bio
-
 KAIST-UCSD researchers build an enzyme discovering AI
- A joint research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Bernhard Palsson of UCSD developed ‘DeepECtransformer’, an artificial intelligence that can predict Enzyme Commission (EC) number of proteins.
- The AI is tasked to discover new enzymes that have not been discovered yet, which would allow prediction for a total of 5,360 types of Enzyme Commission (EC) numbers
- It is expected to be used in the development of microbial cell factories that produce environmentally friendly chemicals as a core technology for analyzing the metabolic network of a genome.
While E. coli is one of the most studied organisms, the function of 30% of proteins that make up E. coli has not yet been clearly revealed. For this, an artificial intelligence was used to discover 464 types of enzymes from the proteins that were unknown, and the researchers went on to verify the predictions of 3 types of proteins were successfully identified through in vitro enzyme assay.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that a joint research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jong An Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Dr. Charles J. Norsigian and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Bioengineering at UCSD has developed DeepECtransformer, an artificial intelligence that can predict the enzyme functions from the protein sequence, and has established a prediction system by utilizing the AI to quickly and accurately identify the enzyme function.
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biological reactions, and identifying the function of each enzyme is essential to understanding the various chemical reactions that exist in living organisms and the metabolic characteristics of those organisms. Enzyme Commission (EC) number is an enzyme function classification system designed by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and in order to understand the metabolic characteristics of various organisms, it is necessary to develop a technology that can quickly analyze enzymes and EC numbers of the enzymes present in the genome.
Various methodologies based on deep learning have been developed to analyze the features of biological sequences, including protein function prediction, but most of them have a problem of a black box, where the inference process of AI cannot be interpreted. Various prediction systems that utilize AI for enzyme function prediction have also been reported, but they do not solve this black box problem, or cannot interpret the reasoning process in fine-grained level (e.g., the level of amino acid residues in the enzyme sequence).
The joint team developed DeepECtransformer, an AI that utilizes deep learning and a protein homology analysis module to predict the enzyme function of a given protein sequence. To better understand the features of protein sequences, the transformer architecture, which is commonly used in natural language processing, was additionally used to extract important features about enzyme functions in the context of the entire protein sequence, which enabled the team to accurately predict the EC number of the enzyme. The developed DeepECtransformer can predict a total of 5360 EC numbers.
The joint team further analyzed the transformer architecture to understand the inference process of DeepECtransformer, and found that in the inference process, the AI utilizes information on catalytic active sites and/or the cofactor binding sites which are important for enzyme function. By analyzing the black box of DeepECtransformer, it was confirmed that the AI was able to identify the features that are important for enzyme function on its own during the learning process.
"By utilizing the prediction system we developed, we were able to predict the functions of enzymes that had not yet been identified and verify them experimentally," said Gi Bae Kim, the first author of the paper. "By using DeepECtransformer to identify previously unknown enzymes in living organisms, we will be able to more accurately analyze various facets involved in the metabolic processes of organisms, such as the enzymes needed to biosynthesize various useful compounds or the enzymes needed to biodegrade plastics." he added.
"DeepECtransformer, which quickly and accurately predicts enzyme functions, is a key technology in functional genomics, enabling us to analyze the function of entire enzymes at the systems level," said Professor Sang Yup Lee. He added, “We will be able to use it to develop eco-friendly microbial factories based on comprehensive genome-scale metabolic models, potentially minimizing missing information of metabolism.”
The joint team’s work on DeepECtransformer is described in the paper titled "Functional annotation of enzyme-encoding genes using deep learning with transformer layers" written by Gi Bae Kim, Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST and their colleagues. The paper was published via peer-review on the 14th of November on “Nature Communications”.
This research was conducted with the support by “the Development of next-generation biorefinery platform technologies for leading bio-based chemicals industry project (2022M3J5A1056072)” and by “Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (2022M3J5A1056117)” from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST).
< Figure 1. The structure of DeepECtransformer's artificial neural network >
2023.11.24 View 6631
KAIST-UCSD researchers build an enzyme discovering AI
- A joint research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Bernhard Palsson of UCSD developed ‘DeepECtransformer’, an artificial intelligence that can predict Enzyme Commission (EC) number of proteins.
- The AI is tasked to discover new enzymes that have not been discovered yet, which would allow prediction for a total of 5,360 types of Enzyme Commission (EC) numbers
- It is expected to be used in the development of microbial cell factories that produce environmentally friendly chemicals as a core technology for analyzing the metabolic network of a genome.
While E. coli is one of the most studied organisms, the function of 30% of proteins that make up E. coli has not yet been clearly revealed. For this, an artificial intelligence was used to discover 464 types of enzymes from the proteins that were unknown, and the researchers went on to verify the predictions of 3 types of proteins were successfully identified through in vitro enzyme assay.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that a joint research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jong An Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, and Dr. Charles J. Norsigian and Professor Bernhard O. Palsson of the Department of Bioengineering at UCSD has developed DeepECtransformer, an artificial intelligence that can predict the enzyme functions from the protein sequence, and has established a prediction system by utilizing the AI to quickly and accurately identify the enzyme function.
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biological reactions, and identifying the function of each enzyme is essential to understanding the various chemical reactions that exist in living organisms and the metabolic characteristics of those organisms. Enzyme Commission (EC) number is an enzyme function classification system designed by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and in order to understand the metabolic characteristics of various organisms, it is necessary to develop a technology that can quickly analyze enzymes and EC numbers of the enzymes present in the genome.
Various methodologies based on deep learning have been developed to analyze the features of biological sequences, including protein function prediction, but most of them have a problem of a black box, where the inference process of AI cannot be interpreted. Various prediction systems that utilize AI for enzyme function prediction have also been reported, but they do not solve this black box problem, or cannot interpret the reasoning process in fine-grained level (e.g., the level of amino acid residues in the enzyme sequence).
The joint team developed DeepECtransformer, an AI that utilizes deep learning and a protein homology analysis module to predict the enzyme function of a given protein sequence. To better understand the features of protein sequences, the transformer architecture, which is commonly used in natural language processing, was additionally used to extract important features about enzyme functions in the context of the entire protein sequence, which enabled the team to accurately predict the EC number of the enzyme. The developed DeepECtransformer can predict a total of 5360 EC numbers.
The joint team further analyzed the transformer architecture to understand the inference process of DeepECtransformer, and found that in the inference process, the AI utilizes information on catalytic active sites and/or the cofactor binding sites which are important for enzyme function. By analyzing the black box of DeepECtransformer, it was confirmed that the AI was able to identify the features that are important for enzyme function on its own during the learning process.
"By utilizing the prediction system we developed, we were able to predict the functions of enzymes that had not yet been identified and verify them experimentally," said Gi Bae Kim, the first author of the paper. "By using DeepECtransformer to identify previously unknown enzymes in living organisms, we will be able to more accurately analyze various facets involved in the metabolic processes of organisms, such as the enzymes needed to biosynthesize various useful compounds or the enzymes needed to biodegrade plastics." he added.
"DeepECtransformer, which quickly and accurately predicts enzyme functions, is a key technology in functional genomics, enabling us to analyze the function of entire enzymes at the systems level," said Professor Sang Yup Lee. He added, “We will be able to use it to develop eco-friendly microbial factories based on comprehensive genome-scale metabolic models, potentially minimizing missing information of metabolism.”
The joint team’s work on DeepECtransformer is described in the paper titled "Functional annotation of enzyme-encoding genes using deep learning with transformer layers" written by Gi Bae Kim, Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST and their colleagues. The paper was published via peer-review on the 14th of November on “Nature Communications”.
This research was conducted with the support by “the Development of next-generation biorefinery platform technologies for leading bio-based chemicals industry project (2022M3J5A1056072)” and by “Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (2022M3J5A1056117)” from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST).
< Figure 1. The structure of DeepECtransformer's artificial neural network >
2023.11.24 View 6631 -
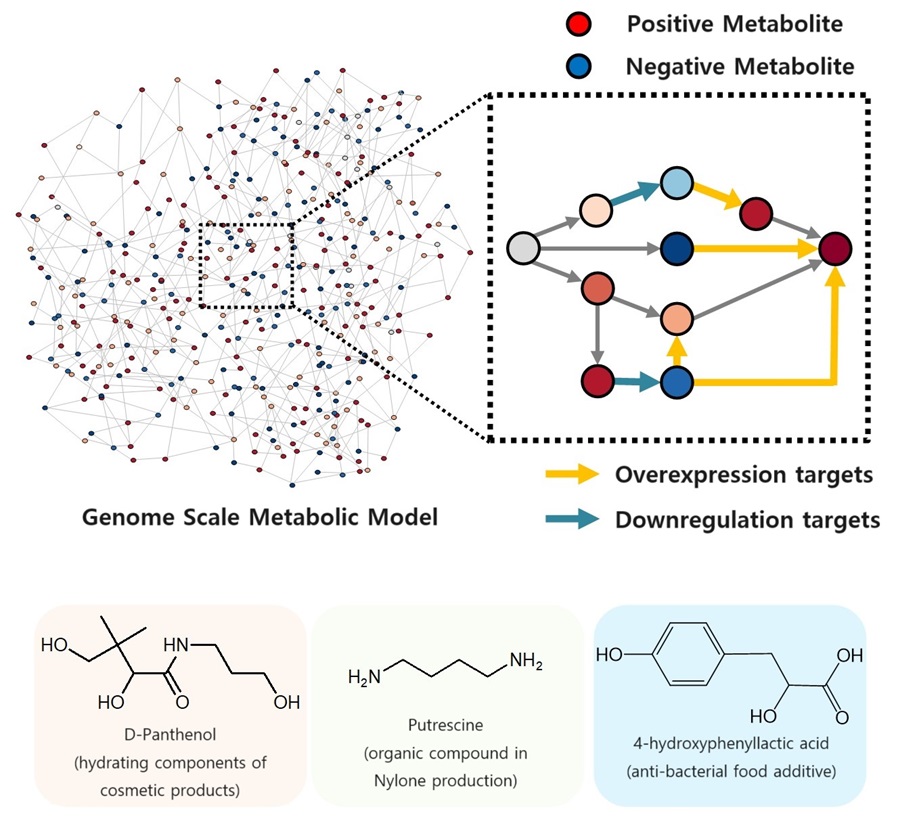 KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 8883
KAIST proposes alternatives to chemical factories through “iBridge”
- A computer simulation program “iBridge” was developed at KAIST that can put together microbial cell factories quickly and efficiently to produce cosmetics and food additives, and raw materials for nylons
- Eco-friendly and sustainable fermentation process to establish an alternative to chemical plants
As climate change and environmental concerns intensify, sustainable microbial cell factories garner significant attention as candidates to replace chemical plants. To develop microorganisms to be used in the microbial cell factories, it is crucial to modify their metabolic processes to induce efficient target chemical production by modulating its gene expressions. Yet, the challenge persists in determining which gene expressions to amplify and suppress, and the experimental verification of these modification targets is a time- and resource-intensive process even for experts. The challenges were addressed by a team of researchers at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
It was announced on the 9th by the school that a method for building a microbial factory at low cost, quickly and efficiently, was presented by a novel computer simulation program developed by the team under Professor Lee’s guidance, which is named “iBridge”. This innovative system is designed to predict gene targets to either overexpress or downregulate in the goal of producing a desired compound to enable the cost-effective and efficient construction of microbial cell factories specifically tailored for producing the chemical compound in demand from renewable biomass.
Systems metabolic engineering is a field of research and engineering pioneered by KAIST’s Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee that seeks to produce valuable compounds in industrial demands using microorganisms that are re-configured by a combination of methods including, but not limited to, metabolic engineering, synthetic biology, systems biology, and fermentation engineering.
In order to improve microorganisms’ capability to produce useful compounds, it is essential to delete, suppress, or overexpress microbial genes. However, it is difficult even for the experts to identify the gene targets to modify without experimental confirmations for each of them, which can take up immeasurable amount of time and resources.
The newly developed iBridge identifies positive and negative metabolites within cells, which exert positive and/or negative impact on formation of the products, by calculating the sum of covariances of their outgoing (consuming) reaction fluxes for a target chemical. Subsequently, it pinpoints "bridge" reactions responsible for converting negative metabolites into positive ones as candidates for overexpression, while identifying the opposites as targets for downregulation.
The research team successfully utilized the iBridge simulation to establish E. coli microbial cell factories each capable of producing three of the compounds that are in high demands at a production capacity that has not been reported around the world. They developed E. coli strains that can each produce panthenol, a moisturizing agent found in many cosmetics, putrescine, which is one of the key components in nylon production, and 4-hydroxyphenyllactic acid, an anti-bacterial food additive. In addition to these three compounds, the study presents predictions for overexpression and suppression genes to construct microbial factories for 298 other industrially valuable compounds.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, emphasized the accelerated construction of various microbial factories the newly developed simulation enabled. He stated, "With the use of this simulation, multiple microbial cell factories have been established significantly faster than it would have been using the conventional methods. Microbial cell factories producing a wider range of valuable compounds can now be constructed quickly using this technology."
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "Systems metabolic engineering is a crucial technology for addressing the current climate change issues." He added, "This simulation could significantly expedite the transition from resorting to conventional chemical factories to utilizing environmentally friendly microbial factories."
< Figure. Conceptual diagram of the flow of iBridge simulation >
The team’s work on iBridge is described in a paper titled "Genome-Wide Identification of Overexpression and Downregulation Gene Targets Based on the Sum of Covariances of the Outgoing Reaction Fluxes" written by Dr. Won Jun Kim, and Dr. Youngjoon Lee of the Bioprocess Research Center and Professors Hyun Uk Kim and Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of KAIST. The paper was published via peer-review on the 6th of November on “Cell Systems” by Cell Press.
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) and Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic using Microbial Cell Factories Project (Project Leader: Research Professor So Young Choi, KAIST) of the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.11.09 View 8883 -
 A KAIST Research Team Produces Eco-Friendly Nylon with Engineered Bacterium
With worsening climate change and environmental issues, in recent years, there has been increased interest in the eco-friendly production of polymers like nylon.
On August 10, Dr. Taehee Han from a KAIST research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the successful development of a microbial strain that produces valerolactam, a monomer of nylon-5.
Valerolactam is an important monomer that constitutes nylon-5 and nylon-6,5. Nylon is the oldest synthetic polymer, and nylon-5 is one of its derivatives composed of monomers with five carbons, while nylon-5,6 is composed of two types of monomers with either five or six carbons. They not only have excellent processability, but are also light and tough, which allows them to be applied in a wide range of industrial sectors including clothing, badminton rackets, fishing nets, tents, and gear parts. Monomers are materials that can be built into polymers, and synthetic processes are what connects them into a polymer.
The chemical production of valerolactam, however, is based on petrochemistry, where extreme reaction conditions are required and toxic waste is produced. To solve these problems, efforts are being made to develop environmentally friendly and highly efficient microbial cell factories for lactam production. Systems metabolic engineering, a key strategy for effective microbial strain development, is a research field pioneered by Professor Sang Yup Lee.
Professor Lee’s team used metabolic engineering, a technique for manipulating microbial metabolic pathways, to construct a synthetic metabolic pathway for valerolactam production in Corynebacteriam glutamicum, a bacterium commonly used for amino acid production. With this, they successfully developed a microbial strain that utilizes biomass-derived glucose as a carbon source to produce high-value valerolactam.
In 2017, the team suggested a novel method that metabolically manipulates Escherichia coli to produce valerolactam. However, there were several limitations at the time including low producibility and the generation of harmful byproducts.
< Figure 1. Schematic graphical representation of the development of microorganisms that produce valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer >
In this research, the team improved valerolactam producibility and incorporated an additional systems metabolic strategy to the developed microbial strain while eliminating the harmful byproducts. By removing the gene involved in the production of the main byproduct and through gene screening, the team successfully converted 5-aminovaleric acid, a byproduct and a precursor, into valerolactam.
Furthermore, by employing a strategy where the 5-aminovaleric acid-converting gene is inserted multiple times into the genome, the team strengthened the metabolic flux for valerolactam production. As a result, they reached a world-record concentration of 76.1 g/L, which is 6.17 times greater than what was previously reported.
This study was published in Metabolic Engineering on July 12, under the title, “Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the high-level production of valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer”.
Dr. Taehee Han, the first author of the paper, said, “The significance of this research lies in our development of an environmentally friendly technology that efficiently produces monomer lactam for nylon production using microorganisms.” She added, “Through this technology, we will be able to take a step forward in replacing the petrochemical industry with a microorganism-based biopolymer industry.”
This work was supported by the “Development of Next-Generation Biofinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project” funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.08.24 View 6826
A KAIST Research Team Produces Eco-Friendly Nylon with Engineered Bacterium
With worsening climate change and environmental issues, in recent years, there has been increased interest in the eco-friendly production of polymers like nylon.
On August 10, Dr. Taehee Han from a KAIST research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering revealed the successful development of a microbial strain that produces valerolactam, a monomer of nylon-5.
Valerolactam is an important monomer that constitutes nylon-5 and nylon-6,5. Nylon is the oldest synthetic polymer, and nylon-5 is one of its derivatives composed of monomers with five carbons, while nylon-5,6 is composed of two types of monomers with either five or six carbons. They not only have excellent processability, but are also light and tough, which allows them to be applied in a wide range of industrial sectors including clothing, badminton rackets, fishing nets, tents, and gear parts. Monomers are materials that can be built into polymers, and synthetic processes are what connects them into a polymer.
The chemical production of valerolactam, however, is based on petrochemistry, where extreme reaction conditions are required and toxic waste is produced. To solve these problems, efforts are being made to develop environmentally friendly and highly efficient microbial cell factories for lactam production. Systems metabolic engineering, a key strategy for effective microbial strain development, is a research field pioneered by Professor Sang Yup Lee.
Professor Lee’s team used metabolic engineering, a technique for manipulating microbial metabolic pathways, to construct a synthetic metabolic pathway for valerolactam production in Corynebacteriam glutamicum, a bacterium commonly used for amino acid production. With this, they successfully developed a microbial strain that utilizes biomass-derived glucose as a carbon source to produce high-value valerolactam.
In 2017, the team suggested a novel method that metabolically manipulates Escherichia coli to produce valerolactam. However, there were several limitations at the time including low producibility and the generation of harmful byproducts.
< Figure 1. Schematic graphical representation of the development of microorganisms that produce valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer >
In this research, the team improved valerolactam producibility and incorporated an additional systems metabolic strategy to the developed microbial strain while eliminating the harmful byproducts. By removing the gene involved in the production of the main byproduct and through gene screening, the team successfully converted 5-aminovaleric acid, a byproduct and a precursor, into valerolactam.
Furthermore, by employing a strategy where the 5-aminovaleric acid-converting gene is inserted multiple times into the genome, the team strengthened the metabolic flux for valerolactam production. As a result, they reached a world-record concentration of 76.1 g/L, which is 6.17 times greater than what was previously reported.
This study was published in Metabolic Engineering on July 12, under the title, “Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the high-level production of valerolactam, a nylon-5 monomer”.
Dr. Taehee Han, the first author of the paper, said, “The significance of this research lies in our development of an environmentally friendly technology that efficiently produces monomer lactam for nylon production using microorganisms.” She added, “Through this technology, we will be able to take a step forward in replacing the petrochemical industry with a microorganism-based biopolymer industry.”
This work was supported by the “Development of Next-Generation Biofinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project” funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.08.24 View 6826 -
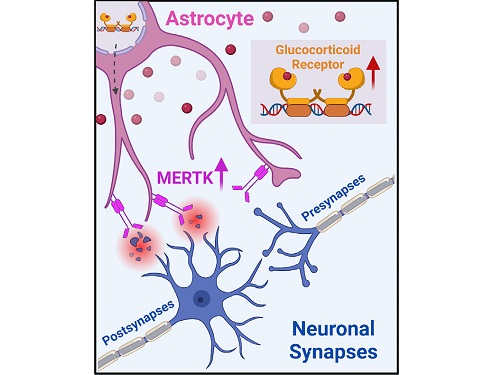 A KAIST research team identifies a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse
Childhood neglect and/or abuse can induce extreme stress that significantly changes neural networks and functions during growth. This can lead to mental illnesses, including depression and schizophrenia, but the exact mechanism and means to control it were yet to be discovered.
On August 1, a KAIST research team led by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences announced the identification of excessive synapse removal mediated by astrocytes as the cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse trauma. Their research was published in Immunity, a top international journal in the field of immunology.
The research team discovered that the excessive astrocyte-mediated removal of excitatory synapses in the brain in response to stress hormones is a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood neglect and abuse. Clinical data have previously shown that high levels of stress can lead to various mental diseases, but the exact mechanism has been unknown. The results of this research therefore are expected to be widely applied to the prevention and treatment of such diseases.
The research team clinically screened an FDA-approved drug to uncover the mechanism that regulates the phagocytotic role of astrocytes, in which they capture external substances and eliminate them. As a result, the team found that synthetic glucocorticoids, namely stress hormones, enhanced astrocyte-mediated phagocytosis to an abnormal level. Glucocorticoids play essential roles in processes that maintain life, such as carbohydrate metabolism and anti-inflammation, but are also secreted in response to external stimuli such as stress, allowing the body to respond appropriately. However, excessive and long-term exposure to glucocorticoids caused by chronic stress can lead to various mental diseases including depression, cognitive disorders, and anxiety.
< Figure 1. Results of screening for compounds that increase astrocyte phagocytosis
(A) Discovered that synthetic glucocorticoid (stress hormone) increases the phagocytosis of astrocytes through screening of FDA-approved clinical compounds. (B-C) When treated with stress hormones, the phagocytosis of astrocytes is greatly increased, but this phenomenon is strongly suppressed by the GR antagonist (Mifepristone). CORT: corticosterone (stress hormone), Eplerenone: mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist, Mifepristone: glucocorticoid receptor (GR) antagonist >
To understand the changes in astrocyte functions caused by childhood stress, the research team used mice models with early social deprivation, and discovered that stress hormones bind to the glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) of astrocytes. This significantly increased the expression of Mer tyrosine kinase (MERK), which plays an essential role in astrocyte phagocytosis. Surprisingly, out of the various neurons in the cerebral cortex, astrocytes would eliminate only the excitatory synapses of specific neurons. The team found that this builds abnormal neural networks, which can lead to complex behavioral abnormalities such as social deficiencies and depression in adulthood.
The team also observed that microglia, which also play an important role in cerebral immunity, did not contribute to synapse removal in the mice models with early social deprivation. This confirms that the response to stress hormones during childhood is specifically astrocyte-mediated.
To find out whether these results are also applicable in humans, the research team used a brain organoid grown from human-induced pluripotent stem cells to observe human responses to stress hormones. The team observed that the stress hormones induced astrocyte GRs and phagocyte activation in the human brain organoid as well, and confirmed that the astrocytes subsequently eliminated excessive amounts of excitatory synapses. By showing that mice and humans both showed the same synapse control mechanism in response to stress, the team suggested that this discovery is applicable to mental disorders in humans.
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the study published in Immunity. Excessive stress hormone secretion in childhood increases the expression of the MERTK phagocytic receptor through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) of astrocytes, resulting in excessive elimination of excitatory synapses. Excessive synaptic elimination by astrocytes during brain development causes permanent damage to brain circuits, resulting in abnormal neural activity in the adult brain and psychiatric behaviors such as depression and anti-social tendencies. >
Prof. Won-Suk Chung said, “Until now, we did not know the exact mechanism for how childhood stress caused brain diseases. This research was the first to show that the excessive phagocytosis of astrocytes could be an important cause of such diseases.” He added, “In the future, controlling the immune response of astrocytes will be used as a fundamental target for understanding and treating brain diseases.”
This research, written by co-first authors Youkyeong Byun (Ph.D. candidate) and Nam-Shik Kim (post-doctoral associate) from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, was published in the internationally renowned journal Immunity, a sister magazine of Cell and one of the best journal in the field of immunology, on July 31 under the title "Stress induces behavioral abnormalities by increasing expression of phagocytic receptor MERTK in astrocytes to promote synapse phagocytosis."
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea grant, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC).
2023.08.04 View 8335
A KAIST research team identifies a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse
Childhood neglect and/or abuse can induce extreme stress that significantly changes neural networks and functions during growth. This can lead to mental illnesses, including depression and schizophrenia, but the exact mechanism and means to control it were yet to be discovered.
On August 1, a KAIST research team led by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences announced the identification of excessive synapse removal mediated by astrocytes as the cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse trauma. Their research was published in Immunity, a top international journal in the field of immunology.
The research team discovered that the excessive astrocyte-mediated removal of excitatory synapses in the brain in response to stress hormones is a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood neglect and abuse. Clinical data have previously shown that high levels of stress can lead to various mental diseases, but the exact mechanism has been unknown. The results of this research therefore are expected to be widely applied to the prevention and treatment of such diseases.
The research team clinically screened an FDA-approved drug to uncover the mechanism that regulates the phagocytotic role of astrocytes, in which they capture external substances and eliminate them. As a result, the team found that synthetic glucocorticoids, namely stress hormones, enhanced astrocyte-mediated phagocytosis to an abnormal level. Glucocorticoids play essential roles in processes that maintain life, such as carbohydrate metabolism and anti-inflammation, but are also secreted in response to external stimuli such as stress, allowing the body to respond appropriately. However, excessive and long-term exposure to glucocorticoids caused by chronic stress can lead to various mental diseases including depression, cognitive disorders, and anxiety.
< Figure 1. Results of screening for compounds that increase astrocyte phagocytosis
(A) Discovered that synthetic glucocorticoid (stress hormone) increases the phagocytosis of astrocytes through screening of FDA-approved clinical compounds. (B-C) When treated with stress hormones, the phagocytosis of astrocytes is greatly increased, but this phenomenon is strongly suppressed by the GR antagonist (Mifepristone). CORT: corticosterone (stress hormone), Eplerenone: mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist, Mifepristone: glucocorticoid receptor (GR) antagonist >
To understand the changes in astrocyte functions caused by childhood stress, the research team used mice models with early social deprivation, and discovered that stress hormones bind to the glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) of astrocytes. This significantly increased the expression of Mer tyrosine kinase (MERK), which plays an essential role in astrocyte phagocytosis. Surprisingly, out of the various neurons in the cerebral cortex, astrocytes would eliminate only the excitatory synapses of specific neurons. The team found that this builds abnormal neural networks, which can lead to complex behavioral abnormalities such as social deficiencies and depression in adulthood.
The team also observed that microglia, which also play an important role in cerebral immunity, did not contribute to synapse removal in the mice models with early social deprivation. This confirms that the response to stress hormones during childhood is specifically astrocyte-mediated.
To find out whether these results are also applicable in humans, the research team used a brain organoid grown from human-induced pluripotent stem cells to observe human responses to stress hormones. The team observed that the stress hormones induced astrocyte GRs and phagocyte activation in the human brain organoid as well, and confirmed that the astrocytes subsequently eliminated excessive amounts of excitatory synapses. By showing that mice and humans both showed the same synapse control mechanism in response to stress, the team suggested that this discovery is applicable to mental disorders in humans.
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the study published in Immunity. Excessive stress hormone secretion in childhood increases the expression of the MERTK phagocytic receptor through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) of astrocytes, resulting in excessive elimination of excitatory synapses. Excessive synaptic elimination by astrocytes during brain development causes permanent damage to brain circuits, resulting in abnormal neural activity in the adult brain and psychiatric behaviors such as depression and anti-social tendencies. >
Prof. Won-Suk Chung said, “Until now, we did not know the exact mechanism for how childhood stress caused brain diseases. This research was the first to show that the excessive phagocytosis of astrocytes could be an important cause of such diseases.” He added, “In the future, controlling the immune response of astrocytes will be used as a fundamental target for understanding and treating brain diseases.”
This research, written by co-first authors Youkyeong Byun (Ph.D. candidate) and Nam-Shik Kim (post-doctoral associate) from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, was published in the internationally renowned journal Immunity, a sister magazine of Cell and one of the best journal in the field of immunology, on July 31 under the title "Stress induces behavioral abnormalities by increasing expression of phagocytic receptor MERTK in astrocytes to promote synapse phagocytosis."
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea grant, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC).
2023.08.04 View 8335 -
 KAIST presents a microbial cell factory as a source of eco-friendly food and cosmetic coloring
Despite decades of global population growth, global food crisis seems to be at hand yet again because the food productivity is cut severely due to prolonged presence of abnormal weather from intensifying climate change and global food supply chain is deteriorated due to international conflicts such as wars exacerbating food shortages and nutritional inequality around the globe. At the same time, however, as awareness of the environment and sustainability rises, an increase in demand for more eco-friendly and high-quality food and beauty products is being observed not without a sense of irony. At a time like this, microorganisms are attracting attention as a key that can handle this couple of seemingly distant problems.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that Kyeong Rok Choi, a research professor of the Bioprocess Research Center and Sang Yup Lee, a Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled “Metabolic Engineering of Microorganisms for Food and Cosmetics Production” upon invitation by “Nature Reviews Bioengineering” to be published online published by Nature after peer review.
※ Paper title: Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms for food and cosmetics production
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
Systems metabolic engineering is a research field founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of KAIST to more effectively develop microbial cell factories, the core factor of the next-generation bio industry to replace the existing chemical industry that relies heavily on petroleum. By applying a systemic metabolic engineering strategy, the researchers have developed a number of high-performance microbial cell factories that produce a variety of food and cosmetic compounds including natural substances like heme and zinc protoporphyrin IX compounds which can improve the flavor and color of synthetic meat, lycopene and β-carotene which are functional natural pigments that can be widely used in food and cosmetics, and methyl anthranilate, a grape-derived compound widely used to impart grape flavor in food and beverage manufacturing.
In this paper written upon invitation by Nature, the research team covered remarkable cases of microbial cell factory that can produce amino acids, proteins, fats and fatty acids, vitamins, flavors, pigments, alcohols, functional compounds and other food additives used in various foods and cosmetics and the companies that have successfully commercialized these microbial-derived materials Furthermore, the paper organized and presents systems metabolic engineering strategies that can spur the development of industrial microbial cell factories that can produce more diverse food and cosmetic compounds in an eco-friendly way with economic feasibility.
< Figure 1. Examples of production of food and cosmetic compounds using microbial cell factories >
For example, by producing proteins or amino acids with high nutritional value through non-edible biomass used as animal feed or fertilizer through the microbial fermentation process, it will contribute to the increase in production and stable supply of food around the world. Furthermore, by contributing to developing more viable alternative meat, further reducing dependence on animal protein, it can also contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and environmental pollution generated through livestock breeding or fish farming.
In addition, vanillin or methyl anthranilate, which give off vanilla or grape flavor, are widely added to various foods, but natural products isolated and refined from plants are low in production and high in production cost, so in most cases, petrochemicals substances derived from vanillin and methylanthranilic acid are added to food. These materials can also be produced through an eco-friendly and human-friendly method by borrowing the power of microorganisms.
Ethical and resource problems that arise in producing compounds like Calmin (cochineal pigment), a coloring added to various cosmetics and foods such as red lipstick and strawberry-flavored milk, which must be extracted from cochineal insects that live only in certain cacti. and Hyaluronic acid, which is widely consumed as a health supplement, but is only present in omega-3 fatty acids extracted from shark or fish livers, can also be resolved when they can be produced in an eco-friendly way using microorganisms.
KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “In addition to traditional fermented foods such as kimchi and yogurt, foods produced with the help of microorganisms like cocoa butter, a base ingredient for chocolate that can only be obtained from fermented cacao beans, and monosodium glutamate, a seasoning produced through microbial fermentation are already familiar to us”. “In the future, we will be able to acquire a wider variety of foods and cosmetics even more easily produced in an eco-friendly and sustainable way in our daily lives through microbial cell factories.” he added.
< Figure 2. Systems metabolic engineering strategy to improve metabolic flow in microbial cell factories >
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is engineers’ mission to make the world a better place utilizing science and technology.” and added, “Continuous advancement and active use of systems metabolic engineering will contribute greatly to easing and resolving the problems arising from both the food crisis and the climate change."
This research was carried out as a part of the “Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Control of Microbial Metabolism System Project” (Project Leader: Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST Research Professor) of the the Center for Agricultural Microorganism and Enzyme (Director Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration and the “Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project” (Project Leader: Sang Yup Lee, KAIST Distinguished Professor) of the Petroleum-Substitute Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.07.28 View 9778
KAIST presents a microbial cell factory as a source of eco-friendly food and cosmetic coloring
Despite decades of global population growth, global food crisis seems to be at hand yet again because the food productivity is cut severely due to prolonged presence of abnormal weather from intensifying climate change and global food supply chain is deteriorated due to international conflicts such as wars exacerbating food shortages and nutritional inequality around the globe. At the same time, however, as awareness of the environment and sustainability rises, an increase in demand for more eco-friendly and high-quality food and beauty products is being observed not without a sense of irony. At a time like this, microorganisms are attracting attention as a key that can handle this couple of seemingly distant problems.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that Kyeong Rok Choi, a research professor of the Bioprocess Research Center and Sang Yup Lee, a Distinguished Professor of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled “Metabolic Engineering of Microorganisms for Food and Cosmetics Production” upon invitation by “Nature Reviews Bioengineering” to be published online published by Nature after peer review.
※ Paper title: Systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms for food and cosmetics production
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
Systems metabolic engineering is a research field founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of KAIST to more effectively develop microbial cell factories, the core factor of the next-generation bio industry to replace the existing chemical industry that relies heavily on petroleum. By applying a systemic metabolic engineering strategy, the researchers have developed a number of high-performance microbial cell factories that produce a variety of food and cosmetic compounds including natural substances like heme and zinc protoporphyrin IX compounds which can improve the flavor and color of synthetic meat, lycopene and β-carotene which are functional natural pigments that can be widely used in food and cosmetics, and methyl anthranilate, a grape-derived compound widely used to impart grape flavor in food and beverage manufacturing.
In this paper written upon invitation by Nature, the research team covered remarkable cases of microbial cell factory that can produce amino acids, proteins, fats and fatty acids, vitamins, flavors, pigments, alcohols, functional compounds and other food additives used in various foods and cosmetics and the companies that have successfully commercialized these microbial-derived materials Furthermore, the paper organized and presents systems metabolic engineering strategies that can spur the development of industrial microbial cell factories that can produce more diverse food and cosmetic compounds in an eco-friendly way with economic feasibility.
< Figure 1. Examples of production of food and cosmetic compounds using microbial cell factories >
For example, by producing proteins or amino acids with high nutritional value through non-edible biomass used as animal feed or fertilizer through the microbial fermentation process, it will contribute to the increase in production and stable supply of food around the world. Furthermore, by contributing to developing more viable alternative meat, further reducing dependence on animal protein, it can also contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and environmental pollution generated through livestock breeding or fish farming.
In addition, vanillin or methyl anthranilate, which give off vanilla or grape flavor, are widely added to various foods, but natural products isolated and refined from plants are low in production and high in production cost, so in most cases, petrochemicals substances derived from vanillin and methylanthranilic acid are added to food. These materials can also be produced through an eco-friendly and human-friendly method by borrowing the power of microorganisms.
Ethical and resource problems that arise in producing compounds like Calmin (cochineal pigment), a coloring added to various cosmetics and foods such as red lipstick and strawberry-flavored milk, which must be extracted from cochineal insects that live only in certain cacti. and Hyaluronic acid, which is widely consumed as a health supplement, but is only present in omega-3 fatty acids extracted from shark or fish livers, can also be resolved when they can be produced in an eco-friendly way using microorganisms.
KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “In addition to traditional fermented foods such as kimchi and yogurt, foods produced with the help of microorganisms like cocoa butter, a base ingredient for chocolate that can only be obtained from fermented cacao beans, and monosodium glutamate, a seasoning produced through microbial fermentation are already familiar to us”. “In the future, we will be able to acquire a wider variety of foods and cosmetics even more easily produced in an eco-friendly and sustainable way in our daily lives through microbial cell factories.” he added.
< Figure 2. Systems metabolic engineering strategy to improve metabolic flow in microbial cell factories >
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is engineers’ mission to make the world a better place utilizing science and technology.” and added, “Continuous advancement and active use of systems metabolic engineering will contribute greatly to easing and resolving the problems arising from both the food crisis and the climate change."
This research was carried out as a part of the “Development of Protein Production Technology from Inorganic Substances through Control of Microbial Metabolism System Project” (Project Leader: Kyeong Rok Choi, KAIST Research Professor) of the the Center for Agricultural Microorganism and Enzyme (Director Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration and the “Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project” (Project Leader: Sang Yup Lee, KAIST Distinguished Professor) of the Petroleum-Substitute Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2023.07.28 View 9778 -
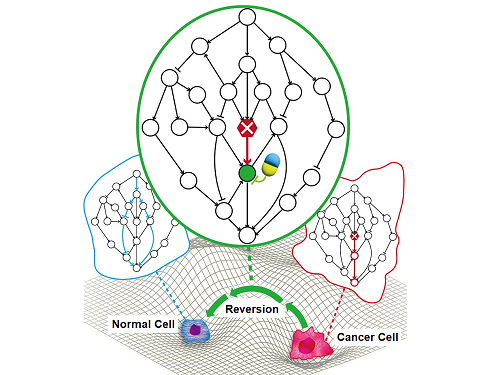 A KAIST Research Team Identifies a Cancer Reversion Mechanism
Despite decades of intensive cancer research by numerous biomedical scientists, cancer still holds its place as the number one cause of death in Korea. The fundamental reason behind the limitations of current cancer treatment methods is the fact that they all aim to completely destroy cancer cells, which eventually allows the cancer cells to acquire immunity. In other words, recurrences and side-effects caused by the destruction of healthy cells are inevitable. To this end, some have suggested anticancer treatment methods based on cancer reversion, which can revert cancer cells back to normal or near-normal cells under certain conditions. However, the practical development of this idea has not yet been attempted.
On June 8, a KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported to have successfully identified the fundamental principle of a process that can revert cancer cells back to normal cells without killing the cells.
Professor Cho’s team focused on the fact that unlike normal cells, which react according to external stimuli, cancer cells tend to ignore such stimuli and only undergo uncontrolled cell division. Through computer simulation analysis, the team discovered that the input-output (I/O) relationships that were distorted by genetic mutations could be reverted back to normal I/O relationships under certain conditions. The team then demonstrated through molecular cell experiments that such I/O relationship recovery also occurred in real cancer cells.
The results of this study, written by Dr. Jae Il Joo and Dr. Hwa-Jeong Park, were published in Wiley’s Advanced Science online on June 2 under the title, "Normalizing input-output relationships of cancer networks for reversion therapy."
< Image 1. Input-output (I/O) relationships in gene regulatory networks >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team classified genes into four types by simulation-analyzing the effect of gene mutations on the I/O relationship of gene regulatory networks. (Figure A-J) In addition, by analyzing 18 genes of the cancer-related gene regulatory network, it was confirmed that when mutations occur in more than half of the genes constituting each network, reversibility is possible through appropriate control. (Figure K)
Professor Cho’s team uncovered that the reason the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells could be reverted back to normal ones was the robustness and redundancy of intracellular gene control networks that developed over the course of evolution. In addition, they found that some genes were more promising as targets for cancer reversion than others, and showed through molecular cell experiments that controlling such genes could revert the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells back to normal ones.
< Image 2. Simulation results of restoration of bladder cancer gene regulation network and I/O relationship of bladder cancer cells. >
The research team classified the effects of gene mutations on the I/O relationship in the bladder cancer gene regulation network by simulation analysis and classified them into 4 types. (Figure A) Through this, it was found that the distorted input-output relationship between bladder cancer cell lines KU-1919 and HCT-1197 could be restored to normal. (Figure B)
< Image 3. Analysis of survival of bladder cancer patients according to reversible gene mutation and I/O recovery experiment of bladder cancer cells. >
As predicted through network simulation analysis, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team confirmed through molecular cell experiments that the response to TGF-b was normally restored when AKT and MAP3K1 were inhibited in the bladder cancer cell line KU-1919. (Figure A-G) In addition, it was confirmed that there is a difference in the survival rate of bladder cancer patients depending on the presence or absence of a reversible gene mutation. (Figure H)
The results of this research show that the reversion of real cancer cells does not happen by chance, and that it is possible to systematically explore targets that can induce this phenomenon, thereby creating the potential for the development of innovative anticancer drugs that can control such target genes.
< Image 4. Cancer cell reversibility principle >
The research team analyzed the reversibility, redundancy, and robustness of various networks and found that there was a positive correlation between them. From this, it was found that reversibility was additionally inherent in the process of evolution in which the gene regulatory network acquired redundancy and consistency.
Professor Cho said, “By uncovering the fundamental principles of a new cancer reversion treatment strategy that may overcome the unresolved limitations of existing chemotherapy, we have increased the possibility of developing new and innovative drugs that can improve both the prognosis and quality of life of cancer patients.”
< Image 5. Conceptual diagram of research results >
The research team identified the fundamental control principle of cancer cell reversibility through systems biology research. When the I/O relationship of the intracellular gene regulatory network is distorted by mutation, the distorted I/O relationship can be restored to a normal state by identifying and adjusting the reversible gene target based on the redundancy of the molecular circuit inherent in the complex network.
After Professor Cho’s team first suggested the concept of reversion treatment, they published their results for reverting colorectal cancer in January 2020, and in January 2022 they successfully re-programmed malignant breast cancer cells back into hormone-treatable ones. In January 2023, the team successfully removed the metastasis ability from lung cancer cells and reverted them back to a state that allowed improved drug reactivity. However, these results were case studies of specific types of cancer and did not reveal what common principle allowed cancer reversion across all cancer types, making this the first revelation of the general principle of cancer reversion and its evolutionary origins.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2023.06.20 View 12121
A KAIST Research Team Identifies a Cancer Reversion Mechanism
Despite decades of intensive cancer research by numerous biomedical scientists, cancer still holds its place as the number one cause of death in Korea. The fundamental reason behind the limitations of current cancer treatment methods is the fact that they all aim to completely destroy cancer cells, which eventually allows the cancer cells to acquire immunity. In other words, recurrences and side-effects caused by the destruction of healthy cells are inevitable. To this end, some have suggested anticancer treatment methods based on cancer reversion, which can revert cancer cells back to normal or near-normal cells under certain conditions. However, the practical development of this idea has not yet been attempted.
On June 8, a KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering reported to have successfully identified the fundamental principle of a process that can revert cancer cells back to normal cells without killing the cells.
Professor Cho’s team focused on the fact that unlike normal cells, which react according to external stimuli, cancer cells tend to ignore such stimuli and only undergo uncontrolled cell division. Through computer simulation analysis, the team discovered that the input-output (I/O) relationships that were distorted by genetic mutations could be reverted back to normal I/O relationships under certain conditions. The team then demonstrated through molecular cell experiments that such I/O relationship recovery also occurred in real cancer cells.
The results of this study, written by Dr. Jae Il Joo and Dr. Hwa-Jeong Park, were published in Wiley’s Advanced Science online on June 2 under the title, "Normalizing input-output relationships of cancer networks for reversion therapy."
< Image 1. Input-output (I/O) relationships in gene regulatory networks >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team classified genes into four types by simulation-analyzing the effect of gene mutations on the I/O relationship of gene regulatory networks. (Figure A-J) In addition, by analyzing 18 genes of the cancer-related gene regulatory network, it was confirmed that when mutations occur in more than half of the genes constituting each network, reversibility is possible through appropriate control. (Figure K)
Professor Cho’s team uncovered that the reason the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells could be reverted back to normal ones was the robustness and redundancy of intracellular gene control networks that developed over the course of evolution. In addition, they found that some genes were more promising as targets for cancer reversion than others, and showed through molecular cell experiments that controlling such genes could revert the distorted I/O relationships of cancer cells back to normal ones.
< Image 2. Simulation results of restoration of bladder cancer gene regulation network and I/O relationship of bladder cancer cells. >
The research team classified the effects of gene mutations on the I/O relationship in the bladder cancer gene regulation network by simulation analysis and classified them into 4 types. (Figure A) Through this, it was found that the distorted input-output relationship between bladder cancer cell lines KU-1919 and HCT-1197 could be restored to normal. (Figure B)
< Image 3. Analysis of survival of bladder cancer patients according to reversible gene mutation and I/O recovery experiment of bladder cancer cells. >
As predicted through network simulation analysis, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team confirmed through molecular cell experiments that the response to TGF-b was normally restored when AKT and MAP3K1 were inhibited in the bladder cancer cell line KU-1919. (Figure A-G) In addition, it was confirmed that there is a difference in the survival rate of bladder cancer patients depending on the presence or absence of a reversible gene mutation. (Figure H)
The results of this research show that the reversion of real cancer cells does not happen by chance, and that it is possible to systematically explore targets that can induce this phenomenon, thereby creating the potential for the development of innovative anticancer drugs that can control such target genes.
< Image 4. Cancer cell reversibility principle >
The research team analyzed the reversibility, redundancy, and robustness of various networks and found that there was a positive correlation between them. From this, it was found that reversibility was additionally inherent in the process of evolution in which the gene regulatory network acquired redundancy and consistency.
Professor Cho said, “By uncovering the fundamental principles of a new cancer reversion treatment strategy that may overcome the unresolved limitations of existing chemotherapy, we have increased the possibility of developing new and innovative drugs that can improve both the prognosis and quality of life of cancer patients.”
< Image 5. Conceptual diagram of research results >
The research team identified the fundamental control principle of cancer cell reversibility through systems biology research. When the I/O relationship of the intracellular gene regulatory network is distorted by mutation, the distorted I/O relationship can be restored to a normal state by identifying and adjusting the reversible gene target based on the redundancy of the molecular circuit inherent in the complex network.
After Professor Cho’s team first suggested the concept of reversion treatment, they published their results for reverting colorectal cancer in January 2020, and in January 2022 they successfully re-programmed malignant breast cancer cells back into hormone-treatable ones. In January 2023, the team successfully removed the metastasis ability from lung cancer cells and reverted them back to a state that allowed improved drug reactivity. However, these results were case studies of specific types of cancer and did not reveal what common principle allowed cancer reversion across all cancer types, making this the first revelation of the general principle of cancer reversion and its evolutionary origins.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2023.06.20 View 12121 -
 Synthetic sRNAs to knockdown genes in medical and industrial bacteria
Bacteria are intimately involved in our daily lives. These microorganisms have been used in human history for food such as cheese, yogurt, and wine, In more recent years, through metabolic engineering, microorganisms been used extensively as microbial cell factories to manufacture plastics, feed for livestock, dietary supplements, and drugs. However, in addition to these bacteria that are beneficial to human lives, pathogens such as Pneumonia, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus that cause various infectious diseases are also ubiquitously present. It is important to be able to metabolically control these beneficial industrial bacteria for high value-added chemicals production and to manipulate harmful pathogens to suppress its pathogenic traits.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed a new sRNA tool that can effectively inhibit target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The research results were published online on April 24 in Nature Communications.
※ Thesis title: Targeted and high-throughput gene knockdown in diverse bacteria using synthetic sRNAs
※ Author information : Jae Sung Cho (co-1st), Dongsoo Yang (co-1st), Cindy Pricilia Surya Prabowo (co-author), Mohammad Rifqi Ghiffary (co-author), Taehee Han (co-author), Kyeong Rok Choi (co-author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-author), Hengrui Zhou (co-author), Jae Yong Ryu (co-author), Hyun Uk Kim (co-author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author).
sRNA is an effective tool for synthesizing and regulating target genes in E. coli, but it has been difficult to apply to industrially useful Gram-positive bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis and Corynebacterium in addition to Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli.
To address this issue, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a new sRNA platform that can effectively suppress target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and positive bacteria. The research team surveyed thousands of microbial-derived sRNA systems in the microbial database, and eventually designated the sRNA system derived from 'Bacillus subtilis' that showed the highest gene knockdown efficiency, and designated it as “Broad-Host-Range sRNA”, or BHR-sRNA.
A similar well-known system is the CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) system, which is a modified CRISPR system that knocks down gene expression by suppressing the gene transcription process. However, the Cas9 protein in the CRISPRi system has a very high molecular weight, and there have been reports growth inhibition in bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system developed in this study did not affect bacterial growth while showing similar gene knockdown efficiencies to CRISPRi.
< Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration demonstrating the mechanism of syntetic sRNA b) Phylogenetic tree of the 16 Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial species tested for gene knockdown by the BHR-sRNA system. >
To validate the versatility of the BHR-sRNA system, 16 different gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria were selected and tested, where the BHR-sRNA system worked successfully in 15 of them. In addition, it was demonstrated that the gene knockdown capability was more effective than that of the existing E. coli-based sRNA system in 10 bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system proved to be a universal tool capable of effectively inhibiting gene expression in various bacteria.
In order to address the problem of antibiotic-resistant pathogens that have recently become more serious, the BHR-sRNA was demonstrated to suppress the pathogenicity by suppressing the gene producing the virulence factor. By using BHR-sRNA, biofilm formation, one of the factors resulting in antibiotic resistance, was inhibited by 73% in Staphylococcus epidermidis a pathogen that can cause hospital-acquired infections. Antibiotic resistance was also weakened by 58% in the pneumonia causing bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae. In addition, BHR-sRNA was applied to industrial bacteria to develop microbial cell factories to produce high value-added chemicals with better production performance. Notably, superior industrial strains were constructed with the aid of BHR-sRNA to produce the following chemicals: valerolactam, a raw material for polyamide polymers, methyl-anthranilate, a grape-flavor food additive, and indigoidine, a blue-toned natural dye.
The BHR-sRNA developed through this study will help expedite the commercialization of bioprocesses to produce high value-added compounds and materials such as artificial meat, jet fuel, health supplements, pharmaceuticals, and plastics. It is also anticipated that to help eradicating antibiotic-resistant pathogens in preparation for another upcoming pandemic. “In the past, we could only develop new tools for gene knockdown for each bacterium, but now we have developed a tool that works for a variety of bacteria” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project from NRF supported by the Korean MSIT.
2023.05.10 View 8657
Synthetic sRNAs to knockdown genes in medical and industrial bacteria
Bacteria are intimately involved in our daily lives. These microorganisms have been used in human history for food such as cheese, yogurt, and wine, In more recent years, through metabolic engineering, microorganisms been used extensively as microbial cell factories to manufacture plastics, feed for livestock, dietary supplements, and drugs. However, in addition to these bacteria that are beneficial to human lives, pathogens such as Pneumonia, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus that cause various infectious diseases are also ubiquitously present. It is important to be able to metabolically control these beneficial industrial bacteria for high value-added chemicals production and to manipulate harmful pathogens to suppress its pathogenic traits.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed a new sRNA tool that can effectively inhibit target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The research results were published online on April 24 in Nature Communications.
※ Thesis title: Targeted and high-throughput gene knockdown in diverse bacteria using synthetic sRNAs
※ Author information : Jae Sung Cho (co-1st), Dongsoo Yang (co-1st), Cindy Pricilia Surya Prabowo (co-author), Mohammad Rifqi Ghiffary (co-author), Taehee Han (co-author), Kyeong Rok Choi (co-author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-author), Hengrui Zhou (co-author), Jae Yong Ryu (co-author), Hyun Uk Kim (co-author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author).
sRNA is an effective tool for synthesizing and regulating target genes in E. coli, but it has been difficult to apply to industrially useful Gram-positive bacteria such as Bacillus subtilis and Corynebacterium in addition to Gram-negative bacteria such as E. coli.
To address this issue, a research team led by Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a new sRNA platform that can effectively suppress target genes in various bacteria, including both Gram-negative and positive bacteria. The research team surveyed thousands of microbial-derived sRNA systems in the microbial database, and eventually designated the sRNA system derived from 'Bacillus subtilis' that showed the highest gene knockdown efficiency, and designated it as “Broad-Host-Range sRNA”, or BHR-sRNA.
A similar well-known system is the CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) system, which is a modified CRISPR system that knocks down gene expression by suppressing the gene transcription process. However, the Cas9 protein in the CRISPRi system has a very high molecular weight, and there have been reports growth inhibition in bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system developed in this study did not affect bacterial growth while showing similar gene knockdown efficiencies to CRISPRi.
< Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration demonstrating the mechanism of syntetic sRNA b) Phylogenetic tree of the 16 Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacterial species tested for gene knockdown by the BHR-sRNA system. >
To validate the versatility of the BHR-sRNA system, 16 different gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria were selected and tested, where the BHR-sRNA system worked successfully in 15 of them. In addition, it was demonstrated that the gene knockdown capability was more effective than that of the existing E. coli-based sRNA system in 10 bacteria. The BHR-sRNA system proved to be a universal tool capable of effectively inhibiting gene expression in various bacteria.
In order to address the problem of antibiotic-resistant pathogens that have recently become more serious, the BHR-sRNA was demonstrated to suppress the pathogenicity by suppressing the gene producing the virulence factor. By using BHR-sRNA, biofilm formation, one of the factors resulting in antibiotic resistance, was inhibited by 73% in Staphylococcus epidermidis a pathogen that can cause hospital-acquired infections. Antibiotic resistance was also weakened by 58% in the pneumonia causing bacteria Klebsiella pneumoniae. In addition, BHR-sRNA was applied to industrial bacteria to develop microbial cell factories to produce high value-added chemicals with better production performance. Notably, superior industrial strains were constructed with the aid of BHR-sRNA to produce the following chemicals: valerolactam, a raw material for polyamide polymers, methyl-anthranilate, a grape-flavor food additive, and indigoidine, a blue-toned natural dye.
The BHR-sRNA developed through this study will help expedite the commercialization of bioprocesses to produce high value-added compounds and materials such as artificial meat, jet fuel, health supplements, pharmaceuticals, and plastics. It is also anticipated that to help eradicating antibiotic-resistant pathogens in preparation for another upcoming pandemic. “In the past, we could only develop new tools for gene knockdown for each bacterium, but now we have developed a tool that works for a variety of bacteria” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project from NRF supported by the Korean MSIT.
2023.05.10 View 8657 -
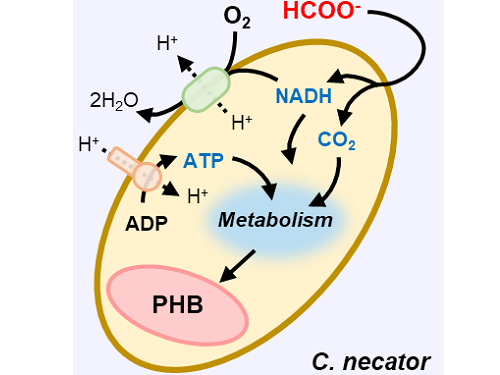 A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 12072
A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 12072 -
 KAIST research team develops clathrin assembly for targeted protein delivery to cancer cells
In order to effectively treat cancer without additional side effects, we need a way to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. Protein assemblies have been widely used for drug delivery in the field of cancer treatment, but to use them for drug delivery they must first be functionalized, meaning they must be bound to the protein that recognizes the target tumor cell and deliver a drug that kills it. However, the functionalization process of protein assemblies is very complex, inefficient, and limited to small-sized chemical drugs, which limits their real-life applicability.
On March 14, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hak-Sung Kim from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences reported the development of a clathrin assembly that can specifically deliver drugs to cancer cells.
Clathrin assemblies transport materials efficiently through endocytosis in living organisms. They are formed by the self-assembly of triskelion units, which are composed of three heavy chains bonded with three light chains. Inspired by this mechanism, the research team designed a clathrin chain to facilitate the functionalization of tumor cell recognition proteins and toxin proteins in order to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. From this, the team created a new type of clathrin assembly.
Figure 1. (Upper) Schematic diagram of the development of a new clathrin assembly that simultaneously functionalizes two types of proteins (cancer cell recognition protein and toxin protein) on heavy and light chains of clathrin in a one-pot reaction (bottom, left) Electron microscopy image of clathrin assembly: formation of an assembly with a diameter of about 28 nanometers (bottom, right) Cancer cell killing effect of CLA: CLA functionalized with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) recognition protein and toxin protein kills only the cancer cells that overexpress EGFR.
The newly developed clathrin assembly requires a one-pot reaction, meaning both the toxin and tumor-recognition proteins can be functionalized simultaneously and show high efficiency. As a result, this technique is expected to be used in a wide variety of applications in the fields of biology and medicine including drug delivery, vaccine development, and diagnosing illnesses.
In this research, an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a common tumor marker, was used as the recognition protein, allowing drug delivery only to tumor cells. The clathrin assemblies that were functionalized to recognize EGFR showed a bonding strength 900-times stronger than it normally would due to the avidity effect. Based on this finding, the research team confirmed that treatment with toxin-functionalized clathrin assembly led to effective cell death for tumor cells, while it showed no such effect on healthy cells.
This research by Dr. Hong-Sik Kim and his colleagues was published in Small volume 19, issue 8 on February 22 under the title, "Construction and Functionalization of a Clathrin Assembly for a Targeted Protein Delivery", and it was selected as the cover paper.
Figure 2. Cover Paper: This study was published in the international journal 'Small' on February 22nd, Volume 19, No. 8, and was selected as the cover paper.
First author Dr. Hong-Sik Kim said, “Clathrin is difficult to functionalize, and since it is extracted from mammals, realistic applications have been limited.” He added, “But the new clathrin assembly we designed for this research can be functionalized with two different types of proteins through a single-step reaction, and can be produced from E. coli, meaning it can become an applicable protein assembly technology for a wide range of biomedical fields.”
This research was funded by the Global Ph.D. Fellowship and the Mid-career Researcher Grant of the National Research Foundation.
2023.03.22 View 7365
KAIST research team develops clathrin assembly for targeted protein delivery to cancer cells
In order to effectively treat cancer without additional side effects, we need a way to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. Protein assemblies have been widely used for drug delivery in the field of cancer treatment, but to use them for drug delivery they must first be functionalized, meaning they must be bound to the protein that recognizes the target tumor cell and deliver a drug that kills it. However, the functionalization process of protein assemblies is very complex, inefficient, and limited to small-sized chemical drugs, which limits their real-life applicability.
On March 14, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hak-Sung Kim from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences reported the development of a clathrin assembly that can specifically deliver drugs to cancer cells.
Clathrin assemblies transport materials efficiently through endocytosis in living organisms. They are formed by the self-assembly of triskelion units, which are composed of three heavy chains bonded with three light chains. Inspired by this mechanism, the research team designed a clathrin chain to facilitate the functionalization of tumor cell recognition proteins and toxin proteins in order to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. From this, the team created a new type of clathrin assembly.
Figure 1. (Upper) Schematic diagram of the development of a new clathrin assembly that simultaneously functionalizes two types of proteins (cancer cell recognition protein and toxin protein) on heavy and light chains of clathrin in a one-pot reaction (bottom, left) Electron microscopy image of clathrin assembly: formation of an assembly with a diameter of about 28 nanometers (bottom, right) Cancer cell killing effect of CLA: CLA functionalized with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) recognition protein and toxin protein kills only the cancer cells that overexpress EGFR.
The newly developed clathrin assembly requires a one-pot reaction, meaning both the toxin and tumor-recognition proteins can be functionalized simultaneously and show high efficiency. As a result, this technique is expected to be used in a wide variety of applications in the fields of biology and medicine including drug delivery, vaccine development, and diagnosing illnesses.
In this research, an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a common tumor marker, was used as the recognition protein, allowing drug delivery only to tumor cells. The clathrin assemblies that were functionalized to recognize EGFR showed a bonding strength 900-times stronger than it normally would due to the avidity effect. Based on this finding, the research team confirmed that treatment with toxin-functionalized clathrin assembly led to effective cell death for tumor cells, while it showed no such effect on healthy cells.
This research by Dr. Hong-Sik Kim and his colleagues was published in Small volume 19, issue 8 on February 22 under the title, "Construction and Functionalization of a Clathrin Assembly for a Targeted Protein Delivery", and it was selected as the cover paper.
Figure 2. Cover Paper: This study was published in the international journal 'Small' on February 22nd, Volume 19, No. 8, and was selected as the cover paper.
First author Dr. Hong-Sik Kim said, “Clathrin is difficult to functionalize, and since it is extracted from mammals, realistic applications have been limited.” He added, “But the new clathrin assembly we designed for this research can be functionalized with two different types of proteins through a single-step reaction, and can be produced from E. coli, meaning it can become an applicable protein assembly technology for a wide range of biomedical fields.”
This research was funded by the Global Ph.D. Fellowship and the Mid-career Researcher Grant of the National Research Foundation.
2023.03.22 View 7365 -
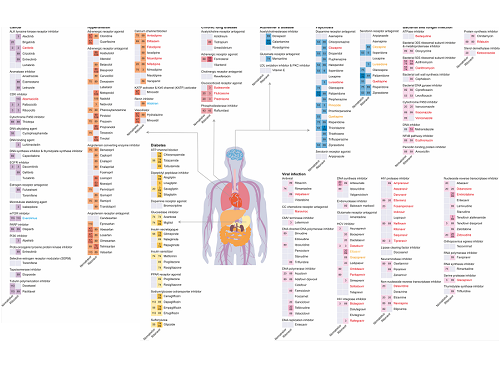 KAIST leads AI-based analysis on drug-drug interactions involving Paxlovid
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th that an advanced AI-based drug interaction prediction technology developed by the Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team in the Department of Biochemical Engineering that analyzed the interaction between the PaxlovidTM ingredients that are used as COVID-19 treatment and other prescription drugs was published as a thesis. This paper was published in the online edition of 「Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of America」 (PNAS), an internationally renowned academic journal, on the 13th of March.
* Thesis Title: Computational prediction of interactions between Paxlovid and prescription drugs (Authored by Yeji Kim (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Yong Ryu (Duksung Women's University, co-first author), Hyun Uk Kim (KAIST, co-first author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author))
In this study, the research team developed DeepDDI2, an advanced version of DeepDDI, an AI-based drug interaction prediction model they developed in 2018. DeepDDI2 is able to compute for and process a total of 113 drug-drug interaction (DDI) types, more than the 86 DDI types covered by the existing DeepDDI.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict possible interactions between the ingredients (ritonavir, nirmatrelvir) of Paxlovid*, a COVID-19 treatment, and other prescription drugs. The research team said that while among COVID-19 patients, high-risk patients with chronic diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes are likely to be taking other drugs, drug-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions for Paxlovid have not been sufficiently analyzed, yet. This study was pursued in light of seeing how continued usage of the drug may lead to serious and unwanted complications.
* Paxlovid: Paxlovid is a COVID-19 treatment developed by Pfizer, an American pharmaceutical company, and received emergency use approval (EUA) from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2021.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict how Paxrovid's components, ritonavir and nirmatrelvir, would interact with 2,248 prescription drugs. As a result of the prediction, ritonavir was predicted to interact with 1,403 prescription drugs and nirmatrelvir with 673 drugs.
Using the prediction results, the research team proposed alternative drugs with the same mechanism but low drug interaction potential for prescription drugs with high adverse drug events (ADEs). Accordingly, 124 alternative drugs that could reduce the possible adverse DDI with ritonavir and 239 alternative drugs for nirmatrelvir were identified.
Through this research achievement, it became possible to use an deep learning technology to accurately predict drug-drug interactions (DDIs), and this is expected to play an important role in the digital healthcare, precision medicine and pharmaceutical industries by providing useful information in the process of developing new drugs and making prescriptions.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "The results of this study are meaningful at times like when we would have to resort to using drugs that are developed in a hurry in the face of an urgent situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, that it is now possible to identify and take necessary actions against adverse drug reactions caused by drug-drug interactions very quickly.”
This research was carried out with the support of the KAIST New-Deal Project for COVID-19 Science and Technology and the Bio·Medical Technology Development Project supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Results of drug interaction prediction between Paxlovid ingredients and representative approved drugs using DeepDDI2
2023.03.16 View 9709
KAIST leads AI-based analysis on drug-drug interactions involving Paxlovid
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th that an advanced AI-based drug interaction prediction technology developed by the Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team in the Department of Biochemical Engineering that analyzed the interaction between the PaxlovidTM ingredients that are used as COVID-19 treatment and other prescription drugs was published as a thesis. This paper was published in the online edition of 「Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of America」 (PNAS), an internationally renowned academic journal, on the 13th of March.
* Thesis Title: Computational prediction of interactions between Paxlovid and prescription drugs (Authored by Yeji Kim (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Yong Ryu (Duksung Women's University, co-first author), Hyun Uk Kim (KAIST, co-first author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author))
In this study, the research team developed DeepDDI2, an advanced version of DeepDDI, an AI-based drug interaction prediction model they developed in 2018. DeepDDI2 is able to compute for and process a total of 113 drug-drug interaction (DDI) types, more than the 86 DDI types covered by the existing DeepDDI.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict possible interactions between the ingredients (ritonavir, nirmatrelvir) of Paxlovid*, a COVID-19 treatment, and other prescription drugs. The research team said that while among COVID-19 patients, high-risk patients with chronic diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes are likely to be taking other drugs, drug-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions for Paxlovid have not been sufficiently analyzed, yet. This study was pursued in light of seeing how continued usage of the drug may lead to serious and unwanted complications.
* Paxlovid: Paxlovid is a COVID-19 treatment developed by Pfizer, an American pharmaceutical company, and received emergency use approval (EUA) from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2021.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict how Paxrovid's components, ritonavir and nirmatrelvir, would interact with 2,248 prescription drugs. As a result of the prediction, ritonavir was predicted to interact with 1,403 prescription drugs and nirmatrelvir with 673 drugs.
Using the prediction results, the research team proposed alternative drugs with the same mechanism but low drug interaction potential for prescription drugs with high adverse drug events (ADEs). Accordingly, 124 alternative drugs that could reduce the possible adverse DDI with ritonavir and 239 alternative drugs for nirmatrelvir were identified.
Through this research achievement, it became possible to use an deep learning technology to accurately predict drug-drug interactions (DDIs), and this is expected to play an important role in the digital healthcare, precision medicine and pharmaceutical industries by providing useful information in the process of developing new drugs and making prescriptions.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "The results of this study are meaningful at times like when we would have to resort to using drugs that are developed in a hurry in the face of an urgent situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, that it is now possible to identify and take necessary actions against adverse drug reactions caused by drug-drug interactions very quickly.”
This research was carried out with the support of the KAIST New-Deal Project for COVID-19 Science and Technology and the Bio·Medical Technology Development Project supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Results of drug interaction prediction between Paxlovid ingredients and representative approved drugs using DeepDDI2
2023.03.16 View 9709 -
 The cause of disability in aged brain meningeal membranes identified
Due to the increase in average age, studies on changes in the brain following general aging process without serious brain diseases have also become an issue that requires in-depth studies. Regarding aging research, as aging progresses, ‘sugar’ accumulates in the body, and the accumulated sugar becomes a causative agent for various diseases such as aging-related inflammation and vascular disease. In the end, “surplus” sugar molecules attach to various proteins in the body and interfere with their functions.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee), a joint research team of Professor Pilnam Kim and Professor Yong Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, revealed on the 15th that it was confirmed that the function of being the “front line of defense” for the cerebrocortex of the brain meninges, the layers of membranes that surrounds the brain, is hindered when 'sugar' begins to build up on them as aging progresses.
Professor Kim's research team confirmed excessive accumulation of sugar molecules in the meninges of the elderly and also confirmed that sugar accumulation occurs mouse models in accordance with certain age levels. The meninges are thin membranes that surround the brain and exist at the boundary between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cortex and play an important role in protecting the brain. In this study, it was revealed that the dysfunction of these brain membranes caused by aging is induced by 'excess' sugar in the brain. In particular, as the meningeal membrane becomes thinner and stickier due to aging, a new paradigm has been provided for the discovery of the principle of the decrease in material exchange between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cerebral cortex.
This research was conducted by the Ph.D. candidate Hyo Min Kim and Dr. Shinheun Kim as the co-first authors to be published online on February 28th in the international journal, Aging Cell. (Paper Title: Glycation-mediated tissue-level remodeling of brain meningeal membrane by aging)
The meninges, which are in direct contact with the cerebrospinal fluid, are mainly composed of collagen, an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein, and are composed of fibroblasts, which are cells that produce this protein. The cells that come in contact with collagen proteins that are attached with sugar have a low collagen production function, while the meningeal membrane continuously thins and collapses as the expression of collagen degrading enzymes increases.
Studies on the relationship between excess sugar molecules accumulation in the brain due to continued sugar intake and the degeneration of neurons and brain diseases have been continuously conducted. However, this study was the first to identify meningeal degeneration and dysfunction caused by glucose accumulation with the focus on the meninges itself, and the results are expected to present new ideas for research into approach towards discoveries of new treatments for brain disease.
Researcher Hyomin Kim, the first author, introduced the research results as “an interesting study that identified changes in the barriers of the brain due to aging through a convergent approach, starting from the human brain and utilizing an animal model with a biomimetic meningeal model”.
Professor Pilnam Kim's research team is conducting research and development to remove sugar that accumulated throughout the human body, including the meninges. Advanced glycation end products, which are waste products formed when proteins and sugars meet in the human body, are partially removed by macrophages. However, glycated products bound to extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen are difficult to remove naturally. Through the KAIST-Ceragem Research Center, this research team is developing a healthcare medical device to remove 'sugar residue' in the body.
This study was carried out with the National Research Foundation of Korea's collective research support.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of proposed mechanism showing aging‐related ECM remodeling through meningeal fibroblasts on the brain leptomeninges. Meningeal fibroblasts in the young brain showed dynamic COL1A1 synthetic and COL1‐interactive function on the collagen membrane. They showed ITGB1‐mediated adhesion on the COL1‐composed leptomeningeal membrane and induction of COL1A1 synthesis for maintaining the collagen membrane. With aging, meningeal fibroblasts showed depletion of COL1A1 synthetic function and altered cell–matrix interaction.
Figure 2. Representative rat meningeal images observed in the study. Compared to young rats, it was confirmed that type 1 collagen (COL1) decreased along with the accumulation of glycated end products (AGE) in the brain membrane of aged rats, and the activity of integrin beta 1 (ITGB1), a representative receptor corresponding to cell-collagen interaction. Instead, it was observed that the activity of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2), one of the tyrosine kinases, increased.
Figure 3. Substance flux through the brain membrane decreases with aging. It was confirmed that the degree of adsorption of fluorescent substances contained in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the brain membrane increased and the degree of entry into the periphery of the cerebral blood vessels decreased in the aged rats. In this study, only the influx into the brain was confirmed during the entry and exit of substances, but the degree of outflow will also be confirmed through future studies.
2023.03.15 View 9796
The cause of disability in aged brain meningeal membranes identified
Due to the increase in average age, studies on changes in the brain following general aging process without serious brain diseases have also become an issue that requires in-depth studies. Regarding aging research, as aging progresses, ‘sugar’ accumulates in the body, and the accumulated sugar becomes a causative agent for various diseases such as aging-related inflammation and vascular disease. In the end, “surplus” sugar molecules attach to various proteins in the body and interfere with their functions.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee), a joint research team of Professor Pilnam Kim and Professor Yong Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, revealed on the 15th that it was confirmed that the function of being the “front line of defense” for the cerebrocortex of the brain meninges, the layers of membranes that surrounds the brain, is hindered when 'sugar' begins to build up on them as aging progresses.
Professor Kim's research team confirmed excessive accumulation of sugar molecules in the meninges of the elderly and also confirmed that sugar accumulation occurs mouse models in accordance with certain age levels. The meninges are thin membranes that surround the brain and exist at the boundary between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cortex and play an important role in protecting the brain. In this study, it was revealed that the dysfunction of these brain membranes caused by aging is induced by 'excess' sugar in the brain. In particular, as the meningeal membrane becomes thinner and stickier due to aging, a new paradigm has been provided for the discovery of the principle of the decrease in material exchange between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cerebral cortex.
This research was conducted by the Ph.D. candidate Hyo Min Kim and Dr. Shinheun Kim as the co-first authors to be published online on February 28th in the international journal, Aging Cell. (Paper Title: Glycation-mediated tissue-level remodeling of brain meningeal membrane by aging)
The meninges, which are in direct contact with the cerebrospinal fluid, are mainly composed of collagen, an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein, and are composed of fibroblasts, which are cells that produce this protein. The cells that come in contact with collagen proteins that are attached with sugar have a low collagen production function, while the meningeal membrane continuously thins and collapses as the expression of collagen degrading enzymes increases.
Studies on the relationship between excess sugar molecules accumulation in the brain due to continued sugar intake and the degeneration of neurons and brain diseases have been continuously conducted. However, this study was the first to identify meningeal degeneration and dysfunction caused by glucose accumulation with the focus on the meninges itself, and the results are expected to present new ideas for research into approach towards discoveries of new treatments for brain disease.
Researcher Hyomin Kim, the first author, introduced the research results as “an interesting study that identified changes in the barriers of the brain due to aging through a convergent approach, starting from the human brain and utilizing an animal model with a biomimetic meningeal model”.
Professor Pilnam Kim's research team is conducting research and development to remove sugar that accumulated throughout the human body, including the meninges. Advanced glycation end products, which are waste products formed when proteins and sugars meet in the human body, are partially removed by macrophages. However, glycated products bound to extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen are difficult to remove naturally. Through the KAIST-Ceragem Research Center, this research team is developing a healthcare medical device to remove 'sugar residue' in the body.
This study was carried out with the National Research Foundation of Korea's collective research support.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of proposed mechanism showing aging‐related ECM remodeling through meningeal fibroblasts on the brain leptomeninges. Meningeal fibroblasts in the young brain showed dynamic COL1A1 synthetic and COL1‐interactive function on the collagen membrane. They showed ITGB1‐mediated adhesion on the COL1‐composed leptomeningeal membrane and induction of COL1A1 synthesis for maintaining the collagen membrane. With aging, meningeal fibroblasts showed depletion of COL1A1 synthetic function and altered cell–matrix interaction.
Figure 2. Representative rat meningeal images observed in the study. Compared to young rats, it was confirmed that type 1 collagen (COL1) decreased along with the accumulation of glycated end products (AGE) in the brain membrane of aged rats, and the activity of integrin beta 1 (ITGB1), a representative receptor corresponding to cell-collagen interaction. Instead, it was observed that the activity of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2), one of the tyrosine kinases, increased.
Figure 3. Substance flux through the brain membrane decreases with aging. It was confirmed that the degree of adsorption of fluorescent substances contained in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the brain membrane increased and the degree of entry into the periphery of the cerebral blood vessels decreased in the aged rats. In this study, only the influx into the brain was confirmed during the entry and exit of substances, but the degree of outflow will also be confirmed through future studies.
2023.03.15 View 9796 -
 KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 11652
KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 11652