THE
-
 KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 8593
KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 8593 -
 KAIST Holds 2023 Commencement Ceremony
< Photo 1. On the 17th, KAIST held the 2023 Commencement Ceremony for a total of 2,870 students, including 691 doctors. >
KAIST held its 2023 commencement ceremony at the Sports Complex of its main campus in Daejeon at 2 p.m. on February 27. It was the first commencement ceremony to invite all its graduates since the start of COVID-19 quarantine measures.
KAIST awarded a total of 2,870 degrees including 691 PhD degrees, 1,464 master’s degrees, and 715 bachelor’s degrees, which adds to the total of 74,999 degrees KAIST has conferred since its foundation in 1971, which includes 15,772 PhD, 38,360 master’s and 20,867 bachelor’s degrees.
This year’s Cum Laude, Gabin Ryu, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the Minister of Science and ICT Award. Seung-ju Lee from the School of Computing received the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award, while Jantakan Nedsaengtip, an international student from Thailand received the KAIST Presidential Award, and Jaeyong Hwang from the Department of Physics and Junmo Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering each received the President of the Alumni Association Award and the Chairman of the KAIST Development Foundation Award, respectively.
Minister Jong-ho Lee of the Ministry of Science and ICT awarded the recipients of the academic awards and delivered a congratulatory speech.
Yujin Cha from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, who received a PhD degree after 19 years since his entrance to KAIST as an undergraduate student in 2004 gave a speech on behalf of the graduates to move and inspire the graduates and the guests.
After Cha received a bachelor’s degree from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, he entered a medical graduate school and became a radiation oncology specialist. But after experiencing the death of a young patient who suffered from osteosarcoma, he returned to his alma mater to become a scientist. As he believes that science and technology is the ultimate solution to the limitations of modern medicine, he started as a PhD student at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2018, hoping to find such solutions.
During his course, he identified the characteristics of the decision-making process of doctors during diagnosis, and developed a brain-inspired AI algorithm. It is an original and challenging study that attempted to develop a fundamental machine learning theory from the data he collected from 200 doctors of different specialties.
Cha said, “Humans and AI can cooperate by humans utilizing the unique learning abilities of AI to develop our expertise, while AIs can mimic us humans’ learning abilities to improve.” He added, “My ultimate goal is to develop technology to a level at which humans and machines influence each other and ‘coevolve’, and applying it not only to medicine, but in all areas.”
Cha, who is currently an assistant professor at the KAIST Biomedical Research Center, has also written Artificial Intelligence for Doctors in 2017 to help medical personnel use AI in clinical fields, and the book was selected as one of the 2018 Sejong Books in the academic category.
During his speech at this year’s commencement ceremony, he shared that “there are so many things in the world that are difficult to solve and many things to solve them with, but I believe the things that can really broaden the horizons of the world and find fundamental solutions to the problems at hand are science and technology.”
Meanwhile, singer-songwriter Sae Byul Park who studied at the KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology will also receive her PhD degree.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a field in AI that teaches a computer to understand and analyze human language that is actively being studied. An example of NLP is ChatGTP, which recently received a lot of attention. For her research, Park analyzed music rather than language using NLP technology.
To analyze music, which is in the form of sound, using the methods for NLP, it is necessary to rebuild notes and beats into a form of words or sentences as in a language. For this, Park designed an algorithm called Mel2Word and applied it to her research.
She also suggested that by converting melodies into texts for analysis, one would be able to quantitatively express music as sentences or words with meaning and context rather than as simple sounds representing a certain note.
Park said, “music has always been considered as a product of subjective emotion, but this research provides a framework that can calculate and analyze music.”
Park’s study can later be developed into a tool to measure the similarities between musical work, as well as a piece’s originality, artistry and popularity, and it can be used as a clue to explore the fundamental principles of how humans respond to music from a cognitive science perspective.
Park began her Ph.D. program in 2014, while carrying on with her musical activities as well as public and university lectures alongside, and dealing with personally major events including marriage and childbirth during the course of years. She already met the requirements to receive her degree in 2019, but delayed her graduation in order to improve the level of completion of her research, and finally graduated with her current achievements after nine years.
Professor Juhan Nam, who supervised Park’s research, said, “Park, who has a bachelor’s degree in psychology, later learned to code for graduate school, and has complete high-quality research in the field of artificial intelligence.” He added, “Though it took a long time, her attitude of not giving up until the end as a researcher is also excellent.”
Sae Byul Park is currently lecturing courses entitled Culture Technology and Music Information Retrieval at the Underwood International College of Yonsei University.
Park said, “the 10 or so years I’ve spent at KAIST as a graduate student was a time I could learn and prosper not only academically but from all angles of life.” She added, “having received a doctorate degree is not the end, but a ‘commencement’. Therefore, I will start to root deeper from the seeds I sowed and work harder as a both a scholar and an artist.”
< Photo 2. From left) Yujin Cha (Valedictorian, Medical-Scientist Program Ph.D. graduate), Saebyeol Park (a singer-songwriter, Ph.D. graduate from the Graduate School of Culture and Technology), Junseok Moon and Inah Seo (the two highlighted CEO graduates from the Department of Management Engineering's master’s program) >
Young entrepreneurs who dream of solving social problems will also be wearing their graduation caps. Two such graduates are Jun-seok Moon and Inah Seo, receiving their master’s degrees in social entrepreneurship MBA from the KAIST College of Business.
Before entrance, Moon ran a café helping African refugees stand on their own feet. Then, he entered KAIST to later expand his business and learn social entrepreneurship in order to sustainably help refugees in the blind spots of human rights and welfare.
During his master’s course, Moon realized that he could achieve active carbon reduction by changing the coffee alone, and switched his business field and founded Equal Table. The amount of carbon an individual can reduce by refraining from using a single paper cup is 10g, while changing the coffee itself can reduce it by 300g.
1kg of coffee emits 15kg of carbon over the course of its production, distribution, processing, and consumption, but Moon produces nearly carbon-neutral coffee beans by having innovated the entire process. In particular, the company-to-company ESG business solution is Moon’s new start-up area. It provides companies with carbon-reduced coffee made by roasting raw beans from carbon-neutral certified farms with 100% renewable energy, and shows how much carbon has been reduced in its making. Equal Table will launch the service this month in collaboration with SK Telecom, its first partner.
Inah Seo, who also graduated with Moon, founded Conscious Wear to start a fashion business reducing environmental pollution. In order to realize her mission, she felt the need to gain the appropriate expertise in management, and enrolled for the social entrepreneurship MBA.
Out of the various fashion industries, Seo focused on the leather market, which is worth 80 trillion won. Due to thickness or contamination issues, only about 60% of animal skin fabric is used, and the rest is discarded. Heavy metals are used during such processes, which also directly affects the environment.
During the social entrepreneurship MBA course, Seo collaborated with SK Chemicals, which had links through the program, and launched eco-friendly leather bags. The bags used discarded leather that was recycled by grinding and reprocessing into a biomaterial called PO3G. It was the first case in which PO3G that is over 90% biodegradable was applied to regenerated leather. In other words, it can reduce environmental pollution in the processing and disposal stages, while also reducing carbon emissions and water usage by one-tenth compared to existing cowhide products.
The social entrepreneurship MBA course, from which Moon and Seo graduated, will run in integration with the Graduate School of Green Growth as an Impact MBA program starting this year. KAIST plans to steadily foster entrepreneurs who will lead meaningful changes in the environment and society as well as economic values through innovative technologies and ideas.
< Photo 3. NYU President Emeritus John Sexton (left), who received this year's honorary doctorate of science, poses with President Kwang Hyung Lee >
Meanwhile, during this day’s commencement ceremony, KAIST also presented President Emeritus John Sexton of New York University with an honorary doctorate in science. He was recognized for laying the foundation for the cooperation between KAIST and New York University, such as promoting joint campuses.
< Photo 4. At the commencement ceremony of KAIST held on the 17th, President Kwang Hyung Lee is encouraging the graduates with his commencement address. >
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized in his commencement speech that, “if you can draw up the future and work hard toward your goal, the future can become a work of art that you create with your own hands,” and added, “Never stop on the journey toward your dreams, and do not give up even when you are met with failure. Failure happens to everyone, all the time. The important thing is to know 'why you failed', and to use those elements of failure as the driving force for the next try.”
2023.02.20 View 17186
KAIST Holds 2023 Commencement Ceremony
< Photo 1. On the 17th, KAIST held the 2023 Commencement Ceremony for a total of 2,870 students, including 691 doctors. >
KAIST held its 2023 commencement ceremony at the Sports Complex of its main campus in Daejeon at 2 p.m. on February 27. It was the first commencement ceremony to invite all its graduates since the start of COVID-19 quarantine measures.
KAIST awarded a total of 2,870 degrees including 691 PhD degrees, 1,464 master’s degrees, and 715 bachelor’s degrees, which adds to the total of 74,999 degrees KAIST has conferred since its foundation in 1971, which includes 15,772 PhD, 38,360 master’s and 20,867 bachelor’s degrees.
This year’s Cum Laude, Gabin Ryu, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the Minister of Science and ICT Award. Seung-ju Lee from the School of Computing received the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award, while Jantakan Nedsaengtip, an international student from Thailand received the KAIST Presidential Award, and Jaeyong Hwang from the Department of Physics and Junmo Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering each received the President of the Alumni Association Award and the Chairman of the KAIST Development Foundation Award, respectively.
Minister Jong-ho Lee of the Ministry of Science and ICT awarded the recipients of the academic awards and delivered a congratulatory speech.
Yujin Cha from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, who received a PhD degree after 19 years since his entrance to KAIST as an undergraduate student in 2004 gave a speech on behalf of the graduates to move and inspire the graduates and the guests.
After Cha received a bachelor’s degree from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, he entered a medical graduate school and became a radiation oncology specialist. But after experiencing the death of a young patient who suffered from osteosarcoma, he returned to his alma mater to become a scientist. As he believes that science and technology is the ultimate solution to the limitations of modern medicine, he started as a PhD student at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering in 2018, hoping to find such solutions.
During his course, he identified the characteristics of the decision-making process of doctors during diagnosis, and developed a brain-inspired AI algorithm. It is an original and challenging study that attempted to develop a fundamental machine learning theory from the data he collected from 200 doctors of different specialties.
Cha said, “Humans and AI can cooperate by humans utilizing the unique learning abilities of AI to develop our expertise, while AIs can mimic us humans’ learning abilities to improve.” He added, “My ultimate goal is to develop technology to a level at which humans and machines influence each other and ‘coevolve’, and applying it not only to medicine, but in all areas.”
Cha, who is currently an assistant professor at the KAIST Biomedical Research Center, has also written Artificial Intelligence for Doctors in 2017 to help medical personnel use AI in clinical fields, and the book was selected as one of the 2018 Sejong Books in the academic category.
During his speech at this year’s commencement ceremony, he shared that “there are so many things in the world that are difficult to solve and many things to solve them with, but I believe the things that can really broaden the horizons of the world and find fundamental solutions to the problems at hand are science and technology.”
Meanwhile, singer-songwriter Sae Byul Park who studied at the KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology will also receive her PhD degree.
Natural language processing (NLP) is a field in AI that teaches a computer to understand and analyze human language that is actively being studied. An example of NLP is ChatGTP, which recently received a lot of attention. For her research, Park analyzed music rather than language using NLP technology.
To analyze music, which is in the form of sound, using the methods for NLP, it is necessary to rebuild notes and beats into a form of words or sentences as in a language. For this, Park designed an algorithm called Mel2Word and applied it to her research.
She also suggested that by converting melodies into texts for analysis, one would be able to quantitatively express music as sentences or words with meaning and context rather than as simple sounds representing a certain note.
Park said, “music has always been considered as a product of subjective emotion, but this research provides a framework that can calculate and analyze music.”
Park’s study can later be developed into a tool to measure the similarities between musical work, as well as a piece’s originality, artistry and popularity, and it can be used as a clue to explore the fundamental principles of how humans respond to music from a cognitive science perspective.
Park began her Ph.D. program in 2014, while carrying on with her musical activities as well as public and university lectures alongside, and dealing with personally major events including marriage and childbirth during the course of years. She already met the requirements to receive her degree in 2019, but delayed her graduation in order to improve the level of completion of her research, and finally graduated with her current achievements after nine years.
Professor Juhan Nam, who supervised Park’s research, said, “Park, who has a bachelor’s degree in psychology, later learned to code for graduate school, and has complete high-quality research in the field of artificial intelligence.” He added, “Though it took a long time, her attitude of not giving up until the end as a researcher is also excellent.”
Sae Byul Park is currently lecturing courses entitled Culture Technology and Music Information Retrieval at the Underwood International College of Yonsei University.
Park said, “the 10 or so years I’ve spent at KAIST as a graduate student was a time I could learn and prosper not only academically but from all angles of life.” She added, “having received a doctorate degree is not the end, but a ‘commencement’. Therefore, I will start to root deeper from the seeds I sowed and work harder as a both a scholar and an artist.”
< Photo 2. From left) Yujin Cha (Valedictorian, Medical-Scientist Program Ph.D. graduate), Saebyeol Park (a singer-songwriter, Ph.D. graduate from the Graduate School of Culture and Technology), Junseok Moon and Inah Seo (the two highlighted CEO graduates from the Department of Management Engineering's master’s program) >
Young entrepreneurs who dream of solving social problems will also be wearing their graduation caps. Two such graduates are Jun-seok Moon and Inah Seo, receiving their master’s degrees in social entrepreneurship MBA from the KAIST College of Business.
Before entrance, Moon ran a café helping African refugees stand on their own feet. Then, he entered KAIST to later expand his business and learn social entrepreneurship in order to sustainably help refugees in the blind spots of human rights and welfare.
During his master’s course, Moon realized that he could achieve active carbon reduction by changing the coffee alone, and switched his business field and founded Equal Table. The amount of carbon an individual can reduce by refraining from using a single paper cup is 10g, while changing the coffee itself can reduce it by 300g.
1kg of coffee emits 15kg of carbon over the course of its production, distribution, processing, and consumption, but Moon produces nearly carbon-neutral coffee beans by having innovated the entire process. In particular, the company-to-company ESG business solution is Moon’s new start-up area. It provides companies with carbon-reduced coffee made by roasting raw beans from carbon-neutral certified farms with 100% renewable energy, and shows how much carbon has been reduced in its making. Equal Table will launch the service this month in collaboration with SK Telecom, its first partner.
Inah Seo, who also graduated with Moon, founded Conscious Wear to start a fashion business reducing environmental pollution. In order to realize her mission, she felt the need to gain the appropriate expertise in management, and enrolled for the social entrepreneurship MBA.
Out of the various fashion industries, Seo focused on the leather market, which is worth 80 trillion won. Due to thickness or contamination issues, only about 60% of animal skin fabric is used, and the rest is discarded. Heavy metals are used during such processes, which also directly affects the environment.
During the social entrepreneurship MBA course, Seo collaborated with SK Chemicals, which had links through the program, and launched eco-friendly leather bags. The bags used discarded leather that was recycled by grinding and reprocessing into a biomaterial called PO3G. It was the first case in which PO3G that is over 90% biodegradable was applied to regenerated leather. In other words, it can reduce environmental pollution in the processing and disposal stages, while also reducing carbon emissions and water usage by one-tenth compared to existing cowhide products.
The social entrepreneurship MBA course, from which Moon and Seo graduated, will run in integration with the Graduate School of Green Growth as an Impact MBA program starting this year. KAIST plans to steadily foster entrepreneurs who will lead meaningful changes in the environment and society as well as economic values through innovative technologies and ideas.
< Photo 3. NYU President Emeritus John Sexton (left), who received this year's honorary doctorate of science, poses with President Kwang Hyung Lee >
Meanwhile, during this day’s commencement ceremony, KAIST also presented President Emeritus John Sexton of New York University with an honorary doctorate in science. He was recognized for laying the foundation for the cooperation between KAIST and New York University, such as promoting joint campuses.
< Photo 4. At the commencement ceremony of KAIST held on the 17th, President Kwang Hyung Lee is encouraging the graduates with his commencement address. >
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized in his commencement speech that, “if you can draw up the future and work hard toward your goal, the future can become a work of art that you create with your own hands,” and added, “Never stop on the journey toward your dreams, and do not give up even when you are met with failure. Failure happens to everyone, all the time. The important thing is to know 'why you failed', and to use those elements of failure as the driving force for the next try.”
2023.02.20 View 17186 -
 KAIST presents a fundamental technology to remove metastatic traits from lung cancer cells
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 30th that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in using systems biology research to change the properties of carcinogenic cells in the lungs and eliminate both drug resistance and their ability to proliferate out to other areas of the body.
As the incidences of cancer increase within aging populations, cancer has become the most lethal disease threatening healthy life. Fatality rates are especially high when early detection does not happen in time and metastasis has occurred in various organs. In order to resolve this problem, a series of attempts were made to remove or lower the ability of cancer cells to spread, but they resulted in cancer cells in the intermediate state becoming more unstable and even more malignant, which created serious treatment challenges.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team simulated various cancer cell states in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) of lung cancer cells, between epithelial cells without metastatic ability and mesenchymal cells with metastatic ability. A mathematical model of molecular network was established, and key regulators that could reverse the state of invasive and drug resistant mesenchymal cells back to the epithelial state were discovered through computer simulation analysis and molecular cell experiments. In particular, this process succeeded in properly reverting the mesenchymal lung cancer cells to a state where they were sensitive to chemotherapy treatment while avoiding the unstable EMT hybrid cell state in the middle process, which had remained a difficult problem.
The results of this research, in which KAIST Ph.D. student Namhee Kim, Dr. Chae Young Hwang, Researcher Taeyoung Kim, and Ph.D. student Hyunjin Kim participated, were published as an online paper in the international journal “Cancer Research” published by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) on January 30th. (Paper title: A cell fate reprogramming strategy reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells while avoiding hybrid states)
Cells in an EMT hybrid state, which are caused by incomplete transitions during the EMT process in cancer cells, have the characteristics of both epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells, and are known to have high drug resistance and metastatic potential by acquiring high stem cell capacity. In particular, EMT is further enhanced through factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) secreted from the tumor microenvironment (TME) and, as a result, various cell states with high plasticity appear. Due to the complexity of EMT, it has been very difficult to completely reverse the transitional process of the mesenchymal cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are eliminated while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state with high metastatic ability and drug resistance.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a mathematical model of the gene regulation network that governs the complex process of EMT, and then applied large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology to identify and verify 'p53', 'SMAD4', and 'ERK1' and 'ERK 2' (collectively ERKs) through molecular cell experiments as the three key molecular targets that can transform lung cancer cells in the mesenchymal cell state, reversed back to an epithelial cell state that no longer demonstrates the ability to metastasize, while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state.
In particular, by analyzing the molecular regulatory mechanism of the complex EMT process at the system level, the key pathways were identified that were linked to the positive feedback that plays an important role in completely returning cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are removed.
This discovery is significant in that it proved that mesenchymal cells can be reverted to the state of epithelial cells under conditions where TGF-β stimulation are present, like they are in the actual environment where cancer tissue forms in the human body.
Abnormal EMT in cancer cells leads to various malignant traits such as the migration and invasion of cancer cells, changes in responsiveness to chemotherapy treatment, enhanced stem cell function, and the dissemination of cancer. In particular, the acquisition of the metastatic ability of cancer cells is a key determinant factor for the prognosis of cancer patients. The EMT reversal technology in lung cancer cells developed in this research is a new anti-cancer treatment strategy that reprograms cancer cells to eliminate their high plasticity and metastatic potential and increase their responsiveness to chemotherapy.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "By succeeding in reversing the state of lung cancer cells that acquired high metastatic traits and resistance to drugs and reverting them to a treatable epithelial cell state with renewed sensitivity to chemotherapy, the research findings propose a new strategy for treatments that can improve the prognosis of cancer patients.”
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team was the first to present the principle of reversal treatment to revert cancer cells to normal cells, following through with the announcement of the results of their study that reverted colon cancer cells to normal colon cells in January of 2020, and also presenting successful re-programming research where the most malignant basal type breast cancer cells turned into less-malignant luminal type breast cancer cells that were treatable with hormonal therapies in January of 2022. This latest research result is the third in the development of reversal technology where lung cancer cells that had acquired metastatic traits returned to a state in which their metastatic ability was removed and drug sensitivity was enhanced.
This research was carried out with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers.
< Figure 1. Construction of the mathematical model of the regulatory network to represent the EMT phenotype based on the interaction between various molecules related to EMT.
(A) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team investigated numerous literatures and databases related to complex EMT, and based on comparative analysis of cell line data showing epithelial and mesenchymal cell conditions, they extracted key signaling pathways related to EMT and built a mathematical model of regulatory network (B) By comparing the results of computer simulation analysis and the molecular cell experiments, it was verified how well the constructed mathematical model simulated the actual cellular phenomena. >
< Figure 2. Understanding of various EMT phenotypes through large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology.
(A) Through computer simulation analysis and experiments, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team found that complete control of EMT is impossible with single-molecule control alone. In particular, through comparison of the relative stability of attractors, it was revealed that the cell state exhibiting EMT hybrid characteristics has unstable properties. (B), (C) Based on these results, Prof. Cho’s team identified two feedbacks (positive feedback consisting of Snail-miR-34 and ZEB1-miR-200) that play an important role in avoiding the EMT hybrid state that appeared in the TGF-β-ON state. It was found through computer simulation analysis that the two feedbacks restore relatively high stability when the excavated p53 and SMAD4 are regulated. In addition, molecular cell experiments demonstrated that the expression levels of E-cad and ZEB1, which are representative phenotypic markers of EMT, changed similarly to the expression profile in the epithelial cell state, despite the TGF-β-ON state. >
< Figure 3. Complex molecular network analysis and discovery of reprogramming molecular targets for intact elimination of EMT hybrid features.
(A) Controlling the expression of p53 and SMAD4 in lung cancer cell lines was expected to overcome drug resistance, but contrary to expectations, chemotherapy responsiveness was not restored. (B) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team additionally analyzed computer simulations, genome data, and experimental results and found that high expression levels of TWIST1 and EPCAM were related to drug resistance. (C) Prof. Cho’s team identified three key molecular targets: p53, SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2. (D), (E) Furthermore, they identified a key pathway that plays an important role in completely reversing into epithelial cells while avoiding EMT hybrid characteristics, and confirmed through network analysis and attractor analysis that high stability of the key pathway was restored when the proposed molecular target was controlled. >
< Figure 4. Verification through experiments with lung cancer cell lines.
When p53 was activated and SMAD4 and ERK1/2 were inhibited in lung cancer cell lines, (A), (B) E-cad protein expression increased and ZEB1 protein expression decreased, and (C) mesenchymal cell status including TWIST1 and EPCAM and gene expression of markers related to stem cell potential characteristics were completely inhibited. In addition, (D) it was confirmed that resistance to chemotherapy treatment was also overcome as the cell state was reversed by the regulated target. >
< Figure 5. A schematic representation of the research results.
Prof. Cho’s research team identified key molecular regulatory pathways to avoid high plasticity formed by abnormal EMT of cancer cells and reverse it to an epithelial cell state through systems biology research. From this analysis, a reprogramming molecular target that can reverse the state of mesenchymal cells with acquired invasiveness and drug resistance to the state of epithelial cells with restored drug responsiveness was discovered.
For lung cancer cells, when a drug that enhances the expression of p53, one of the molecular targets discovered, and inhibits the expression of SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2 is administered, the molecular network of genes in the state of mesenchymal cells is modified, eventually eliminating metastatic ability and it is reprogrammed to turn into epithelial cells without the resistance to chemotherapy treatments. >
2023.01.30 View 15903
KAIST presents a fundamental technology to remove metastatic traits from lung cancer cells
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 30th that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in using systems biology research to change the properties of carcinogenic cells in the lungs and eliminate both drug resistance and their ability to proliferate out to other areas of the body.
As the incidences of cancer increase within aging populations, cancer has become the most lethal disease threatening healthy life. Fatality rates are especially high when early detection does not happen in time and metastasis has occurred in various organs. In order to resolve this problem, a series of attempts were made to remove or lower the ability of cancer cells to spread, but they resulted in cancer cells in the intermediate state becoming more unstable and even more malignant, which created serious treatment challenges.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team simulated various cancer cell states in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) of lung cancer cells, between epithelial cells without metastatic ability and mesenchymal cells with metastatic ability. A mathematical model of molecular network was established, and key regulators that could reverse the state of invasive and drug resistant mesenchymal cells back to the epithelial state were discovered through computer simulation analysis and molecular cell experiments. In particular, this process succeeded in properly reverting the mesenchymal lung cancer cells to a state where they were sensitive to chemotherapy treatment while avoiding the unstable EMT hybrid cell state in the middle process, which had remained a difficult problem.
The results of this research, in which KAIST Ph.D. student Namhee Kim, Dr. Chae Young Hwang, Researcher Taeyoung Kim, and Ph.D. student Hyunjin Kim participated, were published as an online paper in the international journal “Cancer Research” published by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) on January 30th. (Paper title: A cell fate reprogramming strategy reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells while avoiding hybrid states)
Cells in an EMT hybrid state, which are caused by incomplete transitions during the EMT process in cancer cells, have the characteristics of both epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells, and are known to have high drug resistance and metastatic potential by acquiring high stem cell capacity. In particular, EMT is further enhanced through factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) secreted from the tumor microenvironment (TME) and, as a result, various cell states with high plasticity appear. Due to the complexity of EMT, it has been very difficult to completely reverse the transitional process of the mesenchymal cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are eliminated while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state with high metastatic ability and drug resistance.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a mathematical model of the gene regulation network that governs the complex process of EMT, and then applied large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology to identify and verify 'p53', 'SMAD4', and 'ERK1' and 'ERK 2' (collectively ERKs) through molecular cell experiments as the three key molecular targets that can transform lung cancer cells in the mesenchymal cell state, reversed back to an epithelial cell state that no longer demonstrates the ability to metastasize, while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state.
In particular, by analyzing the molecular regulatory mechanism of the complex EMT process at the system level, the key pathways were identified that were linked to the positive feedback that plays an important role in completely returning cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are removed.
This discovery is significant in that it proved that mesenchymal cells can be reverted to the state of epithelial cells under conditions where TGF-β stimulation are present, like they are in the actual environment where cancer tissue forms in the human body.
Abnormal EMT in cancer cells leads to various malignant traits such as the migration and invasion of cancer cells, changes in responsiveness to chemotherapy treatment, enhanced stem cell function, and the dissemination of cancer. In particular, the acquisition of the metastatic ability of cancer cells is a key determinant factor for the prognosis of cancer patients. The EMT reversal technology in lung cancer cells developed in this research is a new anti-cancer treatment strategy that reprograms cancer cells to eliminate their high plasticity and metastatic potential and increase their responsiveness to chemotherapy.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "By succeeding in reversing the state of lung cancer cells that acquired high metastatic traits and resistance to drugs and reverting them to a treatable epithelial cell state with renewed sensitivity to chemotherapy, the research findings propose a new strategy for treatments that can improve the prognosis of cancer patients.”
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team was the first to present the principle of reversal treatment to revert cancer cells to normal cells, following through with the announcement of the results of their study that reverted colon cancer cells to normal colon cells in January of 2020, and also presenting successful re-programming research where the most malignant basal type breast cancer cells turned into less-malignant luminal type breast cancer cells that were treatable with hormonal therapies in January of 2022. This latest research result is the third in the development of reversal technology where lung cancer cells that had acquired metastatic traits returned to a state in which their metastatic ability was removed and drug sensitivity was enhanced.
This research was carried out with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers.
< Figure 1. Construction of the mathematical model of the regulatory network to represent the EMT phenotype based on the interaction between various molecules related to EMT.
(A) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team investigated numerous literatures and databases related to complex EMT, and based on comparative analysis of cell line data showing epithelial and mesenchymal cell conditions, they extracted key signaling pathways related to EMT and built a mathematical model of regulatory network (B) By comparing the results of computer simulation analysis and the molecular cell experiments, it was verified how well the constructed mathematical model simulated the actual cellular phenomena. >
< Figure 2. Understanding of various EMT phenotypes through large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology.
(A) Through computer simulation analysis and experiments, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team found that complete control of EMT is impossible with single-molecule control alone. In particular, through comparison of the relative stability of attractors, it was revealed that the cell state exhibiting EMT hybrid characteristics has unstable properties. (B), (C) Based on these results, Prof. Cho’s team identified two feedbacks (positive feedback consisting of Snail-miR-34 and ZEB1-miR-200) that play an important role in avoiding the EMT hybrid state that appeared in the TGF-β-ON state. It was found through computer simulation analysis that the two feedbacks restore relatively high stability when the excavated p53 and SMAD4 are regulated. In addition, molecular cell experiments demonstrated that the expression levels of E-cad and ZEB1, which are representative phenotypic markers of EMT, changed similarly to the expression profile in the epithelial cell state, despite the TGF-β-ON state. >
< Figure 3. Complex molecular network analysis and discovery of reprogramming molecular targets for intact elimination of EMT hybrid features.
(A) Controlling the expression of p53 and SMAD4 in lung cancer cell lines was expected to overcome drug resistance, but contrary to expectations, chemotherapy responsiveness was not restored. (B) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team additionally analyzed computer simulations, genome data, and experimental results and found that high expression levels of TWIST1 and EPCAM were related to drug resistance. (C) Prof. Cho’s team identified three key molecular targets: p53, SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2. (D), (E) Furthermore, they identified a key pathway that plays an important role in completely reversing into epithelial cells while avoiding EMT hybrid characteristics, and confirmed through network analysis and attractor analysis that high stability of the key pathway was restored when the proposed molecular target was controlled. >
< Figure 4. Verification through experiments with lung cancer cell lines.
When p53 was activated and SMAD4 and ERK1/2 were inhibited in lung cancer cell lines, (A), (B) E-cad protein expression increased and ZEB1 protein expression decreased, and (C) mesenchymal cell status including TWIST1 and EPCAM and gene expression of markers related to stem cell potential characteristics were completely inhibited. In addition, (D) it was confirmed that resistance to chemotherapy treatment was also overcome as the cell state was reversed by the regulated target. >
< Figure 5. A schematic representation of the research results.
Prof. Cho’s research team identified key molecular regulatory pathways to avoid high plasticity formed by abnormal EMT of cancer cells and reverse it to an epithelial cell state through systems biology research. From this analysis, a reprogramming molecular target that can reverse the state of mesenchymal cells with acquired invasiveness and drug resistance to the state of epithelial cells with restored drug responsiveness was discovered.
For lung cancer cells, when a drug that enhances the expression of p53, one of the molecular targets discovered, and inhibits the expression of SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2 is administered, the molecular network of genes in the state of mesenchymal cells is modified, eventually eliminating metastatic ability and it is reprogrammed to turn into epithelial cells without the resistance to chemotherapy treatments. >
2023.01.30 View 15903 -
 Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
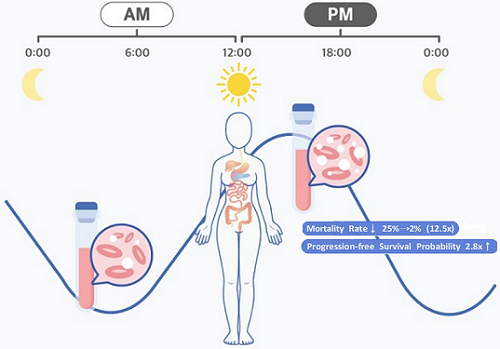
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 6418
Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 6418 -
 Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 11950
Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 11950 -
 KAIST Team Develops Surface-Lighting MicroLED Patch with Significant Melanogenesis Inhibition Effect
A KAIST research team led by Ph.d candidate Jae Hee Lee and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a surface-lighting microLED patch for UV-induced melanogenesis inhibition.
Melanin is brown or dark pigments existing in the skin, which can be abnormally synthesized by external UV or stress. Since the excessive melanin leads to skin diseases such as spots and freckles, proper treatment is required to return normal skin condition.
Recently, LED-based photo-stimulators have been released for skin care, however, their therapeutic effect is still controversial. Since conventional LED stimulators cannot conformally attach to the human skin, distance-induced side effects are caused by light loss and high heat transfer. To achieve effective phototreatment, the LED stimulator needs to be irradiated in contact with the human skin surface, enabling proper and uniform light deliver to the dermis with minimal optical loss.
In this work, the research team fabricated skin-attachable surface-lighting microLED (SµLED, 4 × 4 cm2) patch by utilizing a thousand of microLED chips and silica-embedded light diffusion layer. 100 µm-sized LED chips are vertically-interconnected for high flexibility and low heat generation, allowing its long-term operation on the human skin.
< Image 1. The overall concept of SµLED patch. a) SµLED patch operated on the human skin. b) Schematic illustration of SµLED patch structure. c) 4 × 4 cm2-sized SµLED patch. d) Schematic illustration of the advantages of SµLED patch such as efficient light delivery, low heat generation, and surface-lighting irradiation. >
The research team confirmed melanogenesis inhibition by irradiating the SµLED patch and the conventional LED (CLED) on the artificial human skin and mice dorsal skin. The SµLED-treated groups of human cells and mouse tissues showed minimal epidermal photo-toxicity and consistently effective reduction in synthesized melanin, compared to CLED-treated groups. In addition, significant suppression of proteins/catalysts expression involved in melanin synthesis such as MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor), Melan-A and tyrosinase was verified.
< Image 2. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on 3D human skin cells. a). Different irradiation conditions for a-MSH (major factor to stimulate melanin synthesis) treated cells. b) The ratio of pigmented area to total epidermis area. c) Relative variance of melanin level in 1 cm2-sized skin cells. A low variance means that melanin is evenly distributed, and a high variance means that the melanin is irregularly distributed. d) Optical images after in vitro experiments for 12 days. Scale bar, 1cm. e) Histological analysis of 3D skin, showing the greatest reduction in melanin after SµLED irradiation. Scale bar, 20 µm. >
< Image 3. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on mouse dorsal skin. a) Optical images of mice dorsal skin after photo-treatment for 20 days. b) Histological analysis of mice dorsal skin. Less brown color means less expression of protein/catalysis involved in melanin synthesis. Scale bar, 50 µm. >
Prof. Keon Jae Lee said, “Our inorganic-based SµLED patch has outstanding characteristics in light efficiency, reliability, and durability. The SµLED patch is expected to give a great impact on the cosmetic field by reducing side effects and maximizing phototherapeutic effects.” The core technology of cosmetic SµLED has been transferred to Fronics co., Ltd, founded by Prof. Lee. Fronics is building foundry and equipment for mass production of SµLED masks for whole face cover and plans to release the products in March next year.
This paper entitled “Wearable Surface-Lighting Micro-Light-Emitting Diode Patch for Melanogenesis Inhibition” was published in the November 2022 issue of Advanced Healthcare Materials.
2022.11.22 View 10225
KAIST Team Develops Surface-Lighting MicroLED Patch with Significant Melanogenesis Inhibition Effect
A KAIST research team led by Ph.d candidate Jae Hee Lee and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a surface-lighting microLED patch for UV-induced melanogenesis inhibition.
Melanin is brown or dark pigments existing in the skin, which can be abnormally synthesized by external UV or stress. Since the excessive melanin leads to skin diseases such as spots and freckles, proper treatment is required to return normal skin condition.
Recently, LED-based photo-stimulators have been released for skin care, however, their therapeutic effect is still controversial. Since conventional LED stimulators cannot conformally attach to the human skin, distance-induced side effects are caused by light loss and high heat transfer. To achieve effective phototreatment, the LED stimulator needs to be irradiated in contact with the human skin surface, enabling proper and uniform light deliver to the dermis with minimal optical loss.
In this work, the research team fabricated skin-attachable surface-lighting microLED (SµLED, 4 × 4 cm2) patch by utilizing a thousand of microLED chips and silica-embedded light diffusion layer. 100 µm-sized LED chips are vertically-interconnected for high flexibility and low heat generation, allowing its long-term operation on the human skin.
< Image 1. The overall concept of SµLED patch. a) SµLED patch operated on the human skin. b) Schematic illustration of SµLED patch structure. c) 4 × 4 cm2-sized SµLED patch. d) Schematic illustration of the advantages of SµLED patch such as efficient light delivery, low heat generation, and surface-lighting irradiation. >
The research team confirmed melanogenesis inhibition by irradiating the SµLED patch and the conventional LED (CLED) on the artificial human skin and mice dorsal skin. The SµLED-treated groups of human cells and mouse tissues showed minimal epidermal photo-toxicity and consistently effective reduction in synthesized melanin, compared to CLED-treated groups. In addition, significant suppression of proteins/catalysts expression involved in melanin synthesis such as MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor), Melan-A and tyrosinase was verified.
< Image 2. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on 3D human skin cells. a). Different irradiation conditions for a-MSH (major factor to stimulate melanin synthesis) treated cells. b) The ratio of pigmented area to total epidermis area. c) Relative variance of melanin level in 1 cm2-sized skin cells. A low variance means that melanin is evenly distributed, and a high variance means that the melanin is irregularly distributed. d) Optical images after in vitro experiments for 12 days. Scale bar, 1cm. e) Histological analysis of 3D skin, showing the greatest reduction in melanin after SµLED irradiation. Scale bar, 20 µm. >
< Image 3. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on mouse dorsal skin. a) Optical images of mice dorsal skin after photo-treatment for 20 days. b) Histological analysis of mice dorsal skin. Less brown color means less expression of protein/catalysis involved in melanin synthesis. Scale bar, 50 µm. >
Prof. Keon Jae Lee said, “Our inorganic-based SµLED patch has outstanding characteristics in light efficiency, reliability, and durability. The SµLED patch is expected to give a great impact on the cosmetic field by reducing side effects and maximizing phototherapeutic effects.” The core technology of cosmetic SµLED has been transferred to Fronics co., Ltd, founded by Prof. Lee. Fronics is building foundry and equipment for mass production of SµLED masks for whole face cover and plans to release the products in March next year.
This paper entitled “Wearable Surface-Lighting Micro-Light-Emitting Diode Patch for Melanogenesis Inhibition” was published in the November 2022 issue of Advanced Healthcare Materials.
2022.11.22 View 10225 -
 NYC-KAIST Cooperation Agreement Signed in New York for KAIST NYU Joint Campus
A ceremony was held to celebrate the signing of the Cooperative Agreement between NYC and KAIST and the presentation of the signage for KAIST NYU Joint Campus at NYU’s Kimmel Center in Manhattan.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYU President Andrew Hamilton (right)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) signed a cooperative agreement with the City of New York and had an official showing of the signage for the Joint Campus of KAIST and New York University (NYU) on September 21 at 4:00 pm (Eastern Standard Time) at NYU’s Kimmel Center in New York City with the NYC Mayor Eric Adams, the Korean Minister of Science and ICT Dr. Lee Jong-ho, NYU Chairman William Berkley, NYU President Andrew Hamilton, and other distinguished guests in attendance.
KAIST and NYU signed a Memorandum of Understanding in June about building a joint campus in an effort to educate global talent. As a follow-up measure, NYU has provided KAIST with space to begin joint research programs and held a ceremony to present the signage designed for the future KAIST NYU Campus. In line with these efforts, KAIST has also signed an agreement with New York City, the administrative authority in charge of the establishment of the campus, for mutual cooperation.
NYU is a prestigious university headquartered in Manhattan, New York. It has nurtured outstanding talents in the humanities, art, and basic sciences, including 38 Nobel Prize winners, 5 Fields Prize winners, 26 Pulitzer Prize winners, and 38 Academy Award winners to be deserving of the evaluation.
The proposed joint campus is to be centered on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by combining NYU's excellent basic sciences and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's globally renowned science and technology capabilities. The joint initiative is expected to launch in 2023; its programs will focus on areas such as AI Basic Science, AI Convergence Brain Science, AI-Applied Cyber Security, Cyber Security, and Sustainable High-Tech Smart City/Climate Change in order to lead the Digital Era and to solve the problems that surfaced following the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, in order to prepare for the Post-AI Era, it was decided to create the “New Engineering” program for undergraduate program that employs a hyper-convergence learning model that combines project-based, problem-solving learning (PBL, PSL) pedagogy.
▲ Biomedical Engineering- Research and development of technology to respond to the entire cycle (prevention-treatment-diagnosis-prediction) for a new infectious disease (Disease X) by converging new technologies such as IT and NT with biomedical technologies
▲ AI Convergence Neuroscience- Research on brain-machine interaction and brain-based machine learning through AI technology convergence
▲ AI Science- Algorithm development and in-depth research in preparation for the post AI era
▲ Sustainability and Climate Change- R&DB for advanced smart cities, sustainability for the global environment and carbon zero
▲ Next-generation Wireless Communications- From ICT to AIT: Research on 6G/7G related technologies, new communications theories, and etc.
▲ Cyber Security- Advanced research on protection of digital information and information safety/reliability
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYC Mayor Eric Adams (right)
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus has started enlisting professors and researchers from both institutions to participate in the collaboration. The campus will also function as the headquarter that will oversee the operation of the joint research program. At Daejeon, KAIST is also setting up a location for NYU on its main campus to provide space for NYU researchers upon their visit to KAIST.
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus, which has begun to take basic shape with the space for collaboration rendered this time, is to be upgraded to “KAIST New York Campus” in the future to function also as an industry-academic cooperation campus in which that promotes strategic cooperation with industries and expands start-up opportunities. To this end, the related procedures from the detailing of the establishment plans through a preliminary feasibility studies, to deliberation and decision on whether to proceed with the establishment by the KAIST Board of Trustees, will be taken.
The KAIST NYU Campus is expected to serve as a stepping stone for the outstanding talents of KAIST to pursue their dreams in the global market and research environment while seizing the attention of the world-class talents drawn to New York at the same time. In addition, by combining NYU's strong basic academic capabilities with KAIST’s strengths, it is expected to contribute to achieving 'global innovation' by creating synergies in various fields such as education, research, and entrepreneurship. The future KAIST-NYU Campus is also expected to encompass an industry-academic cooperation campus with industrial partners and startups.
Meanwhile, KAIST is planning to expand its excellent scientific and technological capabilities to the global stage through the cooperative agreement with New York City, and to prepare a pathway for KAIST students, faculty, and startups to enter their respective fields in the global markets. In the future, KAIST plans to explore areas of cooperation in different fields, such as education, economy, society, and culture, to prepare and implement detailed cooperation plans.
< KAIST-New York City Cooperation Items (Example) >
▲ Education: Joint degree program with a university in New York City, training of key talents in the field of artificial intelligence, etc.
▲ Economy: A hub for technology startups, job creation in the tech sector, etc.
▲ Society: Economics, finance, media-related engineering research, etc.
▲ Culture: Diversity-based culture and art-tech research, etc.▲ Etc: Joint research in the field of artificial intelligence healthcare, etc.
As a global mecca for startups, education, and investment, New York has a well-developed global network for cultural diversity and successful career development, and has great power to attract various resources including funds and talented individuals. Based on this, it has established itself as a mecca of global tech companies and global top media groups, and is building the reputation as 'Silicon Alley' in addition to its legends of the ‘Wall Street'.
Dr. Andrew Hamilton, the president of NYU, said, “We’re delighted by our newly established partnership with KAIST. We see great potential in the opportunities to collaborate on development of courses, research, cutting edge technologies, university-level courses, degrees, entrepreneurship initiatives and industrial partnerships, and exchanges. We believe this partnership is very much in line with NYU’s commitment to global engagement and will make important contributions to New York’s tech sector. It’s exciting to think how much NYU and KAIST have much to learn from one another, and how much we may accomplish together.”
New York City Mayor Eric Adams said, “We’re proud to have helped facilitate this partnership between KAIST and New York University, which will be a real win for students and help drive continued innovation in our city.” He added, “From the time that senior members of our administration learned about this opportunity during a recent trip to South Korea, we have worked closely with KAIST to develop strategies for increasing their presence and investments in New York. This is the start of a relationship that I am confident will bring even more academic, business, and technological opportunities to the five boroughs.”
Dr. Kwang Hyung Lee, the president of KAIST, urged, “Based on the KAIST-NYU partnership, we must create an interdisciplinary hyper-convergence model of collaboration and use cutting-edge tools to create an innovative model for new type of problem-solving engineering education to prepare to solve the challenges facing the world.” He went on to stress, “The new fusion engineering degree program will leverage the unique strengths of the two institutions to provide a uniquely colored education not found anywhere else.” In addition, he added, “KAIST will utilize the advantages that are unique to the global city of New York to contribute to advancing the science and technology research in New York City and creating jobs in the tech sector to lead the renaissance of Silicon Alley.”
2022.09.27 View 12472
NYC-KAIST Cooperation Agreement Signed in New York for KAIST NYU Joint Campus
A ceremony was held to celebrate the signing of the Cooperative Agreement between NYC and KAIST and the presentation of the signage for KAIST NYU Joint Campus at NYU’s Kimmel Center in Manhattan.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYU President Andrew Hamilton (right)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) signed a cooperative agreement with the City of New York and had an official showing of the signage for the Joint Campus of KAIST and New York University (NYU) on September 21 at 4:00 pm (Eastern Standard Time) at NYU’s Kimmel Center in New York City with the NYC Mayor Eric Adams, the Korean Minister of Science and ICT Dr. Lee Jong-ho, NYU Chairman William Berkley, NYU President Andrew Hamilton, and other distinguished guests in attendance.
KAIST and NYU signed a Memorandum of Understanding in June about building a joint campus in an effort to educate global talent. As a follow-up measure, NYU has provided KAIST with space to begin joint research programs and held a ceremony to present the signage designed for the future KAIST NYU Campus. In line with these efforts, KAIST has also signed an agreement with New York City, the administrative authority in charge of the establishment of the campus, for mutual cooperation.
NYU is a prestigious university headquartered in Manhattan, New York. It has nurtured outstanding talents in the humanities, art, and basic sciences, including 38 Nobel Prize winners, 5 Fields Prize winners, 26 Pulitzer Prize winners, and 38 Academy Award winners to be deserving of the evaluation.
The proposed joint campus is to be centered on science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) by combining NYU's excellent basic sciences and convergence research capabilities with KAIST's globally renowned science and technology capabilities. The joint initiative is expected to launch in 2023; its programs will focus on areas such as AI Basic Science, AI Convergence Brain Science, AI-Applied Cyber Security, Cyber Security, and Sustainable High-Tech Smart City/Climate Change in order to lead the Digital Era and to solve the problems that surfaced following the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, in order to prepare for the Post-AI Era, it was decided to create the “New Engineering” program for undergraduate program that employs a hyper-convergence learning model that combines project-based, problem-solving learning (PBL, PSL) pedagogy.
▲ Biomedical Engineering- Research and development of technology to respond to the entire cycle (prevention-treatment-diagnosis-prediction) for a new infectious disease (Disease X) by converging new technologies such as IT and NT with biomedical technologies
▲ AI Convergence Neuroscience- Research on brain-machine interaction and brain-based machine learning through AI technology convergence
▲ AI Science- Algorithm development and in-depth research in preparation for the post AI era
▲ Sustainability and Climate Change- R&DB for advanced smart cities, sustainability for the global environment and carbon zero
▲ Next-generation Wireless Communications- From ICT to AIT: Research on 6G/7G related technologies, new communications theories, and etc.
▲ Cyber Security- Advanced research on protection of digital information and information safety/reliability
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee (left) and NYC Mayor Eric Adams (right)
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus has started enlisting professors and researchers from both institutions to participate in the collaboration. The campus will also function as the headquarter that will oversee the operation of the joint research program. At Daejeon, KAIST is also setting up a location for NYU on its main campus to provide space for NYU researchers upon their visit to KAIST.
The KAIST NYU Joint Campus, which has begun to take basic shape with the space for collaboration rendered this time, is to be upgraded to “KAIST New York Campus” in the future to function also as an industry-academic cooperation campus in which that promotes strategic cooperation with industries and expands start-up opportunities. To this end, the related procedures from the detailing of the establishment plans through a preliminary feasibility studies, to deliberation and decision on whether to proceed with the establishment by the KAIST Board of Trustees, will be taken.
The KAIST NYU Campus is expected to serve as a stepping stone for the outstanding talents of KAIST to pursue their dreams in the global market and research environment while seizing the attention of the world-class talents drawn to New York at the same time. In addition, by combining NYU's strong basic academic capabilities with KAIST’s strengths, it is expected to contribute to achieving 'global innovation' by creating synergies in various fields such as education, research, and entrepreneurship. The future KAIST-NYU Campus is also expected to encompass an industry-academic cooperation campus with industrial partners and startups.
Meanwhile, KAIST is planning to expand its excellent scientific and technological capabilities to the global stage through the cooperative agreement with New York City, and to prepare a pathway for KAIST students, faculty, and startups to enter their respective fields in the global markets. In the future, KAIST plans to explore areas of cooperation in different fields, such as education, economy, society, and culture, to prepare and implement detailed cooperation plans.
< KAIST-New York City Cooperation Items (Example) >
▲ Education: Joint degree program with a university in New York City, training of key talents in the field of artificial intelligence, etc.
▲ Economy: A hub for technology startups, job creation in the tech sector, etc.
▲ Society: Economics, finance, media-related engineering research, etc.
▲ Culture: Diversity-based culture and art-tech research, etc.▲ Etc: Joint research in the field of artificial intelligence healthcare, etc.
As a global mecca for startups, education, and investment, New York has a well-developed global network for cultural diversity and successful career development, and has great power to attract various resources including funds and talented individuals. Based on this, it has established itself as a mecca of global tech companies and global top media groups, and is building the reputation as 'Silicon Alley' in addition to its legends of the ‘Wall Street'.
Dr. Andrew Hamilton, the president of NYU, said, “We’re delighted by our newly established partnership with KAIST. We see great potential in the opportunities to collaborate on development of courses, research, cutting edge technologies, university-level courses, degrees, entrepreneurship initiatives and industrial partnerships, and exchanges. We believe this partnership is very much in line with NYU’s commitment to global engagement and will make important contributions to New York’s tech sector. It’s exciting to think how much NYU and KAIST have much to learn from one another, and how much we may accomplish together.”
New York City Mayor Eric Adams said, “We’re proud to have helped facilitate this partnership between KAIST and New York University, which will be a real win for students and help drive continued innovation in our city.” He added, “From the time that senior members of our administration learned about this opportunity during a recent trip to South Korea, we have worked closely with KAIST to develop strategies for increasing their presence and investments in New York. This is the start of a relationship that I am confident will bring even more academic, business, and technological opportunities to the five boroughs.”
Dr. Kwang Hyung Lee, the president of KAIST, urged, “Based on the KAIST-NYU partnership, we must create an interdisciplinary hyper-convergence model of collaboration and use cutting-edge tools to create an innovative model for new type of problem-solving engineering education to prepare to solve the challenges facing the world.” He went on to stress, “The new fusion engineering degree program will leverage the unique strengths of the two institutions to provide a uniquely colored education not found anywhere else.” In addition, he added, “KAIST will utilize the advantages that are unique to the global city of New York to contribute to advancing the science and technology research in New York City and creating jobs in the tech sector to lead the renaissance of Silicon Alley.”
2022.09.27 View 12472 -
 A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 11918
A KAIST Research Team Develops Diesel Reforming Catalyst Enabling Hydrogen Production for Future Mobile Fuel Cells
This catalyst capability allowing stable hydrogen production from commercial diesel is expected to be applied in mobile fuel cell systems in the future hydrogen economy
On August 16, a joint research team led by Professors Joongmyeon Bae and Kang Taek Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) announced the successful development of a highly active and durable reforming catalyst allowing hydrogen production from commercial diesel.
Fuel reforming is a hydrogen production technique that extracts hydrogen from hydrocarbons through catalytic reactions. Diesel, being a liquid fuel, has a high storage density for hydrogen and is easy to transport and store. There have therefore been continuous research efforts to apply hydrogel supply systems using diesel reformation in mobile fuel cells, such as for auxiliary power in heavy trucks or air-independent propulsion (AIP) systems in submarines.
However, diesel is a mixture of high hydrocarbons including long-chained paraffin, double-bonded olefin, and aromatic hydrocarbons with benzene groups, and it requires a highly active catalyst to effectively break them down. In addition, the catalyst must be extremely durable against caulking and sintering, as they are often the main causes of catalyst degradation. Such challenges have limited the use of diesel reformation technologies to date.
The joint research team successfully developed a highly active and durable diesel reforming catalyst through elution (a heat treatment method used to uniformly grow active metals retained in an oxide support as ions in the form of metal nanoparticles), forming alloy nanoparticles. The design was based on the fact that eluted nanoparticles strongly interact with the support, allowing a high degree of dispersion at high temperatures, and that producing an alloy from dissimilar metals can increase the performance of catalysts through a synergistic effect.
The research team introduced a solution combustion synthesis method to produce a multi-component catalyst with a trace amount of platinum (Pt) and ruthenium (Ru) penetrated into a ceria (CeO2) lattice, which is a structure commonly used as a support for catalysts in redox reactions. When exposed to a diesel reforming reaction environment, the catalyst induces Pt-Ru alloy nanoparticle formation upon Pt and Ru elution onto the support surface.
In addition to the catalyst analysis, the research team also succeeded in characterizing the behaviour of active metal elution and alloy formation from an energetic perspective using a density functional theory-based calculation. In a performance comparison test between the Pt-Ru alloy catalyst against existing single-metal catalysts, the reforming activity was shown to have improved, as it showed a 100% fuel conversion rate even at a low temperature (600oC, compared to the original 800oC). In a long-term durability test (800oC, 200 hours), the catalyst showed commercial stability by successfully producing hydrogen from commercial diesel without performance degradation.
The study was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jaemyung Lee of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author. Ph.D. candidate Changho Yeon of KIER, Dr. Jiwoo Oh of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, Dr. Gwangwoo Han of KIER, Ph.D. candidate Jeong Do Yoo of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr. Hyung Joong Yun of the Korea Basic Science Institute contributed as co-authors. Dr. Chan-Woo Lee of KIER and Professors Kang Taek Lee and Joongmyeon Bae of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering contributed as corresponding authors. The research was published in the online version of Applied Catalysis B: Environmental (IF 24.319, JCR 0.93%) on June 17, under the title “Highly Active and Stable Catalyst with Exsolved PtRu Alloy Nanoparticles for Hydrogen Production via Commercial Diesel Reforming”.
Professor Joongmyeon Bae said, “The fact that hydrogen can be stably produced from commercial diesel makes this a very meaningful achievement, and we look forward to this technology contributing to the active introduction of mobile fuel cell systems in the early hydrogen economy.” He added, “Our approach to catalyst design may be applied not only to reforming reactions, but also in various other fields.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through funding from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure. Schematic diagram of high-performance diesel reforming catalyst with eluted platinum-ruthenium alloy nanoparticles and long-term durability verification experiment results for commercial diesel reforming reaction
2022.09.07 View 11918 -
 Establishing a novel strategy to tackle Huntington’s disease
A platform to take on the Huntington’s disease via an innovative approach established by KAIST’s researchers through international collaboration with scientists in the Netherlands, France, and Sweden.
Through an international joint research effort involving ProQR Therapeutics of the Netherlands, Université Grenoble Alpes of France, and KTH Royal Institute of Technology of Sweden, Professor Ji-Soon Song's research team in the Department of Biological Sciences and KAIST Institute for BioCentury of KAIST, established a noble strategy to treat Huntington's disease. The new works showed that the protein converted from disease form to its disease-free form maintains its original function, providing new roadblocks to approach Huntington’s disease.
This research, titled, “A pathogenic-proteolysis resistant huntingtin isoform induced by an antisense oligonucleotide maintains huntingtin function”, co-authored by Hyeongju Kim, was published in the online edition of 'Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight' on August 9, 2022.
Huntington's disease is a dominantly inherited neurodegenerative disease and is caused by a mutation in a protein called ‘huntingtin’, which adds a distinctive feature of an expanded stretch of glutamine amino acids called polyglutamine to the protein. It is estimated that one in every 10,000 have Huntington's disease in United States. The patients would suffer a decade of regression before death, and, thus far, there is no known cure for the disease.
The cleavage near the stretched polyglutamine in mutated huntingtin is known to be the cause of the Huntington’s disease. However, as huntingtin protein is required for the development and normal function of the brain, it is critical to specifically eliminate the disease-causing protein while maintaining the ones that are still normally functioning.
The research team showed that huntingtin delta 12, the converted form of huntingtin that is resistant to developing cleavages at the ends of the protein, the known cause of the Huntington’s disease (HD), alleviated the disease’s symptoms while maintaining the functions of normal huntingtin.
Figure. Huntington's disease resistance huntingtin protein induced by antisense oligonucleotide (AON) is resistant to Caspase-6 cleavage, therefore, does not cause Huntington’s disease while maintaining normal functions of huntingtin.
The research was welcomed as it is sure to fuel innovate strategies to tackle Huntington’s disease without altering the essential function of huntingtin.
This work was supported by a Global Research Lab grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and by a EUREKA Eurostars 2 grant from European Union Horizon 2020.
2022.09.02 View 6839
Establishing a novel strategy to tackle Huntington’s disease
A platform to take on the Huntington’s disease via an innovative approach established by KAIST’s researchers through international collaboration with scientists in the Netherlands, France, and Sweden.
Through an international joint research effort involving ProQR Therapeutics of the Netherlands, Université Grenoble Alpes of France, and KTH Royal Institute of Technology of Sweden, Professor Ji-Soon Song's research team in the Department of Biological Sciences and KAIST Institute for BioCentury of KAIST, established a noble strategy to treat Huntington's disease. The new works showed that the protein converted from disease form to its disease-free form maintains its original function, providing new roadblocks to approach Huntington’s disease.
This research, titled, “A pathogenic-proteolysis resistant huntingtin isoform induced by an antisense oligonucleotide maintains huntingtin function”, co-authored by Hyeongju Kim, was published in the online edition of 'Journal of Clinical Investigation Insight' on August 9, 2022.
Huntington's disease is a dominantly inherited neurodegenerative disease and is caused by a mutation in a protein called ‘huntingtin’, which adds a distinctive feature of an expanded stretch of glutamine amino acids called polyglutamine to the protein. It is estimated that one in every 10,000 have Huntington's disease in United States. The patients would suffer a decade of regression before death, and, thus far, there is no known cure for the disease.
The cleavage near the stretched polyglutamine in mutated huntingtin is known to be the cause of the Huntington’s disease. However, as huntingtin protein is required for the development and normal function of the brain, it is critical to specifically eliminate the disease-causing protein while maintaining the ones that are still normally functioning.
The research team showed that huntingtin delta 12, the converted form of huntingtin that is resistant to developing cleavages at the ends of the protein, the known cause of the Huntington’s disease (HD), alleviated the disease’s symptoms while maintaining the functions of normal huntingtin.
Figure. Huntington's disease resistance huntingtin protein induced by antisense oligonucleotide (AON) is resistant to Caspase-6 cleavage, therefore, does not cause Huntington’s disease while maintaining normal functions of huntingtin.
The research was welcomed as it is sure to fuel innovate strategies to tackle Huntington’s disease without altering the essential function of huntingtin.
This work was supported by a Global Research Lab grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and by a EUREKA Eurostars 2 grant from European Union Horizon 2020.
2022.09.02 View 6839 -
 Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 11876
Phage resistant Escherichia coli strains developed to reduce fermentation failure
A genome engineering-based systematic strategy for developing phage resistant Escherichia coli strains has been successfully developed through the collaborative efforts of a team led by Professor Sang Yup Lee, Professor Shi Chen, and Professor Lianrong Wang. This study by Xuan Zou et al. was published in Nature Communications in August 2022 and featured in Nature Communications Editors’ Highlights. The collaboration by the School of Pharmaceutical Sciences at Wuhan University, the First Affiliated Hospital of Shenzhen University, and the KAIST Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has made an important advance in the metabolic engineering and fermentation industry as it solves a big problem of phage infection causing fermentation failure.
Systems metabolic engineering is a highly interdisciplinary field that has made the development of microbial cell factories to produce various bioproducts including chemicals, fuels, and materials possible in a sustainable and environmentally friendly way, mitigating the impact of worldwide resource depletion and climate change. Escherichia coli is one of the most important chassis microbial strains, given its wide applications in the bio-based production of a diverse range of chemicals and materials. With the development of tools and strategies for systems metabolic engineering using E. coli, a highly optimized and well-characterized cell factory will play a crucial role in converting cheap and readily available raw materials into products of great economic and industrial value.
However, the consistent problem of phage contamination in fermentation imposes a devastating impact on host cells and threatens the productivity of bacterial bioprocesses in biotechnology facilities, which can lead to widespread fermentation failure and immeasurable economic loss. Host-controlled defense systems can be developed into effective genetic engineering solutions to address bacteriophage contamination in industrial-scale fermentation; however, most of the resistance mechanisms only narrowly restrict phages and their effect on phage contamination will be limited.
There have been attempts to develop diverse abilities/systems for environmental adaptation or antiviral defense. The team’s collaborative efforts developed a new type II single-stranded DNA phosphorothioation (Ssp) defense system derived from E. coli 3234/A, which can be used in multiple industrial E. coli strains (e.g., E. coli K-12, B and W) to provide broad protection against various types of dsDNA coliphages. Furthermore, they developed a systematic genome engineering strategy involving the simultaneous genomic integration of the Ssp defense module and mutations in components that are essential to the phage life cycle. This strategy can be used to transform E. coli hosts that are highly susceptible to phage attack into strains with powerful restriction effects on the tested bacteriophages. This endows hosts with strong resistance against a wide spectrum of phage infections without affecting bacterial growth and normal physiological function. More importantly, the resulting engineered phage-resistant strains maintained the capabilities of producing the desired chemicals and recombinant proteins even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge, which provides crucial protection against phage attacks.
This is a major step forward, as it provides a systematic solution for engineering phage-resistant bacterial strains, especially industrial bioproduction strains, to protect cells from a wide range of bacteriophages. Considering the functionality of this engineering strategy with diverse E. coli strains, the strategy reported in this study can be widely extended to other bacterial species and industrial applications, which will be of great interest to researchers in academia and industry alike.
Fig. A schematic model of the systematic strategy for engineering phage-sensitive industrial E. coli strains into strains with broad antiphage activities. Through the simultaneous genomic integration of a DNA phosphorothioation-based Ssp defense module and mutations of components essential for the phage life cycle, the engineered E. coli strains show strong resistance against diverse phages tested and maintain the capabilities of producing example recombinant proteins, even under high levels of phage cocktail challenge.
2022.08.23 View 11876 -
 Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 12979
Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 12979 -
 A New Therapeutic Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease without Inflammatory Side Effects
Although Aduhelm, a monoclonal antibody targeting amyloid beta (Aβ), recently became the first US FDA approved drug for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) based on its ability to decrease Aβ plaque burden in AD patients, its effect on cognitive improvement is still controversial. Moreover, about 40% of the patients treated with this antibody experienced serious side effects including cerebral edemas (ARIA-E) and hemorrhages (ARIA-H) that are likely related to inflammatory responses in the brain when the Aβ antibody binds Fc receptors (FCR) of immune cells such as microglia and macrophages.
These inflammatory side effects can cause neuronal cell death and synapse elimination by activated microglia, and even have the potential to exacerbate cognitive impairment in AD patients. Thus, current Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy holds the inherent risk of doing more harm than good due to their inflammatory side effects.
To overcome these problems, a team of researchers at KAIST in South Korea has developed a novel fusion protein drug, αAβ-Gas6, which efficiently eliminates Aβ via an entirely different mechanism than Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy. In a mouse model of AD, αAβ-Gas6 not only removed Aβ with higher potency, but also circumvented the neurotoxic inflammatory side effects associated with conventional antibody treatments.
Their findings were published on August 4 in Nature Medicine.
Schematic of a chimeric Gas6 fusion protein. A single chain variable fragment (scFv) of
an Amyloid β (Aβ)-targeting monoclonal antibody is fused with a truncated receptor binding
domain of Gas6, a bridging molecule for the clearance of dead cells via TAM (TYRO3, AXL,
and MERTK) receptors, which are expressed by microglia and astrocytes.
“FcR activation by Aβ targeting antibodies induces microglia-mediated Aβ phagocytosis, but it also produces inflammatory signals, inevitably damaging brain tissues,” said paper authors Chan Hyuk Kim and Won-Suk Chung, associate professors in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
“Therefore, we utilized efferocytosis, a cellular process by which dead cells are removed by phagocytes as an alternative pathway for the clearance of Aβ in the brain,” Prof. Kim and Chung said. “Efferocytosis is accompanied by anti-inflammatory responses to maintain tissue homeostasis. To exploit this process, we engineered Gas6, a soluble adaptor protein that mediates efferocytosis via TAM phagocytic receptors in such a way that its target specificity was redirected from dead cells to Aβ plaques.”
The professors and their team demonstrated that the resulting αAβ-Gas6 induced Aβ engulfment by activating not only microglial but also astrocytic phagocytosis since TAM phagocytic receptors are highly expressed by these two major phagocytes in the brain. Importantly, αAβ-Gas6 promoted the robust uptake of Aβ without showing any signs of inflammation and neurotoxicity, which contrasts sharply with the treatment using an Aβ monoclonal antibody. Moreover, they showed that αAβ-Gas6 substantially reduced excessive synapse elimination by microglia, consequently leading to better behavioral rescues in AD model mice.
“By using a mouse model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), a cerebrovascular disorder caused by the deposition of Aβ within the walls of the brain’s blood vessels, we also showed that the intrathecal administration of Gas6 fusion protein significantly eliminated cerebrovascular amyloids, along with a reduction of microhemorrhages. These data demonstrate that aAb-Gas6 is a potent therapeutic agent in eliminating Aβ without exacerbating CAA-related microhemorrhages.”
The resulting αAβ-Gas6 clears Aβ oligomers and fibrils without causing neurotoxicity (a-b, neurons: red, and fragmented axons: yellow) and proinflammatory responses (c, TNF release), which are conversely exacerbated by the treatment of an Aβ-targeting monoclonal antibody (Aducanumab).
Professors Kim and Chung noted, “We believe our approach can be a breakthrough in treating AD without causing inflammatory side effects and synapse loss. Our approach holds promise as a novel therapeutic platform that is applicable to more than AD. By modifying the target-specificity of the fusion protein, the Gas6-fusion protein can be applied to various neurological disorders as well as autoimmune diseases affected by toxic molecules that should be removed without causing inflammatory responses.”
The number and total area of Aβ plaques (Thioflavin-T, green) were significantly reduced in αAβ-Gas6-treated AD mouse brains compared to Aducanumab-treated ones (a, b). The cognitive functions of AD model mice were significantly rescued by αAβ-Gas6 treatment, whereas Aducanumab-treated AD mice showed partial rescue in these cognitive tests (c-e).
Professors Kim and Chung founded “Illimis Therapeutics” based on this strategy of designing chimeric Gas6 fusion proteins that would remove toxic aggregates from the nervous system. Through this company, they are planning to further develop various Gas6-fusion proteins not only for Ab but also for Tau to treat AD symptoms.
This work was supported by KAIST and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project that was administered by the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MOHW) and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and KAIST.
Other contributors include Hyuncheol Jung and Se Young Lee, Sungjoon Lim, Hyeong Ryeol Choi, Yeseong Choi, Minjin Kim, Segi Kim, the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST).
To receive more up-to-date information on this new development, follow “Illimis Therapeutics” on twitter @Illimistx.
2022.08.05 View 11194
A New Therapeutic Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease without Inflammatory Side Effects
Although Aduhelm, a monoclonal antibody targeting amyloid beta (Aβ), recently became the first US FDA approved drug for Alzheimer’s disease (AD) based on its ability to decrease Aβ plaque burden in AD patients, its effect on cognitive improvement is still controversial. Moreover, about 40% of the patients treated with this antibody experienced serious side effects including cerebral edemas (ARIA-E) and hemorrhages (ARIA-H) that are likely related to inflammatory responses in the brain when the Aβ antibody binds Fc receptors (FCR) of immune cells such as microglia and macrophages.
These inflammatory side effects can cause neuronal cell death and synapse elimination by activated microglia, and even have the potential to exacerbate cognitive impairment in AD patients. Thus, current Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy holds the inherent risk of doing more harm than good due to their inflammatory side effects.
To overcome these problems, a team of researchers at KAIST in South Korea has developed a novel fusion protein drug, αAβ-Gas6, which efficiently eliminates Aβ via an entirely different mechanism than Aβ antibody-based immunotherapy. In a mouse model of AD, αAβ-Gas6 not only removed Aβ with higher potency, but also circumvented the neurotoxic inflammatory side effects associated with conventional antibody treatments.
Their findings were published on August 4 in Nature Medicine.
Schematic of a chimeric Gas6 fusion protein. A single chain variable fragment (scFv) of
an Amyloid β (Aβ)-targeting monoclonal antibody is fused with a truncated receptor binding
domain of Gas6, a bridging molecule for the clearance of dead cells via TAM (TYRO3, AXL,
and MERTK) receptors, which are expressed by microglia and astrocytes.
“FcR activation by Aβ targeting antibodies induces microglia-mediated Aβ phagocytosis, but it also produces inflammatory signals, inevitably damaging brain tissues,” said paper authors Chan Hyuk Kim and Won-Suk Chung, associate professors in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
“Therefore, we utilized efferocytosis, a cellular process by which dead cells are removed by phagocytes as an alternative pathway for the clearance of Aβ in the brain,” Prof. Kim and Chung said. “Efferocytosis is accompanied by anti-inflammatory responses to maintain tissue homeostasis. To exploit this process, we engineered Gas6, a soluble adaptor protein that mediates efferocytosis via TAM phagocytic receptors in such a way that its target specificity was redirected from dead cells to Aβ plaques.”
The professors and their team demonstrated that the resulting αAβ-Gas6 induced Aβ engulfment by activating not only microglial but also astrocytic phagocytosis since TAM phagocytic receptors are highly expressed by these two major phagocytes in the brain. Importantly, αAβ-Gas6 promoted the robust uptake of Aβ without showing any signs of inflammation and neurotoxicity, which contrasts sharply with the treatment using an Aβ monoclonal antibody. Moreover, they showed that αAβ-Gas6 substantially reduced excessive synapse elimination by microglia, consequently leading to better behavioral rescues in AD model mice.
“By using a mouse model of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), a cerebrovascular disorder caused by the deposition of Aβ within the walls of the brain’s blood vessels, we also showed that the intrathecal administration of Gas6 fusion protein significantly eliminated cerebrovascular amyloids, along with a reduction of microhemorrhages. These data demonstrate that aAb-Gas6 is a potent therapeutic agent in eliminating Aβ without exacerbating CAA-related microhemorrhages.”
The resulting αAβ-Gas6 clears Aβ oligomers and fibrils without causing neurotoxicity (a-b, neurons: red, and fragmented axons: yellow) and proinflammatory responses (c, TNF release), which are conversely exacerbated by the treatment of an Aβ-targeting monoclonal antibody (Aducanumab).
Professors Kim and Chung noted, “We believe our approach can be a breakthrough in treating AD without causing inflammatory side effects and synapse loss. Our approach holds promise as a novel therapeutic platform that is applicable to more than AD. By modifying the target-specificity of the fusion protein, the Gas6-fusion protein can be applied to various neurological disorders as well as autoimmune diseases affected by toxic molecules that should be removed without causing inflammatory responses.”
The number and total area of Aβ plaques (Thioflavin-T, green) were significantly reduced in αAβ-Gas6-treated AD mouse brains compared to Aducanumab-treated ones (a, b). The cognitive functions of AD model mice were significantly rescued by αAβ-Gas6 treatment, whereas Aducanumab-treated AD mice showed partial rescue in these cognitive tests (c-e).
Professors Kim and Chung founded “Illimis Therapeutics” based on this strategy of designing chimeric Gas6 fusion proteins that would remove toxic aggregates from the nervous system. Through this company, they are planning to further develop various Gas6-fusion proteins not only for Ab but also for Tau to treat AD symptoms.
This work was supported by KAIST and the Korea Health Technology R&D Project that was administered by the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC) funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MOHW) and the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), and KAIST.
Other contributors include Hyuncheol Jung and Se Young Lee, Sungjoon Lim, Hyeong Ryeol Choi, Yeseong Choi, Minjin Kim, Segi Kim, the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST).
To receive more up-to-date information on this new development, follow “Illimis Therapeutics” on twitter @Illimistx.
2022.08.05 View 11194