AR
-
 Professor Cho Young-ho wins 'E2 Star' award
Professor Cho Young-ho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST was chosen as the ‘E2 Star’ at the ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ in academics. The ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology was held to display outstanding research results and to conceptualize the future of science education.
The ‘E2 star’ award is given to renowned figures in industry, academia and society. A total of 35 candidates were recommended for the 3 fields and Professor Cho received the first place in the online voting.
Professor Cho received high marks for his work in engineering education, research development and increasing the communication between academia and industry, as well as the commercialization of science and technology. Professor Cho was especially praised for the specialization of engineering education in integrated fields and the joint research with US and Swiss universities.
Professor Cho Young-ho(Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST)
2012.12.26 View 10873
Professor Cho Young-ho wins 'E2 Star' award
Professor Cho Young-ho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST was chosen as the ‘E2 Star’ at the ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ in academics. The ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology was held to display outstanding research results and to conceptualize the future of science education.
The ‘E2 star’ award is given to renowned figures in industry, academia and society. A total of 35 candidates were recommended for the 3 fields and Professor Cho received the first place in the online voting.
Professor Cho received high marks for his work in engineering education, research development and increasing the communication between academia and industry, as well as the commercialization of science and technology. Professor Cho was especially praised for the specialization of engineering education in integrated fields and the joint research with US and Swiss universities.
Professor Cho Young-ho(Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST)
2012.12.26 View 10873 -
 Ph.D. students Hyowon Park and Won Ma receive Grand Prizes in Mathematics and Biology respectively.
Researchers in KAIST received best paper awards in two out of three fields at this year’s award ceremony for the “Second Annual Best Thesis Paper Award” held collectively by the Korea University Presidents’ Federation (with Chairman DaeSoon Lee) and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (with Director GilSang Jung).
Two researchers from KAIST, Hyowon Park (Department of Mathematics) and Won Ma (Department of Biology) received best paper awards.
This prize, given by the both the Korea University Presidents’ Federation and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology since last year, is awarded to researchers and assistant professors who write the most outstanding thesis papers in the field of basic sciences.
Park, who received the best paper award this year, did research on graph braid groups. He was supervised by Professor Kihyung Ko, who received the best supervisor reward.
Ma, who received the best paper award in the field of biological science, researched about the Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder due to deficiency of the GIT1 synapse protein. His supervising professor also received the supervisor award.
The award ceremony was held in the auditorium of the S-OIL headquarters in Seoul on November 30.
Meanwhile, NASA researcher Jaehwa Lee received the best paper award in the field of earth science, and his supervising professor, Professor Jun Kim from Yonsei University who studies atmospheric science, received the best supervisor award.
2012.12.21 View 10962
Ph.D. students Hyowon Park and Won Ma receive Grand Prizes in Mathematics and Biology respectively.
Researchers in KAIST received best paper awards in two out of three fields at this year’s award ceremony for the “Second Annual Best Thesis Paper Award” held collectively by the Korea University Presidents’ Federation (with Chairman DaeSoon Lee) and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (with Director GilSang Jung).
Two researchers from KAIST, Hyowon Park (Department of Mathematics) and Won Ma (Department of Biology) received best paper awards.
This prize, given by the both the Korea University Presidents’ Federation and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology since last year, is awarded to researchers and assistant professors who write the most outstanding thesis papers in the field of basic sciences.
Park, who received the best paper award this year, did research on graph braid groups. He was supervised by Professor Kihyung Ko, who received the best supervisor reward.
Ma, who received the best paper award in the field of biological science, researched about the Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder due to deficiency of the GIT1 synapse protein. His supervising professor also received the supervisor award.
The award ceremony was held in the auditorium of the S-OIL headquarters in Seoul on November 30.
Meanwhile, NASA researcher Jaehwa Lee received the best paper award in the field of earth science, and his supervising professor, Professor Jun Kim from Yonsei University who studies atmospheric science, received the best supervisor award.
2012.12.21 View 10962 -
 Principle behind increasing the catalytic property of nanocatalysts proven
The technology that allows full control of the catalytic property of nanocatalysts using oxide formation on nanocatalysts has been developed by KAIST researchers. The breakthrough opens up the possibility of the development of a new kind of catalysts that maximizes catalytic property and minimizes waste.
*nanocatalyst is a material that catalyzes gas reactions on its surface. It is composed of a high surface area oxide scaffold with nano-sized metal particles dispersed.
The team was led by Professor Park Jeong Young of the KAIST EEWS Graduate School and consists of Kamran Qadir Ph.D. candidate (1st Author), Professor Joo Sang Hoon of UNIST, Professor Moon Bong Jin of Hanyang University, and Professor Gabor Somorajai of UC Berkeley. Support for the research was provided from Ministry of Education Science and Technology, National Research Foundation, and Ministry of Knowledge Economy. The results were published as the online edition of Nano Letters: “Intrinsic Relation between Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation on Ru Nanoparticles and Ru Oxides Uncovered with Ambient Pressure XPS”.
Catalysts are included in above 80% of all the products used in everyday life and are therefore included in most aspects of our lives.
The focus on nanocatalysts is based on finding solutions to increasing the efficiency for application to energy production and for solving environmental issues.
Most nanocatalysts are composed of nanoparticles and oxides where the nanoparticles increase the surface area of the catalyst to increase its activity.
The efficiency of a nanocatalyst is affected by the surface oxide of the nanoparticles. However the proving of this assumption remained difficult to do as it required in-situ measurement of the oxide state of the nanoparticles in the specific environment. Thus far, the experiments were conducted in a vacuum and therefore did not reflect the actual behavior in real life. The recently developed X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy allows for measurement of the oxidization state at standard atmospheric pressure.
Professor Park’s research team successfully measured the oxidization state of the nanoparticle using the atmospheric pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in the specified environment.
They confirmed the effect the oxidization state on the catalytic effect of the nanoparticles and additionally found that a thin layer of oxide can increase the catalytic effect and the effectiveness of the nanoparticle can controlled by the oxidation state.
2012.11.29 View 9175
Principle behind increasing the catalytic property of nanocatalysts proven
The technology that allows full control of the catalytic property of nanocatalysts using oxide formation on nanocatalysts has been developed by KAIST researchers. The breakthrough opens up the possibility of the development of a new kind of catalysts that maximizes catalytic property and minimizes waste.
*nanocatalyst is a material that catalyzes gas reactions on its surface. It is composed of a high surface area oxide scaffold with nano-sized metal particles dispersed.
The team was led by Professor Park Jeong Young of the KAIST EEWS Graduate School and consists of Kamran Qadir Ph.D. candidate (1st Author), Professor Joo Sang Hoon of UNIST, Professor Moon Bong Jin of Hanyang University, and Professor Gabor Somorajai of UC Berkeley. Support for the research was provided from Ministry of Education Science and Technology, National Research Foundation, and Ministry of Knowledge Economy. The results were published as the online edition of Nano Letters: “Intrinsic Relation between Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation on Ru Nanoparticles and Ru Oxides Uncovered with Ambient Pressure XPS”.
Catalysts are included in above 80% of all the products used in everyday life and are therefore included in most aspects of our lives.
The focus on nanocatalysts is based on finding solutions to increasing the efficiency for application to energy production and for solving environmental issues.
Most nanocatalysts are composed of nanoparticles and oxides where the nanoparticles increase the surface area of the catalyst to increase its activity.
The efficiency of a nanocatalyst is affected by the surface oxide of the nanoparticles. However the proving of this assumption remained difficult to do as it required in-situ measurement of the oxide state of the nanoparticles in the specific environment. Thus far, the experiments were conducted in a vacuum and therefore did not reflect the actual behavior in real life. The recently developed X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy allows for measurement of the oxidization state at standard atmospheric pressure.
Professor Park’s research team successfully measured the oxidization state of the nanoparticle using the atmospheric pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in the specified environment.
They confirmed the effect the oxidization state on the catalytic effect of the nanoparticles and additionally found that a thin layer of oxide can increase the catalytic effect and the effectiveness of the nanoparticle can controlled by the oxidation state.
2012.11.29 View 9175 -
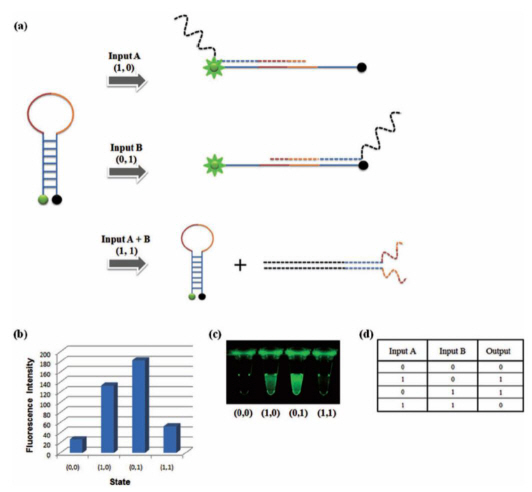 DNA based semiconductor technology developed
Professor Park Hyun Gyu’s research team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has successfully implemented all logic gates using DNA, a feat that led the research to be published as the cover paper for the international nanotechnology paper "Small".
Even with the latest technology, it was impossible to create a silicon based semiconductor smaller than 10nm, but because DNA has a thickness of only 2nm, this could lead to the creation of semiconductors with groundbreaking degrees of integration.
A 2 nm semiconductor will be able to store 10,000 HD movies within a size of a postage stamp, at least 100 times more than the current 20nm semiconductors.
DNAs are comprised of 4 bases which are continually connected: Adenine (A) with Thymine (T), and Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C).
For this research, the team used the specific binding properties of DNA, which forms its helix-shape, and a circular molecular beacon that has fluorescent signaling properties under structural changes.
The research team used input signals to open and close the circular DNA, the same principle that is applied to logic gates in digital circuits.
The output signal was measured using the increase and decrease of the fluorescent signal from the molecular beacon due to the opening and closing of the circular DNA respectively.
The team overcame the limited system problems of the existing logic gates and managed to implement all 8 logic gates (AND, OR, XOR, INHIBIT, NAND, NOR, XNOR, IMPlCATION). A multilevel circuit that connects different logic gates was also tested to show its regenerative properties.
Professor Park said that “cheap bio-electric devices with high degrees of integration will be made possible by this research” and that “there will be a large difference in the field of molecular level electronic research”
Mr. Park Gi Su, a doctoral candidate and the 1st author of this research, said that “a DNA sequence of 10 bases is only 3.4nm long and 2nm thick, which can be used to effectively increase the degree of integration of electronic devices” and that “a bio computer could materialize in the near future through DNA semiconductors with accurate logic gates”.
XOR Gate: The output signal 1 comes through the open circular DNA when either input DNA A or input DNA B is present. When both inputs are not present, the flourescent signal does not come through
2012.09.27 View 10061
DNA based semiconductor technology developed
Professor Park Hyun Gyu’s research team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has successfully implemented all logic gates using DNA, a feat that led the research to be published as the cover paper for the international nanotechnology paper "Small".
Even with the latest technology, it was impossible to create a silicon based semiconductor smaller than 10nm, but because DNA has a thickness of only 2nm, this could lead to the creation of semiconductors with groundbreaking degrees of integration.
A 2 nm semiconductor will be able to store 10,000 HD movies within a size of a postage stamp, at least 100 times more than the current 20nm semiconductors.
DNAs are comprised of 4 bases which are continually connected: Adenine (A) with Thymine (T), and Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C).
For this research, the team used the specific binding properties of DNA, which forms its helix-shape, and a circular molecular beacon that has fluorescent signaling properties under structural changes.
The research team used input signals to open and close the circular DNA, the same principle that is applied to logic gates in digital circuits.
The output signal was measured using the increase and decrease of the fluorescent signal from the molecular beacon due to the opening and closing of the circular DNA respectively.
The team overcame the limited system problems of the existing logic gates and managed to implement all 8 logic gates (AND, OR, XOR, INHIBIT, NAND, NOR, XNOR, IMPlCATION). A multilevel circuit that connects different logic gates was also tested to show its regenerative properties.
Professor Park said that “cheap bio-electric devices with high degrees of integration will be made possible by this research” and that “there will be a large difference in the field of molecular level electronic research”
Mr. Park Gi Su, a doctoral candidate and the 1st author of this research, said that “a DNA sequence of 10 bases is only 3.4nm long and 2nm thick, which can be used to effectively increase the degree of integration of electronic devices” and that “a bio computer could materialize in the near future through DNA semiconductors with accurate logic gates”.
XOR Gate: The output signal 1 comes through the open circular DNA when either input DNA A or input DNA B is present. When both inputs are not present, the flourescent signal does not come through
2012.09.27 View 10061 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 9500
Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 9500 -
 Professor Soon-Heung Chang meets with Bill Gates and discusses possible collaboration
Professor Soon-Heung Chang from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST, who is also the president of Korea Nuclear Society (KNS), met Bill Gates, the co-founder and former chief executive officer (CEO) of Microsoft, on August 16, 2012 and discussed ways to cooperate for the development of a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), a next generation nuclear power reactor.
According to Professor Chang, Bill Gates was amazed at Korea’s successful bids for nuclear power plants in the United Arab Emirates, even though Korea was a latecomer in the field of nuclear power. Bill Gates also showed a keen interest in Korea’s low electricity rates.
Gates focuses on solving fundamental problems in order to help improve the quality of life for humanity, rather than short-term temporary solutions, through infrastructure development such as energy. Particularly, he considers nuclear power as one of the most effective ways to supply clean energy which can provide electricity at a low cost while keeping carbon dioxide emission levels much lower than fossil fuels.
Bill Gates is a primary investor for an energy company called “TerraPower” based in Bellevue, Washington. TerraPower develops and commercializes nuclear power technology for a traveling wave reactor (TWR) that is designed to use spent fuels, i.e., depleted uranium, and runs technically “forever” because once fueled, the reactor does not need to be refueled for over 50 years. TerraPower’s TWR is to use metallic fuel, and Korea is the only country that currently develops SFR (KALIMER 600) using metallic fuel.
“Korea has an outstanding supply chain for the entire lifecycle of a nuclear power station from equipment manufacturing to operation,” said Professor Chang, while emphasizing the synergistic effects of forming partnership between Korea and TerraPower.
Professor Chang emphasized that Korea should create an opportunity based on lessons learned from the Fukushima crisis and actively move forward to achieve its leading position in the field of next generation nuclear reactors. He said that cooperation with Bill Gates will be a significant step towards the development of next generation nuclear reactors.
About Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR)
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) is a next-generation nuclear power reactor that will use spent fuels from conventional reactors. Arrangement of a fuel recycling system in
conjunction with currently-developing pyroprocessing technology would enable U-238, which makes up over 99% of natural uranium, to be used as a nuclear fuel. This would greatly reduce the toxicity and volume of spent fuels by up to 1,000 times and 100 times respectively when compared to existing reactors. This is truly a breakthrough innovation in spent fuel disposal and recycling.
2012.09.20 View 10930
Professor Soon-Heung Chang meets with Bill Gates and discusses possible collaboration
Professor Soon-Heung Chang from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST, who is also the president of Korea Nuclear Society (KNS), met Bill Gates, the co-founder and former chief executive officer (CEO) of Microsoft, on August 16, 2012 and discussed ways to cooperate for the development of a sodium-cooled fast reactor (SFR), a next generation nuclear power reactor.
According to Professor Chang, Bill Gates was amazed at Korea’s successful bids for nuclear power plants in the United Arab Emirates, even though Korea was a latecomer in the field of nuclear power. Bill Gates also showed a keen interest in Korea’s low electricity rates.
Gates focuses on solving fundamental problems in order to help improve the quality of life for humanity, rather than short-term temporary solutions, through infrastructure development such as energy. Particularly, he considers nuclear power as one of the most effective ways to supply clean energy which can provide electricity at a low cost while keeping carbon dioxide emission levels much lower than fossil fuels.
Bill Gates is a primary investor for an energy company called “TerraPower” based in Bellevue, Washington. TerraPower develops and commercializes nuclear power technology for a traveling wave reactor (TWR) that is designed to use spent fuels, i.e., depleted uranium, and runs technically “forever” because once fueled, the reactor does not need to be refueled for over 50 years. TerraPower’s TWR is to use metallic fuel, and Korea is the only country that currently develops SFR (KALIMER 600) using metallic fuel.
“Korea has an outstanding supply chain for the entire lifecycle of a nuclear power station from equipment manufacturing to operation,” said Professor Chang, while emphasizing the synergistic effects of forming partnership between Korea and TerraPower.
Professor Chang emphasized that Korea should create an opportunity based on lessons learned from the Fukushima crisis and actively move forward to achieve its leading position in the field of next generation nuclear reactors. He said that cooperation with Bill Gates will be a significant step towards the development of next generation nuclear reactors.
About Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR)
Sodium-cooled Fast Reactor (SFR) is a next-generation nuclear power reactor that will use spent fuels from conventional reactors. Arrangement of a fuel recycling system in
conjunction with currently-developing pyroprocessing technology would enable U-238, which makes up over 99% of natural uranium, to be used as a nuclear fuel. This would greatly reduce the toxicity and volume of spent fuels by up to 1,000 times and 100 times respectively when compared to existing reactors. This is truly a breakthrough innovation in spent fuel disposal and recycling.
2012.09.20 View 10930 -
 Professor Kim Eun Joon receives In Chon Award
Professor Kim Eun Joon (Department of Biological Sciences) received the In Chon Awarded hosted by In Chon Memorial and Dong Ah Newspaper.
The Award Ceremony will be held on the 8th of October in Seoul Lotte Hotel and Professor Kim will be given a medal and prize money amounting 100million Korean Won.
Professor Kim is a world renowned research in the field of Synapses. Professor Kim graduated from the Department of Pharmacy in Pusan University, B.A. at KAIST, and Ph.D at Michigan University. He has been a Professor at KAIST since 2000.
2012.09.11 View 8475
Professor Kim Eun Joon receives In Chon Award
Professor Kim Eun Joon (Department of Biological Sciences) received the In Chon Awarded hosted by In Chon Memorial and Dong Ah Newspaper.
The Award Ceremony will be held on the 8th of October in Seoul Lotte Hotel and Professor Kim will be given a medal and prize money amounting 100million Korean Won.
Professor Kim is a world renowned research in the field of Synapses. Professor Kim graduated from the Department of Pharmacy in Pusan University, B.A. at KAIST, and Ph.D at Michigan University. He has been a Professor at KAIST since 2000.
2012.09.11 View 8475 -
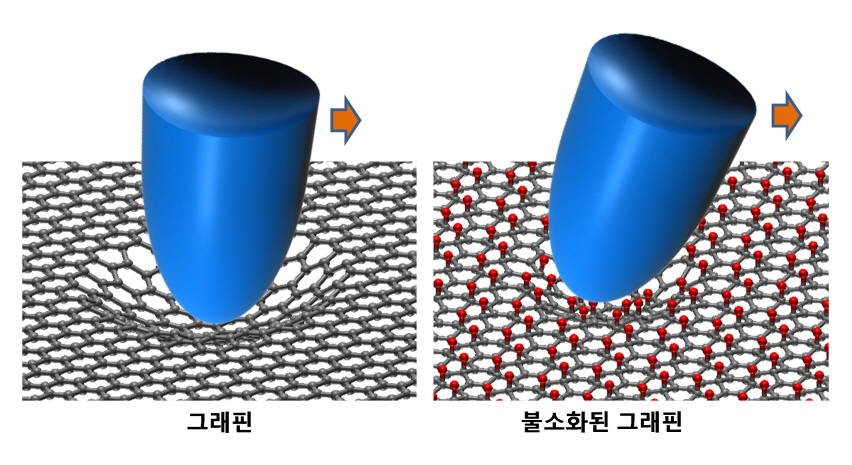 KAIST researchers verify and control the mechanical properties of graphene
KAIST researchers have successfully verified and controlled the mechanical properties of graphene, a next-generation material. Professor Park Jung Yong from the EEWS Graduate School and Professor Kim Yong Hyun from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology have succeeded in fluorinating a single atomic-layered graphene sample and controlling its frictional and adhesive properties. This is the first time the frictional properties of graphene have been examined at the atomic level, and the technology is expected to be applied to nano-sized robots and microscopic joints.
Graphene is often dubbed “the dream material” because of its ability to conduct high amounts of electricity even when bent, making it the next-generation substitute for silicon semiconductors, paving the way for flexible display and wearable computer technologies. Graphene also has high potential applications in mechanical engineering because of its great material strength, but its mechanical properties remained elusive until now.
Professor Park’s research team successfully produced individual graphene samples with fluorine-deficiency at the atomic level by placing the samples in Fluoro-xenon (XeF2) gas and applying heat. The surface of the graphene was scanned using a micro probe and a high vacuum atomic microscope to measure its dynamic properties.
The research team found that the fluorinated graphene sample had 6 times more friction and 0.7 times more adhesiveness than the original graphene. Electrical measurements confirmed the fluorination process, and the analysis of the findings helped setup the theory of frictional changes in graphene.
Professor Park stated that “graphene can be used for the lubrication of joints in nano-sized devices” and that this research has numerous applications such as the coating of graphene-based microdynamic devices.
This research was published in the online June edition of Nano Letters and was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Education and the National Research Foundation as part of the World Class University (WCU) program.
2012.07.24 View 16343
KAIST researchers verify and control the mechanical properties of graphene
KAIST researchers have successfully verified and controlled the mechanical properties of graphene, a next-generation material. Professor Park Jung Yong from the EEWS Graduate School and Professor Kim Yong Hyun from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology have succeeded in fluorinating a single atomic-layered graphene sample and controlling its frictional and adhesive properties. This is the first time the frictional properties of graphene have been examined at the atomic level, and the technology is expected to be applied to nano-sized robots and microscopic joints.
Graphene is often dubbed “the dream material” because of its ability to conduct high amounts of electricity even when bent, making it the next-generation substitute for silicon semiconductors, paving the way for flexible display and wearable computer technologies. Graphene also has high potential applications in mechanical engineering because of its great material strength, but its mechanical properties remained elusive until now.
Professor Park’s research team successfully produced individual graphene samples with fluorine-deficiency at the atomic level by placing the samples in Fluoro-xenon (XeF2) gas and applying heat. The surface of the graphene was scanned using a micro probe and a high vacuum atomic microscope to measure its dynamic properties.
The research team found that the fluorinated graphene sample had 6 times more friction and 0.7 times more adhesiveness than the original graphene. Electrical measurements confirmed the fluorination process, and the analysis of the findings helped setup the theory of frictional changes in graphene.
Professor Park stated that “graphene can be used for the lubrication of joints in nano-sized devices” and that this research has numerous applications such as the coating of graphene-based microdynamic devices.
This research was published in the online June edition of Nano Letters and was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Education and the National Research Foundation as part of the World Class University (WCU) program.
2012.07.24 View 16343 -
 High Capacity Molecular Storage Technology Developed by KAIST Professor Omar M. Yaghi
KAIST research team has succeeded in developing the technology that allows high capacity protein storage.
Professor Omar M. Yaghi (Graduate School of EEWS) and his research team succeeded in developing the core technology that enables the storage of various types of proteins by developing a metal organic structure. The result of their research was published in the May edition of Science magazine.
The newly developed technology can store various types and sizes of proteins. This property is expected to pave way to: 1) development of high capacity, high integration drugs 2) development of virus separation compounds 3) selective removal of protein causing negative reactions in the body 4) permanent preservation of rare polymeric proteins, among other expectations.
In addition it becomes possible to selectively remove and preserve all the body’s cells including stem cells which will aid the development of cures for incurable diseases and increase life expectancy and medical technology in general.
Conventional metal-organic structure used 7 Angstrom large small single molecules and therefore could not be used in the storage of large molecules or proteins. Its usability was proven only as potential high capacity gas storage structure. In addition the internal structure of the metal organic structure is cross linked which made it even more difficult to store large proteins within the structure.
Professor Yaghi’s team used molecular structure over 5nm in length in the development of the metal-organic structure to solve the problem associated with size of structure. The ordered structure of the structure’s pore was observed for the first time using Transmission Electron Microscope.
The new structure enables the ordered storage of large proteins and was able to store vitamin and proteins like myoglobin at high capacity for the first time in the world.
2012.05.30 View 9136
High Capacity Molecular Storage Technology Developed by KAIST Professor Omar M. Yaghi
KAIST research team has succeeded in developing the technology that allows high capacity protein storage.
Professor Omar M. Yaghi (Graduate School of EEWS) and his research team succeeded in developing the core technology that enables the storage of various types of proteins by developing a metal organic structure. The result of their research was published in the May edition of Science magazine.
The newly developed technology can store various types and sizes of proteins. This property is expected to pave way to: 1) development of high capacity, high integration drugs 2) development of virus separation compounds 3) selective removal of protein causing negative reactions in the body 4) permanent preservation of rare polymeric proteins, among other expectations.
In addition it becomes possible to selectively remove and preserve all the body’s cells including stem cells which will aid the development of cures for incurable diseases and increase life expectancy and medical technology in general.
Conventional metal-organic structure used 7 Angstrom large small single molecules and therefore could not be used in the storage of large molecules or proteins. Its usability was proven only as potential high capacity gas storage structure. In addition the internal structure of the metal organic structure is cross linked which made it even more difficult to store large proteins within the structure.
Professor Yaghi’s team used molecular structure over 5nm in length in the development of the metal-organic structure to solve the problem associated with size of structure. The ordered structure of the structure’s pore was observed for the first time using Transmission Electron Microscope.
The new structure enables the ordered storage of large proteins and was able to store vitamin and proteins like myoglobin at high capacity for the first time in the world.
2012.05.30 View 9136 -
 Professor Kyung Wook Baek Wins the Best Thesis Award at the 2012 Pan-Pacific Microelectronic Symposium
Prof. Kyung Wook Baek from KAIST"s material science department has won the Best Thesis Award at the 2012 Pan-Pacific Microelectronic Symposium.
The title of this thesis was "Recent Advances in Anisotropic Conductive Adhesives Technology : Materials and Processes". Prof Baek had the honor of having his thesis be appointed the best thesis of the symposium.
This thesis includes his 15 years of research on ACAs which are a key element of display and semiconductor packaging technology.
Prof. Baek"s research results has been recognized as incredibly innovative in the field of ACAs and ultrasonic connection devices. This thesis has been recognized as setting the foundation for commercialization by professionals from all over the world at the symposium.
Prof. Baek has announced two innovative technologies on ACAs at the symposium.
One is a technology that merges the nanofiber technology with the ATAs. This technology was highly applauded for overcoming the problem of electric connection in micro-pitch display semiconductors, and successfully applying this to electronic packaging materials.
Currently, commercialization process based on the patent is ongoing. It is expected that we will be able to take hold of the entire market once the commercialization succeeds.
The other technology was to improve the liability and overcome the limits of the current flow in ACAs through the use of solder molecules. This is also undergoing commercialization process for use in mobile electronic devices.
Together with this, Prof.Baek has reported an innovative case where the original heat compression process was replaced with a new ultrasonic process. This discovery is deemed to be extremely great due to its implications in replacing all heat compression systems. This too will soon be commercialized
Prof.Baek has played a crucial role in the development of electronic packaging material and processing technology. He has written the largest number of theses in this area, and has proven himself to be the world"s best through winning this award.
2012.05.10 View 10418
Professor Kyung Wook Baek Wins the Best Thesis Award at the 2012 Pan-Pacific Microelectronic Symposium
Prof. Kyung Wook Baek from KAIST"s material science department has won the Best Thesis Award at the 2012 Pan-Pacific Microelectronic Symposium.
The title of this thesis was "Recent Advances in Anisotropic Conductive Adhesives Technology : Materials and Processes". Prof Baek had the honor of having his thesis be appointed the best thesis of the symposium.
This thesis includes his 15 years of research on ACAs which are a key element of display and semiconductor packaging technology.
Prof. Baek"s research results has been recognized as incredibly innovative in the field of ACAs and ultrasonic connection devices. This thesis has been recognized as setting the foundation for commercialization by professionals from all over the world at the symposium.
Prof. Baek has announced two innovative technologies on ACAs at the symposium.
One is a technology that merges the nanofiber technology with the ATAs. This technology was highly applauded for overcoming the problem of electric connection in micro-pitch display semiconductors, and successfully applying this to electronic packaging materials.
Currently, commercialization process based on the patent is ongoing. It is expected that we will be able to take hold of the entire market once the commercialization succeeds.
The other technology was to improve the liability and overcome the limits of the current flow in ACAs through the use of solder molecules. This is also undergoing commercialization process for use in mobile electronic devices.
Together with this, Prof.Baek has reported an innovative case where the original heat compression process was replaced with a new ultrasonic process. This discovery is deemed to be extremely great due to its implications in replacing all heat compression systems. This too will soon be commercialized
Prof.Baek has played a crucial role in the development of electronic packaging material and processing technology. He has written the largest number of theses in this area, and has proven himself to be the world"s best through winning this award.
2012.05.10 View 10418 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in '2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit'
Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in ‘2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit’ held in Chang’an, Beijing
Professor Lee gave a lecture on the vitalization strategy of ‘Bio-Refinery’, which is ‘A bio-based chemical industry to replace fossil fuel-based petro chemistry.
Professor Lee, insisted that for the successful construction of ‘Bio-Refinery’, there should be innovation in all value chain of biomass; biomass producer, bio-refinery business, consumer, government, etc. ▲Securement and distribution of Biomass ▲Development of strain and process for fermentation separation to effectively change biomass into chemical substance and fuel ▲Optimization of transportation and marketing.
During this summit, high-ranking government officials in politics and economics, executives of multicultural and Chinese business participated. From Korea, Do-Young Seung of Manager of technology research of GS and Hang-Deok Roh of laboratory chief of SK Chemical participated as panelist.
World Economy Forum, the gathering of leaders and experts in politics, economics, and policy created a ‘Global Agenda Council’ to find solutions on the issue of ‘sustainable growth of environment of the Earth and humanity’. Professor Lee is the chairperson of ‘Emerging Technologies Global Agenda Council (GAC)’ of Word Economy Forum.
Professor Lee, founder of ‘Systems Metabolic Engineering’, has made remarkable achievements world-wide, including a technology that manipulates metabolic circuit of microorganisms to purify various crude-originated chemical substances into environmentally friendly substances.
Currently, he is working on Systems biology research business in Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Global Frontier Biomass business, Global Frontier Intelligent Bio-system construction and composition, to make progress in metabolic engineering which is essential for the bio-chemical industry.
2012.03.06 View 12367
Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in '2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit'
Distinguished Professor Sang-Yeop Lee gave keynote speech in ‘2011 China Bio-Refinery Summit’ held in Chang’an, Beijing
Professor Lee gave a lecture on the vitalization strategy of ‘Bio-Refinery’, which is ‘A bio-based chemical industry to replace fossil fuel-based petro chemistry.
Professor Lee, insisted that for the successful construction of ‘Bio-Refinery’, there should be innovation in all value chain of biomass; biomass producer, bio-refinery business, consumer, government, etc. ▲Securement and distribution of Biomass ▲Development of strain and process for fermentation separation to effectively change biomass into chemical substance and fuel ▲Optimization of transportation and marketing.
During this summit, high-ranking government officials in politics and economics, executives of multicultural and Chinese business participated. From Korea, Do-Young Seung of Manager of technology research of GS and Hang-Deok Roh of laboratory chief of SK Chemical participated as panelist.
World Economy Forum, the gathering of leaders and experts in politics, economics, and policy created a ‘Global Agenda Council’ to find solutions on the issue of ‘sustainable growth of environment of the Earth and humanity’. Professor Lee is the chairperson of ‘Emerging Technologies Global Agenda Council (GAC)’ of Word Economy Forum.
Professor Lee, founder of ‘Systems Metabolic Engineering’, has made remarkable achievements world-wide, including a technology that manipulates metabolic circuit of microorganisms to purify various crude-originated chemical substances into environmentally friendly substances.
Currently, he is working on Systems biology research business in Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Global Frontier Biomass business, Global Frontier Intelligent Bio-system construction and composition, to make progress in metabolic engineering which is essential for the bio-chemical industry.
2012.03.06 View 12367 -
 Professor Sang-Min Bae appears on EBS Global Theme Travel.
"We want to present "hope" by designing schools and homes for the third-world countries, while considering the culture of the nation.”
Professor Bae and his team went to Ethiopia, Africa, for "Design for Social Donation and Design Research for isolated third-world nations".
Professor Bae commented that, "We have visited for preparatory investigation, experiencing and investigating the life and cultures of the third-world nations in order to design schools and homes."
He continued, "From this visit, we want to develop adequate technology catered for the locals and create a design guideline." He added "We also want to propose a new model using design and technology that contributes to social welfare".
Meanwhile, EBS team accompanied to cover the report and was broadcasted through "EBS Global Theme Travel.
2012.03.06 View 8830
Professor Sang-Min Bae appears on EBS Global Theme Travel.
"We want to present "hope" by designing schools and homes for the third-world countries, while considering the culture of the nation.”
Professor Bae and his team went to Ethiopia, Africa, for "Design for Social Donation and Design Research for isolated third-world nations".
Professor Bae commented that, "We have visited for preparatory investigation, experiencing and investigating the life and cultures of the third-world nations in order to design schools and homes."
He continued, "From this visit, we want to develop adequate technology catered for the locals and create a design guideline." He added "We also want to propose a new model using design and technology that contributes to social welfare".
Meanwhile, EBS team accompanied to cover the report and was broadcasted through "EBS Global Theme Travel.
2012.03.06 View 8830