ES
-
 KAIST and Audi Korea Sign a Memorandum of Understanding to Establish a Startup Incubator
For the next five years, Audi Korea will provide USD 250,000 for the startup program.
KAIST recently signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Audi Korea to establish a student-led startup program, the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge, to promote design and product development on May 19, 2015, at the KAIST Institute of Entrepreneurship on campus.
Directed by Professor Sang-Min Bae of the Industrial Design Department (IDD), the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge will operate a global business incubator where IDD undergraduate and graduate students cultivate their entrepreneurship skills and explore business opportunities to develop commercially-applicable product designs. Audi Korea will invest USD 250,000 in the Innovation Lounge project for the next five years.
Students will receive support from the Lounge to turn their ideas, class assignments, and graduation theses into business products through a full cycle of the product development process such as inquiry, prototype development, and commercialization. The Lounge will also provide students with mentoring services from industry professionals and experts who can assist the students in finding design solutions and building prototypes using 3D printers.
The Dean of IDD, Kun-Pyo Lee, said, “Audi has been known for its initiatives which blend technological innovations into design. Likewise, our department offers students an integrative approach to design education and research which incorporates human factors and technology as important features in the design process. I believe that the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge will help us lead such efforts in the future.”
Professor Bae added, “This MOU is quite significant because it shows an excellent collaboration between academia and industry. Ideas created in universities should not be left to languish as just an idea or research. Rather, they should be utilized as ways to serve the needs of our society, and to do so, it is important for the government and companies to pay more attention to these interactions taking place between academia and private sectors.”
The Head of Marketing at Audi Korea, Jorg Dietzel, said, “As seen in our corporate slogan, "Advancement through Technology," Audi has grown through numerous technological innovations. I hope Audi Korea can contribute to the support of KAIST students from the Industrial Design Department to realize their dreams as future entrepreneurs and bring more innovative ideas to their field.”
Picture: Jorg Dietzel (fifth from the left), the Head of Marketing at Audi Korea, and Kun-Pyo Lee (sixth from the left), the Dean of Industrial Design Department, KAIST, pose together right after signing an agreement to create the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge on May 19, 2015.
2015.05.22 View 9741
KAIST and Audi Korea Sign a Memorandum of Understanding to Establish a Startup Incubator
For the next five years, Audi Korea will provide USD 250,000 for the startup program.
KAIST recently signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with Audi Korea to establish a student-led startup program, the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge, to promote design and product development on May 19, 2015, at the KAIST Institute of Entrepreneurship on campus.
Directed by Professor Sang-Min Bae of the Industrial Design Department (IDD), the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge will operate a global business incubator where IDD undergraduate and graduate students cultivate their entrepreneurship skills and explore business opportunities to develop commercially-applicable product designs. Audi Korea will invest USD 250,000 in the Innovation Lounge project for the next five years.
Students will receive support from the Lounge to turn their ideas, class assignments, and graduation theses into business products through a full cycle of the product development process such as inquiry, prototype development, and commercialization. The Lounge will also provide students with mentoring services from industry professionals and experts who can assist the students in finding design solutions and building prototypes using 3D printers.
The Dean of IDD, Kun-Pyo Lee, said, “Audi has been known for its initiatives which blend technological innovations into design. Likewise, our department offers students an integrative approach to design education and research which incorporates human factors and technology as important features in the design process. I believe that the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge will help us lead such efforts in the future.”
Professor Bae added, “This MOU is quite significant because it shows an excellent collaboration between academia and industry. Ideas created in universities should not be left to languish as just an idea or research. Rather, they should be utilized as ways to serve the needs of our society, and to do so, it is important for the government and companies to pay more attention to these interactions taking place between academia and private sectors.”
The Head of Marketing at Audi Korea, Jorg Dietzel, said, “As seen in our corporate slogan, "Advancement through Technology," Audi has grown through numerous technological innovations. I hope Audi Korea can contribute to the support of KAIST students from the Industrial Design Department to realize their dreams as future entrepreneurs and bring more innovative ideas to their field.”
Picture: Jorg Dietzel (fifth from the left), the Head of Marketing at Audi Korea, and Kun-Pyo Lee (sixth from the left), the Dean of Industrial Design Department, KAIST, pose together right after signing an agreement to create the Audi-KAIST Innovation Lounge on May 19, 2015.
2015.05.22 View 9741 -
 Professor Sang-Yup Lee Receives the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes from the Korean Government
The government of the Republic of Korea named Professor Sang-Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Bio-molecular Engineering at KAIST as the fiftieth recipient of the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes on May 19, 2015.
This medal is awarded to government employees, officials, and teachers in recognition of their contributions to public services including education.
Professor Lee is regarded as a leading scientist in the field of metabolic engineering, genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and bioinformatics on microorganism producing various primary and secondary metabolites. He contributed significantly to the advancement of bio-based engineering research in Korea.
In addition, his research in microorganism metabolic engineering propelled him to the front of his field, making him the world’s founder of systems metabolic engineering, inventing numerous technologies in strain development.
Professor Lee has received many patent rights in bioprocess engineering. While at KAIST, he applied for 585 patents and registered 227 patents. In particular, he has applied for 135 patents and registered 99 patents in the past five years, successfully turning research results into commercial applications.
Professor Lee said, “I’m glad to contribute to the development of Korean science and technology as a researcher and teacher. I would like to share this honor with my students, master’s and doctoral students in particular, because without their support, it wouldn’t have been possible to pull off the highest level of research results recognized by this medal.”
2015.05.21 View 8488
Professor Sang-Yup Lee Receives the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes from the Korean Government
The government of the Republic of Korea named Professor Sang-Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Bio-molecular Engineering at KAIST as the fiftieth recipient of the Order of Service Merit Red Stripes on May 19, 2015.
This medal is awarded to government employees, officials, and teachers in recognition of their contributions to public services including education.
Professor Lee is regarded as a leading scientist in the field of metabolic engineering, genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and bioinformatics on microorganism producing various primary and secondary metabolites. He contributed significantly to the advancement of bio-based engineering research in Korea.
In addition, his research in microorganism metabolic engineering propelled him to the front of his field, making him the world’s founder of systems metabolic engineering, inventing numerous technologies in strain development.
Professor Lee has received many patent rights in bioprocess engineering. While at KAIST, he applied for 585 patents and registered 227 patents. In particular, he has applied for 135 patents and registered 99 patents in the past five years, successfully turning research results into commercial applications.
Professor Lee said, “I’m glad to contribute to the development of Korean science and technology as a researcher and teacher. I would like to share this honor with my students, master’s and doctoral students in particular, because without their support, it wouldn’t have been possible to pull off the highest level of research results recognized by this medal.”
2015.05.21 View 8488 -
 KAIST Holds a Ceremony to Present the Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award
Doctor Gyu-Tae Kim from General Electric (GE) received the eleventh Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award. The award ceremony took place in the main conference room of the administration building on campus on May 13, 2015.
Dr. Kim, a graduate of KAIST, conducts research in the field of instable swirl combustion of gas turbines and has contributed to the development of aircraft engines. He earned his name as a researcher by identifying, for the first time in the world, the correlation between the thermoacoustic instability of gas turbine engines and the complex response of swirl flames.
Along with Dr. Kim, Shin-Jae Kang of the Aerospace Engineering Department, KAIST, Yong-Gyun Bae of the Mechanical Engineering Department, Korea University, and Ji-Won Kim from Kongju National University High School, received the Cho Jeong-Hoon scholarship.
The award was created in commemoration of Cho Jeong-Hoon who was killed in an explosion during his research at the KAIST Rocket Laboratory on May 13, 2003. Cho’s parents donated USD 450,000 to KAIST in his memory. Since 2005, a total of four students from KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School, all of which the late Honorary Doctor Cho attended, have received the scholarship.
2015.05.19 View 8049
KAIST Holds a Ceremony to Present the Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award
Doctor Gyu-Tae Kim from General Electric (GE) received the eleventh Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award. The award ceremony took place in the main conference room of the administration building on campus on May 13, 2015.
Dr. Kim, a graduate of KAIST, conducts research in the field of instable swirl combustion of gas turbines and has contributed to the development of aircraft engines. He earned his name as a researcher by identifying, for the first time in the world, the correlation between the thermoacoustic instability of gas turbine engines and the complex response of swirl flames.
Along with Dr. Kim, Shin-Jae Kang of the Aerospace Engineering Department, KAIST, Yong-Gyun Bae of the Mechanical Engineering Department, Korea University, and Ji-Won Kim from Kongju National University High School, received the Cho Jeong-Hoon scholarship.
The award was created in commemoration of Cho Jeong-Hoon who was killed in an explosion during his research at the KAIST Rocket Laboratory on May 13, 2003. Cho’s parents donated USD 450,000 to KAIST in his memory. Since 2005, a total of four students from KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School, all of which the late Honorary Doctor Cho attended, have received the scholarship.
2015.05.19 View 8049 -
 Professor Duck-Joo Lee Is Elected Vice Chairman of the American Helicopter Society
Professor Duck-Joo Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST was elected to become the first Korean vice president of the American Helicopter Society (AHS). He will serve a two-year term, starting this July, and his responsibilities will cover Asia, Australia, and Russia.
AHS, established in 1943, is the biggest association in the field with 6,800 members. The society is intended to advance helicopter technology and vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) in airplane technology.
The AHS’s board of directors consists of thirty experts in rotorcrafts, including the president of Sikorsky Aircraft Corporation, a renowned American helicopter manufacturing company.
Professor Lee started his career as a researcher in NASA Ames Research Center in the United States, and is now an acknowledged scholar in the field of aircraft jet engines and helicopter Aero-Acoustics. He also worked as the Assistant Editor-in-Chief of Journal of the American Helicopter Society, the President of the first Asia-Australia Rotorcraft Forum, and the leader of National Task Force Team of Korean Military and Civil Helicopter.
2015.05.18 View 8412
Professor Duck-Joo Lee Is Elected Vice Chairman of the American Helicopter Society
Professor Duck-Joo Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST was elected to become the first Korean vice president of the American Helicopter Society (AHS). He will serve a two-year term, starting this July, and his responsibilities will cover Asia, Australia, and Russia.
AHS, established in 1943, is the biggest association in the field with 6,800 members. The society is intended to advance helicopter technology and vertical take-off and landing (VTOL) in airplane technology.
The AHS’s board of directors consists of thirty experts in rotorcrafts, including the president of Sikorsky Aircraft Corporation, a renowned American helicopter manufacturing company.
Professor Lee started his career as a researcher in NASA Ames Research Center in the United States, and is now an acknowledged scholar in the field of aircraft jet engines and helicopter Aero-Acoustics. He also worked as the Assistant Editor-in-Chief of Journal of the American Helicopter Society, the President of the first Asia-Australia Rotorcraft Forum, and the leader of National Task Force Team of Korean Military and Civil Helicopter.
2015.05.18 View 8412 -
 KAIST's Patina Engraving System Awarded at ACM CHI
Professor Tek-Jin Nam’s research team of the Industrial Design Department of KAIST received the Best Paper Award in the 2015 Association for Computing Machinery’s (ACM) Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI) which was held from April 18 to 23, 2015. The team consisted of two KAIST students: Moon-Hwan Lee, a Ph.D. candidate, and Sejin Cha, a master's student. The team was the first in Asia to receive the award.
The ACM CHI represents the premier conference in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). This year’s event, held in Seoul, South Korea, was the first conference that the ACM had held in Asia in its thirty-three year history. The KAIST team’s paper, entitled “Patina Engraver: Visualizing Activity Logs as Patina in Fashionable Trackers,” ranked in the top 1% of 2,000 submitted papers.
The team developed Patina Engraver, an activity tracker, which monitors and tracks fitness-related metrics such as distances walked or run, calorie consumption, heartbeat, sleep quality, and blood pressure. The device wirelessly connects to a computer or smartphone so that it can store and utilize long-term tracking data.
However, what makes Patina Engraver, a smart wristband, different from other health trackers is its ability to display different design patterns based on users’ activity on the surface of the wristband. The research team was inspired to build this system from the fact that wearable electronics including activity trackers can be used not only as health care devices, but also as fashion items to express emotions and personalities.
Equipped with an engraving feature, the charging pad or holder for Patina Engraver draws individualized patterns to reflect the user’s activities, such as walking or running, while the device is being charged. The pattern display syncs with the frequency of usage, therefore, the more the tracker is used, the greater the number of patterns will show up.
According to the team, since Patina Engraver provides users with a personalized illustration of their activity on the tracker, users are more motivated to put on the tracker and exercise.
Professor Nam said, “This research can be applied in producing other wearable devices to enhance users’ emotional satisfaction. When wearable technology is combined with design and emotion, the industry market will quickly expand.”
Figure 1: Patina engraving system developed by KAIST research team
Figure 2: The process of engraving illustrations of the activity records onto the tracker
Figure 3: Personalized activity trackers based on activity records
2015.05.15 View 13783
KAIST's Patina Engraving System Awarded at ACM CHI
Professor Tek-Jin Nam’s research team of the Industrial Design Department of KAIST received the Best Paper Award in the 2015 Association for Computing Machinery’s (ACM) Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI) which was held from April 18 to 23, 2015. The team consisted of two KAIST students: Moon-Hwan Lee, a Ph.D. candidate, and Sejin Cha, a master's student. The team was the first in Asia to receive the award.
The ACM CHI represents the premier conference in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). This year’s event, held in Seoul, South Korea, was the first conference that the ACM had held in Asia in its thirty-three year history. The KAIST team’s paper, entitled “Patina Engraver: Visualizing Activity Logs as Patina in Fashionable Trackers,” ranked in the top 1% of 2,000 submitted papers.
The team developed Patina Engraver, an activity tracker, which monitors and tracks fitness-related metrics such as distances walked or run, calorie consumption, heartbeat, sleep quality, and blood pressure. The device wirelessly connects to a computer or smartphone so that it can store and utilize long-term tracking data.
However, what makes Patina Engraver, a smart wristband, different from other health trackers is its ability to display different design patterns based on users’ activity on the surface of the wristband. The research team was inspired to build this system from the fact that wearable electronics including activity trackers can be used not only as health care devices, but also as fashion items to express emotions and personalities.
Equipped with an engraving feature, the charging pad or holder for Patina Engraver draws individualized patterns to reflect the user’s activities, such as walking or running, while the device is being charged. The pattern display syncs with the frequency of usage, therefore, the more the tracker is used, the greater the number of patterns will show up.
According to the team, since Patina Engraver provides users with a personalized illustration of their activity on the tracker, users are more motivated to put on the tracker and exercise.
Professor Nam said, “This research can be applied in producing other wearable devices to enhance users’ emotional satisfaction. When wearable technology is combined with design and emotion, the industry market will quickly expand.”
Figure 1: Patina engraving system developed by KAIST research team
Figure 2: The process of engraving illustrations of the activity records onto the tracker
Figure 3: Personalized activity trackers based on activity records
2015.05.15 View 13783 -
 KAIST Hosts the Wearable Computer Contest 2015
Deadlines for Prototype Contest by May 30, 2015 and August 15 for Idea Contest
KAIST will hold the Wearable Computer Contest 2015 in November, which will be sponsored by Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Wearable computers have emerged as next-generation mobile devices, and are gaining more popularity with the growth of the Internet of Things. KAIST has introduced wearable devices such as K-Glass 2, a smart glass with augmented reality embedded. The Glass also works on commands by blinking eyes.
This year’s contest with the theme of “Wearable Computers for Internet of Things” is divided into two parts: the Prototype Competition and Idea Contest.
With the fusion of information technology (IT) and fashion, contestants are encouraged to submit prototypes of their ideas by May 30, 2015. The ten teams that make it to the finals will receive a wearable computer platform and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) education, along with a prize of USD 1,000 for prototype production costs. The winner of the Prototype Contest will receive a prize of USD 5,000 and an award from the Minister of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of the Republic of Korea.
In the Idea Contest, posters containing ideas and concepts of wearable devices should be submitted by August 15, 2015. The teams that make it to the finals will have to display a life-size mockup in the final stage. The winner of the contest will receive a prize of USD 1,000 and an award from the Minister of MSIP.
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can enter the Prototype Competition and anyone can participate in the Idea Contest.
The chairman of the event, Hoi-Jun Yoo, a professor of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, noted:
“There is a growing interest in wearable computers in the industry. I can easily envisage that there will be a new IT world where wearable computers are integrated into the Internet of Things, healthcare, and smart homes.”
More information on the contest can be found online at http://www.ufcom.org.
Picture: Finalists in the last year’s contest
2015.05.11 View 8240
KAIST Hosts the Wearable Computer Contest 2015
Deadlines for Prototype Contest by May 30, 2015 and August 15 for Idea Contest
KAIST will hold the Wearable Computer Contest 2015 in November, which will be sponsored by Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Wearable computers have emerged as next-generation mobile devices, and are gaining more popularity with the growth of the Internet of Things. KAIST has introduced wearable devices such as K-Glass 2, a smart glass with augmented reality embedded. The Glass also works on commands by blinking eyes.
This year’s contest with the theme of “Wearable Computers for Internet of Things” is divided into two parts: the Prototype Competition and Idea Contest.
With the fusion of information technology (IT) and fashion, contestants are encouraged to submit prototypes of their ideas by May 30, 2015. The ten teams that make it to the finals will receive a wearable computer platform and Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) education, along with a prize of USD 1,000 for prototype production costs. The winner of the Prototype Contest will receive a prize of USD 5,000 and an award from the Minister of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of the Republic of Korea.
In the Idea Contest, posters containing ideas and concepts of wearable devices should be submitted by August 15, 2015. The teams that make it to the finals will have to display a life-size mockup in the final stage. The winner of the contest will receive a prize of USD 1,000 and an award from the Minister of MSIP.
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can enter the Prototype Competition and anyone can participate in the Idea Contest.
The chairman of the event, Hoi-Jun Yoo, a professor of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, noted:
“There is a growing interest in wearable computers in the industry. I can easily envisage that there will be a new IT world where wearable computers are integrated into the Internet of Things, healthcare, and smart homes.”
More information on the contest can be found online at http://www.ufcom.org.
Picture: Finalists in the last year’s contest
2015.05.11 View 8240 -
 Professor Jinwoo Shin Receives the Bloomberg Scientific Research Award
Professor Jinwoo Shin (https://sites.google.com/site/mijirim/) of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been selected as one of the three winners to receive the first Bloomberg Scientific Research Award this month. The newly created award is presented to researchers in computer science who conduct high-quality research in such areas as machine learning, natural language processing, machine translation, statistics, and theory.
Professor Shin submitted his research proposal entitled “Scalable Probabilistic Deep Leaning,” and the award will support funding his research for one year. For details, please click on the link below for an article released by Bloomberg News, announcing the winners of the award:
Bloomberg News, April 28, 2015
“Announcing the Winners of the Bloomberg’s First Scientific Research Program”
https://3blmedia.com/News/Announcing-Winners-Bloombergs-First-Scientific-Research-Program
2015.04.30 View 8301
Professor Jinwoo Shin Receives the Bloomberg Scientific Research Award
Professor Jinwoo Shin (https://sites.google.com/site/mijirim/) of the Electrical Engineering Department at KAIST has been selected as one of the three winners to receive the first Bloomberg Scientific Research Award this month. The newly created award is presented to researchers in computer science who conduct high-quality research in such areas as machine learning, natural language processing, machine translation, statistics, and theory.
Professor Shin submitted his research proposal entitled “Scalable Probabilistic Deep Leaning,” and the award will support funding his research for one year. For details, please click on the link below for an article released by Bloomberg News, announcing the winners of the award:
Bloomberg News, April 28, 2015
“Announcing the Winners of the Bloomberg’s First Scientific Research Program”
https://3blmedia.com/News/Announcing-Winners-Bloombergs-First-Scientific-Research-Program
2015.04.30 View 8301 -
 Professor Sang Ouk Kim Receives the POSCO Academic Award
Professor Sang Ouk Kim of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering received the 2015 POSCO Academic Award. The award ceremony took place at the annual conference of the Korean Institute of Metals and Materials on April 23, 2015.
The POSCO Academic Award has been presented to the Institute's researchers and academics in recognition of their contributions to the advancement of metals and materials engineering in Korea.
Professor Kim is known for his pioneering work in manipulating the properties (work function, conductivity, surface energy, chemo-responsiveness, etc.) of carbon-based materials using double-element doping. Through his research, Professor Kim showed that carbon materials could be extremely useful in various areas including solar batteries and flexible devices. His work has been recognized and published in such journals as Advanced Materials, which invited him to write a review paper on his research in its 25th anniversary issue in 2014, along with world-renowned scholars including the Nobel laureate Alan Heeger.
Professor Kim has published a total of 143 Science Citation Index papers in journals like Nature, Science, Nature Materials, Nature Communications, Advanced Materials, Nano Letters, and Physical Review Letters. According to Scopus, a bibliographic database containing abstracts and citations for academic journal articles, he has been cited 6,456 times and has the h-index of 44, an index describing the scientific productivity and impact of a researcher.
2015.04.22 View 10473
Professor Sang Ouk Kim Receives the POSCO Academic Award
Professor Sang Ouk Kim of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering received the 2015 POSCO Academic Award. The award ceremony took place at the annual conference of the Korean Institute of Metals and Materials on April 23, 2015.
The POSCO Academic Award has been presented to the Institute's researchers and academics in recognition of their contributions to the advancement of metals and materials engineering in Korea.
Professor Kim is known for his pioneering work in manipulating the properties (work function, conductivity, surface energy, chemo-responsiveness, etc.) of carbon-based materials using double-element doping. Through his research, Professor Kim showed that carbon materials could be extremely useful in various areas including solar batteries and flexible devices. His work has been recognized and published in such journals as Advanced Materials, which invited him to write a review paper on his research in its 25th anniversary issue in 2014, along with world-renowned scholars including the Nobel laureate Alan Heeger.
Professor Kim has published a total of 143 Science Citation Index papers in journals like Nature, Science, Nature Materials, Nature Communications, Advanced Materials, Nano Letters, and Physical Review Letters. According to Scopus, a bibliographic database containing abstracts and citations for academic journal articles, he has been cited 6,456 times and has the h-index of 44, an index describing the scientific productivity and impact of a researcher.
2015.04.22 View 10473 -
 KAIST and the Naver Corporation Agree to Cooperate in Computer Science
KAIST and Naver, a Korean Internet corporation, concluded a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on April 17, 2015, to cooperate in advancing research and education in computer science.
Doo-Hwan Bae (pictured on the right below), the Dean of School of Computing at KAIST and Jong-Mok Park (pictured on left), the Director of Technical Cooperation at Naver, signed the MOU.
Under this agreement, the two organizations will foster computer scientists and engineers, conduct joint research projects, and develop training programs for entrepreneurs.
KAIST and Naver will organize a steering committee to lay out further details on the agreement.
2015.04.17 View 8301
KAIST and the Naver Corporation Agree to Cooperate in Computer Science
KAIST and Naver, a Korean Internet corporation, concluded a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on April 17, 2015, to cooperate in advancing research and education in computer science.
Doo-Hwan Bae (pictured on the right below), the Dean of School of Computing at KAIST and Jong-Mok Park (pictured on left), the Director of Technical Cooperation at Naver, signed the MOU.
Under this agreement, the two organizations will foster computer scientists and engineers, conduct joint research projects, and develop training programs for entrepreneurs.
KAIST and Naver will organize a steering committee to lay out further details on the agreement.
2015.04.17 View 8301 -
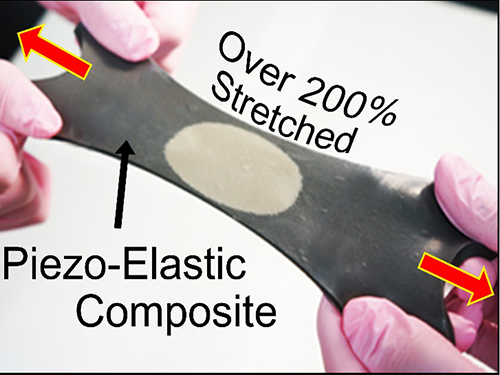 KAIST Researchers Develops Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee (http://fand.kaist.ac.kr) of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed a hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvesting device called a nanogenerator.
Flexible electronics have come into the market and are enabling new technologies like flexible displays in mobile phone, wearable electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoTs). However, is the degree of flexibility enough for most applications? For many flexible devices, elasticity is a very important issue. For example, wearable/biomedical devices and electronic skins (e-skins) should stretch to conform to arbitrarily curved surfaces and moving body parts such as joints, diaphragms, and tendons. They must be able to withstand the repeated and prolonged mechanical stresses of stretching. In particular, the development of elastic energy devices is regarded as critical to establish power supplies in stretchable applications. Although several researchers have explored diverse stretchable electronics, due to the absence of the appropriate device structures and correspondingly electrodes, researchers have not developed ultra-stretchable and fully-reversible energy conversion devices properly.
Recently, researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) have collaborated and demonstrated a facile methodology to obtain a high-performance and hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator (SEG) using very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes. Their stretchable piezoelectric generator can harvest mechanical energy to produce high power output (~4 V) with large elasticity (~250%) and excellent durability (over 104 cycles). These noteworthy results were achieved by the non-destructive stress- relaxation ability of the unique electrodes as well as the good piezoelectricity of the device components. The new SEG can be applied to a wide-variety of wearable energy-harvesters to transduce biomechanical-stretching energy from the body (or machines) to electrical energy.
Professor Lee said, “This exciting approach introduces an ultra-stretchable piezoelectric generator. It can open avenues for power supplies in universal wearable and biomedical applications as well as self-powered ultra-stretchable electronics.”
This result was published online in the March issue of Advanced Materials, which is entitled “A Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester.”
YouTube Link: “A hyper-stretchable energy harvester”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBByFvPVRiU&feature=youtu.be
Figure: Top row: Schematics of hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator enabled by very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes.
Bottom row: The SEG energy harvester stretched by human hands over 200% strain.
2015.04.14 View 13872
KAIST Researchers Develops Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee (http://fand.kaist.ac.kr) of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST has developed a hyper-stretchable elastic-composite energy harvesting device called a nanogenerator.
Flexible electronics have come into the market and are enabling new technologies like flexible displays in mobile phone, wearable electronics, and the Internet of Things (IoTs). However, is the degree of flexibility enough for most applications? For many flexible devices, elasticity is a very important issue. For example, wearable/biomedical devices and electronic skins (e-skins) should stretch to conform to arbitrarily curved surfaces and moving body parts such as joints, diaphragms, and tendons. They must be able to withstand the repeated and prolonged mechanical stresses of stretching. In particular, the development of elastic energy devices is regarded as critical to establish power supplies in stretchable applications. Although several researchers have explored diverse stretchable electronics, due to the absence of the appropriate device structures and correspondingly electrodes, researchers have not developed ultra-stretchable and fully-reversible energy conversion devices properly.
Recently, researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) have collaborated and demonstrated a facile methodology to obtain a high-performance and hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator (SEG) using very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes. Their stretchable piezoelectric generator can harvest mechanical energy to produce high power output (~4 V) with large elasticity (~250%) and excellent durability (over 104 cycles). These noteworthy results were achieved by the non-destructive stress- relaxation ability of the unique electrodes as well as the good piezoelectricity of the device components. The new SEG can be applied to a wide-variety of wearable energy-harvesters to transduce biomechanical-stretching energy from the body (or machines) to electrical energy.
Professor Lee said, “This exciting approach introduces an ultra-stretchable piezoelectric generator. It can open avenues for power supplies in universal wearable and biomedical applications as well as self-powered ultra-stretchable electronics.”
This result was published online in the March issue of Advanced Materials, which is entitled “A Hyper-Stretchable Elastic-Composite Energy Harvester.”
YouTube Link: “A hyper-stretchable energy harvester”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EBByFvPVRiU&feature=youtu.be
Figure: Top row: Schematics of hyper-stretchable elastic-composite generator enabled by very long silver nanowire-based stretchable electrodes.
Bottom row: The SEG energy harvester stretched by human hands over 200% strain.
2015.04.14 View 13872 -
 Professor Rim Presents at IAEA Workshop in Vienna
Professor Chun-Taek Rim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST recently attended the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’s workshop on the Application of Wireless Technologies in Nuclear Power Plant Instrumentation and Control System. It took place on March 30-April 2, 2015, in Vienna, Austria.
Representing Korea, Professor Rim gave a talk entitled “Highly Reliable Wireless Power and Communications under Severe Accident of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs).” About 20 industry experts from 12 countries such as AREVA (France), Westinghouse (US), Oak Ridge National Laboratory (US), Hitachi (Japan), and ENEA (Italy) joined the meeting.
The IAEA hosted the workshop to explore the application of wireless technology for the operation and management of NPPs. It formed a committee consisting of eminent professionals worldwide in NPP instrumentation and control systems, communications, and nuclear power to examine this issue in-depth and to conduct various research projects for the next three years.
In particular, the committee will concentrate its research on improving the reliability and safety of using wireless technology, not only in the normal operation of nuclear plants but also in extreme conditions such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. The complementation, economic feasibility, and standardization of NPPs when applying wireless technology will be also discussed.
Professor Rim currently leads the Nuclear Power Electronics
and Robotics Lab at KAIST (http://tesla.kaist.ac.kr/index_eng.php?lag=eng).
Picture 1: Professors Rim presents his topic at the IAEA Workshop in Vienna.
Picture 2: The IAEA Workshop Participants
2015.04.07 View 12938
Professor Rim Presents at IAEA Workshop in Vienna
Professor Chun-Taek Rim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST recently attended the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’s workshop on the Application of Wireless Technologies in Nuclear Power Plant Instrumentation and Control System. It took place on March 30-April 2, 2015, in Vienna, Austria.
Representing Korea, Professor Rim gave a talk entitled “Highly Reliable Wireless Power and Communications under Severe Accident of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs).” About 20 industry experts from 12 countries such as AREVA (France), Westinghouse (US), Oak Ridge National Laboratory (US), Hitachi (Japan), and ENEA (Italy) joined the meeting.
The IAEA hosted the workshop to explore the application of wireless technology for the operation and management of NPPs. It formed a committee consisting of eminent professionals worldwide in NPP instrumentation and control systems, communications, and nuclear power to examine this issue in-depth and to conduct various research projects for the next three years.
In particular, the committee will concentrate its research on improving the reliability and safety of using wireless technology, not only in the normal operation of nuclear plants but also in extreme conditions such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. The complementation, economic feasibility, and standardization of NPPs when applying wireless technology will be also discussed.
Professor Rim currently leads the Nuclear Power Electronics
and Robotics Lab at KAIST (http://tesla.kaist.ac.kr/index_eng.php?lag=eng).
Picture 1: Professors Rim presents his topic at the IAEA Workshop in Vienna.
Picture 2: The IAEA Workshop Participants
2015.04.07 View 12938 -
 Polymers with Highly Improved Light-transformation Efficiency
A joint Korean research team, led by Professor Bum-Joon Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST and Professor Young-Woo Han of the Department of Nanofusion Engineering at Pusan National University, has developed a new type of electrically-conductive polymer for solar batteries with an improved light-transformation efficiency of up to 5%. The team considers it a viable replacement for existing plastic batteries for solar power which is viewed as the energy source of the future.
Polymer solar cells have greater structural stability and heat resistance compared to fullerene organic solar cells. However, they have lower light-transformation efficiency—below 4%—compared to 10% of the latter. The low efficiency is due to the failure of blending among the polymers that compose the active layer of the cell. This phenomenon deters the formation and movement of electrons and thus lowers light-transformation efficiency.
By manipulating the structure and concentration of conductive polymers, the team was able to effectively increase the polymer blending and increase light-transformation efficiency. The team was able to maximize the efficiency up to 6% which is the highest reported ratio.
Professor Kim said, “This research demonstrates that conductive polymer plastics can be used widely for solar cells and batteries for mobile devices.”
The research findings were published in the February 18th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Picture: Flexible Solar Cell Polymer Developed by the Research Team
2015.04.05 View 11138
Polymers with Highly Improved Light-transformation Efficiency
A joint Korean research team, led by Professor Bum-Joon Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST and Professor Young-Woo Han of the Department of Nanofusion Engineering at Pusan National University, has developed a new type of electrically-conductive polymer for solar batteries with an improved light-transformation efficiency of up to 5%. The team considers it a viable replacement for existing plastic batteries for solar power which is viewed as the energy source of the future.
Polymer solar cells have greater structural stability and heat resistance compared to fullerene organic solar cells. However, they have lower light-transformation efficiency—below 4%—compared to 10% of the latter. The low efficiency is due to the failure of blending among the polymers that compose the active layer of the cell. This phenomenon deters the formation and movement of electrons and thus lowers light-transformation efficiency.
By manipulating the structure and concentration of conductive polymers, the team was able to effectively increase the polymer blending and increase light-transformation efficiency. The team was able to maximize the efficiency up to 6% which is the highest reported ratio.
Professor Kim said, “This research demonstrates that conductive polymer plastics can be used widely for solar cells and batteries for mobile devices.”
The research findings were published in the February 18th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Picture: Flexible Solar Cell Polymer Developed by the Research Team
2015.04.05 View 11138