SMA
-
 ICISTS Hosts the International Interdisciplinary Conference
A KAIST student organization, The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS), will host ICISTS 2016 at the Hotel ICC in Daejeon from 3 to 7 August with the participation of around 300 Korean and international students.
ICISTS was first established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for delegates and speakers to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology, and society regardless of their academic backgrounds.
This year’s conference, with the theme of “Beyond the Center,” emphasizes the ways in which technological advancements can change central organizations in areas such as financial technology, healthcare, and global governance.
The keynote speakers include Dennis Hong, a developer of the first automobile for the blind and a professor of the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department at UCLA, Dor Konforty, a founder and a CEO of SNS platform Synereo, and Marzena Rostek, a professor of Economics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Other notable speakers include: Gi-Jung Jung, Head of the National Fusion Research Institute; Janos Barberis, Founder of FinTech HK; Tae-Hoon Kim, CEO and Founder of Rainist; Gulrez Shah Azhar, Assistant Policy Analyst at RAND Corporation; Thomas Concannon, Senior Policy Researcher at RAND Corporation; Leah Vriesman, Professor at the School of Public Health, UCLA; and Bjorn Cumps, Professor of Management Practice at Vlerick Business School in Belgium.
The conference consists of keynote speeches, panel discussions, open talks, experience sessions, team project presentations, a culture night, and a beer party, at which all participants will be encouraged to interact with speakers and delegates and to discuss the topics of their interest.
Han-Kyul Jung, ICISTS’s Head of Public Relations, said, “This conference will not only allow the delegates to understand the trends of future technology, but also be an opportunity for KAIST students to form valuable contacts with students from around the world.”
For more information, please go to www.icists.org.
2016.07.20 View 9568
ICISTS Hosts the International Interdisciplinary Conference
A KAIST student organization, The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS), will host ICISTS 2016 at the Hotel ICC in Daejeon from 3 to 7 August with the participation of around 300 Korean and international students.
ICISTS was first established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for delegates and speakers to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology, and society regardless of their academic backgrounds.
This year’s conference, with the theme of “Beyond the Center,” emphasizes the ways in which technological advancements can change central organizations in areas such as financial technology, healthcare, and global governance.
The keynote speakers include Dennis Hong, a developer of the first automobile for the blind and a professor of the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department at UCLA, Dor Konforty, a founder and a CEO of SNS platform Synereo, and Marzena Rostek, a professor of Economics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Other notable speakers include: Gi-Jung Jung, Head of the National Fusion Research Institute; Janos Barberis, Founder of FinTech HK; Tae-Hoon Kim, CEO and Founder of Rainist; Gulrez Shah Azhar, Assistant Policy Analyst at RAND Corporation; Thomas Concannon, Senior Policy Researcher at RAND Corporation; Leah Vriesman, Professor at the School of Public Health, UCLA; and Bjorn Cumps, Professor of Management Practice at Vlerick Business School in Belgium.
The conference consists of keynote speeches, panel discussions, open talks, experience sessions, team project presentations, a culture night, and a beer party, at which all participants will be encouraged to interact with speakers and delegates and to discuss the topics of their interest.
Han-Kyul Jung, ICISTS’s Head of Public Relations, said, “This conference will not only allow the delegates to understand the trends of future technology, but also be an opportunity for KAIST students to form valuable contacts with students from around the world.”
For more information, please go to www.icists.org.
2016.07.20 View 9568 -
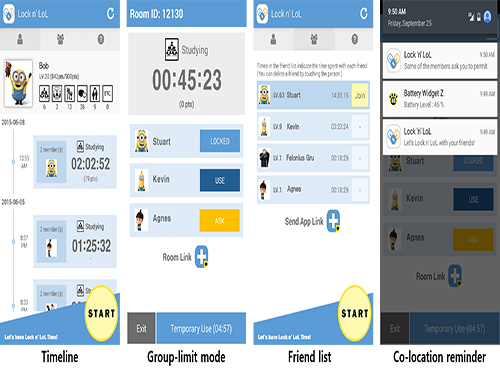 An App to Digitally Detox from Smartphone Addiction: Lock n' LOL
KAIST researchers have developed an application that helps people restrain themselves from using smartphones during meetings or social gatherings.
The app’s group limit mode enforces users to curtail their smartphone usage through peer-pressure while offering flexibility to use the phone in an emergency.
When a fake phone company released its line of products, NoPhones, a thin, rectangular-shaped plastic block that looked just like a smartphone but did not function, many doubted that the simulated smartphones would find any users. Surprisingly, close to 4,000 fake phones were sold to consumers who wanted to curb their phone usage.
As smartphones penetrate every facet of our daily lives, a growing number of people have expressed concern about distractions or even the addictions they suffer from overusing smartphones.
Professor Uichin Lee of the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and his research team have recently introduced a solution to this problem by developing an application, Lock n’ LoL (Lock Your Smartphone and Laugh Out Loud), to help people lock their smartphones altogether and keep them from using the phone while engaged in social activities such as meetings, conferences, and discussions.
Researchers note that the overuse of smartphones often results from users’ habitual checking of messages, emails, or other online contents such as status updates in social networking service (SNS). External stimuli, for example, notification alarms, add to smartphone distractions and interruptions in group interactions.
The Lock n’ LoL allows users to create a new room or join an existing room. The users then invite meeting participants or friends to the room and share its ID with them to enact the Group Limit (lock) mode. When phones are in the lock mode, all alarms and notifications are automatically muted, and users must ask permission to unlock their phones. However, in an emergency, users can access their phones for accumulative five minutes in a temporary unlimit mode.
In addition, the app’s Co-location Reminder detects and lists nearby users to encourage app users to limit their phone use. The Lock n’ LoL also displays important statistics to monitor users’ behavior such as the current week’s total limit time, the weekly average usage time, top friends ranked by time spent together, and top activities in which the users participated.
Professor Lee said,
“We conducted the Lock n’ LoL campaign throughout the campus for one month this year with 1,000 students participating. As a result, we discovered that students accumulated more than 10,000 free hours from using the app on their smartphones. The students said that they were able to focus more on their group activities. In an age of the Internet of Things, we expect that the adverse effects of mobile distractions and addictions will emerge as a social concern, and our Lock n’ LoL is a key effort to address this issue.”
He added, “This app will certainly help family members to interact more with each other during the holiday season.”
The Lock n’ LoL is available for free download on the App Store and Google Play: https://itunes.apple.com/lc/app/lock-n-lol/id1030287673?mt=8.
YouTube link: https://youtu.be/1wY2pI9qFYM
Figure 1: User Interfaces of Lock n’ LoL
This shows the final design of Lock n’ LoL, which consists of three tabs: My Info, Friends, and Group Limit Mode. Users can activate the limit mode by clicking the start button at the bottom of the screen.
Figure 2: Statistics of Field Deployment
This shows the deployment summary of Lock n’ LoL campaign in May 2015.
2015.12.17 View 10952
An App to Digitally Detox from Smartphone Addiction: Lock n' LOL
KAIST researchers have developed an application that helps people restrain themselves from using smartphones during meetings or social gatherings.
The app’s group limit mode enforces users to curtail their smartphone usage through peer-pressure while offering flexibility to use the phone in an emergency.
When a fake phone company released its line of products, NoPhones, a thin, rectangular-shaped plastic block that looked just like a smartphone but did not function, many doubted that the simulated smartphones would find any users. Surprisingly, close to 4,000 fake phones were sold to consumers who wanted to curb their phone usage.
As smartphones penetrate every facet of our daily lives, a growing number of people have expressed concern about distractions or even the addictions they suffer from overusing smartphones.
Professor Uichin Lee of the Department of Knowledge Service Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and his research team have recently introduced a solution to this problem by developing an application, Lock n’ LoL (Lock Your Smartphone and Laugh Out Loud), to help people lock their smartphones altogether and keep them from using the phone while engaged in social activities such as meetings, conferences, and discussions.
Researchers note that the overuse of smartphones often results from users’ habitual checking of messages, emails, or other online contents such as status updates in social networking service (SNS). External stimuli, for example, notification alarms, add to smartphone distractions and interruptions in group interactions.
The Lock n’ LoL allows users to create a new room or join an existing room. The users then invite meeting participants or friends to the room and share its ID with them to enact the Group Limit (lock) mode. When phones are in the lock mode, all alarms and notifications are automatically muted, and users must ask permission to unlock their phones. However, in an emergency, users can access their phones for accumulative five minutes in a temporary unlimit mode.
In addition, the app’s Co-location Reminder detects and lists nearby users to encourage app users to limit their phone use. The Lock n’ LoL also displays important statistics to monitor users’ behavior such as the current week’s total limit time, the weekly average usage time, top friends ranked by time spent together, and top activities in which the users participated.
Professor Lee said,
“We conducted the Lock n’ LoL campaign throughout the campus for one month this year with 1,000 students participating. As a result, we discovered that students accumulated more than 10,000 free hours from using the app on their smartphones. The students said that they were able to focus more on their group activities. In an age of the Internet of Things, we expect that the adverse effects of mobile distractions and addictions will emerge as a social concern, and our Lock n’ LoL is a key effort to address this issue.”
He added, “This app will certainly help family members to interact more with each other during the holiday season.”
The Lock n’ LoL is available for free download on the App Store and Google Play: https://itunes.apple.com/lc/app/lock-n-lol/id1030287673?mt=8.
YouTube link: https://youtu.be/1wY2pI9qFYM
Figure 1: User Interfaces of Lock n’ LoL
This shows the final design of Lock n’ LoL, which consists of three tabs: My Info, Friends, and Group Limit Mode. Users can activate the limit mode by clicking the start button at the bottom of the screen.
Figure 2: Statistics of Field Deployment
This shows the deployment summary of Lock n’ LoL campaign in May 2015.
2015.12.17 View 10952 -
 Professor Woontack Woo Demonstrates an Optical Platform Technology for Augmented Reality at Smart Cloud Show
Professor Woontack Woo of the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST participated in the Smart Cloud Show, a technology exhibition, hosted by the university’s Augmented Human Research Center and presented the latest development of his research, an optical platform system for augmented reality.
This event took place on September 16-17, 2015 at Grand Seoul Nine Tree Convention Center in Seoul.
At the event, Professor Woo introduced a smart glass with an embedded augmented reality system, which permits remote collaboration between an avatar and the user’s hand.
The previous remote collaboration was difficult for ordinary users to employ because of its two-dimensional screen and complicated virtual reality system.
However, with the new technology, the camera attached to artificial reality (AR) glasses recognizes the user’s hand and tracks it down to collaborate. The avatar in the virtual space and the user’s hand interact in real space and time.
The key to this technology is the stable, real-time hand-tracking technique that allows the detection of the hand’s locations and the recognition of finger movements even in situations of self-occlusion.
Through this method, a user can touch and manipulate augmented contents as if they were real-life objects, thereby collaborating remotely with another user who is physically distant by linking his or her movements with an avatar.
If this technology is adopted widely, it may bring some economic benefits such as increased productivity due to lower costs for mobility and reduction in social overhead costs from the decrease in the need of traveling long distance.
Professor Woo said, “This technology will provide us with a greater opportunity for collaboration, not necessarily restricted to physical travelling, which can be widely used in the fields of medicine, education, entertainment, and tourism.”
Professor Woo plans to present his research results on hand-movement tracking and detection at the 12th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI 2015), to be held on October 28-30, 2015, at Kintex in Goyang, Korea.
He will also present a research paper on remote collaboration at the ICAT-EGVE 2015 conference, the merger of the 25th International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence (ICAT 2015) and the 20th Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (EGVE 2015), which will take place on October 28-30, 2015 at the Kyoto International Community House, Kyoto, Japan.
2015.09.16 View 10749
Professor Woontack Woo Demonstrates an Optical Platform Technology for Augmented Reality at Smart Cloud Show
Professor Woontack Woo of the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST participated in the Smart Cloud Show, a technology exhibition, hosted by the university’s Augmented Human Research Center and presented the latest development of his research, an optical platform system for augmented reality.
This event took place on September 16-17, 2015 at Grand Seoul Nine Tree Convention Center in Seoul.
At the event, Professor Woo introduced a smart glass with an embedded augmented reality system, which permits remote collaboration between an avatar and the user’s hand.
The previous remote collaboration was difficult for ordinary users to employ because of its two-dimensional screen and complicated virtual reality system.
However, with the new technology, the camera attached to artificial reality (AR) glasses recognizes the user’s hand and tracks it down to collaborate. The avatar in the virtual space and the user’s hand interact in real space and time.
The key to this technology is the stable, real-time hand-tracking technique that allows the detection of the hand’s locations and the recognition of finger movements even in situations of self-occlusion.
Through this method, a user can touch and manipulate augmented contents as if they were real-life objects, thereby collaborating remotely with another user who is physically distant by linking his or her movements with an avatar.
If this technology is adopted widely, it may bring some economic benefits such as increased productivity due to lower costs for mobility and reduction in social overhead costs from the decrease in the need of traveling long distance.
Professor Woo said, “This technology will provide us with a greater opportunity for collaboration, not necessarily restricted to physical travelling, which can be widely used in the fields of medicine, education, entertainment, and tourism.”
Professor Woo plans to present his research results on hand-movement tracking and detection at the 12th International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots and Ambient Intelligence (URAI 2015), to be held on October 28-30, 2015, at Kintex in Goyang, Korea.
He will also present a research paper on remote collaboration at the ICAT-EGVE 2015 conference, the merger of the 25th International Conference on Artificial Reality and Telexistence (ICAT 2015) and the 20th Eurographics Symposium on Virtual Environments (EGVE 2015), which will take place on October 28-30, 2015 at the Kyoto International Community House, Kyoto, Japan.
2015.09.16 View 10749 -
 KAIST and Hancom Sign for Development of Mobile Healthcare
KAIST signed a memorandum of understanding with Hancom, Inc., an office suite developer in Korea, to foster mobile healthcare software programs. President Steve Kang and Chairman Sang-Chul Kim of Hancom held a signing ceremony on March 13, 2015 at the KAIST campus.
Based on the agreement, KAIST and Hancom will exchange research personnel to build Dr. M, a smart healthcare platform developed by the university, collaborate in research and development, and cooperate in the transfer of research developments from the university to the software industry including Hancom.
KAIST and Hancom also signed a memorandum of understanding on the development of software in April 2014. The Hancom-KAIST Research Center opened on campus last October.
2015.03.20 View 10628
KAIST and Hancom Sign for Development of Mobile Healthcare
KAIST signed a memorandum of understanding with Hancom, Inc., an office suite developer in Korea, to foster mobile healthcare software programs. President Steve Kang and Chairman Sang-Chul Kim of Hancom held a signing ceremony on March 13, 2015 at the KAIST campus.
Based on the agreement, KAIST and Hancom will exchange research personnel to build Dr. M, a smart healthcare platform developed by the university, collaborate in research and development, and cooperate in the transfer of research developments from the university to the software industry including Hancom.
KAIST and Hancom also signed a memorandum of understanding on the development of software in April 2014. The Hancom-KAIST Research Center opened on campus last October.
2015.03.20 View 10628 -
 'Dr. M,' Mobile Healthcare Showroom Opened at KI
Portable and wearable computers have made the way we manage our health easier and potentially more effective. Researchers from six departments and one graduate school at KAIST collaborated and conducted a one-year project called the “Mobile Healthcare Innovation” to develop a mobile healthcare system. Their research results are on exhibit on campus at the “Dr. M Showroom” which was open on March 13, 2015.
Located on the second floor of the College of Information and Electrical Engineering building, the showroom displays the entirety of mobile healthcare system developed during 2014, from the collection of biological data through smart sensors to analyzing big data to provide customized healthcare models for patients.
Standing in for a mobile doctor, Dr. M is a networked medical service system provided through the Internet of Things (IoC), wearable electronics, smart home, and smart car. Under this care, people can monitor their health on a daily basis at any-time and place, helping them to lower the risk of serious health problems. Patients who have chronic diseases such as diabetes or cardiovascular illness can inform doctors of their health status in real time. Moreover, people living in remote regions can receive quality medical services without traveling long distances.
At the showroom, about 40 convergence technologies are displayed, including biological sensors, low-power communication devices, IoC technology, big data, disease analysis, and prediction technology, presenting how these technologies are connected and worked systematically. For example, all the data earned from biological sensors are analyzed to produce relevant user information. Once abnormalities are discovered, the results would be sent immediately to medical staff for treatment.
As part of Dr. M, KAIST has been implementing the establishment of a “Mobile Healthcare Campus,” distributing small, wearable wristbands to 100 students. The wristbands read students’ biological signals and send them to researchers for monitoring. In addition, KAIST plans to collaborate with local hospitals, nursing care centers, communications, and mobile healthcare service providers for the commercialization of Dr. M system.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Electrical Engineering Department, who has led the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project said, “One of the great advantages Dr. M can offer is the capability to customize healthcare service based on individuals and ages. For individuals in their twenties, for example, healthcare services such as skincare and diet programs will be more relevant whereas blood pressure monitoring for patients in their fifties and early diagnosis for the recurrence of diseases for those in their seventies. If we define human history in terms of major technology advancements, the first big one was computation, communication for the second, and I think ubiquitous healthcare will be the third one. We will continue to develop Dr. M in collaboration with medical and research organizations.”
A total of 32 professors from the Departments of Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, Industrial and Systems Engineering, Industrial Design, Web Science, Knowledge Service Engineering, and the Information Security Graduate School participated in the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project.
2015.03.17 View 11348
'Dr. M,' Mobile Healthcare Showroom Opened at KI
Portable and wearable computers have made the way we manage our health easier and potentially more effective. Researchers from six departments and one graduate school at KAIST collaborated and conducted a one-year project called the “Mobile Healthcare Innovation” to develop a mobile healthcare system. Their research results are on exhibit on campus at the “Dr. M Showroom” which was open on March 13, 2015.
Located on the second floor of the College of Information and Electrical Engineering building, the showroom displays the entirety of mobile healthcare system developed during 2014, from the collection of biological data through smart sensors to analyzing big data to provide customized healthcare models for patients.
Standing in for a mobile doctor, Dr. M is a networked medical service system provided through the Internet of Things (IoC), wearable electronics, smart home, and smart car. Under this care, people can monitor their health on a daily basis at any-time and place, helping them to lower the risk of serious health problems. Patients who have chronic diseases such as diabetes or cardiovascular illness can inform doctors of their health status in real time. Moreover, people living in remote regions can receive quality medical services without traveling long distances.
At the showroom, about 40 convergence technologies are displayed, including biological sensors, low-power communication devices, IoC technology, big data, disease analysis, and prediction technology, presenting how these technologies are connected and worked systematically. For example, all the data earned from biological sensors are analyzed to produce relevant user information. Once abnormalities are discovered, the results would be sent immediately to medical staff for treatment.
As part of Dr. M, KAIST has been implementing the establishment of a “Mobile Healthcare Campus,” distributing small, wearable wristbands to 100 students. The wristbands read students’ biological signals and send them to researchers for monitoring. In addition, KAIST plans to collaborate with local hospitals, nursing care centers, communications, and mobile healthcare service providers for the commercialization of Dr. M system.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Electrical Engineering Department, who has led the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project said, “One of the great advantages Dr. M can offer is the capability to customize healthcare service based on individuals and ages. For individuals in their twenties, for example, healthcare services such as skincare and diet programs will be more relevant whereas blood pressure monitoring for patients in their fifties and early diagnosis for the recurrence of diseases for those in their seventies. If we define human history in terms of major technology advancements, the first big one was computation, communication for the second, and I think ubiquitous healthcare will be the third one. We will continue to develop Dr. M in collaboration with medical and research organizations.”
A total of 32 professors from the Departments of Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, Industrial and Systems Engineering, Industrial Design, Web Science, Knowledge Service Engineering, and the Information Security Graduate School participated in the Mobile Healthcare Innovation project.
2015.03.17 View 11348 -
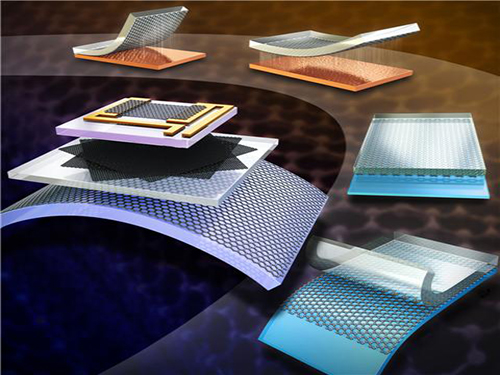 KAIST Develops a Method to Transfer Graphene by Stamping
Professor Sung-Yool Choi’s research team from KAIST's Department of Electrical Engineering has developed a technique that can produce a single-layer graphene from a metal etching. Through this, transferring a graphene layer onto a circuit board can be done as easily as stamping a seal on paper.
The research findings were published in the January 14th issue of Small as the lead article.
This technology will allow different types of wafer transfer methods such as transfer onto a surface of a device or a curved surface, and large surface transfer onto a 4 inch wafer. It will be applied in the field of wearable smart gadgets through commercialization of graphene electronic devices.
The traditional method used to transfer graphene onto a circuit board is a wet transfer. However, it has some drawbacks as the graphene layer can be damaged or contaminated during the transfer process from residue from the metal etching. This may affect the electrical properties of the transferred graphene.
After a graphene growth substrate formed on a catalytic metal substrate is pretreated in an aqueous poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) solution, a PVA film forms on the pretreated substrate. The substrate and the graphene layers bond strongly. The graphene is lifted from the growth substrate by means of an elastomeric stamp.
The delaminated graphene layer is isolated state from the elastomeric stamp and thus can be freely transferred onto a circuit board. As the catalytic metal substrate can be reused and does not contain harmful chemical substances, such transfer method is very eco-friendly.
Professor Choi said, “As the new graphene transfer method has a wide range of applications and allows a large surface transfer, it will contribute to the commercialization of graphene electronic devices.” He added that “because this technique has a high degree of freedom in transfer process, it has a variety of usages for graphene and 2 dimensional nano-devices.”
This research was sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Republic of Korea.
Figure 1. Cover photo of the journal Small which illustrates the research findings
Figure 2. Above view of Graphene layer transferred through the new method
Figure 3. Large surface transfer of Graphene
2015.01.23 View 12401
KAIST Develops a Method to Transfer Graphene by Stamping
Professor Sung-Yool Choi’s research team from KAIST's Department of Electrical Engineering has developed a technique that can produce a single-layer graphene from a metal etching. Through this, transferring a graphene layer onto a circuit board can be done as easily as stamping a seal on paper.
The research findings were published in the January 14th issue of Small as the lead article.
This technology will allow different types of wafer transfer methods such as transfer onto a surface of a device or a curved surface, and large surface transfer onto a 4 inch wafer. It will be applied in the field of wearable smart gadgets through commercialization of graphene electronic devices.
The traditional method used to transfer graphene onto a circuit board is a wet transfer. However, it has some drawbacks as the graphene layer can be damaged or contaminated during the transfer process from residue from the metal etching. This may affect the electrical properties of the transferred graphene.
After a graphene growth substrate formed on a catalytic metal substrate is pretreated in an aqueous poly vinyl alcohol (PVA) solution, a PVA film forms on the pretreated substrate. The substrate and the graphene layers bond strongly. The graphene is lifted from the growth substrate by means of an elastomeric stamp.
The delaminated graphene layer is isolated state from the elastomeric stamp and thus can be freely transferred onto a circuit board. As the catalytic metal substrate can be reused and does not contain harmful chemical substances, such transfer method is very eco-friendly.
Professor Choi said, “As the new graphene transfer method has a wide range of applications and allows a large surface transfer, it will contribute to the commercialization of graphene electronic devices.” He added that “because this technique has a high degree of freedom in transfer process, it has a variety of usages for graphene and 2 dimensional nano-devices.”
This research was sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, the Republic of Korea.
Figure 1. Cover photo of the journal Small which illustrates the research findings
Figure 2. Above view of Graphene layer transferred through the new method
Figure 3. Large surface transfer of Graphene
2015.01.23 View 12401 -
 A KAIST Student Team Wins the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest
A KAIST team consisted of students from the Departments of Industrial Design and Computer Science participated in the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest and received 1st Prize in the category of People’s Choice.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST) is an international forum to promote innovations in human-computer interfaces, which takes place annually and is sponsored by ACM Special Interest Groups on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) and Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH). The ACM UIST conference brings together professionals in the fields of graphical and web-user interfaces, tangible and ubiquitous computing, virtual and augmented reality, multimedia, and input and output devices.
The Student Innovation Contest has been held during the UIST conference since 2009 to innovate new interactions on state-of-the-art hardware. The participating students were given with the hardware platform to build on—this year, it was Kinoma Create, a JavaScript-powered construction kit that allows makers, professional product designers, and web developers to create personal projects, consumer electronics, and "Internet of Things" prototypes. Contestants demonstrated their creations on household interfaces, and two winners in each of three categories -- Most Creative, Most Useful, and the People’s Choice -- were awarded.
Utilizing Kinoma Create, which came with a built-in touchscreen, WiFi, Bluetooth, a front-facing sensor connector, and a 50-pin rear sensor dock, the KAIST team developed a “smart mop,” transforming the irksome task of cleaning into a fun game. The smart mop identifies target dirt and shows its location on the display built in the rod of a mop. If the user turns on a game mode, then winning scores are gained wherever the target dirt is cleaned.
The People’s Choice award was decided by conference attendees, and they voted the smart mop as their most favorite project.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, who advised the students, said, "A total of 24 teams from such prestigious universities as Carnegie Mellon University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and the University of Tokyo joined the contest, and we are pleased with the good results. Many people, in fact, praised the integration of creativity and technical excellence our have shown through the smart mop.”
Team KAIST: pictured from right to left, Sun-Jun Kim, Se-Jin Kim, and Han-Jong Kim
The Smart Mop can clean the floor and offer users a fun game.
2014.11.12 View 12825
A KAIST Student Team Wins the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest
A KAIST team consisted of students from the Departments of Industrial Design and Computer Science participated in the ACM UIST 2014 Student Innovation Contest and received 1st Prize in the category of People’s Choice.
The Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology (UIST) is an international forum to promote innovations in human-computer interfaces, which takes place annually and is sponsored by ACM Special Interest Groups on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) and Computer Graphics (SIGGRAPH). The ACM UIST conference brings together professionals in the fields of graphical and web-user interfaces, tangible and ubiquitous computing, virtual and augmented reality, multimedia, and input and output devices.
The Student Innovation Contest has been held during the UIST conference since 2009 to innovate new interactions on state-of-the-art hardware. The participating students were given with the hardware platform to build on—this year, it was Kinoma Create, a JavaScript-powered construction kit that allows makers, professional product designers, and web developers to create personal projects, consumer electronics, and "Internet of Things" prototypes. Contestants demonstrated their creations on household interfaces, and two winners in each of three categories -- Most Creative, Most Useful, and the People’s Choice -- were awarded.
Utilizing Kinoma Create, which came with a built-in touchscreen, WiFi, Bluetooth, a front-facing sensor connector, and a 50-pin rear sensor dock, the KAIST team developed a “smart mop,” transforming the irksome task of cleaning into a fun game. The smart mop identifies target dirt and shows its location on the display built in the rod of a mop. If the user turns on a game mode, then winning scores are gained wherever the target dirt is cleaned.
The People’s Choice award was decided by conference attendees, and they voted the smart mop as their most favorite project.
Professor Tek-Jin Nam of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, who advised the students, said, "A total of 24 teams from such prestigious universities as Carnegie Mellon University, Georgia Institute of Technology, and the University of Tokyo joined the contest, and we are pleased with the good results. Many people, in fact, praised the integration of creativity and technical excellence our have shown through the smart mop.”
Team KAIST: pictured from right to left, Sun-Jun Kim, Se-Jin Kim, and Han-Jong Kim
The Smart Mop can clean the floor and offer users a fun game.
2014.11.12 View 12825 -
 IAMCOMPANY, an educational technology startup created by a KAIST student, featured online in EdSurge
EdSurge is a U.S.-based online news site focused on education and technology innovation, which published an article, dated August 12, 2014, on IAMCOMPANY (http://iamcompany.net), a startup created by a KAIST student, Inmo (Ryan) Chung.
The article introduced one of the company’s most popular and free smartphone applications called “IAMSCHOOL” that “funnels school announcements and class notices to parents’ smartphones using a format similar to Twitter and Google+.”
For more about IAMCOMPANY, please visit the link below:
EdSurge, August 12, 2014
“South Korea’s Biggest Educational Information App Plans Pan-Asian Expansion”
https://www.edsurge.com/n/2014-08-12-south-korea-s-biggest-educational-information-app-plans-pan-asian-expansion
2014.08.19 View 9045
IAMCOMPANY, an educational technology startup created by a KAIST student, featured online in EdSurge
EdSurge is a U.S.-based online news site focused on education and technology innovation, which published an article, dated August 12, 2014, on IAMCOMPANY (http://iamcompany.net), a startup created by a KAIST student, Inmo (Ryan) Chung.
The article introduced one of the company’s most popular and free smartphone applications called “IAMSCHOOL” that “funnels school announcements and class notices to parents’ smartphones using a format similar to Twitter and Google+.”
For more about IAMCOMPANY, please visit the link below:
EdSurge, August 12, 2014
“South Korea’s Biggest Educational Information App Plans Pan-Asian Expansion”
https://www.edsurge.com/n/2014-08-12-south-korea-s-biggest-educational-information-app-plans-pan-asian-expansion
2014.08.19 View 9045 -
 KAIST's Center for Integrated Smart Sensors made a partnership with a Silicon Valley start-up
KAIST's Center for Integrated Smart Sensors (CISS) will implement a joint venture project with Dual Aperture, Inc., a leading digital camera provider based in Palo Alto, California. The two will work on the development of 3-D imaging technology.
CISS, headed by Professor Chong-Min Kyung of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, is dedicated to technological advancement by developing innovative devices, circuits, and smart sensors.
In its press release dated June 18, 2014, Dual Aperture, Inc. stated that “by combining top talents in engineering, the partnership will establish a groundbreaking smart sensor technology accessible on multiple platforms and devices.”
For details, a Fox news article follows below:
Dual Aperture, Inc., June 18, 2014
“Image technology leader and top research institute collaborate engineering resources to create world’s first-ever smart sensor technology”
http://www.fox14tv.com/story/25808022/dual-aperture-announces-joint-venture-with-kaists-center-for-integrated-smart-sensors
2014.06.19 View 10392
KAIST's Center for Integrated Smart Sensors made a partnership with a Silicon Valley start-up
KAIST's Center for Integrated Smart Sensors (CISS) will implement a joint venture project with Dual Aperture, Inc., a leading digital camera provider based in Palo Alto, California. The two will work on the development of 3-D imaging technology.
CISS, headed by Professor Chong-Min Kyung of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, is dedicated to technological advancement by developing innovative devices, circuits, and smart sensors.
In its press release dated June 18, 2014, Dual Aperture, Inc. stated that “by combining top talents in engineering, the partnership will establish a groundbreaking smart sensor technology accessible on multiple platforms and devices.”
For details, a Fox news article follows below:
Dual Aperture, Inc., June 18, 2014
“Image technology leader and top research institute collaborate engineering resources to create world’s first-ever smart sensor technology”
http://www.fox14tv.com/story/25808022/dual-aperture-announces-joint-venture-with-kaists-center-for-integrated-smart-sensors
2014.06.19 View 10392 -
 KAIST Holds 'Wearable Computer Contest'
Application for ‘2014 Wearable Computer Contest’ until May 23rd
KAIST is holding the 2014 Wearable Computer Contest (WCC) sponsored by Samsung Electronics in November and is currently receiving applications until May 23rd.
Wearable Computer is a device that can be worn on body or clothing, which allows users to be connected while on the move. It is currently receiving attention as the next generation of computer industry that will replace smart phones.
The Wearable Computer Contest will be held under the topic “Smart Fashion to Simple Life” and will be divided into a designated topic contest and an idea contest.
In the “designated topic contest,” each group will compete with their prototypes based on their own ideas about a wearable computer that combines IT and fashion. A total of 15 teams that enter the finals after a document review will be provided with USD 1,400 for a prototype production, Samsung's smart IT devices, and a systematic training program.
For the “idea contest,” competitors will present their ideas for a wearable computer in a poster format. The teams qualified to continue onto the finals will be given an opportunity to create and exhibit a life-sized model.
Chairman of the Wearable Computer Contest (WCC), Professor Hoejun Yoo from the KAIST Department of Electrical Engineering said, “Wearable Computer is the major future growth industry that will lead IT industry after smart phones. I hope WCC will help nurture the future professionals in the field of wearable computer industry.”
The applications for the Wearable Computer Contest can be found on the main website (http://www.ufcom.org) until May 23rd. Both undergraduate and graduate students can participate as a team for the “designated topic contest,” and there are no qualifications required for those who enter the “idea contest.”
Last year, a total of 104 teams from universities all around Korea has participated in the Wearable Computer Contest. The finalist, team 'Jump' from Chungnam University, received the Award of the Minister of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
2014.03.28 View 11761
KAIST Holds 'Wearable Computer Contest'
Application for ‘2014 Wearable Computer Contest’ until May 23rd
KAIST is holding the 2014 Wearable Computer Contest (WCC) sponsored by Samsung Electronics in November and is currently receiving applications until May 23rd.
Wearable Computer is a device that can be worn on body or clothing, which allows users to be connected while on the move. It is currently receiving attention as the next generation of computer industry that will replace smart phones.
The Wearable Computer Contest will be held under the topic “Smart Fashion to Simple Life” and will be divided into a designated topic contest and an idea contest.
In the “designated topic contest,” each group will compete with their prototypes based on their own ideas about a wearable computer that combines IT and fashion. A total of 15 teams that enter the finals after a document review will be provided with USD 1,400 for a prototype production, Samsung's smart IT devices, and a systematic training program.
For the “idea contest,” competitors will present their ideas for a wearable computer in a poster format. The teams qualified to continue onto the finals will be given an opportunity to create and exhibit a life-sized model.
Chairman of the Wearable Computer Contest (WCC), Professor Hoejun Yoo from the KAIST Department of Electrical Engineering said, “Wearable Computer is the major future growth industry that will lead IT industry after smart phones. I hope WCC will help nurture the future professionals in the field of wearable computer industry.”
The applications for the Wearable Computer Contest can be found on the main website (http://www.ufcom.org) until May 23rd. Both undergraduate and graduate students can participate as a team for the “designated topic contest,” and there are no qualifications required for those who enter the “idea contest.”
Last year, a total of 104 teams from universities all around Korea has participated in the Wearable Computer Contest. The finalist, team 'Jump' from Chungnam University, received the Award of the Minister of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
2014.03.28 View 11761 -
 ACM Interactions: Demo Hour, March and April 2014 Issue
The
Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), the largest educational and scientific
computing society in the world, publishes a magazine called
Interactions
bi-monthly.
Interactions
is the flagship magazine
for the ACM’s Special Interest Group on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) with
a global circulation that includes all SIGCHI members.
In
its March and April 2014 issue, the Smart E-book was introduced. It was developed by Sangtae Kim, Jaejeung
Kim, and Soobin Lee at the Information Technology Convergence in KAIST
Institute, KAIST.
For
the article, please go to the link or download the .pdf files below:
Interactions,
March &
April 2014
Demo Hour: Bezel-Flipper
Bezel-Flipper
Interactions_Mar & Apr 2014.pdf
http://interactions.acm.org/archive/view/march-april-2014/demo-hour29
2014.03.28 View 11970
ACM Interactions: Demo Hour, March and April 2014 Issue
The
Association for Computing Machinery (ACM), the largest educational and scientific
computing society in the world, publishes a magazine called
Interactions
bi-monthly.
Interactions
is the flagship magazine
for the ACM’s Special Interest Group on Computer-Human Interaction (SIGCHI) with
a global circulation that includes all SIGCHI members.
In
its March and April 2014 issue, the Smart E-book was introduced. It was developed by Sangtae Kim, Jaejeung
Kim, and Soobin Lee at the Information Technology Convergence in KAIST
Institute, KAIST.
For
the article, please go to the link or download the .pdf files below:
Interactions,
March &
April 2014
Demo Hour: Bezel-Flipper
Bezel-Flipper
Interactions_Mar & Apr 2014.pdf
http://interactions.acm.org/archive/view/march-april-2014/demo-hour29
2014.03.28 View 11970 -
 Box-shaped Pressure Vessel for LNG Developed by KAIST Research Team
Earlier today, Korean researchers successfully showcased the installation and operation of a box-shaped, high-pressure tank for the storage of liquefied natural gas in Pohang, Republic of Korea. The development was the first of its kind in the world. Pressure vessels have many applications and are widely used within the petrochemical, energy, and other industrial sectors where the transport and storage of many types of pressurized gases and fluids are essential. Pressure vessels must be designed, manufactured, installed, and operated strictly in accordance with the appropriate codes and standards since they can, in cases of leak or rupture, pose considerable health and safety hazards. Pressure vessels are normally designed in the form of a cylindrical or spherical tank. These shapes are, in principle, highly efficient in withstanding internal pressure, but rather inefficient in terms of space utilization. The tanks fit very poorly within a typically prismatic-shaped room. They cannot be packed closely together, so they do not efficiently utilize the overall space. Moreover, cylindrical or spherical tanks are not easily scalable to very large sizes because the wall thickness of the tank must increase proportionally to its overall radius. Therefore, a large pressure vessel unavoidably will have very thick walls, which are difficult and expensive to manufacture, requiring a great amount of thick-walled steel to be rolled, forged, and welded together. KAIST researchers, sponsored by POSCO, a multinational steel-making company based in Pohang, Republic of Korea, have taken a turnabout approach to construct a pressure vessel that is neither cylindrical nor spherical. Professors Pål G. Bergan and Daejun Chang and of Ocean Systems Engineering at KAIST developed a box-type, large size pressure vessel for the storage and transportation of liquids such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), compressed natural gas (CNG), or liquefied natural gas (LNG). The box-shaped pressure vessel has an internal, load-carrying lattice-type structure. The lattice pattern is modular in all three spatial directions, thereby effectively anchoring and balancing pressure forces on the external walls of the vessel. The modular lattice can easily be adapted to prescribed pressure levels as the overall volumetric dimensions are directly linked to the number of repetitive modules. A giant prismatic pressure vessel with a size of 20,000 m3 and a design pressure of 10 atmospheres (10 barg) can be built simply by scaling up a smaller size pressure vessel. It is interesting to note that the thickness of steel walls remains unchanged and that the weight of steel per unit storage volume goes down as the vessel size increases. Professor Chang explained the benefit of a prismatic or box-shaped pressure vessel.“If we use cylindrical pressure vessels to supply LNG fuel for a large container ship, for example, many fuel tanks will be needed. Those tanks will take up large and valuable space onboard because the cylinders have to be lined up. In our case, however, much less space is needed. The operation of a ship becomes simpler with one fuel tank rather than with many. Furthermore, our box-type pressure vessel can be designed with dimensions that precisely fit a ship. For a container ship, there may be room for a substantially higher number of containers to be loaded than when using cylindrical vessels. In a case study on a 13,000 TEU container ship, the value of the increased transport capacity tuned out USD 8.4 million for one year of operation for one ship.”The manufacturing cost of a pressure vessel has been reduced as well. Several types of special steel for cryogenic (low temperature) applications have been investigated in design and analysis studies, and this includes a new type of high-manganese steel that is being developed by POSCO. Regardless of materials, in any instance of large pressure vessels, the new lattice tank technology can offer significant savings of combined capital and operational costs. Professor Bergan was also upbeat regarding the impact of the KAIST technology innovation. “Our box-type pressure vessel represents ground-breaking research. This innovative technology will dramatically change the rules of the game for industry concerning production, transportation, and storage of fluids under high pressure and at low temperatures.”The showcased prismatic pressure vessel was a scale-down model with a volume size of 80 m3 and design pressure of 10 atmospheres. The vessel complies with the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC), the international standard for the appropriateness of design, fabrication, and inspection of boilers and pressure vessels. It passed the 15 pressure testing in January 2014 and received an accreditation from the ASME BPVC (ASME U2 Stamp). KAIST’s prismatic pressure vessel will be presented and displayed at Gastech 2014, the largest global conference and exhibition in the natural gas, LNG, and hydrocarbons industry. This event will take place on March 24-27 at KINTEX in Ilsan, Republic of Korea. Youtube: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=woJwc5zisxk&list=TLGOLcI7L6_YYTn0lImPqNyeppQWRXqUt5Picture 1: The prototype of a prismatic pressure vesselPicture 2: A lattice pattern that is lined inside a prismatic pressure tankPicture 3: Above is a container ship having a box-shaped pressure vessel as a fuel tank, and below are traditional cylindrical fuel tanks.
2014.03.25 View 15315
Box-shaped Pressure Vessel for LNG Developed by KAIST Research Team
Earlier today, Korean researchers successfully showcased the installation and operation of a box-shaped, high-pressure tank for the storage of liquefied natural gas in Pohang, Republic of Korea. The development was the first of its kind in the world. Pressure vessels have many applications and are widely used within the petrochemical, energy, and other industrial sectors where the transport and storage of many types of pressurized gases and fluids are essential. Pressure vessels must be designed, manufactured, installed, and operated strictly in accordance with the appropriate codes and standards since they can, in cases of leak or rupture, pose considerable health and safety hazards. Pressure vessels are normally designed in the form of a cylindrical or spherical tank. These shapes are, in principle, highly efficient in withstanding internal pressure, but rather inefficient in terms of space utilization. The tanks fit very poorly within a typically prismatic-shaped room. They cannot be packed closely together, so they do not efficiently utilize the overall space. Moreover, cylindrical or spherical tanks are not easily scalable to very large sizes because the wall thickness of the tank must increase proportionally to its overall radius. Therefore, a large pressure vessel unavoidably will have very thick walls, which are difficult and expensive to manufacture, requiring a great amount of thick-walled steel to be rolled, forged, and welded together. KAIST researchers, sponsored by POSCO, a multinational steel-making company based in Pohang, Republic of Korea, have taken a turnabout approach to construct a pressure vessel that is neither cylindrical nor spherical. Professors Pål G. Bergan and Daejun Chang and of Ocean Systems Engineering at KAIST developed a box-type, large size pressure vessel for the storage and transportation of liquids such as liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), compressed natural gas (CNG), or liquefied natural gas (LNG). The box-shaped pressure vessel has an internal, load-carrying lattice-type structure. The lattice pattern is modular in all three spatial directions, thereby effectively anchoring and balancing pressure forces on the external walls of the vessel. The modular lattice can easily be adapted to prescribed pressure levels as the overall volumetric dimensions are directly linked to the number of repetitive modules. A giant prismatic pressure vessel with a size of 20,000 m3 and a design pressure of 10 atmospheres (10 barg) can be built simply by scaling up a smaller size pressure vessel. It is interesting to note that the thickness of steel walls remains unchanged and that the weight of steel per unit storage volume goes down as the vessel size increases. Professor Chang explained the benefit of a prismatic or box-shaped pressure vessel.“If we use cylindrical pressure vessels to supply LNG fuel for a large container ship, for example, many fuel tanks will be needed. Those tanks will take up large and valuable space onboard because the cylinders have to be lined up. In our case, however, much less space is needed. The operation of a ship becomes simpler with one fuel tank rather than with many. Furthermore, our box-type pressure vessel can be designed with dimensions that precisely fit a ship. For a container ship, there may be room for a substantially higher number of containers to be loaded than when using cylindrical vessels. In a case study on a 13,000 TEU container ship, the value of the increased transport capacity tuned out USD 8.4 million for one year of operation for one ship.”The manufacturing cost of a pressure vessel has been reduced as well. Several types of special steel for cryogenic (low temperature) applications have been investigated in design and analysis studies, and this includes a new type of high-manganese steel that is being developed by POSCO. Regardless of materials, in any instance of large pressure vessels, the new lattice tank technology can offer significant savings of combined capital and operational costs. Professor Bergan was also upbeat regarding the impact of the KAIST technology innovation. “Our box-type pressure vessel represents ground-breaking research. This innovative technology will dramatically change the rules of the game for industry concerning production, transportation, and storage of fluids under high pressure and at low temperatures.”The showcased prismatic pressure vessel was a scale-down model with a volume size of 80 m3 and design pressure of 10 atmospheres. The vessel complies with the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code (BPVC), the international standard for the appropriateness of design, fabrication, and inspection of boilers and pressure vessels. It passed the 15 pressure testing in January 2014 and received an accreditation from the ASME BPVC (ASME U2 Stamp). KAIST’s prismatic pressure vessel will be presented and displayed at Gastech 2014, the largest global conference and exhibition in the natural gas, LNG, and hydrocarbons industry. This event will take place on March 24-27 at KINTEX in Ilsan, Republic of Korea. Youtube: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=woJwc5zisxk&list=TLGOLcI7L6_YYTn0lImPqNyeppQWRXqUt5Picture 1: The prototype of a prismatic pressure vesselPicture 2: A lattice pattern that is lined inside a prismatic pressure tankPicture 3: Above is a container ship having a box-shaped pressure vessel as a fuel tank, and below are traditional cylindrical fuel tanks.
2014.03.25 View 15315