CO
-
 Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 8505
Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 8505 -
 Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 11912
Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 11912 -
 KAIST Launches AI Alliance with KT, Hyundai, ETRI, Hanyang University
KAIST launched the AI collaboration alliance “AI One Team” partnering with the nation’s top telecommunications company KT, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), Hyundai Heavy Industries Holdings, and Hanyang University on February 21.
President Sung-Chul Shin signed the MOU with KT CEO Hyun-Mo Koo, Hyundai Heavy Industries Holdings Vice President Ki-Sun Chung, President Myung Joon Kim of ETRI, and Hanyang University President Woo-Seung Kim to help the nation’s AI technology stay ahead of the global level. Vice Minister of Science and ICT Seokyoung Jang also attended the signing ceremony held at KAIST.
Four parties representing the government, industry, research institutes, and universities all agreed to collaborate to establish an educational platform fostering AI talents; develop AI technologies applicable to industrial sites; nurture an AI technology eco-system that will embrace SEMs and venture companies; and incubate startups to help improve their technological competitiveness.
KAIST will take the lead in fostering AI talents in collaboration with ETRI and Hanyang University, offering an online/offline educational program featuring AI curricula that will be practically applicable to the industry. The alliance will also create a platform that will match job seekers and companies, especially for SMEs and venture firms that are having trouble finding competitive experts.
Hyundai Heavy Industries Holdings is focusing on developing technologies in the fields of robotics and smart factories. Hyundai’s collaboration with KT is pushing the digital transformation in the new domains of 5G-based robots and smart factories. The two companies plan to expand their technological know-how to SMEs, venture firms, and startups. The secretariat of the AI One Team will facilitate collaborative projects among the partners to help produce tangible results.
President Shin expressed his high hopes on this alliance for AI technology. He declared, “The winner takes all in the field of AI. Our close collaboration will pave the way for Korea, and each of our partners will lead AI technology in the global market. We will spare no effort for this alliance.”
2020.02.21 View 5808
KAIST Launches AI Alliance with KT, Hyundai, ETRI, Hanyang University
KAIST launched the AI collaboration alliance “AI One Team” partnering with the nation’s top telecommunications company KT, the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), Hyundai Heavy Industries Holdings, and Hanyang University on February 21.
President Sung-Chul Shin signed the MOU with KT CEO Hyun-Mo Koo, Hyundai Heavy Industries Holdings Vice President Ki-Sun Chung, President Myung Joon Kim of ETRI, and Hanyang University President Woo-Seung Kim to help the nation’s AI technology stay ahead of the global level. Vice Minister of Science and ICT Seokyoung Jang also attended the signing ceremony held at KAIST.
Four parties representing the government, industry, research institutes, and universities all agreed to collaborate to establish an educational platform fostering AI talents; develop AI technologies applicable to industrial sites; nurture an AI technology eco-system that will embrace SEMs and venture companies; and incubate startups to help improve their technological competitiveness.
KAIST will take the lead in fostering AI talents in collaboration with ETRI and Hanyang University, offering an online/offline educational program featuring AI curricula that will be practically applicable to the industry. The alliance will also create a platform that will match job seekers and companies, especially for SMEs and venture firms that are having trouble finding competitive experts.
Hyundai Heavy Industries Holdings is focusing on developing technologies in the fields of robotics and smart factories. Hyundai’s collaboration with KT is pushing the digital transformation in the new domains of 5G-based robots and smart factories. The two companies plan to expand their technological know-how to SMEs, venture firms, and startups. The secretariat of the AI One Team will facilitate collaborative projects among the partners to help produce tangible results.
President Shin expressed his high hopes on this alliance for AI technology. He declared, “The winner takes all in the field of AI. Our close collaboration will pave the way for Korea, and each of our partners will lead AI technology in the global market. We will spare no effort for this alliance.”
2020.02.21 View 5808 -
 Professor Minsoo Rhu Recognized as Facebook Research Scholar
Professor Minsoo Rhu from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected as the recipient of the Systems for Machine Learning Research Awards presented by Facebook.
Facebook launched the award last year with the goal of funding impactful solutions in the areas of developer tookits, compilers and code generation, system architecture, memory technologies, and machine learning accelerator support.
A total of 167 scholars from 100 universities representing 26 countries submitted research proposals, and Facebook selected final 10 scholars. Professor Rhu made the list with his research topic ‘A Near-Memory Processing Architecture for Training Recommendation Systems.’ He will receive 5,000 USD in research funds at the award ceremony which will take place during this year’s AI Systems Faculty Summit at the Facebook headquarters in Menlo Park, California.
Professor Rhu’s submission was based on research on ‘Memory-Centric Deep Learning System Architecture’ that he carried out for three years under the auspices of Samsung Science and Technology Foundation from 2017. It was an academic-industrial cooperation research project in which leading domestic companies like Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix collaborated to make a foray into the global memory-centric smart system semiconductor market.
Professor Rhu who joined KAIST in 2018 has led various systems research projects to accelerate the AI computing technology while working at NVIDIA headquarters from 2014.
(END)
2020.02.21 View 11420
Professor Minsoo Rhu Recognized as Facebook Research Scholar
Professor Minsoo Rhu from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected as the recipient of the Systems for Machine Learning Research Awards presented by Facebook.
Facebook launched the award last year with the goal of funding impactful solutions in the areas of developer tookits, compilers and code generation, system architecture, memory technologies, and machine learning accelerator support.
A total of 167 scholars from 100 universities representing 26 countries submitted research proposals, and Facebook selected final 10 scholars. Professor Rhu made the list with his research topic ‘A Near-Memory Processing Architecture for Training Recommendation Systems.’ He will receive 5,000 USD in research funds at the award ceremony which will take place during this year’s AI Systems Faculty Summit at the Facebook headquarters in Menlo Park, California.
Professor Rhu’s submission was based on research on ‘Memory-Centric Deep Learning System Architecture’ that he carried out for three years under the auspices of Samsung Science and Technology Foundation from 2017. It was an academic-industrial cooperation research project in which leading domestic companies like Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix collaborated to make a foray into the global memory-centric smart system semiconductor market.
Professor Rhu who joined KAIST in 2018 has led various systems research projects to accelerate the AI computing technology while working at NVIDIA headquarters from 2014.
(END)
2020.02.21 View 11420 -
 Black Phosphorous Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor as an Alternative Ultra-low Power Switch
Researchers have reported a black phosphorus transistor that can be used as an alternative ultra-low power switch. A research team led by Professor Sungjae Cho in the KAIST Department of Physics developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
The research team said they developed fast and low-power transistors that can replace conventional CMOS transistors. In particular, they solved problems that have degraded TFET operation speed and performance, paving the way to extend Moore’s Law.
In the study featured in Nature Nanotechnology last month, Professor Cho’s team reported a natural heterojunction TFET with spatially varying layer thickness in black phosphorous without interface problems. They achieved record-low average subthreshold swing values over 4-5 dec of current and record-high, on-state current, which allows the TFETs to operate as fast as conventional CMOS transistors with as much lower power consumption.
"We successfully developed the first transistor that achieved the essential criteria for fast, low-power switching. Our newly developed TFETs can replace CMOS transistors by solving a major issue regarding the performance degradation of TFETs,"Professor Cho said.
The continuous down-scaling of transistors has been the key to the successful development of current information technology. However, with Moore’s Law reaching its limits due to the increased power consumption, the development of new alternative transistor designs has emerged as an urgent need.
Reducing both switching and standby power consumption while further scaling transistors requires overcoming the thermionic limit of subthreshold swing, which is defined as the required voltage per ten-fold current increase in the subthreshold region. In order to reduce both the switching and standby power of CMOS circuits, it is critical to reduce the subthreshold swing of the transistors.
However, there is fundamental subthreshold swing limit of 60 mV/dec in CMOS transistors, which originates from thermal carrier injection. The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems has already predicted that new device geometries with new materials beyond CMOS will be required to address transistor scaling challenges in the near future. In particular, TFETs have been suggested as a major alternative to CMOS transistors, since the subthreshold swing in TFETs can be substantially reduced below the thermionic limit of 60 mV/dec. TFETs operate via quantum tunneling, which does not limit subthreshold swing as in thermal injection of CMOS transistors.
In particular, heterojunction TFETs hold significant promise for delivering both low subthreshold swing and high on-state current. High on-current is essential for the fast operation of transistors since charging a device to on state takes a longer time with lower currents. Unlike theoretical expectations, previously developed heterojunction TFETs show 100-100,000x lower on-state current (100-100,000x slower operation speeds) than CMOS transistors due to interface problems in the heterojunction. This low operation speed impedes the replacement of CMOS transistors with low-power TFETs.
Professor Cho said, “We have demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, TFET optimization for both fast and ultra-low-power operations, which is essential to replace CMOS transistors for low-power applications.” He said he is very delighted to extend Moore’s Law, which may eventually affect almost every aspect of life and society. This study (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Kim et al. (2020) Thickness-controlled black phosphorus tunnel field-effect transistor for low-power switches. Nature Nanotechnology. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Seungho Kim, PhD Candidate
krksh21@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
(END)
2020.02.21 View 13597
Black Phosphorous Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor as an Alternative Ultra-low Power Switch
Researchers have reported a black phosphorus transistor that can be used as an alternative ultra-low power switch. A research team led by Professor Sungjae Cho in the KAIST Department of Physics developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
The research team said they developed fast and low-power transistors that can replace conventional CMOS transistors. In particular, they solved problems that have degraded TFET operation speed and performance, paving the way to extend Moore’s Law.
In the study featured in Nature Nanotechnology last month, Professor Cho’s team reported a natural heterojunction TFET with spatially varying layer thickness in black phosphorous without interface problems. They achieved record-low average subthreshold swing values over 4-5 dec of current and record-high, on-state current, which allows the TFETs to operate as fast as conventional CMOS transistors with as much lower power consumption.
"We successfully developed the first transistor that achieved the essential criteria for fast, low-power switching. Our newly developed TFETs can replace CMOS transistors by solving a major issue regarding the performance degradation of TFETs,"Professor Cho said.
The continuous down-scaling of transistors has been the key to the successful development of current information technology. However, with Moore’s Law reaching its limits due to the increased power consumption, the development of new alternative transistor designs has emerged as an urgent need.
Reducing both switching and standby power consumption while further scaling transistors requires overcoming the thermionic limit of subthreshold swing, which is defined as the required voltage per ten-fold current increase in the subthreshold region. In order to reduce both the switching and standby power of CMOS circuits, it is critical to reduce the subthreshold swing of the transistors.
However, there is fundamental subthreshold swing limit of 60 mV/dec in CMOS transistors, which originates from thermal carrier injection. The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems has already predicted that new device geometries with new materials beyond CMOS will be required to address transistor scaling challenges in the near future. In particular, TFETs have been suggested as a major alternative to CMOS transistors, since the subthreshold swing in TFETs can be substantially reduced below the thermionic limit of 60 mV/dec. TFETs operate via quantum tunneling, which does not limit subthreshold swing as in thermal injection of CMOS transistors.
In particular, heterojunction TFETs hold significant promise for delivering both low subthreshold swing and high on-state current. High on-current is essential for the fast operation of transistors since charging a device to on state takes a longer time with lower currents. Unlike theoretical expectations, previously developed heterojunction TFETs show 100-100,000x lower on-state current (100-100,000x slower operation speeds) than CMOS transistors due to interface problems in the heterojunction. This low operation speed impedes the replacement of CMOS transistors with low-power TFETs.
Professor Cho said, “We have demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, TFET optimization for both fast and ultra-low-power operations, which is essential to replace CMOS transistors for low-power applications.” He said he is very delighted to extend Moore’s Law, which may eventually affect almost every aspect of life and society. This study (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Kim et al. (2020) Thickness-controlled black phosphorus tunnel field-effect transistor for low-power switches. Nature Nanotechnology. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Seungho Kim, PhD Candidate
krksh21@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
(END)
2020.02.21 View 13597 -
 New Catalyst Recycles Greenhouse Gases into Fuel and Hydrogen Gas
< Professor Cafer T. Yavuz (left), PhD Candidate Youngdong Song (center), and Researcher Sreerangappa Ramesh (right) >
Scientists have taken a major step toward a circular carbon economy by developing a long-lasting, economical catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas, and other chemicals. The results could be revolutionary in the effort to reverse global warming, according to the researchers. The study was published on February 14 in Science.
“We set out to develop an effective catalyst that can convert large amounts of the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane without failure,” said Cafer T. Yavuz, paper author and associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and of chemistry at KAIST.
The catalyst, made from inexpensive and abundant nickel, magnesium, and molybdenum, initiates and speeds up the rate of reaction that converts carbon dioxide and methane into hydrogen gas. It can work efficiently for more than a month.
This conversion is called ‘dry reforming’, where harmful gases, such as carbon dioxide, are processed to produce more useful chemicals that could be refined for use in fuel, plastics, or even pharmaceuticals. It is an effective process, but it previously required rare and expensive metals such as platinum and rhodium to induce a brief and inefficient chemical reaction.
Other researchers had previously proposed nickel as a more economical solution, but carbon byproducts would build up and the surface nanoparticles would bind together on the cheaper metal, fundamentally changing the composition and geometry of the catalyst and rendering it useless.
“The difficulty arises from the lack of control on scores of active sites over the bulky catalysts surfaces because any refinement procedures attempted also change the nature of the catalyst itself,” Yavuz said.
The researchers produced nickel-molybdenum nanoparticles under a reductive environment in the presence of a single crystalline magnesium oxide. As the ingredients were heated under reactive gas, the nanoparticles moved on the pristine crystal surface seeking anchoring points. The resulting activated catalyst sealed its own high-energy active sites and permanently fixed the location of the nanoparticles — meaning that the nickel-based catalyst will not have a carbon build up, nor will the surface particles bind to one another.
“It took us almost a year to understand the underlying mechanism,” said first author Youngdong Song, a graduate student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. “Once we studied all the chemical events in detail, we were shocked.”
The researchers dubbed the catalyst Nanocatalysts on Single Crystal Edges (NOSCE). The magnesium-oxide nanopowder comes from a finely structured form of magnesium oxide, where the molecules bind continuously to the edge. There are no breaks or defects in the surface, allowing for uniform and predictable reactions.
“Our study solves a number of challenges the catalyst community faces,” Yavuz said. “We believe the NOSCE mechanism will improve other inefficient catalytic reactions and provide even further savings of greenhouse gas emissions.”
This work was supported, in part, by the Saudi-Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Other contributors include Ercan Ozdemir, Sreerangappa Ramesh, Aldiar Adishev, and Saravanan Subramanian, all of whom are affiliated with the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability at KAIST; Aadesh Harale, Mohammed Albuali, Bandar Abdullah Fadhel, and Aqil Jamal, all of whom are with the Research and Development Center in Saudi Arabia; and Dohyun Moon and Sun Hee Choi, both of whom are with the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory in Korea. Ozdemir is also affiliated with the Institute of Nanotechnology at the Gebze Technical University in Turkey; Fadhel and Jamal are also affiliated with the Saudi-Armco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea.
<Newly developed catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas and other chemicals.>
Publication:
Song et al. (2020) Dry reforming of methane by stable Ni–Mo nanocatalysts on single-crystalline MgO. Science, Vol. 367, Issue 6479, pp. 777-781. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aav2412
Profile: Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, MA, PhD
yavuz@kaist.ac.kr
http://yavuz.kaist.ac.kr/
Associate Professor
Oxide and Organic Nanomaterials for the Environment (ONE) Laboratory
Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Youngdong Song ydsong88@kaist.ac.kr
Ph.D. Candidate
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.17 View 19185
New Catalyst Recycles Greenhouse Gases into Fuel and Hydrogen Gas
< Professor Cafer T. Yavuz (left), PhD Candidate Youngdong Song (center), and Researcher Sreerangappa Ramesh (right) >
Scientists have taken a major step toward a circular carbon economy by developing a long-lasting, economical catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas, and other chemicals. The results could be revolutionary in the effort to reverse global warming, according to the researchers. The study was published on February 14 in Science.
“We set out to develop an effective catalyst that can convert large amounts of the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane without failure,” said Cafer T. Yavuz, paper author and associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and of chemistry at KAIST.
The catalyst, made from inexpensive and abundant nickel, magnesium, and molybdenum, initiates and speeds up the rate of reaction that converts carbon dioxide and methane into hydrogen gas. It can work efficiently for more than a month.
This conversion is called ‘dry reforming’, where harmful gases, such as carbon dioxide, are processed to produce more useful chemicals that could be refined for use in fuel, plastics, or even pharmaceuticals. It is an effective process, but it previously required rare and expensive metals such as platinum and rhodium to induce a brief and inefficient chemical reaction.
Other researchers had previously proposed nickel as a more economical solution, but carbon byproducts would build up and the surface nanoparticles would bind together on the cheaper metal, fundamentally changing the composition and geometry of the catalyst and rendering it useless.
“The difficulty arises from the lack of control on scores of active sites over the bulky catalysts surfaces because any refinement procedures attempted also change the nature of the catalyst itself,” Yavuz said.
The researchers produced nickel-molybdenum nanoparticles under a reductive environment in the presence of a single crystalline magnesium oxide. As the ingredients were heated under reactive gas, the nanoparticles moved on the pristine crystal surface seeking anchoring points. The resulting activated catalyst sealed its own high-energy active sites and permanently fixed the location of the nanoparticles — meaning that the nickel-based catalyst will not have a carbon build up, nor will the surface particles bind to one another.
“It took us almost a year to understand the underlying mechanism,” said first author Youngdong Song, a graduate student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. “Once we studied all the chemical events in detail, we were shocked.”
The researchers dubbed the catalyst Nanocatalysts on Single Crystal Edges (NOSCE). The magnesium-oxide nanopowder comes from a finely structured form of magnesium oxide, where the molecules bind continuously to the edge. There are no breaks or defects in the surface, allowing for uniform and predictable reactions.
“Our study solves a number of challenges the catalyst community faces,” Yavuz said. “We believe the NOSCE mechanism will improve other inefficient catalytic reactions and provide even further savings of greenhouse gas emissions.”
This work was supported, in part, by the Saudi-Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Other contributors include Ercan Ozdemir, Sreerangappa Ramesh, Aldiar Adishev, and Saravanan Subramanian, all of whom are affiliated with the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability at KAIST; Aadesh Harale, Mohammed Albuali, Bandar Abdullah Fadhel, and Aqil Jamal, all of whom are with the Research and Development Center in Saudi Arabia; and Dohyun Moon and Sun Hee Choi, both of whom are with the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory in Korea. Ozdemir is also affiliated with the Institute of Nanotechnology at the Gebze Technical University in Turkey; Fadhel and Jamal are also affiliated with the Saudi-Armco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea.
<Newly developed catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas and other chemicals.>
Publication:
Song et al. (2020) Dry reforming of methane by stable Ni–Mo nanocatalysts on single-crystalline MgO. Science, Vol. 367, Issue 6479, pp. 777-781. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aav2412
Profile: Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, MA, PhD
yavuz@kaist.ac.kr
http://yavuz.kaist.ac.kr/
Associate Professor
Oxide and Organic Nanomaterials for the Environment (ONE) Laboratory
Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Youngdong Song ydsong88@kaist.ac.kr
Ph.D. Candidate
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.17 View 19185 -
 Blood-Based Multiplexed Diagnostic Sensor Helps to Accurately Detect Alzheimer’s Disease
A research team at KAIST reported clinically accurate multiplexed electrical biosensor for detecting Alzheimer’s disease by measuring its core biomarkers using densely aligned carbon nanotubes.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, affecting one in ten aged over 65 years. Early diagnosis can reduce the risk of suffering the disease by one-third, according to recent reports. However, its early diagnosis remains challenging due to the low accuracy but high cost of diagnosis.
Research team led by Professors Chan Beum Park and Steve Park described an ultrasensitive detection of multiple Alzheimer's disease core biomarker in human plasma. The team have designed the sensor array by employing a densely aligned single-walled carbon nanotube thin films as a transducer.
The representative biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease are beta-amyloid42, beta-amyloid40, total tau protein, phosphorylated tau protein and the concentrations of these biomarkers in human plasma are directly correlated with the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease.
The research team developed a highly sensitive resistive biosensor based on densely aligned carbon nanotubes fabricated by Langmuir-Blodgett method with a low manufacturing cost.
Aligned carbon nanotubes with high density minimizes the tube-to-tube junction resistance compared with randomly distributed carbon nanotubes, which leads to the improvement of sensor sensitivity. To be more specific, this resistive sensor with densely aligned carbon nanotubes exhibits a sensitivity over 100 times higher than that of conventional carbon nanotube-based biosensors.
By measuring the concentrations of four Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers simultaneously Alzheimer patients can be discriminated from health controls with an average sensitivity of 90.0%, a selectivity of 90.0% and an average accuracy of 88.6%.
This work, titled “Clinically accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via multiplexed sensing of core biomarkers in human plasma”, were published in Nature Communications on January 8th 2020. The authors include PhD candidate Kayoung Kim and MS candidate Min-Ji Kim.
Professor Steve Park said, “This study was conducted on patients who are already confirmed with Alzheimer’s Disease. For further use in practical setting, it is necessary to test the patients with mild cognitive impairment.” He also emphasized that, “It is essential to establish a nationwide infrastructure, such as mild cognitive impairment cohort study and a dementia cohort study. This would enable the establishment of world-wide research network, and will help various private and public institutions.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Human Resource Bank of Chungnam National University Hospital and Chungbuk National University Hospital.
< A schematic diagram of a high-density aligned carbon nanotube-based resistive sensor that distinguishes patients with Alzheimer’s Disease by measuring the concentration of four biomarkers in the blood. >
Profile:
Professor Steve Park
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Professor Chan Beum Park
parkcb at kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
http://biomaterials.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
2020.02.07 View 12362
Blood-Based Multiplexed Diagnostic Sensor Helps to Accurately Detect Alzheimer’s Disease
A research team at KAIST reported clinically accurate multiplexed electrical biosensor for detecting Alzheimer’s disease by measuring its core biomarkers using densely aligned carbon nanotubes.
Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, affecting one in ten aged over 65 years. Early diagnosis can reduce the risk of suffering the disease by one-third, according to recent reports. However, its early diagnosis remains challenging due to the low accuracy but high cost of diagnosis.
Research team led by Professors Chan Beum Park and Steve Park described an ultrasensitive detection of multiple Alzheimer's disease core biomarker in human plasma. The team have designed the sensor array by employing a densely aligned single-walled carbon nanotube thin films as a transducer.
The representative biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease are beta-amyloid42, beta-amyloid40, total tau protein, phosphorylated tau protein and the concentrations of these biomarkers in human plasma are directly correlated with the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease.
The research team developed a highly sensitive resistive biosensor based on densely aligned carbon nanotubes fabricated by Langmuir-Blodgett method with a low manufacturing cost.
Aligned carbon nanotubes with high density minimizes the tube-to-tube junction resistance compared with randomly distributed carbon nanotubes, which leads to the improvement of sensor sensitivity. To be more specific, this resistive sensor with densely aligned carbon nanotubes exhibits a sensitivity over 100 times higher than that of conventional carbon nanotube-based biosensors.
By measuring the concentrations of four Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers simultaneously Alzheimer patients can be discriminated from health controls with an average sensitivity of 90.0%, a selectivity of 90.0% and an average accuracy of 88.6%.
This work, titled “Clinically accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease via multiplexed sensing of core biomarkers in human plasma”, were published in Nature Communications on January 8th 2020. The authors include PhD candidate Kayoung Kim and MS candidate Min-Ji Kim.
Professor Steve Park said, “This study was conducted on patients who are already confirmed with Alzheimer’s Disease. For further use in practical setting, it is necessary to test the patients with mild cognitive impairment.” He also emphasized that, “It is essential to establish a nationwide infrastructure, such as mild cognitive impairment cohort study and a dementia cohort study. This would enable the establishment of world-wide research network, and will help various private and public institutions.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Human Resource Bank of Chungnam National University Hospital and Chungbuk National University Hospital.
< A schematic diagram of a high-density aligned carbon nanotube-based resistive sensor that distinguishes patients with Alzheimer’s Disease by measuring the concentration of four biomarkers in the blood. >
Profile:
Professor Steve Park
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Professor Chan Beum Park
parkcb at kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
http://biomaterials.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
2020.02.07 View 12362 -
 COVID-19 Update: Precautionary Measures Reschedule Spring Semester to March 16
(Campus-wide preventive measures against the new coronavirus are being enforced.)
In response to the coronavirus outbreak, KAIST has decided to alter the academic calendar, postponing the opening of the spring semester until March 16, two weeks behind the original schedule. This is following the decision of the Deans’ Council to postpone or cancel the major academic ceremonies and events scheduled in February.
According to the decision, the commencement ceremony scheduled on February 21 will be postponed; meanwhile the freshmen orientation and matriculation ceremonies have been cancelled. Additionally, the ceremonies for the KAIST anniversary and faculty retirement ceremony scheduled on February 14 and the faculty workshop on February 27 have been postponed. There have been no confirmed coronavirus cases among the KAIST community as of February 6.
The university is also enhancing campus-wide precautionary safety measures to prevent the spread of the disease. The Facilities Management Office said that they will start disinfecting all dining facilities, cafeterias, libraries, lecture halls, and student halls for two days from Feb. 6. Plastic gloves are provided at cafeteria, which is using buffet spoons and tongs, and cafeteria patrons are being asked to wear the plastic gloves when they place food on their own plate in a preventive measure to avoid possible contact between individuals.
KAIST also launched a 24/7-hour Emergency Response Team and disseminated a response manual to KAIST community members. The Office of Student Life surveyed students, faculty, and staff to report if anyone has traveled to China or been in contact with visitors who made a trip to China within the last two weeks.
The university designated a building in one of the dorm complexes as a quarantine facility and a total of 11 people who visited China have been self-quarantined for two weeks from January 31.
Provost and Executive Vice President Kwang Hyung Lee explained in his letter to KAIST community members on February 4 that the university is exerting all possible measures and efforts against the spreading virus and asked for every member’s cooperation to prevent the further spread of the disease.
“Those who self-quarantined don’t have any symptoms. This is just a precautionary measure. The self-quarantine at our facility is only limited to those who declared that they do not have a legal residence in Korea,” said Provost Lee. The transportation to the facility is specially arranged and meal boxes are delivered to the quarantined room individually. A full-time guard in front of the isolated dorm building will be on duty 24 hours a day.
He explained the university chose the Hwaam Complex as the self-quarantine facility because each building in the complex is set apart from the others and each room has its own bathroom and shower facilities. Provost Lee said that the university will use another dorm complex if any current dorm residents where the quarantine facility has been set up wish to move to other dorm complexes.
(END)
2020.02.06 View 4951
COVID-19 Update: Precautionary Measures Reschedule Spring Semester to March 16
(Campus-wide preventive measures against the new coronavirus are being enforced.)
In response to the coronavirus outbreak, KAIST has decided to alter the academic calendar, postponing the opening of the spring semester until March 16, two weeks behind the original schedule. This is following the decision of the Deans’ Council to postpone or cancel the major academic ceremonies and events scheduled in February.
According to the decision, the commencement ceremony scheduled on February 21 will be postponed; meanwhile the freshmen orientation and matriculation ceremonies have been cancelled. Additionally, the ceremonies for the KAIST anniversary and faculty retirement ceremony scheduled on February 14 and the faculty workshop on February 27 have been postponed. There have been no confirmed coronavirus cases among the KAIST community as of February 6.
The university is also enhancing campus-wide precautionary safety measures to prevent the spread of the disease. The Facilities Management Office said that they will start disinfecting all dining facilities, cafeterias, libraries, lecture halls, and student halls for two days from Feb. 6. Plastic gloves are provided at cafeteria, which is using buffet spoons and tongs, and cafeteria patrons are being asked to wear the plastic gloves when they place food on their own plate in a preventive measure to avoid possible contact between individuals.
KAIST also launched a 24/7-hour Emergency Response Team and disseminated a response manual to KAIST community members. The Office of Student Life surveyed students, faculty, and staff to report if anyone has traveled to China or been in contact with visitors who made a trip to China within the last two weeks.
The university designated a building in one of the dorm complexes as a quarantine facility and a total of 11 people who visited China have been self-quarantined for two weeks from January 31.
Provost and Executive Vice President Kwang Hyung Lee explained in his letter to KAIST community members on February 4 that the university is exerting all possible measures and efforts against the spreading virus and asked for every member’s cooperation to prevent the further spread of the disease.
“Those who self-quarantined don’t have any symptoms. This is just a precautionary measure. The self-quarantine at our facility is only limited to those who declared that they do not have a legal residence in Korea,” said Provost Lee. The transportation to the facility is specially arranged and meal boxes are delivered to the quarantined room individually. A full-time guard in front of the isolated dorm building will be on duty 24 hours a day.
He explained the university chose the Hwaam Complex as the self-quarantine facility because each building in the complex is set apart from the others and each room has its own bathroom and shower facilities. Provost Lee said that the university will use another dorm complex if any current dorm residents where the quarantine facility has been set up wish to move to other dorm complexes.
(END)
2020.02.06 View 4951 -
 Rachmaninoff the most innovative of 18th and 19th century composers according to network science
Rachmaninoff, followed by Bach, Brahms and Mendelssohn, was the most innovative of the composers who worked during the Baroque, Classical and Romantic eras of music (1700 to 1900) according to a study published in the open access journal EPJ Data Science.
A team of researchers from KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology), calculated novelty scores for 900 classical piano compositions written by 19 composers between approximately 1700 and 1900. The scores were based on how musical compositions differed from all prior pieces of piano music and how they differed from previous piano works by the same composer. The authors found that composers from the Romantic era (1820 to 1910) tended to have high novelty scores.
The authors from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST created a computer model which divided each composition into segments called ‘codewords’. Each ‘codeword’ consisted of all of the notes played together at a given time. Sequences of ‘codewords’ were then compared between compositions. The similarities between the sequences were used to create novelty scores for each composer and to determine the extent to which composers influenced each other.
Juyong Park, the corresponding author, said: “Our model allows us to calculate the degree of shared melodies and harmonies between past and future works and to observe the evolution of western musical styles by demonstrating how prominent composers may have influenced each other. The period of music we studied is widely credited for having produced many musical styles that are still influential today.”
The model distinguished each new musical period from the one before it by the rise of newly dominant and highly influential composers that indicated dramatic shifts in musical styles. The authors found that compositions from the Classical period (1750 to 1820) tended to have the lowest novelty scores. During this period Haydn and Mozart were highly influential but were later overtaken by Beethoven during the Classical-to-Romantic transitional period.
The most innovative composer, indicated by the highest combined novelty score, was Rachmaninoff. His work during the Romantic era was novel when compared to the compositions of the other 18 composers included in the study, and his later works were novel compared to his earlier works.
Lower novelty did not necessarily correlate with low influence. Beethoven was ranked in the lower half of novelty scores yet was the most influential composer during the Romantic period (1820 to 1910) and is widely considered one of the greatest composers of all time.
Dr. Park said: “While novelty is necessary in a creative work it cannot account for all the creative and artistic qualities that go into creating melodies and harmonies that spread to later generations of composers. That may be why being more novel did not necessarily result in composers being more influential.”
The authors suggest that their method could be applied to narrative or visual artworks by creating codewords from groups of words or colours and shapes. However, they caution that as only piano compositions were included in their analysis, it is unknown whether including all works by the 19 composers would have resulted in another composer being identified as the most original.
Profile: Prof. Juyong Park, PhD
juyongp@kaist.ac.kr
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.01.31 View 5774
Rachmaninoff the most innovative of 18th and 19th century composers according to network science
Rachmaninoff, followed by Bach, Brahms and Mendelssohn, was the most innovative of the composers who worked during the Baroque, Classical and Romantic eras of music (1700 to 1900) according to a study published in the open access journal EPJ Data Science.
A team of researchers from KAIST (Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology), calculated novelty scores for 900 classical piano compositions written by 19 composers between approximately 1700 and 1900. The scores were based on how musical compositions differed from all prior pieces of piano music and how they differed from previous piano works by the same composer. The authors found that composers from the Romantic era (1820 to 1910) tended to have high novelty scores.
The authors from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST created a computer model which divided each composition into segments called ‘codewords’. Each ‘codeword’ consisted of all of the notes played together at a given time. Sequences of ‘codewords’ were then compared between compositions. The similarities between the sequences were used to create novelty scores for each composer and to determine the extent to which composers influenced each other.
Juyong Park, the corresponding author, said: “Our model allows us to calculate the degree of shared melodies and harmonies between past and future works and to observe the evolution of western musical styles by demonstrating how prominent composers may have influenced each other. The period of music we studied is widely credited for having produced many musical styles that are still influential today.”
The model distinguished each new musical period from the one before it by the rise of newly dominant and highly influential composers that indicated dramatic shifts in musical styles. The authors found that compositions from the Classical period (1750 to 1820) tended to have the lowest novelty scores. During this period Haydn and Mozart were highly influential but were later overtaken by Beethoven during the Classical-to-Romantic transitional period.
The most innovative composer, indicated by the highest combined novelty score, was Rachmaninoff. His work during the Romantic era was novel when compared to the compositions of the other 18 composers included in the study, and his later works were novel compared to his earlier works.
Lower novelty did not necessarily correlate with low influence. Beethoven was ranked in the lower half of novelty scores yet was the most influential composer during the Romantic period (1820 to 1910) and is widely considered one of the greatest composers of all time.
Dr. Park said: “While novelty is necessary in a creative work it cannot account for all the creative and artistic qualities that go into creating melodies and harmonies that spread to later generations of composers. That may be why being more novel did not necessarily result in composers being more influential.”
The authors suggest that their method could be applied to narrative or visual artworks by creating codewords from groups of words or colours and shapes. However, they caution that as only piano compositions were included in their analysis, it is unknown whether including all works by the 19 composers would have resulted in another composer being identified as the most original.
Profile: Prof. Juyong Park, PhD
juyongp@kaist.ac.kr
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.01.31 View 5774 -
 KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 13568
KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 13568 -
 Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 11875
Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 11875 -
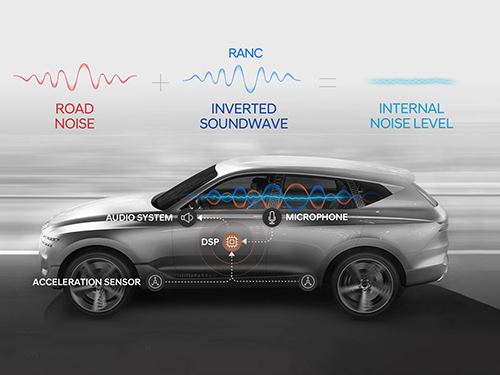 A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 13265
A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 13265