, learning environment, staff-to-student ratio, scholarly papers produced, and the percentage of international staff as part of the institution’s faculty.
Phil Baty, editor of the Times ranking, compared younger and older universities as follows:
“Young universities are free to be more agile, lean, and risk-taking, giving them an advantage in a rapidly changing global marketplace. They are also free to offer innovative teaching and focus their research in niche, high-impact areas.”
KAIST and Pohang University of Science and Technology (ranked first) are the only Korean universities that made the ranking list.
For the full list, please go to:
http://www.timeshighereducation.co.uk/world-university-rankings/2014/one-hundred-under-fifty
This information was provided by the Times Higher Education 100 Under 50.
2014.05.03 View 11180
KAIST ranked third in the top 100 universities under 50 years old
The Times Higher Education (THE) released on April 30, 2014 its annual ranking of 100 top universities whose history is under 50 years.
KAIST placed 3rd, holding the same spot from last year.
The (THE) 100 Under 50 ranking used 13 indicators across five factors to measure the performance of institutions: research, citations, teaching, international outlook, and industry income. The indicators included research volume and income, reputation, learning environment, staff-to-student ratio, scholarly papers produced, and the percentage of international staff as part of the institution’s faculty.
Phil Baty, editor of the Times ranking, compared younger and older universities as follows:
“Young universities are free to be more agile, lean, and risk-taking, giving them an advantage in a rapidly changing global marketplace. They are also free to offer innovative teaching and focus their research in niche, high-impact areas.”
KAIST and Pohang University of Science and Technology (ranked first) are the only Korean universities that made the ranking list.
For the full list, please go to:
http://www.timeshighereducation.co.uk/world-university-rankings/2014/one-hundred-under-fifty
This information was provided by the Times Higher Education 100 Under 50.
2014.05.03 View 11180 -
 Binding Regulatory Mechanism of Protein Biomolecules Revealed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim
A research team led by Professor Hak-Sung Kim of Biological Sciences, KAIST, and Dr. Mun-Hyeong Seo, KAIST, has revealed a regulatory mechanism that controls the binding affinity of protein’s biomolecules, which is crucial for the protein to recognize molecules and carry out functions within the body.
The research results were published in the April 24th online edition of Nature Communications.
The protein, represented by enzyme, antibody, or hormones, specifically recognizes a variety of biomolecules in all organisms and implements signaling or immune response to precisely adjust and maintain important biological processes. The protein binding affinity of biomolecules plays a crucial role in determining the duration of the bond between two molecules, and hence to determine and control the in-vivo function of proteins.
The researchers have noted that, during the process of proteins’ recognizing biomolecules, the protein binding affinity of biomolecules is closely linked not only to the size of non-covalent interaction between two molecules, but also to the unique kinetic properties of proteins.
To identify the basic mechanism that determines the protein binding affinity of biomolecules, Professor Kim and his research team have made mutation in the allosteric site of protein to create a variety of mutant proteins with the same chemical binding surface, but with the binding affinity vastly differing from 10 to 100 times. The allosteric site of the protein refers to a region which does not directly bind with biomolecules, but crucially influences the biomolecule recognition site.
Using real-time analysis at the single-molecule level of unique kinetic properties of the produced mutant proteins, the researchers were able to identify that the protein binding affinity of biomolecules is directly associated with the protein’s specific kinetic characteristics, its structure opening rate.
Also, by proving that unique characteristics of the protein can be changed at the allosteric site, instead of protein’s direct binding site with biomolecules, the researchers have demonstrated a new methodology of regulating the in-vivo function of proteins.
The researchers expect that these results will contribute greatly to a deeper understanding of protein’s nature that governs various life phenomena and help evaluate the proof of interpreting protein binding affinity of biomolecules from the perspective of protein kinetics.
Professor Kim said, “Until now, the protein binding affinity of biomolecules was determined by a direct interaction between two molecules. Our research has identified an important fact that the structure opening rate of proteins also plays a crucial role in determining their binding affinity.”
[Picture]
A correlation graph of opening rate (kopening) and binding affinity (kd) between protein’s stable, open state and its unstable, partially closed state.
2014.05.02 View 9985
Binding Regulatory Mechanism of Protein Biomolecules Revealed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim
A research team led by Professor Hak-Sung Kim of Biological Sciences, KAIST, and Dr. Mun-Hyeong Seo, KAIST, has revealed a regulatory mechanism that controls the binding affinity of protein’s biomolecules, which is crucial for the protein to recognize molecules and carry out functions within the body.
The research results were published in the April 24th online edition of Nature Communications.
The protein, represented by enzyme, antibody, or hormones, specifically recognizes a variety of biomolecules in all organisms and implements signaling or immune response to precisely adjust and maintain important biological processes. The protein binding affinity of biomolecules plays a crucial role in determining the duration of the bond between two molecules, and hence to determine and control the in-vivo function of proteins.
The researchers have noted that, during the process of proteins’ recognizing biomolecules, the protein binding affinity of biomolecules is closely linked not only to the size of non-covalent interaction between two molecules, but also to the unique kinetic properties of proteins.
To identify the basic mechanism that determines the protein binding affinity of biomolecules, Professor Kim and his research team have made mutation in the allosteric site of protein to create a variety of mutant proteins with the same chemical binding surface, but with the binding affinity vastly differing from 10 to 100 times. The allosteric site of the protein refers to a region which does not directly bind with biomolecules, but crucially influences the biomolecule recognition site.
Using real-time analysis at the single-molecule level of unique kinetic properties of the produced mutant proteins, the researchers were able to identify that the protein binding affinity of biomolecules is directly associated with the protein’s specific kinetic characteristics, its structure opening rate.
Also, by proving that unique characteristics of the protein can be changed at the allosteric site, instead of protein’s direct binding site with biomolecules, the researchers have demonstrated a new methodology of regulating the in-vivo function of proteins.
The researchers expect that these results will contribute greatly to a deeper understanding of protein’s nature that governs various life phenomena and help evaluate the proof of interpreting protein binding affinity of biomolecules from the perspective of protein kinetics.
Professor Kim said, “Until now, the protein binding affinity of biomolecules was determined by a direct interaction between two molecules. Our research has identified an important fact that the structure opening rate of proteins also plays a crucial role in determining their binding affinity.”
[Picture]
A correlation graph of opening rate (kopening) and binding affinity (kd) between protein’s stable, open state and its unstable, partially closed state.
2014.05.02 View 9985 -
 Thermoelectric generator on glass fabric for wearable electronic devices
Wearable computers or devices have been hailed as the next generation of mobile electronic gadgets, from smart watches to smart glasses to smart pacemakers. For electronics to be worn by a user, they must be light, flexible, and equipped with a power source, which could be a portable, long-lasting battery or no battery at all but a generator. How to supply power in a stable and reliable manner is one of the most critical issues to commercialize wearable devices.
A team of KAIST researchers headed by Byung Jin Cho, a professor of electrical engineering, proposed a solution to this problem by developing a glass fabric-based thermoelectric (TE) generator that is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. In fact, it is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles.
To date, two types of TE generators have been developed based either on organic or inorganic materials. The organic-based TE generators use polymers that are highly flexible and compatible with human skin, ideal for wearable electronics. The polymers, however, have a low power output. Inorganic-based TE generators produce a high electrical energy, but they are heavy, rigid, and bulky.
Professor Cho came up with a new concept and design technique to build a flexible TE generator that minimizes thermal energy loss but maximizes power output. His team synthesized liquid-like pastes of n-type (Bi2Te3) and p-type (Sb2Te3) TE materials and printed them onto a glass fabric by applying a screen printing technique. The pastes permeated through the meshes of the fabric and formed films of TE materials in a range of thickness of several hundreds of microns. As a result, hundreds of TE material dots (in combination of n and p types) were printed and well arranged on a specific area of the glass fabric.
Professor Cho explained that his TE generator has a self-sustaining structure, eliminating thick external substrates (usually made of ceramic or alumina) that hold inorganic TE materials. These substrates have taken away a great portion of thermal energy, a serious setback which causes low output power.
He also commented,
"For our case, the glass fabric itself serves as the upper and lower substrates of a TE generator, keeping the inorganic TE materials in between. This is quite a revolutionary approach to design a generator. In so doing, we were able to significantly reduce the weight of our generator (~0.13g/cm2), which is an essential element for wearable electronics."
When using KAIST's TE generator (with a size of 10 cm x 10 cm) for a wearable wristband device, it will produce around 40 mW electric power based on the temperature difference of 31 °F between human skin and the surrounding air.
Professor Cho further described about the merits of the new generator:
"Our technology presents an easy and simple way of fabricating an extremely flexible, light, and high-performance TE generator. We expect that this technology will find further applications in scale-up systems such as automobiles, factories, aircrafts, and vessels where we see abundant thermal energy being wasted."
This research result was published online in the March 14th issue of Energy & Environmental Science and was entitled "Wearable Thermoelectric Generator Fabricated on Glass Fabric."
Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BlN9lvEzCuw&feature=youtu.be
[Picture Captions]
Caption 1: The picture shows a high-performance wearable thermoelectric generator that is extremely flexible and light.
Caption 2: A thermoelectric generator developed as a wristband. The generator can be easily curved along with the shape of human body.
Caption 3: KAIST’s thermoelectric generator can be bent as many as 120 times, but it still shows the same high performance.
2014.04.21 View 20590
Thermoelectric generator on glass fabric for wearable electronic devices
Wearable computers or devices have been hailed as the next generation of mobile electronic gadgets, from smart watches to smart glasses to smart pacemakers. For electronics to be worn by a user, they must be light, flexible, and equipped with a power source, which could be a portable, long-lasting battery or no battery at all but a generator. How to supply power in a stable and reliable manner is one of the most critical issues to commercialize wearable devices.
A team of KAIST researchers headed by Byung Jin Cho, a professor of electrical engineering, proposed a solution to this problem by developing a glass fabric-based thermoelectric (TE) generator that is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. In fact, it is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles.
To date, two types of TE generators have been developed based either on organic or inorganic materials. The organic-based TE generators use polymers that are highly flexible and compatible with human skin, ideal for wearable electronics. The polymers, however, have a low power output. Inorganic-based TE generators produce a high electrical energy, but they are heavy, rigid, and bulky.
Professor Cho came up with a new concept and design technique to build a flexible TE generator that minimizes thermal energy loss but maximizes power output. His team synthesized liquid-like pastes of n-type (Bi2Te3) and p-type (Sb2Te3) TE materials and printed them onto a glass fabric by applying a screen printing technique. The pastes permeated through the meshes of the fabric and formed films of TE materials in a range of thickness of several hundreds of microns. As a result, hundreds of TE material dots (in combination of n and p types) were printed and well arranged on a specific area of the glass fabric.
Professor Cho explained that his TE generator has a self-sustaining structure, eliminating thick external substrates (usually made of ceramic or alumina) that hold inorganic TE materials. These substrates have taken away a great portion of thermal energy, a serious setback which causes low output power.
He also commented,
"For our case, the glass fabric itself serves as the upper and lower substrates of a TE generator, keeping the inorganic TE materials in between. This is quite a revolutionary approach to design a generator. In so doing, we were able to significantly reduce the weight of our generator (~0.13g/cm2), which is an essential element for wearable electronics."
When using KAIST's TE generator (with a size of 10 cm x 10 cm) for a wearable wristband device, it will produce around 40 mW electric power based on the temperature difference of 31 °F between human skin and the surrounding air.
Professor Cho further described about the merits of the new generator:
"Our technology presents an easy and simple way of fabricating an extremely flexible, light, and high-performance TE generator. We expect that this technology will find further applications in scale-up systems such as automobiles, factories, aircrafts, and vessels where we see abundant thermal energy being wasted."
This research result was published online in the March 14th issue of Energy & Environmental Science and was entitled "Wearable Thermoelectric Generator Fabricated on Glass Fabric."
Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BlN9lvEzCuw&feature=youtu.be
[Picture Captions]
Caption 1: The picture shows a high-performance wearable thermoelectric generator that is extremely flexible and light.
Caption 2: A thermoelectric generator developed as a wristband. The generator can be easily curved along with the shape of human body.
Caption 3: KAIST’s thermoelectric generator can be bent as many as 120 times, but it still shows the same high performance.
2014.04.21 View 20590 -
 Hidden Mechanism for the Suppression of Colon Cancer Identified
Published in Cell Reports : cells at the risk of causing colorectal cancer due to genetic mutation are discharged outside the colon tissue
Korean researchers have successfully identified the cancer inhibitory mechanism of the colon tissue. The discovery of the inherent defense mechanism of the colon tissues is expected to provide understanding of the cause of colorectal cancer.
The research was led by Kwang-Hyun Cho, a professor of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST (corresponding author) and participated by Dr. Jehun Song (the first author), as well as Dr. Owen Sansom, David Huels, and Rachel Ridgway from the Beatson Institute for Cancer Research in the UK and Dr. Walter Kolch from Conway Institute in Ireland.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, and its results were published in the 28th March online edition of Cell Reports under the title of “The APC network regulates the removal of mutated cells from colonic crypts.”
The organism can repair damaged tissues by itself, but genetic mutations, which may cause cancer, can occur in the process of cell division s for the repair. The rapid cell division s and toxic substances from the digestive process cause a problem especially in colon crypt that has a high probability for genetic mutation.
The research team was able to find out that the colon tissues prevent cancer by rapidly discharging carcinogenic cells with genetic mutations from the colon crypt durin ga frequent tissue repair process.
This defense mechanism, which inhibits abnormal cell division s by reducing the time mutated cells reside in the crypt, is inherent in the colon.
Extensive mathematical simulation results show that the mutated cells with enhanced Wnt signaling acquire increased adhesion in comparison to the normal cells, which therefore move rapidly toward the upper part of the crypt and are discharged more easily.
If beta-catenine, the key factor in Wnt signal transduction pathway, is not degraded due to genetic mutation, the accumulated beta-catenine activates cell proliferation and increases cell adhesion. The special environment of crypt tissue and the tendency of the cells with similar adhesion to aggregate will therefore discharge the mutated cell, hence maintaining the tissue homeostasis.
In vivo experiment with a mouse model confirms the simulation results that, in the case of abnormal crypt, the cells with high proliferation in fact move slower.
Professor Cho said, “This research has identified that multicellular organism is exquisitely designed to maintain the tissue homeostasis despite abnormal cell mutation. This also proves the systems biology research, which is a convergence of information technology and bio-technology , can discover hidden mechanisms behind complex biological phenomena.”
Crypt: Epithelium, consisting of approximately 2,000 cells, forms a colon surface in the shape of a cave.
Wnt Signaling: A signal transduction pathway involved in the proliferation and differentiation of cells that are particularly important for the embryonic development and management of adult tissue homeostasis.
2014.04.17 View 12150
Hidden Mechanism for the Suppression of Colon Cancer Identified
Published in Cell Reports : cells at the risk of causing colorectal cancer due to genetic mutation are discharged outside the colon tissue
Korean researchers have successfully identified the cancer inhibitory mechanism of the colon tissue. The discovery of the inherent defense mechanism of the colon tissues is expected to provide understanding of the cause of colorectal cancer.
The research was led by Kwang-Hyun Cho, a professor of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST (corresponding author) and participated by Dr. Jehun Song (the first author), as well as Dr. Owen Sansom, David Huels, and Rachel Ridgway from the Beatson Institute for Cancer Research in the UK and Dr. Walter Kolch from Conway Institute in Ireland.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, and its results were published in the 28th March online edition of Cell Reports under the title of “The APC network regulates the removal of mutated cells from colonic crypts.”
The organism can repair damaged tissues by itself, but genetic mutations, which may cause cancer, can occur in the process of cell division s for the repair. The rapid cell division s and toxic substances from the digestive process cause a problem especially in colon crypt that has a high probability for genetic mutation.
The research team was able to find out that the colon tissues prevent cancer by rapidly discharging carcinogenic cells with genetic mutations from the colon crypt durin ga frequent tissue repair process.
This defense mechanism, which inhibits abnormal cell division s by reducing the time mutated cells reside in the crypt, is inherent in the colon.
Extensive mathematical simulation results show that the mutated cells with enhanced Wnt signaling acquire increased adhesion in comparison to the normal cells, which therefore move rapidly toward the upper part of the crypt and are discharged more easily.
If beta-catenine, the key factor in Wnt signal transduction pathway, is not degraded due to genetic mutation, the accumulated beta-catenine activates cell proliferation and increases cell adhesion. The special environment of crypt tissue and the tendency of the cells with similar adhesion to aggregate will therefore discharge the mutated cell, hence maintaining the tissue homeostasis.
In vivo experiment with a mouse model confirms the simulation results that, in the case of abnormal crypt, the cells with high proliferation in fact move slower.
Professor Cho said, “This research has identified that multicellular organism is exquisitely designed to maintain the tissue homeostasis despite abnormal cell mutation. This also proves the systems biology research, which is a convergence of information technology and bio-technology , can discover hidden mechanisms behind complex biological phenomena.”
Crypt: Epithelium, consisting of approximately 2,000 cells, forms a colon surface in the shape of a cave.
Wnt Signaling: A signal transduction pathway involved in the proliferation and differentiation of cells that are particularly important for the embryonic development and management of adult tissue homeostasis.
2014.04.17 View 12150 -
 The KAIST Graduate Program for Future Strategy Holds Symposium on Futurology
The KAIST Graduate Program for Future Strategy held the 2014 Futurology Symposium entitled "Limits to Growth and Quantum Jumps"
at the Korea Press Center on April 3rd. The symposium was organized in efforts to
overcome the limits of Korean society’s growth potential and find a new growth momentum.
Three types of sessions took place: special lectures, field-specific subject presentations, and comprehensive debates.
As keynote speakers, Jim Dator, a professor at the University of Hawaii, lectured on Korea’s limits and possibilities, and David E. Van Zandt, the president of the New School in New York City on future social changes and our choice.
The seven field-specific subject presentations included: "The re-framing of social conflicts and frames" by Young-Jin Kang of Sungkyunkwan University, "The limits of technology and three-dimensional tech-knowledge solutions" by Chun-Taek Rim of KAIST, and "The limits of capitalism and the present financial system" by
Su-Chan Chae of KAIST
.
In addition, Yong-Suk Seo of the Korea Institute of Public Administration made a presentation on the "Population structure change and three future strategy options," Se-Yeon Kim, Congressman of the Saenuri party, on "The limits of politics and future strategy organization," and Seung-Bin Park, Dean of the KAIST College of Engineering, on the "Energy exhaustion and environmental problems."
The debate topic at the third session,
chaired by Kyu-Yeon Lee, a member of the editorial board of
Joongang Ilbo,
a Korean
daily newspaper, was "The limits of growth and another leap proposed by opinion leaders of Korea."
The seven
fields
stand for society, technology, economy, population, politics, environment, and resource, the major elements that bring
changes
in future society.
Jim Dator (left) and
David E. Van Zandt (right)
2014.04.04 View 7371
The KAIST Graduate Program for Future Strategy Holds Symposium on Futurology
The KAIST Graduate Program for Future Strategy held the 2014 Futurology Symposium entitled "Limits to Growth and Quantum Jumps"
at the Korea Press Center on April 3rd. The symposium was organized in efforts to
overcome the limits of Korean society’s growth potential and find a new growth momentum.
Three types of sessions took place: special lectures, field-specific subject presentations, and comprehensive debates.
As keynote speakers, Jim Dator, a professor at the University of Hawaii, lectured on Korea’s limits and possibilities, and David E. Van Zandt, the president of the New School in New York City on future social changes and our choice.
The seven field-specific subject presentations included: "The re-framing of social conflicts and frames" by Young-Jin Kang of Sungkyunkwan University, "The limits of technology and three-dimensional tech-knowledge solutions" by Chun-Taek Rim of KAIST, and "The limits of capitalism and the present financial system" by
Su-Chan Chae of KAIST
.
In addition, Yong-Suk Seo of the Korea Institute of Public Administration made a presentation on the "Population structure change and three future strategy options," Se-Yeon Kim, Congressman of the Saenuri party, on "The limits of politics and future strategy organization," and Seung-Bin Park, Dean of the KAIST College of Engineering, on the "Energy exhaustion and environmental problems."
The debate topic at the third session,
chaired by Kyu-Yeon Lee, a member of the editorial board of
Joongang Ilbo,
a Korean
daily newspaper, was "The limits of growth and another leap proposed by opinion leaders of Korea."
The seven
fields
stand for society, technology, economy, population, politics, environment, and resource, the major elements that bring
changes
in future society.
Jim Dator (left) and
David E. Van Zandt (right)
2014.04.04 View 7371 -
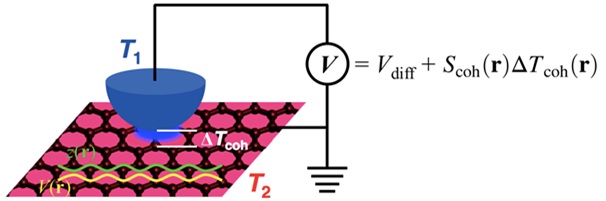 An Electron Cloud Distribution Observed by the Scanning Seebeck Microscope
All matters are made of small particles, namely atoms. An atom is composed of a heavy nucleus and cloud-like, extremely light electrons.
Korean researchers developed an electron microscopy technique that enables the accurate observation of an electron cloud distribution at room-temperature. The achievement is comparable to the invention of the quantum tunneling microscopy technique developed 33 years ago.
Professor Yong-Hyun Kim of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology at KAIST and Dr. Ho-Gi Yeo of the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) developed the Scanning Seebeck Microscope (SSM). The SSM renders clear images of atoms, as well as an electron cloud distribution. This was achieved by creating a voltage difference via a temperature gradient.
The development was introduced in the online edition of Physical Review Letters (April 2014), a prestigious journal published by the American Institute of Physics.
The SSM is expected to be economically competitive as it gives high resolution images at an atomic scale even for graphene and semiconductors, both at room temperature. In addition, if the SSM is applied to thermoelectric material research, it will contribute to the development of high-efficiency thermoelectric materials.
Through numerous hypotheses and experiments, scientists now believe that there exists an electron cloud surrounding a nucleus. IBM's Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) was the first to observe the electron cloud and has remained as the only technique to this day. The developers of IBM microscope, Dr. Gerd Binnig and Dr. Heinrich Rohrer, were awarded the 1986 Nobel Prize in Physics.
There still remains a downside to the STM technique, however: it required high precision and extreme low temperature and vibration. The application of voltage also affects the electron cloud, resulting in a distorted image.
The KAIST research team adopted a different approach by using the Seebeck effect which refers to the voltage generation due to a temperature gradient between two materials.
The team placed an observation sample (graphene) at room temperature (37~57℃) and detected its voltage generation. This technique made it possible to observe an electron cloud at room temperature.
Furthermore, the research team investigated the theoretical quantum mechanics behind the electron cloud using the observation gained through the Seebeck effect and also obtained by simulation capability to analyze the experimental results.
The research was a joint research project between KAIST Professor Yong-Hyun Kim and KRISS researcher Dr. Ho-Gi Yeo. Eui-Seop Lee, a Ph.D. candidate of KAIST, and KRISS researcher Dr. Sang-Hui Cho also participated. The Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, the Global Frontier Initiative, and the Disruptive Convergent Technology Development Initiative funded the project in Korea.
Picture 1: Schematic Diagram of the Scanning Seebeck Microscope (SSM)
Picture 2: Electron cloud distribution observed by SSM at room temperature
Picture 3: Professor Yong-Hyun Kim
2014.04.04 View 14531
An Electron Cloud Distribution Observed by the Scanning Seebeck Microscope
All matters are made of small particles, namely atoms. An atom is composed of a heavy nucleus and cloud-like, extremely light electrons.
Korean researchers developed an electron microscopy technique that enables the accurate observation of an electron cloud distribution at room-temperature. The achievement is comparable to the invention of the quantum tunneling microscopy technique developed 33 years ago.
Professor Yong-Hyun Kim of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology at KAIST and Dr. Ho-Gi Yeo of the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS) developed the Scanning Seebeck Microscope (SSM). The SSM renders clear images of atoms, as well as an electron cloud distribution. This was achieved by creating a voltage difference via a temperature gradient.
The development was introduced in the online edition of Physical Review Letters (April 2014), a prestigious journal published by the American Institute of Physics.
The SSM is expected to be economically competitive as it gives high resolution images at an atomic scale even for graphene and semiconductors, both at room temperature. In addition, if the SSM is applied to thermoelectric material research, it will contribute to the development of high-efficiency thermoelectric materials.
Through numerous hypotheses and experiments, scientists now believe that there exists an electron cloud surrounding a nucleus. IBM's Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM) was the first to observe the electron cloud and has remained as the only technique to this day. The developers of IBM microscope, Dr. Gerd Binnig and Dr. Heinrich Rohrer, were awarded the 1986 Nobel Prize in Physics.
There still remains a downside to the STM technique, however: it required high precision and extreme low temperature and vibration. The application of voltage also affects the electron cloud, resulting in a distorted image.
The KAIST research team adopted a different approach by using the Seebeck effect which refers to the voltage generation due to a temperature gradient between two materials.
The team placed an observation sample (graphene) at room temperature (37~57℃) and detected its voltage generation. This technique made it possible to observe an electron cloud at room temperature.
Furthermore, the research team investigated the theoretical quantum mechanics behind the electron cloud using the observation gained through the Seebeck effect and also obtained by simulation capability to analyze the experimental results.
The research was a joint research project between KAIST Professor Yong-Hyun Kim and KRISS researcher Dr. Ho-Gi Yeo. Eui-Seop Lee, a Ph.D. candidate of KAIST, and KRISS researcher Dr. Sang-Hui Cho also participated. The Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, the Global Frontier Initiative, and the Disruptive Convergent Technology Development Initiative funded the project in Korea.
Picture 1: Schematic Diagram of the Scanning Seebeck Microscope (SSM)
Picture 2: Electron cloud distribution observed by SSM at room temperature
Picture 3: Professor Yong-Hyun Kim
2014.04.04 View 14531 -
 Professor Sang-Yup Lee Named the Winner of the Ho-Am Prize in 2014
The Ho-Am Prize, awarded by Samsung Group’s Ho-Am Foundation, was announced on April 2, 2014 in Seoul. Professor Sang-Yup Lee of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was among the five recipients.
The prize is presented to Koreans who have made great contributions to the development of Korea in the field of science, engineering, medicine, arts, and philanthropy.
Professor Lee received the award in recognition of his pioneering research on systems metabolic engineering.
For the story written by Korea Joongang Daily, please go to the link below:
Ho-Am Foundation Names Annual Prize Winners
Korea Joongang Daily
April 3, 2014
http://koreajoongangdaily.joins.com/news/article/Article.aspx?aid=2987332
2014.04.03 View 10002
Professor Sang-Yup Lee Named the Winner of the Ho-Am Prize in 2014
The Ho-Am Prize, awarded by Samsung Group’s Ho-Am Foundation, was announced on April 2, 2014 in Seoul. Professor Sang-Yup Lee of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was among the five recipients.
The prize is presented to Koreans who have made great contributions to the development of Korea in the field of science, engineering, medicine, arts, and philanthropy.
Professor Lee received the award in recognition of his pioneering research on systems metabolic engineering.
For the story written by Korea Joongang Daily, please go to the link below:
Ho-Am Foundation Names Annual Prize Winners
Korea Joongang Daily
April 3, 2014
http://koreajoongangdaily.joins.com/news/article/Article.aspx?aid=2987332
2014.04.03 View 10002 -
 Press release from the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB International): Eighty-five business schools extend their AACSB accreditation in business or accounting
The Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB International) released a news announcement on April 1, 2014, saying that 85 business schools around the world extended their AACSB accreditation in business or accounting. KAIST is one of the 85 schools which is renewing its business accreditation for another five years.
Founded in 1916, AACSB International is a global accrediting organization for business schools that offer undergraduate, master’s, and doctorate degrees in business and accounting. The release said, “AACSB Accreditation is the hallmark of excellence in business education and has been earned by less than five percent of the world’s business schools. Today, there are 694 business schools in 45 countries and territories that have earned the accreditation.”
For the entirety of the release, please go to:
http://www.aacsb.edu/en/newsroom/2014/4/eighty-five-b-schools-extend-accreditation/
2014.04.02 View 6553
Press release from the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB International): Eighty-five business schools extend their AACSB accreditation in business or accounting
The Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB International) released a news announcement on April 1, 2014, saying that 85 business schools around the world extended their AACSB accreditation in business or accounting. KAIST is one of the 85 schools which is renewing its business accreditation for another five years.
Founded in 1916, AACSB International is a global accrediting organization for business schools that offer undergraduate, master’s, and doctorate degrees in business and accounting. The release said, “AACSB Accreditation is the hallmark of excellence in business education and has been earned by less than five percent of the world’s business schools. Today, there are 694 business schools in 45 countries and territories that have earned the accreditation.”
For the entirety of the release, please go to:
http://www.aacsb.edu/en/newsroom/2014/4/eighty-five-b-schools-extend-accreditation/
2014.04.02 View 6553 -
 Book Announcement: The Transformative Power of Service Innovation
Professor
Tae-Sung Yoon of the Technology Management Graduate School at KAIST has
recently published a book entitled
The
Transformative Power of Service Innovation
(available only in Korean).
In the
book, Professor Yoon presents many examples of successful service innovations
and explores the topic of how excellence in innovation can be achieved through the
convergence of diverse fields and industries.
2014.04.01 View 7745
Book Announcement: The Transformative Power of Service Innovation
Professor
Tae-Sung Yoon of the Technology Management Graduate School at KAIST has
recently published a book entitled
The
Transformative Power of Service Innovation
(available only in Korean).
In the
book, Professor Yoon presents many examples of successful service innovations
and explores the topic of how excellence in innovation can be achieved through the
convergence of diverse fields and industries.
2014.04.01 View 7745