micro
-
 Professor Jungwon Kim Wins Haerim Optics and Photonics Award
(Professor Jungwon Kim)
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the 8th Haerim Optics and Photonics Award from the Optical Society of Korea (OSK).
He was recognized for his dedication to pioneering the field of microwave photonics by developing ultra-low noise fiber photonics lasers.
The Haerim Optics and Photonics Award is given to an outstanding researcher who has made academic contributions in the field of optics and photonics for the last five years.
The name of the award (Haerim) comes from the pen-name of the renowned scholar, Professor Un-Chul Paek, because it is maintained using funds he contributed to the OSK.
The OSK will confer the award on February 8 during the 29th OSK Annual Meeting and Winter Conference of 2018.
2018.02.07 View 7379
Professor Jungwon Kim Wins Haerim Optics and Photonics Award
(Professor Jungwon Kim)
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the 8th Haerim Optics and Photonics Award from the Optical Society of Korea (OSK).
He was recognized for his dedication to pioneering the field of microwave photonics by developing ultra-low noise fiber photonics lasers.
The Haerim Optics and Photonics Award is given to an outstanding researcher who has made academic contributions in the field of optics and photonics for the last five years.
The name of the award (Haerim) comes from the pen-name of the renowned scholar, Professor Un-Chul Paek, because it is maintained using funds he contributed to the OSK.
The OSK will confer the award on February 8 during the 29th OSK Annual Meeting and Winter Conference of 2018.
2018.02.07 View 7379 -
 Meet the KAISTian of 2017, Professor YongKeun Park
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics is one of the star professors in KAIST. Rising to the academic stardom, Professor Park’s daily schedule is filled with series of business meetings in addition to lab meetings and lectures.
The year 2017 must have been special for him. During the year, he published numerous papers in international journals, such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications and Science Advances. These high performances drew international attention from renowned media, including Newsweek and Forbes. Moreover, recognizing his research performance, he was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in his mid-30s. Noting that the members’ age ranges from late 50s to early 60s, Professor Park’s case considered to be quite exceptional.
Adding to his academic achievement, he has launched two startups powered of his own technologies. One is called Tomocube, a company specialized in 3-D imaging microscope using holotomography technology. His company is currently exporting the products to multiple countries, including the United States and Japan. The other one is The.Wave.Talk which has technologies for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
His research career and entrepreneurship are well deserved recipient of many honors. At the 2018 kick-off ceremony, Professor Park was awarded the KAISTian of 2017 in recognition of his developing holographic measure and control technology as well as founding a new field for technology application.
KAISTian of the Year, first presented in 2001, is an award to recognize the achievements and exemplary contribution of KAIST member who has put significant effort nationally and internationally, enhancing the value of KAIST.
While receiving the award, he thanked his colleagues and his students who have achieved this far together. He said, “I would like to thank KAIST for providing environment for young professors like me so that we can engage themselves in research. Also, I would like to mention that I am an idea seeder and my students do the most of the research. So, I appreciate my students for their hard works, and it is very pleasure to have them. Lastly, I thank the professors for teaching these outstanding students. I feel great responsibility over this title. I will dedicate myself to make further progress in commercializing technology in KAIST.”
Expecting his successful startup cases as a model and great inspiration to students as well as professors, KAIST interviewed Professor Park.
Q What made you decide to found your startups?
A I believed that my research areas could be further used. As a professor, I believe that it is a university’s role to create added value through commercializing technology and creating startups.
Q You have co-founded two startups. What is your role in each company?
A So, basically I have two full-time jobs, professor in KAIST and CTO in Tomocube. After transferring the technology, I hold the position of advisor in The.Wave.Talk.
(Holographic images captured by the product Professor Park developed)
Q Do your students also participate in your companies or can they?
A No, the school and companies are separate spaces; in other words, they are not participating in my companies. They have trained my employees when transferring the technologies, but they are not directly working for the companies.
However, they can participate if they want to. If there’s a need to develop a certain technology, an industry-academia contract can be made. According to the agreement, students can work for the companies.
Q Were there any hardships when preparing the startups?
A At the initial stage, I did not have a financial problem, thanks to support from Startup KAIST. Yet, inviting capital is the beginning, and I think every step I made to operate, generate revenue, and so on is not easy.
Q Do you believe KAIST is startup-friendly?
A Yes, there’s no school like KAIST in Korea and any other country. Besides various programs to support startup activities, Startup KAIST has many professors equipped with a great deal of experience. Therefore, I believe that KAIST provides an excellent environment for both students and professors to create startups.
Q Do you have any suggestion to KAIST institutionally?
A Well, I would like to make a comment to students and professors in KAIST. I strongly recommend them to challenge themselves by launching startups if they have good ideas. Many students wish to begin their jobs in government-funded research institutes or major corporates, but I believe that engaging in a startup company will also give them valuable and very productive experience.
Unlike before, startup institutions are well established, so attracting good capital is not so hard. There are various activities offered by Startup KAIST, so it’s worthwhile giving it a try.
Q What is your goal for 2018 as a professor and entrepreneur?
A I don’t have a grand plan, but I will work harder to produce good students with new topics in KAIST while adding power to my companies to grow bigger.
By Se Yi Kim from the PR Office
2018.01.03 View 11309
Meet the KAISTian of 2017, Professor YongKeun Park
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics is one of the star professors in KAIST. Rising to the academic stardom, Professor Park’s daily schedule is filled with series of business meetings in addition to lab meetings and lectures.
The year 2017 must have been special for him. During the year, he published numerous papers in international journals, such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications and Science Advances. These high performances drew international attention from renowned media, including Newsweek and Forbes. Moreover, recognizing his research performance, he was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in his mid-30s. Noting that the members’ age ranges from late 50s to early 60s, Professor Park’s case considered to be quite exceptional.
Adding to his academic achievement, he has launched two startups powered of his own technologies. One is called Tomocube, a company specialized in 3-D imaging microscope using holotomography technology. His company is currently exporting the products to multiple countries, including the United States and Japan. The other one is The.Wave.Talk which has technologies for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
His research career and entrepreneurship are well deserved recipient of many honors. At the 2018 kick-off ceremony, Professor Park was awarded the KAISTian of 2017 in recognition of his developing holographic measure and control technology as well as founding a new field for technology application.
KAISTian of the Year, first presented in 2001, is an award to recognize the achievements and exemplary contribution of KAIST member who has put significant effort nationally and internationally, enhancing the value of KAIST.
While receiving the award, he thanked his colleagues and his students who have achieved this far together. He said, “I would like to thank KAIST for providing environment for young professors like me so that we can engage themselves in research. Also, I would like to mention that I am an idea seeder and my students do the most of the research. So, I appreciate my students for their hard works, and it is very pleasure to have them. Lastly, I thank the professors for teaching these outstanding students. I feel great responsibility over this title. I will dedicate myself to make further progress in commercializing technology in KAIST.”
Expecting his successful startup cases as a model and great inspiration to students as well as professors, KAIST interviewed Professor Park.
Q What made you decide to found your startups?
A I believed that my research areas could be further used. As a professor, I believe that it is a university’s role to create added value through commercializing technology and creating startups.
Q You have co-founded two startups. What is your role in each company?
A So, basically I have two full-time jobs, professor in KAIST and CTO in Tomocube. After transferring the technology, I hold the position of advisor in The.Wave.Talk.
(Holographic images captured by the product Professor Park developed)
Q Do your students also participate in your companies or can they?
A No, the school and companies are separate spaces; in other words, they are not participating in my companies. They have trained my employees when transferring the technologies, but they are not directly working for the companies.
However, they can participate if they want to. If there’s a need to develop a certain technology, an industry-academia contract can be made. According to the agreement, students can work for the companies.
Q Were there any hardships when preparing the startups?
A At the initial stage, I did not have a financial problem, thanks to support from Startup KAIST. Yet, inviting capital is the beginning, and I think every step I made to operate, generate revenue, and so on is not easy.
Q Do you believe KAIST is startup-friendly?
A Yes, there’s no school like KAIST in Korea and any other country. Besides various programs to support startup activities, Startup KAIST has many professors equipped with a great deal of experience. Therefore, I believe that KAIST provides an excellent environment for both students and professors to create startups.
Q Do you have any suggestion to KAIST institutionally?
A Well, I would like to make a comment to students and professors in KAIST. I strongly recommend them to challenge themselves by launching startups if they have good ideas. Many students wish to begin their jobs in government-funded research institutes or major corporates, but I believe that engaging in a startup company will also give them valuable and very productive experience.
Unlike before, startup institutions are well established, so attracting good capital is not so hard. There are various activities offered by Startup KAIST, so it’s worthwhile giving it a try.
Q What is your goal for 2018 as a professor and entrepreneur?
A I don’t have a grand plan, but I will work harder to produce good students with new topics in KAIST while adding power to my companies to grow bigger.
By Se Yi Kim from the PR Office
2018.01.03 View 11309 -
 Professor Je-Kyun Park, Awarded by The Korean BioChip Society
On November 9, Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST received an award from the 2017 Fall Meeting of The Korean BioChip Society held in Paradise Hotel Busan, Korea. This year’s meeting recognized Professor Park for developing lab-on-a-chip and microfluidic analytical technologies.
The Korean BioChip Society is a corporation of biochip professional established in 2006 for the development of biochip technology. Every year, the Society selects a recipient based on the nominees’ academic achievements and contributions to bio-fusion industry.
Professor Park served on the international editorial boards of renowned international journals in related fields, including Biosensors and Bioelectronics and Lab on a Chip. He was also the Committee Chairman of MicroTas in 2015.
2017.11.22 View 8134
Professor Je-Kyun Park, Awarded by The Korean BioChip Society
On November 9, Je-Kyun Park from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST received an award from the 2017 Fall Meeting of The Korean BioChip Society held in Paradise Hotel Busan, Korea. This year’s meeting recognized Professor Park for developing lab-on-a-chip and microfluidic analytical technologies.
The Korean BioChip Society is a corporation of biochip professional established in 2006 for the development of biochip technology. Every year, the Society selects a recipient based on the nominees’ academic achievements and contributions to bio-fusion industry.
Professor Park served on the international editorial boards of renowned international journals in related fields, including Biosensors and Bioelectronics and Lab on a Chip. He was also the Committee Chairman of MicroTas in 2015.
2017.11.22 View 8134 -
 Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 9612
Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 9612 -
 Material-Independent Nanocoating Antimicrobial Spray Significantly Extends the Shelf Life of Produce
The edible coating on produce has drawn a great deal of attention in the food and agricultural industry. It could not only prolong postharvest shelf life of produce against external changes in the environment but also provide additional nutrients to be useful for human health. However, most versions of the coating have had intrinsic limitations in their practical application. First, highly specific interactions between coating materials and target surfaces are required for a stable and durable coating. Even further, the coating of bulk substrates, such as fruits, is time consuming or is not achievable in the conventional solution-based coating. In this respect, material-independent and rapid coating strategies are highly demanded.
The research team led by Professor Insung Choi of the Department of Chemistry developed a sprayable nanocoating technique using plant-derived polyphenol that can be applied to any surface. This new nanocoating process can be completed in seconds to form nanometer-thick films, allowing for the coating of commodity goods, such as shoe insoles and fruits, in a controlled fashion. For example, spray-coated mandarin oranges and strawberries show significantly-prolonged postharvest shelf life, suggesting the practical potential in edible coatings of perishable produce.
The technology has been patented and is currently being commercialized for widespread use as a means of preserving produce. The research results have recently been published in Scientific Reports on Aug 1.
Polyphenols, a metabolite of photosynthesis, possess several hydroxyl groups and are found in a large number of plants showing excellent antioxidant properties. They have been widely used as a nontoxic food additive and are known to exhibit antibacterial, as well as potential anti-carcinogenic capabilities. Polyphenols can also be used with iron ions, which are naturally found in the body, to form an adhesive complex, which has been used in leather tanning, ink, etc.
The research team combined these chemical properties of polyphenol-iron complexes with spray techniques to develop their nanocoating technology. Compared to conventional immersion coating methods, which dip substrates in specialized coating solutions, this spray technique can coat the select areas more quickly. The spray also prevents cross contamination, which is a big concern for immersion methods. The research team has showcased the spray’s ability to coat a variety of different materials, including metals, plastics, glass, as well as textile fabrics. The polyphenol complex has been used to form antifogging films on corrective lenses, as well as antifungal treatments for shoe soles, demonstrating the versatility of their technique.
Furthermore, the spray has been used to coat produce with a naturally antibacterial, edible film. The coatings significantly improved the shelf life of tangerines and strawberries, preserving freshness beyond 28 days and 58 hours, respectively. (Uncoated fruit decomposed and became moldy under the same conditions). See the image below.
a –I, II: Uncoated and coated tangerines incubated for 14 and 28 days in daily-life settings
b –I: Uncoated and coated strawberries incubated for 58 hours in daily-life settings
b –II: Statistical investigation of the resulting edibility.
Professor Choi said, “Nanocoating technologies are still in their infancy, but they have untapped potential for exciting applications. As we have shown, nanocoatings can be easily adapted for several different uses, and the creative combination of existing nanomaterials and coating methods can synergize to unlock this potential.”
2017.08.10 View 9268
Material-Independent Nanocoating Antimicrobial Spray Significantly Extends the Shelf Life of Produce
The edible coating on produce has drawn a great deal of attention in the food and agricultural industry. It could not only prolong postharvest shelf life of produce against external changes in the environment but also provide additional nutrients to be useful for human health. However, most versions of the coating have had intrinsic limitations in their practical application. First, highly specific interactions between coating materials and target surfaces are required for a stable and durable coating. Even further, the coating of bulk substrates, such as fruits, is time consuming or is not achievable in the conventional solution-based coating. In this respect, material-independent and rapid coating strategies are highly demanded.
The research team led by Professor Insung Choi of the Department of Chemistry developed a sprayable nanocoating technique using plant-derived polyphenol that can be applied to any surface. This new nanocoating process can be completed in seconds to form nanometer-thick films, allowing for the coating of commodity goods, such as shoe insoles and fruits, in a controlled fashion. For example, spray-coated mandarin oranges and strawberries show significantly-prolonged postharvest shelf life, suggesting the practical potential in edible coatings of perishable produce.
The technology has been patented and is currently being commercialized for widespread use as a means of preserving produce. The research results have recently been published in Scientific Reports on Aug 1.
Polyphenols, a metabolite of photosynthesis, possess several hydroxyl groups and are found in a large number of plants showing excellent antioxidant properties. They have been widely used as a nontoxic food additive and are known to exhibit antibacterial, as well as potential anti-carcinogenic capabilities. Polyphenols can also be used with iron ions, which are naturally found in the body, to form an adhesive complex, which has been used in leather tanning, ink, etc.
The research team combined these chemical properties of polyphenol-iron complexes with spray techniques to develop their nanocoating technology. Compared to conventional immersion coating methods, which dip substrates in specialized coating solutions, this spray technique can coat the select areas more quickly. The spray also prevents cross contamination, which is a big concern for immersion methods. The research team has showcased the spray’s ability to coat a variety of different materials, including metals, plastics, glass, as well as textile fabrics. The polyphenol complex has been used to form antifogging films on corrective lenses, as well as antifungal treatments for shoe soles, demonstrating the versatility of their technique.
Furthermore, the spray has been used to coat produce with a naturally antibacterial, edible film. The coatings significantly improved the shelf life of tangerines and strawberries, preserving freshness beyond 28 days and 58 hours, respectively. (Uncoated fruit decomposed and became moldy under the same conditions). See the image below.
a –I, II: Uncoated and coated tangerines incubated for 14 and 28 days in daily-life settings
b –I: Uncoated and coated strawberries incubated for 58 hours in daily-life settings
b –II: Statistical investigation of the resulting edibility.
Professor Choi said, “Nanocoating technologies are still in their infancy, but they have untapped potential for exciting applications. As we have shown, nanocoatings can be easily adapted for several different uses, and the creative combination of existing nanomaterials and coating methods can synergize to unlock this potential.”
2017.08.10 View 9268 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Elected to the NAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was elected as a foreign associate to the US National Academy of Sciences (NAS) on May 2. The National Academy of Sciences elected 84 new members and 21 foreign associates in recognition of their distinguished and continuing achievements in their original research. Election to the Academy is widely regarded as one of the highest honors that a scientist can receive.
Professor Lee was also elected in 2010 as a member of the US National Academy of Engineering (NAE) for his leadership in microbial biotechnology and metabolic engineering, including the development of fermentation processes for biodegradable polymers and organic acids. Until 2016, there are only 12 people worldwide who are foreign associates of both NAS and NAE.
He is the first Korean elected to both prestigious academies, the NAS and the NAE in the US. Professor Lee is currently the dean of KAIST Institutes, the world leading institute for multi-and interdisciplinary research. He is also serving as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the World Economic Forum.
2017.05.16 View 9287
Distinguished Professor Lee Elected to the NAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was elected as a foreign associate to the US National Academy of Sciences (NAS) on May 2. The National Academy of Sciences elected 84 new members and 21 foreign associates in recognition of their distinguished and continuing achievements in their original research. Election to the Academy is widely regarded as one of the highest honors that a scientist can receive.
Professor Lee was also elected in 2010 as a member of the US National Academy of Engineering (NAE) for his leadership in microbial biotechnology and metabolic engineering, including the development of fermentation processes for biodegradable polymers and organic acids. Until 2016, there are only 12 people worldwide who are foreign associates of both NAS and NAE.
He is the first Korean elected to both prestigious academies, the NAS and the NAE in the US. Professor Lee is currently the dean of KAIST Institutes, the world leading institute for multi-and interdisciplinary research. He is also serving as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the World Economic Forum.
2017.05.16 View 9287 -
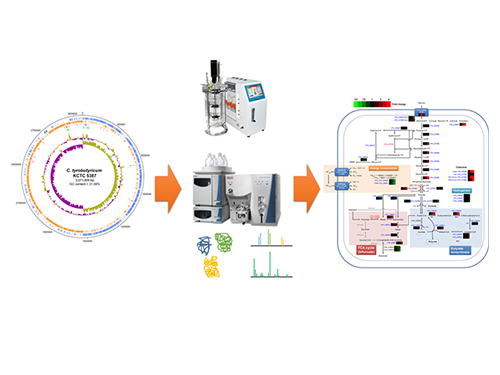 Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 10548
Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 10548 -
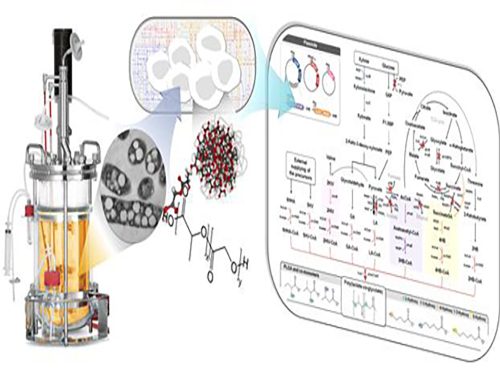 Non-Natural Biomedical Polymers Produced from Microorganisms
KAIST researchers have developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains to synthesize non-natural, biomedically important polymers including poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), previously considered impossible to obtain from biobased materials.
Renewable non-food biomass could potentially replace petrochemical raw materials to produce energy sources, useful chemicals, or a vast array of petroleum-based end products such as plastics, lubricants, paints, fertilizers, and vitamin capsules. In recent years, biorefineries which transform non-edible biomass into fuel, heat, power, chemicals, and materials have received a great deal of attention as a sustainable alternative to decreasing the reliance on fossil fuels.
A research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has established a biorefinery system to create non-natural polymers from natural sources, allowing various plastics to be made in an environmentally-friendly and sustainable manner. The research results were published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 7, 2016. The print version will be issued in April 2016.
The research team adopted a systems metabolic engineering approach to develop a microorganism that can produce diverse non-natural, biomedically important polymers and succeeded in synthesizing poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), a copolymer of two different polymer monomers, lactic and glycolic acid. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic, and has been widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications such as surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Inspired by the biosynthesis process for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), biologically-derived polyesters produced in nature by the bacterial fermentation of sugar or lipids, the research team designed a metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of PLGA through microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains.
The team had previously reported a recombinant E. coli producing PLGA by using the glyoxylate shunt pathway for the generation of glycolate from glucose, which was disclosed in their patents KR10-1575585-0000 (filing date of March 11, 2011), US08883463 and JP5820363. However, they discovered that the polymer content and glycolate fraction of PLGA could not be significantly enhanced via further engineering techniques. Thus, in this research, the team introduced a heterologous pathway to produce glycolate from xylose and succeeded in developing the recombinant E. coli producing PLGA and various novel copolymers much more efficiently.
In order to produce PLGA by microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates, the team incorporated external and engineered enzymes as catalysts to co-polymerize PLGA while establishing a few additional metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis to produce a range of different non-natural polymers, some for the first time. This bio-based synthetic process for PLGA and other polymers could substitute for the existing complicated chemical production that involves the preparation and purification of precursors, chemical polymerization processes, and the elimination of metal catalysts.
Professor Lee and his team performed in silico genome-scale metabolic simulations of the E. coli cell to predict and analyze changes in the metabolic fluxes of cells which were caused by the introduction of external metabolic pathways. Based on these results, genes are manipulated to optimize metabolic fluxes by eliminating the genes responsible for byproducts formation and enhancing the expression levels of certain genes, thereby achieving the effective production of target polymers as well as stimulating cell growth.
The team utilized the structural basis of broad substrate specificity of the key synthesizing enzyme, PHA synthase, to incorporate various co-monomers with main and side chains of different lengths. These monomers were produced inside the cell by metabolic engineering, and then copolymerized to improve the material properties of PLGA. As a result, a variety of PLGA copolymers with different monomer compositions such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved monomers, 3-hydroxyburate, 4-hydroxyburate, and 6-hydroxyhexanoate, were produced. Newly applied bioplastics such as 5-hydroxyvalerate and 2-hydroxyisovalerate were also made.
The team employed a systems metabolic engineering application which, according to the researchers, is the first successful example of biological production of PGLA and several novel copolymers from renewable biomass by one-step direct fermentation of metabolically engineered E.coli.
Professor Lee said, “We presented important findings that non-natural polymers, such as PLGA which is commonly used for drug delivery or biomedical devices, were produced by a metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it proposes a platform strategy in metabolic engineering, which can be further utilized in the development of numerous non-natural, useful polymers.”
Director Ilsub Baek at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said, “Professor Lee has led one of our research projects, the Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries, which began as part of the Ministry’s Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change. He and his team have continuously achieved promising results and been attracting greater interest from the global scientific community. As climate change technology grows more important, this research on the biological production of non-natural, high value polymers will have a great impact on science and industry.”
The title of the research paper is “One-step Fermentative Production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from Carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3485).” The lead authors are So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Si Jae Park, Assistant Professor of the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Myongji University. Won Jun Kim and Jung Eun Yang, both doctoral students in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project titled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Figure: Production of PLGA and Other Non-Natural Copolymers
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced a variety of PLGAs with different monomer compositions, proposing the chemosynthetic process of non-natural polymers from biomass. The non-natural polymer PLGA and its other copolymers, which were produced by engineered bacteria developed by taking a systems metabolic engineering approach, accumulate in granule forms within a cell.
2016.03.08 View 11830
Non-Natural Biomedical Polymers Produced from Microorganisms
KAIST researchers have developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains to synthesize non-natural, biomedically important polymers including poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), previously considered impossible to obtain from biobased materials.
Renewable non-food biomass could potentially replace petrochemical raw materials to produce energy sources, useful chemicals, or a vast array of petroleum-based end products such as plastics, lubricants, paints, fertilizers, and vitamin capsules. In recent years, biorefineries which transform non-edible biomass into fuel, heat, power, chemicals, and materials have received a great deal of attention as a sustainable alternative to decreasing the reliance on fossil fuels.
A research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has established a biorefinery system to create non-natural polymers from natural sources, allowing various plastics to be made in an environmentally-friendly and sustainable manner. The research results were published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 7, 2016. The print version will be issued in April 2016.
The research team adopted a systems metabolic engineering approach to develop a microorganism that can produce diverse non-natural, biomedically important polymers and succeeded in synthesizing poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), a copolymer of two different polymer monomers, lactic and glycolic acid. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic, and has been widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications such as surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Inspired by the biosynthesis process for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), biologically-derived polyesters produced in nature by the bacterial fermentation of sugar or lipids, the research team designed a metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of PLGA through microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains.
The team had previously reported a recombinant E. coli producing PLGA by using the glyoxylate shunt pathway for the generation of glycolate from glucose, which was disclosed in their patents KR10-1575585-0000 (filing date of March 11, 2011), US08883463 and JP5820363. However, they discovered that the polymer content and glycolate fraction of PLGA could not be significantly enhanced via further engineering techniques. Thus, in this research, the team introduced a heterologous pathway to produce glycolate from xylose and succeeded in developing the recombinant E. coli producing PLGA and various novel copolymers much more efficiently.
In order to produce PLGA by microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates, the team incorporated external and engineered enzymes as catalysts to co-polymerize PLGA while establishing a few additional metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis to produce a range of different non-natural polymers, some for the first time. This bio-based synthetic process for PLGA and other polymers could substitute for the existing complicated chemical production that involves the preparation and purification of precursors, chemical polymerization processes, and the elimination of metal catalysts.
Professor Lee and his team performed in silico genome-scale metabolic simulations of the E. coli cell to predict and analyze changes in the metabolic fluxes of cells which were caused by the introduction of external metabolic pathways. Based on these results, genes are manipulated to optimize metabolic fluxes by eliminating the genes responsible for byproducts formation and enhancing the expression levels of certain genes, thereby achieving the effective production of target polymers as well as stimulating cell growth.
The team utilized the structural basis of broad substrate specificity of the key synthesizing enzyme, PHA synthase, to incorporate various co-monomers with main and side chains of different lengths. These monomers were produced inside the cell by metabolic engineering, and then copolymerized to improve the material properties of PLGA. As a result, a variety of PLGA copolymers with different monomer compositions such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved monomers, 3-hydroxyburate, 4-hydroxyburate, and 6-hydroxyhexanoate, were produced. Newly applied bioplastics such as 5-hydroxyvalerate and 2-hydroxyisovalerate were also made.
The team employed a systems metabolic engineering application which, according to the researchers, is the first successful example of biological production of PGLA and several novel copolymers from renewable biomass by one-step direct fermentation of metabolically engineered E.coli.
Professor Lee said, “We presented important findings that non-natural polymers, such as PLGA which is commonly used for drug delivery or biomedical devices, were produced by a metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it proposes a platform strategy in metabolic engineering, which can be further utilized in the development of numerous non-natural, useful polymers.”
Director Ilsub Baek at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said, “Professor Lee has led one of our research projects, the Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries, which began as part of the Ministry’s Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change. He and his team have continuously achieved promising results and been attracting greater interest from the global scientific community. As climate change technology grows more important, this research on the biological production of non-natural, high value polymers will have a great impact on science and industry.”
The title of the research paper is “One-step Fermentative Production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from Carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3485).” The lead authors are So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Si Jae Park, Assistant Professor of the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Myongji University. Won Jun Kim and Jung Eun Yang, both doctoral students in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project titled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Figure: Production of PLGA and Other Non-Natural Copolymers
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced a variety of PLGAs with different monomer compositions, proposing the chemosynthetic process of non-natural polymers from biomass. The non-natural polymer PLGA and its other copolymers, which were produced by engineered bacteria developed by taking a systems metabolic engineering approach, accumulate in granule forms within a cell.
2016.03.08 View 11830 -
 President Steve Kang of KAIST Receives the Outstanding Contribution Award from the Korean-American Scientists and Engineers Association
The Korean-American Scientists and Engineers Association (KSEA), a non-profit Korean professional organization based in the United States with over 6,000 registered members, bestowed upon President Steve Kang of KAIST the 2015 Outstanding Contribution Award.
The award is presented to a person who has made significant contributions to the development of KSEA.
The award ceremony took place during the 2015 US-Korea Conference on Science, Technology, and Entrepreneurship (UKC), which was held on July 30, 2015, at the Hyatt Regency Hotel in Atlanta, Georgia.
The UKC is the flagship conference of KSEA, which takes place every year, and covers science, engineering, technology, industry, entrepreneurship, and leadership. It attracts more than 1,200 participants from the US and Korea. The UKC 2015 was held on July 29-August 1, 2015.
President Kang has participated in UKC conferences over the past few years as a plenary speaker, addressing major issues in science and technology for both nations, and provided generous support for the activities of UKC and KSEA. He also promoted discussions and exchanges of professional knowledge in his field, microelectronics, by organizing fora and symposia.
He addressed the UKC 2015 as a plenary speaker with a speech entitled “Pursuing Excellence with a Servant’s Heart.” President Kang said that good leadership should bring out synergistic contributions from all constituents and achieve excellence under all circumstances. He mentioned one example of good leadership, known as humble leadership, and explained how such leadership played an important role in the development of scientific breakthroughs, such as the world’s premier high-end microprocessor chip sets first produced by his team under extremely high pressure.
2015.08.05 View 7530
President Steve Kang of KAIST Receives the Outstanding Contribution Award from the Korean-American Scientists and Engineers Association
The Korean-American Scientists and Engineers Association (KSEA), a non-profit Korean professional organization based in the United States with over 6,000 registered members, bestowed upon President Steve Kang of KAIST the 2015 Outstanding Contribution Award.
The award is presented to a person who has made significant contributions to the development of KSEA.
The award ceremony took place during the 2015 US-Korea Conference on Science, Technology, and Entrepreneurship (UKC), which was held on July 30, 2015, at the Hyatt Regency Hotel in Atlanta, Georgia.
The UKC is the flagship conference of KSEA, which takes place every year, and covers science, engineering, technology, industry, entrepreneurship, and leadership. It attracts more than 1,200 participants from the US and Korea. The UKC 2015 was held on July 29-August 1, 2015.
President Kang has participated in UKC conferences over the past few years as a plenary speaker, addressing major issues in science and technology for both nations, and provided generous support for the activities of UKC and KSEA. He also promoted discussions and exchanges of professional knowledge in his field, microelectronics, by organizing fora and symposia.
He addressed the UKC 2015 as a plenary speaker with a speech entitled “Pursuing Excellence with a Servant’s Heart.” President Kang said that good leadership should bring out synergistic contributions from all constituents and achieve excellence under all circumstances. He mentioned one example of good leadership, known as humble leadership, and explained how such leadership played an important role in the development of scientific breakthroughs, such as the world’s premier high-end microprocessor chip sets first produced by his team under extremely high pressure.
2015.08.05 View 7530 -
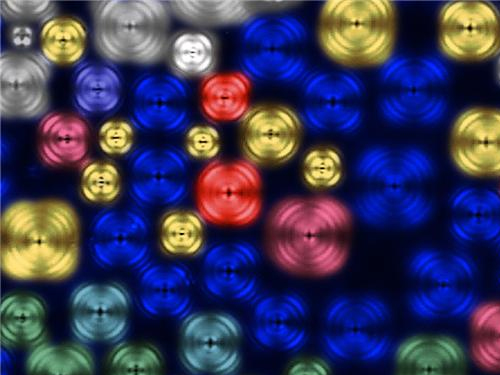 Dr. Se-Jung Kim Receives the Grand Prize at the International Photo and Image Contest on Light
Dr. Se-Jung Kim of the Physics Department at KAIST received the Grand Prize at the 2015 Photo and Image Contest of the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The United Nations has designated the year 2015 as the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The Optical Society of Korea celebrated the UN’s designation by hosting an international photo and image contest on the theme of light and optics related technology.
Dr. Kim presented a photo of images taken from a liquid crystal, which was entitled “A Micro Pinwheel.” She took pictures of liquid crystal images with a polarizing microscope and then colored the pictures. The liquid crystal has self-assembled circle domain structures, and each domain can form vortex optics. Her adviser for the project is Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Physics Department.
Her work was exhibited during the annual conference of the Optical Society of Korea, which was held on July 13-15, 2015 at Gyeong-Ju Hwabaek International Convention Center. It will also be exhibited at the National Science Museum in Gwacheon and the Kim Dae-Jung Convention Center in Gwangju.
Picture: A Micro Pinwheel
2015.07.31 View 10005
Dr. Se-Jung Kim Receives the Grand Prize at the International Photo and Image Contest on Light
Dr. Se-Jung Kim of the Physics Department at KAIST received the Grand Prize at the 2015 Photo and Image Contest of the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The United Nations has designated the year 2015 as the International Year of Light and Light-based Technologies.
The Optical Society of Korea celebrated the UN’s designation by hosting an international photo and image contest on the theme of light and optics related technology.
Dr. Kim presented a photo of images taken from a liquid crystal, which was entitled “A Micro Pinwheel.” She took pictures of liquid crystal images with a polarizing microscope and then colored the pictures. The liquid crystal has self-assembled circle domain structures, and each domain can form vortex optics. Her adviser for the project is Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Physics Department.
Her work was exhibited during the annual conference of the Optical Society of Korea, which was held on July 13-15, 2015 at Gyeong-Ju Hwabaek International Convention Center. It will also be exhibited at the National Science Museum in Gwacheon and the Kim Dae-Jung Convention Center in Gwangju.
Picture: A Micro Pinwheel
2015.07.31 View 10005 -
 Professor Suk-Joong Kang Receives the Richard Brook and Helmholtz Awards
Professor Suk-Joong Kang of KAIST’s Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering received the Richard Brook Award from the European Ceramic Society at its 14th conference held on June 21, 2015, in Toledo, Spain. The award is presented to the most distinguished academic or engineer in ceramics from a non-European country. Professor Kang gave the commemorative lecture after the award ceremony.
Professor Kang is an expert in the field of sintering and microstructural evolution in ceramics and metals. He suggested a new model for grain growth and identified the principles of microstructural evolution.
He also received the 2015 Helmholtz Fellow Award in June. The Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany, confers the award on outstanding senior scientists based outside Germany who have made great academic and research achievements in their fields.
Professor Kang said of the Brook Award, “It is such an honor to receive an award from an eminent global institution. I take this opportunity to thank my students and colleagues for their support, and I will work harder for my research.”
2015.07.20 View 6518
Professor Suk-Joong Kang Receives the Richard Brook and Helmholtz Awards
Professor Suk-Joong Kang of KAIST’s Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering received the Richard Brook Award from the European Ceramic Society at its 14th conference held on June 21, 2015, in Toledo, Spain. The award is presented to the most distinguished academic or engineer in ceramics from a non-European country. Professor Kang gave the commemorative lecture after the award ceremony.
Professor Kang is an expert in the field of sintering and microstructural evolution in ceramics and metals. He suggested a new model for grain growth and identified the principles of microstructural evolution.
He also received the 2015 Helmholtz Fellow Award in June. The Helmholtz Association, the largest scientific organization in Germany, confers the award on outstanding senior scientists based outside Germany who have made great academic and research achievements in their fields.
Professor Kang said of the Brook Award, “It is such an honor to receive an award from an eminent global institution. I take this opportunity to thank my students and colleagues for their support, and I will work harder for my research.”
2015.07.20 View 6518 -
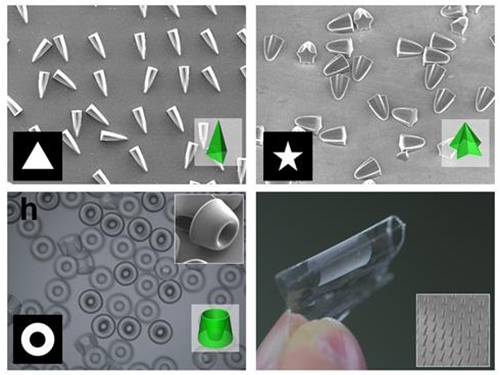 Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 10559
Novel Photolithographic Technology Enabling 3D Control over Functional Shapes of Microstructures
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim and his research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST have developed a novel photolithographic technology enabling control over the functional shapes of micropatterns using oxygen diffusion.
The research was published online in the March 13th issue of Nature Communications and was selected as a featured image for the journal.
Photolithography is a standard optical process for transferring micropatterns on to a substrate by exposing specific regions of the photoresist layer to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is used widely throughout industries that require micropatterns, especially in the semiconductor manufacturing industry.
Conventional photolithography relied on photomasks which protected certain regions of the substrate from the input UV light. Areas covered by the photomasks remain intact with the base layer while the areas exposed to the UV light are washed away, thus creating a micropattern. This technology was limited to a two-dimensional, disc-shaped design as the boundaries between the exposed and roofed regions are always in a parallel arrangement with the direction of the light.
Professor Kim’s research team discovered that: 1) the areas exposed to UV light lowered the concentration of oxygen and thus resulted in oxygen diffusion; and 2) manipulation of the diffusion speed and direction allowed control of the growth, shape and size of the polymers. Based on these findings, the team developed a new photolithographic technology that enabled the production of micropatterns with three-dimensional structures in various shapes and sizes.
Oxygen was considered an inhibitor during photopolymerization. Photoresist under UV light creates radicals which initialize a chemical reaction. These radicals are eliminated with the presence of oxygen and thus prevents the reaction. This suggests that the photoresist must be exposed to UV light for an extended time to completely remove oxygen for a chemical reaction to begin.
The research team, however, exploited the presence of oxygen. While the region affected by the UV light lowered oxygen concentration, the concentration in the untouched region remained unchanged. This difference in the concentrations caused a diffusion of oxygen to the region under UV light.
When the speed of the oxygen flow is slow, the diffusion occurs in parallel with the direction of the UV light. When fast, the diffusion process develops horizontally, outward from the area affected by the UV light. Professor Kim and his team proved this phenomenon both empirically and theoretically. Furthermore, by injecting an external oxygen source, the team was able to manipulate diffusion strength and direction, and thus control the shape and size of the polymer. The use of the polymerization inhibitors enabled and facilitated the fabrication of complex, three-dimensional micropatterns.
Professor Kim said, “While 3D printing is considered an innovative manufacturing technology, it cannot be used for mass-production of microscopic products. The new photolithographic technology will have a broad impact on both the academia and industry especially because existing, conventional photolithographic equipment can be used for the development of more complex micropatterns.” His newest technology will enhance the manufacturing process of three-dimensional polymers which were considered difficult to be commercialized.
The research was also dedicated to the late Professor Seung-Man Yang of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. He was considered one of the greatest scholars in Korea in the field of hydrodynamics and colloids.
Picture 1: Featured Image of Nature Communications, March 2015
Picture 2: Polymers with various shapes and sizes produced with the new photolithographic technology developed by Professor Kim
2015.04.06 View 10559