CT
-
 ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 8743
ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 8743 -
 Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
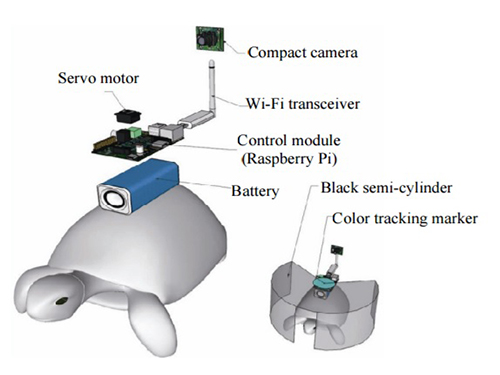
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 14852
Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 14852 -
 An Improved Carbon Nanotube Semiconductor
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi and his research team of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST collaborated with Professor Sung-Jin Choi of Kookmin University to develop a large-scale carbon nanotube semiconductor by using a 3-D fin-gate structure with carbon nanotubes on its top.
Dong Il Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at KAIST’s Electrical Engineering School, participated in this study as the first author. It was published in ACS Nano on November 10, 2016, and was entitled “Three-Dimensional Fin-Structured Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Network Transistor.”
A semiconductor made with carbon nanotubes operates faster than a silicon semiconductor and requires less energy, yielding higher performance.
Most electronic equipment and devices, however, use silicon semiconductors because it is difficult to fabricate highly purified and densely packed semiconductors with carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
To date, the performance of CNTs was limited due to their low density. Their purity was also low, so it was impossible to make products that had a constant yield on a large-surface wafer or substrate. These characteristics made the mass production of semiconducting CNTs difficult.
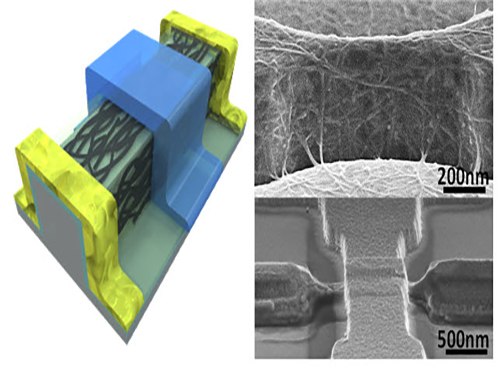
To solve these difficulties, the research team used a 3-D fin-gate to vapor-deposit carbon nanotubes on its top. They developed a semiconductor that had a high current density with a width less than 50 nm.
The three-dimensional fin structure was able to vapor-deposit 600 carbon nanotubes per micrometer. This structure could have 20 times more nanotubes than the two dimensional structure, which could only vapor-deposit thirty in the same 1 micrometer width.
In addition, the research team used semi-conductive carbon nanotubes having a purity rating higher than 99.9% from a previous study to obtain a high yield semiconductor.
The semiconductor from the research group has a high current density even with a width less than 50 μm. The new semiconductor is expected to be five times faster than a silicon-based semiconductor and will require five times less electricity during operation.
Furthermore, the new semiconductor can be made by or will be compatible with the equipment for producing silicon-based semiconductors, so there will be no additional costs.
Researcher Lee said, “As a next generation semiconductor, the carbon nanotube semiconductor will have better performance, and its effectiveness will be higher.” He also added, “Hopefully, the new semiconductor will replace the silicon-based semiconductors in ten years.”
This study received support from the Center for Integrated Smart Sensors funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning of Korea as the Global Frontier Project, and from the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) THz Technology Convergence Center of the Pioneer Research Center Program sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Picture 1: 3D Diagram of the Carbon Nanotube Electronic Device and Its Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Image
Picture 2: 3D Transistor Device on an 8-inch Base and the SEM Image of Its Cross Section
2017.02.16 View 10750
An Improved Carbon Nanotube Semiconductor
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi and his research team of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST collaborated with Professor Sung-Jin Choi of Kookmin University to develop a large-scale carbon nanotube semiconductor by using a 3-D fin-gate structure with carbon nanotubes on its top.
Dong Il Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at KAIST’s Electrical Engineering School, participated in this study as the first author. It was published in ACS Nano on November 10, 2016, and was entitled “Three-Dimensional Fin-Structured Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Network Transistor.”
A semiconductor made with carbon nanotubes operates faster than a silicon semiconductor and requires less energy, yielding higher performance.
Most electronic equipment and devices, however, use silicon semiconductors because it is difficult to fabricate highly purified and densely packed semiconductors with carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
To date, the performance of CNTs was limited due to their low density. Their purity was also low, so it was impossible to make products that had a constant yield on a large-surface wafer or substrate. These characteristics made the mass production of semiconducting CNTs difficult.
To solve these difficulties, the research team used a 3-D fin-gate to vapor-deposit carbon nanotubes on its top. They developed a semiconductor that had a high current density with a width less than 50 nm.
The three-dimensional fin structure was able to vapor-deposit 600 carbon nanotubes per micrometer. This structure could have 20 times more nanotubes than the two dimensional structure, which could only vapor-deposit thirty in the same 1 micrometer width.
In addition, the research team used semi-conductive carbon nanotubes having a purity rating higher than 99.9% from a previous study to obtain a high yield semiconductor.
The semiconductor from the research group has a high current density even with a width less than 50 μm. The new semiconductor is expected to be five times faster than a silicon-based semiconductor and will require five times less electricity during operation.
Furthermore, the new semiconductor can be made by or will be compatible with the equipment for producing silicon-based semiconductors, so there will be no additional costs.
Researcher Lee said, “As a next generation semiconductor, the carbon nanotube semiconductor will have better performance, and its effectiveness will be higher.” He also added, “Hopefully, the new semiconductor will replace the silicon-based semiconductors in ten years.”
This study received support from the Center for Integrated Smart Sensors funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning of Korea as the Global Frontier Project, and from the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) THz Technology Convergence Center of the Pioneer Research Center Program sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Picture 1: 3D Diagram of the Carbon Nanotube Electronic Device and Its Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Image
Picture 2: 3D Transistor Device on an 8-inch Base and the SEM Image of Its Cross Section
2017.02.16 View 10750 -
 Dr.M Drives Smart Healthcare Industry in Partnership with Hancom
President Sung-Mo Kang signed an agreement on January 25 with Hancom Group Chairman Sang Chul Kim to establish a smart healthcare complex in Gapyeong, Kyonggido. With the Gapyeong complex launch, KAIST will come to commercialize Dr. M system along with other Dr.M consortium members as a new growth engine to drive the smart health industry.
Dr. M is a smart healthcare platform developed by the Health Science Research Institute at KAIST in 2014. Dr. M is capable of analyzing and predicting diseases, as well as prescribing, by incorporating ICT and medical technologies. Dr. M applies diverse technologies such as healthcare sensors, wearable devices, low-power communications technology, and cloud and big data collection platforms.
Hancom Group, a leading computer software company in Korea, has participated in the project since 2015 for advancing the smart healthcare market by developing mobile healthcare software program. Hancom joined the Dr.M consortium launched last November.
(President Kang (left) poses with Hancom Chairman Kim after signing.)
2017.02.03 View 6555
Dr.M Drives Smart Healthcare Industry in Partnership with Hancom
President Sung-Mo Kang signed an agreement on January 25 with Hancom Group Chairman Sang Chul Kim to establish a smart healthcare complex in Gapyeong, Kyonggido. With the Gapyeong complex launch, KAIST will come to commercialize Dr. M system along with other Dr.M consortium members as a new growth engine to drive the smart health industry.
Dr. M is a smart healthcare platform developed by the Health Science Research Institute at KAIST in 2014. Dr. M is capable of analyzing and predicting diseases, as well as prescribing, by incorporating ICT and medical technologies. Dr. M applies diverse technologies such as healthcare sensors, wearable devices, low-power communications technology, and cloud and big data collection platforms.
Hancom Group, a leading computer software company in Korea, has participated in the project since 2015 for advancing the smart healthcare market by developing mobile healthcare software program. Hancom joined the Dr.M consortium launched last November.
(President Kang (left) poses with Hancom Chairman Kim after signing.)
2017.02.03 View 6555 -
 EWB-KAIST Wraps up Five-Year Project in Nepal
‘Engineers Without Borders-KAIST (EWB-KAIST)’ led by Professor Tae-ho Song from the Department of Mechanical Engineering returned to Korea on January 10 after a two-week project in Nangi, Nepal.
EWB-KAIST was established in 2012 by KAIST students and professors. Since then, the team visited Nangi, in the Annapurna region of Nepal, to engage in Appropriate Technology (AT) development projects. The projects included building passive houses and small hydroelectric power, and teaching science education. In particular, passive houses that use straw as an insulator received great a reception from the locals.
This was their last visit to Nepal, since the five-year project has now come to an end. Future projects in Mongolia will be led by Professor Buhm Soon Park from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy.
Professor Song commented, “I am glad that the Nepal project was successfully conducted over the last five years. To make sure the support does not end here, I will personally continue to visit the Himalayas to assist the villagers.”
EWB-KAIST is a non-profit organization that conducts activities with the aim of AT development and providing support for less-developed countries in need of the benefits of technology.
( Passive house made of straws by EWB-KAIST team in Nangi, Nepal.)
2017.02.01 View 7240
EWB-KAIST Wraps up Five-Year Project in Nepal
‘Engineers Without Borders-KAIST (EWB-KAIST)’ led by Professor Tae-ho Song from the Department of Mechanical Engineering returned to Korea on January 10 after a two-week project in Nangi, Nepal.
EWB-KAIST was established in 2012 by KAIST students and professors. Since then, the team visited Nangi, in the Annapurna region of Nepal, to engage in Appropriate Technology (AT) development projects. The projects included building passive houses and small hydroelectric power, and teaching science education. In particular, passive houses that use straw as an insulator received great a reception from the locals.
This was their last visit to Nepal, since the five-year project has now come to an end. Future projects in Mongolia will be led by Professor Buhm Soon Park from the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy.
Professor Song commented, “I am glad that the Nepal project was successfully conducted over the last five years. To make sure the support does not end here, I will personally continue to visit the Himalayas to assist the villagers.”
EWB-KAIST is a non-profit organization that conducts activities with the aim of AT development and providing support for less-developed countries in need of the benefits of technology.
( Passive house made of straws by EWB-KAIST team in Nangi, Nepal.)
2017.02.01 View 7240 -
 Nobel Laureate Dr. John Michael Kosterlitz Speaks at KAIST
KAIST’s Department of Physics will invite one of three co-recipients of the Nobel Prize in Physics 2016, Professor John Michael Kosterlitz of Brown University, on January 9, 2017, to speak about the exotic states of matter, which is entitled “Topological Defects and Phase Transitions.”
Professor Kosterlitz shares the Nobel award with two other researchers, David Thouless and Duncan Haldane. He is considered one of the pioneers in the field of topological phases. In the early 1970s, along with Thouless, he demonstrated that superconductivity could occur at low temperatures and explained the mechanism behind, phase transition, that makes superconductivity disappear at higher temperatures.
Over the last decade, topological materials and their applications have been widely studied with the hope of using them in new generations of electronics and superconductors, or in future quantum computers. Details of the lecture follow below:
Distinguished Lecture Series by KAIST’s Physics Department
· Speaker: Professor John Michael Kosterlitz of the Physics Department,
Brown University
· Topic: “Topological Defects and Phase Transitions”
· Date: January 9, 2017, 4:00 PM
· Place: Lecture Hall (#1501), College of Natural Sciences (E6-2)
2017.01.06 View 7326
Nobel Laureate Dr. John Michael Kosterlitz Speaks at KAIST
KAIST’s Department of Physics will invite one of three co-recipients of the Nobel Prize in Physics 2016, Professor John Michael Kosterlitz of Brown University, on January 9, 2017, to speak about the exotic states of matter, which is entitled “Topological Defects and Phase Transitions.”
Professor Kosterlitz shares the Nobel award with two other researchers, David Thouless and Duncan Haldane. He is considered one of the pioneers in the field of topological phases. In the early 1970s, along with Thouless, he demonstrated that superconductivity could occur at low temperatures and explained the mechanism behind, phase transition, that makes superconductivity disappear at higher temperatures.
Over the last decade, topological materials and their applications have been widely studied with the hope of using them in new generations of electronics and superconductors, or in future quantum computers. Details of the lecture follow below:
Distinguished Lecture Series by KAIST’s Physics Department
· Speaker: Professor John Michael Kosterlitz of the Physics Department,
Brown University
· Topic: “Topological Defects and Phase Transitions”
· Date: January 9, 2017, 4:00 PM
· Place: Lecture Hall (#1501), College of Natural Sciences (E6-2)
2017.01.06 View 7326 -
 Professor Dongman Lee Wins the 2016 Korea Internet Award
Professor Dongman Lee of KAIST’s School of Computing received the 11th Korea Internet Award in the category of personal achievement on December 13 at the Creative Economy and Innovation Center in Gyeonggi province.
Hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, the Internet Award recognizes leaders in the Internet industry and their contributions.
Since 2010, Professor Lee has conducted research on the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, resulting in the publication of five research papers in Science Citation Index (SCI) journals, ten papers in Korean journals, 30 best papers nominations at international conferences, and the registration of eleven patents. He has also worked on the creation of an IoT ecosystem through his research on object interworking platforms that can provide diverse user-customized services in the IoT environment.
His research team built a test bed for applicable IoT platforms on the 8th floor of the IT Convergence Center on campus to implement experiments and collect various data, thereby creating a foundation to carry out research projects in this field.
Professor Lee has helped the advancement of an Internet governance system in Korea by researching Internet governance policies, holding important posts in related academic societies including the Chairman of the Korea Internet Governance Alliance (KIGA) Council, and hosting major conferences such as the Asia Pacific Regional Internet Governance Forum (APrIGF).
2016.12.20 View 8171
Professor Dongman Lee Wins the 2016 Korea Internet Award
Professor Dongman Lee of KAIST’s School of Computing received the 11th Korea Internet Award in the category of personal achievement on December 13 at the Creative Economy and Innovation Center in Gyeonggi province.
Hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, the Internet Award recognizes leaders in the Internet industry and their contributions.
Since 2010, Professor Lee has conducted research on the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, resulting in the publication of five research papers in Science Citation Index (SCI) journals, ten papers in Korean journals, 30 best papers nominations at international conferences, and the registration of eleven patents. He has also worked on the creation of an IoT ecosystem through his research on object interworking platforms that can provide diverse user-customized services in the IoT environment.
His research team built a test bed for applicable IoT platforms on the 8th floor of the IT Convergence Center on campus to implement experiments and collect various data, thereby creating a foundation to carry out research projects in this field.
Professor Lee has helped the advancement of an Internet governance system in Korea by researching Internet governance policies, holding important posts in related academic societies including the Chairman of the Korea Internet Governance Alliance (KIGA) Council, and hosting major conferences such as the Asia Pacific Regional Internet Governance Forum (APrIGF).
2016.12.20 View 8171 -
 Professor Ih Reappointed as Vice President of the ICA
Professor Jeong-Guon Ih of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been re-elected as the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics (ICA). His second term of office is from October 16, 2016 to September 30, 2019.
Professor Ih, the first Korean who was selected to a senior position on the ICA management board, took over his current post in 2015 when the vice president at the time passed away in the middle of his term.
During his stint, Professor Ih played a key role in planning the ICA’s triennial gathering, the International Congress on Acoustics, in Gyeongju, Korea, scheduled for October 24-28, 2022. He will also serve as the general chair for the conference.
The International Congress on Acoustics is the largest professional meeting in the field of acoustics. It provides a venue to meet, discuss, and exchange ideas covering all aspects of acoustics including an extensive technical exhibition that highlights the latest advances in acoustical products such as materials, systems, and equipment.
Acoustics has grown to become an important element in the Information Age in the areas of automation, machine learning, and virtual reality. Hosting the Congress will support Korea’s goal to lead acoustic research and development on the global stage.
Professor Ih said, “Serving international academic organizations offers great opportunities to learn global trends and to collaborate with various research institutions, universities, and industries worldwide. I hope my service will inspire many young Korean researchers to pursue their careers in this field.”
Professor Ih is also a member of eight eminent international academic societies such as the Audio Engineering Society, the International Congress on Ultrasonics, and the International Institute of Noise Control Engineering.
The ICA was founded in 1951 as a subcommittee of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP), and it consists of 46 member states and four observer nations. It promotes international development and collaboration in all fields of acoustics including research, development, education, and standardization.
2016.12.16 View 7061
Professor Ih Reappointed as Vice President of the ICA
Professor Jeong-Guon Ih of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been re-elected as the Vice President of the International Commission for Acoustics (ICA). His second term of office is from October 16, 2016 to September 30, 2019.
Professor Ih, the first Korean who was selected to a senior position on the ICA management board, took over his current post in 2015 when the vice president at the time passed away in the middle of his term.
During his stint, Professor Ih played a key role in planning the ICA’s triennial gathering, the International Congress on Acoustics, in Gyeongju, Korea, scheduled for October 24-28, 2022. He will also serve as the general chair for the conference.
The International Congress on Acoustics is the largest professional meeting in the field of acoustics. It provides a venue to meet, discuss, and exchange ideas covering all aspects of acoustics including an extensive technical exhibition that highlights the latest advances in acoustical products such as materials, systems, and equipment.
Acoustics has grown to become an important element in the Information Age in the areas of automation, machine learning, and virtual reality. Hosting the Congress will support Korea’s goal to lead acoustic research and development on the global stage.
Professor Ih said, “Serving international academic organizations offers great opportunities to learn global trends and to collaborate with various research institutions, universities, and industries worldwide. I hope my service will inspire many young Korean researchers to pursue their careers in this field.”
Professor Ih is also a member of eight eminent international academic societies such as the Audio Engineering Society, the International Congress on Ultrasonics, and the International Institute of Noise Control Engineering.
The ICA was founded in 1951 as a subcommittee of the International Union of Pure and Applied Physics (IUPAP), and it consists of 46 member states and four observer nations. It promotes international development and collaboration in all fields of acoustics including research, development, education, and standardization.
2016.12.16 View 7061 -
 Professor Hyun Chung Claims the Elmer L. Hann Award 2016
Professor Hyun Chung of KAIST’s Mechanical Engineering Department received the Elmer L. Hann Award 2016 at the SNAME Maritime Convention (SMC) that took place November 1-5 in Seattle, Washington, in the United States.
Held annually, the SMC is the largest academic gathering for researchers and professionals in maritime and ocean engineering, and it is hosted by the Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers (SNAME).
With more than 6,000 members around the world in 85 countries, SNAME is an internationally-recognized, non-profit, professional society of individual members serving the maritime and offshore industries and their suppliers. It strives to advance the art, science, and practice of naval architecture, marine engineering, ocean engineering, and other marine-related professions through the exchange of knowledge and ideas, as well as the promotion of R&D, and education.
Every year, SNAME selects three research papers that are either published in its academic journal or presented at its sponsored conferences and awards them, respectively. One of the three awards is the Elmer L. Hann Award.
This year, the Society announced Professor Chung’s paper as the Elmer L. Hann Award winner. His paper, entitled “Tolerance Analysis and Diagnosis Model of Compliant Block Assembly Considering Welding Deformation,” was presented at the World Maritime Technology Conference held November 3-7, 2015 in Providence, Rhode Island, USA.
Analysis, management, and diagnostics of tolerance are important factors in the production of ocean structures. In the paper, Professor Chung’s team proposed a simplified tolerance analysis and diagnosis model including the effects of welding distortion for accuracy control in ship block assembly, thereby improving the production process.
Professor Chung said, “This is indeed a wonderful award for our team. From early this year, with support from the U.S. Office of Naval Research, we have collaborated with the University of Michigan, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Ohio State University, and the Edison Welding Institute to study this topic more deeply. We will keep up the good work to make meaningful progress.”
2016.12.10 View 8156
Professor Hyun Chung Claims the Elmer L. Hann Award 2016
Professor Hyun Chung of KAIST’s Mechanical Engineering Department received the Elmer L. Hann Award 2016 at the SNAME Maritime Convention (SMC) that took place November 1-5 in Seattle, Washington, in the United States.
Held annually, the SMC is the largest academic gathering for researchers and professionals in maritime and ocean engineering, and it is hosted by the Society of Naval Architects and Marine Engineers (SNAME).
With more than 6,000 members around the world in 85 countries, SNAME is an internationally-recognized, non-profit, professional society of individual members serving the maritime and offshore industries and their suppliers. It strives to advance the art, science, and practice of naval architecture, marine engineering, ocean engineering, and other marine-related professions through the exchange of knowledge and ideas, as well as the promotion of R&D, and education.
Every year, SNAME selects three research papers that are either published in its academic journal or presented at its sponsored conferences and awards them, respectively. One of the three awards is the Elmer L. Hann Award.
This year, the Society announced Professor Chung’s paper as the Elmer L. Hann Award winner. His paper, entitled “Tolerance Analysis and Diagnosis Model of Compliant Block Assembly Considering Welding Deformation,” was presented at the World Maritime Technology Conference held November 3-7, 2015 in Providence, Rhode Island, USA.
Analysis, management, and diagnostics of tolerance are important factors in the production of ocean structures. In the paper, Professor Chung’s team proposed a simplified tolerance analysis and diagnosis model including the effects of welding distortion for accuracy control in ship block assembly, thereby improving the production process.
Professor Chung said, “This is indeed a wonderful award for our team. From early this year, with support from the U.S. Office of Naval Research, we have collaborated with the University of Michigan, the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Ohio State University, and the Edison Welding Institute to study this topic more deeply. We will keep up the good work to make meaningful progress.”
2016.12.10 View 8156 -
 Mechanical Engineering Building on Campus Refurbished
KAIST’s Mechanical Engineering Department has finished the project to remodel its buildings and hosted an opening ceremony on December 12, 2016, which was attended by the university’s senior management and guests including President Steve Kang and Choong-Hwan Ahn, Architecture Policy Officer at the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korea (MLIT).
With an investment of approximately USD 10 million, the old buildings (each consisting of seven floors and one basement) were transformed into smart, green buildings. Among the upgrades were the establishment of LED lighting systems, the replacement of the exterior walls with insulated materials, and the installation of double-glazed windows, all resulting in the improvement of the buildings’ energy efficiency. Previously, offices and lecture halls in the buildings had individual cooling and heating systems, which consumed a great deal of energy, but they were replaced with a centralized smart energy control system that monitors the operation status as well as energy consumption in real time.
With these new improvements, the Department was able to slash its energy consumption by 32%, for which it received Green Building Conversion Certification from MLIT. The ministry issues the certification to buildings that reduce their energy consumption by over 20% as a result of infrastructure upgrades. Beginning with the Mechanical Engineering buildings, KAIST will work on obtaining this certification for all of its buildings that are either under renovation or construction.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to offer our students a comfortable environment for study and research and will continue improving outdated facilities and infrastructure to make the campus safer and nicer.”
Picture 1: Ribbon-cutting ceremony for the refurbished Mechanical Engineering buildings on campus
Picture 2: Mechanical engineering buildings
2016.12.09 View 7080
Mechanical Engineering Building on Campus Refurbished
KAIST’s Mechanical Engineering Department has finished the project to remodel its buildings and hosted an opening ceremony on December 12, 2016, which was attended by the university’s senior management and guests including President Steve Kang and Choong-Hwan Ahn, Architecture Policy Officer at the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korea (MLIT).
With an investment of approximately USD 10 million, the old buildings (each consisting of seven floors and one basement) were transformed into smart, green buildings. Among the upgrades were the establishment of LED lighting systems, the replacement of the exterior walls with insulated materials, and the installation of double-glazed windows, all resulting in the improvement of the buildings’ energy efficiency. Previously, offices and lecture halls in the buildings had individual cooling and heating systems, which consumed a great deal of energy, but they were replaced with a centralized smart energy control system that monitors the operation status as well as energy consumption in real time.
With these new improvements, the Department was able to slash its energy consumption by 32%, for which it received Green Building Conversion Certification from MLIT. The ministry issues the certification to buildings that reduce their energy consumption by over 20% as a result of infrastructure upgrades. Beginning with the Mechanical Engineering buildings, KAIST will work on obtaining this certification for all of its buildings that are either under renovation or construction.
President Kang said, “We are pleased to offer our students a comfortable environment for study and research and will continue improving outdated facilities and infrastructure to make the campus safer and nicer.”
Picture 1: Ribbon-cutting ceremony for the refurbished Mechanical Engineering buildings on campus
Picture 2: Mechanical engineering buildings
2016.12.09 View 7080 -
 Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 9639
Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 9639 -
 Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
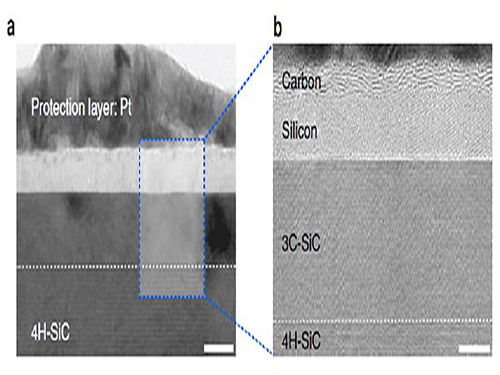
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 11186
Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 11186