Electrical+Engineering
-
 Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee to Co-Chair IEEE MEMS 2025
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed General Chair of the 38th IEEE MEMS 2025 (International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems). Professor Lee, who is 40, is the conference’s youngest General Chair to date and will work jointly with Professor Sheng-Shian Li of Taiwan’s National Tsing Hua University as co-chairs in 2025.
IEEE MEMS is a top-tier international conference on microelectromechanical systems and it serves as a core academic showcase for MEMS research and technology in areas such as microsensors and actuators.
With over 800 MEMS paper submissions each year, the conference only accepts and publishes about 250 of them after a rigorous review process recognized for its world-class prestige. Of all the submissions, fewer than 10% are chosen for oral presentations.
2022.04.18 View 6391
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee to Co-Chair IEEE MEMS 2025
Professor Hyunjoo Jenny Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering has been appointed General Chair of the 38th IEEE MEMS 2025 (International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems). Professor Lee, who is 40, is the conference’s youngest General Chair to date and will work jointly with Professor Sheng-Shian Li of Taiwan’s National Tsing Hua University as co-chairs in 2025.
IEEE MEMS is a top-tier international conference on microelectromechanical systems and it serves as a core academic showcase for MEMS research and technology in areas such as microsensors and actuators.
With over 800 MEMS paper submissions each year, the conference only accepts and publishes about 250 of them after a rigorous review process recognized for its world-class prestige. Of all the submissions, fewer than 10% are chosen for oral presentations.
2022.04.18 View 6391 -
 Professor June-Koo Rhee’s Team Wins the QHack Open Hackathon Science Challenge
The research team consisting of three master students Ju-Young Ryu, Jeung-rak Lee, and Eyel Elala in Professor June-Koo Rhee’s group from the KAIST IRTC of Quantum Computing for AI has won the first place at the QHack 2022 Open Hackathon Science Challenge.
The QHack 2022 Open Hackathon is one of the world’s prestigious quantum software hackathon events held by US Xanadu, in which 250 people from 100 countries participate. Major sponsors such as IBM Quantum, AWS, CERN QTI, and Google Quantum AI proposed challenging problems, and a winning team is selected judged on team projects in each of the 13 challenges.
The KAIST team supervised by Professor Rhee received the First Place prize on the Science Challenge which was organized by the CERN QTI of the European Communities. The team will be awarded an opportunity to tour CERN’s research lab in Europe for one week along with an online internship.
The students on the team presented a method for “Leaning Based Error Mitigation for VQE,” in which they implemented an LBEM protocol to lower the error in quantum computing, and leveraged the protocol in the VQU algorithm which is used to calculate the ground state energy of a given molecule.
Their research successfully demonstrated the ability to effectively mitigate the error in IBM Quantum hardware and the virtual error model. In conjunction, Professor June-Koo (Kevin) Rhee founded a quantum computing venture start-up, Qunova Computing(https://qunovacomputing.com), with technology tranfer from the KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI. Qunova Computing is one of the frontier of the quantum software industry in Korea.
2022.04.08 View 6312
Professor June-Koo Rhee’s Team Wins the QHack Open Hackathon Science Challenge
The research team consisting of three master students Ju-Young Ryu, Jeung-rak Lee, and Eyel Elala in Professor June-Koo Rhee’s group from the KAIST IRTC of Quantum Computing for AI has won the first place at the QHack 2022 Open Hackathon Science Challenge.
The QHack 2022 Open Hackathon is one of the world’s prestigious quantum software hackathon events held by US Xanadu, in which 250 people from 100 countries participate. Major sponsors such as IBM Quantum, AWS, CERN QTI, and Google Quantum AI proposed challenging problems, and a winning team is selected judged on team projects in each of the 13 challenges.
The KAIST team supervised by Professor Rhee received the First Place prize on the Science Challenge which was organized by the CERN QTI of the European Communities. The team will be awarded an opportunity to tour CERN’s research lab in Europe for one week along with an online internship.
The students on the team presented a method for “Leaning Based Error Mitigation for VQE,” in which they implemented an LBEM protocol to lower the error in quantum computing, and leveraged the protocol in the VQU algorithm which is used to calculate the ground state energy of a given molecule.
Their research successfully demonstrated the ability to effectively mitigate the error in IBM Quantum hardware and the virtual error model. In conjunction, Professor June-Koo (Kevin) Rhee founded a quantum computing venture start-up, Qunova Computing(https://qunovacomputing.com), with technology tranfer from the KAIST ITRC of Quantum Computing for AI. Qunova Computing is one of the frontier of the quantum software industry in Korea.
2022.04.08 View 6312 -
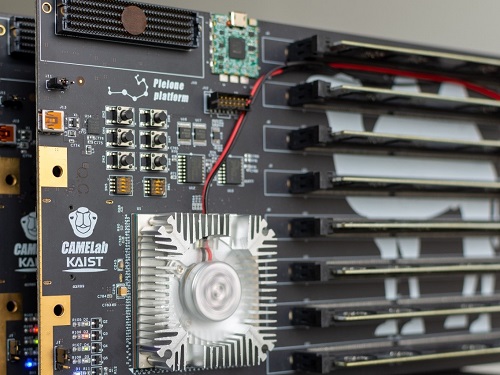 CXL-Based Memory Disaggregation Technology Opens Up a New Direction for Big Data Solution Frameworks
A KAIST team’s compute express link (CXL) provides new insights on memory disaggregation and ensures direct access and high-performance capabilities
A team from the Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL) at KAIST presented a new compute express link (CXL) solution whose directly accessible, and high-performance memory disaggregation opens new directions for big data memory processing. Professor Myoungsoo Jung said the team’s technology significantly improves performance compared to existing remote direct memory access (RDMA)-based memory disaggregation.
CXL is a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCIe)-based new dynamic multi-protocol made for efficiently utilizing memory devices and accelerators. Many enterprise data centers and memory vendors are paying attention to it as the next-generation multi-protocol for the era of big data.
Emerging big data applications such as machine learning, graph analytics, and in-memory databases require large memory capacities. However, scaling out the memory capacity via a prior memory interface like double data rate (DDR) is limited by the number of the central processing units (CPUs) and memory controllers. Therefore, memory disaggregation, which allows connecting a host to another host’s memory or memory nodes, has appeared.
RDMA is a way that a host can directly access another host’s memory via InfiniBand, the commonly used network protocol in data centers. Nowadays, most existing memory disaggregation technologies employ RDMA to get a large memory capacity. As a result, a host can share another host’s memory by transferring the data between local and remote memory.
Although RDMA-based memory disaggregation provides a large memory capacity to a host, two critical problems exist. First, scaling out the memory still needs an extra CPU to be added. Since passive memory such as dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), cannot operate by itself, it should be controlled by the CPU. Second, redundant data copies and software fabric interventions for RDMA-based memory disaggregation cause longer access latency. For example, remote memory access latency in RDMA-based memory disaggregation is multiple orders of magnitude longer than local memory access.
To address these issues, Professor Jung’s team developed the CXL-based memory disaggregation framework, including CXL-enabled customized CPUs, CXL devices, CXL switches, and CXL-aware operating system modules. The team’s CXL device is a pure passive and directly accessible memory node that contains multiple DRAM dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) and a CXL memory controller. Since the CXL memory controller supports the memory in the CXL device, a host can utilize the memory node without processor or software intervention. The team’s CXL switch enables scaling out a host’s memory capacity by hierarchically connecting multiple CXL devices to the CXL switch allowing more than hundreds of devices. Atop the switches and devices, the team’s CXL-enabled operating system removes redundant data copy and protocol conversion exhibited by conventional RDMA, which can significantly decrease access latency to the memory nodes.
In a test comparing loading 64B (cacheline) data from memory pooling devices, CXL-based memory disaggregation showed 8.2 times higher data load performance than RDMA-based memory disaggregation and even similar performance to local DRAM memory. In the team’s evaluations for a big data benchmark such as a machine learning-based test, CXL-based memory disaggregation technology also showed a maximum of 3.7 times higher performance than prior RDMA-based memory disaggregation technologies.
“Escaping from the conventional RDMA-based memory disaggregation, our CXL-based memory disaggregation framework can provide high scalability and performance for diverse datacenters and cloud service infrastructures,” said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “Our CXL-based memory disaggregation research will bring about a new paradigm for memory solutions that will lead the era of big data.”
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.16 View 21751
CXL-Based Memory Disaggregation Technology Opens Up a New Direction for Big Data Solution Frameworks
A KAIST team’s compute express link (CXL) provides new insights on memory disaggregation and ensures direct access and high-performance capabilities
A team from the Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL) at KAIST presented a new compute express link (CXL) solution whose directly accessible, and high-performance memory disaggregation opens new directions for big data memory processing. Professor Myoungsoo Jung said the team’s technology significantly improves performance compared to existing remote direct memory access (RDMA)-based memory disaggregation.
CXL is a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCIe)-based new dynamic multi-protocol made for efficiently utilizing memory devices and accelerators. Many enterprise data centers and memory vendors are paying attention to it as the next-generation multi-protocol for the era of big data.
Emerging big data applications such as machine learning, graph analytics, and in-memory databases require large memory capacities. However, scaling out the memory capacity via a prior memory interface like double data rate (DDR) is limited by the number of the central processing units (CPUs) and memory controllers. Therefore, memory disaggregation, which allows connecting a host to another host’s memory or memory nodes, has appeared.
RDMA is a way that a host can directly access another host’s memory via InfiniBand, the commonly used network protocol in data centers. Nowadays, most existing memory disaggregation technologies employ RDMA to get a large memory capacity. As a result, a host can share another host’s memory by transferring the data between local and remote memory.
Although RDMA-based memory disaggregation provides a large memory capacity to a host, two critical problems exist. First, scaling out the memory still needs an extra CPU to be added. Since passive memory such as dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), cannot operate by itself, it should be controlled by the CPU. Second, redundant data copies and software fabric interventions for RDMA-based memory disaggregation cause longer access latency. For example, remote memory access latency in RDMA-based memory disaggregation is multiple orders of magnitude longer than local memory access.
To address these issues, Professor Jung’s team developed the CXL-based memory disaggregation framework, including CXL-enabled customized CPUs, CXL devices, CXL switches, and CXL-aware operating system modules. The team’s CXL device is a pure passive and directly accessible memory node that contains multiple DRAM dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) and a CXL memory controller. Since the CXL memory controller supports the memory in the CXL device, a host can utilize the memory node without processor or software intervention. The team’s CXL switch enables scaling out a host’s memory capacity by hierarchically connecting multiple CXL devices to the CXL switch allowing more than hundreds of devices. Atop the switches and devices, the team’s CXL-enabled operating system removes redundant data copy and protocol conversion exhibited by conventional RDMA, which can significantly decrease access latency to the memory nodes.
In a test comparing loading 64B (cacheline) data from memory pooling devices, CXL-based memory disaggregation showed 8.2 times higher data load performance than RDMA-based memory disaggregation and even similar performance to local DRAM memory. In the team’s evaluations for a big data benchmark such as a machine learning-based test, CXL-based memory disaggregation technology also showed a maximum of 3.7 times higher performance than prior RDMA-based memory disaggregation technologies.
“Escaping from the conventional RDMA-based memory disaggregation, our CXL-based memory disaggregation framework can provide high scalability and performance for diverse datacenters and cloud service infrastructures,” said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “Our CXL-based memory disaggregation research will bring about a new paradigm for memory solutions that will lead the era of big data.”
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.16 View 21751 -
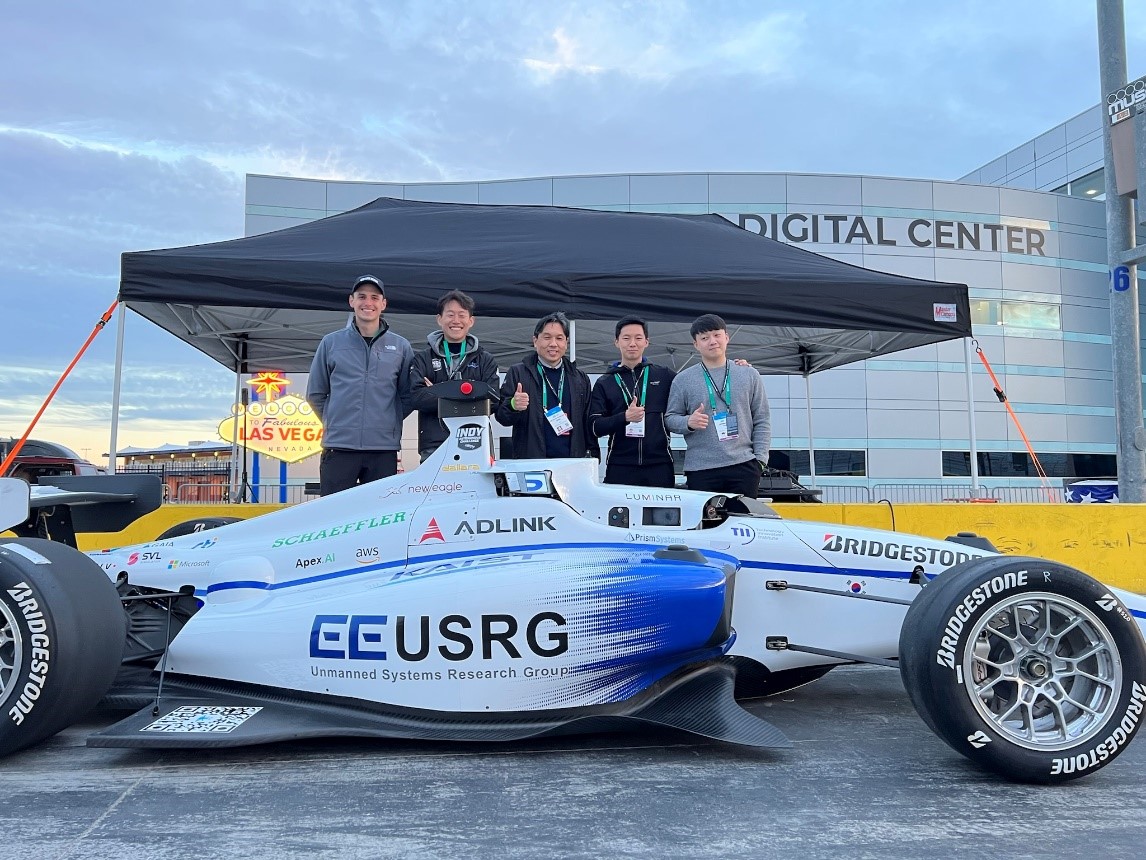 Team KAIST Makes Its Presence Felt in the Self-Driving Tech Industry
Team KAIST finishes 4th at the inaugural CES Autonomous Racing Competition
Team KAIST led by Professor Hyunchul Shim and Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG) placed fourth in an autonomous race car competition in Las Vegas last week, making its presence felt in the self-driving automotive tech industry.
Team KAIST, beat its first competitor, Auburn University, with speeds of up to 131 mph at the Autonomous Challenge at CES held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway. However, the team failed to advance to the final round when it lost to PoliMOVE, comprised of the Polytechnic University of Milan and the University of Alabama, the final winner of the $150,000 USD race.
A total of eight teams competed in the self-driving race. The race was conducted as a single elimination tournament consisting of multiple rounds of matches. Two cars took turns playing the role of defender and attacker, and each car attempted to outpace the other until one of them was unable to complete the mission.
Each team designed the algorithm to control its racecar, the Dallara-built AV-21, which can reach a speed of up to 173 mph, and make it safely drive around the track at high speeds without crashing into the other.
The event is the CES version of the Indy Autonomous Challenge, a competition that took place for the first time in October last year to encourage university students from around the world to develop complicated software for autonomous driving and advance relevant technologies. Team KAIST placed 4th at the Indy Autonomous Challenge, which qualified it to participate in this race.
“The technical level of the CES race is much higher than last October’s and we had a very tough race. We advanced to the semifinals for two consecutive races. I think our autonomous vehicle technology is proving itself to the world,” said Professor Shim.
Professor Shim’s research group has been working on the development of autonomous aerial and ground vehicles for the past 12 years. A self-driving car developed by the lab was certified by the South Korean government to run on public roads.
The vehicle the team used cost more than 1 million USD to build. Many of the other teams had to repair their vehicle more than once due to accidents and had to spend a lot on repairs. “We are the only one who did not have any accidents, and this is a testament to our technological prowess,” said Professor Shim.
He said the financial funding to purchase pricy parts and equipment for the racecar is always a challenge given the very tight research budget and absence of corporate sponsorships.
However, Professor Shim and his research group plan to participate in the next race in September and in the 2023 CES race.
“I think we need more systemic and proactive research and support systems to earn better results but there is nothing better than the group of passionate students who are taking part in this project with us,” Shim added.
2022.01.12 View 10017
Team KAIST Makes Its Presence Felt in the Self-Driving Tech Industry
Team KAIST finishes 4th at the inaugural CES Autonomous Racing Competition
Team KAIST led by Professor Hyunchul Shim and Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG) placed fourth in an autonomous race car competition in Las Vegas last week, making its presence felt in the self-driving automotive tech industry.
Team KAIST, beat its first competitor, Auburn University, with speeds of up to 131 mph at the Autonomous Challenge at CES held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway. However, the team failed to advance to the final round when it lost to PoliMOVE, comprised of the Polytechnic University of Milan and the University of Alabama, the final winner of the $150,000 USD race.
A total of eight teams competed in the self-driving race. The race was conducted as a single elimination tournament consisting of multiple rounds of matches. Two cars took turns playing the role of defender and attacker, and each car attempted to outpace the other until one of them was unable to complete the mission.
Each team designed the algorithm to control its racecar, the Dallara-built AV-21, which can reach a speed of up to 173 mph, and make it safely drive around the track at high speeds without crashing into the other.
The event is the CES version of the Indy Autonomous Challenge, a competition that took place for the first time in October last year to encourage university students from around the world to develop complicated software for autonomous driving and advance relevant technologies. Team KAIST placed 4th at the Indy Autonomous Challenge, which qualified it to participate in this race.
“The technical level of the CES race is much higher than last October’s and we had a very tough race. We advanced to the semifinals for two consecutive races. I think our autonomous vehicle technology is proving itself to the world,” said Professor Shim.
Professor Shim’s research group has been working on the development of autonomous aerial and ground vehicles for the past 12 years. A self-driving car developed by the lab was certified by the South Korean government to run on public roads.
The vehicle the team used cost more than 1 million USD to build. Many of the other teams had to repair their vehicle more than once due to accidents and had to spend a lot on repairs. “We are the only one who did not have any accidents, and this is a testament to our technological prowess,” said Professor Shim.
He said the financial funding to purchase pricy parts and equipment for the racecar is always a challenge given the very tight research budget and absence of corporate sponsorships.
However, Professor Shim and his research group plan to participate in the next race in September and in the 2023 CES race.
“I think we need more systemic and proactive research and support systems to earn better results but there is nothing better than the group of passionate students who are taking part in this project with us,” Shim added.
2022.01.12 View 10017 -
 Team KAIST to Race at CES 2022 Autonomous Challenge
Five top university autonomous racing teams will compete in a head-to-head passing competition in Las Vegas
A self-driving racing team from the KAIST Unmanned System Research Group (USRG) advised by Professor Hyunchul Shim will compete at the Autonomous Challenge at the Consumer Electronic Show (CES) on January 7, 2022. The head-to-head, high speed autonomous racecar passing competition at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway will feature the finalists and semifinalists from the Indy Autonomous Challenge in October of this year. Team KAIST qualified as a semifinalist at the Indy Autonomous Challenge and will join four other university teams including the winner of the competition, Technische Universität München.
Team KAIST’s AV-21 vehicle is capable of driving on its own at more than 200km/h will be expected to show a speed of more than 300 km/h at the race.The participating teams are:1. KAIST2. EuroRacing : University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), University of Pisa (Italy), ETH Zürich (Switzerland), Polish Academy of Sciences (Poland) 3. MIT-PITT-RW, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Pittsburgh, Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Waterloo (Canada)4.PoliMOVE – Politecnico di Milano (Italy), University of Alabama 5.TUM Autonomous Motorsport – Technische Universität München (Germany)
Professor Shim’s team is dedicated to the development and validation of cutting edge technologies for highly autonomous vehicles. In recognition of his pioneering research in unmanned system technologies, Professor Shim was honored with the Grand Prize of the Minister of Science and ICT on December 9.
“We began autonomous vehicle research in 2009 when we signed up for Hyundai Motor Company’s Autonomous Driving Challenge. For this, we developed a complete set of in-house technologies such as low-level vehicle control, perception, localization, and decision making.” In 2019, the team came in third place in the Challenge and they finally won this year.
For years, his team has participated in many unmanned systems challenges at home and abroad, gaining recognition around the world. The team won the inaugural 2016 IROS autonomous drone racing and placed second in the 2018 IROS Autonomous Drone Racing Competition. They also competed in 2017 MBZIRC, ranking fourth in Missions 2 and 3, and fifth in the Grand Challenge.
Most recently, the team won the first round of Lockheed Martin’s Alpha Pilot AI Drone Innovation Challenge. The team is now participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge as a member of Team CoSTAR with NASA JPL, MIT, and Caltech.
“We have accumulated plenty of first-hand experience developing autonomous vehicles with the support of domestic companies such as Hyundai Motor Company, Samsung, LG, and NAVER. In 2017, the autonomous vehicle platform “EureCar” that we developed in-house was authorized by the Korean government to lawfully conduct autonomous driving experiment on public roads,” said Professor Shim.
The team has developed various key technologies and algorithms related to unmanned systems that can be categorized into three major components: perception, planning, and control. Considering the characteristics of the algorithms that make up each module, their technology operates using a distributed computing system.
Since 2015, the team has been actively using deep learning algorithms in the form of perception subsystems. Contextual information extracted from multi-modal sensory data gathered via cameras, lidar, radar, GPS, IMU, etc. is forwarded to the planning subsystem. The planning module is responsible for the decision making and planning required for autonomous driving such as lane change determination and trajectory planning, emergency stops, and velocity command generation. The results from the planner are fed into the controller to follow the planned high-level command. The team has also developed and verified the possibility of an end-to-end deep learning based autonomous driving approach that replaces a complex system with one single AI network.
2021.12.17 View 10281
Team KAIST to Race at CES 2022 Autonomous Challenge
Five top university autonomous racing teams will compete in a head-to-head passing competition in Las Vegas
A self-driving racing team from the KAIST Unmanned System Research Group (USRG) advised by Professor Hyunchul Shim will compete at the Autonomous Challenge at the Consumer Electronic Show (CES) on January 7, 2022. The head-to-head, high speed autonomous racecar passing competition at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway will feature the finalists and semifinalists from the Indy Autonomous Challenge in October of this year. Team KAIST qualified as a semifinalist at the Indy Autonomous Challenge and will join four other university teams including the winner of the competition, Technische Universität München.
Team KAIST’s AV-21 vehicle is capable of driving on its own at more than 200km/h will be expected to show a speed of more than 300 km/h at the race.The participating teams are:1. KAIST2. EuroRacing : University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), University of Pisa (Italy), ETH Zürich (Switzerland), Polish Academy of Sciences (Poland) 3. MIT-PITT-RW, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, University of Pittsburgh, Rochester Institute of Technology, University of Waterloo (Canada)4.PoliMOVE – Politecnico di Milano (Italy), University of Alabama 5.TUM Autonomous Motorsport – Technische Universität München (Germany)
Professor Shim’s team is dedicated to the development and validation of cutting edge technologies for highly autonomous vehicles. In recognition of his pioneering research in unmanned system technologies, Professor Shim was honored with the Grand Prize of the Minister of Science and ICT on December 9.
“We began autonomous vehicle research in 2009 when we signed up for Hyundai Motor Company’s Autonomous Driving Challenge. For this, we developed a complete set of in-house technologies such as low-level vehicle control, perception, localization, and decision making.” In 2019, the team came in third place in the Challenge and they finally won this year.
For years, his team has participated in many unmanned systems challenges at home and abroad, gaining recognition around the world. The team won the inaugural 2016 IROS autonomous drone racing and placed second in the 2018 IROS Autonomous Drone Racing Competition. They also competed in 2017 MBZIRC, ranking fourth in Missions 2 and 3, and fifth in the Grand Challenge.
Most recently, the team won the first round of Lockheed Martin’s Alpha Pilot AI Drone Innovation Challenge. The team is now participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge as a member of Team CoSTAR with NASA JPL, MIT, and Caltech.
“We have accumulated plenty of first-hand experience developing autonomous vehicles with the support of domestic companies such as Hyundai Motor Company, Samsung, LG, and NAVER. In 2017, the autonomous vehicle platform “EureCar” that we developed in-house was authorized by the Korean government to lawfully conduct autonomous driving experiment on public roads,” said Professor Shim.
The team has developed various key technologies and algorithms related to unmanned systems that can be categorized into three major components: perception, planning, and control. Considering the characteristics of the algorithms that make up each module, their technology operates using a distributed computing system.
Since 2015, the team has been actively using deep learning algorithms in the form of perception subsystems. Contextual information extracted from multi-modal sensory data gathered via cameras, lidar, radar, GPS, IMU, etc. is forwarded to the planning subsystem. The planning module is responsible for the decision making and planning required for autonomous driving such as lane change determination and trajectory planning, emergency stops, and velocity command generation. The results from the planner are fed into the controller to follow the planned high-level command. The team has also developed and verified the possibility of an end-to-end deep learning based autonomous driving approach that replaces a complex system with one single AI network.
2021.12.17 View 10281 -
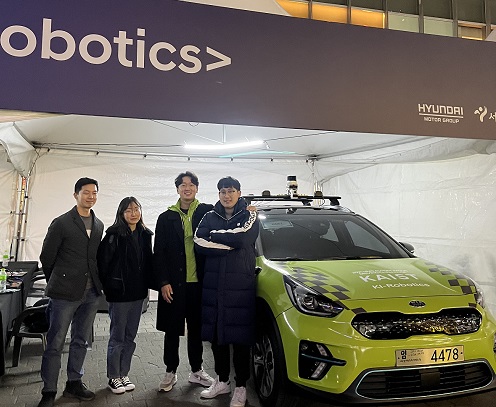 KI-Robotics Wins the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge
Professor Hyunchul Shim’s autonomous driving team topped the challenge
KI-Robotics, a KAIST autonomous driving research team led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electric Engineering won the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge held in Seoul on November 29. The KI-Robotics team received 100 million won in prize money and a field trip to the US.
Out of total 23 teams, the six teams competed in the finals by simultaneously driving through a 4km section within the test operation region, where other traffic was constrained. The challenge included avoiding and overtaking vehicles, crossing intersections, and keeping to traffic laws including traffic lights, lanes, speed limit, and school zones. The contestants were ranked by their order of course completion, but points were deducted every time they violated a traffic rule. A driver and an invigilator rode in each car in case of an emergency, and the race was broadcasted live on a large screen on stage and via YouTube.
In the first round, KI-Robotics came in first with a score of 11 minutes and 27 seconds after a tight race with Incheon University. Although the team’s result in the second round exceeded 16 minutes due to traffic conditions like traffic lights, the 11 minutes and 27 seconds ultimately ranked first out of the six universities. It is worth noting that KI-Robotics focused on its vehicle’s perception and judgement rather than speed when building its algorithm. Out of the six universities that made it to the final round, KI-Robotics was the only team that excluded GPS from the vehicle to minimize its risk.
The team considered the fact that GPS signals are not accurate in urban settings, meaning location errors can cause problems while driving. As an alternative, the team added three radar sensors and cameras in the front and the back of the vehicle. They also used the urban-specific SLAM technology they developed to construct a precise map and were more successful in location determination.
As opposed to other teams that focused on speed, the KAIST team also developed overtaking route construction technology, taking into consideration the locations of surrounding cars, which gave them an advantage in responding to obstacles while keeping to real urban traffic rules. Through this, the KAIST team could score highest in rounds one and two combined.
Professor Shim said, “I am very glad that the autonomous driving technology our research team has been developing over the last ten years has borne fruit. I would like to thank the leader, Daegyu Lee, and all the students that participated in the development, as they did more than their best under difficult conditions.”
Dae-Gyu Lee, the leader of KI-Robotics and a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering, explained, “Since we came in fourth in the preliminary round, we were further behind than we expected. But we were able to overtake the cars ahead of us and shorten our record.”
2021.12.07 View 6302
KI-Robotics Wins the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge
Professor Hyunchul Shim’s autonomous driving team topped the challenge
KI-Robotics, a KAIST autonomous driving research team led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electric Engineering won the 2021 Hyundai Motor Autonomous Driving Challenge held in Seoul on November 29. The KI-Robotics team received 100 million won in prize money and a field trip to the US.
Out of total 23 teams, the six teams competed in the finals by simultaneously driving through a 4km section within the test operation region, where other traffic was constrained. The challenge included avoiding and overtaking vehicles, crossing intersections, and keeping to traffic laws including traffic lights, lanes, speed limit, and school zones. The contestants were ranked by their order of course completion, but points were deducted every time they violated a traffic rule. A driver and an invigilator rode in each car in case of an emergency, and the race was broadcasted live on a large screen on stage and via YouTube.
In the first round, KI-Robotics came in first with a score of 11 minutes and 27 seconds after a tight race with Incheon University. Although the team’s result in the second round exceeded 16 minutes due to traffic conditions like traffic lights, the 11 minutes and 27 seconds ultimately ranked first out of the six universities. It is worth noting that KI-Robotics focused on its vehicle’s perception and judgement rather than speed when building its algorithm. Out of the six universities that made it to the final round, KI-Robotics was the only team that excluded GPS from the vehicle to minimize its risk.
The team considered the fact that GPS signals are not accurate in urban settings, meaning location errors can cause problems while driving. As an alternative, the team added three radar sensors and cameras in the front and the back of the vehicle. They also used the urban-specific SLAM technology they developed to construct a precise map and were more successful in location determination.
As opposed to other teams that focused on speed, the KAIST team also developed overtaking route construction technology, taking into consideration the locations of surrounding cars, which gave them an advantage in responding to obstacles while keeping to real urban traffic rules. Through this, the KAIST team could score highest in rounds one and two combined.
Professor Shim said, “I am very glad that the autonomous driving technology our research team has been developing over the last ten years has borne fruit. I would like to thank the leader, Daegyu Lee, and all the students that participated in the development, as they did more than their best under difficult conditions.”
Dae-Gyu Lee, the leader of KI-Robotics and a Ph.D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering, explained, “Since we came in fourth in the preliminary round, we were further behind than we expected. But we were able to overtake the cars ahead of us and shorten our record.”
2021.12.07 View 6302 -
 A Team of Three PhD Candidates Wins the Korea Semiconductor Design Contest
“We felt a sense of responsibility to help the nation advance its semiconductor design technology”
A CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor)-based “ultra-low noise signal chip” for 6G communications designed by three PhD candidates at the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering won the Presidential Award at the 22nd Korea Semiconductor Design Contest.
The winners are PhD candidates Sun-Eui Park, Yoon-Seo Cho, and Ju-Eun Bang from the Integrated Circuits and System Lab run by Professor Jaehyouk Choi. The contest, which is hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and the Korea Semiconductors Industry Association, is one of the top national semiconductor design contests for college students.
Park said the team felt a sense of responsibility to help advance semiconductor design technology in Korea when deciding to participate the contest. The team expressed deep gratitude to Professor Choi for guiding their research on 6G communications.
“Our colleagues from other labs and seniors who already graduated helped us a great deal, so we owe them a lot,” explained Park. Cho added that their hard work finally got recognized and that acknowledgement pushes her to move forward with her research. Meanwhile, Bang said she is delighted to see that many people seem to be interested in her research topic.
Research for 6G is attempting to reach 1 tera bps (Tbps), 50 times faster than 5G communications with transmission speeds of up to 20 gigabytes. In general, the wider the communication frequency band, the higher the data transmission speed. Thus, the use of frequency bands above 100 gigahertz is essential for delivering high data transmission speeds for 6G communications.
However, it remains a big challenge to make a precise benchmark signal that can be used as a carrier wave in a high frequency band. Despite the advantages of CMOS’s ultra-small and low-power design, it still has limitations at high frequency bands and its operating frequency. Thus, it was difficult to achieve a frequency band above 100 gigahertz.
To overcome these challenges, the three students introduced ultra-low noise signal generation technology that can support high-order modulation technologies. This technology is expected to contribute to increasing the price competitiveness and density of 6G communication chips that will be used in the future.
5G just got started in 2020 and still has long way to go for full commercialization. Nevertheless, many researchers have started preparing for 6G technology, targeting 2030 since a new cellular communication appears in every other decade.
Professor Choi said, “Generating ultra-high frequency signals in bands above 100 GHz with highly accurate timing is one of the key technologies for implementing 6G communication hardware. Our research is significant for the development of the world’s first semiconductor chip that will use the CMOS process to achieve noise performance of less than 80fs in a frequency band above 100 GHz.”
The team members plan to work as circuit designers in Korean semiconductor companies after graduation. “We will continue to research the development of signal generators on the topic of award-winning 6G. We would like to continue our research on high-speed circuit designs such as ultra-fast analog-to-digital converters,” Park added.
2021.11.30 View 8583
A Team of Three PhD Candidates Wins the Korea Semiconductor Design Contest
“We felt a sense of responsibility to help the nation advance its semiconductor design technology”
A CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor)-based “ultra-low noise signal chip” for 6G communications designed by three PhD candidates at the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering won the Presidential Award at the 22nd Korea Semiconductor Design Contest.
The winners are PhD candidates Sun-Eui Park, Yoon-Seo Cho, and Ju-Eun Bang from the Integrated Circuits and System Lab run by Professor Jaehyouk Choi. The contest, which is hosted by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy and the Korea Semiconductors Industry Association, is one of the top national semiconductor design contests for college students.
Park said the team felt a sense of responsibility to help advance semiconductor design technology in Korea when deciding to participate the contest. The team expressed deep gratitude to Professor Choi for guiding their research on 6G communications.
“Our colleagues from other labs and seniors who already graduated helped us a great deal, so we owe them a lot,” explained Park. Cho added that their hard work finally got recognized and that acknowledgement pushes her to move forward with her research. Meanwhile, Bang said she is delighted to see that many people seem to be interested in her research topic.
Research for 6G is attempting to reach 1 tera bps (Tbps), 50 times faster than 5G communications with transmission speeds of up to 20 gigabytes. In general, the wider the communication frequency band, the higher the data transmission speed. Thus, the use of frequency bands above 100 gigahertz is essential for delivering high data transmission speeds for 6G communications.
However, it remains a big challenge to make a precise benchmark signal that can be used as a carrier wave in a high frequency band. Despite the advantages of CMOS’s ultra-small and low-power design, it still has limitations at high frequency bands and its operating frequency. Thus, it was difficult to achieve a frequency band above 100 gigahertz.
To overcome these challenges, the three students introduced ultra-low noise signal generation technology that can support high-order modulation technologies. This technology is expected to contribute to increasing the price competitiveness and density of 6G communication chips that will be used in the future.
5G just got started in 2020 and still has long way to go for full commercialization. Nevertheless, many researchers have started preparing for 6G technology, targeting 2030 since a new cellular communication appears in every other decade.
Professor Choi said, “Generating ultra-high frequency signals in bands above 100 GHz with highly accurate timing is one of the key technologies for implementing 6G communication hardware. Our research is significant for the development of the world’s first semiconductor chip that will use the CMOS process to achieve noise performance of less than 80fs in a frequency band above 100 GHz.”
The team members plan to work as circuit designers in Korean semiconductor companies after graduation. “We will continue to research the development of signal generators on the topic of award-winning 6G. We would like to continue our research on high-speed circuit designs such as ultra-fast analog-to-digital converters,” Park added.
2021.11.30 View 8583 -
 Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 14275
Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 14275 -
 Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 7043
Professor Sung-Ju Lee’s Team Wins the Best Paper and the Methods Recognition Awards at the ACM CSCW
A research team led by Professor Sung-Ju Lee at the School of Electrical Engineering won the Best Paper Award and the Methods Recognition Award from ACM CSCW (International Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing) 2021 for their paper “Reflect, not Regret: Understanding Regretful Smartphone Use with App Feature-Level Analysis”.
Founded in 1986, CSCW has been a premier conference on HCI (Human Computer Interaction) and Social Computing. This year, 340 full papers were presented and the best paper awards are given to the top 1% papers of the submitted. Methods Recognition, which is a new award, is given “for strong examples of work that includes well developed, explained, or implemented methods, and methodological innovation.”
Hyunsung Cho (KAIST alumus and currently a PhD candidate at Carnegie Mellon University), Daeun Choi (KAIST undergraduate researcher), Donghwi Kim (KAIST PhD Candidate), Wan Ju Kang (KAIST PhD Candidate), and Professor Eun Kyoung Choe (University of Maryland and KAIST alumna) collaborated on this research.
The authors developed a tool that tracks and analyzes which features of a mobile app (e.g., Instagram’s following post, following story, recommended post, post upload, direct messaging, etc.) are in use based on a smartphone’s User Interface (UI) layout. Utilizing this novel method, the authors revealed which feature usage patterns result in regretful smartphone use.
Professor Lee said, “Although many people enjoy the benefits of smartphones, issues have emerged from the overuse of smartphones. With this feature level analysis, users can reflect on their smartphone usage based on finer grained analysis and this could contribute to digital wellbeing.”
2021.11.22 View 7043 -
 3 KAIST PhD Candidates Selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows
PhD candidates Soo Ye Kim and Sanghyun Woo from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Hae Beom Lee from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI were selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows. The Google PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that supports graduate school students from around the world that have produced excellent achievements from promising computer science-related fields. The 75 selected fellows will receive ten thousand dollars of funding with the opportunity to discuss research and receive one-on-one feedback from experts in related fields at Google.
Kim and Woo were named fellows in the field of "Machine Perception, Speech Technology and Computer Vision" with research of deep learning based super-resolution and computer vision respectively. Lee was named a fellow in the field of "Machine Learning" for his research in meta-learning.
Kim's research includes the formulation of novel methods for super-resolution and HDR video restoration and deep joint frame interpolation and super-resolution methods. Many of her works have been presented in leading conferences in computer vision and AI such as CVPR, ICCV, and AAAI. In addition, she has been collaborating as a research intern with the Vision Group Team at Adobe Research to study depth map refinement techniques.
(Kim's research on deep learning based joint super-resolution and inverse tone-mapping framework for HDR videos)
Woo’s research includes an effective deep learning model design based on the attention mechanism and learning methods based on self-learning and simulators. His works have been also presented in leading conferences such as CVPR, ECCV, and NeurIPS. In particular, his work on the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) which was presented at ECCV in 2018 has surpassed over 2700 citations on Google Scholar after being referenced in many computer vision applications. He was also a recipient of Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship in 2020.
(Woo's research on attention mechanism based deep learning models)
Lee’s research focuses effectively overcoming various limitations of the existing meta-learning framework. Specifically, he proposed to deal with a realistic task distribution with imbalances, improved the practicality of meta-knowledge, and made meta-learning possible even in large-scale task scenarios. These various studies have been accepted to numerous top-tier machine learning conferences such as NeurIPS, ICML, and ICLR. In particular, one of his papers has been selected as an oral presentation at ICLR 2020 and another as a spotlight presentation at NeurIPS 2020.
(Lee's research on learning to balance and continual trajectory shifting)
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the award ceremony was held virtually at the Google PhD Fellowship Summit from August 31st to September 1st. The list of fellowship recipients is displayed on the Google webpage.
2021.10.18 View 5780
3 KAIST PhD Candidates Selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows
PhD candidates Soo Ye Kim and Sanghyun Woo from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Hae Beom Lee from the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI were selected as the 2021 Google PhD Fellows. The Google PhD Fellowship is a scholarship program that supports graduate school students from around the world that have produced excellent achievements from promising computer science-related fields. The 75 selected fellows will receive ten thousand dollars of funding with the opportunity to discuss research and receive one-on-one feedback from experts in related fields at Google.
Kim and Woo were named fellows in the field of "Machine Perception, Speech Technology and Computer Vision" with research of deep learning based super-resolution and computer vision respectively. Lee was named a fellow in the field of "Machine Learning" for his research in meta-learning.
Kim's research includes the formulation of novel methods for super-resolution and HDR video restoration and deep joint frame interpolation and super-resolution methods. Many of her works have been presented in leading conferences in computer vision and AI such as CVPR, ICCV, and AAAI. In addition, she has been collaborating as a research intern with the Vision Group Team at Adobe Research to study depth map refinement techniques.
(Kim's research on deep learning based joint super-resolution and inverse tone-mapping framework for HDR videos)
Woo’s research includes an effective deep learning model design based on the attention mechanism and learning methods based on self-learning and simulators. His works have been also presented in leading conferences such as CVPR, ECCV, and NeurIPS. In particular, his work on the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) which was presented at ECCV in 2018 has surpassed over 2700 citations on Google Scholar after being referenced in many computer vision applications. He was also a recipient of Microsoft Research PhD Fellowship in 2020.
(Woo's research on attention mechanism based deep learning models)
Lee’s research focuses effectively overcoming various limitations of the existing meta-learning framework. Specifically, he proposed to deal with a realistic task distribution with imbalances, improved the practicality of meta-knowledge, and made meta-learning possible even in large-scale task scenarios. These various studies have been accepted to numerous top-tier machine learning conferences such as NeurIPS, ICML, and ICLR. In particular, one of his papers has been selected as an oral presentation at ICLR 2020 and another as a spotlight presentation at NeurIPS 2020.
(Lee's research on learning to balance and continual trajectory shifting)
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the award ceremony was held virtually at the Google PhD Fellowship Summit from August 31st to September 1st. The list of fellowship recipients is displayed on the Google webpage.
2021.10.18 View 5780 -
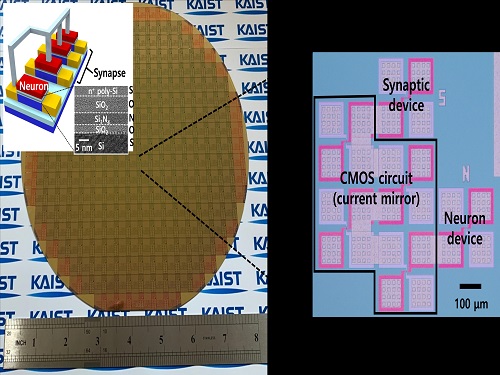 Brain-Inspired Highly Scalable Neuromorphic Hardware Presented
Neurons and synapses based on single transistor can dramatically reduce the hardware cost and accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware
KAIST researchers fabricated a brain-inspired highly scalable neuromorphic hardware by co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses. Using standard silicon complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, the neuromorphic hardware is expected to reduce chip cost and simplify fabrication procedures.
The research team led by Yang-Kyu Choi and Sung-Yool Choi produced a neurons and synapses based on single transistor for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware and showed the ability to recognize text and face images. This research was featured in Science Advances on August 4.
Neuromorphic hardware has attracted a great deal of attention because of its artificial intelligence functions, but consuming ultra-low power of less than 20 watts by mimicking the human brain. To make neuromorphic hardware work, a neuron that generates a spike when integrating a certain signal, and a synapse remembering the connection between two neurons are necessary, just like the biological brain. However, since neurons and synapses constructed on digital or analog circuits occupy a large space, there is a limit in terms of hardware efficiency and costs. Since the human brain consists of about 1011 neurons and 1014 synapses, it is necessary to improve the hardware cost in order to apply it to mobile and IoT devices.
To solve the problem, the research team mimicked the behavior of biological neurons and synapses with a single transistor, and co-integrated them onto an 8-inch wafer. The manufactured neuromorphic transistors have the same structure as the transistors for memory and logic that are currently mass-produced. In addition, the neuromorphic transistors proved for the first time that they can be implemented with a ‘Janus structure’ that functions as both neuron and synapse, just like coins have heads and tails.
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi said that this work can dramatically reduce the hardware cost by replacing the neurons and synapses that were based on complex digital and analog circuits with a single transistor. "We have demonstrated that neurons and synapses can be implemented using a single transistor," said Joon-Kyu Han, the first author. "By co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses on the same wafer using a standard CMOS process, the hardware cost of the neuromorphic hardware has been improved, which will accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware,” Han added.This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) and IC Design Education Center (IDEC).
-PublicationJoon-Kyu Han, Sung-Yool Choi, Yang-Kyu Choi, et al.“Cointegration of single-transistor neurons and synapses by nanoscale CMOS fabrication for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware,” Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg8836)
-ProfileProfessor Yang-Kyu ChoiNano-Oriented Bio-Electronics Labhttps://sites.google.com/view/nobelab/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sung-Yool ChoiMolecular and Nano Device Laboratoryhttps://www.mndl.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.05 View 10296
Brain-Inspired Highly Scalable Neuromorphic Hardware Presented
Neurons and synapses based on single transistor can dramatically reduce the hardware cost and accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware
KAIST researchers fabricated a brain-inspired highly scalable neuromorphic hardware by co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses. Using standard silicon complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) technology, the neuromorphic hardware is expected to reduce chip cost and simplify fabrication procedures.
The research team led by Yang-Kyu Choi and Sung-Yool Choi produced a neurons and synapses based on single transistor for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware and showed the ability to recognize text and face images. This research was featured in Science Advances on August 4.
Neuromorphic hardware has attracted a great deal of attention because of its artificial intelligence functions, but consuming ultra-low power of less than 20 watts by mimicking the human brain. To make neuromorphic hardware work, a neuron that generates a spike when integrating a certain signal, and a synapse remembering the connection between two neurons are necessary, just like the biological brain. However, since neurons and synapses constructed on digital or analog circuits occupy a large space, there is a limit in terms of hardware efficiency and costs. Since the human brain consists of about 1011 neurons and 1014 synapses, it is necessary to improve the hardware cost in order to apply it to mobile and IoT devices.
To solve the problem, the research team mimicked the behavior of biological neurons and synapses with a single transistor, and co-integrated them onto an 8-inch wafer. The manufactured neuromorphic transistors have the same structure as the transistors for memory and logic that are currently mass-produced. In addition, the neuromorphic transistors proved for the first time that they can be implemented with a ‘Janus structure’ that functions as both neuron and synapse, just like coins have heads and tails.
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi said that this work can dramatically reduce the hardware cost by replacing the neurons and synapses that were based on complex digital and analog circuits with a single transistor. "We have demonstrated that neurons and synapses can be implemented using a single transistor," said Joon-Kyu Han, the first author. "By co-integrating single transistor neurons and synapses on the same wafer using a standard CMOS process, the hardware cost of the neuromorphic hardware has been improved, which will accelerate the commercialization of neuromorphic hardware,” Han added.This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) and IC Design Education Center (IDEC).
-PublicationJoon-Kyu Han, Sung-Yool Choi, Yang-Kyu Choi, et al.“Cointegration of single-transistor neurons and synapses by nanoscale CMOS fabrication for highly scalable neuromorphic hardware,” Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abg8836)
-ProfileProfessor Yang-Kyu ChoiNano-Oriented Bio-Electronics Labhttps://sites.google.com/view/nobelab/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sung-Yool ChoiMolecular and Nano Device Laboratoryhttps://www.mndl.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.08.05 View 10296 -
 Prof. Changho Suh Named the 2021 James L. Massey Awardee
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering was named the recipient of the 2021 James L.Massey Award. The award recognizes outstanding achievement in research and teaching by young scholars in the information theory community. The award is named in honor of James L. Massey, who was an internationally acclaimed pioneer in digital communications and revered teacher and mentor to communications engineers.
Professor Suh is a recipient of numerous awards, including the 2021 James L. Massey Research & Teaching Award for Young Scholars from the IEEE Information Theory Society, the 2019 AFOSR Grant, the 2019 Google Education Grant, the 2018 IEIE/IEEE Joint Award, the 2015 IEIE Haedong Young Engineer Award, the 2013 IEEE Communications Society Stephen O. Rice Prize, the 2011 David J. Sakrison Memorial Prize (the best dissertation award in UC Berkeley EECS), the 2009 IEEE ISIT Best Student Paper Award, the 2020 LINKGENESIS Best Teacher Award (the campus-wide Grand Prize in Teaching), and the four Departmental Teaching Awards (2013, 2019, 2020, 2021).
Dr. Suh is an IEEE Information Theory Society Distinguished Lecturer, the General Chair of the Inaugural IEEE East Asian School of Information Theory, and a Member of the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology. He is also an Associate Editor of Machine Learning for the IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, the Editor for the IEEE Information Theory Newsletter, a Column Editor for IEEE BITS the Information Theory Magazine, an Area Chair of NeurIPS 2021, and on the Senior Program Committee of IJCAI 2019–2021.
2021.07.27 View 7848
Prof. Changho Suh Named the 2021 James L. Massey Awardee
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering was named the recipient of the 2021 James L.Massey Award. The award recognizes outstanding achievement in research and teaching by young scholars in the information theory community. The award is named in honor of James L. Massey, who was an internationally acclaimed pioneer in digital communications and revered teacher and mentor to communications engineers.
Professor Suh is a recipient of numerous awards, including the 2021 James L. Massey Research & Teaching Award for Young Scholars from the IEEE Information Theory Society, the 2019 AFOSR Grant, the 2019 Google Education Grant, the 2018 IEIE/IEEE Joint Award, the 2015 IEIE Haedong Young Engineer Award, the 2013 IEEE Communications Society Stephen O. Rice Prize, the 2011 David J. Sakrison Memorial Prize (the best dissertation award in UC Berkeley EECS), the 2009 IEEE ISIT Best Student Paper Award, the 2020 LINKGENESIS Best Teacher Award (the campus-wide Grand Prize in Teaching), and the four Departmental Teaching Awards (2013, 2019, 2020, 2021).
Dr. Suh is an IEEE Information Theory Society Distinguished Lecturer, the General Chair of the Inaugural IEEE East Asian School of Information Theory, and a Member of the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology. He is also an Associate Editor of Machine Learning for the IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, the Editor for the IEEE Information Theory Newsletter, a Column Editor for IEEE BITS the Information Theory Magazine, an Area Chair of NeurIPS 2021, and on the Senior Program Committee of IJCAI 2019–2021.
2021.07.27 View 7848