ES
-
 Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
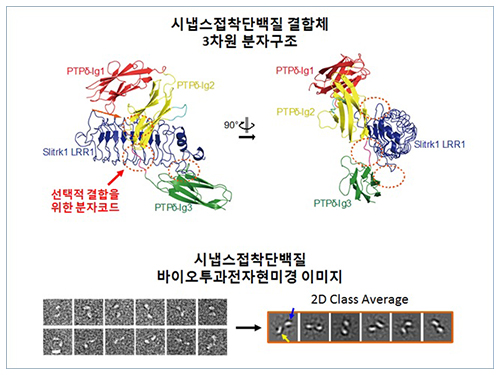
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 12175
Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 12175 -
 Elsevier Selects a KAIST Graduate's Paper as the Top Cited Papers in 2011-2012
Dr. Myung-Won Seo, a graduate from the Department of Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering at KAIST, published a paper in January 2011 in Chemical Engineering Journal, which was entitled “Solid Circulation and Loop-seal Characteristics of a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed: Experiments and CFD Simulation.” His paper was selected by Elsevier as the Top Cited Papers of 2011-2012. The Chemical Engineering Journal is a renowned peer-reviewed journal issued by Elsevier.
Dr. Seo published another paper, “CFD Simulation with Experiments in a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed Gasifier,” in January 2012 in Computers & Chemical Engineering, which was also selected as the Most Downloaded Papers in 2012-2013.
Dr. Seo graduated with a doctoral degree from KAIST in 2011. He is currently working at the Clean Fuel Laboratory, the Korea Institute of Energy Research, Daejeon, as a researcher. His research areas are coal gasification, upgrading, and liquefaction, as well as energy and chemical production from low-grade fuels such as biomass and wastes.
2014.11.24 View 9959
Elsevier Selects a KAIST Graduate's Paper as the Top Cited Papers in 2011-2012
Dr. Myung-Won Seo, a graduate from the Department of Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering at KAIST, published a paper in January 2011 in Chemical Engineering Journal, which was entitled “Solid Circulation and Loop-seal Characteristics of a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed: Experiments and CFD Simulation.” His paper was selected by Elsevier as the Top Cited Papers of 2011-2012. The Chemical Engineering Journal is a renowned peer-reviewed journal issued by Elsevier.
Dr. Seo published another paper, “CFD Simulation with Experiments in a Dual Circulating Fluidized Bed Gasifier,” in January 2012 in Computers & Chemical Engineering, which was also selected as the Most Downloaded Papers in 2012-2013.
Dr. Seo graduated with a doctoral degree from KAIST in 2011. He is currently working at the Clean Fuel Laboratory, the Korea Institute of Energy Research, Daejeon, as a researcher. His research areas are coal gasification, upgrading, and liquefaction, as well as energy and chemical production from low-grade fuels such as biomass and wastes.
2014.11.24 View 9959 -
 3D Printer Developed by KAIST Undergraduate Students
More than 100 Pre-orders Prior to Product Launch Made
KAIST undergraduate students received more than 100 pre-orders before the launch for 3D printers they developed and became a hot topic of interest.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations (Head Hong-Kyu Lee) had a launch party at Daejeon Riviera Hotel on 17 November 2014 for “Commercial Delta 3D Printer” developed by KAIST undergraduate students inviting around 50 businesses, buyers and representatives of 3D Printing Industry Association.
“3D Printer” uses blueprints of products such as toys, mug cups and chairs to make 3D objects and is thought to be revolutionary technology in manufacturing industry. The interest has grown as recent printers could print even fruits and cosmetics.
The printing structure of 3D printer can be divided roughly into horizontal Mendel method and Delta method. KAIST students focused on the Delta method to give a differentiated product from 90% of commercial products that use Mendel method.
First, the students focused on lowering the cost of unit price by using self-developed components. The carriage (transport machine) of the product is replaced by self-developed components instead of bearing to reduce the noise and the linking method was changed to beads from loop guide to increase the completeness of the printed product. Also, an auto-levelling is loaded to ensure the nozzle and the bed is parallel and hence increasing convenience for the users. Further, the printer, designed by a product designer in Germany, is linked to a smartphone application for blueprints.
A student in the development team, Seokhyeon Seo (Department of Computer Science, 3rd Year Undergraduate) said, “The biggest merits of the product are lowering the price to a 1/3 by using self-developed components and reducing the noise.” He continued, “By using a smartphone application, anyone can easily design the product. So it is applicable to use for education or at home”
In the exhibit, “3D Printing Korea 2014,” in Coex, Seoul the printer had a preview demonstration, and received more than 100 pre-orders from educational and business training institutions. Further, buyers from Canada and the US requested opening agencies in their countries.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations Head Hong-Kyu Lee said, “3D printing is an innovative technology that could bring the 3rd industrial revolution.” He continued, “It is still early days but the demand will increase exponentially.”
This project was a research project of KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations led by a development team consisting of 4 undergraduate students of KAIST, one student from University of Oxford and one German product designer.
Students in the picture below are Won-Hoi Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering), Sung-Hyun Cho (Department of Mechanical Engineering), and Suk-Hyun Seo (Department of Computer Science) from left to right.
2014.11.19 View 11193
3D Printer Developed by KAIST Undergraduate Students
More than 100 Pre-orders Prior to Product Launch Made
KAIST undergraduate students received more than 100 pre-orders before the launch for 3D printers they developed and became a hot topic of interest.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations (Head Hong-Kyu Lee) had a launch party at Daejeon Riviera Hotel on 17 November 2014 for “Commercial Delta 3D Printer” developed by KAIST undergraduate students inviting around 50 businesses, buyers and representatives of 3D Printing Industry Association.
“3D Printer” uses blueprints of products such as toys, mug cups and chairs to make 3D objects and is thought to be revolutionary technology in manufacturing industry. The interest has grown as recent printers could print even fruits and cosmetics.
The printing structure of 3D printer can be divided roughly into horizontal Mendel method and Delta method. KAIST students focused on the Delta method to give a differentiated product from 90% of commercial products that use Mendel method.
First, the students focused on lowering the cost of unit price by using self-developed components. The carriage (transport machine) of the product is replaced by self-developed components instead of bearing to reduce the noise and the linking method was changed to beads from loop guide to increase the completeness of the printed product. Also, an auto-levelling is loaded to ensure the nozzle and the bed is parallel and hence increasing convenience for the users. Further, the printer, designed by a product designer in Germany, is linked to a smartphone application for blueprints.
A student in the development team, Seokhyeon Seo (Department of Computer Science, 3rd Year Undergraduate) said, “The biggest merits of the product are lowering the price to a 1/3 by using self-developed components and reducing the noise.” He continued, “By using a smartphone application, anyone can easily design the product. So it is applicable to use for education or at home”
In the exhibit, “3D Printing Korea 2014,” in Coex, Seoul the printer had a preview demonstration, and received more than 100 pre-orders from educational and business training institutions. Further, buyers from Canada and the US requested opening agencies in their countries.
KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations Head Hong-Kyu Lee said, “3D printing is an innovative technology that could bring the 3rd industrial revolution.” He continued, “It is still early days but the demand will increase exponentially.”
This project was a research project of KAIST Research Institute for Social Technology and Innovations led by a development team consisting of 4 undergraduate students of KAIST, one student from University of Oxford and one German product designer.
Students in the picture below are Won-Hoi Kim (Department of Mechanical Engineering), Sung-Hyun Cho (Department of Mechanical Engineering), and Suk-Hyun Seo (Department of Computer Science) from left to right.
2014.11.19 View 11193 -
 The Website of the KAIST Industrial Design Department Receives a Design Award
The 10th QS-Apple Higher Education Conference and Exhibition took place on November 11-13, 2014 in Taipei, Taiwan. The conference was hosted by Quacquarelli Symonds, a British company specializing in education, which publishes annually its world university rankings. Apple stands for Asia Pacific Professional Leaders in Education.
The QS-Apple conference supports the internationalization of Asia Pacific universities by providing opportunities for networking, exchanging best practices, and discussing recent developments in higher education. During the conference, the organizers presented the Creative Awards for best international education promotional designs in four categories: Website Pages, Video, Print Advertisement, and International Student Recruitment Brochures.
KAIST’s Industrial Design Department received the Best Website Pages Award for their website in recognition of high levels of user convenience and satisfaction as well as English language services. A total of 39 universities in the Asia and Pacific region competed in this category, and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore came in second place, followed by Hong Kong Baptist University in third.
2014.11.13 View 9187
The Website of the KAIST Industrial Design Department Receives a Design Award
The 10th QS-Apple Higher Education Conference and Exhibition took place on November 11-13, 2014 in Taipei, Taiwan. The conference was hosted by Quacquarelli Symonds, a British company specializing in education, which publishes annually its world university rankings. Apple stands for Asia Pacific Professional Leaders in Education.
The QS-Apple conference supports the internationalization of Asia Pacific universities by providing opportunities for networking, exchanging best practices, and discussing recent developments in higher education. During the conference, the organizers presented the Creative Awards for best international education promotional designs in four categories: Website Pages, Video, Print Advertisement, and International Student Recruitment Brochures.
KAIST’s Industrial Design Department received the Best Website Pages Award for their website in recognition of high levels of user convenience and satisfaction as well as English language services. A total of 39 universities in the Asia and Pacific region competed in this category, and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore came in second place, followed by Hong Kong Baptist University in third.
2014.11.13 View 9187 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 11884
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Accepts an Honorary Professorship at Beijing University of Chemical Technology
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed an honorary professor at Beijing University of Chemical Technology (BUCT). Founded in 1958, BUCT is one of the outstanding universities in mainland China, especially in chemistry studies.
In addition to the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2012), Shanghai Jiao Tong University (2013), Wuhan University (2014), and Hebei University of Technology (2014), this is the fifth honorary professorship Professor Lee has received from higher education institutions in China.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving as the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
2014.11.13 View 11884 -
 A KAIST Student Team Wins the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest
A KAIST team consisted of students from the Departments of Industrial Design and Computer Science participated in the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest and received 1st Prize in the category of People’s Choice.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST) is an international forum to promote innovations in human-computer interfaces, which takes place annually and is sponsored by ACM Special Interest Groups on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) and Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH). The ACM UIST conference brings together professionals in the fields of graphical and web-user interfaces, tangible and ubiquitous computing, virtual and augmented reality, multimedia, and input and output devices.
The Student Innovation Contest has been held during the UIST conference since 2009 to innovate new interactions on state-of-the-art hardware. The participating students were given with the hardware platform to build on—this year, it was Kinoma Create, a JavaScript-powered construction kit that allows makers, professional product designers, and web developers to create personal projects, consumer electronics, and "Internet of Things" prototypes. Contestants demonstrated their creations on household interfaces, and two winners in each of three categories -- Most Creative, Most Useful, and the People’s Choice -- were awarded.
Utilizing Kinoma Create, which came with a built-in touchscreen, WiFi, Bluetooth, a front-facing sensor connector, and a 50-pin rear sensor dock, the KAIST team developed a “smart mop,” transforming the irksome task of cleaning into a fun game. The smart mop identifies target dirt and shows its location on the display built in the rod of a mop. If the user turns on a game mode, then winning scores are gained wherever the target dirt is cleaned.
The People’s Choice award was decided by conference attendees, and they voted the smart mop as their most favorite project.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, who advised the students, said, "A total of 24 teams from such prestigious universities as Carnegie Mellon University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and the University of Tokyo joined the contest, and we are pleased with the good results. Many people, in fact, praised the integration of creativity and technical excellence our have shown through the smart mop.”
Team KAIST: pictured from right to left, Sun-Jun Kim, Se-Jin Kim, and Han-Jong Kim
The Smart Mop can clean the floor and offer users a fun game.
2014.11.12 View 11558
A KAIST Student Team Wins the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest
A KAIST team consisted of students from the Departments of Industrial Design and Computer Science participated in the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest and received 1st Prize in the category of People’s Choice.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST) is an international forum to promote innovations in human-computer interfaces, which takes place annually and is sponsored by ACM Special Interest Groups on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) and Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH). The ACM UIST conference brings together professionals in the fields of graphical and web-user interfaces, tangible and ubiquitous computing, virtual and augmented reality, multimedia, and input and output devices.
The Student Innovation Contest has been held during the UIST conference since 2009 to innovate new interactions on state-of-the-art hardware. The participating students were given with the hardware platform to build on—this year, it was Kinoma Create, a JavaScript-powered construction kit that allows makers, professional product designers, and web developers to create personal projects, consumer electronics, and "Internet of Things" prototypes. Contestants demonstrated their creations on household interfaces, and two winners in each of three categories -- Most Creative, Most Useful, and the People’s Choice -- were awarded.
Utilizing Kinoma Create, which came with a built-in touchscreen, WiFi, Bluetooth, a front-facing sensor connector, and a 50-pin rear sensor dock, the KAIST team developed a “smart mop,” transforming the irksome task of cleaning into a fun game. The smart mop identifies target dirt and shows its location on the display built in the rod of a mop. If the user turns on a game mode, then winning scores are gained wherever the target dirt is cleaned.
The People’s Choice award was decided by conference attendees, and they voted the smart mop as their most favorite project.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, who advised the students, said, "A total of 24 teams from such prestigious universities as Carnegie Mellon University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and the University of Tokyo joined the contest, and we are pleased with the good results. Many people, in fact, praised the integration of creativity and technical excellence our have shown through the smart mop.”
Team KAIST: pictured from right to left, Sun-Jun Kim, Se-Jin Kim, and Han-Jong Kim
The Smart Mop can clean the floor and offer users a fun game.
2014.11.12 View 11558 -
 President Steve Kang will serve as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council on the Future of Electronics of the World Economic Forum
President Steve Kang of KAIST has been appointed to the Chairman of the Global Agenda Council (GAC) on the Future of Electronics of the World Economic Forum (WEF). He will serve the position for two years until September 2016.
President Kang and WEF council members co-hosted, with the government of the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the Future Circles Initiative, a future-focused, innovative brainstorming conference to help find strategies and ideas for the development of UAE. The conference took place on November 11-12, 2014 at the Mina Al Salam Hotel in Dubai.
WEF has about 80 GACs. Each council consists of 15 experts and thought leaders from the academia, industry, government, business, and non-profit sector and deals with specific issues that are important and relevant to the global community such as ageing, artificial intelligence and robotics, brain research, food and nutrition security, education, social media, and future of chemicals, advanced materials and biotechnology.
President Kang was recognized for his contribution to the advancement of science and higher education as an engineer, scholar, and professor. He led the development of the world’s premier CMOS 32-bit microprocessors while working at the AT&T Bell Laboratories. He also taught and conducted research at the University of California, Santa Cruz, and the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. President Kang served as the chancellor of the University of California at Merced from March 2007 to June 2011.
2014.11.11 View 9406
President Steve Kang will serve as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council on the Future of Electronics of the World Economic Forum
President Steve Kang of KAIST has been appointed to the Chairman of the Global Agenda Council (GAC) on the Future of Electronics of the World Economic Forum (WEF). He will serve the position for two years until September 2016.
President Kang and WEF council members co-hosted, with the government of the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the Future Circles Initiative, a future-focused, innovative brainstorming conference to help find strategies and ideas for the development of UAE. The conference took place on November 11-12, 2014 at the Mina Al Salam Hotel in Dubai.
WEF has about 80 GACs. Each council consists of 15 experts and thought leaders from the academia, industry, government, business, and non-profit sector and deals with specific issues that are important and relevant to the global community such as ageing, artificial intelligence and robotics, brain research, food and nutrition security, education, social media, and future of chemicals, advanced materials and biotechnology.
President Kang was recognized for his contribution to the advancement of science and higher education as an engineer, scholar, and professor. He led the development of the world’s premier CMOS 32-bit microprocessors while working at the AT&T Bell Laboratories. He also taught and conducted research at the University of California, Santa Cruz, and the University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. President Kang served as the chancellor of the University of California at Merced from March 2007 to June 2011.
2014.11.11 View 9406 -
 KAIST and Petersburg State Transport University Sign a MOU on Green Transportation
The Petersburg State Transport University (PSTU) in Russia is a higher education institution specializing in railway transport.
KAIST and PSTU signed a memorandum of understating (MOU) on October 28, 2014 at the KAIST campus and agreed to collaborate in the research of and hold academic exchanges for green transportation.
Based on the agreement, the two institutions will collaborate in the development of a high capacity railway that is powered through wireless power transfer technology and will exchange personnel and academic knowledge to advance the field of green transportation.
The Graduate School for Green Transportation (GSGT) at KAIST organized a seminar which took place after the MOU signing ceremony. Professor Dong-Ho Cho, the Dean of GSGT, presented a keynote speech at the seminar on “Korea’s Green Transportation Policy and Its Technology Development Status” to the audience including the PSTU delegation.
Established in 1809, PSTU is one of the oldest and most prestigious engineering universities in Russia, serving as an important scientific and research center in the area of engineering, construction, and railway operation.
2014.11.04 View 9396
KAIST and Petersburg State Transport University Sign a MOU on Green Transportation
The Petersburg State Transport University (PSTU) in Russia is a higher education institution specializing in railway transport.
KAIST and PSTU signed a memorandum of understating (MOU) on October 28, 2014 at the KAIST campus and agreed to collaborate in the research of and hold academic exchanges for green transportation.
Based on the agreement, the two institutions will collaborate in the development of a high capacity railway that is powered through wireless power transfer technology and will exchange personnel and academic knowledge to advance the field of green transportation.
The Graduate School for Green Transportation (GSGT) at KAIST organized a seminar which took place after the MOU signing ceremony. Professor Dong-Ho Cho, the Dean of GSGT, presented a keynote speech at the seminar on “Korea’s Green Transportation Policy and Its Technology Development Status” to the audience including the PSTU delegation.
Established in 1809, PSTU is one of the oldest and most prestigious engineering universities in Russia, serving as an important scientific and research center in the area of engineering, construction, and railway operation.
2014.11.04 View 9396 -
 KAIST Develops Core Technology to Synthesize a Helical Nanostructure
Professor Dong-Ki Yoon’s research team of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology (GSNT) at KAIST has developed helical nanostructures using self-assembly processes. The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America(PNAS) on the October 7th.
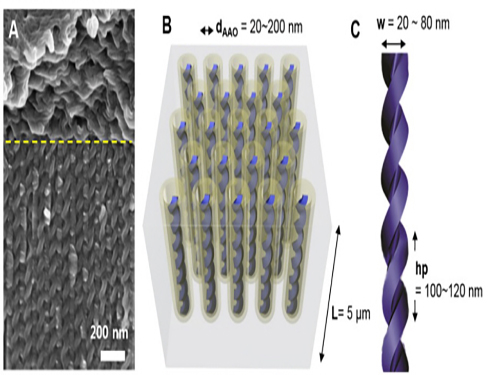
This technology enables the synthesis of various helical structures on a relatively large confined area. Its synthesis is often considered the most arduous for three dimensional structures. Formed from liquid crystal, the structure holds a regular helical structure within the confined space of 20 to 300 nanometers. Also, the distance between each pattern increased as the diameter of the nanostructure increased.
Liquid crystals have a unique property of responding sensitively to the surrounding electromagnetic field. The technology, in combination with the electromagnetic property of liquid crystal, is expected to foster the development of highly efficient optoelectronic devices.
Using this technology, it is possible to develop three dimensional patterning technology beyond the current semiconductor manufacturing technology which uses two dimensional photolithography processes. Three-dimensional semiconductor devices are expected to store hundred times more data than current devices. They will also lower costs by simplifying manufacturing processes.
The essence of this research, “self-assembly in confined space,” refers to controlling complex nanostructures, which can be synthesized from materials such as macromolecules, liquid crystal molecules, and biomolecules in relation to surrounding environments including the temperature, concentration, and pH.
The research team produced a confined space with a length of tens of nanometers by using a porous anodized aluminum membrane induced from an electrochemical reaction. They successfully synthesized independently controlled helical nanostructures by forming the helical structures from liquid crystal molecules within that space.
Professor Yoon said, “This research examines the physicochemical principle of controlling helical nanostructures.” He highlighted the significance of the research and commented, “The technology enables the control of complex nanostructures from organic molecules by using confined space and surface reforming.”
He added that, “When grafted with nanotechnology or information technology, this technology will spur new growth to liquid crystal-related industries such as the LCD.”
The research was led by two Ph.D. candidates, Hanim Kim and Sunhee Lee, under the guidance of Professor Yoon. Dr. Tae-Joo Shin of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Professor Sang-Bok Lee of the University of Maryland, and Professor Noel Clark of the University of Colorado also participated.
Picture 1. Electron Microscopy Pictures and Conceptual Diagrams of Helical Nanostructures
Picture 2. Electron Microscopy Pictures of Manufactured Helical Nanostructures
2014.10.29 View 9138
KAIST Develops Core Technology to Synthesize a Helical Nanostructure
Professor Dong-Ki Yoon’s research team of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology (GSNT) at KAIST has developed helical nanostructures using self-assembly processes. The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America(PNAS) on the October 7th.
This technology enables the synthesis of various helical structures on a relatively large confined area. Its synthesis is often considered the most arduous for three dimensional structures. Formed from liquid crystal, the structure holds a regular helical structure within the confined space of 20 to 300 nanometers. Also, the distance between each pattern increased as the diameter of the nanostructure increased.
Liquid crystals have a unique property of responding sensitively to the surrounding electromagnetic field. The technology, in combination with the electromagnetic property of liquid crystal, is expected to foster the development of highly efficient optoelectronic devices.
Using this technology, it is possible to develop three dimensional patterning technology beyond the current semiconductor manufacturing technology which uses two dimensional photolithography processes. Three-dimensional semiconductor devices are expected to store hundred times more data than current devices. They will also lower costs by simplifying manufacturing processes.
The essence of this research, “self-assembly in confined space,” refers to controlling complex nanostructures, which can be synthesized from materials such as macromolecules, liquid crystal molecules, and biomolecules in relation to surrounding environments including the temperature, concentration, and pH.
The research team produced a confined space with a length of tens of nanometers by using a porous anodized aluminum membrane induced from an electrochemical reaction. They successfully synthesized independently controlled helical nanostructures by forming the helical structures from liquid crystal molecules within that space.
Professor Yoon said, “This research examines the physicochemical principle of controlling helical nanostructures.” He highlighted the significance of the research and commented, “The technology enables the control of complex nanostructures from organic molecules by using confined space and surface reforming.”
He added that, “When grafted with nanotechnology or information technology, this technology will spur new growth to liquid crystal-related industries such as the LCD.”
The research was led by two Ph.D. candidates, Hanim Kim and Sunhee Lee, under the guidance of Professor Yoon. Dr. Tae-Joo Shin of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Professor Sang-Bok Lee of the University of Maryland, and Professor Noel Clark of the University of Colorado also participated.
Picture 1. Electron Microscopy Pictures and Conceptual Diagrams of Helical Nanostructures
Picture 2. Electron Microscopy Pictures of Manufactured Helical Nanostructures
2014.10.29 View 9138 -
 KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries Celebrate 20 Years of Cooperation
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) celebrated the twentieth anniversary of their university-industry cooperation in shipbuilding and ocean technology research. Established in 1995, the cooperation has remained steadfast for two decades, even times when Korea suffered gravely from its financial crisis in late 1990s.
A ceremony to commemorate the cooperation took place at the Mechanical Engineering Building on October 17, 2014. About thirty distinguished guests including the Head of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Choong-Sik Bae, and the chief engineer of SHI Marine Research Institute, Dr. Jong-Soo Seo, participated in the ceremony.
The cooperation programs included appointing advisory professors for technological support, implementing business-based academic courses, offering university-industry wide open lectures, opening regular courses for auditing, and finding possible joint researches. Through this cooperation, Samsung has secured technologies needed for industry, and KAIST has produced students who have real-world experience in industrial fields.
Twenty years of cooperation has produced shining results by running various programs such as technological advice, special lectures, small-scale research projects, consignment research projects, and courses for research and design personnel.
For example, what started as a small-scale research project with USD 4,800 in funding, the LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) related research has grown into a large-scale research project with a total of USD 2.85 million in funding. As a result, they developed a secondary barrier for LNG carriers which was recognized by Lloyd‘s Register. Their research eventually lowered ship manufacturing costs tremendously.
In 2003, the cooperation project received the presidential citation from the University-Industry Cooperation Competition organized by the Federation of Korean Industries.
KAIST and SHI planned to increase their cooperation to make it Korea’s leading university-industry cooperation program.
Professor Bae said, “Our programs to focus on solving industrial problems have turned out quite successful.” He emphasized that “for this reason, the cooperation even continued during the Asian financial crisis in 1997.”
He added, “By expanding the current cooperation, we aim to make it an exemplary program that contributes to Korea’s shipbuilding and ocean plant industries.”
2014.10.21 View 10064
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries Celebrate 20 Years of Cooperation
KAIST and Samsung Heavy Industries (SHI) celebrated the twentieth anniversary of their university-industry cooperation in shipbuilding and ocean technology research. Established in 1995, the cooperation has remained steadfast for two decades, even times when Korea suffered gravely from its financial crisis in late 1990s.
A ceremony to commemorate the cooperation took place at the Mechanical Engineering Building on October 17, 2014. About thirty distinguished guests including the Head of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Choong-Sik Bae, and the chief engineer of SHI Marine Research Institute, Dr. Jong-Soo Seo, participated in the ceremony.
The cooperation programs included appointing advisory professors for technological support, implementing business-based academic courses, offering university-industry wide open lectures, opening regular courses for auditing, and finding possible joint researches. Through this cooperation, Samsung has secured technologies needed for industry, and KAIST has produced students who have real-world experience in industrial fields.
Twenty years of cooperation has produced shining results by running various programs such as technological advice, special lectures, small-scale research projects, consignment research projects, and courses for research and design personnel.
For example, what started as a small-scale research project with USD 4,800 in funding, the LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) related research has grown into a large-scale research project with a total of USD 2.85 million in funding. As a result, they developed a secondary barrier for LNG carriers which was recognized by Lloyd‘s Register. Their research eventually lowered ship manufacturing costs tremendously.
In 2003, the cooperation project received the presidential citation from the University-Industry Cooperation Competition organized by the Federation of Korean Industries.
KAIST and SHI planned to increase their cooperation to make it Korea’s leading university-industry cooperation program.
Professor Bae said, “Our programs to focus on solving industrial problems have turned out quite successful.” He emphasized that “for this reason, the cooperation even continued during the Asian financial crisis in 1997.”
He added, “By expanding the current cooperation, we aim to make it an exemplary program that contributes to Korea’s shipbuilding and ocean plant industries.”
2014.10.21 View 10064 -
 Wuhan University, China, Appoints Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee as Honorary Professor
Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, has been appointed an honorary professor at Wuhan University in Hubei Province, China. This is the third time that Professor Lee has received an honorary professorship from Chinese academic institutions. The Chinese Academy of Sciences appointed him an honorary professor in 2012, and Shanghai Jia Tong University asked him to serve as an advisory professor in 2013, respectively.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
Wuhan University is a comprehensive and key national university selected by the Chinese government as a major recipient of state funding for research. It is also known as one of the most beautiful campuses in China.
2014.10.20 View 9681
Wuhan University, China, Appoints Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee as Honorary Professor
Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, has been appointed an honorary professor at Wuhan University in Hubei Province, China. This is the third time that Professor Lee has received an honorary professorship from Chinese academic institutions. The Chinese Academy of Sciences appointed him an honorary professor in 2012, and Shanghai Jia Tong University asked him to serve as an advisory professor in 2013, respectively.
Professor Lee was recognized for his pioneering research in systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms necessary for the development of green chemical industries. He succeeded in producing succinic acid through bacterial fermentation and engineering plastic raw materials in the most effective and economical method for the first time in the world. Professor Lee also developed polylactic acid, a bio-based polymer that allows plastics to be produced through natural and renewable resources, as well as the microbial production of alkanes, an alternative to gasoline that can be produced from fatty acids.
Professor Lee has been actively working as a member of a group of global leaders supported by the World Economic Forum (WEF), serving the Chairman of the Future of Chemicals, Advanced Materials & Biotechnology, Global Agenda Councils, WEF.
Wuhan University is a comprehensive and key national university selected by the Chinese government as a major recipient of state funding for research. It is also known as one of the most beautiful campuses in China.
2014.10.20 View 9681 -
 KAIST Registers an Internationally Recognized Standard Patent
A video compression technology, jointly developed by Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), and the Korean Broadcasting System (KBS), is registered internationally as the standard patent in the next-generation High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
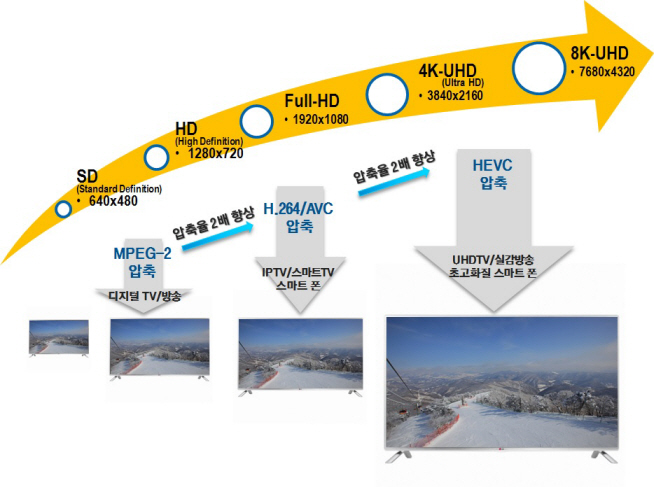
HEVC (H.265) is an international technology standard that compresses large image data for Ultra High Definition (UHD) televisions and smartphones. It has the twice the compression efficiency as that of H.264/AVC which is most commonly used for processing full HD sources. This means that it is able to compress a video file to half the size while maintaining the same image quality.
Although the related market is at a nascent stage, HEVC technology has already been applied to the latest version of televisions and smartphones. Experts predict that the market will grow to USD 200 billion by 2016, and KAIST is expected to receive a royalty payment of USD 9.3 million from this patent.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC) established the HEVC standard in January 2013. Also, an international patent pool licensing corporation, MPEG LA announced the HEVC standard patent pool on September 29, 2014.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae, Dean of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) of KAIST, said, “This is an unprecedented case for Korea whereby a core technology developed by a university became an international standard, which has a vast impact on the market.”
President of KAIST, Steve Kang commented, “With its advanced technology, KAIST joined the HEVC standard patent pool as one of the 23 founding members along with Apple, Siemens, and NEC. This is a remarkable achievement.”
Picture 1: Improvements in video compression technology
Picture 2: Comparison of different screen resolutions
2014.10.09 View 12937
KAIST Registers an Internationally Recognized Standard Patent
A video compression technology, jointly developed by Professor Mun-Chul Kim of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), and the Korean Broadcasting System (KBS), is registered internationally as the standard patent in the next-generation High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC).
HEVC (H.265) is an international technology standard that compresses large image data for Ultra High Definition (UHD) televisions and smartphones. It has the twice the compression efficiency as that of H.264/AVC which is most commonly used for processing full HD sources. This means that it is able to compress a video file to half the size while maintaining the same image quality.
Although the related market is at a nascent stage, HEVC technology has already been applied to the latest version of televisions and smartphones. Experts predict that the market will grow to USD 200 billion by 2016, and KAIST is expected to receive a royalty payment of USD 9.3 million from this patent.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC) established the HEVC standard in January 2013. Also, an international patent pool licensing corporation, MPEG LA announced the HEVC standard patent pool on September 29, 2014.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae, Dean of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) of KAIST, said, “This is an unprecedented case for Korea whereby a core technology developed by a university became an international standard, which has a vast impact on the market.”
President of KAIST, Steve Kang commented, “With its advanced technology, KAIST joined the HEVC standard patent pool as one of the 23 founding members along with Apple, Siemens, and NEC. This is a remarkable achievement.”
Picture 1: Improvements in video compression technology
Picture 2: Comparison of different screen resolutions
2014.10.09 View 12937