TOM
-
 Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives IEEE ICRA 2020 Outstanding Reviewer Award
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was selected as this year’s winner of the Outstanding Reviewer Award presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation (IEEE ICRA). The award ceremony took place on June 5 during the conference that is being held online May 31 through August 31 for three months.
The IEEE ICRA Outstanding Reviewer Award is given every year to the top reviewers who have provided constructive and high-quality thesis reviews, and contributed to improving the quality of papers published as results of the conference.
Professor Ryu was one of the four winners of this year’s award. He was selected from 9,425 candidates, which was approximately three times bigger than the candidate pool in previous years. He was strongly recommended by the editorial committee of the conference.
(END)
2020.06.10 View 9101
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives IEEE ICRA 2020 Outstanding Reviewer Award
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was selected as this year’s winner of the Outstanding Reviewer Award presented by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers International Conference on Robotics and Automation (IEEE ICRA). The award ceremony took place on June 5 during the conference that is being held online May 31 through August 31 for three months.
The IEEE ICRA Outstanding Reviewer Award is given every year to the top reviewers who have provided constructive and high-quality thesis reviews, and contributed to improving the quality of papers published as results of the conference.
Professor Ryu was one of the four winners of this year’s award. He was selected from 9,425 candidates, which was approximately three times bigger than the candidate pool in previous years. He was strongly recommended by the editorial committee of the conference.
(END)
2020.06.10 View 9101 -
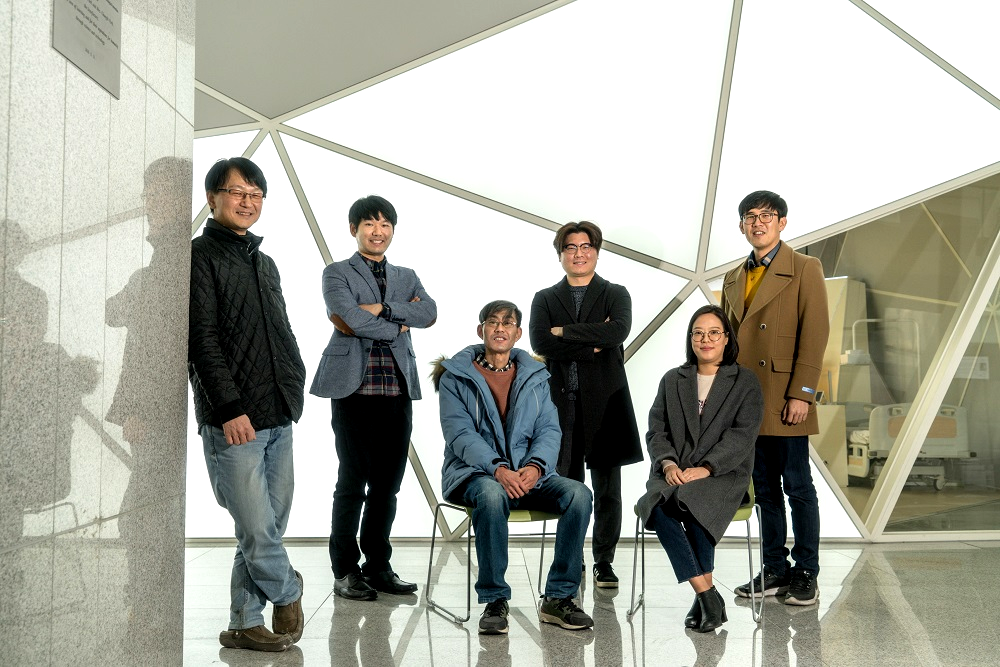 Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 10173
Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 10173 -
 Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 20905
Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 20905 -
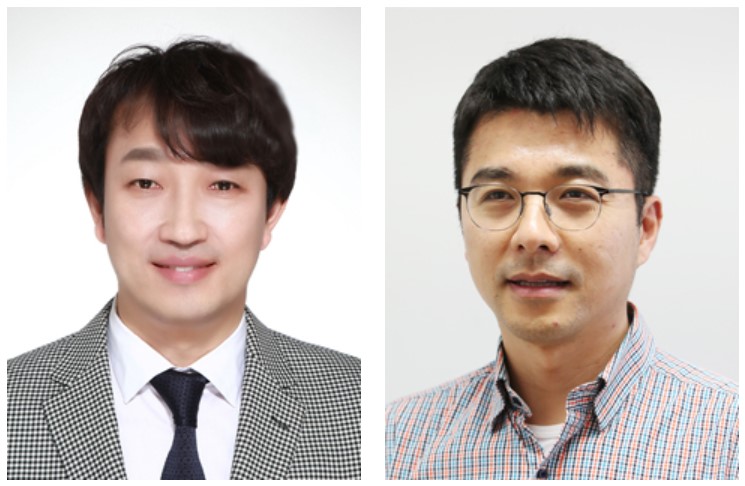 Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 11746
Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 11746 -
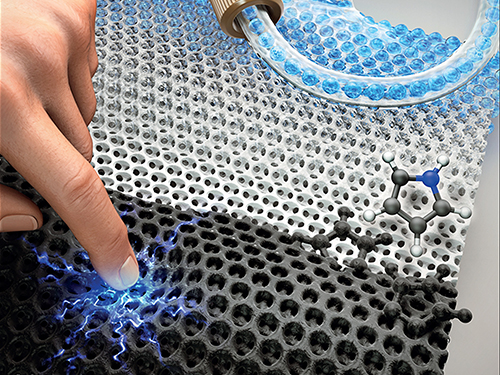 Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Pressure Sensor to Increase Practical Applicability
< Professor Steve Park (left) and the First Author Mr. Jinwon Oh (right) >
Researchers have designed a flexible pressure sensor that is expected to have a much wider applicability. A KAIST research team fabricated a piezoresistive pressure sensor of high uniformity with low hysteresis by chemically grafting a conductive polymer onto a porous elastomer template.
The team discovered that the uniformity of pore size and shape is directly related to the uniformity of the sensor. The team noted that by increasing pore size and shape variability, the variability of the sensor characteristics also increases.
Researchers led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering confirmed that compared to other sensors composed of randomly sized and shaped pores, which had a coefficient of variation in relative resistance change of 69.65%, their newly developed sensor exhibited much higher uniformity with a coefficient of variation of 2.43%. This study was reported in Small as the cover article on August 16.
Flexible pressure sensors have been actively researched and widely applied in electronic equipment such as touch screens, robots, wearable healthcare devices, electronic skin, and human-machine interfaces. In particular, piezoresistive pressure sensors based on elastomer‐conductive material composites hold significant potential due to their many advantages including a simple and low-cost fabrication process.
Various research results have been reported for ways to improve the performance of piezoresistive pressure sensors, most of which have been focused on increasing the sensitivity. Despite its significance, maximizing the sensitivity of composite-based piezoresistive pressure sensors is not necessary for many applications. On the other hand, sensor-to-sensor uniformity and hysteresis are two properties that are of critical importance to realize any application.
The importance of sensor-to-sensor uniformity is obvious. If the sensors manufactured under the same conditions have different properties, measurement reliability is compromised, and therefore the sensor cannot be used in a practical setting.
In addition, low hysteresis is also essential for improved measurement reliability. Hysteresis is a phenomenon in which the electrical readings differ depending on how fast or slow the sensor is being pressed, whether pressure is being released or applied, and how long and to what degree the sensor has been pressed. When a sensor has high hysteresis, the electrical readings will differ even under the same pressure, making the measurements unreliable.
Researchers said they observed a negligible hysteresis degree which was only 2%. This was attributed to the strong chemical bonding between the conductive polymer and the elastomer template, which prevents their relative sliding and displacement, and the porosity of the elastomer that enhances elastic behavior.
“This technology brings forth insight into how to address the two critical issues in pressure sensors: uniformity and hysteresis. We expect our technology to play an important role in increasing practical applications and the commercialization of pressure sensors in the near future,” said Professor Park.
This work was conducted as part of the KAIST‐funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2019, and also supported by the KUSTAR‐KAIST Institute.
Figure 1. Image of a porous elastomer template with uniform pore size and shape (left), Graph showing high uniformity in the sensors’ performance (right).
Figure 2. Hysteresis loops of the sensor at different pressure levels (left), and after a different number of cycles (right).
Figure 3. The cover page of Small Journal, Volume 15, Issue 33.
Publication:
Jinwon Oh, Jin‐Oh Kim, Yunjoo Kim, Han Byul Choi, Jun Chang Yang, Serin Lee, Mikhail Pyatykh, Jung Kim, Joo Yong Sim, and Steve Park. 2019. Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors Based on Chemical Grafting of Polypyrrole on Elastomer Template with Uniform Pore Size. Small. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Weinheim, Germany, Volume No. 15, Issue No. 33, Full Paper No. 201901744, 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901744
Profile: Prof. Steve Park, MS, PhD
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Mr. Jinwon Oh, MS
jwoh1701@gmail.com
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Researcher
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Jung Kim, MS, PhD
jungkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://medev.kaist.ac.kr/
Professor
Biorobotics Laboratory
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Joo Yong Sim, PhD
jsim@etri.re.kr
Researcher
Bio-Medical IT Convergence Research Department
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)
https://www.etri.re.krDaejeon 34129, Korea
(END)
2019.08.19 View 27696
Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Pressure Sensor to Increase Practical Applicability
< Professor Steve Park (left) and the First Author Mr. Jinwon Oh (right) >
Researchers have designed a flexible pressure sensor that is expected to have a much wider applicability. A KAIST research team fabricated a piezoresistive pressure sensor of high uniformity with low hysteresis by chemically grafting a conductive polymer onto a porous elastomer template.
The team discovered that the uniformity of pore size and shape is directly related to the uniformity of the sensor. The team noted that by increasing pore size and shape variability, the variability of the sensor characteristics also increases.
Researchers led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering confirmed that compared to other sensors composed of randomly sized and shaped pores, which had a coefficient of variation in relative resistance change of 69.65%, their newly developed sensor exhibited much higher uniformity with a coefficient of variation of 2.43%. This study was reported in Small as the cover article on August 16.
Flexible pressure sensors have been actively researched and widely applied in electronic equipment such as touch screens, robots, wearable healthcare devices, electronic skin, and human-machine interfaces. In particular, piezoresistive pressure sensors based on elastomer‐conductive material composites hold significant potential due to their many advantages including a simple and low-cost fabrication process.
Various research results have been reported for ways to improve the performance of piezoresistive pressure sensors, most of which have been focused on increasing the sensitivity. Despite its significance, maximizing the sensitivity of composite-based piezoresistive pressure sensors is not necessary for many applications. On the other hand, sensor-to-sensor uniformity and hysteresis are two properties that are of critical importance to realize any application.
The importance of sensor-to-sensor uniformity is obvious. If the sensors manufactured under the same conditions have different properties, measurement reliability is compromised, and therefore the sensor cannot be used in a practical setting.
In addition, low hysteresis is also essential for improved measurement reliability. Hysteresis is a phenomenon in which the electrical readings differ depending on how fast or slow the sensor is being pressed, whether pressure is being released or applied, and how long and to what degree the sensor has been pressed. When a sensor has high hysteresis, the electrical readings will differ even under the same pressure, making the measurements unreliable.
Researchers said they observed a negligible hysteresis degree which was only 2%. This was attributed to the strong chemical bonding between the conductive polymer and the elastomer template, which prevents their relative sliding and displacement, and the porosity of the elastomer that enhances elastic behavior.
“This technology brings forth insight into how to address the two critical issues in pressure sensors: uniformity and hysteresis. We expect our technology to play an important role in increasing practical applications and the commercialization of pressure sensors in the near future,” said Professor Park.
This work was conducted as part of the KAIST‐funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2019, and also supported by the KUSTAR‐KAIST Institute.
Figure 1. Image of a porous elastomer template with uniform pore size and shape (left), Graph showing high uniformity in the sensors’ performance (right).
Figure 2. Hysteresis loops of the sensor at different pressure levels (left), and after a different number of cycles (right).
Figure 3. The cover page of Small Journal, Volume 15, Issue 33.
Publication:
Jinwon Oh, Jin‐Oh Kim, Yunjoo Kim, Han Byul Choi, Jun Chang Yang, Serin Lee, Mikhail Pyatykh, Jung Kim, Joo Yong Sim, and Steve Park. 2019. Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors Based on Chemical Grafting of Polypyrrole on Elastomer Template with Uniform Pore Size. Small. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Weinheim, Germany, Volume No. 15, Issue No. 33, Full Paper No. 201901744, 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901744
Profile: Prof. Steve Park, MS, PhD
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Mr. Jinwon Oh, MS
jwoh1701@gmail.com
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Researcher
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Jung Kim, MS, PhD
jungkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://medev.kaist.ac.kr/
Professor
Biorobotics Laboratory
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Joo Yong Sim, PhD
jsim@etri.re.kr
Researcher
Bio-Medical IT Convergence Research Department
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)
https://www.etri.re.krDaejeon 34129, Korea
(END)
2019.08.19 View 27696 -
 Wearable Robot 'WalkON Suit' Off to Cybathlon 2020
Standing upright and walking alone are very simple but noble motions that separate humans from many other creatures. Wearable and prosthetic technologies have emerged to augment human function in locomotion and manipulation. However, advances in wearable robot technology have been especially momentous to Byoung-Wook Kim, a triplegic for 22 years following a devastating car accident.
Kim rejoiced after standing upright and walking again by putting on the ‘WalkON Suit,’ the wearable robot developed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team. Even more, Kim won third prize in the powered exoskeleton race at Cybathlon 2016, an international cyborg Olympics hosted by ETH Zurich.
Now Kim and Professor Kong’s team are all geared up for the Cybathlon Championship 2020. Professor Kong and his startup, Angel Robotics, held a kickoff ceremony for Cybathlon 2020 at KAIST on June 24. The 2020 championship will take place in Switzerland.
Only pilots with complete paralysis of the legs resulting from spinal cord injuries are eligible to participate in the Cybathlon, which takes place every four years. Pilots compete against each other while completing everyday tasks using technical assistance systems in six different disciplines: a brain-computer interface race, a functional electrical stimulation bike race, a powered arm prosthesis race, a powered leg prosthesis race, a powered exoskeleton race, and a powered wheelchair race. The 2016 championship drew 66 pilots from 56 teams representing 25 countries.
In the powered exoskeleton race, pilots complete everyday activities such as getting up from a sofa and overcoming obstacles such as stairs, ramps, or slopes and up to four pilots compete simultaneously on tracks to solve six tasks; and the pilot that solves the most tasks in the least amount of time wins the race.
(Kim, a triplegic for 22 years demonstrates walking and climbing the stairs (below photo) wearing the WalkOn Suit during the media day on June 21 at KAIST.)
Kim, who demonstrated walking and climbing the stairs wearing the WalkON Suit during the media day for the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony on June 21 at KAIST, said, “I have been confined to a wheelchair for more than 20 years. I am used to it so I feel like the wheelchair is one of my body parts. Actually, I don’t feel any big difficulties in doing everyday tasks in wheelchair. But whenever I face the fact that I will never be able to stand up with my own two legs again, I am so devastated.” He continued, “I still remember the day when I stood up with my own two legs by myself after 22 years. It was beyond description.”
The market for wearable robots, especially for exoskeleton robots, is continuing to grow as the aging population has been a major challenge in almost every advanced country. The global market for these robots expects to see annual growth of 41.2% to 8.3 billion US dollars by 2025. Healthcare wearable robots for the elderly and rehabilitation take up the half of the market share followed by wearable robots for industrial and defense purposes.
Professor Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his colleagues have developed two wearable robot systems in 2014: The "WalkON Suit" for complete paraplegics and “Angel Suit” for those with partial impairment in walking ability such as the elderly and rehabilitation patients.
Professor Kong said after 15 years of basic research, the team is now able to develop its own distinct technologies. He said their robots are powered by non-resistant precision drives with algorithms recognizing the user’s moving intention. Incorporated with prosthetic devices technology from the Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, their control technology has led to the production of a customizable robot suit optimized for each user’s physical condition.
The WalkON Suit, which boasts a maximum force of 250 Nm and maximum rotation speed of 45 RPM, gives the user high-energy efficiency modeled after the physiology of the human leg. It allows users to walk on flat ground and down stairs, climb up and down inclines, and sit and lie down. Currently the battery lasts five to six hours for locomotion and the approximate 25 kg of robot weight still remains a technical challenge to upgrade.
Professor Kong’s team has grafted AR glass technology into the WalkOn Suit that one of his pilots put on for the torch relay of the PyongChang Paralympics in 2018. His team is now upgrading the WalkON Suit 4.0 for next year’s competition. Severance Rehabilitation Hospital will help the seven pilots with their training.
Professor Kong said his goal is to make robots that can make people with disabilities much more independent. He stressed, “Wearable robots should be designed for each single user. We provide a very good graphical user interface so that we can design, check, and also verify our optimized design for users’ best performance.”
(Seven pilots and Professor Kong (fifth from left in second row) pose with guests who joined the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony. President Shin (fifth from right) made a congratulatory remarks during the ceremony.)
2019.06.25 View 40504
Wearable Robot 'WalkON Suit' Off to Cybathlon 2020
Standing upright and walking alone are very simple but noble motions that separate humans from many other creatures. Wearable and prosthetic technologies have emerged to augment human function in locomotion and manipulation. However, advances in wearable robot technology have been especially momentous to Byoung-Wook Kim, a triplegic for 22 years following a devastating car accident.
Kim rejoiced after standing upright and walking again by putting on the ‘WalkON Suit,’ the wearable robot developed by Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team. Even more, Kim won third prize in the powered exoskeleton race at Cybathlon 2016, an international cyborg Olympics hosted by ETH Zurich.
Now Kim and Professor Kong’s team are all geared up for the Cybathlon Championship 2020. Professor Kong and his startup, Angel Robotics, held a kickoff ceremony for Cybathlon 2020 at KAIST on June 24. The 2020 championship will take place in Switzerland.
Only pilots with complete paralysis of the legs resulting from spinal cord injuries are eligible to participate in the Cybathlon, which takes place every four years. Pilots compete against each other while completing everyday tasks using technical assistance systems in six different disciplines: a brain-computer interface race, a functional electrical stimulation bike race, a powered arm prosthesis race, a powered leg prosthesis race, a powered exoskeleton race, and a powered wheelchair race. The 2016 championship drew 66 pilots from 56 teams representing 25 countries.
In the powered exoskeleton race, pilots complete everyday activities such as getting up from a sofa and overcoming obstacles such as stairs, ramps, or slopes and up to four pilots compete simultaneously on tracks to solve six tasks; and the pilot that solves the most tasks in the least amount of time wins the race.
(Kim, a triplegic for 22 years demonstrates walking and climbing the stairs (below photo) wearing the WalkOn Suit during the media day on June 21 at KAIST.)
Kim, who demonstrated walking and climbing the stairs wearing the WalkON Suit during the media day for the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony on June 21 at KAIST, said, “I have been confined to a wheelchair for more than 20 years. I am used to it so I feel like the wheelchair is one of my body parts. Actually, I don’t feel any big difficulties in doing everyday tasks in wheelchair. But whenever I face the fact that I will never be able to stand up with my own two legs again, I am so devastated.” He continued, “I still remember the day when I stood up with my own two legs by myself after 22 years. It was beyond description.”
The market for wearable robots, especially for exoskeleton robots, is continuing to grow as the aging population has been a major challenge in almost every advanced country. The global market for these robots expects to see annual growth of 41.2% to 8.3 billion US dollars by 2025. Healthcare wearable robots for the elderly and rehabilitation take up the half of the market share followed by wearable robots for industrial and defense purposes.
Professor Kong from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his colleagues have developed two wearable robot systems in 2014: The "WalkON Suit" for complete paraplegics and “Angel Suit” for those with partial impairment in walking ability such as the elderly and rehabilitation patients.
Professor Kong said after 15 years of basic research, the team is now able to develop its own distinct technologies. He said their robots are powered by non-resistant precision drives with algorithms recognizing the user’s moving intention. Incorporated with prosthetic devices technology from the Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, their control technology has led to the production of a customizable robot suit optimized for each user’s physical condition.
The WalkON Suit, which boasts a maximum force of 250 Nm and maximum rotation speed of 45 RPM, gives the user high-energy efficiency modeled after the physiology of the human leg. It allows users to walk on flat ground and down stairs, climb up and down inclines, and sit and lie down. Currently the battery lasts five to six hours for locomotion and the approximate 25 kg of robot weight still remains a technical challenge to upgrade.
Professor Kong’s team has grafted AR glass technology into the WalkOn Suit that one of his pilots put on for the torch relay of the PyongChang Paralympics in 2018. His team is now upgrading the WalkON Suit 4.0 for next year’s competition. Severance Rehabilitation Hospital will help the seven pilots with their training.
Professor Kong said his goal is to make robots that can make people with disabilities much more independent. He stressed, “Wearable robots should be designed for each single user. We provide a very good graphical user interface so that we can design, check, and also verify our optimized design for users’ best performance.”
(Seven pilots and Professor Kong (fifth from left in second row) pose with guests who joined the Cybathlon 2020 kickoff ceremony. President Shin (fifth from right) made a congratulatory remarks during the ceremony.)
2019.06.25 View 40504 -
 Professor Jeong-Ho Lee Named the KAISTian of 2018
(Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) poses with President Sung-Chul Shin)
Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was selected as the KAISTian of the Year of 2018. The award was established in 2001 and recognizes the most outstanding scholars who have made significant research and scholastic achievements during the year. Professor Lee was awarded during the New Year ceremony held in the auditorium on January 2.
Professor Lee has investigated mutations arising in the brain for decades and has published in renowned journals such as Nature, Nature Medicine, and Cell. Last August, Professor Lee reported breakthrough research on glioblastoma in Nature, giving insight into understanding how the mutation causing glioblastoma starts and suggested novel ways to treat glioblastoma, which was thought to be incurable. (Click for more)
Professor Lee’s Translational Neurogenetics Laboratory lab is investigating innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma. To commercialize his technology, he established the tech-startup SoVarGen and now works as its CTO.
Professor Lee credited all his lab colleagues and staff. “I know all of this research would not have possible without their sweat and effort. I am happy to receive this honorable award on behalf of them.”
Remembering the beginning of his career at KAIST in 2012, Professor Lee said “KAIST seemed to be a very high and formidable barrier for me, after completing my medical education in Korea. I thank my department professors and colleagues who led me to focus on the research path that I really wanted. They provided everything for my research environment to help make good results.”
“I will continue to strive for promoting the well-being of humanity by addressing various incurable diseases as well as developing novel therapeutics. That will be the way to promote the stature of KAIST at home and abroad,” he added.
2019.01.02 View 5910
Professor Jeong-Ho Lee Named the KAISTian of 2018
(Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) poses with President Sung-Chul Shin)
Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was selected as the KAISTian of the Year of 2018. The award was established in 2001 and recognizes the most outstanding scholars who have made significant research and scholastic achievements during the year. Professor Lee was awarded during the New Year ceremony held in the auditorium on January 2.
Professor Lee has investigated mutations arising in the brain for decades and has published in renowned journals such as Nature, Nature Medicine, and Cell. Last August, Professor Lee reported breakthrough research on glioblastoma in Nature, giving insight into understanding how the mutation causing glioblastoma starts and suggested novel ways to treat glioblastoma, which was thought to be incurable. (Click for more)
Professor Lee’s Translational Neurogenetics Laboratory lab is investigating innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma. To commercialize his technology, he established the tech-startup SoVarGen and now works as its CTO.
Professor Lee credited all his lab colleagues and staff. “I know all of this research would not have possible without their sweat and effort. I am happy to receive this honorable award on behalf of them.”
Remembering the beginning of his career at KAIST in 2012, Professor Lee said “KAIST seemed to be a very high and formidable barrier for me, after completing my medical education in Korea. I thank my department professors and colleagues who led me to focus on the research path that I really wanted. They provided everything for my research environment to help make good results.”
“I will continue to strive for promoting the well-being of humanity by addressing various incurable diseases as well as developing novel therapeutics. That will be the way to promote the stature of KAIST at home and abroad,” he added.
2019.01.02 View 5910 -
 Meet the KAISTian of 2017, Professor YongKeun Park
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics is one of the star professors in KAIST. Rising to the academic stardom, Professor Park’s daily schedule is filled with series of business meetings in addition to lab meetings and lectures.
The year 2017 must have been special for him. During the year, he published numerous papers in international journals, such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications and Science Advances. These high performances drew international attention from renowned media, including Newsweek and Forbes. Moreover, recognizing his research performance, he was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in his mid-30s. Noting that the members’ age ranges from late 50s to early 60s, Professor Park’s case considered to be quite exceptional.
Adding to his academic achievement, he has launched two startups powered of his own technologies. One is called Tomocube, a company specialized in 3-D imaging microscope using holotomography technology. His company is currently exporting the products to multiple countries, including the United States and Japan. The other one is The.Wave.Talk which has technologies for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
His research career and entrepreneurship are well deserved recipient of many honors. At the 2018 kick-off ceremony, Professor Park was awarded the KAISTian of 2017 in recognition of his developing holographic measure and control technology as well as founding a new field for technology application.
KAISTian of the Year, first presented in 2001, is an award to recognize the achievements and exemplary contribution of KAIST member who has put significant effort nationally and internationally, enhancing the value of KAIST.
While receiving the award, he thanked his colleagues and his students who have achieved this far together. He said, “I would like to thank KAIST for providing environment for young professors like me so that we can engage themselves in research. Also, I would like to mention that I am an idea seeder and my students do the most of the research. So, I appreciate my students for their hard works, and it is very pleasure to have them. Lastly, I thank the professors for teaching these outstanding students. I feel great responsibility over this title. I will dedicate myself to make further progress in commercializing technology in KAIST.”
Expecting his successful startup cases as a model and great inspiration to students as well as professors, KAIST interviewed Professor Park.
Q What made you decide to found your startups?
A I believed that my research areas could be further used. As a professor, I believe that it is a university’s role to create added value through commercializing technology and creating startups.
Q You have co-founded two startups. What is your role in each company?
A So, basically I have two full-time jobs, professor in KAIST and CTO in Tomocube. After transferring the technology, I hold the position of advisor in The.Wave.Talk.
(Holographic images captured by the product Professor Park developed)
Q Do your students also participate in your companies or can they?
A No, the school and companies are separate spaces; in other words, they are not participating in my companies. They have trained my employees when transferring the technologies, but they are not directly working for the companies.
However, they can participate if they want to. If there’s a need to develop a certain technology, an industry-academia contract can be made. According to the agreement, students can work for the companies.
Q Were there any hardships when preparing the startups?
A At the initial stage, I did not have a financial problem, thanks to support from Startup KAIST. Yet, inviting capital is the beginning, and I think every step I made to operate, generate revenue, and so on is not easy.
Q Do you believe KAIST is startup-friendly?
A Yes, there’s no school like KAIST in Korea and any other country. Besides various programs to support startup activities, Startup KAIST has many professors equipped with a great deal of experience. Therefore, I believe that KAIST provides an excellent environment for both students and professors to create startups.
Q Do you have any suggestion to KAIST institutionally?
A Well, I would like to make a comment to students and professors in KAIST. I strongly recommend them to challenge themselves by launching startups if they have good ideas. Many students wish to begin their jobs in government-funded research institutes or major corporates, but I believe that engaging in a startup company will also give them valuable and very productive experience.
Unlike before, startup institutions are well established, so attracting good capital is not so hard. There are various activities offered by Startup KAIST, so it’s worthwhile giving it a try.
Q What is your goal for 2018 as a professor and entrepreneur?
A I don’t have a grand plan, but I will work harder to produce good students with new topics in KAIST while adding power to my companies to grow bigger.
By Se Yi Kim from the PR Office
2018.01.03 View 11513
Meet the KAISTian of 2017, Professor YongKeun Park
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics is one of the star professors in KAIST. Rising to the academic stardom, Professor Park’s daily schedule is filled with series of business meetings in addition to lab meetings and lectures.
The year 2017 must have been special for him. During the year, he published numerous papers in international journals, such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications and Science Advances. These high performances drew international attention from renowned media, including Newsweek and Forbes. Moreover, recognizing his research performance, he was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in his mid-30s. Noting that the members’ age ranges from late 50s to early 60s, Professor Park’s case considered to be quite exceptional.
Adding to his academic achievement, he has launched two startups powered of his own technologies. One is called Tomocube, a company specialized in 3-D imaging microscope using holotomography technology. His company is currently exporting the products to multiple countries, including the United States and Japan. The other one is The.Wave.Talk which has technologies for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
His research career and entrepreneurship are well deserved recipient of many honors. At the 2018 kick-off ceremony, Professor Park was awarded the KAISTian of 2017 in recognition of his developing holographic measure and control technology as well as founding a new field for technology application.
KAISTian of the Year, first presented in 2001, is an award to recognize the achievements and exemplary contribution of KAIST member who has put significant effort nationally and internationally, enhancing the value of KAIST.
While receiving the award, he thanked his colleagues and his students who have achieved this far together. He said, “I would like to thank KAIST for providing environment for young professors like me so that we can engage themselves in research. Also, I would like to mention that I am an idea seeder and my students do the most of the research. So, I appreciate my students for their hard works, and it is very pleasure to have them. Lastly, I thank the professors for teaching these outstanding students. I feel great responsibility over this title. I will dedicate myself to make further progress in commercializing technology in KAIST.”
Expecting his successful startup cases as a model and great inspiration to students as well as professors, KAIST interviewed Professor Park.
Q What made you decide to found your startups?
A I believed that my research areas could be further used. As a professor, I believe that it is a university’s role to create added value through commercializing technology and creating startups.
Q You have co-founded two startups. What is your role in each company?
A So, basically I have two full-time jobs, professor in KAIST and CTO in Tomocube. After transferring the technology, I hold the position of advisor in The.Wave.Talk.
(Holographic images captured by the product Professor Park developed)
Q Do your students also participate in your companies or can they?
A No, the school and companies are separate spaces; in other words, they are not participating in my companies. They have trained my employees when transferring the technologies, but they are not directly working for the companies.
However, they can participate if they want to. If there’s a need to develop a certain technology, an industry-academia contract can be made. According to the agreement, students can work for the companies.
Q Were there any hardships when preparing the startups?
A At the initial stage, I did not have a financial problem, thanks to support from Startup KAIST. Yet, inviting capital is the beginning, and I think every step I made to operate, generate revenue, and so on is not easy.
Q Do you believe KAIST is startup-friendly?
A Yes, there’s no school like KAIST in Korea and any other country. Besides various programs to support startup activities, Startup KAIST has many professors equipped with a great deal of experience. Therefore, I believe that KAIST provides an excellent environment for both students and professors to create startups.
Q Do you have any suggestion to KAIST institutionally?
A Well, I would like to make a comment to students and professors in KAIST. I strongly recommend them to challenge themselves by launching startups if they have good ideas. Many students wish to begin their jobs in government-funded research institutes or major corporates, but I believe that engaging in a startup company will also give them valuable and very productive experience.
Unlike before, startup institutions are well established, so attracting good capital is not so hard. There are various activities offered by Startup KAIST, so it’s worthwhile giving it a try.
Q What is your goal for 2018 as a professor and entrepreneur?
A I don’t have a grand plan, but I will work harder to produce good students with new topics in KAIST while adding power to my companies to grow bigger.
By Se Yi Kim from the PR Office
2018.01.03 View 11513 -
 Strengthening Industry-Academia Cooperation with LG CNS
On November 20, KAIST signed an MoU with LG CNS for industry-academia partnership in education, research, and business in the fields of AI and Big Data. Rather than simply developing education programs or supporting industry-academia scholarships, both organizations agreed to carry out a joint research project on AI and Big Data that can be applied to practical business.
KAIST will collaborate with LG CNS in the fields of smart factories, customer analysis, and supply chain management analysis.
Not only will LG CNS offer internships to KAIST students, but it also will support professors and students who propose innovative startup ideas for AI and Big Data. Offering an industry-academia scholarship for graduate students is also being discussed. Together with LG CNS, KAIST will put its efforts into propose projects regarding AI and Big Data in the public sector.
Furthermore, KAIST and LG CNS will jointly explore and carry out industry-academia projects that could be practically used in business. Both will carry out the project vigorously through strong cooperation; for instance, LG CNS employees can be assigned to KAIST, if necessary. Also, LG CNS’s AI and Big Data platform, called DAP (Data Analytics & AI Platform) will be used as a data analysis tool during the project and the joint outcomes will be installed in DAP.
KAIST professors with expertise in AI deep learning have trained LG CNS employees since the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering established ‘KAIST AI Academy’ in LG CNS last August.
“With KAIST, the best research-centered university in Korea, we will continue to lead in developing the field of AI and Big Data and provide innovative services that create value by connecting them to customer business,” Yong Shub Kim, the CEO of LG CNS, highlighted.
2017.11.22 View 11263
Strengthening Industry-Academia Cooperation with LG CNS
On November 20, KAIST signed an MoU with LG CNS for industry-academia partnership in education, research, and business in the fields of AI and Big Data. Rather than simply developing education programs or supporting industry-academia scholarships, both organizations agreed to carry out a joint research project on AI and Big Data that can be applied to practical business.
KAIST will collaborate with LG CNS in the fields of smart factories, customer analysis, and supply chain management analysis.
Not only will LG CNS offer internships to KAIST students, but it also will support professors and students who propose innovative startup ideas for AI and Big Data. Offering an industry-academia scholarship for graduate students is also being discussed. Together with LG CNS, KAIST will put its efforts into propose projects regarding AI and Big Data in the public sector.
Furthermore, KAIST and LG CNS will jointly explore and carry out industry-academia projects that could be practically used in business. Both will carry out the project vigorously through strong cooperation; for instance, LG CNS employees can be assigned to KAIST, if necessary. Also, LG CNS’s AI and Big Data platform, called DAP (Data Analytics & AI Platform) will be used as a data analysis tool during the project and the joint outcomes will be installed in DAP.
KAIST professors with expertise in AI deep learning have trained LG CNS employees since the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering established ‘KAIST AI Academy’ in LG CNS last August.
“With KAIST, the best research-centered university in Korea, we will continue to lead in developing the field of AI and Big Data and provide innovative services that create value by connecting them to customer business,” Yong Shub Kim, the CEO of LG CNS, highlighted.
2017.11.22 View 11263 -
 Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 11884
Professor YongKeun Park Elected as a Fellow of the Optical Society
Professor YongKeun Park, from the Department of Physics at KAIST, was elected as a fellow member of the Optical Society (OSA) in Washington, D.C. on September 12. Fellow membership is given to members who have made a significant contribution to the advancement of optics and photonics.
Professor Park was recognized for his research on digital holography and wavefront control technology.
Professor Park has been producing outstanding research outcomes in the field of holographic technology and light scattering control since joining KAIST in 2010. In particular, he developed and commercialized technology for a holographic telescope. He applied it to various medical and biological research projects, leading the field worldwide.
In the past, cells needed to be dyed with fluorescent materials to capture a 3-D image. However, Professor Park’s holotomography (HT) technology can capture 3-D images of living cells and tissues in real time without color dyeing. This technology allows diversified research in the biological and medical field.
Professor Park established a company, Tomocube, Inc. in 2015 to commercialize the technology. In 2016, he received funding from SoftBank Ventures and Hanmi Pharmaceutical. Currently, major institutes, including MIT, the University of Pittsburgh, the German Cancer Research Center, and Seoul National University Hospital are using his equipment.
Recently, Professor Park and his team developed technology based on light scattering measurements. With this technology, they established a company called The Wave Talk and received funding from various organizations, such as NAVER. Its first product is about to be released.
Professor Park said, “I am glad to become a fellow member based on the research outcomes I produced since I was appointed as a professor at KAIST. I would like to thank the excellent researchers as well as the school for its support. I will devote myself to continuously producing novel outcomes in both basic and applied fields.”
Professor Park has published nearly 100 papers in renowned journals including Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, Science Advances, and Physical Review Letters.
2017.10.18 View 11884 -
 Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 9849
Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 9849 -
 Professor Tae-Eog Lee Receives December's Scientist of the Month Award by the Korean Government
Professor Tae-Eog Lee of the Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST received the Scientist of the Month Award for December 2015. The award is sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, which was hosted by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
The award recognizes Professor Lee’s efforts to advance the field of semiconductor device fabrication processing. This includes the development of the most efficient scheduling and controlling of cluster tools. He also created mathematical solutions to optimize the complicated cycle time of cluster tools in semiconductor manufacturing and the process of robot task workload.
Professor Lee contributed to the formation of various discrete event systems and automation systems based on his mathematical theories and solutions and advanced a scheduling technology for the automation of semiconductor production.
He has published 18 research papers in the past three years and has pioneered to develop Korean tool schedulers through the private sector-university cooperation.
2015.12.10 View 7724
Professor Tae-Eog Lee Receives December's Scientist of the Month Award by the Korean Government
Professor Tae-Eog Lee of the Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST received the Scientist of the Month Award for December 2015. The award is sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, which was hosted by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
The award recognizes Professor Lee’s efforts to advance the field of semiconductor device fabrication processing. This includes the development of the most efficient scheduling and controlling of cluster tools. He also created mathematical solutions to optimize the complicated cycle time of cluster tools in semiconductor manufacturing and the process of robot task workload.
Professor Lee contributed to the formation of various discrete event systems and automation systems based on his mathematical theories and solutions and advanced a scheduling technology for the automation of semiconductor production.
He has published 18 research papers in the past three years and has pioneered to develop Korean tool schedulers through the private sector-university cooperation.
2015.12.10 View 7724