AND
-
 Professor Otfried Cheong Named as Distinguished Scientist by ACM
Professor Otfried Cheong (Schwarzkopf) of the School of Computing was named as a Distinguished Scientist of 2016 by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM).
The ACM recognized 45 Distinguished Members in the category of Distinguished Scientist, Educator, and Engineer for their individual contributions to the field of computing. Professor Cheong is the sole recipient from a Korean institution. The recipients were selected among the top 10 percent of ACM members with at least 15 years of professional experience and five years of continuous professional membership.
He is known as one of the authors of the widely used computational geometry textbook Computational Geometry: Algorithms and Applications and as the developer of Ipe, a vector graphics editor. Professor Cheong joined KAIST in 2005, after earning his doctorate from the Free University of Berlin in 1992. He previously taught at Ultrecht University, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and the Eindhoven University of Technology.
2017.04.17 View 7933
Professor Otfried Cheong Named as Distinguished Scientist by ACM
Professor Otfried Cheong (Schwarzkopf) of the School of Computing was named as a Distinguished Scientist of 2016 by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM).
The ACM recognized 45 Distinguished Members in the category of Distinguished Scientist, Educator, and Engineer for their individual contributions to the field of computing. Professor Cheong is the sole recipient from a Korean institution. The recipients were selected among the top 10 percent of ACM members with at least 15 years of professional experience and five years of continuous professional membership.
He is known as one of the authors of the widely used computational geometry textbook Computational Geometry: Algorithms and Applications and as the developer of Ipe, a vector graphics editor. Professor Cheong joined KAIST in 2005, after earning his doctorate from the Free University of Berlin in 1992. He previously taught at Ultrecht University, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and the Eindhoven University of Technology.
2017.04.17 View 7933 -
 Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 8555
Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 8555 -
 ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 8889
ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 8889 -
 Professor Jae Kyoung Kim Receives the 2017 HSFP Award
The Human Frontier Science Program (HSFP), one of the most competitive research grants in life sciences, has funded researchers worldwide across and beyond the field since 1990. Each year, the program selects a handful of recipients who push the envelope of basic research in biology to bring breakthroughs from novel approaches. Among its 7,000 recipients thus far, 26 scientists have received the Nobel Prize. For that reason, HSFP grants are often referred to as “Nobel Prize Grants.”
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of the Mathematical Sciences Department at KAIST and his international collaborators, Professor Robert Havekes from the University of Groningen, the Netherlands, Professor Sara Aton from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, the United States, and Professor Matias Zurbriggen from the University of Düsseldorf, Germany, won the Young Investigator Grants of the 2017 HSFP.
The 30 winning teams of the 2017 competition (in 9 Young Investigator Grants and 21 Program Grants) went through a rigorous year-long review process from a total of 1,073 applications submitted from more than 60 countries around the world. Each winning team will receive financial support averaging 110,000-125,000 USD per year for three years.
Although Professor Kim was trained as a mathematician, he has extended his research focus into biological sciences and attempted to solve some of the most difficult problems in biology by employing mathematical theories and applications including nonlinear dynamics, stochastic process, singular perturbation, and parameter estimation.
The project that won the Young Investigator Grants was a study on how a molecular circadian clock may affect sleep-regulated neurophysiology in mammals. Physiological and metabolic processes such as sleep, blood pressure, and hormone secretion exhibit circadian rhythms in mammals. Professor Kim used mathematical modeling and analysis to explain that the mammalian circadian clock is a hierarchical system, in which the master clock in the superchiasmatic nucleus, a tiny region in the brain that controls circadian rhythms, functions as a pacemaker and synchronizer of peripheral clocks to generate coherent systematic rhythms throughout the body.
Professor Kim said, “The mechanisms of our neuronal and hormonal activities regulating many of our bodily functions over a 24-hour cycle are not yet fully known. We go to sleep every night, but do not really know how it affects our brain functions. I hope my experience in mathematics, along with insights from biologists, can find meaningful answers to some of today’s puzzling problems in biological sciences, for example, revealing the complexities of our brains and showing how they work.”
“In the meantime, I hope collaborations between the fields of mathematics and biology, as yet a rare phenomenon in the Korean scientific community, will become more popular in the near future.”
Professor Kim received his doctoral degree in Applied and Interdisciplinary Mathematics in 2013 from the University of Michigan and joined KAIST in 2015. He has published numerous articles in reputable science journals such as Science, Molecular Cell, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Nature Communications.
Both the Program Grants and Young Investigator Grants support international teams with members from at least two countries for innovative and creative research. This year, the Program Grants were awarded to research topics ranging from the evolution of counting and the role of extracellular vesicles in breast cancer bone metastasis to the examination of obesity from a mechanobiological point of view.
The Young Investigator Grants are limited to teams that established their independent research within the last five years and received their doctoral degrees within the last decade. Besides Professor Kim’s study, such topics as the use of infrasound for navigation by seabirds and protein formation in photochemistry and photophysics were awarded in 2017.
Full lists of the 2017 HFSP winners are available at: http://www.hfsp.org/awardees/newly-awarded.
About the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP):
The HFSP is a research funding program implemented by the International Human Frontier Science Program (HFSPO) based in Strasbourg, France. It promotes intercontinental collaboration and training in cutting-edge, interdisciplinary research specializing in life sciences. Founded in 1989, the HFSPO consists of the European Union and 14 other countries including the G7 nations and South Korea.
2017.03.21 View 10499
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim Receives the 2017 HSFP Award
The Human Frontier Science Program (HSFP), one of the most competitive research grants in life sciences, has funded researchers worldwide across and beyond the field since 1990. Each year, the program selects a handful of recipients who push the envelope of basic research in biology to bring breakthroughs from novel approaches. Among its 7,000 recipients thus far, 26 scientists have received the Nobel Prize. For that reason, HSFP grants are often referred to as “Nobel Prize Grants.”
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of the Mathematical Sciences Department at KAIST and his international collaborators, Professor Robert Havekes from the University of Groningen, the Netherlands, Professor Sara Aton from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, the United States, and Professor Matias Zurbriggen from the University of Düsseldorf, Germany, won the Young Investigator Grants of the 2017 HSFP.
The 30 winning teams of the 2017 competition (in 9 Young Investigator Grants and 21 Program Grants) went through a rigorous year-long review process from a total of 1,073 applications submitted from more than 60 countries around the world. Each winning team will receive financial support averaging 110,000-125,000 USD per year for three years.
Although Professor Kim was trained as a mathematician, he has extended his research focus into biological sciences and attempted to solve some of the most difficult problems in biology by employing mathematical theories and applications including nonlinear dynamics, stochastic process, singular perturbation, and parameter estimation.
The project that won the Young Investigator Grants was a study on how a molecular circadian clock may affect sleep-regulated neurophysiology in mammals. Physiological and metabolic processes such as sleep, blood pressure, and hormone secretion exhibit circadian rhythms in mammals. Professor Kim used mathematical modeling and analysis to explain that the mammalian circadian clock is a hierarchical system, in which the master clock in the superchiasmatic nucleus, a tiny region in the brain that controls circadian rhythms, functions as a pacemaker and synchronizer of peripheral clocks to generate coherent systematic rhythms throughout the body.
Professor Kim said, “The mechanisms of our neuronal and hormonal activities regulating many of our bodily functions over a 24-hour cycle are not yet fully known. We go to sleep every night, but do not really know how it affects our brain functions. I hope my experience in mathematics, along with insights from biologists, can find meaningful answers to some of today’s puzzling problems in biological sciences, for example, revealing the complexities of our brains and showing how they work.”
“In the meantime, I hope collaborations between the fields of mathematics and biology, as yet a rare phenomenon in the Korean scientific community, will become more popular in the near future.”
Professor Kim received his doctoral degree in Applied and Interdisciplinary Mathematics in 2013 from the University of Michigan and joined KAIST in 2015. He has published numerous articles in reputable science journals such as Science, Molecular Cell, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Nature Communications.
Both the Program Grants and Young Investigator Grants support international teams with members from at least two countries for innovative and creative research. This year, the Program Grants were awarded to research topics ranging from the evolution of counting and the role of extracellular vesicles in breast cancer bone metastasis to the examination of obesity from a mechanobiological point of view.
The Young Investigator Grants are limited to teams that established their independent research within the last five years and received their doctoral degrees within the last decade. Besides Professor Kim’s study, such topics as the use of infrasound for navigation by seabirds and protein formation in photochemistry and photophysics were awarded in 2017.
Full lists of the 2017 HFSP winners are available at: http://www.hfsp.org/awardees/newly-awarded.
About the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP):
The HFSP is a research funding program implemented by the International Human Frontier Science Program (HFSPO) based in Strasbourg, France. It promotes intercontinental collaboration and training in cutting-edge, interdisciplinary research specializing in life sciences. Founded in 1989, the HFSPO consists of the European Union and 14 other countries including the G7 nations and South Korea.
2017.03.21 View 10499 -
 Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 8319
Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 8319 -
 Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 10325
Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 10325 -
 13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 17714
13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 17714 -
 Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 11265
Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 11265 -
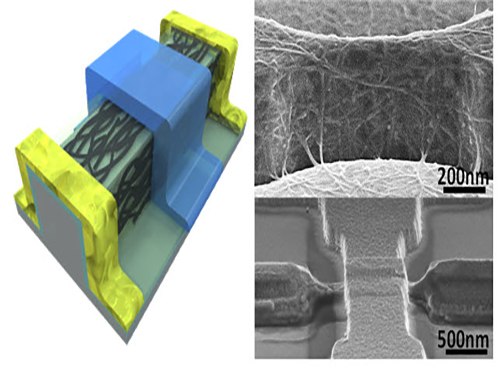 An Improved Carbon Nanotube Semiconductor
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi and his research team of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST collaborated with Professor Sung-Jin Choi of Kookmin University to develop a large-scale carbon nanotube semiconductor by using a 3-D fin-gate structure with carbon nanotubes on its top.
Dong Il Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at KAIST’s Electrical Engineering School, participated in this study as the first author. It was published in ACS Nano on November 10, 2016, and was entitled “Three-Dimensional Fin-Structured Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Network Transistor.”
A semiconductor made with carbon nanotubes operates faster than a silicon semiconductor and requires less energy, yielding higher performance.
Most electronic equipment and devices, however, use silicon semiconductors because it is difficult to fabricate highly purified and densely packed semiconductors with carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
To date, the performance of CNTs was limited due to their low density. Their purity was also low, so it was impossible to make products that had a constant yield on a large-surface wafer or substrate. These characteristics made the mass production of semiconducting CNTs difficult.
To solve these difficulties, the research team used a 3-D fin-gate to vapor-deposit carbon nanotubes on its top. They developed a semiconductor that had a high current density with a width less than 50 nm.
The three-dimensional fin structure was able to vapor-deposit 600 carbon nanotubes per micrometer. This structure could have 20 times more nanotubes than the two dimensional structure, which could only vapor-deposit thirty in the same 1 micrometer width.
In addition, the research team used semi-conductive carbon nanotubes having a purity rating higher than 99.9% from a previous study to obtain a high yield semiconductor.
The semiconductor from the research group has a high current density even with a width less than 50 μm. The new semiconductor is expected to be five times faster than a silicon-based semiconductor and will require five times less electricity during operation.
Furthermore, the new semiconductor can be made by or will be compatible with the equipment for producing silicon-based semiconductors, so there will be no additional costs.
Researcher Lee said, “As a next generation semiconductor, the carbon nanotube semiconductor will have better performance, and its effectiveness will be higher.” He also added, “Hopefully, the new semiconductor will replace the silicon-based semiconductors in ten years.”
This study received support from the Center for Integrated Smart Sensors funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning of Korea as the Global Frontier Project, and from the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) THz Technology Convergence Center of the Pioneer Research Center Program sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Picture 1: 3D Diagram of the Carbon Nanotube Electronic Device and Its Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Image
Picture 2: 3D Transistor Device on an 8-inch Base and the SEM Image of Its Cross Section
2017.02.16 View 10956
An Improved Carbon Nanotube Semiconductor
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi and his research team of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST collaborated with Professor Sung-Jin Choi of Kookmin University to develop a large-scale carbon nanotube semiconductor by using a 3-D fin-gate structure with carbon nanotubes on its top.
Dong Il Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at KAIST’s Electrical Engineering School, participated in this study as the first author. It was published in ACS Nano on November 10, 2016, and was entitled “Three-Dimensional Fin-Structured Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Network Transistor.”
A semiconductor made with carbon nanotubes operates faster than a silicon semiconductor and requires less energy, yielding higher performance.
Most electronic equipment and devices, however, use silicon semiconductors because it is difficult to fabricate highly purified and densely packed semiconductors with carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
To date, the performance of CNTs was limited due to their low density. Their purity was also low, so it was impossible to make products that had a constant yield on a large-surface wafer or substrate. These characteristics made the mass production of semiconducting CNTs difficult.
To solve these difficulties, the research team used a 3-D fin-gate to vapor-deposit carbon nanotubes on its top. They developed a semiconductor that had a high current density with a width less than 50 nm.
The three-dimensional fin structure was able to vapor-deposit 600 carbon nanotubes per micrometer. This structure could have 20 times more nanotubes than the two dimensional structure, which could only vapor-deposit thirty in the same 1 micrometer width.
In addition, the research team used semi-conductive carbon nanotubes having a purity rating higher than 99.9% from a previous study to obtain a high yield semiconductor.
The semiconductor from the research group has a high current density even with a width less than 50 μm. The new semiconductor is expected to be five times faster than a silicon-based semiconductor and will require five times less electricity during operation.
Furthermore, the new semiconductor can be made by or will be compatible with the equipment for producing silicon-based semiconductors, so there will be no additional costs.
Researcher Lee said, “As a next generation semiconductor, the carbon nanotube semiconductor will have better performance, and its effectiveness will be higher.” He also added, “Hopefully, the new semiconductor will replace the silicon-based semiconductors in ten years.”
This study received support from the Center for Integrated Smart Sensors funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning of Korea as the Global Frontier Project, and from the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) THz Technology Convergence Center of the Pioneer Research Center Program sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Picture 1: 3D Diagram of the Carbon Nanotube Electronic Device and Its Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Image
Picture 2: 3D Transistor Device on an 8-inch Base and the SEM Image of Its Cross Section
2017.02.16 View 10956 -
 New Building Endowed in Bio and Brain Engineering Department
An endowment from the former Chairman of Mirae Industries, Moon Soul Chung, was used to establish the Yang Bun Soon Building in the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST. The opening ceremony for the building took place on February 8 and was attended by President Sung-Mo Kang, KAIST administrators, faculty, and students.
The Yang Bun Soon Building, named after the wife of Chairman Chung, is a new addition to the Bio and Brain Engineering Department complex. The five-story building was erected next to the 11-story Chung Moon Soul Building, which was completed in 2003 using a portion of his first endowment to KAIST. Chairman Chung donated approximately 30 billion KRW for funding a convergence research for IT and BT in 2001.
The new building was completed with financing from Chung’s second endowment of 21.5 billion KRW in support of the fields of brain and cognitive sciences in 2014. The building will accommodate both lab facilities and lecture halls.
At the ceremony, President Kang thanked the Chungs for their continuing generosity to KAIST. He commended Chung for showing how entrepreneurs can fulfill their social responsibility by supporting Korea’s future through donations and support.
(Photo caption: Chung Moon Soul Building (left) and Yang Bun Soon Building(right))
2017.02.09 View 6020
New Building Endowed in Bio and Brain Engineering Department
An endowment from the former Chairman of Mirae Industries, Moon Soul Chung, was used to establish the Yang Bun Soon Building in the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST. The opening ceremony for the building took place on February 8 and was attended by President Sung-Mo Kang, KAIST administrators, faculty, and students.
The Yang Bun Soon Building, named after the wife of Chairman Chung, is a new addition to the Bio and Brain Engineering Department complex. The five-story building was erected next to the 11-story Chung Moon Soul Building, which was completed in 2003 using a portion of his first endowment to KAIST. Chairman Chung donated approximately 30 billion KRW for funding a convergence research for IT and BT in 2001.
The new building was completed with financing from Chung’s second endowment of 21.5 billion KRW in support of the fields of brain and cognitive sciences in 2014. The building will accommodate both lab facilities and lecture halls.
At the ceremony, President Kang thanked the Chungs for their continuing generosity to KAIST. He commended Chung for showing how entrepreneurs can fulfill their social responsibility by supporting Korea’s future through donations and support.
(Photo caption: Chung Moon Soul Building (left) and Yang Bun Soon Building(right))
2017.02.09 View 6020 -
 KAIST Intensive Science Camp for Middle-High School Students
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education (Director: Dong-Soo Kwon) invited around 90 middle and high school students for an advanced science intensive camp from January 22 to 24.
This camp targeted middle and high school students in community centers or child-care institutions. It aims to increase students’ interest in science and engineering, and assist them with their career paths through programs such as special lectures on science, advanced science projects, and career mentoring.
Participating students were divided into groups of seven or eight with a KAIST student as a mentor to conduct advanced science projects such as VR controller production and robot arm programming. The camp included exploring future career options and science and engineering college admission counselling.
Jiyoung Ryu, Research Professor for the KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education, said, “KAIST started the science and engineering career experience program in 2016 with the Ministry of Education and Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training (KRIVET). So far, 6000 middle and high school students from around the country have participated. The camp is more meaningful since it educates students in social responsibility, in addition to the fields of science and engineering, both of which are missions and goals that KAIST strives for.” She continued to say, “We plan to continue to expand the program in the future.”
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education is actively conducting research and projects on national education for talented youth such as policy research concerning gifted education, science and engineering career education, advanced science camps, training for gifted education teachers, and cyber gifted education programs.
2017.02.01 View 8276
KAIST Intensive Science Camp for Middle-High School Students
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education (Director: Dong-Soo Kwon) invited around 90 middle and high school students for an advanced science intensive camp from January 22 to 24.
This camp targeted middle and high school students in community centers or child-care institutions. It aims to increase students’ interest in science and engineering, and assist them with their career paths through programs such as special lectures on science, advanced science projects, and career mentoring.
Participating students were divided into groups of seven or eight with a KAIST student as a mentor to conduct advanced science projects such as VR controller production and robot arm programming. The camp included exploring future career options and science and engineering college admission counselling.
Jiyoung Ryu, Research Professor for the KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education, said, “KAIST started the science and engineering career experience program in 2016 with the Ministry of Education and Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training (KRIVET). So far, 6000 middle and high school students from around the country have participated. The camp is more meaningful since it educates students in social responsibility, in addition to the fields of science and engineering, both of which are missions and goals that KAIST strives for.” She continued to say, “We plan to continue to expand the program in the future.”
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education is actively conducting research and projects on national education for talented youth such as policy research concerning gifted education, science and engineering career education, advanced science camps, training for gifted education teachers, and cyber gifted education programs.
2017.02.01 View 8276 -
 JETS Conference 2017
KAIST and four science and technology research universities in Korea co-hosted a technology start-up fair, the 2017 JETS (Job, Exhibition, Tech Forum, and Startup) Conference January 19 ~20 in the Ryu Geun-chul Sports Complex at KAIST.
Korea’s major science and technology research universities, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Pohang University of Science and Technology (Postech), and Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), held the event in a collaborative effort to educate, inspire, and connect young entrepreneurs, especially those who will launch technology start-ups.
The conference brought entrepreneurs and innovators together who seek ways of working with and supporting start-ups and for their sustainable growth. It also drew aspiring young students and researchers from universities and the government-funded research institutions who are in the process of commercializing their technology. Students from each university’s industry-academia cooperation program who incubated their technology and ideas were key contributors.
At the Tech Forum, entrepreneurship and technology consultation specialists including Joe Jasin, managing director at DNA Investment Partners in the US, the founder of Cyworld Dong-Hyung Lee, and Professor Hawoong Jeong, a complex bio-network specialist from the Department of Physics of KAIST lectured on the ecosystem of start-ups and its trends and development.
The Dean of University-Industry Cooperation at KAIST Joongmyeon Bae said, "We organized this event in collaboration with four major research universities to further encourage technology start-ups from young students and help their ideas and technology bear fruit. We will continue to strive to create an ecosystem of start-ups which works efficiently.”
(Above photo: Founder of the Cyworld, Dong-Hyung Lee gives a lecture at the Tech Forum. Below photo: Students visit exhibition booth of each participating institution.)
2017.01.20 View 11929
JETS Conference 2017
KAIST and four science and technology research universities in Korea co-hosted a technology start-up fair, the 2017 JETS (Job, Exhibition, Tech Forum, and Startup) Conference January 19 ~20 in the Ryu Geun-chul Sports Complex at KAIST.
Korea’s major science and technology research universities, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST), Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST), Pohang University of Science and Technology (Postech), and Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology (UNIST), held the event in a collaborative effort to educate, inspire, and connect young entrepreneurs, especially those who will launch technology start-ups.
The conference brought entrepreneurs and innovators together who seek ways of working with and supporting start-ups and for their sustainable growth. It also drew aspiring young students and researchers from universities and the government-funded research institutions who are in the process of commercializing their technology. Students from each university’s industry-academia cooperation program who incubated their technology and ideas were key contributors.
At the Tech Forum, entrepreneurship and technology consultation specialists including Joe Jasin, managing director at DNA Investment Partners in the US, the founder of Cyworld Dong-Hyung Lee, and Professor Hawoong Jeong, a complex bio-network specialist from the Department of Physics of KAIST lectured on the ecosystem of start-ups and its trends and development.
The Dean of University-Industry Cooperation at KAIST Joongmyeon Bae said, "We organized this event in collaboration with four major research universities to further encourage technology start-ups from young students and help their ideas and technology bear fruit. We will continue to strive to create an ecosystem of start-ups which works efficiently.”
(Above photo: Founder of the Cyworld, Dong-Hyung Lee gives a lecture at the Tech Forum. Below photo: Students visit exhibition booth of each participating institution.)
2017.01.20 View 11929