THE
-
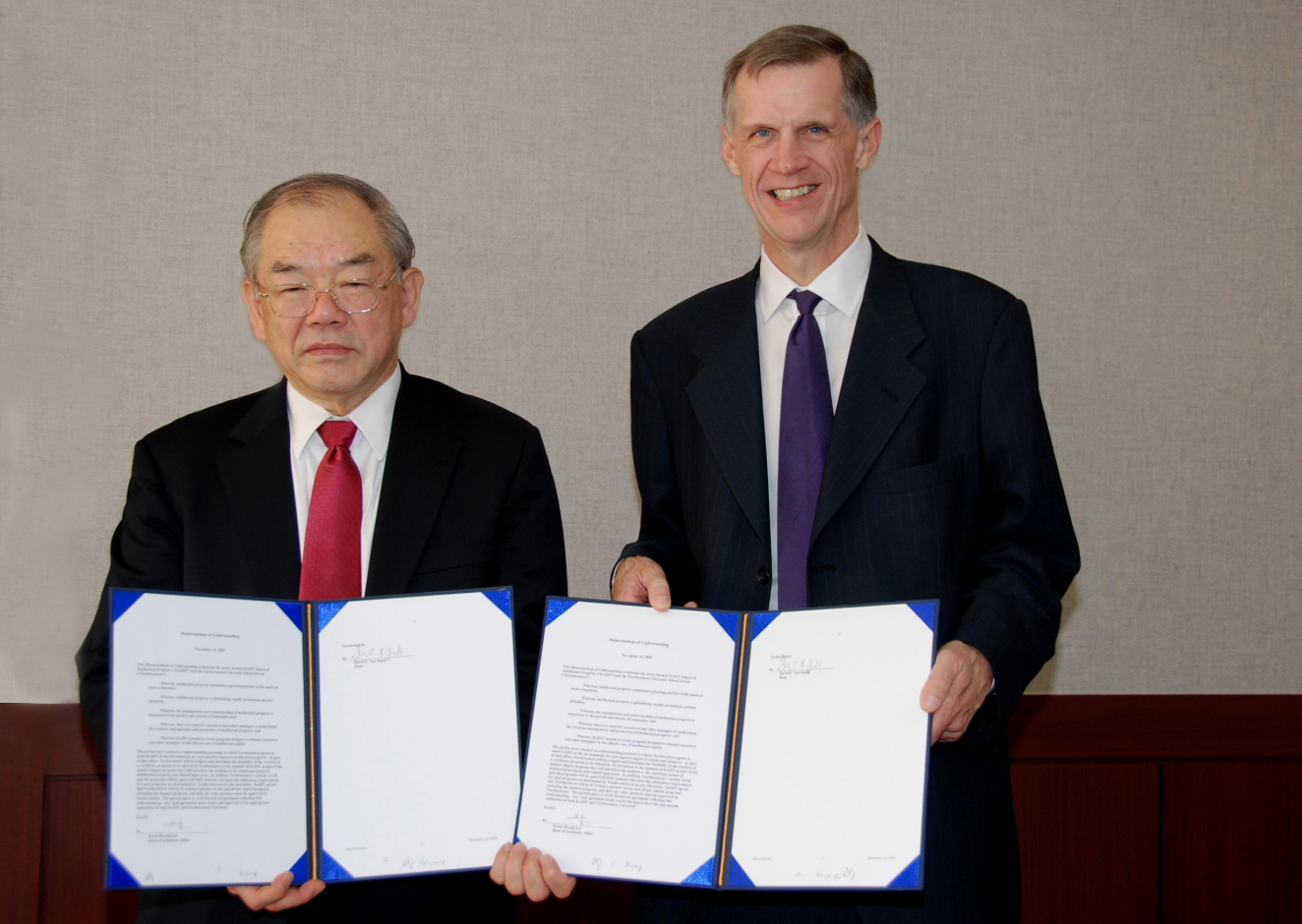 KAIST to Join Forces with Northwestern School of Law in MIP Program
KAIST has agreed to collaborate in its Master of Intellectual Property (MIP) program with Northwestern University School of Law, the university authorities said on Wednesday (Nov. 11).
KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh and Northwestern Univ. School of Law Dean David Van Zandt signed a memorandum of understanding for the establishment of the certificate and degree programs of the Anglo-American law in February 2010, at the president"s office Wednesday.
The latest agreement represents an expansion of the existing KAIST-Northwestern Executive LLM program that the two schools have successfully operated for the past eight years. It is aimed at boosting KAIST"s global intellectual property capabilities at a time when the strategic management of intellectual properties and capabilities to deal with international intellectual property disputes are gaining growing importance.
The newly-established two-year, six-semester program is designed to offer a certificate program in the Anglo-American and intellectual property laws to make students better armed with legal knowledge in a competitive global environment.
Northwestern University School of Law is regarded as one of the top law schools in the United States. American law schools are better positioned than any other institutions to prepare students to move from domestic to international practice in today"s complex global economy.
LLM is Latin for Legum Magister, signifying Master of Laws
. course and neto ba ... signing an agreement to run a joint masters degree program at the KAIST campus in Seou
2009.11.19 View 13354
KAIST to Join Forces with Northwestern School of Law in MIP Program
KAIST has agreed to collaborate in its Master of Intellectual Property (MIP) program with Northwestern University School of Law, the university authorities said on Wednesday (Nov. 11).
KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh and Northwestern Univ. School of Law Dean David Van Zandt signed a memorandum of understanding for the establishment of the certificate and degree programs of the Anglo-American law in February 2010, at the president"s office Wednesday.
The latest agreement represents an expansion of the existing KAIST-Northwestern Executive LLM program that the two schools have successfully operated for the past eight years. It is aimed at boosting KAIST"s global intellectual property capabilities at a time when the strategic management of intellectual properties and capabilities to deal with international intellectual property disputes are gaining growing importance.
The newly-established two-year, six-semester program is designed to offer a certificate program in the Anglo-American and intellectual property laws to make students better armed with legal knowledge in a competitive global environment.
Northwestern University School of Law is regarded as one of the top law schools in the United States. American law schools are better positioned than any other institutions to prepare students to move from domestic to international practice in today"s complex global economy.
LLM is Latin for Legum Magister, signifying Master of Laws
. course and neto ba ... signing an agreement to run a joint masters degree program at the KAIST campus in Seou
2009.11.19 View 13354 -
 KAIST, CJ Sign MOU for Joint Research in Fundamental Technologies
KAIST and CJ Corporation, Korea"s leading foodstuff maker, have reached an agreement for an enhanced industry-academy cooperation in the biotechnology area, the university authorities said on Tuesday (Nov. 10).
KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh signed a memorandum of understanding with Kim Jin-soo, CEO of CJ, at the KAIST campus on Tuesday (Nov. 10).
Under the agreement, KAIST and CJ will cooperate in nurturing elite research manpower and conducting joint researches in fundamental technologies. Specifically, CJ researchers will suggest research subjects linked with doctorate programs to KAIST, and once these subjects are accepted by KAIST, CJ researchers will conduct research under the guidance of KAIST professors to get doctorate degrees. All the costs including research expenses incurred during the program will be provided by CJ.
The agreement also calls for CJ to provide funding for the research subjects it selected among the ones suggested by KAIST"s biotechnology professors.
CJ CEO Jin-Soo Kim said: "Through the joint researches with KAIST which has the highest research capabilities, CJ can strengthen basic research capabilities and secure elite research manpower. We hope that the KAIST-CJ partnership will become a successful model for cooperation between industry and academia."
2009.11.11 View 12633
KAIST, CJ Sign MOU for Joint Research in Fundamental Technologies
KAIST and CJ Corporation, Korea"s leading foodstuff maker, have reached an agreement for an enhanced industry-academy cooperation in the biotechnology area, the university authorities said on Tuesday (Nov. 10).
KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh signed a memorandum of understanding with Kim Jin-soo, CEO of CJ, at the KAIST campus on Tuesday (Nov. 10).
Under the agreement, KAIST and CJ will cooperate in nurturing elite research manpower and conducting joint researches in fundamental technologies. Specifically, CJ researchers will suggest research subjects linked with doctorate programs to KAIST, and once these subjects are accepted by KAIST, CJ researchers will conduct research under the guidance of KAIST professors to get doctorate degrees. All the costs including research expenses incurred during the program will be provided by CJ.
The agreement also calls for CJ to provide funding for the research subjects it selected among the ones suggested by KAIST"s biotechnology professors.
CJ CEO Jin-Soo Kim said: "Through the joint researches with KAIST which has the highest research capabilities, CJ can strengthen basic research capabilities and secure elite research manpower. We hope that the KAIST-CJ partnership will become a successful model for cooperation between industry and academia."
2009.11.11 View 12633 -
 KAIST Signs MOU with Macquarie for Cooperation in Green Growth Projects
KAIST and Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory Co. have reached an agreement for cooperation in the development and commercialization of the KAIST-led two national green growth projects, On-line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) and Mobile Harbor (MH) programs, university authorities said.
KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh signed a memorandum of understanding with John Walker, Chairman of Macquarie Group of Companies in Korea, and Woo-Gon Hwang, Representative Director of Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory Co. on Wednesday, Oct. 21.
Under the agreement, KAIST and Macquarie will cooperate in developing an optimal business structure for a rapid commercialization of OLEV and MH. Specifically, Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory will provide financial advice, including basis financial analysis, potential investor inducement and feasibility analysis of the projects.
Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory Co. is a joint venture between Shinhan Financial Group of Korea and the Australia-based Macquarie Bank Group which provides global investment banking and diversified financial services.
KAIST"s OLEV is a project to develop a new growth engine for Korea and lead the future of global automotive industry. It is an entirely new concept: the electric vehicle picks up power from underground power supplier lines, while either running or standing, through the non-contact magnetic charging method.
The MH program is designed to develop a system that can load/unload containers from a containership in the open sea and deliver them to their destinations at the harbor.
The Korean government has included these KAIST projects, which both are great technical and engineering challenges, in the nation"s sustainable growth programs, providing substantial research grants. KAIST offers its advanced research capabilities for the nation"s efforts to achieve efficient, environment-friendly utilization of resources as new growth engines that spur the development of related industries and explore global markets.
2009.10.22 View 14592
KAIST Signs MOU with Macquarie for Cooperation in Green Growth Projects
KAIST and Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory Co. have reached an agreement for cooperation in the development and commercialization of the KAIST-led two national green growth projects, On-line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) and Mobile Harbor (MH) programs, university authorities said.
KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh signed a memorandum of understanding with John Walker, Chairman of Macquarie Group of Companies in Korea, and Woo-Gon Hwang, Representative Director of Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory Co. on Wednesday, Oct. 21.
Under the agreement, KAIST and Macquarie will cooperate in developing an optimal business structure for a rapid commercialization of OLEV and MH. Specifically, Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory will provide financial advice, including basis financial analysis, potential investor inducement and feasibility analysis of the projects.
Shinhan Macquarie Financial Advisory Co. is a joint venture between Shinhan Financial Group of Korea and the Australia-based Macquarie Bank Group which provides global investment banking and diversified financial services.
KAIST"s OLEV is a project to develop a new growth engine for Korea and lead the future of global automotive industry. It is an entirely new concept: the electric vehicle picks up power from underground power supplier lines, while either running or standing, through the non-contact magnetic charging method.
The MH program is designed to develop a system that can load/unload containers from a containership in the open sea and deliver them to their destinations at the harbor.
The Korean government has included these KAIST projects, which both are great technical and engineering challenges, in the nation"s sustainable growth programs, providing substantial research grants. KAIST offers its advanced research capabilities for the nation"s efforts to achieve efficient, environment-friendly utilization of resources as new growth engines that spur the development of related industries and explore global markets.
2009.10.22 View 14592 -
 KAIST Wins Official Membership of ERCIS
The Center for Software Policy Study of KAIST has recently become the 20th official member of the European Research Center for Information Systems (ERCIS) by signing an agreement with the organization, university authorities said on Thursday (Oct. 22).
The ERCIS is a network of scientists who conduct cooperative research in the field of integrated information systems development and organizational design. The Center undertakes interdisciplinary research with the participation of computer scientists, business management experts and law scholars.
KAIST will seek to activate exchange of professors, research fellows and graduate students with ERCIS members, as well as implementing credit exchange and dual degree programs.
ERCIS, was first organized by the German state of North Rhine-Westfahlia, is currently managed by the University of Muenster, a global leader in the field of information systems and business administration. Joining the ERCIS are one university each from New Zealand, the Netherlands, Germany, Russia, Liechtenstein, the United States, Switzerland, Spain, Slovenia, Ireland, Britain, Austria, Italy, the Czech Republic, Poland, France, Finland and Australia.
KAIST"s Center for Software Policy Study is currently preparing for the establishment of a support system for developers of the mobile application software as part of the EUREKA project. Korea is playing a leading role in this project on the strength of its competitiveness in the mobile phone industry.
EUREKA is a pan-European intergovernmental network for market-oriented, industrial R&D aimed at enhancing European competitiveness through its support to businesses, research centers and universities who carry out pan-European projects to develop innovative products, processes and services.
2009.10.22 View 13671
KAIST Wins Official Membership of ERCIS
The Center for Software Policy Study of KAIST has recently become the 20th official member of the European Research Center for Information Systems (ERCIS) by signing an agreement with the organization, university authorities said on Thursday (Oct. 22).
The ERCIS is a network of scientists who conduct cooperative research in the field of integrated information systems development and organizational design. The Center undertakes interdisciplinary research with the participation of computer scientists, business management experts and law scholars.
KAIST will seek to activate exchange of professors, research fellows and graduate students with ERCIS members, as well as implementing credit exchange and dual degree programs.
ERCIS, was first organized by the German state of North Rhine-Westfahlia, is currently managed by the University of Muenster, a global leader in the field of information systems and business administration. Joining the ERCIS are one university each from New Zealand, the Netherlands, Germany, Russia, Liechtenstein, the United States, Switzerland, Spain, Slovenia, Ireland, Britain, Austria, Italy, the Czech Republic, Poland, France, Finland and Australia.
KAIST"s Center for Software Policy Study is currently preparing for the establishment of a support system for developers of the mobile application software as part of the EUREKA project. Korea is playing a leading role in this project on the strength of its competitiveness in the mobile phone industry.
EUREKA is a pan-European intergovernmental network for market-oriented, industrial R&D aimed at enhancing European competitiveness through its support to businesses, research centers and universities who carry out pan-European projects to develop innovative products, processes and services.
2009.10.22 View 13671 -
 Board Chairman Chung Makes First Visit to Building Named After Him
Moon-Soul Chung, chairman of the KAIST board of trustees, visited the building built with his donation on Monday (Oct. 19) for the first time since he made the deed of gift eight years ago, university authorities said on Monday (Oct. 19).
In 2000, Chung, founder and former CEO of Mirae Corp, manufacturer of semiconductor testing equipment, announced retirement and handed over the presidency of his company to one of his managing directors. One year later in 2001, he donated 30 billion won, then equivalent to $30 million, to KAIST. It was by then the largest amount given by a single donor.
The major part of his donation went to constructing a building for the newly-established Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, and it was named after him. However, Chung did not attend the ground-breaking and dedication ceremonies, saying that he would not enter the building until KAIST achieved a breakthrough technology which can inject a hope to Koreans.
On his first visit to the building, he was briefed on the major research outcomes of the department over the past seven years, which were highlighted by the recent invention of an apparatus for measuring perfusion rate of legs. A KAIST team headed by Prof. Chul-Hee Choi invented a light leakage prevention unit including a light emitting device for radiating light having a certain wavelength onto a living body injected with Indocyanine Green (ICG).
According to Prof. Choi, the invention relates to an apparatus for measuring the perfusion rate of legs. The invention also includes a light leakage prevention housing formed to prevent transmission of external light.
Chung expressing satisfaction with the achievements and encouraged professors, researchers and students working at the Moon-Soul Chung Building.
2009.10.20 View 14432
Board Chairman Chung Makes First Visit to Building Named After Him
Moon-Soul Chung, chairman of the KAIST board of trustees, visited the building built with his donation on Monday (Oct. 19) for the first time since he made the deed of gift eight years ago, university authorities said on Monday (Oct. 19).
In 2000, Chung, founder and former CEO of Mirae Corp, manufacturer of semiconductor testing equipment, announced retirement and handed over the presidency of his company to one of his managing directors. One year later in 2001, he donated 30 billion won, then equivalent to $30 million, to KAIST. It was by then the largest amount given by a single donor.
The major part of his donation went to constructing a building for the newly-established Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, and it was named after him. However, Chung did not attend the ground-breaking and dedication ceremonies, saying that he would not enter the building until KAIST achieved a breakthrough technology which can inject a hope to Koreans.
On his first visit to the building, he was briefed on the major research outcomes of the department over the past seven years, which were highlighted by the recent invention of an apparatus for measuring perfusion rate of legs. A KAIST team headed by Prof. Chul-Hee Choi invented a light leakage prevention unit including a light emitting device for radiating light having a certain wavelength onto a living body injected with Indocyanine Green (ICG).
According to Prof. Choi, the invention relates to an apparatus for measuring the perfusion rate of legs. The invention also includes a light leakage prevention housing formed to prevent transmission of external light.
Chung expressing satisfaction with the achievements and encouraged professors, researchers and students working at the Moon-Soul Chung Building.
2009.10.20 View 14432 -
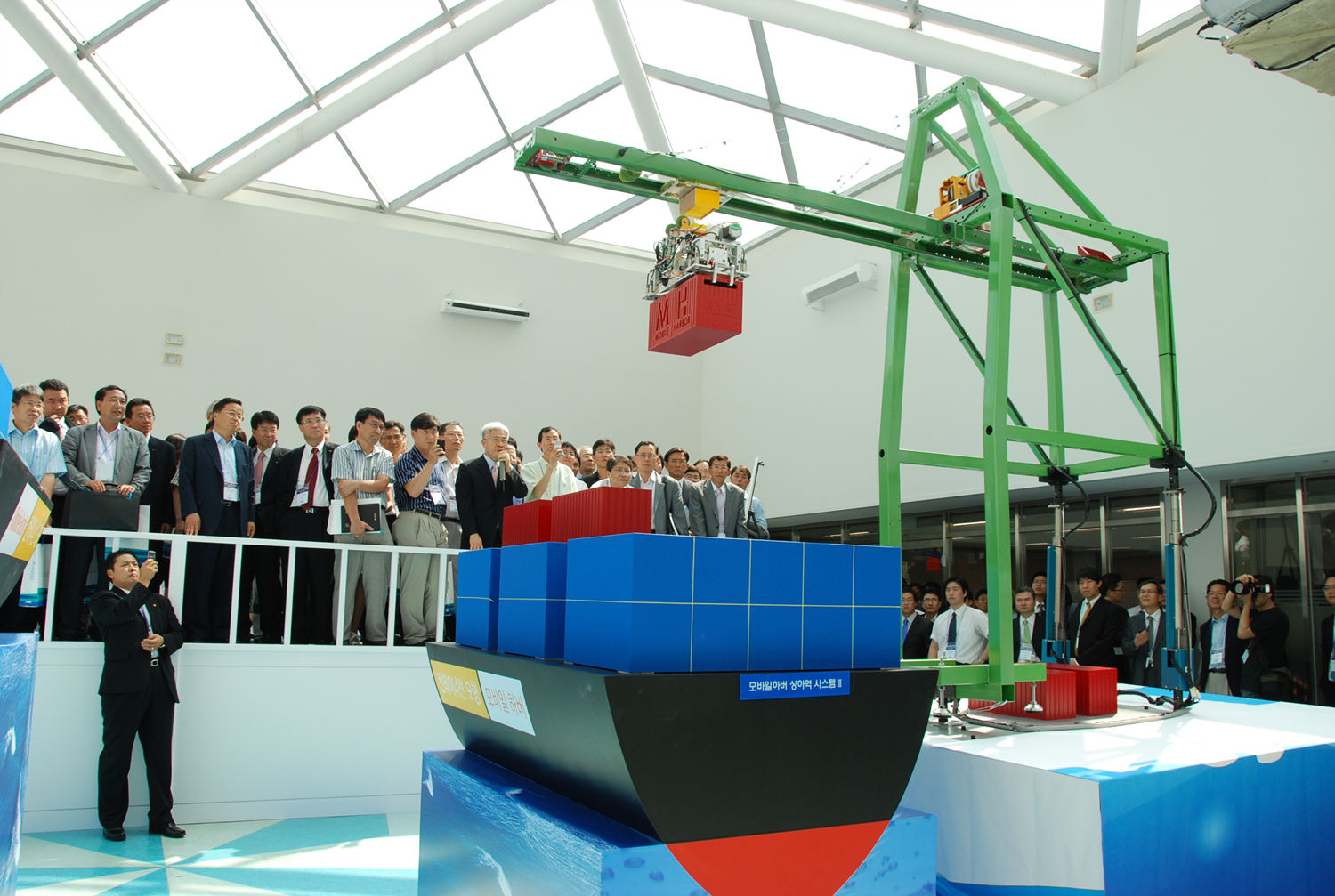 KAIST's Mobile Harbor Program Attracts Two Corporate Investments
KAIST-developed Mobile Harbor Program has attracted investments from Korea"s two big-name industrial corporations, university authorities said on Monday (Oct. 19).
KAIST has recently signed an agreement with Hyundai Wia Corp., a machine parts supplier, to collaborate in the researches of the mobile harbor programs and commercialization. Under the agreement, Hyundai WIA will invest a total of 7.5 billion won in the program for two years starting from January 2010.
KAIST has also received a letter of intent from the Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co. on investing 20 billion won in the commercialization of the project.
The Mobile Harbor Program is designed to create mobile units that can go out to the ship which are anchored off-shore and unload the cargo and take it to where it is needed. It is aimed at overcoming the shortcomings of the current maritime container transportation systems. Container ships are getting larger and larger, requiring deep waters, large and complex loading and unloading systems, and major investments in facilities.
Prof. Byung-Man Kwak, leader of the program"s R&D team, said: "With the investment from two global industrial companies, the program has gained a crucial momentum. The development of the program is expected to help Korea to become a global leader in marine transportation and maintain its supremacy in shipbuilding."
2009.10.20 View 16221
KAIST's Mobile Harbor Program Attracts Two Corporate Investments
KAIST-developed Mobile Harbor Program has attracted investments from Korea"s two big-name industrial corporations, university authorities said on Monday (Oct. 19).
KAIST has recently signed an agreement with Hyundai Wia Corp., a machine parts supplier, to collaborate in the researches of the mobile harbor programs and commercialization. Under the agreement, Hyundai WIA will invest a total of 7.5 billion won in the program for two years starting from January 2010.
KAIST has also received a letter of intent from the Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering Co. on investing 20 billion won in the commercialization of the project.
The Mobile Harbor Program is designed to create mobile units that can go out to the ship which are anchored off-shore and unload the cargo and take it to where it is needed. It is aimed at overcoming the shortcomings of the current maritime container transportation systems. Container ships are getting larger and larger, requiring deep waters, large and complex loading and unloading systems, and major investments in facilities.
Prof. Byung-Man Kwak, leader of the program"s R&D team, said: "With the investment from two global industrial companies, the program has gained a crucial momentum. The development of the program is expected to help Korea to become a global leader in marine transportation and maintain its supremacy in shipbuilding."
2009.10.20 View 16221 -
 KAIST Ranked 21st among World's Engineering Universities
KAIST was placed 21st in the area of engineering and information technology in this year"s world university rankings released on Oct. 8 (Thursday), climbing 13 notches from last year"s 34th. Seoul National University (SNU) ranked 27th, which made KAIST and SNU the only two institutions making it to the top 50 list. POSTECH ascended to 81st from last year"s 143rd.
In the "Times Higher Education--QS World University Rankings," Korean universities showed remarkable advancement this year; all-told five Korean universities made it to the top 200 list, as Yonsei and Korea universities were included in the list for the first time.
In overall rankings, KAIST moved 26 notches upward to grab the 69th position in the list, while SNU was placed 47th (50th last year).
The list, compiled by The Times (of London) newspaper annually, is topped by Harvard University, followed by University of Cambridge and Yale University.
Again this year, the United States had most of the top 100 universities in the world, with 32 included in the list. It was followed by the United Kingdom (18), Australia (8) and Japan (6).
Now in their 6th edition, the Times Higher Education--QS World University Rankings received a record level of responses from both the academic community and employers in 2009. A total of 9,386 academics (or 47 percent over 6,354 in 2008) and 3,281 employers (compared to 2,339 in 2008) responded to the surveys.
Times Higher Education -- QS World University Rankings evaluates institutions worldwide in four main categories: quality of research, globalization, quality of education, and contributions of graduates to society. The evaluation also considers academic peer review, citations per faculty, recruiter review, international faculty, international students and faculty-student ratio.
2009.10.09 View 14586
KAIST Ranked 21st among World's Engineering Universities
KAIST was placed 21st in the area of engineering and information technology in this year"s world university rankings released on Oct. 8 (Thursday), climbing 13 notches from last year"s 34th. Seoul National University (SNU) ranked 27th, which made KAIST and SNU the only two institutions making it to the top 50 list. POSTECH ascended to 81st from last year"s 143rd.
In the "Times Higher Education--QS World University Rankings," Korean universities showed remarkable advancement this year; all-told five Korean universities made it to the top 200 list, as Yonsei and Korea universities were included in the list for the first time.
In overall rankings, KAIST moved 26 notches upward to grab the 69th position in the list, while SNU was placed 47th (50th last year).
The list, compiled by The Times (of London) newspaper annually, is topped by Harvard University, followed by University of Cambridge and Yale University.
Again this year, the United States had most of the top 100 universities in the world, with 32 included in the list. It was followed by the United Kingdom (18), Australia (8) and Japan (6).
Now in their 6th edition, the Times Higher Education--QS World University Rankings received a record level of responses from both the academic community and employers in 2009. A total of 9,386 academics (or 47 percent over 6,354 in 2008) and 3,281 employers (compared to 2,339 in 2008) responded to the surveys.
Times Higher Education -- QS World University Rankings evaluates institutions worldwide in four main categories: quality of research, globalization, quality of education, and contributions of graduates to society. The evaluation also considers academic peer review, citations per faculty, recruiter review, international faculty, international students and faculty-student ratio.
2009.10.09 View 14586 -
 KAIST Secures Top Ranking of Korean Universities
KAIST won the No. 1 position for the second year in a row in the daily JoongAng Ilbo"s university rankings for 2009. Seoul National University took back the No. 2 spot, followed in order by POSTECH, Korea and Yonsei universities.
The survey was conducted in the four categories, educational environment/finance, professors" research, general reputation/social advancement and globalization. KAIST scored 293 points out of possible 400 this year, while the second-ranking SNU and third-ranking POSTECH earned 234 and 226 points, respectively.
The daily noted that KAIST particularly excelled in the category of educational environment/finance. It observed that donations to KAIST surged almost 100 times for the past three years since 2006 when President Suh took office.
In specific rankings of universities by academic disciplines, SNU came in first overall. KAIST topped in the science and engineering field, while Korea University ranked first in liberal arts studies.
This year, 88 four-year universities participated in the survey. The daily JoongAng Ilbo started its annual evaluation of Koran universities in 1994 to stimulate productive competition among institutions of higher learning and to provide objective standards for students and their parents to select schools for application.
For more information, news.joins.com/article/391/3789391.html
2009.09.24 View 15429
KAIST Secures Top Ranking of Korean Universities
KAIST won the No. 1 position for the second year in a row in the daily JoongAng Ilbo"s university rankings for 2009. Seoul National University took back the No. 2 spot, followed in order by POSTECH, Korea and Yonsei universities.
The survey was conducted in the four categories, educational environment/finance, professors" research, general reputation/social advancement and globalization. KAIST scored 293 points out of possible 400 this year, while the second-ranking SNU and third-ranking POSTECH earned 234 and 226 points, respectively.
The daily noted that KAIST particularly excelled in the category of educational environment/finance. It observed that donations to KAIST surged almost 100 times for the past three years since 2006 when President Suh took office.
In specific rankings of universities by academic disciplines, SNU came in first overall. KAIST topped in the science and engineering field, while Korea University ranked first in liberal arts studies.
This year, 88 four-year universities participated in the survey. The daily JoongAng Ilbo started its annual evaluation of Koran universities in 1994 to stimulate productive competition among institutions of higher learning and to provide objective standards for students and their parents to select schools for application.
For more information, news.joins.com/article/391/3789391.html
2009.09.24 View 15429 -
 World Research University Heads Discuss Challenges in Global Financial Turmoil at 2009 International Presidential Forum in Seoul
Leaders of the world"s major research universities discussed the impact of the global economic crisis on institutions of higher learning and their research activities in particular and exchanged opinions and visions on ways to increase cooperation with governments and industry at a symposium organized by KAIST Monday (Sept. 21) at the Westin Chosun Hotel in Seoul.
More than 50 participants of the 2nd International Presidential Forum on Global Research Universities represented institutions in North America, Europe, Southeast Asia, Australia, China and Japan. They were joined by 20 presidents of Korean universities and two dozens of leaders from industry and the government.
Under the main subject of "Challenges to Global Research Universities," the international symposium proceeded in four panel sessions. The subjects of each session and their keynote speakers were:
-- "Institutional Management in Times of Financial Crisis" by Kurt Kutzler, President of Berlin Institute of Technology
-- "Innovations in Education & Research" by Brian Cantor, Vice Chancellor of University of York
-- "Globalization of Institutes of Higher Learning" by Gary Schuster, Provost and Executive Vice President of Georgia Institute of Technology
-- "The Roles of Government, University and Industry in Green Technology Development" by KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh
KAIST President Suh expressed deep gratitude to all participants for their presentations focused on how universities weathered the difficulties from the economic turmoil and how they were continuing efforts for innovation in research and education. He observed that the 2009 International Presidential Forum was again most successful and productive after the first in 2008 and offered a precious opportunity for leaders of research universities to establish effective networking among their institutions.
"The world has witnessed a global financial turmoil of unseen magnitude and many nations are still struggling under the devastating impacts. While universities were no exception in facing economic turmoil, they have realized renewed pressures and expectations from their respective communities to provide answers to the great challenges,” he said in his welcoming remarks.
"The conference I am sure will have a far-reaching influence on the course our research universities will take to shoulder greater responsibilities for building a better future of the mankind."
Some of the participants in the 2009 International Presidential Forum came to KAIST’s Daejeon campus to take part in the EEWS (energy, environment, water and sustainability) workshop which was held on Tuesday, Sept. 22.
The Chronicle of Higher Learning, the Washington-based newspaper specializing in university education, reported from Seoul that the Forum revealed that, while American universities struggle amid the harshest economic climate in a generation, institutions in much of the rest of the world are sheltered from the fallout by strong government backing.
“Delegates to a conference of university presidents (in Seoul on Monday, Sept. 22) heard that colleges in Asia and Europe are pushing ahead with expansion plans – even as their U.S. counterparts cut back.
“The 2009 International Presidential Forum… was marked by a sharp divide in the tone set by European, Asian, and U.S. college leaders. The Americans often sounded a deeply gloomy note,” The Chronicle reported. “Never before has the impact been this bad,” the paper quoted Vishwanath Prasad, vice president for research and economic development at the University of North Texas, as saying.
On the other hand, Yves Poilane, vice president of the Paris Institute of Technology, said, according to The Chronicle, “The largely state financing of most European universities has so far acted as a shelter, and higher education remains a priority for both European and French Universities.”
The Korea Herald, published in Seoul, said in its Sept. 23 editorial:
“This week in Seoul, a symposium of leaders from international and Korean research universities heard top scholars and administrators reveal how their schools have suffered through the year under reduced government subsidies and private endowments which forced them to postpone various globalization schemes and cut down on research expenditures. Applications for master"s and Ph.D. programs declined while large percentages of graduates failed to find jobs.
“With their country showing a rapid pace of recovery, universities in Korea are in a better situation than many of their overseas counterparts, especially considering the substantial government outlays for research and development in "low carbon, green growth" projects that are largely dependent on research universities. The more the government seeks their direct contributions, the harder universities should try to increase transparency and accountability in the use of taxpayer money, so as not to betray the nation"s trust in them.
“In the wake of the global economic crisis, academia, government and industry find themselves in closer ties as they share new concepts of innovation and development in a common quest for growth. The tripartite cooperation has new significance in the recovery process. To achieve any development objectives, the other two partners must prioritize the funding of universities.”
2009.09.24 View 14505
World Research University Heads Discuss Challenges in Global Financial Turmoil at 2009 International Presidential Forum in Seoul
Leaders of the world"s major research universities discussed the impact of the global economic crisis on institutions of higher learning and their research activities in particular and exchanged opinions and visions on ways to increase cooperation with governments and industry at a symposium organized by KAIST Monday (Sept. 21) at the Westin Chosun Hotel in Seoul.
More than 50 participants of the 2nd International Presidential Forum on Global Research Universities represented institutions in North America, Europe, Southeast Asia, Australia, China and Japan. They were joined by 20 presidents of Korean universities and two dozens of leaders from industry and the government.
Under the main subject of "Challenges to Global Research Universities," the international symposium proceeded in four panel sessions. The subjects of each session and their keynote speakers were:
-- "Institutional Management in Times of Financial Crisis" by Kurt Kutzler, President of Berlin Institute of Technology
-- "Innovations in Education & Research" by Brian Cantor, Vice Chancellor of University of York
-- "Globalization of Institutes of Higher Learning" by Gary Schuster, Provost and Executive Vice President of Georgia Institute of Technology
-- "The Roles of Government, University and Industry in Green Technology Development" by KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh
KAIST President Suh expressed deep gratitude to all participants for their presentations focused on how universities weathered the difficulties from the economic turmoil and how they were continuing efforts for innovation in research and education. He observed that the 2009 International Presidential Forum was again most successful and productive after the first in 2008 and offered a precious opportunity for leaders of research universities to establish effective networking among their institutions.
"The world has witnessed a global financial turmoil of unseen magnitude and many nations are still struggling under the devastating impacts. While universities were no exception in facing economic turmoil, they have realized renewed pressures and expectations from their respective communities to provide answers to the great challenges,” he said in his welcoming remarks.
"The conference I am sure will have a far-reaching influence on the course our research universities will take to shoulder greater responsibilities for building a better future of the mankind."
Some of the participants in the 2009 International Presidential Forum came to KAIST’s Daejeon campus to take part in the EEWS (energy, environment, water and sustainability) workshop which was held on Tuesday, Sept. 22.
The Chronicle of Higher Learning, the Washington-based newspaper specializing in university education, reported from Seoul that the Forum revealed that, while American universities struggle amid the harshest economic climate in a generation, institutions in much of the rest of the world are sheltered from the fallout by strong government backing.
“Delegates to a conference of university presidents (in Seoul on Monday, Sept. 22) heard that colleges in Asia and Europe are pushing ahead with expansion plans – even as their U.S. counterparts cut back.
“The 2009 International Presidential Forum… was marked by a sharp divide in the tone set by European, Asian, and U.S. college leaders. The Americans often sounded a deeply gloomy note,” The Chronicle reported. “Never before has the impact been this bad,” the paper quoted Vishwanath Prasad, vice president for research and economic development at the University of North Texas, as saying.
On the other hand, Yves Poilane, vice president of the Paris Institute of Technology, said, according to The Chronicle, “The largely state financing of most European universities has so far acted as a shelter, and higher education remains a priority for both European and French Universities.”
The Korea Herald, published in Seoul, said in its Sept. 23 editorial:
“This week in Seoul, a symposium of leaders from international and Korean research universities heard top scholars and administrators reveal how their schools have suffered through the year under reduced government subsidies and private endowments which forced them to postpone various globalization schemes and cut down on research expenditures. Applications for master"s and Ph.D. programs declined while large percentages of graduates failed to find jobs.
“With their country showing a rapid pace of recovery, universities in Korea are in a better situation than many of their overseas counterparts, especially considering the substantial government outlays for research and development in "low carbon, green growth" projects that are largely dependent on research universities. The more the government seeks their direct contributions, the harder universities should try to increase transparency and accountability in the use of taxpayer money, so as not to betray the nation"s trust in them.
“In the wake of the global economic crisis, academia, government and industry find themselves in closer ties as they share new concepts of innovation and development in a common quest for growth. The tripartite cooperation has new significance in the recovery process. To achieve any development objectives, the other two partners must prioritize the funding of universities.”
2009.09.24 View 14505 -
 Prof. Cho Elected Editor-in-Chief of Systems Biology
Prof. Kwang-Hyun Cho of Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST has been recently elected editor-in-chief of the Systems Biology, an international journal published by the London-based Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET), the university authorities said on Wednesday (Sept. 23)
By the year 2012, Cho will oversee the editorial process of the journal covering intra- and inter-cellular dynamics, using systems- and signal-oriented approaches. IET, one of the world"s leading professional societies for the engineering and technology community, has a worldwide membership of more than 150,000.
Prof. Cho"s research interests cover the areas of systems science with bio-medical applications including systems biology and bio-inspired engineering based on molecular systems biology. He is currently an editorial board member of Systems and Synthetic Biology (Springer, Netherlands, from 2006), BMC Systems Biology (BMC, London, U.K., from 2007), Gene Regulation and Systems Biology (Libertas Academica, New Zealand, from 2007), and Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (Springer, New York, from 2008), and an editorial advisory board member of Molecular BioSystems (The Royal Society of Chemistry, U.K.).
2009.09.24 View 16632
Prof. Cho Elected Editor-in-Chief of Systems Biology
Prof. Kwang-Hyun Cho of Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST has been recently elected editor-in-chief of the Systems Biology, an international journal published by the London-based Institution of Engineering and Technology (IET), the university authorities said on Wednesday (Sept. 23)
By the year 2012, Cho will oversee the editorial process of the journal covering intra- and inter-cellular dynamics, using systems- and signal-oriented approaches. IET, one of the world"s leading professional societies for the engineering and technology community, has a worldwide membership of more than 150,000.
Prof. Cho"s research interests cover the areas of systems science with bio-medical applications including systems biology and bio-inspired engineering based on molecular systems biology. He is currently an editorial board member of Systems and Synthetic Biology (Springer, Netherlands, from 2006), BMC Systems Biology (BMC, London, U.K., from 2007), Gene Regulation and Systems Biology (Libertas Academica, New Zealand, from 2007), and Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (Springer, New York, from 2008), and an editorial advisory board member of Molecular BioSystems (The Royal Society of Chemistry, U.K.).
2009.09.24 View 16632 -
 World Research University Heads to Discuss Challenges in Global Financial Turmoil
About 70 leaders of the world"s major research universities will discuss how to better contribute to continued development of human society in global financial turmoil at a symposium organized by KAIST Monday (Sept. 21) at the Westin Chosun Hotel in Seoul.
Participants of the 2nd International Presidential Forum on Global Research Universities are from 40 universities in 25 countries, including Stanford University and Georgia Institute of Technology of the United States, Berlin Institute of Technology of Germany, Paris Institute of Technology of France, Technical University of Denmark, National University of Singapore and Tokyo Institute of Technology. They include 20 presidents of Korean universities and two dozens of leaders from industry and the government.
Under the main subject of "Challenges to Global Research Universities," the international symposium will proceed in four panel sessions. The subjects of each session and their keynote speakers are:
-- "Institutional Management in Times of Financial Crisis" by Kurt Kutzler, President of Berlin Institute of Technology
-- "Innovations in Education & Research" by Brian Cantor, Vice Chancellor of University of York
-- "Globalization of Institutes of Higher Learning" by Gary Schuster, Provost and Executive Vice President of Georgia Institute of Technology
-- "The Roles of Government, University and Industry in Green Technology Development" by KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh
KAIST President Suh said of the purpose of the conference: "The world has witnessed a global financial turmoil of unseen magnitude and many nations are still struggling under the devastating impacts. While universities were no exception in facing economic turmoil, they have realized renewed pressures and expectations from their respective communities to provide answers to the great challenges."
"The conference will serve as an opportunity for the representatives of research universities to compare their visions of networking among theier institutions and initiate steps for new relationships. The conference I am sure will have a far-reaching influence on the course our research universities will take to shoulder greater responsibilities for building a better future of the mankind."
For more information, visit forum.kaist.ac.kr
2009.09.16 View 17082
World Research University Heads to Discuss Challenges in Global Financial Turmoil
About 70 leaders of the world"s major research universities will discuss how to better contribute to continued development of human society in global financial turmoil at a symposium organized by KAIST Monday (Sept. 21) at the Westin Chosun Hotel in Seoul.
Participants of the 2nd International Presidential Forum on Global Research Universities are from 40 universities in 25 countries, including Stanford University and Georgia Institute of Technology of the United States, Berlin Institute of Technology of Germany, Paris Institute of Technology of France, Technical University of Denmark, National University of Singapore and Tokyo Institute of Technology. They include 20 presidents of Korean universities and two dozens of leaders from industry and the government.
Under the main subject of "Challenges to Global Research Universities," the international symposium will proceed in four panel sessions. The subjects of each session and their keynote speakers are:
-- "Institutional Management in Times of Financial Crisis" by Kurt Kutzler, President of Berlin Institute of Technology
-- "Innovations in Education & Research" by Brian Cantor, Vice Chancellor of University of York
-- "Globalization of Institutes of Higher Learning" by Gary Schuster, Provost and Executive Vice President of Georgia Institute of Technology
-- "The Roles of Government, University and Industry in Green Technology Development" by KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh
KAIST President Suh said of the purpose of the conference: "The world has witnessed a global financial turmoil of unseen magnitude and many nations are still struggling under the devastating impacts. While universities were no exception in facing economic turmoil, they have realized renewed pressures and expectations from their respective communities to provide answers to the great challenges."
"The conference will serve as an opportunity for the representatives of research universities to compare their visions of networking among theier institutions and initiate steps for new relationships. The conference I am sure will have a far-reaching influence on the course our research universities will take to shoulder greater responsibilities for building a better future of the mankind."
For more information, visit forum.kaist.ac.kr
2009.09.16 View 17082 -
 Prof. Ryoo's Team Discovers Breakthrough Method to Create New Zeolite
A group of scientists led by Prof. Ryong Ryoo of the Department of Chemistry, KAIST, has found a method to direct the growth of zeolite, a crystalline substance that is frequently used as catalyst in the chemical and petrochemical industries, the university authorities said on Thursday (Sept. 10).
Ryoo"s research team successfully created ultrathin nano-sheets, only two nano-meters thick, that are efficiently used as long-life catalysts for hydrocarbon cracking and other petrochemical applications. The breakthrough finding, which is credited with taking acidic zeolite catalysts to the limit in terms of thickness, was published in the latest edition of the peer-review journal, "Nature."
A team from the Polytechnic Univeristy of Valencia, Spain, also contributed to the research.
Zeolites are already widely used in the petrochemical industry, but making the catalysts very thin means that reactant molecules can easily diffuse into the zeolite structure and product molecules can get out quickly. This improves the efficiency of the catalyst and reduces unwanted side reactions that can produce polymeric hydrocarbon "coke" that clogs the zeolite pores and eventually kills the catalytic activity, Prof. Yoo said.
To make the thin sheets, Ryoo and his team used a surfactant as a template to direct the growth of the zeolite structure. The surfactant molecule has a polar "head" group - with two quaternary ammonium groups around which the aluminosilicate zeolite crystal grows - and a long hydrocarbon "tail," which prevents the sheets from aggregating together into larger, three dimensional crystals. When the surfactant is removed, these flakes pile up randomly with gaps in between which further aids diffusion to the catalyst sites.
"Zeolite could be used as a catalyst to convert heavy oil into gasoline. Our new zeolite could provide even more possibilities, such as being used as catalysts for transforming methanol into gasline," Ryoo said.
Prof. Ryoo, a Distinguished Professor of KAIST, has won a variety of academic awards, which included the Top Scientist Award given by the Korean government in 2005 and the 2001 KOSEF Science and Technology Award for his work on the synthesis and crystal structure of mezzoporous silica.
Ryoo obtained his bachelor"s degree from Seoul National University in 1977, master"s from KAIST in 1979, and doctorate from Stanford University in 1985.
In 2006, Ryoo and his research team announced the discovery of a form of zeolite that can catalyze petrochemical reactions much more effectively than previous zeolites. Because of the potential of this to streamline the gasoline refining process, it was greeted as a "magical substance" by the South Korean press.
2009.09.11 View 12832
Prof. Ryoo's Team Discovers Breakthrough Method to Create New Zeolite
A group of scientists led by Prof. Ryong Ryoo of the Department of Chemistry, KAIST, has found a method to direct the growth of zeolite, a crystalline substance that is frequently used as catalyst in the chemical and petrochemical industries, the university authorities said on Thursday (Sept. 10).
Ryoo"s research team successfully created ultrathin nano-sheets, only two nano-meters thick, that are efficiently used as long-life catalysts for hydrocarbon cracking and other petrochemical applications. The breakthrough finding, which is credited with taking acidic zeolite catalysts to the limit in terms of thickness, was published in the latest edition of the peer-review journal, "Nature."
A team from the Polytechnic Univeristy of Valencia, Spain, also contributed to the research.
Zeolites are already widely used in the petrochemical industry, but making the catalysts very thin means that reactant molecules can easily diffuse into the zeolite structure and product molecules can get out quickly. This improves the efficiency of the catalyst and reduces unwanted side reactions that can produce polymeric hydrocarbon "coke" that clogs the zeolite pores and eventually kills the catalytic activity, Prof. Yoo said.
To make the thin sheets, Ryoo and his team used a surfactant as a template to direct the growth of the zeolite structure. The surfactant molecule has a polar "head" group - with two quaternary ammonium groups around which the aluminosilicate zeolite crystal grows - and a long hydrocarbon "tail," which prevents the sheets from aggregating together into larger, three dimensional crystals. When the surfactant is removed, these flakes pile up randomly with gaps in between which further aids diffusion to the catalyst sites.
"Zeolite could be used as a catalyst to convert heavy oil into gasoline. Our new zeolite could provide even more possibilities, such as being used as catalysts for transforming methanol into gasline," Ryoo said.
Prof. Ryoo, a Distinguished Professor of KAIST, has won a variety of academic awards, which included the Top Scientist Award given by the Korean government in 2005 and the 2001 KOSEF Science and Technology Award for his work on the synthesis and crystal structure of mezzoporous silica.
Ryoo obtained his bachelor"s degree from Seoul National University in 1977, master"s from KAIST in 1979, and doctorate from Stanford University in 1985.
In 2006, Ryoo and his research team announced the discovery of a form of zeolite that can catalyze petrochemical reactions much more effectively than previous zeolites. Because of the potential of this to streamline the gasoline refining process, it was greeted as a "magical substance" by the South Korean press.
2009.09.11 View 12832