TE
-
 Chem-E-Car Team to Vie for World Title
Team KAItalyst, composed of KAIST undergraduate students, celebrated victory in the regional qualifying rounds of the 2019 International Chem-E-Car Competition held at KAIST’s Main Campus in Daejeon on July 20. The high finish in the national rankings qualified the team for a trip to the world finals to be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, in November.
The Chem-E-Car Competition involves designing and building a shoebox-sized model car that is powered and controlled by chemical reactions. University students from all over the world have been actively participating in this competition since the competition was introduced by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) in 1999.
KAIST first entered the competition in 2014, won the world finals in 2016, and then received the Most Consistent Award in 2017 and 2018. In recognition of KAIST’s consistently outstanding performance in the competition, AIChE asked KAIST to host this year’s regional competition for the first time in Korea.
Although a number of Korean university student teams have shown great interest in participating in this regional competition, most were not able to successfully implement their technology, and only two teams each from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) joined the competition.
Each team collaborated to fabricate a chemically powered model car that could carry a payload, and travel any distance between 15 and 30 meters. The weight of the payload and the travelling distance were randomly set an hour before the competition started, to require the participating teams adapt and perform calculations in a short period of time. The goal was to stop travelling exactly at the randomly chosen distance. The car closest to the finish line at the end of the race earned the highest amount of points. Precise control over chemical reactions was key to landing directly on the mark.
Team KAItalyst, consisting of six KAIST undergraduate students majoring in chemical and biomolecular engineering and mechanical engineering, beat their SNU rivals by stopping their car 1.5 meters closer to the goal at the end of the 22.5 meter-long race. Team KAItalyst loaded vanadium redox flow batteries onto their car to stabilize its output, and further increased the accuracy and velocity of chemical reactions through iodine clock reactions. 200 USD was awarded to Team KAItalyst, and 100 USD in prize money went to the SNU team.
KAItalyst team leader Jee-Hyun Hong said, “This was the first time for us to develop and drive our own chemically-powered model car, and we learned a lot from the challenges we faced,” Hong continued, “We will step up our efforts to perform better in the upcoming international competition.” The world finals will be held during the AIChE Fall Meeting in Orlando, Florida in November. Students from over 50 universities worldwide including the Georgia Institute of Technology and Carnegie Mellon University will compete against each other. The first, second, and third prizes at the finals will be 2,000, 1,000, and 500 USD respectively.
Professor Dong-Yeun Koh of the KAIST Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department who advised Team KAItalyst remarked, “I hope this year’s regional competition that KAIST held for the first time as a Korean university will be a possible starting point for more Korean universities to participate and compete in the future.”
(END)
2019.08.05 View 6567
Chem-E-Car Team to Vie for World Title
Team KAItalyst, composed of KAIST undergraduate students, celebrated victory in the regional qualifying rounds of the 2019 International Chem-E-Car Competition held at KAIST’s Main Campus in Daejeon on July 20. The high finish in the national rankings qualified the team for a trip to the world finals to be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, in November.
The Chem-E-Car Competition involves designing and building a shoebox-sized model car that is powered and controlled by chemical reactions. University students from all over the world have been actively participating in this competition since the competition was introduced by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) in 1999.
KAIST first entered the competition in 2014, won the world finals in 2016, and then received the Most Consistent Award in 2017 and 2018. In recognition of KAIST’s consistently outstanding performance in the competition, AIChE asked KAIST to host this year’s regional competition for the first time in Korea.
Although a number of Korean university student teams have shown great interest in participating in this regional competition, most were not able to successfully implement their technology, and only two teams each from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) joined the competition.
Each team collaborated to fabricate a chemically powered model car that could carry a payload, and travel any distance between 15 and 30 meters. The weight of the payload and the travelling distance were randomly set an hour before the competition started, to require the participating teams adapt and perform calculations in a short period of time. The goal was to stop travelling exactly at the randomly chosen distance. The car closest to the finish line at the end of the race earned the highest amount of points. Precise control over chemical reactions was key to landing directly on the mark.
Team KAItalyst, consisting of six KAIST undergraduate students majoring in chemical and biomolecular engineering and mechanical engineering, beat their SNU rivals by stopping their car 1.5 meters closer to the goal at the end of the 22.5 meter-long race. Team KAItalyst loaded vanadium redox flow batteries onto their car to stabilize its output, and further increased the accuracy and velocity of chemical reactions through iodine clock reactions. 200 USD was awarded to Team KAItalyst, and 100 USD in prize money went to the SNU team.
KAItalyst team leader Jee-Hyun Hong said, “This was the first time for us to develop and drive our own chemically-powered model car, and we learned a lot from the challenges we faced,” Hong continued, “We will step up our efforts to perform better in the upcoming international competition.” The world finals will be held during the AIChE Fall Meeting in Orlando, Florida in November. Students from over 50 universities worldwide including the Georgia Institute of Technology and Carnegie Mellon University will compete against each other. The first, second, and third prizes at the finals will be 2,000, 1,000, and 500 USD respectively.
Professor Dong-Yeun Koh of the KAIST Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department who advised Team KAItalyst remarked, “I hope this year’s regional competition that KAIST held for the first time as a Korean university will be a possible starting point for more Korean universities to participate and compete in the future.”
(END)
2019.08.05 View 6567 -
 KAMP to Help SMEs Achieve Technological Independence
As the Japanese government dropped Korea from its ‘White List’ of favored trade partner status last week, KAIST launched an advisory group to help the SMEs that are expected to be the most affected by the decision.
President Sung-Chul Shin announced on August 5 that KAIST is launching KAIST Advisors on Materials and Parts (KAMP), which is composed of 100 faculty members from five fields. President Shin said that KAIST would like to use this national crisis as an opportunity to make another leap forward by taking very timely and appropriate actions to help Korean SMEs achieve technological independence.
Headed by the Vice Dean of the College of Engineering, Sung-Yool Choi, KAMP will mainly advise in the fields of materials, parts, and equipment, which are crucial components for Korea’s key industries of semiconductors, energy, and automobiles. President Shin made the announcement following a meeting with senior leadership over the weekend. Faculty members including honorary professors from each committee’s department will be included as advisory group members.
In the letter sent out to the entire faculty right after the meeting, President Shin stressed the roles and responsibilities of scientists and engineers, especially from KAIST, which was founded with the national mission to foster the scientists and engineers urgently needed to work for the nation’s industrialization and R&D. He also said, “We now take on our new calling to deal with technology hegemony in the midst of this crisis caused by the worsening tensions between the two countries.” He added, “Soldiers were the main force in the frontline protecting the country during the period in which the military ruled. However, in this era where technology reigns, especially in the face of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, scientists and engineers should come forward to the frontlines.”
KAMP will be composed of the following five technology committees:
- The Advanced Materials Committee led by the Head of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
- The Chemistry and Biology Committee led by the Head of the Department of Chemistry
- The Chemical Engineering and Equipment Committee led by the Head of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- The Electronics and Computer Committee led by the Head of the School of Electrical Engineering - The Machinery and Aerospace Committee led by the Head of Department of the Mechanical Engineering
KAMP will support the development of 159 key technologies out of the 1,194 on the affected list. To promptly respond to the SMEs’ technological challenges, KAMP will designate an exclusive advisor based on the technological challenges they are experiencing.
Serving as emergency tech service providers, KAMP will identify and analyze the problems and will systematically manage the problem-solving procedures. In close collaboration with the Office of University-Industry Cooperation, KAMP will drive the innovative growth of Korea and will help it become highly technologically competitive and independent in the fields of key materials, parts, and equipment. President Shin said the university will make every effort institutionally and financially to make this advisory group’s work successful.
For SMEs who wish to use the KAMP advisory service, call +82-(0)42-350-6119 or send an email to smbrnd@kaist.ac.kr.
(END)
2019.08.05 View 4199
KAMP to Help SMEs Achieve Technological Independence
As the Japanese government dropped Korea from its ‘White List’ of favored trade partner status last week, KAIST launched an advisory group to help the SMEs that are expected to be the most affected by the decision.
President Sung-Chul Shin announced on August 5 that KAIST is launching KAIST Advisors on Materials and Parts (KAMP), which is composed of 100 faculty members from five fields. President Shin said that KAIST would like to use this national crisis as an opportunity to make another leap forward by taking very timely and appropriate actions to help Korean SMEs achieve technological independence.
Headed by the Vice Dean of the College of Engineering, Sung-Yool Choi, KAMP will mainly advise in the fields of materials, parts, and equipment, which are crucial components for Korea’s key industries of semiconductors, energy, and automobiles. President Shin made the announcement following a meeting with senior leadership over the weekend. Faculty members including honorary professors from each committee’s department will be included as advisory group members.
In the letter sent out to the entire faculty right after the meeting, President Shin stressed the roles and responsibilities of scientists and engineers, especially from KAIST, which was founded with the national mission to foster the scientists and engineers urgently needed to work for the nation’s industrialization and R&D. He also said, “We now take on our new calling to deal with technology hegemony in the midst of this crisis caused by the worsening tensions between the two countries.” He added, “Soldiers were the main force in the frontline protecting the country during the period in which the military ruled. However, in this era where technology reigns, especially in the face of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, scientists and engineers should come forward to the frontlines.”
KAMP will be composed of the following five technology committees:
- The Advanced Materials Committee led by the Head of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
- The Chemistry and Biology Committee led by the Head of the Department of Chemistry
- The Chemical Engineering and Equipment Committee led by the Head of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
- The Electronics and Computer Committee led by the Head of the School of Electrical Engineering - The Machinery and Aerospace Committee led by the Head of Department of the Mechanical Engineering
KAMP will support the development of 159 key technologies out of the 1,194 on the affected list. To promptly respond to the SMEs’ technological challenges, KAMP will designate an exclusive advisor based on the technological challenges they are experiencing.
Serving as emergency tech service providers, KAMP will identify and analyze the problems and will systematically manage the problem-solving procedures. In close collaboration with the Office of University-Industry Cooperation, KAMP will drive the innovative growth of Korea and will help it become highly technologically competitive and independent in the fields of key materials, parts, and equipment. President Shin said the university will make every effort institutionally and financially to make this advisory group’s work successful.
For SMEs who wish to use the KAMP advisory service, call +82-(0)42-350-6119 or send an email to smbrnd@kaist.ac.kr.
(END)
2019.08.05 View 4199 -
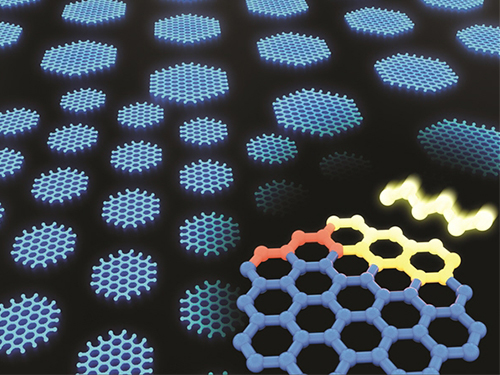 Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 33276
Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 33276 -
 FIRIC-EU JRC Joint Workshop on Smart Specialization
The Fourth Industrial Revolution Intelligence Center (FIRIC) at KAIST discussed ‘Smart Specialization’ for regional innovation and economic growth in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution during the workshop with the EU Joint Research Center (EU-JRC) in Seville, Spain last week. The two sides also agreed to sign an MOU to expand mutual collaboration.
KAIST’s FIRIC was founded in cooperation with the World Economic Forum in July 2017 to carry out policy research for the promotion of science and technology-based inclusive growth and innovation and to lead related global efforts. The EU-JRC has committed to developing cohesive policies that aim to narrow regional gaps within the European Union. Founded in 1958 in Brussels, the EU-JRC has long been in charge of EU strategies for regional innovation based on emerging technologies.
The workshop also covered issues related to public-private partnerships and innovation clusters from the perspective of the EU and Asia, such as the global value chain and the implementation of industrial clusters policy amid the changes in the industrial ecosystem due to digitalization, automation, and the utilization of robotics during the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In addition, the session included discussions on inclusive growth and job market changes in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, addressing how Smart Specialization and the outcomes of the 4IR will shift the paradigm of current job and technology capabilities, as well as employment issues in many relevant industries. In particular, the actual case studies and their related policies and regulatory trends regarding the potential risks and ethical issues of artificial intelligence were introduced.
Regarding the financial services that utilize blockchain technologies and the establishment of public sector governance for such technologies, the participating experts noted difficulties in the diffusion of blockchain-based local currencies or public services, which call for a sophisticated analytical and practical framework for innovative and transparent governance.
Dr. Mark Boden, the Team Leader of the EU-JRC, introduced the EU’s initiatives to promote Smart Specialization, such as its policy process, governance design, vision sharing, and priority setting, with particular emphasis on targeted support for Smart Specialization in lagging regions. Professor So Young Kim, who is the dean of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy and FIRIC’s Deputy Director said, “KAIST’s global role regarding the Fourth Industrial Revolution will be expanded in the process of exploring and developing innovative models of technology-policy governance while working jointly with the EU-JRC.”
2019.08.02 View 7526
FIRIC-EU JRC Joint Workshop on Smart Specialization
The Fourth Industrial Revolution Intelligence Center (FIRIC) at KAIST discussed ‘Smart Specialization’ for regional innovation and economic growth in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution during the workshop with the EU Joint Research Center (EU-JRC) in Seville, Spain last week. The two sides also agreed to sign an MOU to expand mutual collaboration.
KAIST’s FIRIC was founded in cooperation with the World Economic Forum in July 2017 to carry out policy research for the promotion of science and technology-based inclusive growth and innovation and to lead related global efforts. The EU-JRC has committed to developing cohesive policies that aim to narrow regional gaps within the European Union. Founded in 1958 in Brussels, the EU-JRC has long been in charge of EU strategies for regional innovation based on emerging technologies.
The workshop also covered issues related to public-private partnerships and innovation clusters from the perspective of the EU and Asia, such as the global value chain and the implementation of industrial clusters policy amid the changes in the industrial ecosystem due to digitalization, automation, and the utilization of robotics during the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In addition, the session included discussions on inclusive growth and job market changes in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, addressing how Smart Specialization and the outcomes of the 4IR will shift the paradigm of current job and technology capabilities, as well as employment issues in many relevant industries. In particular, the actual case studies and their related policies and regulatory trends regarding the potential risks and ethical issues of artificial intelligence were introduced.
Regarding the financial services that utilize blockchain technologies and the establishment of public sector governance for such technologies, the participating experts noted difficulties in the diffusion of blockchain-based local currencies or public services, which call for a sophisticated analytical and practical framework for innovative and transparent governance.
Dr. Mark Boden, the Team Leader of the EU-JRC, introduced the EU’s initiatives to promote Smart Specialization, such as its policy process, governance design, vision sharing, and priority setting, with particular emphasis on targeted support for Smart Specialization in lagging regions. Professor So Young Kim, who is the dean of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy and FIRIC’s Deputy Director said, “KAIST’s global role regarding the Fourth Industrial Revolution will be expanded in the process of exploring and developing innovative models of technology-policy governance while working jointly with the EU-JRC.”
2019.08.02 View 7526 -
 'Flying Drones for Rescue'
(Video Credit: ⓒNASA JPL)
< Team USRG and Professor Shim (second from the right) >
Having recently won the AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition in Korea, Team USRG (Unmanned System Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering is all geared up to take on their next challenges: the ‘Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency Subterranean Challenge (DARPA SubT Challenge)’ and ‘Lockheed Martin’s AlphaPilot Challenge’ next month.
Team USRG won the obstacle course race in the ‘2019 AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition’ on July 12. They managed to successfully dominate the challenging category of ‘control intelligence.’ Having to complete the obstacle course race solely using AI systems without any connection to the internet made it difficult for most of the eight participating teams to pass the third section of the race, and only Team USRG passed the long pipeline course during their attempt in the main event. They also demonstrated, after the main event, that their drone can navigate all of the checkpoints including landing on the “H” mark using deep learning.
Their drone flew through polls and pipes, and escaped from windows and mazes against strong winds, amid cheers and groans from the crowd gathered at the Korea Exhibition Center (KINTEX) in Goyang, Korea. The team was awarded three million KRW in prize money, and received a research grant worth six hundred million KRW from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
“Being ranked first in the race for which we were never given a chance for a test flight means a lot to our team. Considering that we had no information on the exact size of the course in advance, this is a startling result,” said Professor Shim. “We will carry out further research with this funding, and compete once again with the improved AI and drone technology in the 2020 competition,” he added.
The AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition, which was first started in 2017, has been designed to promote AI research and development and expand its application to addressing high-risk technical challenges with significant socio-economic impact.
This year’s competition presented participants with a task where they had to develop AI software technology for drones to navigate themselves autonomously during complex disaster relief operations such as aid delivery.
Each team participated in one of the four tracks of the competition, and their drones were evaluated based on the criteria for each track. The divisions were broken up into intelligent context-awareness, intelligent character recognition, auditory intelligence, and control intelligence.
Team USRG’s technological prowess has been already well acclaimed among international peer groups. Teamed up with NASA JPL, Caltech, and MIT, they will compete in the subterranean mission during the ‘DARPA SubT Challenge’.
Team CoSTAR, as its name stands for, is working together to build ‘Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Resilient Robots.’ Professor Shim emphasized the role KAIST plays in Team CoSTAR as a leader in drone technology.
“I think when our drone technology will be added to our peers’ AI and robotics, Team CoSTAR will bring out unsurpassable synergy in completing the subterrestrial and planetary applications. I would like to follow the footprint of Hubo, the winning champion of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge and even extend it to subterranean exploration,” he said.
These next generation autonomous subsurface explorers are now all optimizing the physical AI robot systems developed by Team CoSTAR. They will test their systems in more realistic field environments August 15 through 22 in Pittsburgh, USA. They have already received funding from DARPA for participating.
Team CoSTAR will compete in three consecutive yearly events starting this year, and the last event, planned for 2021, will put the team to the final test with courses that incorporate diverse challenges from all three events. Two million USD will be awarded to the winner after the final event, with additional prizes of up to 200,000 USD for self-funded teams.
Team USRG also ranked third in the recent Hyundai Motor Company’s ‘Autonomous Vehicle Competition’ and another challenge is on the horizon: Lockheed Martin’s ‘AlphaPilot Challenge’. In this event, the teams will be flying their drones through a series of racing gates, trying to beat the best human pilot. The challenge is hosted by Lockheed Martin, the world’s largest military contractor and the maker of the famed F-22 and F-35 stealth fighters, with the goal of stimulating the development of autonomous drones. Team USRG was selected from out of more than 400 teams from around the world and is preparing for a series of races this fall, beginning from the end of August.
Professor Shim said, “It is not easy to perform in a series of competitions in just a few months, but my students are smart, hardworking, and highly motivated. These events indeed demand a lot, but they really challenge the researchers to come up with technologies that work in the real world. This is the way robotics really should be.”
(END)
2019.07.26 View 12312
'Flying Drones for Rescue'
(Video Credit: ⓒNASA JPL)
< Team USRG and Professor Shim (second from the right) >
Having recently won the AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition in Korea, Team USRG (Unmanned System Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering is all geared up to take on their next challenges: the ‘Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency Subterranean Challenge (DARPA SubT Challenge)’ and ‘Lockheed Martin’s AlphaPilot Challenge’ next month.
Team USRG won the obstacle course race in the ‘2019 AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition’ on July 12. They managed to successfully dominate the challenging category of ‘control intelligence.’ Having to complete the obstacle course race solely using AI systems without any connection to the internet made it difficult for most of the eight participating teams to pass the third section of the race, and only Team USRG passed the long pipeline course during their attempt in the main event. They also demonstrated, after the main event, that their drone can navigate all of the checkpoints including landing on the “H” mark using deep learning.
Their drone flew through polls and pipes, and escaped from windows and mazes against strong winds, amid cheers and groans from the crowd gathered at the Korea Exhibition Center (KINTEX) in Goyang, Korea. The team was awarded three million KRW in prize money, and received a research grant worth six hundred million KRW from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
“Being ranked first in the race for which we were never given a chance for a test flight means a lot to our team. Considering that we had no information on the exact size of the course in advance, this is a startling result,” said Professor Shim. “We will carry out further research with this funding, and compete once again with the improved AI and drone technology in the 2020 competition,” he added.
The AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition, which was first started in 2017, has been designed to promote AI research and development and expand its application to addressing high-risk technical challenges with significant socio-economic impact.
This year’s competition presented participants with a task where they had to develop AI software technology for drones to navigate themselves autonomously during complex disaster relief operations such as aid delivery.
Each team participated in one of the four tracks of the competition, and their drones were evaluated based on the criteria for each track. The divisions were broken up into intelligent context-awareness, intelligent character recognition, auditory intelligence, and control intelligence.
Team USRG’s technological prowess has been already well acclaimed among international peer groups. Teamed up with NASA JPL, Caltech, and MIT, they will compete in the subterranean mission during the ‘DARPA SubT Challenge’.
Team CoSTAR, as its name stands for, is working together to build ‘Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Resilient Robots.’ Professor Shim emphasized the role KAIST plays in Team CoSTAR as a leader in drone technology.
“I think when our drone technology will be added to our peers’ AI and robotics, Team CoSTAR will bring out unsurpassable synergy in completing the subterrestrial and planetary applications. I would like to follow the footprint of Hubo, the winning champion of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge and even extend it to subterranean exploration,” he said.
These next generation autonomous subsurface explorers are now all optimizing the physical AI robot systems developed by Team CoSTAR. They will test their systems in more realistic field environments August 15 through 22 in Pittsburgh, USA. They have already received funding from DARPA for participating.
Team CoSTAR will compete in three consecutive yearly events starting this year, and the last event, planned for 2021, will put the team to the final test with courses that incorporate diverse challenges from all three events. Two million USD will be awarded to the winner after the final event, with additional prizes of up to 200,000 USD for self-funded teams.
Team USRG also ranked third in the recent Hyundai Motor Company’s ‘Autonomous Vehicle Competition’ and another challenge is on the horizon: Lockheed Martin’s ‘AlphaPilot Challenge’. In this event, the teams will be flying their drones through a series of racing gates, trying to beat the best human pilot. The challenge is hosted by Lockheed Martin, the world’s largest military contractor and the maker of the famed F-22 and F-35 stealth fighters, with the goal of stimulating the development of autonomous drones. Team USRG was selected from out of more than 400 teams from around the world and is preparing for a series of races this fall, beginning from the end of August.
Professor Shim said, “It is not easy to perform in a series of competitions in just a few months, but my students are smart, hardworking, and highly motivated. These events indeed demand a lot, but they really challenge the researchers to come up with technologies that work in the real world. This is the way robotics really should be.”
(END)
2019.07.26 View 12312 -
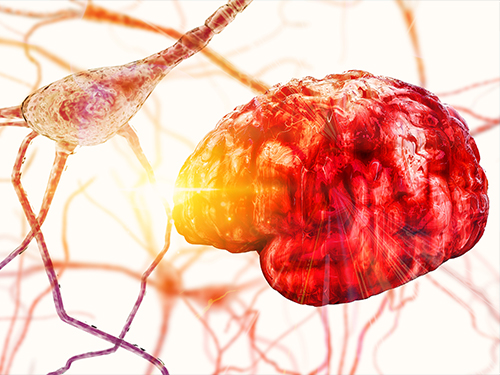 Newly Identified Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels Answers the Key Questions on Brain Clearance
(Figure: Schematic images of location and features of meningeal lymphatic vessels and their changes associated with ageing.)
Just see what happens when your neighborhood’s waste disposal system is out of service. Not only do the piles of trash stink but they can indeed hinder the area’s normal functioning. That is also the case when the brain’s waste management is on the blink.
The buildup of toxic proteins in the brain causes a massive damage to the nerves, leading to cognitive dysfunction and increased probability of developing neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Though the brain drains its waste via the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), little has been understood about an accurate route for the brain’s cleansing mechanism.
Medical scientists led by Professor Gou Young Koh at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering have reported the basal side of the skull as the major route, so called “hotspot” for CSF drainage.
They found that basal meningeal lymphatic vessels (mLVs) function as the main plumbing pipes for CSF. They confirmed macromolecules in the CSF mainly runs through the basal mLVs. Notably, the team also revealed that the brain’s major drainage system, specifically basal mLVs are impaired with aging. Their findings have been reported in the journal Nature on July 24.
Throughout our body, excess fluids and waste products are removed from tissues via lymphatic vessels. It was only recently discovered that the brain also has a lymphatic drainage system. mLVs are supposed to carry waste from the brain tissue fluid and the CSF down the deep cervical lymph nodes for disposal. Still scientist are left with one perplexing question — where is the main exit for the CSF? Though mLVs in the upper part of the skull (dorsal meningeal lymphatic vessels) were reported as the brain’s clearance pathways in 2014, no substantial drainage mechanism was observed in that section.
“As a hidden exit for CSF, we looked into the mLVs trapped within complex structures at the base of the skull,” says Dr. Ji Hoon Ahn, the first author of this study. The researchers used several techniques to characterize the basal mLVs in detail. They used a genetically engineered lymphatic-reporter mouse model to visualize mLVs under a fluorescence microscope. By performing a careful examination of the mice skull, they found distinctive features of basal mLVs that make them suitable for CSF uptake and drainage. Just like typical functional lymphatic vessels, basal mLVs are found to have abundant lymphatic vessel branches with finger-like protrusions. Additionally, valves inside the basal mLVs allow the flow to go in one direction. In particular, they found that the basal mLVs are closely located to the CSF. Dr. Hyunsoo Cho, the first author of this study explains, “All up, it seemed a solid case that basal mLVs are the brain’s main clearance pathways.
The researchers verified such specialized morphologic characteristics of basal mLVs indeed facilitate the CSF uptake and drainage. Using CSF contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a rat model, they found that CSF is drained preferentially through the basal mLVs. They also utilized a lymphatic-reporter mouse model and discovered that fluorescence-tagged tracer injected into the brain itself or the CSF is cleared mainly through the basal mLVs. Jun-Hee Kim, the first author of this study notes, “We literally saw that the brain clearance mechanism utilizing basal outflow route to exit the skull.
It has long been suggested that CSF turnover and drainage declines with ageing. However, alteration of mLVs associated with ageing is poorly understood. In this study, the researchers observed changes of mLVs in young (3-month-old) and aged (24~27-months-old) mice. They found that the structure of the basal mLVs and their lymphatic valves in aged mice become severely flawed, thus hampering CSF clearance. The corresponding author of this study, Dr. Koh says, “By characterizing the precise route for fluids leaving the brain, this study improves our understanding on how waste is cleared from the brain. Our findings also provide further insights into the role of impaired CSF clearance in the development of age-related neurodegenerative diseases.”
Many current therapies for Alzheimer’s disease target abnormally accumulated proteins, such as beta-amyloid. By mapping out a precise route for the brain’s waste clearance system, this study may be able to help find ways to improve the brain’s cleansing function. Such breakthrough might become quite a sensational strategy for eliminating the buildup of aging-related toxic proteins. “It definitely warrants more extensive investigation of mLVs in patients with age-related neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease prior to clinical investigation,” adds Professor Koh.
2019.07.25 View 32426
Newly Identified Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels Answers the Key Questions on Brain Clearance
(Figure: Schematic images of location and features of meningeal lymphatic vessels and their changes associated with ageing.)
Just see what happens when your neighborhood’s waste disposal system is out of service. Not only do the piles of trash stink but they can indeed hinder the area’s normal functioning. That is also the case when the brain’s waste management is on the blink.
The buildup of toxic proteins in the brain causes a massive damage to the nerves, leading to cognitive dysfunction and increased probability of developing neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Though the brain drains its waste via the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), little has been understood about an accurate route for the brain’s cleansing mechanism.
Medical scientists led by Professor Gou Young Koh at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering have reported the basal side of the skull as the major route, so called “hotspot” for CSF drainage.
They found that basal meningeal lymphatic vessels (mLVs) function as the main plumbing pipes for CSF. They confirmed macromolecules in the CSF mainly runs through the basal mLVs. Notably, the team also revealed that the brain’s major drainage system, specifically basal mLVs are impaired with aging. Their findings have been reported in the journal Nature on July 24.
Throughout our body, excess fluids and waste products are removed from tissues via lymphatic vessels. It was only recently discovered that the brain also has a lymphatic drainage system. mLVs are supposed to carry waste from the brain tissue fluid and the CSF down the deep cervical lymph nodes for disposal. Still scientist are left with one perplexing question — where is the main exit for the CSF? Though mLVs in the upper part of the skull (dorsal meningeal lymphatic vessels) were reported as the brain’s clearance pathways in 2014, no substantial drainage mechanism was observed in that section.
“As a hidden exit for CSF, we looked into the mLVs trapped within complex structures at the base of the skull,” says Dr. Ji Hoon Ahn, the first author of this study. The researchers used several techniques to characterize the basal mLVs in detail. They used a genetically engineered lymphatic-reporter mouse model to visualize mLVs under a fluorescence microscope. By performing a careful examination of the mice skull, they found distinctive features of basal mLVs that make them suitable for CSF uptake and drainage. Just like typical functional lymphatic vessels, basal mLVs are found to have abundant lymphatic vessel branches with finger-like protrusions. Additionally, valves inside the basal mLVs allow the flow to go in one direction. In particular, they found that the basal mLVs are closely located to the CSF. Dr. Hyunsoo Cho, the first author of this study explains, “All up, it seemed a solid case that basal mLVs are the brain’s main clearance pathways.
The researchers verified such specialized morphologic characteristics of basal mLVs indeed facilitate the CSF uptake and drainage. Using CSF contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a rat model, they found that CSF is drained preferentially through the basal mLVs. They also utilized a lymphatic-reporter mouse model and discovered that fluorescence-tagged tracer injected into the brain itself or the CSF is cleared mainly through the basal mLVs. Jun-Hee Kim, the first author of this study notes, “We literally saw that the brain clearance mechanism utilizing basal outflow route to exit the skull.
It has long been suggested that CSF turnover and drainage declines with ageing. However, alteration of mLVs associated with ageing is poorly understood. In this study, the researchers observed changes of mLVs in young (3-month-old) and aged (24~27-months-old) mice. They found that the structure of the basal mLVs and their lymphatic valves in aged mice become severely flawed, thus hampering CSF clearance. The corresponding author of this study, Dr. Koh says, “By characterizing the precise route for fluids leaving the brain, this study improves our understanding on how waste is cleared from the brain. Our findings also provide further insights into the role of impaired CSF clearance in the development of age-related neurodegenerative diseases.”
Many current therapies for Alzheimer’s disease target abnormally accumulated proteins, such as beta-amyloid. By mapping out a precise route for the brain’s waste clearance system, this study may be able to help find ways to improve the brain’s cleansing function. Such breakthrough might become quite a sensational strategy for eliminating the buildup of aging-related toxic proteins. “It definitely warrants more extensive investigation of mLVs in patients with age-related neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease prior to clinical investigation,” adds Professor Koh.
2019.07.25 View 32426 -
 KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research
Google has agreed to support KAIST students and professors in the fields of AI research and education. President Sung-Chul Shin and Google Korea Country Director John Lee signed the collaboration agreement during a ceremony on July 19 at KAIST.
Under the agreement, Google will fund the Google AI-Focused Research Awards Program, the PhD Fellowship Program, and Student Travel Grants for KAIST. In addition, Google will continue to provide more academic and career building opportunities for students, including Google internship programs.
KAIST and Google has been collaborating for years. Professor Steven Whang at the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sung Ju Hwang at the School of Computing won the AI-Focused Award in 2018 and conduct their researches on "Improving Generalization and Reliability of Any Deep Neural Networks" and "Automatic and Acitionable Model Analysis for TFX," respectively. Outstanding PhD students have been recognized through the PhD Fellowship Program. However, this new collaboration agreement will focus on research, academic development, and technological innovation in AI.
Google plans to support research in the fields of deep learning, cloud machine learning, and voice technologies. Google will fund the development of two educational programs based on Google open source technology each year for two years that will be used in the new AI Graduate School opening for the fall semester.
John Lee of Google Korea said, “This partnership lays a solid foundation for deeper collaboration.” President Shin added, “This partnership will not only advance Korea’s global competitiveness in AI-powered industries but also contribute to the global community by nurturing talents in this most extensive discipline.”
2019.07.22 View 8327
KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research
Google has agreed to support KAIST students and professors in the fields of AI research and education. President Sung-Chul Shin and Google Korea Country Director John Lee signed the collaboration agreement during a ceremony on July 19 at KAIST.
Under the agreement, Google will fund the Google AI-Focused Research Awards Program, the PhD Fellowship Program, and Student Travel Grants for KAIST. In addition, Google will continue to provide more academic and career building opportunities for students, including Google internship programs.
KAIST and Google has been collaborating for years. Professor Steven Whang at the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sung Ju Hwang at the School of Computing won the AI-Focused Award in 2018 and conduct their researches on "Improving Generalization and Reliability of Any Deep Neural Networks" and "Automatic and Acitionable Model Analysis for TFX," respectively. Outstanding PhD students have been recognized through the PhD Fellowship Program. However, this new collaboration agreement will focus on research, academic development, and technological innovation in AI.
Google plans to support research in the fields of deep learning, cloud machine learning, and voice technologies. Google will fund the development of two educational programs based on Google open source technology each year for two years that will be used in the new AI Graduate School opening for the fall semester.
John Lee of Google Korea said, “This partnership lays a solid foundation for deeper collaboration.” President Shin added, “This partnership will not only advance Korea’s global competitiveness in AI-powered industries but also contribute to the global community by nurturing talents in this most extensive discipline.”
2019.07.22 View 8327 -
 Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 39637
Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 39637 -
 President Shin Shares Innovation Strategy at Moscow
President Sung-Chul Shin shared the recipe for success for rapid national development through university education during the Island 10-22 Conference held at the Skolov Institute of Science and Technology in Moscow on July 16.
President Shin stressed how urgent it is for higher education to rapidly embrace the new global economic environment brought about by the Fourth Industrial Revolution in his keynote address entitled ‘Roles and Responsibilities of Universities for Rapid National Development’.
The Island 10-22 Conference is a summit co-organized by the National University of Science and Technology MISIS and University of the National Technological Initiative 2035 and supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation. More than 30 world-renowned experts, presidents of leading technological universities including President Peretz Lavie from the Israel Institute of Technology Technion, President Scott Pulsipher from Western Governors University and specialists in big data participated in the conference as speakers and discussed a diverse spectrum of ideas for making innovations and digital transformations in universities. More than 1,600 participants joined the conference.
During his keynote speech, President Shin explained how Korea has achieved such rapid economic growth over the past half century. He cited the Korean government’s vision and innovation policies as factors leading to Korea’s phenomenal success. KAIST, one of the results of the Korean government’s innovation policy, led the nation to advanced technological breakthroughs in industries such as semiconductors. Such visionary policies and investments in science, technology, and education eventually made the Korea of today possible.
President Shin said that KAIST distinguished itself through its new vision of C3 that fosters intellectual creativity, caring for others, and a challenging mind . Under Vision 2031, a blueprint for becoming a leading global university, President Shin said the KAIST continues to strive for innovations in convergent education,research and entreprenurship.
2019.07.18 View 6744
President Shin Shares Innovation Strategy at Moscow
President Sung-Chul Shin shared the recipe for success for rapid national development through university education during the Island 10-22 Conference held at the Skolov Institute of Science and Technology in Moscow on July 16.
President Shin stressed how urgent it is for higher education to rapidly embrace the new global economic environment brought about by the Fourth Industrial Revolution in his keynote address entitled ‘Roles and Responsibilities of Universities for Rapid National Development’.
The Island 10-22 Conference is a summit co-organized by the National University of Science and Technology MISIS and University of the National Technological Initiative 2035 and supported by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation. More than 30 world-renowned experts, presidents of leading technological universities including President Peretz Lavie from the Israel Institute of Technology Technion, President Scott Pulsipher from Western Governors University and specialists in big data participated in the conference as speakers and discussed a diverse spectrum of ideas for making innovations and digital transformations in universities. More than 1,600 participants joined the conference.
During his keynote speech, President Shin explained how Korea has achieved such rapid economic growth over the past half century. He cited the Korean government’s vision and innovation policies as factors leading to Korea’s phenomenal success. KAIST, one of the results of the Korean government’s innovation policy, led the nation to advanced technological breakthroughs in industries such as semiconductors. Such visionary policies and investments in science, technology, and education eventually made the Korea of today possible.
President Shin said that KAIST distinguished itself through its new vision of C3 that fosters intellectual creativity, caring for others, and a challenging mind . Under Vision 2031, a blueprint for becoming a leading global university, President Shin said the KAIST continues to strive for innovations in convergent education,research and entreprenurship.
2019.07.18 View 6744 -
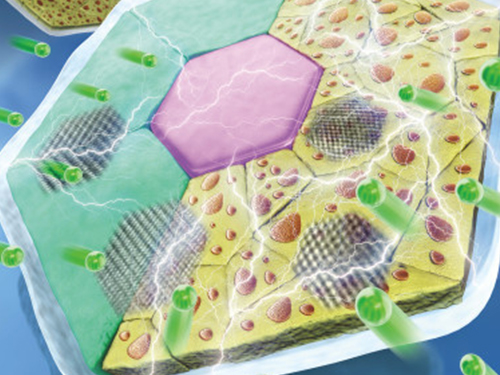 High-Performance Sodium Ion Batteries Using Copper Sulfide
(Prof.Yuk and his two PhD candidates Parks)
Researchers presented a new strategy for extending sodium ion batteries’ cyclability using copper sulfide as the electrode material. This strategy has led to high-performance conversion reactions and is expected to advance the commercialization of sodium ion batteries as they emerge as an alternative to lithium ion batteries.
Professor Jong Min Yuk’s team confirmed the stable sodium storage mechanism using copper sulfide, a superior electrode material that is pulverization-tolerant and induces capacity recovery. Their findings suggest that when employing copper sulfide, sodium ion batteries will have a lifetime of more than five years with one charge per a day. Even better, copper sulfide, composed of abundant natural materials such as copper and sulfur, has better cost competitiveness than lithium ion batteries, which use lithium and cobalt.
Intercalation-type materials such as graphite, which serve as commercialized anode materials in lithium ion batteries, have not been viable for high-capacity sodium storage due to their insufficient interlayer spacing. Thus, conversion and alloying reactions type materials have been explored to meet higher capacity in the anode part. However, those materials generally bring up large volume expansions and abrupt crystallographic changes, which lead to severe capacity degradation.
The team confirmed that semi-coherent phase interfaces and grain boundaries in conversion reactions played key roles in enabling pulverization-tolerant conversion reactions and capacity recovery, respectively.
Most of conversion and alloying reactions type battery materials usually experience severe capacity degradations due to having completely different crystal structures and large volume expansion before and after the reactions. However, copper sulfides underwent a gradual crystallographic change to make the semi-coherent interfaces, which eventually prevented the pulverization of particles. Based on this unique mechanism, the team confirmed that copper sulfide exhibits a high capacity and high cycling stability regardless of its size and morphology.
Professor Yuk said, “Sodium ion batteries employing copper sulfide can advance sodium ion batteries, which could contribute to the development of low-cost energy storage systems and address the micro-dust issue”
This study was posted in Advanced Science on April 26 online and selected as the inside back cover for June issue.
(Figure: Schematic model demonstrating grain boundaries and phase interfaces formations.)
2019.07.15 View 28142
High-Performance Sodium Ion Batteries Using Copper Sulfide
(Prof.Yuk and his two PhD candidates Parks)
Researchers presented a new strategy for extending sodium ion batteries’ cyclability using copper sulfide as the electrode material. This strategy has led to high-performance conversion reactions and is expected to advance the commercialization of sodium ion batteries as they emerge as an alternative to lithium ion batteries.
Professor Jong Min Yuk’s team confirmed the stable sodium storage mechanism using copper sulfide, a superior electrode material that is pulverization-tolerant and induces capacity recovery. Their findings suggest that when employing copper sulfide, sodium ion batteries will have a lifetime of more than five years with one charge per a day. Even better, copper sulfide, composed of abundant natural materials such as copper and sulfur, has better cost competitiveness than lithium ion batteries, which use lithium and cobalt.
Intercalation-type materials such as graphite, which serve as commercialized anode materials in lithium ion batteries, have not been viable for high-capacity sodium storage due to their insufficient interlayer spacing. Thus, conversion and alloying reactions type materials have been explored to meet higher capacity in the anode part. However, those materials generally bring up large volume expansions and abrupt crystallographic changes, which lead to severe capacity degradation.
The team confirmed that semi-coherent phase interfaces and grain boundaries in conversion reactions played key roles in enabling pulverization-tolerant conversion reactions and capacity recovery, respectively.
Most of conversion and alloying reactions type battery materials usually experience severe capacity degradations due to having completely different crystal structures and large volume expansion before and after the reactions. However, copper sulfides underwent a gradual crystallographic change to make the semi-coherent interfaces, which eventually prevented the pulverization of particles. Based on this unique mechanism, the team confirmed that copper sulfide exhibits a high capacity and high cycling stability regardless of its size and morphology.
Professor Yuk said, “Sodium ion batteries employing copper sulfide can advance sodium ion batteries, which could contribute to the development of low-cost energy storage systems and address the micro-dust issue”
This study was posted in Advanced Science on April 26 online and selected as the inside back cover for June issue.
(Figure: Schematic model demonstrating grain boundaries and phase interfaces formations.)
2019.07.15 View 28142 -
 Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 37131
Deep Learning-Powered 'DeepEC' Helps Accurately Understand Enzyme Functions
(Figure: Overall scheme of DeepEC)
A deep learning-powered computational framework, ‘DeepEC,’ will allow the high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers, which is essential for the accurate understanding of enzyme functions.
A team of Dr. Jae Yong Ryu, Professor Hyun Uk Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST reported the computational framework powered by deep learning that predicts enzyme commission (EC) numbers with high precision in a high-throughput manner.
DeepEC takes a protein sequence as an input and accurately predicts EC numbers as an output. Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions and EC numbers consisting of four level numbers (i.e., a.b.c.d) indicate biochemical reactions. Thus, the identification of EC numbers is critical for accurately understanding enzyme functions and metabolism.
EC numbers are usually given to a protein sequence encoding an enzyme during a genome annotation procedure. Because of the importance of EC numbers, several EC number prediction tools have been developed, but they have room for further improvement with respect to computation time, precision, coverage, and the total size of the files needed for the EC number prediction.
DeepEC uses three convolutional neural networks (CNNs) as a major engine for the prediction of EC numbers, and also implements homology analysis for EC numbers if the three CNNs do not produce reliable EC numbers for a given protein sequence. DeepEC was developed by using a gold standard dataset covering 1,388,606 protein sequences and 4,669 EC numbers.
In particular, benchmarking studies of DeepEC and five other representative EC number prediction tools showed that DeepEC made the most precise and fastest predictions for EC numbers. DeepEC also required the smallest disk space for implementation, which makes it an ideal third-party software component.
Furthermore, DeepEC was the most sensitive in detecting enzymatic function loss as a result of mutations in domains/binding site residue of protein sequences; in this comparative analysis, all the domains or binding site residue were substituted with L-alanine residue in order to remove the protein function, which is known as the L-alanine scanning method.
This study was published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 20, 2019, entitled “Deep learning enables high-quality and high-throughput prediction of enzyme commission numbers.”
“DeepEC can be used as an independent tool and also as a third-party software component in combination with other computational platforms that examine metabolic reactions. DeepEC is freely available online,” said Professor Kim.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “With DeepEC, it has become possible to process ever-increasing volumes of protein sequence data more efficiently and more accurately.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea. This work was also funded by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Korean government, the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile:
-Professor Hyun Uk Kim (ehukim@kaist.ac.kr)
https://sites.google.com/view/ehukim
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
-Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee (leesy@kaist.ac.kr)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
2019.07.09 View 37131 -
 Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 12007
Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 12007