Science
-
 Professor Eunjoon Kim Is KAIST's Person of the Year 2014
KAIST announced that it has named Chair Professor Eunjoon Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences as its “Person of the Year 2014.” The award ceremony took place at the auditorium on campus on January 5, 2014.
Established in 2001, the award has been presented to a KAIST faculty member who has made great achievements in research and education, thereby contributing to the advancement of KAIST.
Professor Kim was the first to identify the mechanism of synapse formation between neurons during his post-doctoral program at Harvard Medical School in 1995. The research was published in Nature.
In 2011, Professor Kim discovered that the lack of protein GIT1, a neuronal synapse in the brain, caused ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). He is widely recognized for his work concerning synapse proteins and brain disease related research that set the foundation for future medical developments.
In his award speech, Professor Kim said, “Whenever a research finding concerning a new drug therapy or research is published, I receive many inquiries from the parents of children with ADHD or autism. As a scientist, I would like to focus my research ultimately to help those in pain, rather than just pursuing research excellence or reputation.”
2015.01.06 View 11458
Professor Eunjoon Kim Is KAIST's Person of the Year 2014
KAIST announced that it has named Chair Professor Eunjoon Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences as its “Person of the Year 2014.” The award ceremony took place at the auditorium on campus on January 5, 2014.
Established in 2001, the award has been presented to a KAIST faculty member who has made great achievements in research and education, thereby contributing to the advancement of KAIST.
Professor Kim was the first to identify the mechanism of synapse formation between neurons during his post-doctoral program at Harvard Medical School in 1995. The research was published in Nature.
In 2011, Professor Kim discovered that the lack of protein GIT1, a neuronal synapse in the brain, caused ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder). He is widely recognized for his work concerning synapse proteins and brain disease related research that set the foundation for future medical developments.
In his award speech, Professor Kim said, “Whenever a research finding concerning a new drug therapy or research is published, I receive many inquiries from the parents of children with ADHD or autism. As a scientist, I would like to focus my research ultimately to help those in pain, rather than just pursuing research excellence or reputation.”
2015.01.06 View 11458 -
 Professor Mikyoung Lim Receives the MediaV Young Researcher Award
Professor Mikyoung Lim of the Department of Mathematical Sciences at KAIST received the MediaV Young Researchers Award at the International Conference on Inverse Problems and Related Topics that took place at the National Taiwan University, Taiwan, on December 15-19, 2014.
The Conference established the MediaV Young Researcher Award in 2010 to recognize distinguished scholars who are age 40 or younger and have made important contributions to the field of inverse problems. This year, two recipients were chosen for the award.
Professor Lim has focused her research on the incremental reading of incomprehensible materials’ imaging and the effect of invisibility cloaking.
The other awardee was Kui Ren, a professor at the University of Texas at Austin.
2014.12.27 View 12626
Professor Mikyoung Lim Receives the MediaV Young Researcher Award
Professor Mikyoung Lim of the Department of Mathematical Sciences at KAIST received the MediaV Young Researchers Award at the International Conference on Inverse Problems and Related Topics that took place at the National Taiwan University, Taiwan, on December 15-19, 2014.
The Conference established the MediaV Young Researcher Award in 2010 to recognize distinguished scholars who are age 40 or younger and have made important contributions to the field of inverse problems. This year, two recipients were chosen for the award.
Professor Lim has focused her research on the incremental reading of incomprehensible materials’ imaging and the effect of invisibility cloaking.
The other awardee was Kui Ren, a professor at the University of Texas at Austin.
2014.12.27 View 12626 -
 KAIST Partners with Science-focused Universities in Korea for Student Exchange Programs
KAIST and four science-focused universities in Korea (Pohang University of Science and Technology, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, and Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology) agreed to exchange programs during academic semesters including summer and winter terms by signing a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on November 28, 2014. The signing ceremony took place at the KAIST campus with the participation of academic affairs deans from all five universities.
Based on the agreement, KAIST students can take up to 12 credits of coursework at any of the said universities and have unimpeded access to the university facilities during their coursework.
Dean Hyun-Wook Park of Academic Affairs at KASIT said, “Through exchange programs, students can capitalize on each university’s advantages, and this eventually will lead to greater advancement in science and technology in the nation.”
2014.12.08 View 8770
KAIST Partners with Science-focused Universities in Korea for Student Exchange Programs
KAIST and four science-focused universities in Korea (Pohang University of Science and Technology, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology, and Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology) agreed to exchange programs during academic semesters including summer and winter terms by signing a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on November 28, 2014. The signing ceremony took place at the KAIST campus with the participation of academic affairs deans from all five universities.
Based on the agreement, KAIST students can take up to 12 credits of coursework at any of the said universities and have unimpeded access to the university facilities during their coursework.
Dean Hyun-Wook Park of Academic Affairs at KASIT said, “Through exchange programs, students can capitalize on each university’s advantages, and this eventually will lead to greater advancement in science and technology in the nation.”
2014.12.08 View 8770 -
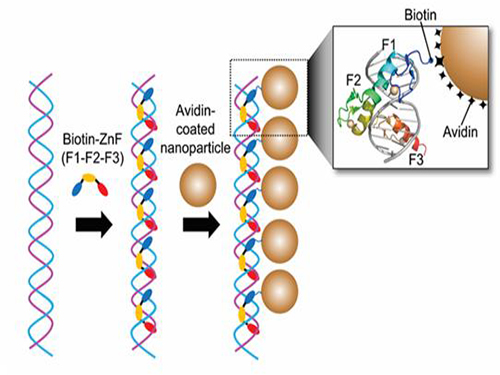 Nanoparticle Cluster Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Yiseul Ryu, a doctoral candidate, used the Zinc Finger protein that specifically binds to target DNA sequence to develop a new manufacturing technique for size-controllable magnetic Nanoparticle Clusters (NPCs). Their research results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition online on 25 November 2014.
NPCs are structures consisting of magnetic nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and quantum dots, each of which are smaller than 100 nm (10-9m). NPCs have a distinctive property of collectivity not seen in single nanoparticles.
Specifically NPCS differ in physical and optical properties such as Plasmon coupling absorbance, energy transfers between particles, electron transfers, and conductivity. Therefore, NPCs can be employed in biological and medical research as well as the development of nanoelectric and nanoplasmon devices.
To make use of these novel properties, the size and the composition of the cluster must be exquisitely controlled. However, previous techniques relied on chemical binding which required complex steps, making it difficult to control the size and composition of NPCs.
Professor Kim’s team used Zinc Finger, a DNA binding protein, to develop a NPCs manufacturing technique to create clusters of the desired size easily. The Zinc Finger protein contains a zinc ion and specifically recognizes DNA sequence upon binding, which allows the exquisite control of the size and the cluster composition. The technique is also bio-friendly.
Professor Kim’s team created linear structure of different sizes of NPCs using Zinc Finger proteins and three DNA sequences of different lengths. The NPCs they produced confirmed their ability to control the size and structure of the cluster by using different DNA lengths.
The NPCs showed tripled T2 relaxation rates compared to the existing MRI contrast media (Feridex) and effectively transported to targeted cells. The research findings show the potential use of NPCs in biological and medical fields such as MRI contrast media, fluorescence imaging, and drug transport.
The research used the specific binding property of protein and DNA to develop a new method to create an inorganic nanoparticle’s supramolecular assembly. The technique can be used and applied extensively in other nanoparticles for future research in diagnosis, imaging, and drug and gene delivery.
Figure 1. A Mimetic Diagram of NPCs Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Zinc Finger
Figure 2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Images showing different sizes of NPCs depending on the length of the DNA
2014.12.04 View 14504
Nanoparticle Cluster Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Yiseul Ryu, a doctoral candidate, used the Zinc Finger protein that specifically binds to target DNA sequence to develop a new manufacturing technique for size-controllable magnetic Nanoparticle Clusters (NPCs). Their research results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition online on 25 November 2014.
NPCs are structures consisting of magnetic nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and quantum dots, each of which are smaller than 100 nm (10-9m). NPCs have a distinctive property of collectivity not seen in single nanoparticles.
Specifically NPCS differ in physical and optical properties such as Plasmon coupling absorbance, energy transfers between particles, electron transfers, and conductivity. Therefore, NPCs can be employed in biological and medical research as well as the development of nanoelectric and nanoplasmon devices.
To make use of these novel properties, the size and the composition of the cluster must be exquisitely controlled. However, previous techniques relied on chemical binding which required complex steps, making it difficult to control the size and composition of NPCs.
Professor Kim’s team used Zinc Finger, a DNA binding protein, to develop a NPCs manufacturing technique to create clusters of the desired size easily. The Zinc Finger protein contains a zinc ion and specifically recognizes DNA sequence upon binding, which allows the exquisite control of the size and the cluster composition. The technique is also bio-friendly.
Professor Kim’s team created linear structure of different sizes of NPCs using Zinc Finger proteins and three DNA sequences of different lengths. The NPCs they produced confirmed their ability to control the size and structure of the cluster by using different DNA lengths.
The NPCs showed tripled T2 relaxation rates compared to the existing MRI contrast media (Feridex) and effectively transported to targeted cells. The research findings show the potential use of NPCs in biological and medical fields such as MRI contrast media, fluorescence imaging, and drug transport.
The research used the specific binding property of protein and DNA to develop a new method to create an inorganic nanoparticle’s supramolecular assembly. The technique can be used and applied extensively in other nanoparticles for future research in diagnosis, imaging, and drug and gene delivery.
Figure 1. A Mimetic Diagram of NPCs Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Zinc Finger
Figure 2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Images showing different sizes of NPCs depending on the length of the DNA
2014.12.04 View 14504 -
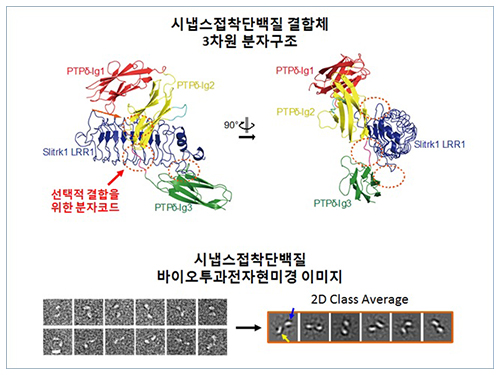 Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 13147
Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 13147 -
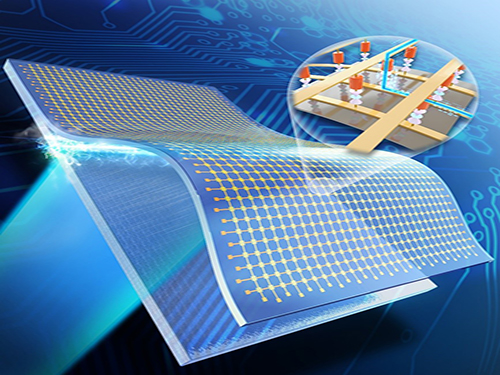 Breakthrough in Flexible Electronics Enabled by Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off
Flexible electronics have been touted as the next generation in electronics in various areas, ranging from consumer electronics to bio-integrated medical devices. In spite of their merits, insufficient performance of organic materials arising from inherent material properties and processing limitations in scalability have posed big challenges to developing all-in-one flexible electronics systems in which display, processor, memory, and energy devices are integrated. The high temperature processes, essential for high performance electronic devices, have severely restricted the development of flexible electronics because of the fundamental thermal instabilities of polymer materials.
A research team headed by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST provides an easier methodology to realize high performance flexible electronics by using the Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off (ILLO).
The ILLO process involves depositing a laser-reactive exfoliation layer on rigid substrates, and then fabricating ultrathin inorganic electronic devices, e.g., high density crossbar memristive memory on top of the exfoliation layer. By laser irradiation through the back of the substrate, only the ultrathin inorganic device layers are exfoliated from the substrate as a result of the reaction between laser and exfoliation layer, and then subsequently transferred onto any kind of receiver substrate such as plastic, paper, and even fabric.
This ILLO process can enable not only nanoscale processes for high density flexible devices but also the high temperature process that was previously difficult to achieve on plastic substrates. The transferred device successfully demonstrates fully-functional random access memory operation on flexible substrates even under severe bending.
Professor Lee said, “By selecting an optimized set of inorganic exfoliation layer and substrate, a nanoscale process at a high temperature of over 1000 °C can be utilized for high performance flexible electronics. The ILLO process can be applied to diverse flexible electronics, such as driving circuits for displays and inorganic-based energy devices such as battery, solar cell, and self-powered devices that require high temperature processes.”
The team’s results were published in the November issue of Wiley’s journal, ‘ Advanced Materials, ’ as a cover article entitled “ Flexible Crossbar-Structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substrates via Inorganic-Based Laser Lift-Off.”
( http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201402472/abstract )
This schematic picture shows the flexible crossbar memory developed via the ILLO process.
This photo shows the flexible RRAM device on a plastic substrate.
2014.11.26 View 10904
Breakthrough in Flexible Electronics Enabled by Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off
Flexible electronics have been touted as the next generation in electronics in various areas, ranging from consumer electronics to bio-integrated medical devices. In spite of their merits, insufficient performance of organic materials arising from inherent material properties and processing limitations in scalability have posed big challenges to developing all-in-one flexible electronics systems in which display, processor, memory, and energy devices are integrated. The high temperature processes, essential for high performance electronic devices, have severely restricted the development of flexible electronics because of the fundamental thermal instabilities of polymer materials.
A research team headed by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST provides an easier methodology to realize high performance flexible electronics by using the Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off (ILLO).
The ILLO process involves depositing a laser-reactive exfoliation layer on rigid substrates, and then fabricating ultrathin inorganic electronic devices, e.g., high density crossbar memristive memory on top of the exfoliation layer. By laser irradiation through the back of the substrate, only the ultrathin inorganic device layers are exfoliated from the substrate as a result of the reaction between laser and exfoliation layer, and then subsequently transferred onto any kind of receiver substrate such as plastic, paper, and even fabric.
This ILLO process can enable not only nanoscale processes for high density flexible devices but also the high temperature process that was previously difficult to achieve on plastic substrates. The transferred device successfully demonstrates fully-functional random access memory operation on flexible substrates even under severe bending.
Professor Lee said, “By selecting an optimized set of inorganic exfoliation layer and substrate, a nanoscale process at a high temperature of over 1000 °C can be utilized for high performance flexible electronics. The ILLO process can be applied to diverse flexible electronics, such as driving circuits for displays and inorganic-based energy devices such as battery, solar cell, and self-powered devices that require high temperature processes.”
The team’s results were published in the November issue of Wiley’s journal, ‘ Advanced Materials, ’ as a cover article entitled “ Flexible Crossbar-Structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substrates via Inorganic-Based Laser Lift-Off.”
( http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201402472/abstract )
This schematic picture shows the flexible crossbar memory developed via the ILLO process.
This photo shows the flexible RRAM device on a plastic substrate.
2014.11.26 View 10904 -
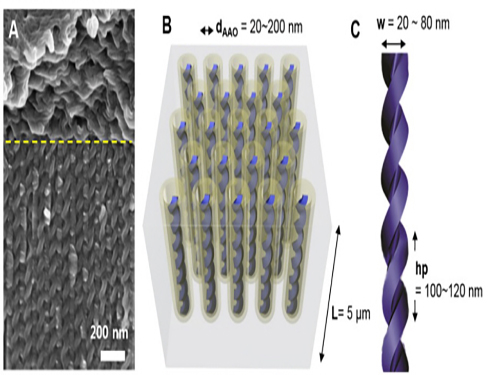 KAIST Develops Core Technology to Synthesize a Helical Nanostructure
Professor Dong-Ki Yoon’s research team of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology (GSNT) at KAIST has developed helical nanostructures using self-assembly processes. The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America(PNAS) on the October 7th.
This technology enables the synthesis of various helical structures on a relatively large confined area. Its synthesis is often considered the most arduous for three dimensional structures. Formed from liquid crystal, the structure holds a regular helical structure within the confined space of 20 to 300 nanometers. Also, the distance between each pattern increased as the diameter of the nanostructure increased.
Liquid crystals have a unique property of responding sensitively to the surrounding electromagnetic field. The technology, in combination with the electromagnetic property of liquid crystal, is expected to foster the development of highly efficient optoelectronic devices.
Using this technology, it is possible to develop three dimensional patterning technology beyond the current semiconductor manufacturing technology which uses two dimensional photolithography processes. Three-dimensional semiconductor devices are expected to store hundred times more data than current devices. They will also lower costs by simplifying manufacturing processes.
The essence of this research, “self-assembly in confined space,” refers to controlling complex nanostructures, which can be synthesized from materials such as macromolecules, liquid crystal molecules, and biomolecules in relation to surrounding environments including the temperature, concentration, and pH.
The research team produced a confined space with a length of tens of nanometers by using a porous anodized aluminum membrane induced from an electrochemical reaction. They successfully synthesized independently controlled helical nanostructures by forming the helical structures from liquid crystal molecules within that space.
Professor Yoon said, “This research examines the physicochemical principle of controlling helical nanostructures.” He highlighted the significance of the research and commented, “The technology enables the control of complex nanostructures from organic molecules by using confined space and surface reforming.”
He added that, “When grafted with nanotechnology or information technology, this technology will spur new growth to liquid crystal-related industries such as the LCD.”
The research was led by two Ph.D. candidates, Hanim Kim and Sunhee Lee, under the guidance of Professor Yoon. Dr. Tae-Joo Shin of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Professor Sang-Bok Lee of the University of Maryland, and Professor Noel Clark of the University of Colorado also participated.
Picture 1. Electron Microscopy Pictures and Conceptual Diagrams of Helical Nanostructures
Picture 2. Electron Microscopy Pictures of Manufactured Helical Nanostructures
2014.10.29 View 9827
KAIST Develops Core Technology to Synthesize a Helical Nanostructure
Professor Dong-Ki Yoon’s research team of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology (GSNT) at KAIST has developed helical nanostructures using self-assembly processes. The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America(PNAS) on the October 7th.
This technology enables the synthesis of various helical structures on a relatively large confined area. Its synthesis is often considered the most arduous for three dimensional structures. Formed from liquid crystal, the structure holds a regular helical structure within the confined space of 20 to 300 nanometers. Also, the distance between each pattern increased as the diameter of the nanostructure increased.
Liquid crystals have a unique property of responding sensitively to the surrounding electromagnetic field. The technology, in combination with the electromagnetic property of liquid crystal, is expected to foster the development of highly efficient optoelectronic devices.
Using this technology, it is possible to develop three dimensional patterning technology beyond the current semiconductor manufacturing technology which uses two dimensional photolithography processes. Three-dimensional semiconductor devices are expected to store hundred times more data than current devices. They will also lower costs by simplifying manufacturing processes.
The essence of this research, “self-assembly in confined space,” refers to controlling complex nanostructures, which can be synthesized from materials such as macromolecules, liquid crystal molecules, and biomolecules in relation to surrounding environments including the temperature, concentration, and pH.
The research team produced a confined space with a length of tens of nanometers by using a porous anodized aluminum membrane induced from an electrochemical reaction. They successfully synthesized independently controlled helical nanostructures by forming the helical structures from liquid crystal molecules within that space.
Professor Yoon said, “This research examines the physicochemical principle of controlling helical nanostructures.” He highlighted the significance of the research and commented, “The technology enables the control of complex nanostructures from organic molecules by using confined space and surface reforming.”
He added that, “When grafted with nanotechnology or information technology, this technology will spur new growth to liquid crystal-related industries such as the LCD.”
The research was led by two Ph.D. candidates, Hanim Kim and Sunhee Lee, under the guidance of Professor Yoon. Dr. Tae-Joo Shin of the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory, Professor Sang-Bok Lee of the University of Maryland, and Professor Noel Clark of the University of Colorado also participated.
Picture 1. Electron Microscopy Pictures and Conceptual Diagrams of Helical Nanostructures
Picture 2. Electron Microscopy Pictures of Manufactured Helical Nanostructures
2014.10.29 View 9827 -
 KAIST's Masters of Science Journalism Presents the 4th Annual Moon-Sul Chung Award
The Masters of Science Journalism (MSJ) program at the Graduate School of Future Strategy, KAIST, hosted a conference and presented its fourth annual Moon-Sul Chung Award to the Hankyoreh newspaper at KAIST’s Seoul campus on October 11, 2014.
MSJ organized the conference to review major issues reported in the Korean news in the context of the sciences, for example, how the Korean media covered the tragic accident of the Sewol Ferry, a passenger ship that capsized and eventually sank with hundreds of passengers on board in the waters off the southern coast of Korea on April 16, 2014. Participants of the conference discussed the approaches taken by the media to report science-related issues such as mechanical problems of the ship and technical errors made by the operator.
MSJ conferred its annual award to a Hankyoreh news team which covered the Sewol incident. The award is named for Moon-Sul Chung, a philanthropist who created a scholarship fund for the school in 2011 to recognize news organizations that have striven to report social issues in a fair and balanced manner.
2014.10.14 View 7003
KAIST's Masters of Science Journalism Presents the 4th Annual Moon-Sul Chung Award
The Masters of Science Journalism (MSJ) program at the Graduate School of Future Strategy, KAIST, hosted a conference and presented its fourth annual Moon-Sul Chung Award to the Hankyoreh newspaper at KAIST’s Seoul campus on October 11, 2014.
MSJ organized the conference to review major issues reported in the Korean news in the context of the sciences, for example, how the Korean media covered the tragic accident of the Sewol Ferry, a passenger ship that capsized and eventually sank with hundreds of passengers on board in the waters off the southern coast of Korea on April 16, 2014. Participants of the conference discussed the approaches taken by the media to report science-related issues such as mechanical problems of the ship and technical errors made by the operator.
MSJ conferred its annual award to a Hankyoreh news team which covered the Sewol incident. The award is named for Moon-Sul Chung, a philanthropist who created a scholarship fund for the school in 2011 to recognize news organizations that have striven to report social issues in a fair and balanced manner.
2014.10.14 View 7003 -
 Thomson Reuters Nominates Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo for Its 2014 Nobel Citation Laureates in Chemistry
The Intellectual Property & Science business of Thomson Reuters announced on September 25th its “2014 Citation Laureates,” a list of candidates considered likely to win the Nobel Prize in the fields of physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, and economics. The annual Thomson Reuters Citation Laureates will be recognized in perpetuity as contenders for a Nobel Prize.
Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo of the Department of Chemistry, KAIST, has been nominated for the 2014 Thomson Reuters Citation Laureates in Chemistry. He is the first Korean scientist who has made the list. In addition to Professor Ryoo, seven other scientists were selected as possible contenders for the 2014 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, or in the future.
Professor Ryoo was named alongside Charles T. Kresge, Chief Technology Officer of Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Galen D. Stucky, Professor of the Department Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California, Santa Barbara, for their research on the design of functional mesoporous materials (http://sciencewatch.com/nobel/2014-predictions/chemistry-laureates). Mesoporous materials have high surface areas with narrow pore-sized distribution and tunable pores diameters, offering promising properties and applications in various areas including adsorption, separation, sensing, and catalysis.
Professor Ryoo has focused his research interest in the synthesis of new functional nanoporous materials such as hierarchical zeolites, mesoporous silicas, carbons, and organic-inorganic composite materials that can be used for advanced applications in the production of alternative energy sources and in green chemical processes.
According to the press release by the Thomson Reuters, the list of the 2014 Nobel predictions includes 27 researchers representing 27 distinct academic and research organizations across nine different countries.
The annual Thomson Reuters Citation Laureates study is based on the analysis of proprietary data from the research and citation database, identifying the most influential researchers in the categories of chemistry, physics, physiology or medicine, and economics. Since its inception in 2002, the study has accurately forecasted 35 Nobel Prize winners. For the full text of the press release, please go to: http://thomsonreuters.com/press-releases/092014/2014-nobel-laureates-predictions.
2014.09.29 View 12637
Thomson Reuters Nominates Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo for Its 2014 Nobel Citation Laureates in Chemistry
The Intellectual Property & Science business of Thomson Reuters announced on September 25th its “2014 Citation Laureates,” a list of candidates considered likely to win the Nobel Prize in the fields of physics, chemistry, physiology or medicine, and economics. The annual Thomson Reuters Citation Laureates will be recognized in perpetuity as contenders for a Nobel Prize.
Distinguished Professor Ryong Ryoo of the Department of Chemistry, KAIST, has been nominated for the 2014 Thomson Reuters Citation Laureates in Chemistry. He is the first Korean scientist who has made the list. In addition to Professor Ryoo, seven other scientists were selected as possible contenders for the 2014 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, or in the future.
Professor Ryoo was named alongside Charles T. Kresge, Chief Technology Officer of Saudi Aramco, Dhahran, and Galen D. Stucky, Professor of the Department Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California, Santa Barbara, for their research on the design of functional mesoporous materials (http://sciencewatch.com/nobel/2014-predictions/chemistry-laureates). Mesoporous materials have high surface areas with narrow pore-sized distribution and tunable pores diameters, offering promising properties and applications in various areas including adsorption, separation, sensing, and catalysis.
Professor Ryoo has focused his research interest in the synthesis of new functional nanoporous materials such as hierarchical zeolites, mesoporous silicas, carbons, and organic-inorganic composite materials that can be used for advanced applications in the production of alternative energy sources and in green chemical processes.
According to the press release by the Thomson Reuters, the list of the 2014 Nobel predictions includes 27 researchers representing 27 distinct academic and research organizations across nine different countries.
The annual Thomson Reuters Citation Laureates study is based on the analysis of proprietary data from the research and citation database, identifying the most influential researchers in the categories of chemistry, physics, physiology or medicine, and economics. Since its inception in 2002, the study has accurately forecasted 35 Nobel Prize winners. For the full text of the press release, please go to: http://thomsonreuters.com/press-releases/092014/2014-nobel-laureates-predictions.
2014.09.29 View 12637 -
 The College of Information Science & Technology names its Alumnus of the Year 2014
The College of Information Science & Technology (CIST), KAIST, selected Tae-Kyung Yoo, the Chief Executive Officer of Lumens, Inc., a Korean company producing semiconductors and light emitting diodes (LEDs), as its Alumnus of the Year 2014.
The award ceremony took place on September 19, 2014 at the KAIST Institute with the participation of the university’s senior management and students.
Mr. Yoo was recognized for his pioneering work to develop the LED industry in Korea as the next-generation growth engine for the nation’s economy.
After the ceremony, he gave a talk entitled “The Past and Future of the LED Industry: Its Important Role in the Change of Korean Industry.”
The CIST created the Alumnus of the Year 2014 award, for the first time this year, to appreciate its alumni’s contribution to the advancement of the industrial and academic sectors of Korean information science and technology, and it will continue presenting the award from this year onwards.
2014.09.22 View 8020
The College of Information Science & Technology names its Alumnus of the Year 2014
The College of Information Science & Technology (CIST), KAIST, selected Tae-Kyung Yoo, the Chief Executive Officer of Lumens, Inc., a Korean company producing semiconductors and light emitting diodes (LEDs), as its Alumnus of the Year 2014.
The award ceremony took place on September 19, 2014 at the KAIST Institute with the participation of the university’s senior management and students.
Mr. Yoo was recognized for his pioneering work to develop the LED industry in Korea as the next-generation growth engine for the nation’s economy.
After the ceremony, he gave a talk entitled “The Past and Future of the LED Industry: Its Important Role in the Change of Korean Industry.”
The CIST created the Alumnus of the Year 2014 award, for the first time this year, to appreciate its alumni’s contribution to the advancement of the industrial and academic sectors of Korean information science and technology, and it will continue presenting the award from this year onwards.
2014.09.22 View 8020 -
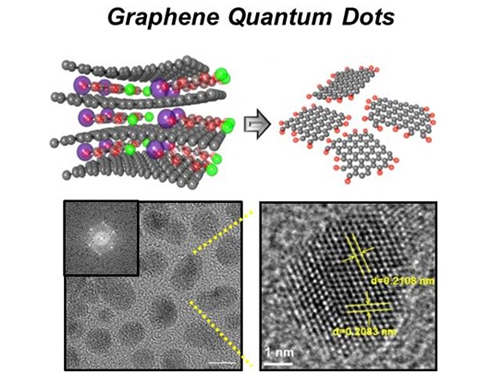 News Article on the Development of Synthesis Process for Graphene Quantum Dots
Before It's News, an international online news agency, highlighted the recent research conducted by KAIST professors (Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering) on the development of synthesis process for graphene quantum dots, nanometer-sized round semiconductor nanoparticles that are very efficient at emitting photons. If commercialized, this synthetic technology will lead the way to the development of paper-thin displays in the future.
For the article, please go to the link below:
Before It’s News, September 3, 2014“Graphene quantum dots prove highly efficient in emitting light”
http://beforeitsnews.com/science-and-technology/2014/09/graphene-quantum-dots-prove-highly-efficient-in-emitting-light-2718190.html
2014.09.07 View 15280
News Article on the Development of Synthesis Process for Graphene Quantum Dots
Before It's News, an international online news agency, highlighted the recent research conducted by KAIST professors (Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering) on the development of synthesis process for graphene quantum dots, nanometer-sized round semiconductor nanoparticles that are very efficient at emitting photons. If commercialized, this synthetic technology will lead the way to the development of paper-thin displays in the future.
For the article, please go to the link below:
Before It’s News, September 3, 2014“Graphene quantum dots prove highly efficient in emitting light”
http://beforeitsnews.com/science-and-technology/2014/09/graphene-quantum-dots-prove-highly-efficient-in-emitting-light-2718190.html
2014.09.07 View 15280 -
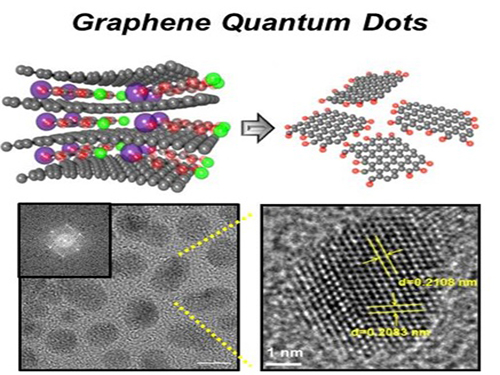 Extracting Light from Graphite: Core Technology of Graphene Quantum Dots Display Developed
Professor Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering announced that they were able to develop topnotch graphene quantum dots from graphite.
Using the method of synthesizing graphite intercalation compound from graphite with salt and water, the research team developed graphene quantum dots in an ecofriendly way.
The quantum dots have a diameter of 5 nanometers with their sizes equal and yield high quantum efficiency. Unlike conventional quantum dots, they are not comprised of toxic materials such as lead or cadmium. As the quantum dots can be developed from materials which can be easily found in the nature, researchers look forward to putting these into mass production at low cost.
The research team also discovered a luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots and confirmed the possibility of commercial use by developing quantum dot light-emitting diodes with brightness of 1,000 cd/m2, which is greater than that of cellphone displays.
Professor Seokwoo Jeon said, “Although quantum dot LEDs have a lower luminous efficiency than existing ones, their luminescent property can be further improved” and emphasized that “using quantum dot displays will allow us to develop not only paper-thin displays but also flexible ones.”
Sponsored by Graphene Research Center in KAIST Institute for NanoCentury, the research finding was published online in the April 20th issue of Advanced Optical Materials.
Picture 1: Graphene quantum dots and their synthesis
Picture 2: Luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots
Picture 3: Structure of graphene quantum dots LED and its emission
2014.09.06 View 19817
Extracting Light from Graphite: Core Technology of Graphene Quantum Dots Display Developed
Professor Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering announced that they were able to develop topnotch graphene quantum dots from graphite.
Using the method of synthesizing graphite intercalation compound from graphite with salt and water, the research team developed graphene quantum dots in an ecofriendly way.
The quantum dots have a diameter of 5 nanometers with their sizes equal and yield high quantum efficiency. Unlike conventional quantum dots, they are not comprised of toxic materials such as lead or cadmium. As the quantum dots can be developed from materials which can be easily found in the nature, researchers look forward to putting these into mass production at low cost.
The research team also discovered a luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots and confirmed the possibility of commercial use by developing quantum dot light-emitting diodes with brightness of 1,000 cd/m2, which is greater than that of cellphone displays.
Professor Seokwoo Jeon said, “Although quantum dot LEDs have a lower luminous efficiency than existing ones, their luminescent property can be further improved” and emphasized that “using quantum dot displays will allow us to develop not only paper-thin displays but also flexible ones.”
Sponsored by Graphene Research Center in KAIST Institute for NanoCentury, the research finding was published online in the April 20th issue of Advanced Optical Materials.
Picture 1: Graphene quantum dots and their synthesis
Picture 2: Luminescence mechanism of graphene quantum dots
Picture 3: Structure of graphene quantum dots LED and its emission
2014.09.06 View 19817