TR
-
 Professor Sang-Min received an award for scholar of the year from the KAISTian of the Year 2013
KAIST nominates a “Scholar of the Year” each year and presents the award to the recipient at a New Year’s opening ceremony. For the year 2013, Professor Sang-Min Bae of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST was named “KAIST Scholar of 2013” and received the award on January 2, 2014.
Professor Bae has been recognized for his design achievement in 2013: D’Light, a kinetic lighting that employs a transformable lampshade using flexible honeycomb structure, became one of the finalists in the living room and bedroom category of the International Design Excellence Award 2013 and was selected one of the best 100 for the 2013 Good Design Award. Users can easily change the shape and light intensity of the lamp by simply pivoting the lampshade with its small handle.
Professor Bae has also actively pursued his own philanthrophic projects through design: he has given the profits from the sales of his designs including D’Light directly toward a scholarship for needy children.
The Scholar of the Year award is presented to a faculty member or researcher at KAIST who has contributed to the advancement of science and technology such as publication of articles with influential research outcomes, invention of breakthrough technology, implementation of outstanding research projects, and improvement of public life. Professor Bae is the 13 th winner of the KAIST award.
The Korea Times, a leading English language newspaper in Korea, published an article on this award. For the article, please visit http://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/people/2014/01/178_149117.html .
2014.01.09 View 10901
Professor Sang-Min received an award for scholar of the year from the KAISTian of the Year 2013
KAIST nominates a “Scholar of the Year” each year and presents the award to the recipient at a New Year’s opening ceremony. For the year 2013, Professor Sang-Min Bae of the Industrial Design Department at KAIST was named “KAIST Scholar of 2013” and received the award on January 2, 2014.
Professor Bae has been recognized for his design achievement in 2013: D’Light, a kinetic lighting that employs a transformable lampshade using flexible honeycomb structure, became one of the finalists in the living room and bedroom category of the International Design Excellence Award 2013 and was selected one of the best 100 for the 2013 Good Design Award. Users can easily change the shape and light intensity of the lamp by simply pivoting the lampshade with its small handle.
Professor Bae has also actively pursued his own philanthrophic projects through design: he has given the profits from the sales of his designs including D’Light directly toward a scholarship for needy children.
The Scholar of the Year award is presented to a faculty member or researcher at KAIST who has contributed to the advancement of science and technology such as publication of articles with influential research outcomes, invention of breakthrough technology, implementation of outstanding research projects, and improvement of public life. Professor Bae is the 13 th winner of the KAIST award.
The Korea Times, a leading English language newspaper in Korea, published an article on this award. For the article, please visit http://www.koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/people/2014/01/178_149117.html .
2014.01.09 View 10901 -
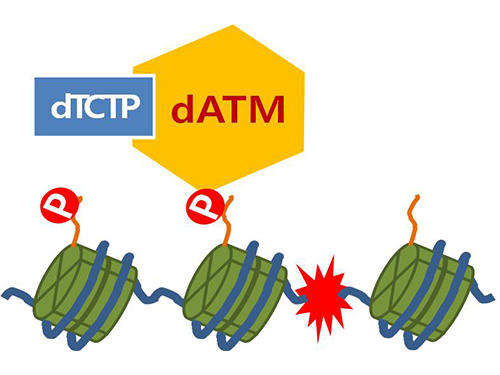 Mechanism in regulation of cancer-related key enzyme, ATM, for DNA damage and repair revealed
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi
A research team led by Professor Kwang-Wook Choi and Dr. Seong-Tae Hong from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has successfully investigated the operational mechanism of the protein Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), an essential protein to the function of a crucial key enzyme that repairs the damaged DNA which stores biometric information. The results were published on December 19th Nature Communications online edition.
All organisms, including humans, constantly strive to protect the information within their DNA from damages posed by a number of factors, such as carbonized materials in our daily food intake, radioactive materials such as radon emitting from the cement of buildings or ultraviolet of the sunlight, which could be a trigger for cancer.
In order to keep the DNA information safe, the organisms are always carrying out complex and sophisticated DNA repair work, which involves the crucial DNA damage repair protein ATM. Consequently, a faulty ATM leads to higher risks of cancer.
Until now, academia predicted that the Translationally Controlled Tumor Protein (TCTP) will play an important role in regulating the function of ATM. However, since most of main research regarding TCTP has only been conducted in cultured cells, it was unable to identify exactly what mechanisms TCTP employs to control ATM.
The KAIST research team identified that TCTP can combine with ATM or increase the enzymatic activity of ATM. In addition, Drosophilia, one of the most widely used model organisms for molecular genetics, has been used to identify that TCTP and ATM play a very important role in repairing the DNA damaged by radiation. This information has allowed the researchers to establish TCTP’s essential function in maintaining the DNA information in cell cultures and even in higher organisms, and to provide specific and important clues to the regulation of ATM by TCTP.
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi said, “Our research is a good example that basic research using Drosophilia can make important contributions to understanding the process of diseases, such as cancer, and to developing adequate treatment.”
The research has been funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, cells of the Drosophila's eye are abnormally deformed by radiation. Scale bars = 200mm
Figure 2. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, the chromosomes of Drosophilia are easily broken by radiation. Scale bars = 10 mm.
Figure 3. When gene expressions of TCTP and ATM are reduced, large defects occur in the normal development of the eye. (Left: normal Drosophilia's eye, right: development-deficient eye)
Figure 4. ATM marks the position of the broken DNA, with TCTP helping to facilitate this reaction. DNA (blue line) within the cell nucleus is coiled around the histone protein (green cylinder). When DNA is broken, ATM protein attaches a phosphate group (P). Multiple DNA repair protein recognizes the phosphate as a signal that requires repair and gathers at the site.
2014.01.07 View 13548
Mechanism in regulation of cancer-related key enzyme, ATM, for DNA damage and repair revealed
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi
A research team led by Professor Kwang-Wook Choi and Dr. Seong-Tae Hong from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has successfully investigated the operational mechanism of the protein Ataxia Telangiectasia Mutated (ATM), an essential protein to the function of a crucial key enzyme that repairs the damaged DNA which stores biometric information. The results were published on December 19th Nature Communications online edition.
All organisms, including humans, constantly strive to protect the information within their DNA from damages posed by a number of factors, such as carbonized materials in our daily food intake, radioactive materials such as radon emitting from the cement of buildings or ultraviolet of the sunlight, which could be a trigger for cancer.
In order to keep the DNA information safe, the organisms are always carrying out complex and sophisticated DNA repair work, which involves the crucial DNA damage repair protein ATM. Consequently, a faulty ATM leads to higher risks of cancer.
Until now, academia predicted that the Translationally Controlled Tumor Protein (TCTP) will play an important role in regulating the function of ATM. However, since most of main research regarding TCTP has only been conducted in cultured cells, it was unable to identify exactly what mechanisms TCTP employs to control ATM.
The KAIST research team identified that TCTP can combine with ATM or increase the enzymatic activity of ATM. In addition, Drosophilia, one of the most widely used model organisms for molecular genetics, has been used to identify that TCTP and ATM play a very important role in repairing the DNA damaged by radiation. This information has allowed the researchers to establish TCTP’s essential function in maintaining the DNA information in cell cultures and even in higher organisms, and to provide specific and important clues to the regulation of ATM by TCTP.
Professor Kwang-Wook Choi said, “Our research is a good example that basic research using Drosophilia can make important contributions to understanding the process of diseases, such as cancer, and to developing adequate treatment.”
The research has been funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure 1. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, cells of the Drosophila's eye are abnormally deformed by radiation. Scale bars = 200mm
Figure 2. When the amount of TCTP protein is reduced, the chromosomes of Drosophilia are easily broken by radiation. Scale bars = 10 mm.
Figure 3. When gene expressions of TCTP and ATM are reduced, large defects occur in the normal development of the eye. (Left: normal Drosophilia's eye, right: development-deficient eye)
Figure 4. ATM marks the position of the broken DNA, with TCTP helping to facilitate this reaction. DNA (blue line) within the cell nucleus is coiled around the histone protein (green cylinder). When DNA is broken, ATM protein attaches a phosphate group (P). Multiple DNA repair protein recognizes the phosphate as a signal that requires repair and gathers at the site.
2014.01.07 View 13548 -
 Professor Dong-Yol Yang received an award for scholar of the year 2013 from the Korean mechanical engineering community
Professor Dong-Yol Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST was selected as “the scholar of the year 2013” at an annual event held by the Korean Federation of Mechanical Engineering Societies, the Korea Association of Machinery Industry, and other mechanical engineering research institutes in Korea. The event, the Day of the Machines, is the nation’s biggest gathering for engineers, scholars, and researchers in mechanical engineering, at which winners of the awards for the person of the year in academia, business, and engineering are announced.
Professor Yang was chosen for his lifetime achievement as a scholar in the field of three-dimensional shape precision processing by developing an innovative processing technology that contributes to the advancement of mechanical engineering and industry. He also introduced the three-dimensional fast processing to Korea from 1990 and developed world-class subminiature fast processing, the first of its kind in Korea.In 2013, Professor Yang identified geometric deformation elements in mechanical engineering for the first time in the world, an essential component for nano mobile system and received the best conference paper award at the 3M-Nano International Conference.
2014.01.05 View 9577
Professor Dong-Yol Yang received an award for scholar of the year 2013 from the Korean mechanical engineering community
Professor Dong-Yol Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST was selected as “the scholar of the year 2013” at an annual event held by the Korean Federation of Mechanical Engineering Societies, the Korea Association of Machinery Industry, and other mechanical engineering research institutes in Korea. The event, the Day of the Machines, is the nation’s biggest gathering for engineers, scholars, and researchers in mechanical engineering, at which winners of the awards for the person of the year in academia, business, and engineering are announced.
Professor Yang was chosen for his lifetime achievement as a scholar in the field of three-dimensional shape precision processing by developing an innovative processing technology that contributes to the advancement of mechanical engineering and industry. He also introduced the three-dimensional fast processing to Korea from 1990 and developed world-class subminiature fast processing, the first of its kind in Korea.In 2013, Professor Yang identified geometric deformation elements in mechanical engineering for the first time in the world, an essential component for nano mobile system and received the best conference paper award at the 3M-Nano International Conference.
2014.01.05 View 9577 -
 Professor Kwy-Ro Lee Appointed Distinguished Member of IEEE
Professor Kwy-Ro Lee from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST was selected as a distinguished member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) where his contribution to research development of the technological management of semiconductors was recognized.
Professor Lee earned his BS from Seoul National University and MS & Ph.D. from the University of Minnesota. He has been working as a professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering since 1986. He has also served as the president of the LG Electronics Research Center in 2005 and the president of the Nanoscience and Technology Center at KAIST in 2010.
IEEE is the largest professional association for the advancement of technology in electrical, electronics, computing and communication with 400,000 members in 160 countries. Only 0.1 percent of members with over ten years of service can be selected as distinguished members based on their research devotion for society.
2014.01.02 View 8385
Professor Kwy-Ro Lee Appointed Distinguished Member of IEEE
Professor Kwy-Ro Lee from the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST was selected as a distinguished member of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) where his contribution to research development of the technological management of semiconductors was recognized.
Professor Lee earned his BS from Seoul National University and MS & Ph.D. from the University of Minnesota. He has been working as a professor in the Department of Electrical Engineering since 1986. He has also served as the president of the LG Electronics Research Center in 2005 and the president of the Nanoscience and Technology Center at KAIST in 2010.
IEEE is the largest professional association for the advancement of technology in electrical, electronics, computing and communication with 400,000 members in 160 countries. Only 0.1 percent of members with over ten years of service can be selected as distinguished members based on their research devotion for society.
2014.01.02 View 8385 -
 KAIST Student Awarded Prize from Energy Saving Contest
Jun-Min Kwon, an undergraduate student in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST, was awarded a prize from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea, at the 35th Energy Saving Contest which was held on November 20.
The student club he has been leading was also selected as one of the best groups by the Save Energy Save Earth (SESE), a volunteer organization supported by the Korea Energy Management Corporation and the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea.
Kwon began promoting energy conservation through a blog and participated in related meetings and workshops as a high school student to improve the understanding on the importance of energy saving and recycling.He also received awards from the Second National Assembly Forum on Climate Change, the Korean National Science Fair, as well as the Samsung Human Tech Paper Award.
2013.12.24 View 12758
KAIST Student Awarded Prize from Energy Saving Contest
Jun-Min Kwon, an undergraduate student in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST, was awarded a prize from the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, Republic of Korea, at the 35th Energy Saving Contest which was held on November 20.
The student club he has been leading was also selected as one of the best groups by the Save Energy Save Earth (SESE), a volunteer organization supported by the Korea Energy Management Corporation and the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea.
Kwon began promoting energy conservation through a blog and participated in related meetings and workshops as a high school student to improve the understanding on the importance of energy saving and recycling.He also received awards from the Second National Assembly Forum on Climate Change, the Korean National Science Fair, as well as the Samsung Human Tech Paper Award.
2013.12.24 View 12758 -
 Opening Ceremony of Genetic Donguibogam held
- Medicine using traditional natural substances • Food product source technology development begins
- Over 150,000,000,000 Won for 10 years of work invested to develop source technology
- Opening ceremony held on November 26th at 3 p.m. in Bio & Brain Engineering Division Building
The research to develop medicine and food source technology using traditional natural substances hasbegun.The opening ceremony of the “Genetic Donguibogam” business group, with KAIST Department of Bio & Brain Engineering Professor Do Heon Lee as the leader, was held on November 26th at 3 p.m. in Dream Hall, Bio & Brain Engineering Division Building, KAIST, Daejeon. The attendees of the opening ceremony included Yo Eop Im, Head of the Future Technology Department of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and around 200 experts in science and technology industry, including the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST, the Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul National University and Yonsei University.
The business group was established to re-interpret traditional natural substances proved to be effective from experience and improve quality of life by researching its applications; and to develop integrated source technology using traditional natural substances. The group is to invest over 150,000,000,000 Won for 10 years of research to secure natural substance source technology in five stages: interpretation technology, analysis technology, verification technology, bio marker technology and human body effectiveness verification technology. Especially, the focus would be on the use of virtual body computer models and Omics* to analyse the effects of traditional natural substances mixture on human body, and to find new materials for healthcare.
This research model, it is hoped, will have a new item to pioneer in the world natural substance market as well as securing a technologically competitive edge in bio industry by developing source technology that investigates the effects of traditional natural substances using cutting edge science.
KAIST Department of Bio & Brain Engineering Professor and Head Do Heon Lee of the “Genetic Donguibogam” Business Group said, “We will push forward to develop source energy by integrating IT-BT technology with a computer virtual body to build a cooperation system with medicine and functional food industries.” He continued: “This will enable not only the creation of a new industry, but also customised medicine.”
The 12 partners of the group include KAIST, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul National University and Yonsei University and 200 experts. The research participation area will be widened to foreign research institutes and associated companies.
* Terminology
Noun) Omics is an academic discipline analysing mass information on metabolism of physiological phenomena in specific cells (transcriptome, proteome and protoplast) with an integrated approach to determine vital phenomena.
2013.12.11 View 9576
Opening Ceremony of Genetic Donguibogam held
- Medicine using traditional natural substances • Food product source technology development begins
- Over 150,000,000,000 Won for 10 years of work invested to develop source technology
- Opening ceremony held on November 26th at 3 p.m. in Bio & Brain Engineering Division Building
The research to develop medicine and food source technology using traditional natural substances hasbegun.The opening ceremony of the “Genetic Donguibogam” business group, with KAIST Department of Bio & Brain Engineering Professor Do Heon Lee as the leader, was held on November 26th at 3 p.m. in Dream Hall, Bio & Brain Engineering Division Building, KAIST, Daejeon. The attendees of the opening ceremony included Yo Eop Im, Head of the Future Technology Department of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and around 200 experts in science and technology industry, including the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST, the Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul National University and Yonsei University.
The business group was established to re-interpret traditional natural substances proved to be effective from experience and improve quality of life by researching its applications; and to develop integrated source technology using traditional natural substances. The group is to invest over 150,000,000,000 Won for 10 years of research to secure natural substance source technology in five stages: interpretation technology, analysis technology, verification technology, bio marker technology and human body effectiveness verification technology. Especially, the focus would be on the use of virtual body computer models and Omics* to analyse the effects of traditional natural substances mixture on human body, and to find new materials for healthcare.
This research model, it is hoped, will have a new item to pioneer in the world natural substance market as well as securing a technologically competitive edge in bio industry by developing source technology that investigates the effects of traditional natural substances using cutting edge science.
KAIST Department of Bio & Brain Engineering Professor and Head Do Heon Lee of the “Genetic Donguibogam” Business Group said, “We will push forward to develop source energy by integrating IT-BT technology with a computer virtual body to build a cooperation system with medicine and functional food industries.” He continued: “This will enable not only the creation of a new industry, but also customised medicine.”
The 12 partners of the group include KAIST, Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Seoul National University and Yonsei University and 200 experts. The research participation area will be widened to foreign research institutes and associated companies.
* Terminology
Noun) Omics is an academic discipline analysing mass information on metabolism of physiological phenomena in specific cells (transcriptome, proteome and protoplast) with an integrated approach to determine vital phenomena.
2013.12.11 View 9576 -
 KAIST Takes Steps towards a Self-Sustainable Campus
KAIST has been selected for a $45-million national smart grid initiative organized under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Ninteen institutions will participate in the 2-year-long initiative. The consortium’s work is expected to take place from 2015 to 2017 after a review by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance.
The Smart Grid Explansion Initiative which has been considered the future of electric power industry implements information and communications technology to conventional grid system to maximize energy efficiency. The ROK government has selected the Smart Grid Expansion Initiative as one of South Korea’s primary national projects and plans to implement it nationwide based on multiple demonstration projects in major cities including Jeju.
KAIST plans to invest $45 million in developing systems for renewable energy power plants, efficient energy management, smart grid data, and electric vehicles to build the energy self-sustainable campus. It also hopes to contribute to fostering specialized talents and companies in energy management.
Byoung-Yoon Kim, the vice-president for research at KAIST, expects that by 2017, KAIST will be able to dramatically improve its energy capacity especially during peak periods and gain energy efficiency around the campus. He hopes that the micro grid project at KAIST will set a new standard for the self-sustainable campus.
2013.12.11 View 9043
KAIST Takes Steps towards a Self-Sustainable Campus
KAIST has been selected for a $45-million national smart grid initiative organized under the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy. Ninteen institutions will participate in the 2-year-long initiative. The consortium’s work is expected to take place from 2015 to 2017 after a review by the Ministry of Strategy and Finance.
The Smart Grid Explansion Initiative which has been considered the future of electric power industry implements information and communications technology to conventional grid system to maximize energy efficiency. The ROK government has selected the Smart Grid Expansion Initiative as one of South Korea’s primary national projects and plans to implement it nationwide based on multiple demonstration projects in major cities including Jeju.
KAIST plans to invest $45 million in developing systems for renewable energy power plants, efficient energy management, smart grid data, and electric vehicles to build the energy self-sustainable campus. It also hopes to contribute to fostering specialized talents and companies in energy management.
Byoung-Yoon Kim, the vice-president for research at KAIST, expects that by 2017, KAIST will be able to dramatically improve its energy capacity especially during peak periods and gain energy efficiency around the campus. He hopes that the micro grid project at KAIST will set a new standard for the self-sustainable campus.
2013.12.11 View 9043 -
 2013 EEWS Forum on National Energy Plan and Smart Grid Strategy
The Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) at KAIST hosted a forum on national energy planning and smart grid strategies on December 2 in the Jong-Hyun Choi Hall on KAIST’s Seoul campus. EEWS is a research and education program operated by KAIST to deal with the issues of energy, global warming, water, and sustainable growth.About 20 specialists including Jae-Kyu Lee, President of the Graduate School of Green Growth at KAIST; Kwang-Sik Choi, President of the EEWS Forum; Seong-Hoon Lee, Chairman of the Presidential Committee on Green Growth; Yang-Hoon Sohn, President of the Energy Economics Institute; and Jun-Dong Kim, Deputy Minister in the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy, participated in the forum. Presentations and discussions were made in the fields of national energy plans, smart grid strategies, energy policy, as well as gas, electricity and sustainable energy.
2013.12.11 View 8207
2013 EEWS Forum on National Energy Plan and Smart Grid Strategy
The Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) at KAIST hosted a forum on national energy planning and smart grid strategies on December 2 in the Jong-Hyun Choi Hall on KAIST’s Seoul campus. EEWS is a research and education program operated by KAIST to deal with the issues of energy, global warming, water, and sustainable growth.About 20 specialists including Jae-Kyu Lee, President of the Graduate School of Green Growth at KAIST; Kwang-Sik Choi, President of the EEWS Forum; Seong-Hoon Lee, Chairman of the Presidential Committee on Green Growth; Yang-Hoon Sohn, President of the Energy Economics Institute; and Jun-Dong Kim, Deputy Minister in the Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy, participated in the forum. Presentations and discussions were made in the fields of national energy plans, smart grid strategies, energy policy, as well as gas, electricity and sustainable energy.
2013.12.11 View 8207 -
 Graduate Student at KAIST Awarded Best Prize at the 9th Inside Edge
Sun-Jin Choi, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, under the guidance of Professor Il-Doo Kim, won the best prize at the 9th Inside Edge Contest hosted by Samsung Electro-Mechanics.
Choi was awarded prize money totaling fifteen million won at the award ceremony held on November 22 at the Mirae Hall at the headquarters of Samsung Electro-Mechanics in Suwon.
Choi’s research, titled “Exhaled Breath Sensor Arrays for the Non-invasive and Real-time Diagnosis of Diabetes by Detection of Acetone,” was recognized for its creativity and uniqueness.The Inside Edge is an international thesis competition which was started in 2005 to encourage and support creative research and potential technological development among young scientists and engineers.
Sun-Jin Choi (left) and Professor Il-Doo Kim (right).
2013.12.11 View 9876
Graduate Student at KAIST Awarded Best Prize at the 9th Inside Edge
Sun-Jin Choi, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, under the guidance of Professor Il-Doo Kim, won the best prize at the 9th Inside Edge Contest hosted by Samsung Electro-Mechanics.
Choi was awarded prize money totaling fifteen million won at the award ceremony held on November 22 at the Mirae Hall at the headquarters of Samsung Electro-Mechanics in Suwon.
Choi’s research, titled “Exhaled Breath Sensor Arrays for the Non-invasive and Real-time Diagnosis of Diabetes by Detection of Acetone,” was recognized for its creativity and uniqueness.The Inside Edge is an international thesis competition which was started in 2005 to encourage and support creative research and potential technological development among young scientists and engineers.
Sun-Jin Choi (left) and Professor Il-Doo Kim (right).
2013.12.11 View 9876 -
 First International Conference on Science and Technology for Society
KAIST co-organized the 2013 International Conference on Science and Technology for Society which was held on November 28 at the Grace Hall in Seoul EL-Tower. More than 300 people, including members of the Global Social Technology Advisory Board, domestic social technology experts, private companies, government officials, private citizens, and students joined the conference to discuss the roles and responsibilities of science and technology for society.
R&D policies and technologies for solving social issues were introduced, and discussions were held on desirable directions for technological development.
The first speaker, Yasushi Watanabe, Director of RISTEX (Research Institute of Science and Technology for Society) in Japan, introduced the importance of science and technology for society under the title “Change of R&D Paradigm for Society.”
Robert Wimmer, GrAT (Center for Appropriate Technology), Vienna University of Technology in Austria, presented “Need-oriented Design & Solutions for Development.” Kiyoaki Murakami, MRI, Japan, presented “Introduction of Platinum Vision” and Robert Ries, University of Florida, U.S.A., presented “Evaluating the Social Impacts of the Built Environment Using Life Cycle Assessment.”
Case studies on social enterprises and presentations on R&D for solving social problems were introduced by ICISTS (International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society), which is a student group at KAIST, National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM), Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KITECH), Electronics and Telecommunication Research Institute (ETRI), and Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT).The conference was hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning and co-organized by NRF, KIMM, KRIBB, KITECH, ETRI and KRICT.
2013.12.11 View 11751
First International Conference on Science and Technology for Society
KAIST co-organized the 2013 International Conference on Science and Technology for Society which was held on November 28 at the Grace Hall in Seoul EL-Tower. More than 300 people, including members of the Global Social Technology Advisory Board, domestic social technology experts, private companies, government officials, private citizens, and students joined the conference to discuss the roles and responsibilities of science and technology for society.
R&D policies and technologies for solving social issues were introduced, and discussions were held on desirable directions for technological development.
The first speaker, Yasushi Watanabe, Director of RISTEX (Research Institute of Science and Technology for Society) in Japan, introduced the importance of science and technology for society under the title “Change of R&D Paradigm for Society.”
Robert Wimmer, GrAT (Center for Appropriate Technology), Vienna University of Technology in Austria, presented “Need-oriented Design & Solutions for Development.” Kiyoaki Murakami, MRI, Japan, presented “Introduction of Platinum Vision” and Robert Ries, University of Florida, U.S.A., presented “Evaluating the Social Impacts of the Built Environment Using Life Cycle Assessment.”
Case studies on social enterprises and presentations on R&D for solving social problems were introduced by ICISTS (International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society), which is a student group at KAIST, National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF), Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM), Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB), Korea Institute of Industrial Technology (KITECH), Electronics and Telecommunication Research Institute (ETRI), and Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT).The conference was hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning and co-organized by NRF, KIMM, KRIBB, KITECH, ETRI and KRICT.
2013.12.11 View 11751 -
 Rechargeable Lithium Sulfur Battery for Greater Battery Capacity
Professor Do Kyung Kim from the Department of Material Science and Engineering and Professor Jang Wook Choi from the Graduate School of EEWS have been featured in the lead story of the renowned nanoscience journal Advanced Materials for their research on the lithium sulfur battery. This new type of battery developed by Professor Kim is expected to have a longer life battery life and [higher] energy density than currently commercial batteries.
With ample energy density up to 2100Wh/kg—almost 5.4 times that of lithium ion batteries—lithium sulfur batteries can withstand the sharp decrease in energy capacity resulting from charging and discharging—which has been considered the inherent limitation of the conventional batteries.
Professor Kim and his research team used one-dimensional, vertical alignment of 75nm tick, 15μm long sulfur nanowires to maximize electric conductivity. Then, to prevent loss of battery life, they carbon-coated each nanowire and prohibited direct contact between the sulfur and electrolyte.
The result was one of the most powerful batteries in terms of both energy performance and density. Compared to conventional batteries which suffer from continuous decrease in energy capacity after being discharged, the lithium sulfur battery maintained 99.2% of its initial capacity after being charged and discharged 300 times and up to 70% even after 1000 times.
Professor Kim claims that his new battery is an important step forward towards a high-performance rechargeable battery which is a vital technology for unmanned vehicles, electric automobiles and energy storage. He hopes that his research can solve the problems of battery-capacity loss and contribute to South Korea’s leading position in battery technology. Professor Kim’s research team has filed applications for one domestic and international patent for their research.
2013.12.11 View 12711
Rechargeable Lithium Sulfur Battery for Greater Battery Capacity
Professor Do Kyung Kim from the Department of Material Science and Engineering and Professor Jang Wook Choi from the Graduate School of EEWS have been featured in the lead story of the renowned nanoscience journal Advanced Materials for their research on the lithium sulfur battery. This new type of battery developed by Professor Kim is expected to have a longer life battery life and [higher] energy density than currently commercial batteries.
With ample energy density up to 2100Wh/kg—almost 5.4 times that of lithium ion batteries—lithium sulfur batteries can withstand the sharp decrease in energy capacity resulting from charging and discharging—which has been considered the inherent limitation of the conventional batteries.
Professor Kim and his research team used one-dimensional, vertical alignment of 75nm tick, 15μm long sulfur nanowires to maximize electric conductivity. Then, to prevent loss of battery life, they carbon-coated each nanowire and prohibited direct contact between the sulfur and electrolyte.
The result was one of the most powerful batteries in terms of both energy performance and density. Compared to conventional batteries which suffer from continuous decrease in energy capacity after being discharged, the lithium sulfur battery maintained 99.2% of its initial capacity after being charged and discharged 300 times and up to 70% even after 1000 times.
Professor Kim claims that his new battery is an important step forward towards a high-performance rechargeable battery which is a vital technology for unmanned vehicles, electric automobiles and energy storage. He hopes that his research can solve the problems of battery-capacity loss and contribute to South Korea’s leading position in battery technology. Professor Kim’s research team has filed applications for one domestic and international patent for their research.
2013.12.11 View 12711 -
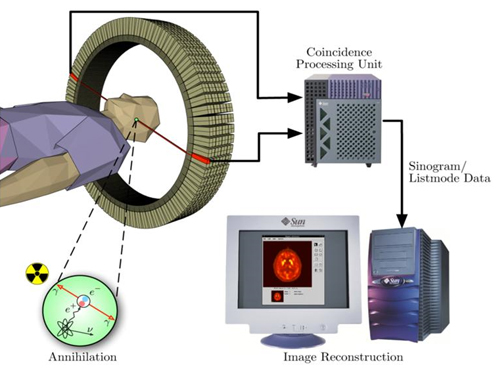 The key to Alzheimer disease, PET-MRI made in Korea
Professor Kyu-Sung Cho
- Simultaneous PET-MRI imaging system commercialization technology developed purely from domestic technology - - Inspiring achievement by KAIST, National NanoFab Center, Sogang University, Seoul National University Hospital –
Hopes are high for the potential of producing domestic products in the field of state-of-the-art medical imaging equipment that used to rely on imported products.
The joint research team (KAIST, Sogang University and Seoul National University) with KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering Professor Kyu-Sung Cho in charge, together with National Nanofab Institution (NNFC; Director Jae-Young Lee), has developed PET-MRI simultaneous imaging system with domestic technology only. The team successfully acquired brain images of 3 volunteers with the newly developed system.
PET-MRI is integrated state-of-the-art medical imaging equipment that combines the advantages of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) that shows anatomical images of the body and Position Emission Tomography (PET) that analyses cell activity and metabolism. Since the anatomical information and functional information can be seen simultaneously, the device can be used to diagnose early onset Alzheimer’s disease and is essential in biological science research, such as new medicine development.
The existing equipment used to take MRI and PET images separately due to the strong magnetic field generated by MRI and combine the images. Hence, it was time consuming and error-prone due to patient’s movement. There was a need to develop PET that functions within a magnetic field to create a simultaneous imaging system.
The newly developed integral PET-MRI has 3 technical characteristics: 1. PET detector without magnetic interference, 2. PET-MRI integration system, 3.PET-MRI imaging processing.
The PET detector is the most important factor and accounts for half the cost of the whole system. KAIST Professor Cho and NNFC Doctor Woo-Suk Seol’s team successfully developed the Silicon Photomultiplier (amplifies light coming into the radiation detector) that can be used in strong magnetic fields. The developed sensor has a global competitive edge since it optimises semiconductor processing to yield over 95% productivity and around 10% gamma radiation energy resolving power.
Sogang University Department and Electrical Engineering Professor Yong Choi developed cutting edge PET system using a new concept of electric charge signal transmission method and imaging location distinction circuit. The creativity and excellence of the research findings were recognised and hence published on the cover of Medical Physics in June.
Seoul National University Hospital Department of Nuclear Medicine Professor Jae-Sung Lee developed the Silicon Photomultiplier sensor based PET imaging reconstitution programme, MRI imaging based PET imaging revision technology and PET-MRI imaging integration software.
Furthermore, KAIST Department of Electrical Engineering Professor Hyun-Wook Park was responsible for the development of RF Shielding technology that enables simultaneous installation of PET and MRI and using this technology, he developed a head coil for the brain that can be connected to PET for installation.
Based on the technology describe above, the joint research team successfully developed PET-MRI system for brains and acquired PET-MRI integrated brain images from 3 volunteers last June.
In particular, this system has the distinct feature of a detachable PET module and MRI head coil to the existing whole body MRI, so that PET-MRI simultaneous imaging is possible with low installation cost.
Professor Cho said, “We have prepared the foundation of domestic commercial PET and the system has a competitive edge in the global market of PET-MRI system technology.” He continued, “It can reduce the cost of the increasing brain related disease diagnosis, including Alzheimer’s, dramatically.”
Funded by Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy as an Industrial Foundation Technology Development Project (98 billion won in 7 years), the research applied for over 20 patents and 20 CSI theses.
Figure 1.Brain phantom images from developed PET-MRI system
Figure 2. Brain images from developed PET-MRI system
Figure 3. Domestic PET-MRI clinical trial
Figure 4. Head RF coil and PET detector inserted in MRI
Figure 5. Insertion type PET detector module
Figure 6. Silicon Photomultiplier sensor (Left) and flash crystal block (right)
Figure7. Silicon Photomultiplier sensor
Figure 8. PET detection principle
2013.11.28 View 14071
The key to Alzheimer disease, PET-MRI made in Korea
Professor Kyu-Sung Cho
- Simultaneous PET-MRI imaging system commercialization technology developed purely from domestic technology - - Inspiring achievement by KAIST, National NanoFab Center, Sogang University, Seoul National University Hospital –
Hopes are high for the potential of producing domestic products in the field of state-of-the-art medical imaging equipment that used to rely on imported products.
The joint research team (KAIST, Sogang University and Seoul National University) with KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering Professor Kyu-Sung Cho in charge, together with National Nanofab Institution (NNFC; Director Jae-Young Lee), has developed PET-MRI simultaneous imaging system with domestic technology only. The team successfully acquired brain images of 3 volunteers with the newly developed system.
PET-MRI is integrated state-of-the-art medical imaging equipment that combines the advantages of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) that shows anatomical images of the body and Position Emission Tomography (PET) that analyses cell activity and metabolism. Since the anatomical information and functional information can be seen simultaneously, the device can be used to diagnose early onset Alzheimer’s disease and is essential in biological science research, such as new medicine development.
The existing equipment used to take MRI and PET images separately due to the strong magnetic field generated by MRI and combine the images. Hence, it was time consuming and error-prone due to patient’s movement. There was a need to develop PET that functions within a magnetic field to create a simultaneous imaging system.
The newly developed integral PET-MRI has 3 technical characteristics: 1. PET detector without magnetic interference, 2. PET-MRI integration system, 3.PET-MRI imaging processing.
The PET detector is the most important factor and accounts for half the cost of the whole system. KAIST Professor Cho and NNFC Doctor Woo-Suk Seol’s team successfully developed the Silicon Photomultiplier (amplifies light coming into the radiation detector) that can be used in strong magnetic fields. The developed sensor has a global competitive edge since it optimises semiconductor processing to yield over 95% productivity and around 10% gamma radiation energy resolving power.
Sogang University Department and Electrical Engineering Professor Yong Choi developed cutting edge PET system using a new concept of electric charge signal transmission method and imaging location distinction circuit. The creativity and excellence of the research findings were recognised and hence published on the cover of Medical Physics in June.
Seoul National University Hospital Department of Nuclear Medicine Professor Jae-Sung Lee developed the Silicon Photomultiplier sensor based PET imaging reconstitution programme, MRI imaging based PET imaging revision technology and PET-MRI imaging integration software.
Furthermore, KAIST Department of Electrical Engineering Professor Hyun-Wook Park was responsible for the development of RF Shielding technology that enables simultaneous installation of PET and MRI and using this technology, he developed a head coil for the brain that can be connected to PET for installation.
Based on the technology describe above, the joint research team successfully developed PET-MRI system for brains and acquired PET-MRI integrated brain images from 3 volunteers last June.
In particular, this system has the distinct feature of a detachable PET module and MRI head coil to the existing whole body MRI, so that PET-MRI simultaneous imaging is possible with low installation cost.
Professor Cho said, “We have prepared the foundation of domestic commercial PET and the system has a competitive edge in the global market of PET-MRI system technology.” He continued, “It can reduce the cost of the increasing brain related disease diagnosis, including Alzheimer’s, dramatically.”
Funded by Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy as an Industrial Foundation Technology Development Project (98 billion won in 7 years), the research applied for over 20 patents and 20 CSI theses.
Figure 1.Brain phantom images from developed PET-MRI system
Figure 2. Brain images from developed PET-MRI system
Figure 3. Domestic PET-MRI clinical trial
Figure 4. Head RF coil and PET detector inserted in MRI
Figure 5. Insertion type PET detector module
Figure 6. Silicon Photomultiplier sensor (Left) and flash crystal block (right)
Figure7. Silicon Photomultiplier sensor
Figure 8. PET detection principle
2013.11.28 View 14071