CES
-
 Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 10426
Sungjoon Park Named Google PhD Fellow
PhD candidate Sungjoon Park from the School of Computing was named a 2019 Google PhD Fellow in the field of natural language processing. The Google PhD fellowship program has recognized and supported outstanding graduate students in computer science and related fields since 2009. Park is one of three Korean students chosen as the recipients of Google Fellowships this year. A total of 54 students across the world in 12 fields were awarded this fellowship.
Park’s research on computational psychotherapy using natural language processing (NLP) powered by machine learning earned him this year’s fellowship. He presented of learning distributed representations in Korean and their interpretations during the 2017 Annual Conference of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. He also applied machine learning-based natural language processing into computational psychotherapy so that a trained machine learning model could categorize client's verbal responses in a counseling dialogue. This was presented at the Annual Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics.
More recently, he has been developing on neural response generation model and the prediction and extraction of complex emotion in text, and computational psychotherapy applications.
2019.09.17 View 10426 -
 Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 12086
Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 12086 -
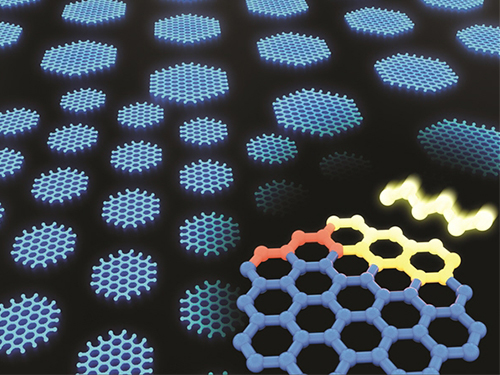 Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 35498
Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 35498 -
 Three Professors Receive Han Sung Science Awards
Three KAIST professors swept the 2nd Han Sung Science Awards. Professor Bum-Ki Min from the Departments of Mechanical Engineering and Physics, Professor Sun-Kyu Han from the Department of Chemistry, and Professor Seung-Jae Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences won all three awards presented by the Han Sung Scholarship Foundation, which recognizes promising mid-career scientists in the fields of physics, chemistry, and biological sciences. The awards ceremony will take place on August 16 in Hwaseong.
Professor Min was declared as the winner of the physics field in recognition of his outstanding research activities including searching for new application areas for metamaterials and investigating their unexplored functionalities. The metamaterials with a high index of refraction developed by Professor Min’s research team have caught the attention of scientists worldwide, as they can help develop high-resolution imaging systems and ultra-small, hyper-sensitive optical devices.
The chemistry field winner, Professor Han, is the youngest awardee so far at 36 years of age. He is often described as one of the most promising next-generation Korean scientists in the field of the total synthesis of complex natural products. Given the fact that this field takes very long-term research, he is making unprecedented research achievements. He is focusing on convergent and flexible synthetic approaches that enable access to not only a single target but various natural products with structural and biosynthetic relevance as well as unnatural products with higher biological potency.
Professor Lee was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of biological sciences, especially in aging research. Professor Lee’s team is taking a novel approach by further investigating complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors that affect aging, and identifying genes that mediate the effects. The team has been conducting large-scale gene discovery efforts by employing RNA sequencing analysis, RNAi screening, and chemical mutagenesis screening. They are striving to determine the functional significance of candidate genes obtained from these experiments and mechanistically characterize these genes.
(END)
2019.07.03 View 11219
Three Professors Receive Han Sung Science Awards
Three KAIST professors swept the 2nd Han Sung Science Awards. Professor Bum-Ki Min from the Departments of Mechanical Engineering and Physics, Professor Sun-Kyu Han from the Department of Chemistry, and Professor Seung-Jae Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences won all three awards presented by the Han Sung Scholarship Foundation, which recognizes promising mid-career scientists in the fields of physics, chemistry, and biological sciences. The awards ceremony will take place on August 16 in Hwaseong.
Professor Min was declared as the winner of the physics field in recognition of his outstanding research activities including searching for new application areas for metamaterials and investigating their unexplored functionalities. The metamaterials with a high index of refraction developed by Professor Min’s research team have caught the attention of scientists worldwide, as they can help develop high-resolution imaging systems and ultra-small, hyper-sensitive optical devices.
The chemistry field winner, Professor Han, is the youngest awardee so far at 36 years of age. He is often described as one of the most promising next-generation Korean scientists in the field of the total synthesis of complex natural products. Given the fact that this field takes very long-term research, he is making unprecedented research achievements. He is focusing on convergent and flexible synthetic approaches that enable access to not only a single target but various natural products with structural and biosynthetic relevance as well as unnatural products with higher biological potency.
Professor Lee was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of biological sciences, especially in aging research. Professor Lee’s team is taking a novel approach by further investigating complex interactions between genetic and environmental factors that affect aging, and identifying genes that mediate the effects. The team has been conducting large-scale gene discovery efforts by employing RNA sequencing analysis, RNAi screening, and chemical mutagenesis screening. They are striving to determine the functional significance of candidate genes obtained from these experiments and mechanistically characterize these genes.
(END)
2019.07.03 View 11219 -
 Wearable Robot 'WalkON Suit' Off to Cybathlon 2020
Standing upright and walking alone are very simple but noble motions that separate humans from many other creatures. Wearable and prosthetic technologies have emerged to augment human function in locomotion and manipulation. However, advances in wearable robot technology have been especially momentous to Byoung-Wook Kim, a triplegic for 22 years following a devastating car accident.
Kim rejoiced after standing upright and walking again by putting on the ‘WalkON Suit,’ the wearable robot developed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team. Even more, Kim won third prize in the powered exoskeleton race at Cybathlon 2016, an international cyborg Olympics hosted by ETH Zurich.
Now Kim and Professor Kong’s team are all geared up for the Cybathlon Championship 2020. Professor Kong and his startup, Angel Robotics, held a kickoff ceremony for Cybathlon 2020 at KAIST on June 24. The 2020 championship will take place in Switzerland.
Only pilots with complete paralysis of the legs resulting from spinal cord injuries are eligible to participate in the Cybathlon, which takes place every four years. Pilots compete against each other while completing everyday tasks using technical assistance systems in six different disciplines: a brain-computer interface race, a functional electrical stimulation bike race, a powered arm prosthesis race, a powered leg prosthesis race, a powered exoskeleton race, and a powered wheelchair race. The 2016 championship drew 66 pilots from 56 teams representing 25 countries.
In the powered exoskeleton race, pilots complete everyday activities such as getting up from a sofa and overcoming obstacles such as stairs, ramps, or slopes and up to four pilots compete simultaneously on tracks to solve six tasks; and the pilot that solves the most tasks in the least amount of time wins the race.
(Kim, a triplegic for 22 years demonstrates walking and climbing the stairs (below photo) wearing the WalkOn Suit during the media day on June 21 at KAIST.)
Kim, who demonstrated walking and climbing the stairs wearing the WalkON Suit during the media day for the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony on June 21 at KAIST, said, “I have been confined to a wheelchair for more than 20 years. I am used to it so I feel like the wheelchair is one of my body parts. Actually, I don’t feel any big difficulties in doing everyday tasks in wheelchair. But whenever I face the fact that I will never be able to stand up with my own two legs again, I am so devastated.” He continued, “I still remember the day when I stood up with my own two legs by myself after 22 years. It was beyond description.”
The market for wearable robots, especially for exoskeleton robots, is continuing to grow as the aging population has been a major challenge in almost every advanced country. The global market for these robots expects to see annual growth of 41.2% to 8.3 billion US dollars by 2025. Healthcare wearable robots for the elderly and rehabilitation take up the half of the market share followed by wearable robots for industrial and defense purposes.
Professor Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his colleagues have developed two wearable robot systems in 2014: The "WalkON Suit" for complete paraplegics and “Angel Suit” for those with partial impairment in walking ability such as the elderly and rehabilitation patients.
Professor Kong said after 15 years of basic research, the team is now able to develop its own distinct technologies. He said their robots are powered by non-resistant precision drives with algorithms recognizing the user’s moving intention. Incorporated with prosthetic devices technology from the Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, their control technology has led to the production of a customizable robot suit optimized for each user’s physical condition.
The WalkON Suit, which boasts a maximum force of 250 Nm and maximum rotation speed of 45 RPM, gives the user high-energy efficiency modeled after the physiology of the human leg. It allows users to walk on flat ground and down stairs, climb up and down inclines, and sit and lie down. Currently the battery lasts five to six hours for locomotion and the approximate 25 kg of robot weight still remains a technical challenge to upgrade.
Professor Kong’s team has grafted AR glass technology into the WalkOn Suit that one of his pilots put on for the torch relay of the PyongChang Paralympics in 2018. His team is now upgrading the WalkON Suit 4.0 for next year’s competition. Severance Rehabilitation Hospital will help the seven pilots with their training.
Professor Kong said his goal is to make robots that can make people with disabilities much more independent. He stressed, “Wearable robots should be designed for each single user. We provide a very good graphical user interface so that we can design, check, and also verify our optimized design for users’ best performance.”
(Seven pilots and Professor Kong (fifth from left in second row) pose with guests who joined the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony. President Shin (fifth from right) made a congratulatory remarks during the ceremony.)
2019.06.25 View 42597
Wearable Robot 'WalkON Suit' Off to Cybathlon 2020
Standing upright and walking alone are very simple but noble motions that separate humans from many other creatures. Wearable and prosthetic technologies have emerged to augment human function in locomotion and manipulation. However, advances in wearable robot technology have been especially momentous to Byoung-Wook Kim, a triplegic for 22 years following a devastating car accident.
Kim rejoiced after standing upright and walking again by putting on the ‘WalkON Suit,’ the wearable robot developed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team. Even more, Kim won third prize in the powered exoskeleton race at Cybathlon 2016, an international cyborg Olympics hosted by ETH Zurich.
Now Kim and Professor Kong’s team are all geared up for the Cybathlon Championship 2020. Professor Kong and his startup, Angel Robotics, held a kickoff ceremony for Cybathlon 2020 at KAIST on June 24. The 2020 championship will take place in Switzerland.
Only pilots with complete paralysis of the legs resulting from spinal cord injuries are eligible to participate in the Cybathlon, which takes place every four years. Pilots compete against each other while completing everyday tasks using technical assistance systems in six different disciplines: a brain-computer interface race, a functional electrical stimulation bike race, a powered arm prosthesis race, a powered leg prosthesis race, a powered exoskeleton race, and a powered wheelchair race. The 2016 championship drew 66 pilots from 56 teams representing 25 countries.
In the powered exoskeleton race, pilots complete everyday activities such as getting up from a sofa and overcoming obstacles such as stairs, ramps, or slopes and up to four pilots compete simultaneously on tracks to solve six tasks; and the pilot that solves the most tasks in the least amount of time wins the race.
(Kim, a triplegic for 22 years demonstrates walking and climbing the stairs (below photo) wearing the WalkOn Suit during the media day on June 21 at KAIST.)
Kim, who demonstrated walking and climbing the stairs wearing the WalkON Suit during the media day for the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony on June 21 at KAIST, said, “I have been confined to a wheelchair for more than 20 years. I am used to it so I feel like the wheelchair is one of my body parts. Actually, I don’t feel any big difficulties in doing everyday tasks in wheelchair. But whenever I face the fact that I will never be able to stand up with my own two legs again, I am so devastated.” He continued, “I still remember the day when I stood up with my own two legs by myself after 22 years. It was beyond description.”
The market for wearable robots, especially for exoskeleton robots, is continuing to grow as the aging population has been a major challenge in almost every advanced country. The global market for these robots expects to see annual growth of 41.2% to 8.3 billion US dollars by 2025. Healthcare wearable robots for the elderly and rehabilitation take up the half of the market share followed by wearable robots for industrial and defense purposes.
Professor Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his colleagues have developed two wearable robot systems in 2014: The "WalkON Suit" for complete paraplegics and “Angel Suit” for those with partial impairment in walking ability such as the elderly and rehabilitation patients.
Professor Kong said after 15 years of basic research, the team is now able to develop its own distinct technologies. He said their robots are powered by non-resistant precision drives with algorithms recognizing the user’s moving intention. Incorporated with prosthetic devices technology from the Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, their control technology has led to the production of a customizable robot suit optimized for each user’s physical condition.
The WalkON Suit, which boasts a maximum force of 250 Nm and maximum rotation speed of 45 RPM, gives the user high-energy efficiency modeled after the physiology of the human leg. It allows users to walk on flat ground and down stairs, climb up and down inclines, and sit and lie down. Currently the battery lasts five to six hours for locomotion and the approximate 25 kg of robot weight still remains a technical challenge to upgrade.
Professor Kong’s team has grafted AR glass technology into the WalkOn Suit that one of his pilots put on for the torch relay of the PyongChang Paralympics in 2018. His team is now upgrading the WalkON Suit 4.0 for next year’s competition. Severance Rehabilitation Hospital will help the seven pilots with their training.
Professor Kong said his goal is to make robots that can make people with disabilities much more independent. He stressed, “Wearable robots should be designed for each single user. We provide a very good graphical user interface so that we can design, check, and also verify our optimized design for users’ best performance.”
(Seven pilots and Professor Kong (fifth from left in second row) pose with guests who joined the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony. President Shin (fifth from right) made a congratulatory remarks during the ceremony.)
2019.06.25 View 42597 -
 Novel Via-Hole-Less Multilevel Metal Interconnection Methods
Forming reliable multi-level metal interconnections is a key technology for integrating devices into organic integrated circuits (ICs). The conventional approach, called “via-hole,” locally removes the insulator and utilizes metal interconnects through the holes. Due to the high sensitivity of organic materials to chemical solvents, heat, and photo-radiation used in conventional “via-hole” methods, alternative printing methods or laser drilling methods have been developed. However, finding a reliable and practical metal interconnection for organic ICs is still challenging.
The research team of KAIST Professor Sung Gap Im and Postech Professor Kim Jae-Joon reported a new interconnection method that does not require via-hole formation, “via-hole-less metal interconnection,” in Nature Communications on June 3.
Metal electrodes in different layers can be isolated from each other by patterned dielectric layers, where they then can be interconnected to others in the open area where the dielectric layer is not present. See the images below. Vapor phase deposition and in-situ patterning of dielectric layer using iCVD (initiated chemical vapor deposition), used in the “via-hole-less” method, ensure a damage-free process for organic semiconductor materials and result in outstanding performance of the organic devices as multilevel metal interconnects are reliably formed. The team successfully demonstrated three-dimensional (3D) stacking of five organic transistors and integrated circuits using the proposed via-hole-less interconnect method. See the image below.
Vapor phase deposition and in-situ patterning of dielectric layer using iCVD (initiated chemical vapor deposition), used in the “via-hole-less” method, ensure a damage-free process for organic semiconductor materials and result in outstanding performance of the organic devices as multilevel metal interconnects are reliably formed. The team successfully demonstrated three-dimensional (3D) stacking of five organic transistors and integrated circuits using the proposed via-hole-less interconnect method. See the image below.
Professor Kim explained, “Our proposed via-hole-less interconnect method using a selectively patterned dielectric overcomes the limitations of the previous time-consuming, one-by-one via-hole formation process and provides reliable methods for creating metal interconnects in organic ICs. We expect the via-hole-less scheme to bring advances to organic IC technology.”
2019.06.18 View 45361
Novel Via-Hole-Less Multilevel Metal Interconnection Methods
Forming reliable multi-level metal interconnections is a key technology for integrating devices into organic integrated circuits (ICs). The conventional approach, called “via-hole,” locally removes the insulator and utilizes metal interconnects through the holes. Due to the high sensitivity of organic materials to chemical solvents, heat, and photo-radiation used in conventional “via-hole” methods, alternative printing methods or laser drilling methods have been developed. However, finding a reliable and practical metal interconnection for organic ICs is still challenging.
The research team of KAIST Professor Sung Gap Im and Postech Professor Kim Jae-Joon reported a new interconnection method that does not require via-hole formation, “via-hole-less metal interconnection,” in Nature Communications on June 3.
Metal electrodes in different layers can be isolated from each other by patterned dielectric layers, where they then can be interconnected to others in the open area where the dielectric layer is not present. See the images below. Vapor phase deposition and in-situ patterning of dielectric layer using iCVD (initiated chemical vapor deposition), used in the “via-hole-less” method, ensure a damage-free process for organic semiconductor materials and result in outstanding performance of the organic devices as multilevel metal interconnects are reliably formed. The team successfully demonstrated three-dimensional (3D) stacking of five organic transistors and integrated circuits using the proposed via-hole-less interconnect method. See the image below.
Vapor phase deposition and in-situ patterning of dielectric layer using iCVD (initiated chemical vapor deposition), used in the “via-hole-less” method, ensure a damage-free process for organic semiconductor materials and result in outstanding performance of the organic devices as multilevel metal interconnects are reliably formed. The team successfully demonstrated three-dimensional (3D) stacking of five organic transistors and integrated circuits using the proposed via-hole-less interconnect method. See the image below.
Professor Kim explained, “Our proposed via-hole-less interconnect method using a selectively patterned dielectric overcomes the limitations of the previous time-consuming, one-by-one via-hole formation process and provides reliable methods for creating metal interconnects in organic ICs. We expect the via-hole-less scheme to bring advances to organic IC technology.”
2019.06.18 View 45361 -
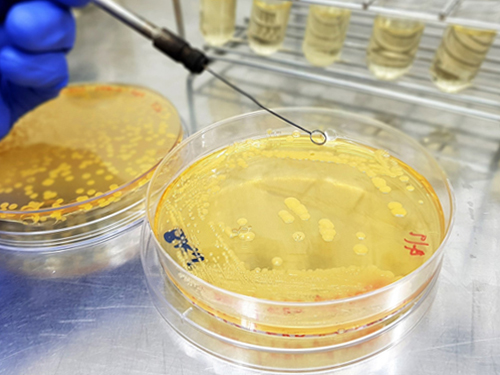 Engineered Microbial Production of Grape Flavoring
(Image 1: Engineered bacteria that produce grape flavoring.)
Researchers report a microbial method for producing an artificial grape flavor. Methyl anthranilate (MANT) is a common grape flavoring and odorant compound currently produced through a petroleum-based process that uses large volumes of toxic acid catalysts.
Professor Sang-Yup Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering demonstrated production of MANT, a naturally occurring compound, via engineered bacteria. The authors engineered strains of Escherichia coli and Corynebacetrium glutamicum to produce MANT through a plant-based engineered metabolic pathway.
The authors tuned the bacterial metabolic pathway by optimizing the levels of AAMT1, the key enzyme in the process. To maximize production of MANT, the authors tested six strategies, including increasing the supply of a precursor compound and enhancing the availability of a co-substrate. The most productive strategy proved to be a two-phase extractive culture, in which MANT was extracted into a solvent. This strategy produced MANT on the scale of 4.47 to 5.74 grams per liter, a significant amount, considering that engineered microbes produce most natural products at a scale of milligrams or micrograms per liter.
According to the authors, the results suggest that MANT and other related molecules produced through industrial processes can be produced at scale by engineered microbes in a manner that would allow them to be marketed as natural one, instead of artificial one.
This study, featured at the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA on May 13, was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Image 2. Overview of the strategies applied for the microbial production of grape flavoring.)
2019.05.15 View 57382
Engineered Microbial Production of Grape Flavoring
(Image 1: Engineered bacteria that produce grape flavoring.)
Researchers report a microbial method for producing an artificial grape flavor. Methyl anthranilate (MANT) is a common grape flavoring and odorant compound currently produced through a petroleum-based process that uses large volumes of toxic acid catalysts.
Professor Sang-Yup Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering demonstrated production of MANT, a naturally occurring compound, via engineered bacteria. The authors engineered strains of Escherichia coli and Corynebacetrium glutamicum to produce MANT through a plant-based engineered metabolic pathway.
The authors tuned the bacterial metabolic pathway by optimizing the levels of AAMT1, the key enzyme in the process. To maximize production of MANT, the authors tested six strategies, including increasing the supply of a precursor compound and enhancing the availability of a co-substrate. The most productive strategy proved to be a two-phase extractive culture, in which MANT was extracted into a solvent. This strategy produced MANT on the scale of 4.47 to 5.74 grams per liter, a significant amount, considering that engineered microbes produce most natural products at a scale of milligrams or micrograms per liter.
According to the authors, the results suggest that MANT and other related molecules produced through industrial processes can be produced at scale by engineered microbes in a manner that would allow them to be marketed as natural one, instead of artificial one.
This study, featured at the Proceeding of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA on May 13, was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Image 2. Overview of the strategies applied for the microbial production of grape flavoring.)
2019.05.15 View 57382 -
 Research Day Highlights Most Outstanding Research Achievements
Professor Byung Jin Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected as the Grand Research Prize Winner in recognition of his innovative research achievement in the fields of nano electric and flexible energy devices during the 2019 KAIST Research Day ceremony held on April 23 at the Chung Kunmo Conference Hall.
The ten most outstanding research achievements from the past year were also awarded in the three areas of Research, Innovation, Convergence Researches.
Professor Cho is an internationally recognized researcher in the field of future nano and energy device technology. Professor Cho’s team has continued to research on advanced CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductors). CMOS has become his key research topic over the past three decades.
In 2014, he developed a glass fabric-based thermoelectric generator, which is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. It is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles. His wearable thermoelectric generator was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015.
He now is working on high-performance and ultra-flexible CMOS IC for biomedical applications, expanding his scope to thermal haptic technology in VR using graphene-CMOS hybrid integrated circuits; to self-powered wireless sensor nodes and self-powered ECG system using wearable thermoelectric generators .
In his special lecture at the ceremony, Professor Cho stressed the importance of collaboration in making scientific research and presented how he moved to future devices after focusing on scaling the devices.
“When I started the research on semiconductors, I focused on how to scale the device down as much as possible. For decades, we have conducted a number of procedures to produce tiny but efficient materials. Now we have shifted to develop flexible thermoelements and wearable devices,” said Professor Cho.
“We all thought the scaling down is the only way to create value-added technological breakthroughs. Now, the devices have been scaled down to 7nm and will go down to 5 nm soon. Over the past few years, I think we have gone through all the possible technological breakthroughs for reducing the size to 5nm. The semiconductor devices are made of more 1 billion transistors and go through 1,000 technological processes. So, there won’t be any possible way for a single genius to make a huge breakthrough. Without collaboration with others, it is nearly impossible to make any new technological breakthroughs.”
Professor Cho has published more than 240 papers in renowned academic journals and presented more than 300 papers at academic conferences. He has also registered approximately 50 patents in the field of semiconductor device technology.
The top ten research highlights of 2018 as follows:
- Rydberg-Atom Quantum Simulator Development by Professor Jaewook Ahn and Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics
- From C-H to C-C Bonds at Room Temperature by Professor Mu-Hyun Baik from the Department of Chemistry
- The Role of Rodlike Counterions on the Interactions of DNAs by Professor Yong Woon Kim of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology
- The Medal Preoptic Area Induces Hunting-Like Behaviors to Target Objects and Prey by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences
- Identification of the Origin of Brain Tumors and New Therapeutic Strategy by Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
- The Linear Frequency Conversion of Light at a Spatiotemporal Boundary by Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering
- An Industrial Grade Flexible Transparent Force Touch Sensor by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering
- The Detection and Clustering of Mixed-Type Defect Patterns in Wafer Bin Maps by Professor Heeyoung Kim from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering
- The Development of a Reconfigurable Spin-Based Logic Device by Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
- The Development of a Miniaturized X-Ray Tube Based on Carbon Nanotube and Electronic Brachytherapy Device by Professor Sung Oh Cho from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics and Professor In-Chel Park from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Research Award. For the Innovation Award, Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering was the recipient and the Convergence Research Awards was conferred to Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Sung Gap Im from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor SangHee Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering during the ceremony.
For more on KAIST’s Top Research Achievements and Highlight of 2018, please refer to the attached below. click.
2019.04.25 View 17847
Research Day Highlights Most Outstanding Research Achievements
Professor Byung Jin Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected as the Grand Research Prize Winner in recognition of his innovative research achievement in the fields of nano electric and flexible energy devices during the 2019 KAIST Research Day ceremony held on April 23 at the Chung Kunmo Conference Hall.
The ten most outstanding research achievements from the past year were also awarded in the three areas of Research, Innovation, Convergence Researches.
Professor Cho is an internationally recognized researcher in the field of future nano and energy device technology. Professor Cho’s team has continued to research on advanced CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductors). CMOS has become his key research topic over the past three decades.
In 2014, he developed a glass fabric-based thermoelectric generator, which is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. It is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles. His wearable thermoelectric generator was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015.
He now is working on high-performance and ultra-flexible CMOS IC for biomedical applications, expanding his scope to thermal haptic technology in VR using graphene-CMOS hybrid integrated circuits; to self-powered wireless sensor nodes and self-powered ECG system using wearable thermoelectric generators .
In his special lecture at the ceremony, Professor Cho stressed the importance of collaboration in making scientific research and presented how he moved to future devices after focusing on scaling the devices.
“When I started the research on semiconductors, I focused on how to scale the device down as much as possible. For decades, we have conducted a number of procedures to produce tiny but efficient materials. Now we have shifted to develop flexible thermoelements and wearable devices,” said Professor Cho.
“We all thought the scaling down is the only way to create value-added technological breakthroughs. Now, the devices have been scaled down to 7nm and will go down to 5 nm soon. Over the past few years, I think we have gone through all the possible technological breakthroughs for reducing the size to 5nm. The semiconductor devices are made of more 1 billion transistors and go through 1,000 technological processes. So, there won’t be any possible way for a single genius to make a huge breakthrough. Without collaboration with others, it is nearly impossible to make any new technological breakthroughs.”
Professor Cho has published more than 240 papers in renowned academic journals and presented more than 300 papers at academic conferences. He has also registered approximately 50 patents in the field of semiconductor device technology.
The top ten research highlights of 2018 as follows:
- Rydberg-Atom Quantum Simulator Development by Professor Jaewook Ahn and Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics
- From C-H to C-C Bonds at Room Temperature by Professor Mu-Hyun Baik from the Department of Chemistry
- The Role of Rodlike Counterions on the Interactions of DNAs by Professor Yong Woon Kim of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology
- The Medal Preoptic Area Induces Hunting-Like Behaviors to Target Objects and Prey by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences
- Identification of the Origin of Brain Tumors and New Therapeutic Strategy by Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
- The Linear Frequency Conversion of Light at a Spatiotemporal Boundary by Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering
- An Industrial Grade Flexible Transparent Force Touch Sensor by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering
- The Detection and Clustering of Mixed-Type Defect Patterns in Wafer Bin Maps by Professor Heeyoung Kim from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering
- The Development of a Reconfigurable Spin-Based Logic Device by Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
- The Development of a Miniaturized X-Ray Tube Based on Carbon Nanotube and Electronic Brachytherapy Device by Professor Sung Oh Cho from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics and Professor In-Chel Park from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Research Award. For the Innovation Award, Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering was the recipient and the Convergence Research Awards was conferred to Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Sung Gap Im from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor SangHee Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering during the ceremony.
For more on KAIST’s Top Research Achievements and Highlight of 2018, please refer to the attached below. click.
2019.04.25 View 17847 -
 KAIST-KU Joint Research Center for Smart Healthcare & Transportation
(President Shin shakes hands with KU acting Presidedent Arif Al Hammdi at the KAIST-KU Joint Research Center opening ceremony on April 8.)
KAIST opened the KAIST-Khalifa University Joint Research Center with Khalifa University on April 8. The opening ceremony was held at Khalifa University and was attended by President Sung-Chul Shin and Khalifa University Acting President Arif Al Hammadi.
The new research center reflects the evolution of the long-established partnership between the two institutions. The two universities have already made very close collaborations in research and education in the fields of nuclear and quantum engineering.
The launch of this center expanded their fields of collaboration to smart healthcare and smart transportation, key emerging sectors in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. President Shin signed an MOU with the UAE Minister of State for Advanced Science Sarah Amiri and Khalifa University to expand mutual collaboration in technology development and fostering human capital last year.
The center will conduct research and education on autonomous vehicles, infrastructure for autonomous vehicle operation, wireless charging for electric vehicles, and infrastructure for electric autonomous vehicles. As for smart healthcare, the center will focus on healthcare robotics as well as sensors and wearable devices for personal healthcare services.
President Shin, who accompanied a research team from the Graduate School of Green Transportation, said, “We are very delighted to enter into this expanded collaboration with KU. This partnership justifies our long-standing collaboration in the areas of emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution while fostering human capital.”
KU Acting President Arif Al Hammadi added, “The outcome of these research projects will establish the status of both institutions as champions of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, bringing benefits to our communities. We believe the new research center will further consolidate our status as a globally active, research-intensive academic institution, developing international collaborations that benefit the community in general.”
2019.04.09 View 9443
KAIST-KU Joint Research Center for Smart Healthcare & Transportation
(President Shin shakes hands with KU acting Presidedent Arif Al Hammdi at the KAIST-KU Joint Research Center opening ceremony on April 8.)
KAIST opened the KAIST-Khalifa University Joint Research Center with Khalifa University on April 8. The opening ceremony was held at Khalifa University and was attended by President Sung-Chul Shin and Khalifa University Acting President Arif Al Hammadi.
The new research center reflects the evolution of the long-established partnership between the two institutions. The two universities have already made very close collaborations in research and education in the fields of nuclear and quantum engineering.
The launch of this center expanded their fields of collaboration to smart healthcare and smart transportation, key emerging sectors in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. President Shin signed an MOU with the UAE Minister of State for Advanced Science Sarah Amiri and Khalifa University to expand mutual collaboration in technology development and fostering human capital last year.
The center will conduct research and education on autonomous vehicles, infrastructure for autonomous vehicle operation, wireless charging for electric vehicles, and infrastructure for electric autonomous vehicles. As for smart healthcare, the center will focus on healthcare robotics as well as sensors and wearable devices for personal healthcare services.
President Shin, who accompanied a research team from the Graduate School of Green Transportation, said, “We are very delighted to enter into this expanded collaboration with KU. This partnership justifies our long-standing collaboration in the areas of emerging technologies in the Fourth Industrial Revolution while fostering human capital.”
KU Acting President Arif Al Hammadi added, “The outcome of these research projects will establish the status of both institutions as champions of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, bringing benefits to our communities. We believe the new research center will further consolidate our status as a globally active, research-intensive academic institution, developing international collaborations that benefit the community in general.”
2019.04.09 View 9443 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with the 23rd NAEK Award
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was honored to be the laureate of the 23rd NAEK Award.
The NAEK (National Academy of Engineering of Korea) Award was instituted in 1997 to honor and recognize engineers who have made significant contributions to the development of the engineering and technology field at universities, industries, and institutions. Every year, it is conferred to only one person who has achieved original and world-leading research that has led to national development.
Distinguished Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of the field of systems metabolic engineering and he was recognized for his significant achievements in the biochemical industry by developing novel microbial bioprocesses. In particular, he is globally renowned for biological plastic synthesis, making or decomposing polymers with microorganisms instead of using fossil resources.
He has produced numerous high-quality research breakthroughs in metabolic and systems engineering. In 2016, he produced an easily degradable plastic with Escherichia coli (E. coli). In 2018, he successfully produced aromatic polyesters, the main material for PET (poly ethylene terephthalate) from E. coli strains. He also identified microorganism structures for PET degradation and improved its degradability with a novel variant.
His research was ranked number one in the research and development division of Top Ten Science and Technology News 2018 announced by Korean Federation of Science & Technology Societies. He is one of highly cited researchers (HCR) ranked in the top 1% by citations for their field by the Clarivate Analytics.
2019.03.21 View 9801
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Honored with the 23rd NAEK Award
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was honored to be the laureate of the 23rd NAEK Award.
The NAEK (National Academy of Engineering of Korea) Award was instituted in 1997 to honor and recognize engineers who have made significant contributions to the development of the engineering and technology field at universities, industries, and institutions. Every year, it is conferred to only one person who has achieved original and world-leading research that has led to national development.
Distinguished Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of the field of systems metabolic engineering and he was recognized for his significant achievements in the biochemical industry by developing novel microbial bioprocesses. In particular, he is globally renowned for biological plastic synthesis, making or decomposing polymers with microorganisms instead of using fossil resources.
He has produced numerous high-quality research breakthroughs in metabolic and systems engineering. In 2016, he produced an easily degradable plastic with Escherichia coli (E. coli). In 2018, he successfully produced aromatic polyesters, the main material for PET (poly ethylene terephthalate) from E. coli strains. He also identified microorganism structures for PET degradation and improved its degradability with a novel variant.
His research was ranked number one in the research and development division of Top Ten Science and Technology News 2018 announced by Korean Federation of Science & Technology Societies. He is one of highly cited researchers (HCR) ranked in the top 1% by citations for their field by the Clarivate Analytics.
2019.03.21 View 9801 -
 OUIC Presents the Six Most Promising Techs Transferrable to Local SMEs
KAIST will showcase the six most promising technologies for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) on November 14 in the Academic Cultural Complex. To strengthen the competitive edge of local SMEs in Daejeon, the Office of University-Industry made a survey of their technological needs and came up with the six most promising technologies. Developers will introduce their technologies during the session.Besides the introduction of the promising technologies, the session will also provide a program named University to Business (U2B) to match up technologies according to the SMEs’ needs. SMEs who wish to engage in technology transfers can receive counseling and other support programs during the session.First, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae from the Department of Industrial Design will present a technology for controlling cooperation robots. Professor Bae inserted flexible materials between the controllers to allow robots to use both hands stably and operate more accurately and swiftly. It can be applied to automatic robots, industrial robots, and service robots.Professor Hyun Myung from the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering will demonstrate a robot navigation system in a dynamic indoor and outdoor environment, which can be applied to robotics in logistics, smart factories, and autonomous vehicles. Providing robust simultaneous localization and mapping systems, this technology shows high-performing navigation with low-cost sensors.Meanwhile, Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will introduce a technology for forming stable adhesive emulsions. An emulsion is a stable mixture of water and oil. Conventionally, a small amount of surfactant is added to stabilize an emulsion. Here, Professor Choi developed a stable emulsion system without using any chemical substances. This technology can be applied to various fields, including the cosmetics, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and painting industries. The session will also present smart IoTs platform technology developed by Professor Jinhong Yang from the KAIST Institute for IT Convergence. His technology minimizes errors occurring when multiple IoT devices are connected simultaneously. Professor Yong Keun Park from the Department of Physics will introduce a technology for measuring glycated hemoglobin by using the optical properties of red blood cells. This technology can be applied to make low-cost, small-sized measuring equipment. It can also be used for vitro diagnoses including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, tumors, kidney disease, and infectious diseases. Professor Yong Man Ro from the School of Electrical Engineering will show technology for biometric access control. Conventional technologies for face recognition fall behind other biometrics. Professor Ro and his team developed a facial dynamics interpreting network which allows very accurate facial recognition by interpreting the relationships between facial local dynamics and estimating facial traits. This technology can be applied to security and communication in finance, computers, and information system.KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “KAIST will continue to support SMEs to have stronger competitiveness in the market. Through technology transfer, we will drive innovation in technological commercialization where a university’s research and development creates economic value.”
2018.11.13 View 10301
OUIC Presents the Six Most Promising Techs Transferrable to Local SMEs
KAIST will showcase the six most promising technologies for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) on November 14 in the Academic Cultural Complex. To strengthen the competitive edge of local SMEs in Daejeon, the Office of University-Industry made a survey of their technological needs and came up with the six most promising technologies. Developers will introduce their technologies during the session.Besides the introduction of the promising technologies, the session will also provide a program named University to Business (U2B) to match up technologies according to the SMEs’ needs. SMEs who wish to engage in technology transfers can receive counseling and other support programs during the session.First, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae from the Department of Industrial Design will present a technology for controlling cooperation robots. Professor Bae inserted flexible materials between the controllers to allow robots to use both hands stably and operate more accurately and swiftly. It can be applied to automatic robots, industrial robots, and service robots.Professor Hyun Myung from the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering will demonstrate a robot navigation system in a dynamic indoor and outdoor environment, which can be applied to robotics in logistics, smart factories, and autonomous vehicles. Providing robust simultaneous localization and mapping systems, this technology shows high-performing navigation with low-cost sensors.Meanwhile, Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will introduce a technology for forming stable adhesive emulsions. An emulsion is a stable mixture of water and oil. Conventionally, a small amount of surfactant is added to stabilize an emulsion. Here, Professor Choi developed a stable emulsion system without using any chemical substances. This technology can be applied to various fields, including the cosmetics, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, and painting industries. The session will also present smart IoTs platform technology developed by Professor Jinhong Yang from the KAIST Institute for IT Convergence. His technology minimizes errors occurring when multiple IoT devices are connected simultaneously. Professor Yong Keun Park from the Department of Physics will introduce a technology for measuring glycated hemoglobin by using the optical properties of red blood cells. This technology can be applied to make low-cost, small-sized measuring equipment. It can also be used for vitro diagnoses including diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, tumors, kidney disease, and infectious diseases. Professor Yong Man Ro from the School of Electrical Engineering will show technology for biometric access control. Conventional technologies for face recognition fall behind other biometrics. Professor Ro and his team developed a facial dynamics interpreting network which allows very accurate facial recognition by interpreting the relationships between facial local dynamics and estimating facial traits. This technology can be applied to security and communication in finance, computers, and information system.KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin said, “KAIST will continue to support SMEs to have stronger competitiveness in the market. Through technology transfer, we will drive innovation in technological commercialization where a university’s research and development creates economic value.”
2018.11.13 View 10301 -
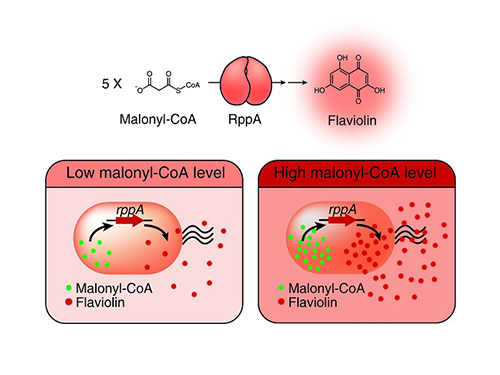 A Novel Biosensor to Advance Diverse High-Level Production of Microbial Cell Factories
A research group at KAIST presented a novel biosensor which can produce diverse, high-level microbial cell factories. The biosensor monitors the concentration of products and even intermediates when new strains are being developed. This strategy provides a new platform for manufacturing diverse natural products from renewable resources. The team succeeded in creating four natural products of high-level pharmaceutical importance with this strategy.
Malonyl-CoA is a major building block for many value-added chemicals including diverse natural products with pharmaceutical importance. However, due to the low availability of malonyl-CoA in bacteria, many malonyl-CoA-derived natural products have been produced by chemical synthesis or extraction from natural resources that are harmful to the environment and are unsustainable. For the sustainable biological production of malonyl-CoA-derived natural products, increasing the intracellular malonyl-CoA pool is necessary. To this end, the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor was required to monitor the concentration of intracellular malonyl-CoA abundance as new strains are developed.
Metabolic engineering researchers at KAIST addressed this issue. This research reports the development of a simple and robust malonyl-CoA biosensor by repurposing a type III polyketide synthase (also known as RppA), which produces flaviolin, a colorimetric indicator of malonyl-CoA. Subsequently, the RppA biosensor was used for the rapid and efficient colorimetric screening of gene manipulation targets enabling enhanced malonyl-CoA abundance. The screened beneficial gene targets were employed for the high-level production of four representative natural products derived from malonyl-CoA. Compared with the previous strategies, which were expensive and time-consuming, the new biosensor could be easily applied to industrially relevant bacteria including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, and Corynebacterium glutamicum to enable a one-step process.
The study employs synthetic small regulatory RNA (sRNA) technology to rapidly and efficiently reduce endogenous target gene expression for improved malonyl-CoA production. The researchers constructed an E. coli genome-scale synthetic sRNA library targeting 1,858 genes covering all major metabolic genes in E. coli. This library was employed with the RppA biosensor to screen for gene targets which are believed to be beneficial for enhancing malonyl-CoA accumulation upon their expression knockdown.
From this colorimetric screening, 14 gene targets were selected, all of which were successful at significantly increasing the production of four natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin). Although specific examples are demonstrated in E. coli as a host, the researchers showed that the biosensor is also functional in P. putida and C. glutamicum, industrially important representative gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, respectively. The malonyl-CoA biosensor developed in this research will serve as an efficient platform for the rapid development of strains capable of producing natural products crucial for the pharmaceutical, chemical, cosmetics, and food industries.
An important aspect of this work is that the high-performance strains constructed in this research were developed rapidly and easily by utilizing the simple approach of colorimetric screening, without involving extensive metabolic engineering approaches. 6-Methylsalicylic acid (an antibiotic) could be produced to the highest titer reported for E. coli, and the microbial production of aloesone (a precursor of aloesin, an anti-inflammatory agent/whitening agent) was achieved for the first time.
“A sustainable process for producing diverse natural products using renewable resources is of great interest. This study represents the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor generally applicable to a wide range of industrially important bacteria. The capability of this biosensor for screening a large library was demonstrated to show that the rapid and efficient construction of high-performance strains is feasible. This research will be useful for further accelerating the development process of strains capable of producing valuable chemicals to industrially relevant levels,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, who led the research.
This study entitled “Repurposing type III polyketide synthase as a malonyl-CoA biosensor for metabolic engineering in bacteria,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on October 02.
PhD students Dongsoo Yang and Won Jun Kim, MS student Shin Hee Ha, research staff Mun Hee Lee, Research Professor Seung Min Yoo, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Dr. Jong Hyun Choi of the Applied Microbiology Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) participated in this research.
Figure: Type III polyketide synthase (RppA) as a malonyl-CoA biosensor. RppA converts five molecules of malonyl-CoA into one molecule of red-colored flaviolin. This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of the malonyl-CoA biosensor by indicating that higher malonyl-CoA abundance leads to higher production and secretion of flaviolin, resulting in a deeper red color of the culture. This system was employed for the enhanced production of four representative natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin) from engineered E. coli strains.
2018.10.11 View 10748
A Novel Biosensor to Advance Diverse High-Level Production of Microbial Cell Factories
A research group at KAIST presented a novel biosensor which can produce diverse, high-level microbial cell factories. The biosensor monitors the concentration of products and even intermediates when new strains are being developed. This strategy provides a new platform for manufacturing diverse natural products from renewable resources. The team succeeded in creating four natural products of high-level pharmaceutical importance with this strategy.
Malonyl-CoA is a major building block for many value-added chemicals including diverse natural products with pharmaceutical importance. However, due to the low availability of malonyl-CoA in bacteria, many malonyl-CoA-derived natural products have been produced by chemical synthesis or extraction from natural resources that are harmful to the environment and are unsustainable. For the sustainable biological production of malonyl-CoA-derived natural products, increasing the intracellular malonyl-CoA pool is necessary. To this end, the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor was required to monitor the concentration of intracellular malonyl-CoA abundance as new strains are developed.
Metabolic engineering researchers at KAIST addressed this issue. This research reports the development of a simple and robust malonyl-CoA biosensor by repurposing a type III polyketide synthase (also known as RppA), which produces flaviolin, a colorimetric indicator of malonyl-CoA. Subsequently, the RppA biosensor was used for the rapid and efficient colorimetric screening of gene manipulation targets enabling enhanced malonyl-CoA abundance. The screened beneficial gene targets were employed for the high-level production of four representative natural products derived from malonyl-CoA. Compared with the previous strategies, which were expensive and time-consuming, the new biosensor could be easily applied to industrially relevant bacteria including Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas putida, and Corynebacterium glutamicum to enable a one-step process.
The study employs synthetic small regulatory RNA (sRNA) technology to rapidly and efficiently reduce endogenous target gene expression for improved malonyl-CoA production. The researchers constructed an E. coli genome-scale synthetic sRNA library targeting 1,858 genes covering all major metabolic genes in E. coli. This library was employed with the RppA biosensor to screen for gene targets which are believed to be beneficial for enhancing malonyl-CoA accumulation upon their expression knockdown.
From this colorimetric screening, 14 gene targets were selected, all of which were successful at significantly increasing the production of four natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin). Although specific examples are demonstrated in E. coli as a host, the researchers showed that the biosensor is also functional in P. putida and C. glutamicum, industrially important representative gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, respectively. The malonyl-CoA biosensor developed in this research will serve as an efficient platform for the rapid development of strains capable of producing natural products crucial for the pharmaceutical, chemical, cosmetics, and food industries.
An important aspect of this work is that the high-performance strains constructed in this research were developed rapidly and easily by utilizing the simple approach of colorimetric screening, without involving extensive metabolic engineering approaches. 6-Methylsalicylic acid (an antibiotic) could be produced to the highest titer reported for E. coli, and the microbial production of aloesone (a precursor of aloesin, an anti-inflammatory agent/whitening agent) was achieved for the first time.
“A sustainable process for producing diverse natural products using renewable resources is of great interest. This study represents the development of a robust and efficient malonyl-CoA biosensor generally applicable to a wide range of industrially important bacteria. The capability of this biosensor for screening a large library was demonstrated to show that the rapid and efficient construction of high-performance strains is feasible. This research will be useful for further accelerating the development process of strains capable of producing valuable chemicals to industrially relevant levels,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, who led the research.
This study entitled “Repurposing type III polyketide synthase as a malonyl-CoA biosensor for metabolic engineering in bacteria,” was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on October 02.
PhD students Dongsoo Yang and Won Jun Kim, MS student Shin Hee Ha, research staff Mun Hee Lee, Research Professor Seung Min Yoo, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Dr. Jong Hyun Choi of the Applied Microbiology Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) participated in this research.
Figure: Type III polyketide synthase (RppA) as a malonyl-CoA biosensor. RppA converts five molecules of malonyl-CoA into one molecule of red-colored flaviolin. This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of the malonyl-CoA biosensor by indicating that higher malonyl-CoA abundance leads to higher production and secretion of flaviolin, resulting in a deeper red color of the culture. This system was employed for the enhanced production of four representative natural products (6-methylsalicylic acid, aloesone, resveratrol, and naringenin) from engineered E. coli strains.
2018.10.11 View 10748