IR
-
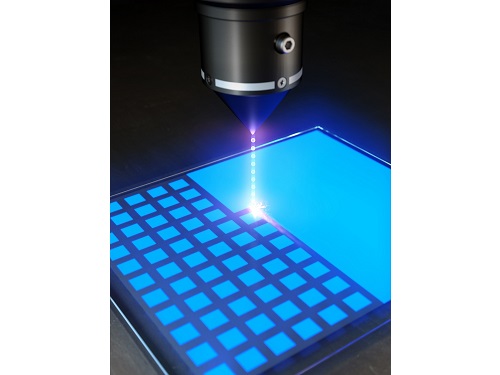 KAIST researchers develops a tech to enable production of ultrahigh-resolution LED with sub-micrometer scale pixels
Ultrahigh-resolution displays are an essential element for developing next-generation electronic products such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and smart watches, and can be applied not only to head-mounted displays, but also to smart glasses and smart lenses. The technology developed through this research is expected to be used to make such next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and other various sub-micro optoelectronic devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team of KAIST Department of Physics developed the core technology for an ultrahigh resolution light-emitting diode (LED) display that can realize 0.5 micron-scale pixels smaller than 1/100 of the average hair thickness (about 100 microns) using focused ion beams.
Commonly, pixelation of ultrahigh-resolution LED displays usually relies on the etching method that physically cuts the area around the pixel, but as the pixel becomes smaller due to the occurrence of various defects around it, leading to side-effects of having leakage of current increased and light-emission efficiency decreased. In addition, various complex processes such as patterning for pixelation and post-processing for prevention of leakage current are required.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team developed a technology that can create pixels down to the size of a microscale without the complicated pre- and post-processing using a focused ion beam. This method has the advantage of being able to freely set the shape of the emitting pixel without causing any structural deformation on the material surface by controlling the intensity of the focused ion beam.
The focused ion beam technology has been widely used for ultrahigh-magnification imaging and nanostructure fabrication in fields such as materials engineering and biology. However, when a focused ion beam is used on a light emitting body such as an LED, light emission of a portion hit by the beam and a surrounding area rapidly decreases, which has been a barrier to fabricating a nano-scale light emitting structure. Upon facing this issue, Professor Cho's research team began the research on the idea that if they turned things around to use these problematic phenomena, they can be used in ultra-fine pixelation method on a sub-micron scale.
The research team used a focused ion beam whose intensity was softened to the extent that the surface was not shaved, and found that not only the light-emission rapidly decreased in the area hit by the focused ion beam, but also the local resistance greatly increased. As a result, while the surface of the LED is kept flat, the portion hit by the focused ion beam is optically and electrically isolated, enabling pixelation for independent operation.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, who led the research, said, “We have newly developed a technology that can create sub-micron-scale pixels without complicated processes using a focused ion beam, which will be a base technology that can be applied to next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and nano-photoelectronic devices.”
This research in which the Master's student Ji-Hwan Moon and the Ph.D. student Baul Kim of KAIST Department of Physics participated as co-first authors, was carried out with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea's Support Program for Mid-Career Researchers and the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation. It was published online in 'Advanced Materials' on February 13, and was also selected as the internal cover of the next offline edition. (Title: Electrically Driven Sub-Micron Light-Emitting Diode Arrays Using Maskless and Etching-Free Pixelation)
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the technology for ultrahigh density sub-micron-sized pixels through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation on an LED device
Figure 2. Ultra-high-density pixelation technology of micro light-emitting diodes (μLED) through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation
Figure 3. Rectangular pixels of different sizes (surface structure picture and luminescence picture) realized by a focused ion beam. Luminescence pictures of pixel arrays ranging in size from 20 µm x 20 µm to 0.5 µm x 0.5 µm, with surface flatness maintained.
2023.03.08 View 8742
KAIST researchers develops a tech to enable production of ultrahigh-resolution LED with sub-micrometer scale pixels
Ultrahigh-resolution displays are an essential element for developing next-generation electronic products such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and smart watches, and can be applied not only to head-mounted displays, but also to smart glasses and smart lenses. The technology developed through this research is expected to be used to make such next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and other various sub-micro optoelectronic devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team of KAIST Department of Physics developed the core technology for an ultrahigh resolution light-emitting diode (LED) display that can realize 0.5 micron-scale pixels smaller than 1/100 of the average hair thickness (about 100 microns) using focused ion beams.
Commonly, pixelation of ultrahigh-resolution LED displays usually relies on the etching method that physically cuts the area around the pixel, but as the pixel becomes smaller due to the occurrence of various defects around it, leading to side-effects of having leakage of current increased and light-emission efficiency decreased. In addition, various complex processes such as patterning for pixelation and post-processing for prevention of leakage current are required.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team developed a technology that can create pixels down to the size of a microscale without the complicated pre- and post-processing using a focused ion beam. This method has the advantage of being able to freely set the shape of the emitting pixel without causing any structural deformation on the material surface by controlling the intensity of the focused ion beam.
The focused ion beam technology has been widely used for ultrahigh-magnification imaging and nanostructure fabrication in fields such as materials engineering and biology. However, when a focused ion beam is used on a light emitting body such as an LED, light emission of a portion hit by the beam and a surrounding area rapidly decreases, which has been a barrier to fabricating a nano-scale light emitting structure. Upon facing this issue, Professor Cho's research team began the research on the idea that if they turned things around to use these problematic phenomena, they can be used in ultra-fine pixelation method on a sub-micron scale.
The research team used a focused ion beam whose intensity was softened to the extent that the surface was not shaved, and found that not only the light-emission rapidly decreased in the area hit by the focused ion beam, but also the local resistance greatly increased. As a result, while the surface of the LED is kept flat, the portion hit by the focused ion beam is optically and electrically isolated, enabling pixelation for independent operation.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, who led the research, said, “We have newly developed a technology that can create sub-micron-scale pixels without complicated processes using a focused ion beam, which will be a base technology that can be applied to next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and nano-photoelectronic devices.”
This research in which the Master's student Ji-Hwan Moon and the Ph.D. student Baul Kim of KAIST Department of Physics participated as co-first authors, was carried out with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea's Support Program for Mid-Career Researchers and the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation. It was published online in 'Advanced Materials' on February 13, and was also selected as the internal cover of the next offline edition. (Title: Electrically Driven Sub-Micron Light-Emitting Diode Arrays Using Maskless and Etching-Free Pixelation)
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the technology for ultrahigh density sub-micron-sized pixels through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation on an LED device
Figure 2. Ultra-high-density pixelation technology of micro light-emitting diodes (μLED) through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation
Figure 3. Rectangular pixels of different sizes (surface structure picture and luminescence picture) realized by a focused ion beam. Luminescence pictures of pixel arrays ranging in size from 20 µm x 20 µm to 0.5 µm x 0.5 µm, with surface flatness maintained.
2023.03.08 View 8742 -
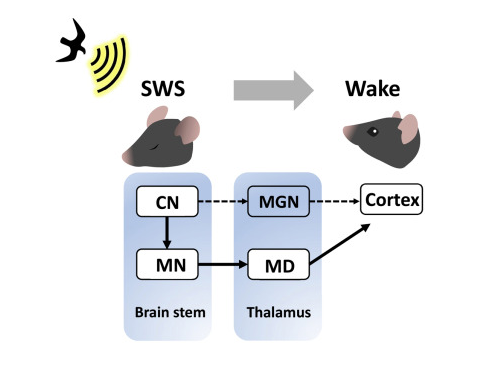 KAIST researchers discovers the neural circuit that reacts to alarm clock
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th that a research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Dr. Jeongjin Kim 's team from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have identified the principle of awakening animals by responding to sounds even while sleeping.
Sleep is a very important physiological process that organizes brain activity and maintains health. During sleep, the function of sensory nerves is blocked, so the ability to detect danger in the proximity is reduced. However, many animals detect approaching predators and respond even while sleeping. Scientists thought that animals ready for danger by alternating between deep sleep and light sleep.
A research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim at KAIST discovered that animals have neural circuits that respond to sounds even during deep sleep. While awake, the medial geniculate thalamus responds to sounds, but during deep sleep, or Non-REM sleep, the Mediodorsal thalamus responds to sounds to wake up the brain.
As a result of the study, when the rats fell into deep sleep, the nerves of the medial geniculate thalamus were also sleeping, but the nerves of mediodorsal thalamus were awake and responded immediately to sounds. In addition, it was observed that when mediodorsal thalamus was inhibited, the rats could not wake up even when a sound was heard, and when the mediodorsal thalamus was stimulated, the rats woke up within a few seconds without sound.
This is the first study to show that sleep and wakefulness can transmit auditory signals through different neural circuits, and was reported in the international journal, Current Biology on February 7, and was highlighted by Nature. (https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-00354-0)
Professor Daesoo Kim explained, “The findings of this study can used in developing digital healthcare technologies to be used to improve understanding of disorders of senses and wakefulness seen in various brain diseases and to control the senses in the future.”
This research was carried out with the support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Research Foundation Program.
Figure 1. Traditionally, sound signals were thought to be propagated from the auditory nerve to the auditory thalamus. However, while in slow-wave sleep, the auditory nerve sends sound signals to the mediodorsal thalamic neurons via the brainstem nerve to induce arousal in the brain.
Figure 2. GRIK4 dorsomedial nerve in response to sound stimulation. The awakening effect is induced as the activity of the GRIK4 dorsal medial nerve increases based on the time when sound stimulation is given.
2023.03.03 View 6663
KAIST researchers discovers the neural circuit that reacts to alarm clock
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th that a research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Dr. Jeongjin Kim 's team from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have identified the principle of awakening animals by responding to sounds even while sleeping.
Sleep is a very important physiological process that organizes brain activity and maintains health. During sleep, the function of sensory nerves is blocked, so the ability to detect danger in the proximity is reduced. However, many animals detect approaching predators and respond even while sleeping. Scientists thought that animals ready for danger by alternating between deep sleep and light sleep.
A research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim at KAIST discovered that animals have neural circuits that respond to sounds even during deep sleep. While awake, the medial geniculate thalamus responds to sounds, but during deep sleep, or Non-REM sleep, the Mediodorsal thalamus responds to sounds to wake up the brain.
As a result of the study, when the rats fell into deep sleep, the nerves of the medial geniculate thalamus were also sleeping, but the nerves of mediodorsal thalamus were awake and responded immediately to sounds. In addition, it was observed that when mediodorsal thalamus was inhibited, the rats could not wake up even when a sound was heard, and when the mediodorsal thalamus was stimulated, the rats woke up within a few seconds without sound.
This is the first study to show that sleep and wakefulness can transmit auditory signals through different neural circuits, and was reported in the international journal, Current Biology on February 7, and was highlighted by Nature. (https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-00354-0)
Professor Daesoo Kim explained, “The findings of this study can used in developing digital healthcare technologies to be used to improve understanding of disorders of senses and wakefulness seen in various brain diseases and to control the senses in the future.”
This research was carried out with the support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Research Foundation Program.
Figure 1. Traditionally, sound signals were thought to be propagated from the auditory nerve to the auditory thalamus. However, while in slow-wave sleep, the auditory nerve sends sound signals to the mediodorsal thalamic neurons via the brainstem nerve to induce arousal in the brain.
Figure 2. GRIK4 dorsomedial nerve in response to sound stimulation. The awakening effect is induced as the activity of the GRIK4 dorsal medial nerve increases based on the time when sound stimulation is given.
2023.03.03 View 6663 -
 KAIST Holds 2023 Commencement Ceremony
< Photo 1. On the 17th, KAIST held the 2023 Commencement Ceremony for a total of 2,870 students, including 691 doctors. >
KAIST held its 2023 commencement ceremony at the Sports Complex of its main campus in Daejeon at 2 p.m. on February 27. It was the first commencement ceremony to invite all its graduates since the start of COVID-19 quarantine measures.
KAIST awarded a total of 2,870 degrees including 691 PhD degrees, 1,464 master’s degrees, and 715 bachelor’s degrees, which adds to the total of 74,999 degrees KAIST has conferred since its foundation in 1971, which includes 15,772 PhD, 38,360 master’s and 20,867 bachelor’s degrees.
This year’s Cum Laude, Gabin Ryu, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the Minister of Science and ICT Award. Seung-ju Lee from the School of Computing received the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award, while Jantakan Nedsaengtip, an international student from Thailand received the KAIST Presidential Award, and Jaeyong Hwang from the Department of Physics and Junmo Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering each received the President of the Alumni Association Award and the Chairman of the KAIST Development Foundation Award, respectively.
Minister Jong-ho Lee of the Ministry of Science and ICT awarded the recipients of the academic awards and delivered a congratulatory speech.
Yujin Cha from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, who received a PhD degree after 19 years since his entrance to KAIST as an undergraduate student in 2004 gave a speech on behalf of the graduates to move and inspire the graduates and the guests.
After Cha received a bachelor’s degree from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, he entered a medical graduate school and became a radiation oncology specialist. But after experiencing the death of a young patient who suffered from osteosarcoma, he returned to his alma mater to become a scientist. As he believes that science and technology is the ultimate solution to the limitations of modern medicine, he started as a PhD student at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2018, hoping to find such solutions.
During his course, he identified the characteristics of the decision-making process of doctors during diagnosis, and developed a brain-inspired AI algorithm. It is an original and challenging study that attempted to develop a fundamental machine learning theory from the data he collected from 200 doctors of different specialties.
Cha said, “Humans and AI can cooperate by humans utilizing the unique learning abilities of AI to develop our expertise, while AIs can mimic us humans’ learning abilities to improve.” He added, “My ultimate goal is to develop technology to a level at which humans and machines influence each other and ‘coevolve’, and applying it not only to medicine, but in all areas.”
Cha, who is currently an assistant professor at the KAIST Biomedical Research Center, has also written Artificial Intelligence for Doctors in 2017 to help medical personnel use AI in clinical fields, and the book was selected as one of the 2018 Sejong Books in the academic category.
During his speech at this year’s commencement ceremony, he shared that “there are so many things in the world that are difficult to solve and many things to solve them with, but I believe the things that can really broaden the horizons of the world and find fundamental solutions to the problems at hand are science and technology.”
Meanwhile, singer-songwriter Sae Byul Park who studied at the KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology will also receive her PhD degree.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a field in AI that teaches a computer to understand and analyze human language that is actively being studied. An example of NLP is ChatGTP, which recently received a lot of attention. For her research, Park analyzed music rather than language using NLP technology.
To analyze music, which is in the form of sound, using the methods for NLP, it is necessary to rebuild notes and beats into a form of words or sentences as in a language. For this, Park designed an algorithm called Mel2Word and applied it to her research.
She also suggested that by converting melodies into texts for analysis, one would be able to quantitatively express music as sentences or words with meaning and context rather than as simple sounds representing a certain note.
Park said, “music has always been considered as a product of subjective emotion, but this research provides a framework that can calculate and analyze music.”
Park’s study can later be developed into a tool to measure the similarities between musical work, as well as a piece’s originality, artistry and popularity, and it can be used as a clue to explore the fundamental principles of how humans respond to music from a cognitive science perspective.
Park began her Ph.D. program in 2014, while carrying on with her musical activities as well as public and university lectures alongside, and dealing with personally major events including marriage and childbirth during the course of years. She already met the requirements to receive her degree in 2019, but delayed her graduation in order to improve the level of completion of her research, and finally graduated with her current achievements after nine years.
Professor Juhan Nam, who supervised Park’s research, said, “Park, who has a bachelor’s degree in psychology, later learned to code for graduate school, and has complete high-quality research in the field of artificial intelligence.” He added, “Though it took a long time, her attitude of not giving up until the end as a researcher is also excellent.”
Sae Byul Park is currently lecturing courses entitled Culture Technology and Music Information Retrieval at the Underwood International College of Yonsei University.
Park said, “the 10 or so years I’ve spent at KAIST as a graduate student was a time I could learn and prosper not only academically but from all angles of life.” She added, “having received a doctorate degree is not the end, but a ‘commencement’. Therefore, I will start to root deeper from the seeds I sowed and work harder as a both a scholar and an artist.”
< Photo 2. From left) Yujin Cha (Valedictorian, Medical-Scientist Program Ph.D. graduate), Saebyeol Park (a singer-songwriter, Ph.D. graduate from the Graduate School of Culture and Technology), Junseok Moon and Inah Seo (the two highlighted CEO graduates from the Department of Management Engineering's master’s program) >
Young entrepreneurs who dream of solving social problems will also be wearing their graduation caps. Two such graduates are Jun-seok Moon and Inah Seo, receiving their master’s degrees in social entrepreneurship MBA from the KAIST College of Business.
Before entrance, Moon ran a café helping African refugees stand on their own feet. Then, he entered KAIST to later expand his business and learn social entrepreneurship in order to sustainably help refugees in the blind spots of human rights and welfare.
During his master’s course, Moon realized that he could achieve active carbon reduction by changing the coffee alone, and switched his business field and founded Equal Table. The amount of carbon an individual can reduce by refraining from using a single paper cup is 10g, while changing the coffee itself can reduce it by 300g.
1kg of coffee emits 15kg of carbon over the course of its production, distribution, processing, and consumption, but Moon produces nearly carbon-neutral coffee beans by having innovated the entire process. In particular, the company-to-company ESG business solution is Moon’s new start-up area. It provides companies with carbon-reduced coffee made by roasting raw beans from carbon-neutral certified farms with 100% renewable energy, and shows how much carbon has been reduced in its making. Equal Table will launch the service this month in collaboration with SK Telecom, its first partner.
Inah Seo, who also graduated with Moon, founded Conscious Wear to start a fashion business reducing environmental pollution. In order to realize her mission, she felt the need to gain the appropriate expertise in management, and enrolled for the social entrepreneurship MBA.
Out of the various fashion industries, Seo focused on the leather market, which is worth 80 trillion won. Due to thickness or contamination issues, only about 60% of animal skin fabric is used, and the rest is discarded. Heavy metals are used during such processes, which also directly affects the environment.
During the social entrepreneurship MBA course, Seo collaborated with SK Chemicals, which had links through the program, and launched eco-friendly leather bags. The bags used discarded leather that was recycled by grinding and reprocessing into a biomaterial called PO3G. It was the first case in which PO3G that is over 90% biodegradable was applied to regenerated leather. In other words, it can reduce environmental pollution in the processing and disposal stages, while also reducing carbon emissions and water usage by one-tenth compared to existing cowhide products.
The social entrepreneurship MBA course, from which Moon and Seo graduated, will run in integration with the Graduate School of Green Growth as an Impact MBA program starting this year. KAIST plans to steadily foster entrepreneurs who will lead meaningful changes in the environment and society as well as economic values through innovative technologies and ideas.
< Photo 3. NYU President Emeritus John Sexton (left), who received this year's honorary doctorate of science, poses with President Kwang Hyung Lee >
Meanwhile, during this day’s commencement ceremony, KAIST also presented President Emeritus John Sexton of New York University with an honorary doctorate in science. He was recognized for laying the foundation for the cooperation between KAIST and New York University, such as promoting joint campuses.
< Photo 4. At the commencement ceremony of KAIST held on the 17th, President Kwang Hyung Lee is encouraging the graduates with his commencement address. >
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized in his commencement speech that, “if you can draw up the future and work hard toward your goal, the future can become a work of art that you create with your own hands,” and added, “Never stop on the journey toward your dreams, and do not give up even when you are met with failure. Failure happens to everyone, all the time. The important thing is to know 'why you failed', and to use those elements of failure as the driving force for the next try.”
2023.02.20 View 22376
KAIST Holds 2023 Commencement Ceremony
< Photo 1. On the 17th, KAIST held the 2023 Commencement Ceremony for a total of 2,870 students, including 691 doctors. >
KAIST held its 2023 commencement ceremony at the Sports Complex of its main campus in Daejeon at 2 p.m. on February 27. It was the first commencement ceremony to invite all its graduates since the start of COVID-19 quarantine measures.
KAIST awarded a total of 2,870 degrees including 691 PhD degrees, 1,464 master’s degrees, and 715 bachelor’s degrees, which adds to the total of 74,999 degrees KAIST has conferred since its foundation in 1971, which includes 15,772 PhD, 38,360 master’s and 20,867 bachelor’s degrees.
This year’s Cum Laude, Gabin Ryu, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the Minister of Science and ICT Award. Seung-ju Lee from the School of Computing received the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award, while Jantakan Nedsaengtip, an international student from Thailand received the KAIST Presidential Award, and Jaeyong Hwang from the Department of Physics and Junmo Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering each received the President of the Alumni Association Award and the Chairman of the KAIST Development Foundation Award, respectively.
Minister Jong-ho Lee of the Ministry of Science and ICT awarded the recipients of the academic awards and delivered a congratulatory speech.
Yujin Cha from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, who received a PhD degree after 19 years since his entrance to KAIST as an undergraduate student in 2004 gave a speech on behalf of the graduates to move and inspire the graduates and the guests.
After Cha received a bachelor’s degree from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, he entered a medical graduate school and became a radiation oncology specialist. But after experiencing the death of a young patient who suffered from osteosarcoma, he returned to his alma mater to become a scientist. As he believes that science and technology is the ultimate solution to the limitations of modern medicine, he started as a PhD student at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2018, hoping to find such solutions.
During his course, he identified the characteristics of the decision-making process of doctors during diagnosis, and developed a brain-inspired AI algorithm. It is an original and challenging study that attempted to develop a fundamental machine learning theory from the data he collected from 200 doctors of different specialties.
Cha said, “Humans and AI can cooperate by humans utilizing the unique learning abilities of AI to develop our expertise, while AIs can mimic us humans’ learning abilities to improve.” He added, “My ultimate goal is to develop technology to a level at which humans and machines influence each other and ‘coevolve’, and applying it not only to medicine, but in all areas.”
Cha, who is currently an assistant professor at the KAIST Biomedical Research Center, has also written Artificial Intelligence for Doctors in 2017 to help medical personnel use AI in clinical fields, and the book was selected as one of the 2018 Sejong Books in the academic category.
During his speech at this year’s commencement ceremony, he shared that “there are so many things in the world that are difficult to solve and many things to solve them with, but I believe the things that can really broaden the horizons of the world and find fundamental solutions to the problems at hand are science and technology.”
Meanwhile, singer-songwriter Sae Byul Park who studied at the KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology will also receive her PhD degree.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a field in AI that teaches a computer to understand and analyze human language that is actively being studied. An example of NLP is ChatGTP, which recently received a lot of attention. For her research, Park analyzed music rather than language using NLP technology.
To analyze music, which is in the form of sound, using the methods for NLP, it is necessary to rebuild notes and beats into a form of words or sentences as in a language. For this, Park designed an algorithm called Mel2Word and applied it to her research.
She also suggested that by converting melodies into texts for analysis, one would be able to quantitatively express music as sentences or words with meaning and context rather than as simple sounds representing a certain note.
Park said, “music has always been considered as a product of subjective emotion, but this research provides a framework that can calculate and analyze music.”
Park’s study can later be developed into a tool to measure the similarities between musical work, as well as a piece’s originality, artistry and popularity, and it can be used as a clue to explore the fundamental principles of how humans respond to music from a cognitive science perspective.
Park began her Ph.D. program in 2014, while carrying on with her musical activities as well as public and university lectures alongside, and dealing with personally major events including marriage and childbirth during the course of years. She already met the requirements to receive her degree in 2019, but delayed her graduation in order to improve the level of completion of her research, and finally graduated with her current achievements after nine years.
Professor Juhan Nam, who supervised Park’s research, said, “Park, who has a bachelor’s degree in psychology, later learned to code for graduate school, and has complete high-quality research in the field of artificial intelligence.” He added, “Though it took a long time, her attitude of not giving up until the end as a researcher is also excellent.”
Sae Byul Park is currently lecturing courses entitled Culture Technology and Music Information Retrieval at the Underwood International College of Yonsei University.
Park said, “the 10 or so years I’ve spent at KAIST as a graduate student was a time I could learn and prosper not only academically but from all angles of life.” She added, “having received a doctorate degree is not the end, but a ‘commencement’. Therefore, I will start to root deeper from the seeds I sowed and work harder as a both a scholar and an artist.”
< Photo 2. From left) Yujin Cha (Valedictorian, Medical-Scientist Program Ph.D. graduate), Saebyeol Park (a singer-songwriter, Ph.D. graduate from the Graduate School of Culture and Technology), Junseok Moon and Inah Seo (the two highlighted CEO graduates from the Department of Management Engineering's master’s program) >
Young entrepreneurs who dream of solving social problems will also be wearing their graduation caps. Two such graduates are Jun-seok Moon and Inah Seo, receiving their master’s degrees in social entrepreneurship MBA from the KAIST College of Business.
Before entrance, Moon ran a café helping African refugees stand on their own feet. Then, he entered KAIST to later expand his business and learn social entrepreneurship in order to sustainably help refugees in the blind spots of human rights and welfare.
During his master’s course, Moon realized that he could achieve active carbon reduction by changing the coffee alone, and switched his business field and founded Equal Table. The amount of carbon an individual can reduce by refraining from using a single paper cup is 10g, while changing the coffee itself can reduce it by 300g.
1kg of coffee emits 15kg of carbon over the course of its production, distribution, processing, and consumption, but Moon produces nearly carbon-neutral coffee beans by having innovated the entire process. In particular, the company-to-company ESG business solution is Moon’s new start-up area. It provides companies with carbon-reduced coffee made by roasting raw beans from carbon-neutral certified farms with 100% renewable energy, and shows how much carbon has been reduced in its making. Equal Table will launch the service this month in collaboration with SK Telecom, its first partner.
Inah Seo, who also graduated with Moon, founded Conscious Wear to start a fashion business reducing environmental pollution. In order to realize her mission, she felt the need to gain the appropriate expertise in management, and enrolled for the social entrepreneurship MBA.
Out of the various fashion industries, Seo focused on the leather market, which is worth 80 trillion won. Due to thickness or contamination issues, only about 60% of animal skin fabric is used, and the rest is discarded. Heavy metals are used during such processes, which also directly affects the environment.
During the social entrepreneurship MBA course, Seo collaborated with SK Chemicals, which had links through the program, and launched eco-friendly leather bags. The bags used discarded leather that was recycled by grinding and reprocessing into a biomaterial called PO3G. It was the first case in which PO3G that is over 90% biodegradable was applied to regenerated leather. In other words, it can reduce environmental pollution in the processing and disposal stages, while also reducing carbon emissions and water usage by one-tenth compared to existing cowhide products.
The social entrepreneurship MBA course, from which Moon and Seo graduated, will run in integration with the Graduate School of Green Growth as an Impact MBA program starting this year. KAIST plans to steadily foster entrepreneurs who will lead meaningful changes in the environment and society as well as economic values through innovative technologies and ideas.
< Photo 3. NYU President Emeritus John Sexton (left), who received this year's honorary doctorate of science, poses with President Kwang Hyung Lee >
Meanwhile, during this day’s commencement ceremony, KAIST also presented President Emeritus John Sexton of New York University with an honorary doctorate in science. He was recognized for laying the foundation for the cooperation between KAIST and New York University, such as promoting joint campuses.
< Photo 4. At the commencement ceremony of KAIST held on the 17th, President Kwang Hyung Lee is encouraging the graduates with his commencement address. >
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized in his commencement speech that, “if you can draw up the future and work hard toward your goal, the future can become a work of art that you create with your own hands,” and added, “Never stop on the journey toward your dreams, and do not give up even when you are met with failure. Failure happens to everyone, all the time. The important thing is to know 'why you failed', and to use those elements of failure as the driving force for the next try.”
2023.02.20 View 22376 -
 Prof. Austin Givens of KAIST Language Center receives Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Austin Givens posing with the Letter of Commendation by the Miniser Hwang-Keun Chung of the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs at the Language Center >
Professor Austin Givens of our Language Center received a Ministerial Commendation from the Korean Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs dated December 21st, 2022 for his contribution for the development of the Korean Foodservices Industry through his active and prominent media presence.
Professor Austin Givens has been working with the KAIST Language Center since 2017, and has shown his passion for Korean food through his YouTube channel "Austin! Eating What is Given", introducing not only the food but also the culture of Korea and KAIST to his international viewers through the videos he shares of his candid reviews of the food and restaurants around town on the popular video streaming platform.
< Thumbnail introductions of Professor Givens' videos on his YouTube channel, "Austin! Eating What is Given" >
- KAIST Language Center
2023.02.09 View 9589
Prof. Austin Givens of KAIST Language Center receives Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Austin Givens posing with the Letter of Commendation by the Miniser Hwang-Keun Chung of the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs at the Language Center >
Professor Austin Givens of our Language Center received a Ministerial Commendation from the Korean Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs dated December 21st, 2022 for his contribution for the development of the Korean Foodservices Industry through his active and prominent media presence.
Professor Austin Givens has been working with the KAIST Language Center since 2017, and has shown his passion for Korean food through his YouTube channel "Austin! Eating What is Given", introducing not only the food but also the culture of Korea and KAIST to his international viewers through the videos he shares of his candid reviews of the food and restaurants around town on the popular video streaming platform.
< Thumbnail introductions of Professor Givens' videos on his YouTube channel, "Austin! Eating What is Given" >
- KAIST Language Center
2023.02.09 View 9589 -
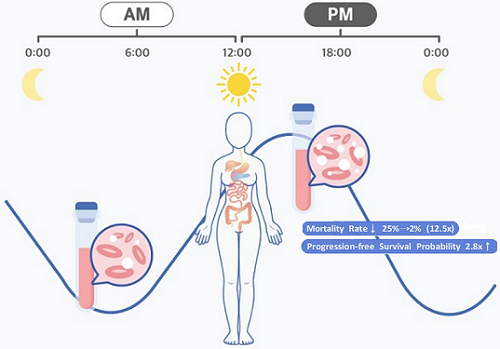 Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 8046
Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 8046 -
 UAE Space Program Leaders named to be the 1st of the honorees of KAIST Alumni Association's special recognition for graduates of foreign nationality
The KAIST Alumni Association (Chairman, Chil-Hee Chung) announced on the 12th that the winners of the 2023 KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award and International Alumni Award has been selected.
The KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award, which produced the first recipient in 1992, is an award given to alumni who have contributed to the development of the nation and society, or who have glorified the honor of their alma mater with outstanding academic achievements and social and/or communal contributions.
On a special note, this year, there has been an addition to the honors, “the KAIST Distinguished International Alumni Award” to honor and encourage overseas alumni who are making their marks in the international community that will boost positive recognition of KAIST in the global setting and will later become a bridge that will expedite Korea's international efforts in the future.
As of 2022, the number of international students who succeeded in earning KAIST degrees has exceeded 1,700, and they are actively doing their part back in their home countries as leaders in various fields in which they belong, spanning from science and technology, to politics, industry and other corners of the society.
(From left) Omran Sharaf, the Assistant Minister of UAE Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation for Advanced Science and Technology, Amer Al Sayegh the Director General of Space Project at MBRSC, and Mohammed Al Harmi the Director General of Administration at MBRSC (Photos provided by the courtesy of MBRSC)
To celebrate and honor their outstanding achievements, the KAIST Alumni Association selected a team of three alumni of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to receive the Distinguished International Alumni Award for the first time. The named honorees are Omran Sharaf, a master’s graduate from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, and Amer Al Sayegh and Mohammed Al Harmi, master’s graduates of the Department of Aerospace Engineering - all three of the class of 2013 in leading positions in the UAE space program to lead the advancement of the science and technology of the country.
Currently, the three alums are in directorship of the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) with Mr. Omran Sharaf, who has recently been appointed as the Assistant Minister in charge of Advanced Science and Technology at the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, being the Project Director of the Emirates Mars Mission of MBRSC and Mr. Amer Al Sayegh in the Director General position in charge of Space Project and Mr. Mohammed Al Harmi, the Director General of Administration, at MBRSC.
They received technology transfer from “SatRec I”, Korea's first satellite system exporter and KAIST alumni company, for about 10 years from 2006, while carrying out their master’s studies at the same time.
Afterwards, they returned to UAE to lead the Emirates Mars Mission, which is already showing tangible progress including the successful launch of the Mars probe "Amal" (ال امل, meaning ‘Hope’ in Arabic), which was the first in the Arab world and the fifth in the world to successfully enter into orbit around Mars, and the UAE’s first independently developed Earth observation satellite "KhalifaSat".
An official from the KAIST Alumni Association said, "We selected the Distinguished International Alumni after evaluating their industrious leadership in promoting various space industry strategies, ranging from the development of Mars probes and Earth observation satellites, as well as lunar exploration, asteroid exploration, and Mars residence plans."
(From left) Joo-Sun Choi, President & CEO of Samsung Display Co. Ltd., Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), Kyunghyun Cho, Professor of New York University (NYU)
Also, four of the Korean graduates, Joo-Sun Choi, the CEO of Samsung Display, Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), and Kyunghyun Cho, a Professor of New York University (NYU), were selected as the winners of the “Distinguished Alumni Award”.
Mr. Joo-Sun Choi (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1989, Ph.D. in 1995), the CEO of Samsung Display, led the successful development and mass-production of the world's first ultra-high-definition QD-OLED Displays, and preemptively transformed the structure of business of the industry and has been leading the way in technological innovation.
Mr. Jung Goo Cho (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D. in 1992), the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., developed wireless power technology for the first time in Korea in the early 2000s and applied it to semiconductor/display lines and led the wireless power charging technology in various fields, such as developing KAIST On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEV) and commercializing the world's first wireless charger for 11kW electric vehicles.
Mr. Jong Seung Park (Mechanical Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D., in 1991), The President of ADD is an expert with abundant science and technology knowledge and organizational management capabilities. He is contributing greatly to national defense and security through science and technology.
Mr. Kyunghyun Cho (Computer Science, B.S., in 2009), the Professor of Computer Science and Data Science at NYU, is a world-renowned expert in Artificial Intelligence (AI), advancing the concept of 'Neural Machine Translation' in the field of natural language processing, to make great contributions to AI translation technology and related industries.
Chairman Chil-Hee Chung, the 26th Chair of KAIST Alumni Association “As each year goes by, I feel that the influence of KAIST alumni goes beyond science and technology to affect our society as a whole.” He went on to say, “This year, as it was more meaningful to extend the award to honor the international members of our Alums, we look forward to seeing more of our alumni continuing their social and academic endeavors to play an active role in the global stage in taking on the global challenges.”
The Ceremony for KAIST Distinguished Alumni and International Alumni Award Honorees will be conducted at the Annual New Year’s Event of KAIST Alumni Association for 2023 to be held on Friday, January 13th, at the Grand InterContinental Seoul Parnas.
2023.01.12 View 16958
UAE Space Program Leaders named to be the 1st of the honorees of KAIST Alumni Association's special recognition for graduates of foreign nationality
The KAIST Alumni Association (Chairman, Chil-Hee Chung) announced on the 12th that the winners of the 2023 KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award and International Alumni Award has been selected.
The KAIST Distinguished Alumni Award, which produced the first recipient in 1992, is an award given to alumni who have contributed to the development of the nation and society, or who have glorified the honor of their alma mater with outstanding academic achievements and social and/or communal contributions.
On a special note, this year, there has been an addition to the honors, “the KAIST Distinguished International Alumni Award” to honor and encourage overseas alumni who are making their marks in the international community that will boost positive recognition of KAIST in the global setting and will later become a bridge that will expedite Korea's international efforts in the future.
As of 2022, the number of international students who succeeded in earning KAIST degrees has exceeded 1,700, and they are actively doing their part back in their home countries as leaders in various fields in which they belong, spanning from science and technology, to politics, industry and other corners of the society.
(From left) Omran Sharaf, the Assistant Minister of UAE Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation for Advanced Science and Technology, Amer Al Sayegh the Director General of Space Project at MBRSC, and Mohammed Al Harmi the Director General of Administration at MBRSC (Photos provided by the courtesy of MBRSC)
To celebrate and honor their outstanding achievements, the KAIST Alumni Association selected a team of three alumni of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) to receive the Distinguished International Alumni Award for the first time. The named honorees are Omran Sharaf, a master’s graduate from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy, and Amer Al Sayegh and Mohammed Al Harmi, master’s graduates of the Department of Aerospace Engineering - all three of the class of 2013 in leading positions in the UAE space program to lead the advancement of the science and technology of the country.
Currently, the three alums are in directorship of the Mohammed Bin Rashid Space Centre (MBRSC) with Mr. Omran Sharaf, who has recently been appointed as the Assistant Minister in charge of Advanced Science and Technology at the UAE Ministry of Foreign Affairs and International Cooperation, being the Project Director of the Emirates Mars Mission of MBRSC and Mr. Amer Al Sayegh in the Director General position in charge of Space Project and Mr. Mohammed Al Harmi, the Director General of Administration, at MBRSC.
They received technology transfer from “SatRec I”, Korea's first satellite system exporter and KAIST alumni company, for about 10 years from 2006, while carrying out their master’s studies at the same time.
Afterwards, they returned to UAE to lead the Emirates Mars Mission, which is already showing tangible progress including the successful launch of the Mars probe "Amal" (ال امل, meaning ‘Hope’ in Arabic), which was the first in the Arab world and the fifth in the world to successfully enter into orbit around Mars, and the UAE’s first independently developed Earth observation satellite "KhalifaSat".
An official from the KAIST Alumni Association said, "We selected the Distinguished International Alumni after evaluating their industrious leadership in promoting various space industry strategies, ranging from the development of Mars probes and Earth observation satellites, as well as lunar exploration, asteroid exploration, and Mars residence plans."
(From left) Joo-Sun Choi, President & CEO of Samsung Display Co. Ltd., Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), Kyunghyun Cho, Professor of New York University (NYU)
Also, four of the Korean graduates, Joo-Sun Choi, the CEO of Samsung Display, Jung Goo Cho, the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., Jong Seung Park, the President of Agency for Defense Development (ADD), and Kyunghyun Cho, a Professor of New York University (NYU), were selected as the winners of the “Distinguished Alumni Award”.
Mr. Joo-Sun Choi (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1989, Ph.D. in 1995), the CEO of Samsung Display, led the successful development and mass-production of the world's first ultra-high-definition QD-OLED Displays, and preemptively transformed the structure of business of the industry and has been leading the way in technological innovation.
Mr. Jung Goo Cho (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D. in 1992), the CEO of Green Power Co. Ltd., developed wireless power technology for the first time in Korea in the early 2000s and applied it to semiconductor/display lines and led the wireless power charging technology in various fields, such as developing KAIST On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEV) and commercializing the world's first wireless charger for 11kW electric vehicles.
Mr. Jong Seung Park (Mechanical Engineering, M.S. in 1988, Ph.D., in 1991), The President of ADD is an expert with abundant science and technology knowledge and organizational management capabilities. He is contributing greatly to national defense and security through science and technology.
Mr. Kyunghyun Cho (Computer Science, B.S., in 2009), the Professor of Computer Science and Data Science at NYU, is a world-renowned expert in Artificial Intelligence (AI), advancing the concept of 'Neural Machine Translation' in the field of natural language processing, to make great contributions to AI translation technology and related industries.
Chairman Chil-Hee Chung, the 26th Chair of KAIST Alumni Association “As each year goes by, I feel that the influence of KAIST alumni goes beyond science and technology to affect our society as a whole.” He went on to say, “This year, as it was more meaningful to extend the award to honor the international members of our Alums, we look forward to seeing more of our alumni continuing their social and academic endeavors to play an active role in the global stage in taking on the global challenges.”
The Ceremony for KAIST Distinguished Alumni and International Alumni Award Honorees will be conducted at the Annual New Year’s Event of KAIST Alumni Association for 2023 to be held on Friday, January 13th, at the Grand InterContinental Seoul Parnas.
2023.01.12 View 16958 -
 KAIST to showcase a pack of KAIST Start-ups at CES 2023
- KAIST is to run an Exclusive Booth at the Venetian Expo (Hall G) in Eureka Park, at CES 2023, to be held in Las Vegas from Thursday, January 5th through Sunday, the 8th.
- Twelve businesses recently put together by KAIST faculty, alumni, and the start-ups given legal usage of KAIST technologies will be showcased.
- Out of the participating start-ups, the products by Fluiz and Hills Robotics were selected as the “CES Innovation Award 2023 Honoree”, scoring top in their respective categories.
On January 3, KAIST announced that there will be a KAIST booth at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2023, the most influential tech event in the world, to be held in Las Vegas from January 3 to 8.
At this exclusive corner, KAIST will introduce the technologies of KAIST start-ups over the exhibition period.
KAIST first started holding its exclusive booth in CES 2019 with five start-up businesses, following up at CES 2020 with 12 start-ups and at CES 2022 with 10 start-ups. At CES 2023, which would be KAIST’s fourth conference, KAIST will be accompanying 12 businesses including start-ups by the faculty members, alumni, and technology transfer companies that just began their businesses with technologies from their research findings that stands a head above others.
To maximize the publicity opportunity, KAIST will support each company’s marketing strategies through cooperation with the Korea International Trade Association (KITA), and provide an opportunity for the school and each startup to create global identity and exhibit the excellence of their technologies at the convention.
The following companies will be at the KAIST Booth in Eureka Park:
The twelve startups mentioned above aim to achieve global technology commecialization in their respective fields of expertise spanning from eXtended Reality (XR) and gaming, to AI and robotics, vehicle and transport, mobile platform, smart city, autonomous driving, healthcare, internet of thing (IoT), through joint research and development, technology transfer and investment attraction from world’s leading institutions and enterprises.
In particular, Fluiz and Hills Robotics won the CES Innovation Award as 2023 Honorees and is expected to attain greater achievements in the future.
A staff member from the KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation said, “The KAIST Showcase for CES 2023 has prepared a new pitching space for each of the companies for their own IR efforts, and we hope that KAIST startups will actively and effectively market their products and technologies while they are at the convention. We hope it will help them utilize their time here to establish their name in presence here which will eventually serve as a good foothold for them and their predecessors to further global commercialization goals.”
2023.01.04 View 17608
KAIST to showcase a pack of KAIST Start-ups at CES 2023
- KAIST is to run an Exclusive Booth at the Venetian Expo (Hall G) in Eureka Park, at CES 2023, to be held in Las Vegas from Thursday, January 5th through Sunday, the 8th.
- Twelve businesses recently put together by KAIST faculty, alumni, and the start-ups given legal usage of KAIST technologies will be showcased.
- Out of the participating start-ups, the products by Fluiz and Hills Robotics were selected as the “CES Innovation Award 2023 Honoree”, scoring top in their respective categories.
On January 3, KAIST announced that there will be a KAIST booth at Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2023, the most influential tech event in the world, to be held in Las Vegas from January 3 to 8.
At this exclusive corner, KAIST will introduce the technologies of KAIST start-ups over the exhibition period.
KAIST first started holding its exclusive booth in CES 2019 with five start-up businesses, following up at CES 2020 with 12 start-ups and at CES 2022 with 10 start-ups. At CES 2023, which would be KAIST’s fourth conference, KAIST will be accompanying 12 businesses including start-ups by the faculty members, alumni, and technology transfer companies that just began their businesses with technologies from their research findings that stands a head above others.
To maximize the publicity opportunity, KAIST will support each company’s marketing strategies through cooperation with the Korea International Trade Association (KITA), and provide an opportunity for the school and each startup to create global identity and exhibit the excellence of their technologies at the convention.
The following companies will be at the KAIST Booth in Eureka Park:
The twelve startups mentioned above aim to achieve global technology commecialization in their respective fields of expertise spanning from eXtended Reality (XR) and gaming, to AI and robotics, vehicle and transport, mobile platform, smart city, autonomous driving, healthcare, internet of thing (IoT), through joint research and development, technology transfer and investment attraction from world’s leading institutions and enterprises.
In particular, Fluiz and Hills Robotics won the CES Innovation Award as 2023 Honorees and is expected to attain greater achievements in the future.
A staff member from the KAIST Institute of Technology Value Creation said, “The KAIST Showcase for CES 2023 has prepared a new pitching space for each of the companies for their own IR efforts, and we hope that KAIST startups will actively and effectively market their products and technologies while they are at the convention. We hope it will help them utilize their time here to establish their name in presence here which will eventually serve as a good foothold for them and their predecessors to further global commercialization goals.”
2023.01.04 View 17608 -
 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF)
From November 30 to December 1, 2022, the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST held the 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF) on-line and off-line, as well.
Including the globally acknowledged unicorn companies such as PsiQuantum and Moloco, eleven startups — ImpriMed, Vessel AI, Genedit, Medic Life Sciences, Bringko, Brave Turtles, Neozips, Luckmon and CUPIX — joined the fair. Among the eleven invited companies, six were founded by KAIST Alumni representatives. The invited companies sought student interns in the field of AI, biotechnology, quantum, logistics, games, advertisement, real estate, and e-commerce. In response, about 100 KAIST students with various backgrounds have shown their interest in the event through pre-reservation.
Participating companies at this fair introduced their companies and conducted recruitment and career counseling with KAIST students. Sungwon Lim, the CEO of ImpriMed and a KAIST alumni, said, “It was very meaningful to introduce ImpriMed to junior students and share my experiences that I gained while pioneering and operating startups in the United States.” To share his journey as a global startup CEO, Lim has been invited as an off-line speaker during this event.
< ImpriMed CEO, Sungwon Lim >
In addition to the recruiting sessions, the fair held information sessions offering guidelines and useful tips on seeking opportunities overseas including information on obtaining a J1 visa, applying to U.S. internships, relocating to Silicon Valley, and writing CVs, cover letters, and business emails.
Professor Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President of the International Office at KAIST, stressed, “A growing number of students at KAIST want to become a global entrepreneur, and hands-on experience gained from U.S. startups is absolutely necessary to achieve their goals.” He added, “the 2022 GSIF was one of those opportunities for KAIST students to further their dream of becoming global leaders.”
2022.12.01 View 7692
2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF)
From November 30 to December 1, 2022, the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST held the 2022 Global Startup Internship Fair (GSIF) on-line and off-line, as well.
Including the globally acknowledged unicorn companies such as PsiQuantum and Moloco, eleven startups — ImpriMed, Vessel AI, Genedit, Medic Life Sciences, Bringko, Brave Turtles, Neozips, Luckmon and CUPIX — joined the fair. Among the eleven invited companies, six were founded by KAIST Alumni representatives. The invited companies sought student interns in the field of AI, biotechnology, quantum, logistics, games, advertisement, real estate, and e-commerce. In response, about 100 KAIST students with various backgrounds have shown their interest in the event through pre-reservation.
Participating companies at this fair introduced their companies and conducted recruitment and career counseling with KAIST students. Sungwon Lim, the CEO of ImpriMed and a KAIST alumni, said, “It was very meaningful to introduce ImpriMed to junior students and share my experiences that I gained while pioneering and operating startups in the United States.” To share his journey as a global startup CEO, Lim has been invited as an off-line speaker during this event.
< ImpriMed CEO, Sungwon Lim >
In addition to the recruiting sessions, the fair held information sessions offering guidelines and useful tips on seeking opportunities overseas including information on obtaining a J1 visa, applying to U.S. internships, relocating to Silicon Valley, and writing CVs, cover letters, and business emails.
Professor Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President of the International Office at KAIST, stressed, “A growing number of students at KAIST want to become a global entrepreneur, and hands-on experience gained from U.S. startups is absolutely necessary to achieve their goals.” He added, “the 2022 GSIF was one of those opportunities for KAIST students to further their dream of becoming global leaders.”
2022.12.01 View 7692 -
 Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 15211
Yuji Roh Awarded 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship
KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh of the School of Electrical Engineering (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) was selected as a recipient of the 2022 Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship.
< KAIST PhD candidate Yuji Roh (advisor: Prof. Steven Euijong Whang) >
The Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that recognizes outstanding graduate students for their exceptional and innovative research in areas relevant to computer science and related fields. This year, 36 people from around the world received the fellowship, and Yuji Roh from KAIST EE is the only recipient from universities in Korea. Each selected fellow will receive a $10,000 scholarship and an opportunity to intern at Microsoft under the guidance of an experienced researcher.
Yuji Roh was named a fellow in the field of “Machine Learning” for her outstanding achievements in Trustworthy AI. Her research highlights include designing a state-of-the-art fair training framework using batch selection and developing novel algorithms for both fair and robust training. Her works have been presented at the top machine learning conferences ICML, ICLR, and NeurIPS among others. She also co-presented a tutorial on Trustworthy AI at the top data mining conference ACM SIGKDD. She is currently interning at the NVIDIA Research AI Algorithms Group developing large-scale real-world fair AI frameworks.
The list of fellowship recipients and the interview videos are displayed on the Microsoft webpage and Youtube.
The list of recipients: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/academic-program/phd-fellowship/2022-recipients/
Interview (Global): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T4Q-XwOOoJc
Interview (Asia): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qwq3R1XU8UE
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair batch selection framework]
[Highlighted research achievements by Yuji Roh: Fair and robust training framework]
2022.10.28 View 15211 -
 KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 12814
KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 12814 -
 Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 15402
Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 15402 -
 KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 16489
KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 16489