AT
-
 'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5186
'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5186 -
 Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 11130
Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 11130 -
 Synthesized Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons
Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, who is also the Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and his research team have recently published their research results entitled "Lanthanum-catalysed Synthesis of Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons in a Zeolite Template" on June 29, 2016 in Nature on a new method to synthesize carbons having graphene structures with 3D periodic micropores, a trait resulted from using a zeolite as a template for the synthesis. The research team expects this technology to find a range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts.
Graphene, an allotrope of carbon, which was discovered more than a decade ago, has led to myriad research that seeks to unlock its vast potential. Zeolites, commonly used microporous solid catalysts in the petrochemical industry, have recently attracted attention in the field of material science as a template for carbon synthesis. Zeolites’ individual crystal is distinguished by its unique 1 nanometer (nm)-size pore structures. These structures facilitate the accommodation of carbon nanotubes inside zeolites. In their paper, the research team showed that these nanoporous systems are an ideal template for the carbon synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) graphene architecture, but zeolite pores are too small to accommodate bulky molecular compounds like polyaromatic and furfuryl alcohol that are often used in carbon synthesis. Small molecules like ethylene and acetylene can be used as a carbon source to achieve successful carbonization within zeolite pores, but it comes at a great cost. The high temperatures required for the synthesis cause reactions of carbons being deposited randomly on the external surfaces of zeolites as well as their internal pore walls, resulting in coke deposition and consequently, causing serious diffusion limitations in the zeolite pores.
The team from the IBS Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials solved this conundrum with a novel approach. First author Dr. KIM Kyoungsoo explains: “The zeolite-template carbon synthesis has existed for a long time, but the problem with temperatures has foiled many scientists from extracting their full potential. Here, our team sought to find the answer by embedding lanthanum ions (La3+), a silvery-white metal element, in zeolite pores. This lowers the temperature required for the carbonization of ethylene or acetylene. Graphene-like sp2 carbon structures can be selectively formed inside the zeolite template, without carbon deposition at the external surfaces. After the zeolite template is removed, the carbon framework exhibits the electrical conductivity two orders of magnitude higher than amorphous mesoporous carbon, which is a pretty astonishing result. This highly efficient synthesis strategy based on the lanthanum ions renders the carbon framework to be formed in pores with a less than 1 nm diameter, just like as easily reproducible as in mesoporous templates. This provides a general method to synthesize carbon nanostructures with various topologies corresponding to the template zeolite pore topologies, such as FAU, EMT, beta, LTL, MFI, and LTA. Also, all the synthesis can be readily scaled up, which is important for practical applications in areas of batteries, fuel storage, and other zeolite-like catalyst supports.”
The research team began their experiment by utilizing La3+ ions. Dr. KIM elucidates why this silvery-white element proved so beneficial to the team, “La3+ ions are unreducible under carbonization process condition, so they can stay inside the zeolite pores instead of moving to the outer zeolite surface in the form of reduced metal particles. Within the pores, they can stabilize ethylene and the pyrocondensation intermediately to form a carbon framework in zeolites.”
In order to test this hypothesis, the team compared the amount of carbon deposited in La3+-containing form of Y zeolite (LaY) sample against a host of other samples such as NaY and HY. The experimental results indicate that all the LaY, NaY, and HY zeolite samples show rapid carbon deposition at 800°C. However, as the temperature decreases, there appears to be a dramatic difference between the different ionic forms of zeolites. At 600°C, the LaY zeolite is still active as a carbon deposition template. In contrast, both NaY and HY lose their carbon deposition functions almost completely.
The results, according to their paper published in Nature, highlight a catalytic effect of lanthanum for carbonization. By making graphene with 3D periodic nanoporous architectures, it promises a wide range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts but due to the lack of efficient synthetic strategies, such applications have not yet been successful. By taking advantage of the pore-selective carbon filling at decreased temperatures, the synthesis can readily be scaled up for studies requiring bulk quantities of carbon, in particular high electrical conductivity, which is a highly sought aspect for the production of batteries.
YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/lkNiHiB8lBk
Image 1: (Top to Bottom) Zeolite Template: Microporous Aluminosilicate; Zeolite ion exchanged with La3+ ions in aqueous solution; and Zeolite Template with La3+ ions
Image 2: (Top to Bottom) Catalytic carbonization progressed at La3+ ions-exchanged sites using ethylene as a carbon precursor. Carbon is highlighted in grey; Zeolite template removed in an acid solution (HF/ HCl); Microporous 3D graphene-like carbon
2016.07.01 View 9390
Synthesized Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons
Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, who is also the Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and his research team have recently published their research results entitled "Lanthanum-catalysed Synthesis of Microporous 3D Graphene-like Carbons in a Zeolite Template" on June 29, 2016 in Nature on a new method to synthesize carbons having graphene structures with 3D periodic micropores, a trait resulted from using a zeolite as a template for the synthesis. The research team expects this technology to find a range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts.
Graphene, an allotrope of carbon, which was discovered more than a decade ago, has led to myriad research that seeks to unlock its vast potential. Zeolites, commonly used microporous solid catalysts in the petrochemical industry, have recently attracted attention in the field of material science as a template for carbon synthesis. Zeolites’ individual crystal is distinguished by its unique 1 nanometer (nm)-size pore structures. These structures facilitate the accommodation of carbon nanotubes inside zeolites. In their paper, the research team showed that these nanoporous systems are an ideal template for the carbon synthesis of three-dimensional (3D) graphene architecture, but zeolite pores are too small to accommodate bulky molecular compounds like polyaromatic and furfuryl alcohol that are often used in carbon synthesis. Small molecules like ethylene and acetylene can be used as a carbon source to achieve successful carbonization within zeolite pores, but it comes at a great cost. The high temperatures required for the synthesis cause reactions of carbons being deposited randomly on the external surfaces of zeolites as well as their internal pore walls, resulting in coke deposition and consequently, causing serious diffusion limitations in the zeolite pores.
The team from the IBS Center for Nanomaterials and Carbon Materials solved this conundrum with a novel approach. First author Dr. KIM Kyoungsoo explains: “The zeolite-template carbon synthesis has existed for a long time, but the problem with temperatures has foiled many scientists from extracting their full potential. Here, our team sought to find the answer by embedding lanthanum ions (La3+), a silvery-white metal element, in zeolite pores. This lowers the temperature required for the carbonization of ethylene or acetylene. Graphene-like sp2 carbon structures can be selectively formed inside the zeolite template, without carbon deposition at the external surfaces. After the zeolite template is removed, the carbon framework exhibits the electrical conductivity two orders of magnitude higher than amorphous mesoporous carbon, which is a pretty astonishing result. This highly efficient synthesis strategy based on the lanthanum ions renders the carbon framework to be formed in pores with a less than 1 nm diameter, just like as easily reproducible as in mesoporous templates. This provides a general method to synthesize carbon nanostructures with various topologies corresponding to the template zeolite pore topologies, such as FAU, EMT, beta, LTL, MFI, and LTA. Also, all the synthesis can be readily scaled up, which is important for practical applications in areas of batteries, fuel storage, and other zeolite-like catalyst supports.”
The research team began their experiment by utilizing La3+ ions. Dr. KIM elucidates why this silvery-white element proved so beneficial to the team, “La3+ ions are unreducible under carbonization process condition, so they can stay inside the zeolite pores instead of moving to the outer zeolite surface in the form of reduced metal particles. Within the pores, they can stabilize ethylene and the pyrocondensation intermediately to form a carbon framework in zeolites.”
In order to test this hypothesis, the team compared the amount of carbon deposited in La3+-containing form of Y zeolite (LaY) sample against a host of other samples such as NaY and HY. The experimental results indicate that all the LaY, NaY, and HY zeolite samples show rapid carbon deposition at 800°C. However, as the temperature decreases, there appears to be a dramatic difference between the different ionic forms of zeolites. At 600°C, the LaY zeolite is still active as a carbon deposition template. In contrast, both NaY and HY lose their carbon deposition functions almost completely.
The results, according to their paper published in Nature, highlight a catalytic effect of lanthanum for carbonization. By making graphene with 3D periodic nanoporous architectures, it promises a wide range of useful applications such as in batteries and catalysts but due to the lack of efficient synthetic strategies, such applications have not yet been successful. By taking advantage of the pore-selective carbon filling at decreased temperatures, the synthesis can readily be scaled up for studies requiring bulk quantities of carbon, in particular high electrical conductivity, which is a highly sought aspect for the production of batteries.
YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/lkNiHiB8lBk
Image 1: (Top to Bottom) Zeolite Template: Microporous Aluminosilicate; Zeolite ion exchanged with La3+ ions in aqueous solution; and Zeolite Template with La3+ ions
Image 2: (Top to Bottom) Catalytic carbonization progressed at La3+ ions-exchanged sites using ethylene as a carbon precursor. Carbon is highlighted in grey; Zeolite template removed in an acid solution (HF/ HCl); Microporous 3D graphene-like carbon
2016.07.01 View 9390 -
 Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11057
Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 11057 -
 KAIST to Participate in Summer Davos Forum 2016 in China
A group of KAIST researchers will share their insights on the future and challenges of the current technological innovations impacting all aspects of society, while showcasing their research excellence in artificial intelligence and robotics.
Scientific and technological breakthroughs are more important than ever as key agents to drive social, economic, and political changes and advancements in today’s world. The World Economic Forum (WEF), an international organization that provides one of the broadest engagement platforms to address issues of major concern to the global community, will discuss the effects of these breakthroughs at its 10th Annual Meeting of the New Champions, a.k.a., the Summer Davos Forum, in Tianjin, China, June 26-28, 2016.
Three professors from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will join the Annual Meeting and offer their expertise in the fields of biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and robotics to explore the conference theme, “The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Its Transformational Impact.” The Fourth Industrial Revolution, a term coined by WEF founder, Klaus Schwab, is characterized by a range of new technologies that fuse the physical, digital, and biological worlds, such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and automation.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will speak at the Experts Reception to be held on June 25, 2016 on the topic of “The Summer Davos Forum and Science and Technology in Asia.” On June 27, 2016, he will participate in two separate discussion sessions.
In the first session entitled “What If Drugs Are Printed from the Internet?,” Professor Lee will discuss the impacts of advancements in biotechnology and 3D printing technology on the future of medicine with Nita A. Farahany, a Duke University professor. Clare Matterson, the Director of Strategy at Wellcome Trust in the United Kingdom, will serve as the moderator. The discussants will note recent developments made in the way patients receive their medicine, for example, downloading drugs directly from the internet and the production of yeast strains to make opioids for pain treatment through systems metabolic engineering. They will also suggest how these emerging technologies will transform the landscape of the pharmaceutical industry in the years to come.
In the second session, “Lessons for Life,” Professor Lee will talk about how to nurture life-long learning and creativity to support personal and professional growth necessary in an era of the new industrial revolution.
During the Annual Meeting, Professors Jong-Hwan Kim of the Electrical Engineering School and David Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Department will host, together with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and AnthroTronix, an engineering research and development company, a technological exhibition on robotics. Professor Kim, the founder of the internally renowned Robot World Cup, will showcase his humanoid soccer-playing micro-robots and display their various cutting-edge technologies such as imaging processing, artificial intelligence, walking, and balancing. Professor Shim will present a human-like robotic piloting system, PIBOT, which autonomously operates a simulated flight program by employing control sticks and guiding an airplane from takeoff to landing.
In addition, the two professors will join Professor Lee, who is also a moderator, to host a KAIST-led session on June 26, 2016, entitled “Science in Depth: From Deep Learning to Autonomous Machines.” Professors Kim and Shim will explore new opportunities and challenges in their fields from machine learning to autonomous robotics, including unmanned vehicles and drones.
Since 2011, KAIST has participated in the World Economic Forum’s two flagship conferences, the January and June Davos Forums, to introduce outstanding talents, share their latest research achievements, and interact with global leaders.
KAIST President Steve Kang said, “It is important for KAIST to be involved in global forums that identify issues critical to humanity and seek answers to solve them, and where our skills and knowledge in science and technology can play a meaningful role. The Annual Meeting in China will become another venue to accomplish this.”
2016.06.27 View 12558
KAIST to Participate in Summer Davos Forum 2016 in China
A group of KAIST researchers will share their insights on the future and challenges of the current technological innovations impacting all aspects of society, while showcasing their research excellence in artificial intelligence and robotics.
Scientific and technological breakthroughs are more important than ever as key agents to drive social, economic, and political changes and advancements in today’s world. The World Economic Forum (WEF), an international organization that provides one of the broadest engagement platforms to address issues of major concern to the global community, will discuss the effects of these breakthroughs at its 10th Annual Meeting of the New Champions, a.k.a., the Summer Davos Forum, in Tianjin, China, June 26-28, 2016.
Three professors from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will join the Annual Meeting and offer their expertise in the fields of biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and robotics to explore the conference theme, “The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Its Transformational Impact.” The Fourth Industrial Revolution, a term coined by WEF founder, Klaus Schwab, is characterized by a range of new technologies that fuse the physical, digital, and biological worlds, such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and automation.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will speak at the Experts Reception to be held on June 25, 2016 on the topic of “The Summer Davos Forum and Science and Technology in Asia.” On June 27, 2016, he will participate in two separate discussion sessions.
In the first session entitled “What If Drugs Are Printed from the Internet?,” Professor Lee will discuss the impacts of advancements in biotechnology and 3D printing technology on the future of medicine with Nita A. Farahany, a Duke University professor. Clare Matterson, the Director of Strategy at Wellcome Trust in the United Kingdom, will serve as the moderator. The discussants will note recent developments made in the way patients receive their medicine, for example, downloading drugs directly from the internet and the production of yeast strains to make opioids for pain treatment through systems metabolic engineering. They will also suggest how these emerging technologies will transform the landscape of the pharmaceutical industry in the years to come.
In the second session, “Lessons for Life,” Professor Lee will talk about how to nurture life-long learning and creativity to support personal and professional growth necessary in an era of the new industrial revolution.
During the Annual Meeting, Professors Jong-Hwan Kim of the Electrical Engineering School and David Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Department will host, together with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and AnthroTronix, an engineering research and development company, a technological exhibition on robotics. Professor Kim, the founder of the internally renowned Robot World Cup, will showcase his humanoid soccer-playing micro-robots and display their various cutting-edge technologies such as imaging processing, artificial intelligence, walking, and balancing. Professor Shim will present a human-like robotic piloting system, PIBOT, which autonomously operates a simulated flight program by employing control sticks and guiding an airplane from takeoff to landing.
In addition, the two professors will join Professor Lee, who is also a moderator, to host a KAIST-led session on June 26, 2016, entitled “Science in Depth: From Deep Learning to Autonomous Machines.” Professors Kim and Shim will explore new opportunities and challenges in their fields from machine learning to autonomous robotics, including unmanned vehicles and drones.
Since 2011, KAIST has participated in the World Economic Forum’s two flagship conferences, the January and June Davos Forums, to introduce outstanding talents, share their latest research achievements, and interact with global leaders.
KAIST President Steve Kang said, “It is important for KAIST to be involved in global forums that identify issues critical to humanity and seek answers to solve them, and where our skills and knowledge in science and technology can play a meaningful role. The Annual Meeting in China will become another venue to accomplish this.”
2016.06.27 View 12558 -
 Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
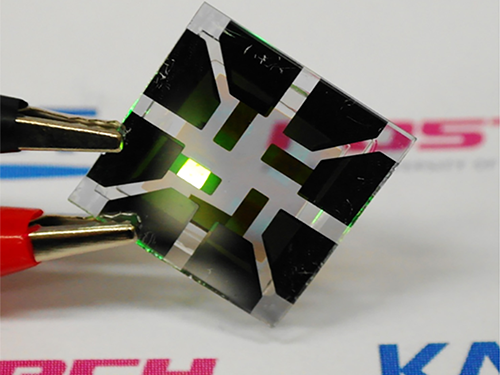
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 13997
Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 13997 -
 KAIST Researchers Receive the 2016 IEEE William R. Bennett Prize
A research team led by Professors Yung Yi and Song Chong from the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been awarded the 2016 William R. Bennett Prize of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which is the most prestigious award in the field of communications network. The IEEE bestows the honor annually and selects winning papers from among those published in the past three years for its quality, originality, scientific citation index, and peer reviews.
The IEEE award ceremony will take place on May 24, 2016 at the IEEE International Conference on Communications in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The team members include Dr. Kyoung-Han Lee, a KAIST graduate, who is currently a professor at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in Korea, Dr. Joo-Hyun Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at Ohio State University in the United States, and In-Jong Rhee, a vice president of the Mobile Division at Samsung Electronics. The same KAIST team previously received the award back in 2013, making them the second recipient ever to win the IEEE William R. Bennett Prize twice.
Past winners include Professors Robert Gallager of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Sachin Katti of Stanford University, and Ion Stoica of the University of California at Berkeley.
The research team received the Bennett award for their work on “Mobile Data Offloading: How Much Can WiFi Deliver?” Their research paper has been cited more than 500 times since its publication in 2013. They proposed an original method to effectively offload the cellular network and maximize the Wi-Fi network usage by analyzing the pattern of individual human mobility in daily life.
2016.05.02 View 13612
KAIST Researchers Receive the 2016 IEEE William R. Bennett Prize
A research team led by Professors Yung Yi and Song Chong from the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been awarded the 2016 William R. Bennett Prize of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which is the most prestigious award in the field of communications network. The IEEE bestows the honor annually and selects winning papers from among those published in the past three years for its quality, originality, scientific citation index, and peer reviews.
The IEEE award ceremony will take place on May 24, 2016 at the IEEE International Conference on Communications in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The team members include Dr. Kyoung-Han Lee, a KAIST graduate, who is currently a professor at Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST) in Korea, Dr. Joo-Hyun Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at Ohio State University in the United States, and In-Jong Rhee, a vice president of the Mobile Division at Samsung Electronics. The same KAIST team previously received the award back in 2013, making them the second recipient ever to win the IEEE William R. Bennett Prize twice.
Past winners include Professors Robert Gallager of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), Sachin Katti of Stanford University, and Ion Stoica of the University of California at Berkeley.
The research team received the Bennett award for their work on “Mobile Data Offloading: How Much Can WiFi Deliver?” Their research paper has been cited more than 500 times since its publication in 2013. They proposed an original method to effectively offload the cellular network and maximize the Wi-Fi network usage by analyzing the pattern of individual human mobility in daily life.
2016.05.02 View 13612 -
 KAIST and McKinsey Korea Agreed to Cultivate Management Leaders
KAIST and McKinsey Korea signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) for the “Joint Research on Innovative Instructional Method to Cultivate Future Management Leaders” on April 8, 2016, at the SUPEX Management Hall of KAIST Management School in Seoul.
Under the MOU, both organizations will cooperate in the following research areas: management strategies to overcome the low growth of Korean economy, instructional methods to foster leaders in the field of business and management, and innovative management systems for business.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to work with McKinsey, a worldwide management consulting firm, to foster leaders in science and business. As we see more demanding challenges of managing and leading science-based businesses today, this alliance is indeed timely and will be very helpful.”
2016.04.15 View 5762
KAIST and McKinsey Korea Agreed to Cultivate Management Leaders
KAIST and McKinsey Korea signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) for the “Joint Research on Innovative Instructional Method to Cultivate Future Management Leaders” on April 8, 2016, at the SUPEX Management Hall of KAIST Management School in Seoul.
Under the MOU, both organizations will cooperate in the following research areas: management strategies to overcome the low growth of Korean economy, instructional methods to foster leaders in the field of business and management, and innovative management systems for business.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to work with McKinsey, a worldwide management consulting firm, to foster leaders in science and business. As we see more demanding challenges of managing and leading science-based businesses today, this alliance is indeed timely and will be very helpful.”
2016.04.15 View 5762 -
 KAIST, NTU, and Technion Collaborate for Research in Emerging Fields
KAIST, Nanyang Technological University (NTU) of Singapore, and Technion of Israel signed an agreement on April 11, 2016 in Seoul to create a five-year joint research program for some of the most innovative and entrepreneurial areas: robotics, medical technologies, satellites, materials science and engineering, and entrepreneurship. Under the agreement, the universities will also offer dual degree opportunities, exchange visits, and internships.
In the picture from the left, Bertil Andersson of NTU, Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST, and Peretz Lavie of Technion hold the signed memorandum of understanding.
2016.04.14 View 11545
KAIST, NTU, and Technion Collaborate for Research in Emerging Fields
KAIST, Nanyang Technological University (NTU) of Singapore, and Technion of Israel signed an agreement on April 11, 2016 in Seoul to create a five-year joint research program for some of the most innovative and entrepreneurial areas: robotics, medical technologies, satellites, materials science and engineering, and entrepreneurship. Under the agreement, the universities will also offer dual degree opportunities, exchange visits, and internships.
In the picture from the left, Bertil Andersson of NTU, Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST, and Peretz Lavie of Technion hold the signed memorandum of understanding.
2016.04.14 View 11545 -
 Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activated by KAIST and UPenn Teams
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik of the Chemistry Department at KAIST and his team collaborated with an international team to discover a novel chemical reaction, carbon-hydrogen borylation using methane, and their research results were published in the March 25th issue of Science.
For details, please refer to the following press release from the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS) in Korea and the University of Pennsylvania in the United States.
Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activation Achieved for the First Time
The Institute for Basic Science, March 24, 2016
Penn Chemists Lay Groundwork for Countless New, Cleaner Uses of Methane
University of Pennsylvania, March 24, 2016
2016.03.25 View 9701
Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activated by KAIST and UPenn Teams
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik of the Chemistry Department at KAIST and his team collaborated with an international team to discover a novel chemical reaction, carbon-hydrogen borylation using methane, and their research results were published in the March 25th issue of Science.
For details, please refer to the following press release from the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS) in Korea and the University of Pennsylvania in the United States.
Efficient Methane C-H Bond Activation Achieved for the First Time
The Institute for Basic Science, March 24, 2016
Penn Chemists Lay Groundwork for Countless New, Cleaner Uses of Methane
University of Pennsylvania, March 24, 2016
2016.03.25 View 9701 -
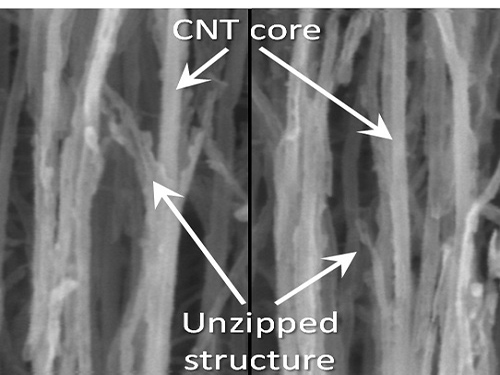 KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 8986
KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 8986 -
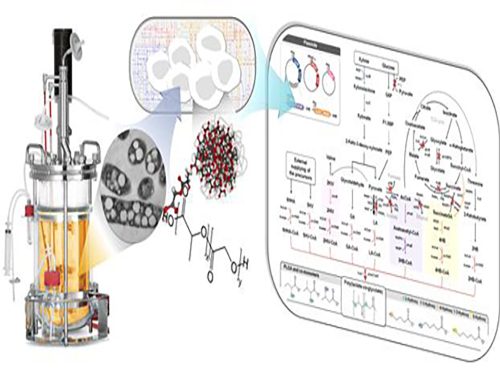 Non-Natural Biomedical Polymers Produced from Microorganisms
KAIST researchers have developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains to synthesize non-natural, biomedically important polymers including poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), previously considered impossible to obtain from biobased materials.
Renewable non-food biomass could potentially replace petrochemical raw materials to produce energy sources, useful chemicals, or a vast array of petroleum-based end products such as plastics, lubricants, paints, fertilizers, and vitamin capsules. In recent years, biorefineries which transform non-edible biomass into fuel, heat, power, chemicals, and materials have received a great deal of attention as a sustainable alternative to decreasing the reliance on fossil fuels.
A research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has established a biorefinery system to create non-natural polymers from natural sources, allowing various plastics to be made in an environmentally-friendly and sustainable manner. The research results were published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 7, 2016. The print version will be issued in April 2016.
The research team adopted a systems metabolic engineering approach to develop a microorganism that can produce diverse non-natural, biomedically important polymers and succeeded in synthesizing poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), a copolymer of two different polymer monomers, lactic and glycolic acid. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic, and has been widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications such as surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Inspired by the biosynthesis process for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), biologically-derived polyesters produced in nature by the bacterial fermentation of sugar or lipids, the research team designed a metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of PLGA through microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains.
The team had previously reported a recombinant E. coli producing PLGA by using the glyoxylate shunt pathway for the generation of glycolate from glucose, which was disclosed in their patents KR10-1575585-0000 (filing date of March 11, 2011), US08883463 and JP5820363. However, they discovered that the polymer content and glycolate fraction of PLGA could not be significantly enhanced via further engineering techniques. Thus, in this research, the team introduced a heterologous pathway to produce glycolate from xylose and succeeded in developing the recombinant E. coli producing PLGA and various novel copolymers much more efficiently.
In order to produce PLGA by microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates, the team incorporated external and engineered enzymes as catalysts to co-polymerize PLGA while establishing a few additional metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis to produce a range of different non-natural polymers, some for the first time. This bio-based synthetic process for PLGA and other polymers could substitute for the existing complicated chemical production that involves the preparation and purification of precursors, chemical polymerization processes, and the elimination of metal catalysts.
Professor Lee and his team performed in silico genome-scale metabolic simulations of the E. coli cell to predict and analyze changes in the metabolic fluxes of cells which were caused by the introduction of external metabolic pathways. Based on these results, genes are manipulated to optimize metabolic fluxes by eliminating the genes responsible for byproducts formation and enhancing the expression levels of certain genes, thereby achieving the effective production of target polymers as well as stimulating cell growth.
The team utilized the structural basis of broad substrate specificity of the key synthesizing enzyme, PHA synthase, to incorporate various co-monomers with main and side chains of different lengths. These monomers were produced inside the cell by metabolic engineering, and then copolymerized to improve the material properties of PLGA. As a result, a variety of PLGA copolymers with different monomer compositions such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved monomers, 3-hydroxyburate, 4-hydroxyburate, and 6-hydroxyhexanoate, were produced. Newly applied bioplastics such as 5-hydroxyvalerate and 2-hydroxyisovalerate were also made.
The team employed a systems metabolic engineering application which, according to the researchers, is the first successful example of biological production of PGLA and several novel copolymers from renewable biomass by one-step direct fermentation of metabolically engineered E.coli.
Professor Lee said, “We presented important findings that non-natural polymers, such as PLGA which is commonly used for drug delivery or biomedical devices, were produced by a metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it proposes a platform strategy in metabolic engineering, which can be further utilized in the development of numerous non-natural, useful polymers.”
Director Ilsub Baek at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said, “Professor Lee has led one of our research projects, the Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries, which began as part of the Ministry’s Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change. He and his team have continuously achieved promising results and been attracting greater interest from the global scientific community. As climate change technology grows more important, this research on the biological production of non-natural, high value polymers will have a great impact on science and industry.”
The title of the research paper is “One-step Fermentative Production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from Carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3485).” The lead authors are So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Si Jae Park, Assistant Professor of the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Myongji University. Won Jun Kim and Jung Eun Yang, both doctoral students in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project titled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
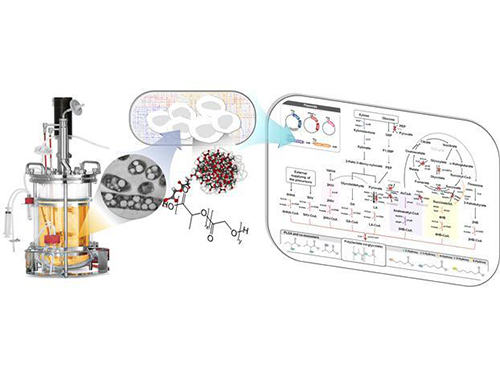
Figure: Production of PLGA and Other Non-Natural Copolymers
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced a variety of PLGAs with different monomer compositions, proposing the chemosynthetic process of non-natural polymers from biomass. The non-natural polymer PLGA and its other copolymers, which were produced by engineered bacteria developed by taking a systems metabolic engineering approach, accumulate in granule forms within a cell.
2016.03.08 View 11947
Non-Natural Biomedical Polymers Produced from Microorganisms
KAIST researchers have developed metabolically engineered Escherichia coli strains to synthesize non-natural, biomedically important polymers including poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), previously considered impossible to obtain from biobased materials.
Renewable non-food biomass could potentially replace petrochemical raw materials to produce energy sources, useful chemicals, or a vast array of petroleum-based end products such as plastics, lubricants, paints, fertilizers, and vitamin capsules. In recent years, biorefineries which transform non-edible biomass into fuel, heat, power, chemicals, and materials have received a great deal of attention as a sustainable alternative to decreasing the reliance on fossil fuels.
A research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST has established a biorefinery system to create non-natural polymers from natural sources, allowing various plastics to be made in an environmentally-friendly and sustainable manner. The research results were published online in Nature Biotechnology on March 7, 2016. The print version will be issued in April 2016.
The research team adopted a systems metabolic engineering approach to develop a microorganism that can produce diverse non-natural, biomedically important polymers and succeeded in synthesizing poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA), a copolymer of two different polymer monomers, lactic and glycolic acid. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and non-toxic, and has been widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications such as surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Inspired by the biosynthesis process for polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), biologically-derived polyesters produced in nature by the bacterial fermentation of sugar or lipids, the research team designed a metabolic pathway for the biosynthesis of PLGA through microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (E. coli) strains.
The team had previously reported a recombinant E. coli producing PLGA by using the glyoxylate shunt pathway for the generation of glycolate from glucose, which was disclosed in their patents KR10-1575585-0000 (filing date of March 11, 2011), US08883463 and JP5820363. However, they discovered that the polymer content and glycolate fraction of PLGA could not be significantly enhanced via further engineering techniques. Thus, in this research, the team introduced a heterologous pathway to produce glycolate from xylose and succeeded in developing the recombinant E. coli producing PLGA and various novel copolymers much more efficiently.
In order to produce PLGA by microbial fermentation directly from carbohydrates, the team incorporated external and engineered enzymes as catalysts to co-polymerize PLGA while establishing a few additional metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis to produce a range of different non-natural polymers, some for the first time. This bio-based synthetic process for PLGA and other polymers could substitute for the existing complicated chemical production that involves the preparation and purification of precursors, chemical polymerization processes, and the elimination of metal catalysts.
Professor Lee and his team performed in silico genome-scale metabolic simulations of the E. coli cell to predict and analyze changes in the metabolic fluxes of cells which were caused by the introduction of external metabolic pathways. Based on these results, genes are manipulated to optimize metabolic fluxes by eliminating the genes responsible for byproducts formation and enhancing the expression levels of certain genes, thereby achieving the effective production of target polymers as well as stimulating cell growth.
The team utilized the structural basis of broad substrate specificity of the key synthesizing enzyme, PHA synthase, to incorporate various co-monomers with main and side chains of different lengths. These monomers were produced inside the cell by metabolic engineering, and then copolymerized to improve the material properties of PLGA. As a result, a variety of PLGA copolymers with different monomer compositions such as the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved monomers, 3-hydroxyburate, 4-hydroxyburate, and 6-hydroxyhexanoate, were produced. Newly applied bioplastics such as 5-hydroxyvalerate and 2-hydroxyisovalerate were also made.
The team employed a systems metabolic engineering application which, according to the researchers, is the first successful example of biological production of PGLA and several novel copolymers from renewable biomass by one-step direct fermentation of metabolically engineered E.coli.
Professor Lee said, “We presented important findings that non-natural polymers, such as PLGA which is commonly used for drug delivery or biomedical devices, were produced by a metabolically engineered gut bacterium. Our research is meaningful in that it proposes a platform strategy in metabolic engineering, which can be further utilized in the development of numerous non-natural, useful polymers.”
Director Ilsub Baek at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said, “Professor Lee has led one of our research projects, the Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries, which began as part of the Ministry’s Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change. He and his team have continuously achieved promising results and been attracting greater interest from the global scientific community. As climate change technology grows more important, this research on the biological production of non-natural, high value polymers will have a great impact on science and industry.”
The title of the research paper is “One-step Fermentative Production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) from Carbohydrates in Escherichia coli (DOI: 10.1038/nbt.3485).” The lead authors are So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Si Jae Park, Assistant Professor of the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Myongji University. Won Jun Kim and Jung Eun Yang, both doctoral students in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project titled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Figure: Production of PLGA and Other Non-Natural Copolymers
This schematic diagram shows the overall conceptualization of how metabolically engineered E. coli produced a variety of PLGAs with different monomer compositions, proposing the chemosynthetic process of non-natural polymers from biomass. The non-natural polymer PLGA and its other copolymers, which were produced by engineered bacteria developed by taking a systems metabolic engineering approach, accumulate in granule forms within a cell.
2016.03.08 View 11947