-
 KAIST Develops Core Technology for Ultra-small 3D Image Sensor
(from left: Dr. Jong-Bum Yo, PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kimand Professor Hyo-Hoon Park)
A KAIST research team developed a silicon optical phased array (OPA) chip, which can be a core component for three-dimensional image sensors. This research was co-led by PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kim and Dr. Jong-Bum You from the National Nanofab Center (NNFC).
A 3D image sensor adds distance information to a two-dimensional image, such as a photo, to recognize it as a 3D image. It plays a vital role in various electronics including autonomous vehicles, drones, robots, and facial recognition systems, which require accurate measurement of the distance from objects.
Many automobile and drone companies are focusing on developing 3D image sensor systems, based on mechanical light detection and ranging (LiDAR) systems. However, it can only get as small as the size of a fist and has a high possibility of malfunctioning because it employs a mechanical method for laser beam-steering.
OPAs have gained a great attention as a key component to implement solid-state LiDAR because it can control the light direction electronically without moving parts. Silicon-based OPAs are small, durable, and can be mass-produced through conventional Si-CMOS processes.
However, in the development of OPAs, a big issue has been raised about how to achieve wide beam-steering in transversal and longitudinal directions. In the transversal direction, a wide beam-steering has been implemented, relatively easily, through a thermo-optic or electro-optic control of the phase shifters integrated with a 1D array. But the longitudinal beam-steering has been remaining as a technical challenge since only a narrow steering was possible with the same 1D array by changing the wavelengths of light, which is hard to implement in semiconductor processes.
If a light wavelength is changed, characteristics of element devices consisting the OPA can vary, which makes it difficult to control the light direction with reliability as well as to integrate a wavelength-tunable laser on a silicon-based chip. Therefore, it is essential to devise a new structure that can easily adjust the radiated light in both transversal and longitudinal directions.
By integrating tunable radiator, instead of tunable laser in a conventional OPA, Professor Hyo-Hoon Park from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team developed an ultra-small, low-power OPA chip that facilitates a wide 2D beam-steering with a monochromatic light source.
This OPA structure allows the minimizing of the 3D image sensors, as small as a dragonfly’s eye.
According to the team, the OPA can function as a 3D image sensor and also as a wireless transmitter sending the image data to a desired direction, enabling high-quality image data to be freely communicated between electronic devices.
Kim said, “It’s not an easy task to integrate a tunable light source in the OPA structures of previous works. We hope our research proposing a tunable radiator makes a big step towards commercializing OPAs.”
Dr. You added, “We will be able to support application researches of 3D image sensors, especially for facial recognition with smartphones and augmented reality services. We will try to prepare a processing platform in NNFC that provides core technologies of the 3D image sensor fabrication.”
This research was published in Optics Letters on January 15.
Figure 1.The manufactured OPA chip
Figure 2. Schematic feature showing an application of the OPA to a 3D image sensor
2019.02.08 View 6977
KAIST Develops Core Technology for Ultra-small 3D Image Sensor
(from left: Dr. Jong-Bum Yo, PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kimand Professor Hyo-Hoon Park)
A KAIST research team developed a silicon optical phased array (OPA) chip, which can be a core component for three-dimensional image sensors. This research was co-led by PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kim and Dr. Jong-Bum You from the National Nanofab Center (NNFC).
A 3D image sensor adds distance information to a two-dimensional image, such as a photo, to recognize it as a 3D image. It plays a vital role in various electronics including autonomous vehicles, drones, robots, and facial recognition systems, which require accurate measurement of the distance from objects.
Many automobile and drone companies are focusing on developing 3D image sensor systems, based on mechanical light detection and ranging (LiDAR) systems. However, it can only get as small as the size of a fist and has a high possibility of malfunctioning because it employs a mechanical method for laser beam-steering.
OPAs have gained a great attention as a key component to implement solid-state LiDAR because it can control the light direction electronically without moving parts. Silicon-based OPAs are small, durable, and can be mass-produced through conventional Si-CMOS processes.
However, in the development of OPAs, a big issue has been raised about how to achieve wide beam-steering in transversal and longitudinal directions. In the transversal direction, a wide beam-steering has been implemented, relatively easily, through a thermo-optic or electro-optic control of the phase shifters integrated with a 1D array. But the longitudinal beam-steering has been remaining as a technical challenge since only a narrow steering was possible with the same 1D array by changing the wavelengths of light, which is hard to implement in semiconductor processes.
If a light wavelength is changed, characteristics of element devices consisting the OPA can vary, which makes it difficult to control the light direction with reliability as well as to integrate a wavelength-tunable laser on a silicon-based chip. Therefore, it is essential to devise a new structure that can easily adjust the radiated light in both transversal and longitudinal directions.
By integrating tunable radiator, instead of tunable laser in a conventional OPA, Professor Hyo-Hoon Park from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team developed an ultra-small, low-power OPA chip that facilitates a wide 2D beam-steering with a monochromatic light source.
This OPA structure allows the minimizing of the 3D image sensors, as small as a dragonfly’s eye.
According to the team, the OPA can function as a 3D image sensor and also as a wireless transmitter sending the image data to a desired direction, enabling high-quality image data to be freely communicated between electronic devices.
Kim said, “It’s not an easy task to integrate a tunable light source in the OPA structures of previous works. We hope our research proposing a tunable radiator makes a big step towards commercializing OPAs.”
Dr. You added, “We will be able to support application researches of 3D image sensors, especially for facial recognition with smartphones and augmented reality services. We will try to prepare a processing platform in NNFC that provides core technologies of the 3D image sensor fabrication.”
This research was published in Optics Letters on January 15.
Figure 1.The manufactured OPA chip
Figure 2. Schematic feature showing an application of the OPA to a 3D image sensor
2019.02.08 View 6977 -
 KAIST Earns AACSB Business School Accreditation
The KAIST College of Business re-earned business school accreditation from the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB) International. The school first earned the accreditation in 2003, and has continued to receive the accreditation four consecutive times. Currently only 5% of the 16,000 business schools around the world have earned AACSB accreditation. KAIST received a good evaluation for the competitive research of its faculty, its executive education programs based on strong industry-academia ties, and specialized MBA and master’s program, which includes programs such as social entrepreneurship and green business and policy.Alexander Triantis, dean of the Robert H. Smith School of Business at the University of Maryland and a judge for AACSB Accreditation said, “I was impressed to see students from KAIST have a high standard of knowledge. A number of its graduates continue to be appointed as professors of top universities abroad, which shows its strong global competence”. AACSB was founded in 1916 by deans of business colleges from prestigious universities such as Harvard University, Stanford University and Columbia University, to provide business and accounting accreditation to universities. Evaluation for AACSB accreditation takes place every five years. Schools are evaluated based on fifteen standards, including student admission and graduation requirements, student-faculty ratios, faculty’s intellectual contributions, research infrastructure, global cooperation, and industry-academia programs. They can be eligible for re-accreditation if they satisfy the conditions offered by AACSB International and are committed to continuous improvement every five years. KAIST also earned the accreditation from the European Foundation for Management Development Quality Improvement System (EQUIS) three consecutive times since 2010. In 2013, it earned membership into the Partnership in International Management (PIM). Membership is only possible for those who have AACSB and EQUIS accreditation and they can be listed as a candidate school through voting. The candidate schools can finally earn membership after one year of strict screening. As of January 2019, there are 65 prestigious graduate schools of business, including KAIST, listed as PIM members.
2019.02.01 View 6001
KAIST Earns AACSB Business School Accreditation
The KAIST College of Business re-earned business school accreditation from the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB) International. The school first earned the accreditation in 2003, and has continued to receive the accreditation four consecutive times. Currently only 5% of the 16,000 business schools around the world have earned AACSB accreditation. KAIST received a good evaluation for the competitive research of its faculty, its executive education programs based on strong industry-academia ties, and specialized MBA and master’s program, which includes programs such as social entrepreneurship and green business and policy.Alexander Triantis, dean of the Robert H. Smith School of Business at the University of Maryland and a judge for AACSB Accreditation said, “I was impressed to see students from KAIST have a high standard of knowledge. A number of its graduates continue to be appointed as professors of top universities abroad, which shows its strong global competence”. AACSB was founded in 1916 by deans of business colleges from prestigious universities such as Harvard University, Stanford University and Columbia University, to provide business and accounting accreditation to universities. Evaluation for AACSB accreditation takes place every five years. Schools are evaluated based on fifteen standards, including student admission and graduation requirements, student-faculty ratios, faculty’s intellectual contributions, research infrastructure, global cooperation, and industry-academia programs. They can be eligible for re-accreditation if they satisfy the conditions offered by AACSB International and are committed to continuous improvement every five years. KAIST also earned the accreditation from the European Foundation for Management Development Quality Improvement System (EQUIS) three consecutive times since 2010. In 2013, it earned membership into the Partnership in International Management (PIM). Membership is only possible for those who have AACSB and EQUIS accreditation and they can be listed as a candidate school through voting. The candidate schools can finally earn membership after one year of strict screening. As of January 2019, there are 65 prestigious graduate schools of business, including KAIST, listed as PIM members.
2019.02.01 View 6001 -
 Stretchable Multi-functional Fiber for Energy Harvesting and Strain Sensing
(from left: Professor Steve Park, Jeongjae Ryu and Professor Seungbum Hong)
Fiber-based electronics are expected to play a vital role in next-generation wearable electronics. Woven into textiles, they can provide higher durability, comfort, and integrated multi-functionality. A KAIST team has developed a stretchable multi-functional fiber (SMF) that can harvest energy and detect strain, which can be applied to future wearable electronics.
With wearable electronics, health and physical conditions can be assessed by analyzing biological signals from the human body, such as pulse and muscle movements. Fibers are highly suitable for future wearable electronics because they can be easily integrated into textiles, which are designed to be conformable to curvilinear surfaces and comfortable to wear. Moreover, their weave structures offer support that makes them resistant to fatigue. Many research groups have developed fiber-based strain sensors to sense external biological signals. However, their sensitivities were relatively low.
The applicability of wearable devices is currently limited by their power source, as the size, weight, and lifetime of the battery lessens their versatility. Harvesting mechanical energy from the human body is a promising solution to overcome such limitations by utilizing various types of motions like bending, stretching, and pressing. However, previously reported, fiber-based energy harvesters were not stretchable and could not fully harvest the available mechanical energy.
Professor Seungbum Hong and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and their team fabricated a stretchable fiber by using a ferroelectric layer composed of P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS sandwiched between stretchable electrodes composed of a composite of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene polystyrenesulfonate (PEDOT:PSS).
Cracks formed in MWCNT/PEDOT:PSS layer help the fiber show high sensitivity compared to the previously reported fiber strain sensors. Furthermore, the new fiber can harvest mechanical energy under various mechanical stimuli such as stretching, tapping, and injecting water into the fiber using the piezoelectric effect of the P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS layer.
Professor Hong said, “This new fiber has various functionalities and makes the device simple and compact. It is a core technology for developing wearable devices with energy harvesting and strain sensing capabilities.”
This article, led by PhD candidate Jeongjae Ryu, was published in the January 2019 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1.Schematic illustration of an SMF fiber and its piezoelectric voltage output and response to strain.
Figure 2. Photographs of a stretchable multi-functional fiber being stretched by 100%, bent, and twisted.
2019.01.31 View 8743
Stretchable Multi-functional Fiber for Energy Harvesting and Strain Sensing
(from left: Professor Steve Park, Jeongjae Ryu and Professor Seungbum Hong)
Fiber-based electronics are expected to play a vital role in next-generation wearable electronics. Woven into textiles, they can provide higher durability, comfort, and integrated multi-functionality. A KAIST team has developed a stretchable multi-functional fiber (SMF) that can harvest energy and detect strain, which can be applied to future wearable electronics.
With wearable electronics, health and physical conditions can be assessed by analyzing biological signals from the human body, such as pulse and muscle movements. Fibers are highly suitable for future wearable electronics because they can be easily integrated into textiles, which are designed to be conformable to curvilinear surfaces and comfortable to wear. Moreover, their weave structures offer support that makes them resistant to fatigue. Many research groups have developed fiber-based strain sensors to sense external biological signals. However, their sensitivities were relatively low.
The applicability of wearable devices is currently limited by their power source, as the size, weight, and lifetime of the battery lessens their versatility. Harvesting mechanical energy from the human body is a promising solution to overcome such limitations by utilizing various types of motions like bending, stretching, and pressing. However, previously reported, fiber-based energy harvesters were not stretchable and could not fully harvest the available mechanical energy.
Professor Seungbum Hong and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and their team fabricated a stretchable fiber by using a ferroelectric layer composed of P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS sandwiched between stretchable electrodes composed of a composite of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene polystyrenesulfonate (PEDOT:PSS).
Cracks formed in MWCNT/PEDOT:PSS layer help the fiber show high sensitivity compared to the previously reported fiber strain sensors. Furthermore, the new fiber can harvest mechanical energy under various mechanical stimuli such as stretching, tapping, and injecting water into the fiber using the piezoelectric effect of the P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS layer.
Professor Hong said, “This new fiber has various functionalities and makes the device simple and compact. It is a core technology for developing wearable devices with energy harvesting and strain sensing capabilities.”
This article, led by PhD candidate Jeongjae Ryu, was published in the January 2019 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1.Schematic illustration of an SMF fiber and its piezoelectric voltage output and response to strain.
Figure 2. Photographs of a stretchable multi-functional fiber being stretched by 100%, bent, and twisted.
2019.01.31 View 8743 -
 KAIST and LG Electronics Team up for 6G Wireless Communications
(LG Electronics CTO Il-Pyung Park (left) and Dean of KAIST Institute Sang Yup Lee)
KAIST and LG Electronics are working together to take the lead in next-generation wireless communications and launched the LG-KAIST 6G Research Center on January 28, 2019.
KAIST Institute has been focusing on developing a new growth engine for the national economy through interdisciplinary research. In particular, its research work in the field of next-generation wireless communication was listed in the National Research and Development Excellence 100 in 2016 and 2017.
LG Electronics has been a global leader in this field for many years. According to TechIPM, the company had the most 4G LTE/LTE-A patents from 2012 to 2016. Also, it first standardized the Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything, which is the core technology for autonomous vehicles.
The new head of the research center, Professor Dong Ho Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering said, “We will work on developing source technology for sixth generation mobile communications, which will enhance national competence and prepare for the future industries.”
CTO of LG Electronics Il-Pyung Park said, “We are hoping to take the lead in the global standardization of sixth generation wireless communications and secure new business opportunities.”
2019.01.29 View 2645
KAIST and LG Electronics Team up for 6G Wireless Communications
(LG Electronics CTO Il-Pyung Park (left) and Dean of KAIST Institute Sang Yup Lee)
KAIST and LG Electronics are working together to take the lead in next-generation wireless communications and launched the LG-KAIST 6G Research Center on January 28, 2019.
KAIST Institute has been focusing on developing a new growth engine for the national economy through interdisciplinary research. In particular, its research work in the field of next-generation wireless communication was listed in the National Research and Development Excellence 100 in 2016 and 2017.
LG Electronics has been a global leader in this field for many years. According to TechIPM, the company had the most 4G LTE/LTE-A patents from 2012 to 2016. Also, it first standardized the Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything, which is the core technology for autonomous vehicles.
The new head of the research center, Professor Dong Ho Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering said, “We will work on developing source technology for sixth generation mobile communications, which will enhance national competence and prepare for the future industries.”
CTO of LG Electronics Il-Pyung Park said, “We are hoping to take the lead in the global standardization of sixth generation wireless communications and secure new business opportunities.”
2019.01.29 View 2645 -
 President Shin Speaks on Closing the Skills Gap at the WEF
(President Shin poses (far right) with the National University of Singapore President Tan Eng Chye (center) along with Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in Davos last week.)
President Sung-Chul Shin shared his ideas on how reskilling is a critical element of growth, dynamism, and competitiveness for countries during a session titled “Closing the Skills Gap: Creating a Reskilling Revolution” at the World Economic Forum on January 24 in Davos.
While discussing a reskilling imperative alongside French Labor Minister Muriel Penicaud, he presented how the Korean government and KAIST are responding to the socio-economic transformation of workforces in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. After their presentation, Minister of Economy and Enterprise of Spain Nadia Calvirno Santamaria, Minister of Commerce and Industry of Oman Ali bin Masoud bin Ali Al Sunaidy, and Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship of India Dharmendra Pradhan shared their views on the course of decision making regarding the proactive practices and policies they have applied for closing the gaps from their countries’ perspectives.
President Shin presented how to upskill and reskill SMEs and startups, the real players who will jumpstart the economy in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He explained that the government is striving to change the existing structure of the economy, which is dominated by a few giant conglomerates. He added that the Korean government is trying to support SMEs and startups in terms of both funding and technology reskilling in order to rejuvenate the economy.
To better align itself with the government’s efforts, KAIST has introduced SME 4.0. SME 4.0 proposes to innovate the production process through the creation of a partnered platform between KAIST and SMEs across the country. With this platform, KAIST assists local SMEs for standardizing and systemizing all their processes of production, delivery, and management with enterprise resources planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). In addition, SME 4.0 offers retraining and re-tooling programs by linking the data generated through this platform in real time to better facilitate SMEs’ smart business.
(President Shin shakes hands with H.E.Mohammed Al-Tuwairi, Minister of Economy and Planning of Saudi Arabia before holding a bilaterla meeting in Davos.)
President Shin also explained about upskilling the leading corporations’ technological competitiveness, partnering with major leading corporations for upskilling their advanced technologies.
He also held a series of bilateral meetings with dignitaries attending the WEF annual meeting to discuss partnerships and collaborations. He also attended the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a community composed of 28 presidents from the world’s top universities on January 23. President Shin, who is on the advisory board of the Center for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR), also participated in the board meeting and discussed the upcoming launching of the Korea C4IR, which will open at KAIST in March.
2019.01.28 View 7146
President Shin Speaks on Closing the Skills Gap at the WEF
(President Shin poses (far right) with the National University of Singapore President Tan Eng Chye (center) along with Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in Davos last week.)
President Sung-Chul Shin shared his ideas on how reskilling is a critical element of growth, dynamism, and competitiveness for countries during a session titled “Closing the Skills Gap: Creating a Reskilling Revolution” at the World Economic Forum on January 24 in Davos.
While discussing a reskilling imperative alongside French Labor Minister Muriel Penicaud, he presented how the Korean government and KAIST are responding to the socio-economic transformation of workforces in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. After their presentation, Minister of Economy and Enterprise of Spain Nadia Calvirno Santamaria, Minister of Commerce and Industry of Oman Ali bin Masoud bin Ali Al Sunaidy, and Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship of India Dharmendra Pradhan shared their views on the course of decision making regarding the proactive practices and policies they have applied for closing the gaps from their countries’ perspectives.
President Shin presented how to upskill and reskill SMEs and startups, the real players who will jumpstart the economy in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He explained that the government is striving to change the existing structure of the economy, which is dominated by a few giant conglomerates. He added that the Korean government is trying to support SMEs and startups in terms of both funding and technology reskilling in order to rejuvenate the economy.
To better align itself with the government’s efforts, KAIST has introduced SME 4.0. SME 4.0 proposes to innovate the production process through the creation of a partnered platform between KAIST and SMEs across the country. With this platform, KAIST assists local SMEs for standardizing and systemizing all their processes of production, delivery, and management with enterprise resources planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). In addition, SME 4.0 offers retraining and re-tooling programs by linking the data generated through this platform in real time to better facilitate SMEs’ smart business.
(President Shin shakes hands with H.E.Mohammed Al-Tuwairi, Minister of Economy and Planning of Saudi Arabia before holding a bilaterla meeting in Davos.)
President Shin also explained about upskilling the leading corporations’ technological competitiveness, partnering with major leading corporations for upskilling their advanced technologies.
He also held a series of bilateral meetings with dignitaries attending the WEF annual meeting to discuss partnerships and collaborations. He also attended the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a community composed of 28 presidents from the world’s top universities on January 23. President Shin, who is on the advisory board of the Center for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR), also participated in the board meeting and discussed the upcoming launching of the Korea C4IR, which will open at KAIST in March.
2019.01.28 View 7146 -
 Hierarchical Porous Titanium Nitride Synthesized by Multiscale Phase Separation for LSBs
(from left: Professor Jinwoo Lee and PhD candidate Won-Gwang Lim)
A KAIST research team developed ultra-stable, high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs) by using hierarchical porous titanium nitride as a sulfur host, and achieved superior cycle stability and high rate performance for LSBs.
The control of large amounts of energy is required for use in an electric vehicle or smart grid system. In this sense, the development of next-generation secondary batteries is in high demand. Theoretically, LSBs have an energy density seven times higher than commercial lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Also, their production cost can be reduced dramatically since sulfur can be obtained at a low price.
Despite these positive aspects, there have been several issues impeding the commercialization of LSBs, such as the low electric conductivity of sulfur, the dissolution of active materials during operation, and sluggish conversion reactions. These issues decrease the cycle stability and rate capability of batteries.
To tackle those issues, Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his team synthesized a well-developed hierarchical macro/mesoporous titanium nitride as a host material for sulfur. The titanium nitride has a high chemical affinity for sulfur and high electrical conductivity. As a result, it prevents the dissolution of active materials and facilitates the charge transfer. Moreover, the synergistic effect of macropore and mesopore structures allows the stable accommodation of large amounts of sulfur and facilitates the electrolyte penetration.
Previously reported polar inorganic materials have a high affinity for sulfur, but it was challenging to control the porous architecture suitable to the sulfur host. This work breaks such limitations by developing a synthetic route to easily control the porous architecture of inorganic materials, which led to obtaining superior cycle stability and high rate capabilities.
Professor Lee said, “Some problems still remain in commercializing LSBs as next-generation batteries. Hence, there should be a continued research on this matter to solve the issues. Through this research, we secured a key technology for ultrastable, high-rate LSBs.”
This research was led by PhD candidate Won-Gwang Lim and collaborated on by Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH. It was chosen as the cover article of Advanced Materials on January 15, 2019.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration for the synthetic route of co-continuous h-TiN
Figure 2. The hierarchical multiscale porous structure is still retained without any collapse after the conversion to h-TiN. The good retention of the porous structure is attributed to the thick pore wall of the h-TiO₂derived from the block copolymer self-assembly
Figure 3. The cover page of Advanced Materials
2019.01.28 View 7231
Hierarchical Porous Titanium Nitride Synthesized by Multiscale Phase Separation for LSBs
(from left: Professor Jinwoo Lee and PhD candidate Won-Gwang Lim)
A KAIST research team developed ultra-stable, high-rate lithium-sulfur batteries (LSBs) by using hierarchical porous titanium nitride as a sulfur host, and achieved superior cycle stability and high rate performance for LSBs.
The control of large amounts of energy is required for use in an electric vehicle or smart grid system. In this sense, the development of next-generation secondary batteries is in high demand. Theoretically, LSBs have an energy density seven times higher than commercial lithium ion batteries (LIBs). Also, their production cost can be reduced dramatically since sulfur can be obtained at a low price.
Despite these positive aspects, there have been several issues impeding the commercialization of LSBs, such as the low electric conductivity of sulfur, the dissolution of active materials during operation, and sluggish conversion reactions. These issues decrease the cycle stability and rate capability of batteries.
To tackle those issues, Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his team synthesized a well-developed hierarchical macro/mesoporous titanium nitride as a host material for sulfur. The titanium nitride has a high chemical affinity for sulfur and high electrical conductivity. As a result, it prevents the dissolution of active materials and facilitates the charge transfer. Moreover, the synergistic effect of macropore and mesopore structures allows the stable accommodation of large amounts of sulfur and facilitates the electrolyte penetration.
Previously reported polar inorganic materials have a high affinity for sulfur, but it was challenging to control the porous architecture suitable to the sulfur host. This work breaks such limitations by developing a synthetic route to easily control the porous architecture of inorganic materials, which led to obtaining superior cycle stability and high rate capabilities.
Professor Lee said, “Some problems still remain in commercializing LSBs as next-generation batteries. Hence, there should be a continued research on this matter to solve the issues. Through this research, we secured a key technology for ultrastable, high-rate LSBs.”
This research was led by PhD candidate Won-Gwang Lim and collaborated on by Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH. It was chosen as the cover article of Advanced Materials on January 15, 2019.
Figure 1. Schematic illustration for the synthetic route of co-continuous h-TiN
Figure 2. The hierarchical multiscale porous structure is still retained without any collapse after the conversion to h-TiN. The good retention of the porous structure is attributed to the thick pore wall of the h-TiO₂derived from the block copolymer self-assembly
Figure 3. The cover page of Advanced Materials
2019.01.28 View 7231 -
 First Korean Member of OceanObs' Organizing Committee
Professor Sung Yong Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering became the first Korean to be elected as an organizing committee member of the international conference OceanObs’19’, specializing in the ocean observing field.
Professor Kim has been actively engaged in advisory panels, technical committees, and working groups for the North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES). Through numerous activities, he was recognized for his professionalism and academic achievements, which led him to be appointed as a member of the organizing committee.
The organizing committee is comprised of leading scholars and researchers from 20 countries, and Professor Kim will be the first Korean scientist to participate on the committee.
Since 1999, the conference has been held every decade. Global experts specializing in oceanic observation gather to discuss research directions for the next ten years by monitoring physical, biological, and chemical variables in regional, national, and global oceans and applying marine engineering.
This year, approximately 20 institutes including NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the National Science Foundation, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the European Space Agency will support funds as well as high-tech equipment to the conference.
This year’s conference theme is the governance of global ocean observing systems such as underwater gliders, unmanned vehicles, remote sensing, and observatories. The conference will hold discussions on monitoring technology and information systems to ensure human safety as well as to develop and preserve food resources. Additionally, participants will explore ways to expand observational infrastructures and carry out multidisciplinary approaches.
There will also be collaborations with the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS) and the Partnership for Observation of the Global Oceans (POGO) to organize ocean observing programs and discuss priorities.
Finally, they will set a long-term plan for solving major scientific issues, such as climate change, ocean acidification, energy, and marine pollution.
Professor Kim said, “Based on the outcomes drawn from the conference, I will carry out research on natural disasters and climate change monitoring by using unmanned observing systems. I will also encourage more multidisciplinary research in this field.”
2019.01.25 View 11083
First Korean Member of OceanObs' Organizing Committee
Professor Sung Yong Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering became the first Korean to be elected as an organizing committee member of the international conference OceanObs’19’, specializing in the ocean observing field.
Professor Kim has been actively engaged in advisory panels, technical committees, and working groups for the North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES). Through numerous activities, he was recognized for his professionalism and academic achievements, which led him to be appointed as a member of the organizing committee.
The organizing committee is comprised of leading scholars and researchers from 20 countries, and Professor Kim will be the first Korean scientist to participate on the committee.
Since 1999, the conference has been held every decade. Global experts specializing in oceanic observation gather to discuss research directions for the next ten years by monitoring physical, biological, and chemical variables in regional, national, and global oceans and applying marine engineering.
This year, approximately 20 institutes including NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), the National Science Foundation, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, and the European Space Agency will support funds as well as high-tech equipment to the conference.
This year’s conference theme is the governance of global ocean observing systems such as underwater gliders, unmanned vehicles, remote sensing, and observatories. The conference will hold discussions on monitoring technology and information systems to ensure human safety as well as to develop and preserve food resources. Additionally, participants will explore ways to expand observational infrastructures and carry out multidisciplinary approaches.
There will also be collaborations with the Global Ocean Observing System (GOOS) and the Partnership for Observation of the Global Oceans (POGO) to organize ocean observing programs and discuss priorities.
Finally, they will set a long-term plan for solving major scientific issues, such as climate change, ocean acidification, energy, and marine pollution.
Professor Kim said, “Based on the outcomes drawn from the conference, I will carry out research on natural disasters and climate change monitoring by using unmanned observing systems. I will also encourage more multidisciplinary research in this field.”
2019.01.25 View 11083 -
 A Novel Material for Transparent and Flexible Displays
(Research team led by Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry)
The next generation of flexible and transparent displays will require a high-performing and flexible polymeric material that has the optical and thermal properties of glass. The material must be transparent to visible light and have a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). Unfortunately, such a polymeric material has not been available. A KAIST research team has succeeded in making a new polymeric material with an exceptionally low CTE value while retaining high transparency and excellent thermal and mechanical properties. The method developed for amorphous polymers with a controlled CTE can be applied to control the thermal expansion of organic materials as well.
Most of objects expands upon heating and shrinks by cooling, and organic polymers have a relatively large CTE compared to that of ceramics or metals. Thin, light-weight planar substrates for semiconductor devices should have a similar CTE of ceramics. Otherwise, the device can be cracked due to the stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction. Therefore, matching the CTE of the semiconductor device and the substrate is crucial for successful manufacturing of display devices. Forming a network structure by connecting polymer chains is a well-known method of reducing the CTE of amorphous polymers. However, polymers with a network structure eventually lose their flexibility and becomes brittle.
As an alternative method, Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry and his team chose to adjust the distance and interaction between polymer chains. Thermal expansion and contraction of polymer films can be minimized by introducing interaction forces between the polymer chains and by arranging the direction of the force perpendicularly. The team successfully implemented this approach by appropriately designing the chemical structure of a transparent polymeric material. It is called poly (amide-imide) film, which is a transparent, flexible, and high-performing polymeric material. It is thermally stable enough to be used in the AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) fabrication process (stable at >400℃) with a low CTE (4ppm/℃).
The team made IGZO TFT (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Thin Film Transistor) devices on the newly synthesized transparent poly(amide-imide) film, and confirmed that the device could indeed operate normally even when it is folded down to a radius of 1mm.
Professor Kim said, “Our results suggest a way of controlling the thermal expansion of amorphous polymers similar to a level of glass without chemical cross-linking, which has long been regarded as a challenging problem. At the same time, we succeeded in making the polymer transparent and flexible. We expect that it can be applied to controlling the thermal expansion of various organic materials.”
This research, led by researchers Sun Dal Kim and Byungyoung Lee, was published in Science Advances on October 26. (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau1956v)
2019.01.24 View 6482
A Novel Material for Transparent and Flexible Displays
(Research team led by Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry)
The next generation of flexible and transparent displays will require a high-performing and flexible polymeric material that has the optical and thermal properties of glass. The material must be transparent to visible light and have a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). Unfortunately, such a polymeric material has not been available. A KAIST research team has succeeded in making a new polymeric material with an exceptionally low CTE value while retaining high transparency and excellent thermal and mechanical properties. The method developed for amorphous polymers with a controlled CTE can be applied to control the thermal expansion of organic materials as well.
Most of objects expands upon heating and shrinks by cooling, and organic polymers have a relatively large CTE compared to that of ceramics or metals. Thin, light-weight planar substrates for semiconductor devices should have a similar CTE of ceramics. Otherwise, the device can be cracked due to the stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction. Therefore, matching the CTE of the semiconductor device and the substrate is crucial for successful manufacturing of display devices. Forming a network structure by connecting polymer chains is a well-known method of reducing the CTE of amorphous polymers. However, polymers with a network structure eventually lose their flexibility and becomes brittle.
As an alternative method, Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry and his team chose to adjust the distance and interaction between polymer chains. Thermal expansion and contraction of polymer films can be minimized by introducing interaction forces between the polymer chains and by arranging the direction of the force perpendicularly. The team successfully implemented this approach by appropriately designing the chemical structure of a transparent polymeric material. It is called poly (amide-imide) film, which is a transparent, flexible, and high-performing polymeric material. It is thermally stable enough to be used in the AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) fabrication process (stable at >400℃) with a low CTE (4ppm/℃).
The team made IGZO TFT (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Thin Film Transistor) devices on the newly synthesized transparent poly(amide-imide) film, and confirmed that the device could indeed operate normally even when it is folded down to a radius of 1mm.
Professor Kim said, “Our results suggest a way of controlling the thermal expansion of amorphous polymers similar to a level of glass without chemical cross-linking, which has long been regarded as a challenging problem. At the same time, we succeeded in making the polymer transparent and flexible. We expect that it can be applied to controlling the thermal expansion of various organic materials.”
This research, led by researchers Sun Dal Kim and Byungyoung Lee, was published in Science Advances on October 26. (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau1956v)
2019.01.24 View 6482 -
 New Members of KAST and Y-KAST 2019
(Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering)
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering became a new fellow of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 25 other scientists in Korea. He is one of the top virus immunologists in Korea and has published a review article in Nature Reviews Immunology.
Meanwhile KAST selected and announced 26 young scientists under the age 43 who have shown great potential and the creativity to carry out next-generation research. The list of Y-KAST (Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology) includes six KAIST professors: Professor Ji Oon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, Professor Shin-Hyun Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Professor Jung-Ryul Lee from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
KAST conferred their fellowships and Y-KAST membership during the New Year Reception.
2019.01.22 View 9132
New Members of KAST and Y-KAST 2019
(Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering)
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering became a new fellow of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 25 other scientists in Korea. He is one of the top virus immunologists in Korea and has published a review article in Nature Reviews Immunology.
Meanwhile KAST selected and announced 26 young scientists under the age 43 who have shown great potential and the creativity to carry out next-generation research. The list of Y-KAST (Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology) includes six KAIST professors: Professor Ji Oon Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, Professor Shin-Hyun Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Professor Jung-Ryul Lee from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
KAST conferred their fellowships and Y-KAST membership during the New Year Reception.
2019.01.22 View 9132 -
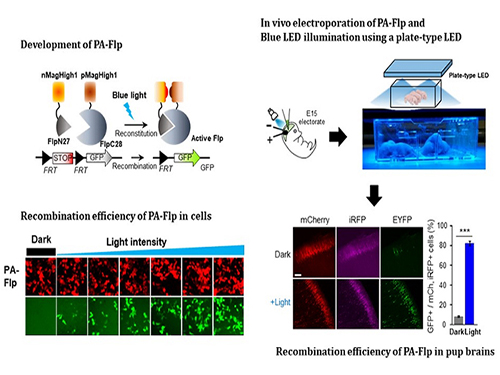 Noninvasive Light-Sensitive Recombinase for Deep Brain Genetic Manipulation
A KAIST team presented a noninvasive light-sensitive photoactivatable recombinase suitable for genetic manipulation in vivo. The highly light-sensitive property of photoactivatable Flp recombinase will be ideal for controlling genetic manipulation in deep mouse brain regions by illumination with a noninvasive light-emitting diode. This easy-to-use optogenetic module made by Professor Won Do Heo and his team will provide a side-effect free and expandable genetic manipulation tool for neuroscience research.
Spatiotemporal control of gene expression has been acclaimed as a valuable strategy for identifying functions of genes with complex neural circuits. Studies of complex brain functions require highly sophisticated and robust technologies that enable specific labeling and rapid genetic modification in live animals. A number of approaches for controlling the activity of proteins or expression of genes in a spatiotemporal manner using light, small molecules, hormones, and peptides have been developed for manipulating intact circuits or functions.
Among them, recombination-employing, chemically inducible systems are the most commonly used in vivo gene-modification systems. Other approaches include selective or conditional Cre-activation systems within subsets of green fluorescent protein-expressing cells or dual-promoter-driven intersectional populations of cells.
However, these methods are limited by the considerable time and effort required to establish knock-in mouse lines and by constraints on spatiotemporal control, which relies on a limited set of available genetic promoters and transgenic mouse resources.
Beyond these constraints, optogenetic approaches allow the activity of genetically defined neurons in the mouse brain to be controlled with high spatiotemporal resolution. However, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing the spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained a challenge.
In the study published at Nature Communication on Jan. 18, the team featured photoactivatable Flp recombinase by searching out split sites of Flp recombinase that were not previously identified, being capable of reconstitution to be active. The team validated the highly light-sensitive, efficient performance of photoactivatable Flp recombinase through precise light targeting by showing transgene expression within anatomically confined mouse brain regions.
The concept of local genetic labeling presented here suggests a new approach for genetically identifying subpopulations of cells defined by the spatial and temporal characteristics of light delivery. To date, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained out of reach and no such light-inducible Flp system has been developed. Accordingly, the team sought to develop a photoactivatable Flp recombinase that takes full advantage of the high spatiotemporal control offered by light stimulation.
This activation through noninvasive light illumination deep inside the brain is advantageous in that it avoids chemical or optic fiber implantation-mediated side effects, such as off-target cytotoxicity or physical lesions that might influence animal physiology or behaviors. The technique provides expandable utilities for transgene expression systems upon Flp recombinase activity in vivo, by designing a viral vector for minimal leaky expression influenced by viral nascent promoters.
The team demonstrated the utility of PA-Flp as a noninvasive in vivo optogenetic manipulation tool for use in the mouse brain, even applicable for deep brain structures as it can reach the hippocampus or medial septum using external LED light illumination.
The study is the result of five years of research by Professor Heo, who has led the bio-imaging and optogenetics fields by developing his own bio-imaging and optogenetics technologies. “It will be a great advantage to control specific gene expression desired by LEDs with little physical and chemical stimulation that can affect the physiological phenomenon in living animals,” he explained.
2019.01.22 View 7171
Noninvasive Light-Sensitive Recombinase for Deep Brain Genetic Manipulation
A KAIST team presented a noninvasive light-sensitive photoactivatable recombinase suitable for genetic manipulation in vivo. The highly light-sensitive property of photoactivatable Flp recombinase will be ideal for controlling genetic manipulation in deep mouse brain regions by illumination with a noninvasive light-emitting diode. This easy-to-use optogenetic module made by Professor Won Do Heo and his team will provide a side-effect free and expandable genetic manipulation tool for neuroscience research.
Spatiotemporal control of gene expression has been acclaimed as a valuable strategy for identifying functions of genes with complex neural circuits. Studies of complex brain functions require highly sophisticated and robust technologies that enable specific labeling and rapid genetic modification in live animals. A number of approaches for controlling the activity of proteins or expression of genes in a spatiotemporal manner using light, small molecules, hormones, and peptides have been developed for manipulating intact circuits or functions.
Among them, recombination-employing, chemically inducible systems are the most commonly used in vivo gene-modification systems. Other approaches include selective or conditional Cre-activation systems within subsets of green fluorescent protein-expressing cells or dual-promoter-driven intersectional populations of cells.
However, these methods are limited by the considerable time and effort required to establish knock-in mouse lines and by constraints on spatiotemporal control, which relies on a limited set of available genetic promoters and transgenic mouse resources.
Beyond these constraints, optogenetic approaches allow the activity of genetically defined neurons in the mouse brain to be controlled with high spatiotemporal resolution. However, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing the spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained a challenge.
In the study published at Nature Communication on Jan. 18, the team featured photoactivatable Flp recombinase by searching out split sites of Flp recombinase that were not previously identified, being capable of reconstitution to be active. The team validated the highly light-sensitive, efficient performance of photoactivatable Flp recombinase through precise light targeting by showing transgene expression within anatomically confined mouse brain regions.
The concept of local genetic labeling presented here suggests a new approach for genetically identifying subpopulations of cells defined by the spatial and temporal characteristics of light delivery. To date, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained out of reach and no such light-inducible Flp system has been developed. Accordingly, the team sought to develop a photoactivatable Flp recombinase that takes full advantage of the high spatiotemporal control offered by light stimulation.
This activation through noninvasive light illumination deep inside the brain is advantageous in that it avoids chemical or optic fiber implantation-mediated side effects, such as off-target cytotoxicity or physical lesions that might influence animal physiology or behaviors. The technique provides expandable utilities for transgene expression systems upon Flp recombinase activity in vivo, by designing a viral vector for minimal leaky expression influenced by viral nascent promoters.
The team demonstrated the utility of PA-Flp as a noninvasive in vivo optogenetic manipulation tool for use in the mouse brain, even applicable for deep brain structures as it can reach the hippocampus or medial septum using external LED light illumination.
The study is the result of five years of research by Professor Heo, who has led the bio-imaging and optogenetics fields by developing his own bio-imaging and optogenetics technologies. “It will be a great advantage to control specific gene expression desired by LEDs with little physical and chemical stimulation that can affect the physiological phenomenon in living animals,” he explained.
2019.01.22 View 7171 -
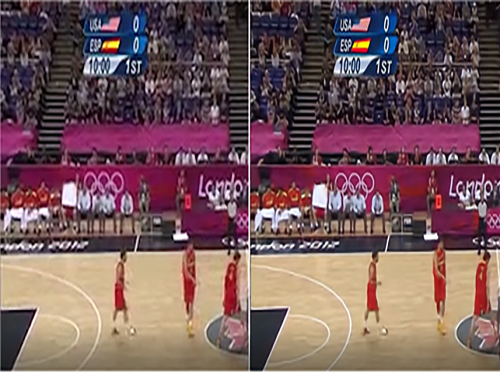 Enhanced Video Quality despite Poor Network Conditions
(from left: Jaehong Kim, Youngmok Jung, Hyunho Yeo, Professor Dongsu Han and Professor Jinwoo Shin)
Professor Jinwoo Shin and Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering developed neural adaptive content-aware internet video delivery. This technology is a novel method that combines adaptive streaming over HTTP, the video transmission system adopted by YouTube and Netflix, with a deep learning model.
This technology is expected to create an internet environment where users can enjoy watching 4K and AV/VR videos with high-quality and high-definition (HD) videos even with weak internet connections.
Thanks to video streaming services, internet video has experienced remarkable growth; nevertheless, users often suffer from low video quality due to unfavorable network conditions. Currently, existing adaptive streaming systems adjust the quality of the video in real time, accommodating the continuously changing internet bandwidth. Various algorithms are being researched for adaptive streaming systems, but there is an inherent limitation; that is, high-quality videos cannot be streamed in poor network environments regardless of which algorithm is used.
By incorporating super-resolution in adaptive streaming, the team overcame the limit of existing content distribution networks, of which their quality relies too much on the bandwidth. In the conventional method, the server that provides the video splits a video into certain lengths of time in advance. But the novel system introduced by the team allows the downloading of neural network segments. To facilitate this method, the video server needs to provide deep neural networks for each video segment as well as sizes of Deep Neural Networks (DNN) according to the specifications of the user’s computing capacity.
The largest neural network size is two megabytes, which is considerably smaller than video. When downloading the neural network from the user’s video player, it is split into several segments. Even its partial download is sufficient for a slightly comprised super-resolution.
While playing the video, the system converts the low quality video to a high-quality version by employing super-resolution based on deep convolution neural networks (CNN). The entire process is done in real time, and users can enjoy the high-definition video.
Even with a 17% smaller bandwidth, the system can provide the Quality of Experience equivalent to the latest adaptive streaming service. At a given internet bandwidth, it can provide 43% higher average QoE than the latest service.
Using a deep learning method allows this system to achieve a higher level of compression than the existing video compression methods. Their technology was recognized as a next-generation internet video system that applies super-resolution based on a deep convolution neural network to online videos.
Professor Han said, “So far, it has only been implemented on desktops, but we will further develop applications that work in mobile devices as well. This technology has been applied to the same video transmission systems used by streaming channels such as YouTube and Netflix, and thus shows good signs for practicability.”
This research, led by Hyunho Yeo, Youngmok Jung and Jaehong Kim, was presented at the 13th UNSENIX OSDI conference on October 10 2018 and completed for filing international patent application.
For further information, please click here.
Figure 1. Image quality before (left) and after (right) the technology application
Figure 2. The technology Concept
Figure 3. A transition from low-quality to high quality video after video transmission from the video server
2019.01.22 View 6814
Enhanced Video Quality despite Poor Network Conditions
(from left: Jaehong Kim, Youngmok Jung, Hyunho Yeo, Professor Dongsu Han and Professor Jinwoo Shin)
Professor Jinwoo Shin and Professor Dongsu Han from the School of Electrical Engineering developed neural adaptive content-aware internet video delivery. This technology is a novel method that combines adaptive streaming over HTTP, the video transmission system adopted by YouTube and Netflix, with a deep learning model.
This technology is expected to create an internet environment where users can enjoy watching 4K and AV/VR videos with high-quality and high-definition (HD) videos even with weak internet connections.
Thanks to video streaming services, internet video has experienced remarkable growth; nevertheless, users often suffer from low video quality due to unfavorable network conditions. Currently, existing adaptive streaming systems adjust the quality of the video in real time, accommodating the continuously changing internet bandwidth. Various algorithms are being researched for adaptive streaming systems, but there is an inherent limitation; that is, high-quality videos cannot be streamed in poor network environments regardless of which algorithm is used.
By incorporating super-resolution in adaptive streaming, the team overcame the limit of existing content distribution networks, of which their quality relies too much on the bandwidth. In the conventional method, the server that provides the video splits a video into certain lengths of time in advance. But the novel system introduced by the team allows the downloading of neural network segments. To facilitate this method, the video server needs to provide deep neural networks for each video segment as well as sizes of Deep Neural Networks (DNN) according to the specifications of the user’s computing capacity.
The largest neural network size is two megabytes, which is considerably smaller than video. When downloading the neural network from the user’s video player, it is split into several segments. Even its partial download is sufficient for a slightly comprised super-resolution.
While playing the video, the system converts the low quality video to a high-quality version by employing super-resolution based on deep convolution neural networks (CNN). The entire process is done in real time, and users can enjoy the high-definition video.
Even with a 17% smaller bandwidth, the system can provide the Quality of Experience equivalent to the latest adaptive streaming service. At a given internet bandwidth, it can provide 43% higher average QoE than the latest service.
Using a deep learning method allows this system to achieve a higher level of compression than the existing video compression methods. Their technology was recognized as a next-generation internet video system that applies super-resolution based on a deep convolution neural network to online videos.
Professor Han said, “So far, it has only been implemented on desktops, but we will further develop applications that work in mobile devices as well. This technology has been applied to the same video transmission systems used by streaming channels such as YouTube and Netflix, and thus shows good signs for practicability.”
This research, led by Hyunho Yeo, Youngmok Jung and Jaehong Kim, was presented at the 13th UNSENIX OSDI conference on October 10 2018 and completed for filing international patent application.
For further information, please click here.
Figure 1. Image quality before (left) and after (right) the technology application
Figure 2. The technology Concept
Figure 3. A transition from low-quality to high quality video after video transmission from the video server
2019.01.22 View 6814 -
 Main Cast Member of Drama KAIST Returns as KAIST Ambassador
(KAIST New Year Alumni Reception)
KAIST appointed Korean actor Min-woo Lee as KAIST Ambassador during the New Year Alumni Reception held on January 19.
Lee was one of the main characters in a popular Korean drama named KAIST, which aired from 1999 to 2000. It drew on a campus story of the top brains at KAIST and he was casted as a student studying electrical engineering. Along with the drama, he was recognized for building the positive image of KAIST.
As KAIST Ambassador, Lee will play various roles involved the promotion of Korea’s science and technology. For one year, he will be participating in major events and giving lectures to students.
Lee said that he still has strong affection for this drama. He added, “It is my great honor to be appointed as KAIST Ambassador and I will do my best to promote KAIST, the global value-creative leading university.”
(From left: Min-woo Lee and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
2019.01.21 View 3287
Main Cast Member of Drama KAIST Returns as KAIST Ambassador
(KAIST New Year Alumni Reception)
KAIST appointed Korean actor Min-woo Lee as KAIST Ambassador during the New Year Alumni Reception held on January 19.
Lee was one of the main characters in a popular Korean drama named KAIST, which aired from 1999 to 2000. It drew on a campus story of the top brains at KAIST and he was casted as a student studying electrical engineering. Along with the drama, he was recognized for building the positive image of KAIST.
As KAIST Ambassador, Lee will play various roles involved the promotion of Korea’s science and technology. For one year, he will be participating in major events and giving lectures to students.
Lee said that he still has strong affection for this drama. He added, “It is my great honor to be appointed as KAIST Ambassador and I will do my best to promote KAIST, the global value-creative leading university.”
(From left: Min-woo Lee and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
2019.01.21 View 3287