American+Chemical+Society
-
 Artificial Spore Production Technology Developed
The core technology needed in the development of ‘biosensors’ so crucial in diagnosing illnesses or pathogens was developed by Korean research team.
KAIST’s Professor Choi In Seung of the department of Chemistry developed the technology that allows for the production of Artificial Spore by selectively coating a live cell.
In the field of engineering the problem in developing the next generation bio sensor, the cell based sensor, was that it was difficult to keep a cell alive without division for a long time. Once a cell is taken out of the body, it will either divide or die easily.
Professor Choi’s research team mimicked the spore, which has the capability to survive harsh conditions without division, and chemically coated a live cell and artificially created a cell similar to that of a spore.
The physical and biological stabilities of the cell increased by coating an artificial shell over the yeast cell. The shell is composed with a protein similar to that of the protein that gives mussels its stickiness. In addition by controlling the thickness of the shell, the division rate of the yeast can be controlled.
Professor Choi commented that this technology will serve as the basis for the single cell based biosensor.
The research was conducted together with Professor Lee Hae Shin of KAIST department of Chemistry and Professor Jeong Taek Dong of Seoul National University’s department of Chemistry and was published as the cover paper of ‘Journal of the American Chemical Society’.
2011.04.01 View 14858
Artificial Spore Production Technology Developed
The core technology needed in the development of ‘biosensors’ so crucial in diagnosing illnesses or pathogens was developed by Korean research team.
KAIST’s Professor Choi In Seung of the department of Chemistry developed the technology that allows for the production of Artificial Spore by selectively coating a live cell.
In the field of engineering the problem in developing the next generation bio sensor, the cell based sensor, was that it was difficult to keep a cell alive without division for a long time. Once a cell is taken out of the body, it will either divide or die easily.
Professor Choi’s research team mimicked the spore, which has the capability to survive harsh conditions without division, and chemically coated a live cell and artificially created a cell similar to that of a spore.
The physical and biological stabilities of the cell increased by coating an artificial shell over the yeast cell. The shell is composed with a protein similar to that of the protein that gives mussels its stickiness. In addition by controlling the thickness of the shell, the division rate of the yeast can be controlled.
Professor Choi commented that this technology will serve as the basis for the single cell based biosensor.
The research was conducted together with Professor Lee Hae Shin of KAIST department of Chemistry and Professor Jeong Taek Dong of Seoul National University’s department of Chemistry and was published as the cover paper of ‘Journal of the American Chemical Society’.
2011.04.01 View 14858 -
 Storing Stably Hydrogen Atoms in Icy Materials Discovered
KAIST, Aug. 8, 2008 -- A KAIST research team led by Prof. Huen Lee of the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering has discovered that icy organic hydrates, which contain small cages that can trap guest molecules, can be used to create and trap hydrogen atoms at higher temperatures.
The properties and reactions of single hydrogen atoms are of great scientific interest because of their inherent quantum mechanical behavior; experimentally, they can be generated and stabilized at very low temperatures (4 K) by high-energy irradiation of solid molecular hydrogen.
The finding was reported in the journal of American Chemical Society and featured in the "Editor"s Choice" in the July 11 issue of Science as a recent research highlight.
Hydrogen is a clean and sustainable form of energy that can be used in mobile and stationary applications. Hydrogen has the potential to solve several major challenges today: depletion of fossil fuels, poor air quality, and green house gas emissions.
However, the trapping of hydrogen atoms in crystalline solid matrix has never been attempted mainly because of experimental difficulties in identifying the generated hydrogen atoms with either spectroscopic or microscopic technique.
"To overcome the barriers and limitations of the existing storage approaches, we have continuously attempted to find the new hydrogen storage media such as icy powders and other related inclusion compounds," said Prof. Lee
The discovery follows the breakthrough concept Prof. Lee"s research team proposed in Nature in 2005 to use pure ice to capture and store hydrogen molecules. At moderate temperature and pressure conditions small guest molecules are entrapped in pure ice powders to form the mixed icy hydrate materials.
"Stable existence of single hydrogen molecule/radical in icy crystalline matrices may offer significant advantages in exploring hydrogen as a quantum medium because icy hydrogen hydrates can be formed at milder conditions when compared with pure solid hydrogen, which requires the ultra low temperature of 4.2 K," said Prof. Lee.
The novel design and synthesis of ionic and radicalized icy hydrates are expected to open a new field for inclusion chemistry and ice-based science and technology. Specifically, the fact that hydrogen atoms can be stably stored in icy materials might provide versatile and practical applications to energy devices including fuel cells, ice-induced reactions, and novel energy storage process, according to the KAIST professor.
2008.08.07 View 15317
Storing Stably Hydrogen Atoms in Icy Materials Discovered
KAIST, Aug. 8, 2008 -- A KAIST research team led by Prof. Huen Lee of the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering has discovered that icy organic hydrates, which contain small cages that can trap guest molecules, can be used to create and trap hydrogen atoms at higher temperatures.
The properties and reactions of single hydrogen atoms are of great scientific interest because of their inherent quantum mechanical behavior; experimentally, they can be generated and stabilized at very low temperatures (4 K) by high-energy irradiation of solid molecular hydrogen.
The finding was reported in the journal of American Chemical Society and featured in the "Editor"s Choice" in the July 11 issue of Science as a recent research highlight.
Hydrogen is a clean and sustainable form of energy that can be used in mobile and stationary applications. Hydrogen has the potential to solve several major challenges today: depletion of fossil fuels, poor air quality, and green house gas emissions.
However, the trapping of hydrogen atoms in crystalline solid matrix has never been attempted mainly because of experimental difficulties in identifying the generated hydrogen atoms with either spectroscopic or microscopic technique.
"To overcome the barriers and limitations of the existing storage approaches, we have continuously attempted to find the new hydrogen storage media such as icy powders and other related inclusion compounds," said Prof. Lee
The discovery follows the breakthrough concept Prof. Lee"s research team proposed in Nature in 2005 to use pure ice to capture and store hydrogen molecules. At moderate temperature and pressure conditions small guest molecules are entrapped in pure ice powders to form the mixed icy hydrate materials.
"Stable existence of single hydrogen molecule/radical in icy crystalline matrices may offer significant advantages in exploring hydrogen as a quantum medium because icy hydrogen hydrates can be formed at milder conditions when compared with pure solid hydrogen, which requires the ultra low temperature of 4.2 K," said Prof. Lee.
The novel design and synthesis of ionic and radicalized icy hydrates are expected to open a new field for inclusion chemistry and ice-based science and technology. Specifically, the fact that hydrogen atoms can be stably stored in icy materials might provide versatile and practical applications to energy devices including fuel cells, ice-induced reactions, and novel energy storage process, according to the KAIST professor.
2008.08.07 View 15317 -
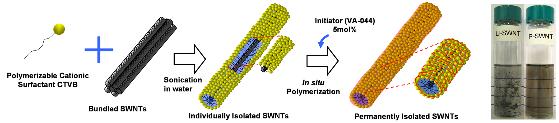 Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
A research team headed by Seong-Min Choi, a professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST, has developed technologies to stably disperse carbon nanotube particles in aqueous solutions and organic solvents, essential for industrial applications of carbon nanotube, and discovered the dispersion characteristics of carbon nanotube. The research outputs have been published by ‘Advanced materials’ (19, 929, 2007), the most distinguished journal in Material Science field, and introduced as Research Highlight at the May 7th edition of ‘Heart Cut’ by the American Chemical Society (ACS).
A number of processes for industrial applications of carbon nanotube require the dispersion of carbon nanotube in aqueous solutions or organic solvents, and thus far, surfactant particles or DNAs have been used to disperse carbon nanotube particles. However, they have shortcomings of easy destruction of dispersion. In order to overcome such shortcomings, Prof. Choi’s team produced carbon nanotube particle-dispersed aqueous solutions by using surfactant particles and then polymerized surfactant particles absorbed to the surfaces of carbon nanotube in situ to develop carbon nanotube with hydrophile and safe surfaces. The functional carbon nanotube so obtained shows features of easy dispersion in aqueous solutions and organic solvents even after being processed, such as freeze drying, therefore, is expected to significantly contribute to the development of application technologies of carbon nanotubes. Tae-Hwan Kim and Chang-Woo Doh, both doctoral students, played key roles in the researches carried out under the auspices of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) as a nuclear power R&D project, and the relevant technologies were filed for patent applications.
Figures: Carbon nanotube before polymerization (left), carbon nanotube polymerized with surfactant particles (right)
2007.05.14 View 15467
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
Research Outputs over Carbon Nanotube by Prof. Choi Selected as Research Highlight by ACS
A research team headed by Seong-Min Choi, a professor of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, KAIST, has developed technologies to stably disperse carbon nanotube particles in aqueous solutions and organic solvents, essential for industrial applications of carbon nanotube, and discovered the dispersion characteristics of carbon nanotube. The research outputs have been published by ‘Advanced materials’ (19, 929, 2007), the most distinguished journal in Material Science field, and introduced as Research Highlight at the May 7th edition of ‘Heart Cut’ by the American Chemical Society (ACS).
A number of processes for industrial applications of carbon nanotube require the dispersion of carbon nanotube in aqueous solutions or organic solvents, and thus far, surfactant particles or DNAs have been used to disperse carbon nanotube particles. However, they have shortcomings of easy destruction of dispersion. In order to overcome such shortcomings, Prof. Choi’s team produced carbon nanotube particle-dispersed aqueous solutions by using surfactant particles and then polymerized surfactant particles absorbed to the surfaces of carbon nanotube in situ to develop carbon nanotube with hydrophile and safe surfaces. The functional carbon nanotube so obtained shows features of easy dispersion in aqueous solutions and organic solvents even after being processed, such as freeze drying, therefore, is expected to significantly contribute to the development of application technologies of carbon nanotubes. Tae-Hwan Kim and Chang-Woo Doh, both doctoral students, played key roles in the researches carried out under the auspices of the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) as a nuclear power R&D project, and the relevant technologies were filed for patent applications.
Figures: Carbon nanotube before polymerization (left), carbon nanotube polymerized with surfactant particles (right)
2007.05.14 View 15467