CT
-
 Professor Sungyeol Choi Receives Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Sungyeol Choi >
Professor Sungyeol Choi from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering received the Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation on the 9th Annual Nuclear Safety and Promotion Day last month, in recognition of his contributions to the promotion of nuclear energy through the safe management of spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste.
Professor Choi developed high-precision, multi-physics codes that can predict and prevent abnormal power fluctuations caused by boron hideout within nuclear fuel in a pressurized water reactor, solving the problem that has caused economic losses of tens of billions of won every year from industrial sites.
He is now developing a new technology that can reduce high-level waste by recycling spent nuclear fuel, while preventing nuclear material from being used for nuclear weapons, which is one of the biggest challenges faced by the nuclear industry.
In 2017, his first year in office as a KAIST professor, Professor Choi was selected as the youngest and the only member under 50 of the Standing Scientific Advisory Committee at the Information Exchange Meeting on Partitioning and Transmutation (IEMPT), an authoritative association on the disposal of high-level nuclear waste.
The following year, he became the first Korean to receive the Early Career Award, which is given to one person every two years by the International Youth Nuclear Congress.
2020.01.15 View 6095
Professor Sungyeol Choi Receives Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Sungyeol Choi >
Professor Sungyeol Choi from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering received the Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation on the 9th Annual Nuclear Safety and Promotion Day last month, in recognition of his contributions to the promotion of nuclear energy through the safe management of spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste.
Professor Choi developed high-precision, multi-physics codes that can predict and prevent abnormal power fluctuations caused by boron hideout within nuclear fuel in a pressurized water reactor, solving the problem that has caused economic losses of tens of billions of won every year from industrial sites.
He is now developing a new technology that can reduce high-level waste by recycling spent nuclear fuel, while preventing nuclear material from being used for nuclear weapons, which is one of the biggest challenges faced by the nuclear industry.
In 2017, his first year in office as a KAIST professor, Professor Choi was selected as the youngest and the only member under 50 of the Standing Scientific Advisory Committee at the Information Exchange Meeting on Partitioning and Transmutation (IEMPT), an authoritative association on the disposal of high-level nuclear waste.
The following year, he became the first Korean to receive the Early Career Award, which is given to one person every two years by the International Youth Nuclear Congress.
2020.01.15 View 6095 -
 KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 13525
KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 13525 -
 Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 11835
Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 11835 -
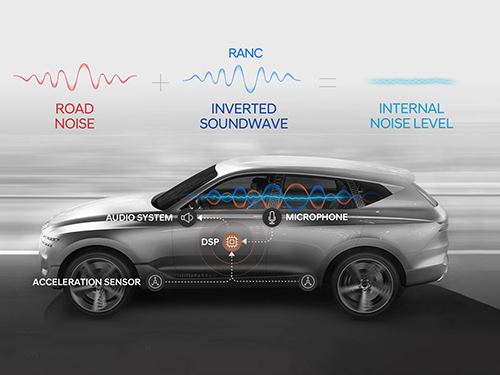 A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 13223
A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 13223 -
 Professor Junil Choi Receives Stephen O. Rice Prize
< Professor Junil Choi (second from the left) >
Professor Junil Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Stephen O. Rice Prize at the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in Hawaii on December 10, 2019.
The Stephen O. Rice Prize is awarded to only one paper of exceptional merit every year. The IEEE Communications Society evaluates all papers published in the IEEE Transactions on Communications journal within the last three years, and marks each paper by aggregating its scores on originality, the number of citations, impact, and peer evaluation.
Professor Choi won the prize for his research on one-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for multiuser massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna systems published in 2016. In his paper, Professor Choi proposed a technology that can drastically reduce the power consumption of the multiuser massive MIMO antenna systems, which are the core technology for 5G and future wireless communication. Professor Choi’s paper has been cited more than 230 times in various academic journals and conference papers since its publication, and multiple follow-up studies are actively ongoing.
In 2015, Professor Choi received the IEEE Signal Processing Society Best Paper Award, an award equals to the Stephen O. Rice Prize. He was also selected as the winner of the 15th Haedong Young Engineering Researcher Award presented by the Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS) on December 6, 2019 for his outstanding academic achievements, including 34 international journal publications and 26 US patent registrations.
(END)
2019.12.23 View 13155
Professor Junil Choi Receives Stephen O. Rice Prize
< Professor Junil Choi (second from the left) >
Professor Junil Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Stephen O. Rice Prize at the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in Hawaii on December 10, 2019.
The Stephen O. Rice Prize is awarded to only one paper of exceptional merit every year. The IEEE Communications Society evaluates all papers published in the IEEE Transactions on Communications journal within the last three years, and marks each paper by aggregating its scores on originality, the number of citations, impact, and peer evaluation.
Professor Choi won the prize for his research on one-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for multiuser massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna systems published in 2016. In his paper, Professor Choi proposed a technology that can drastically reduce the power consumption of the multiuser massive MIMO antenna systems, which are the core technology for 5G and future wireless communication. Professor Choi’s paper has been cited more than 230 times in various academic journals and conference papers since its publication, and multiple follow-up studies are actively ongoing.
In 2015, Professor Choi received the IEEE Signal Processing Society Best Paper Award, an award equals to the Stephen O. Rice Prize. He was also selected as the winner of the 15th Haedong Young Engineering Researcher Award presented by the Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS) on December 6, 2019 for his outstanding academic achievements, including 34 international journal publications and 26 US patent registrations.
(END)
2019.12.23 View 13155 -
 New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 16271
New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 16271 -
 Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 11465
Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 11465 -
 Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 12295
Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 12295 -
 New IEEE Fellow, Professor Jong Chul Ye
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was named a new fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). IEEE announced this on December 1 in recognition of Professor Ye’s contributions to the development of signal processing and artificial intelligence (AI) technology in the field of biomedical imaging.
As the world’s largest society in the electrical and electronics field, IEEE names the top 0.1% of their members as fellows based on their research achievements.Professor Ye has published more than 100 research papers in world-leading journals in the biomedical imaging field, including those affiliated with IEEE.
He also gave a keynote talk at the yearly conference of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ISMRM) on medical AI technology. In addition, Professor Ye has been appointed to serve as the next chair of the Computational Imaging Technical Committee of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, and the chair of the IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020 to be held in April in Iowa, USA.
Professor Ye said, “The importance of AI technology is developing in the biomedical imaging field. I feel proud that my contributions have been internationally recognized and allowed me to be named an IEEE fellow.”
2019.12.18 View 11600
New IEEE Fellow, Professor Jong Chul Ye
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was named a new fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE). IEEE announced this on December 1 in recognition of Professor Ye’s contributions to the development of signal processing and artificial intelligence (AI) technology in the field of biomedical imaging.
As the world’s largest society in the electrical and electronics field, IEEE names the top 0.1% of their members as fellows based on their research achievements.Professor Ye has published more than 100 research papers in world-leading journals in the biomedical imaging field, including those affiliated with IEEE.
He also gave a keynote talk at the yearly conference of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (ISMRM) on medical AI technology. In addition, Professor Ye has been appointed to serve as the next chair of the Computational Imaging Technical Committee of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, and the chair of the IEEE Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI) 2020 to be held in April in Iowa, USA.
Professor Ye said, “The importance of AI technology is developing in the biomedical imaging field. I feel proud that my contributions have been internationally recognized and allowed me to be named an IEEE fellow.”
2019.12.18 View 11600 -
 KAIST Awarded the IPBC R&D Institution Team of the Year
KAIST was awarded the R&D Institution Team of the Year during the annual IPBC (Intellectual Property Business Congress) Asia 2019 held in Tokyo October 28-30. IPBC is a conference dedicated to IP value creation strategies hosted by IAM Media, a world’s leading IP business media platform.
IPBC Asia 2019 recognized the institutions and businesses that employed innovative IP strategies and management to produce the greatest IP value in 11 categories covering automotive, electronics, healthcare and biotechnology, internet and software, R&D institutions, semiconductors, industrials, mobile and telecommunications, Asia IP deals, Asia teams, and Asia individuals. This year, KAIST was recognized as one of the most active patentees in the Asia-Pacific region by significantly increasing its IP value through licensing and tech transfers.
Associate Vice President Kyung Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation remarked, “We are so delighted to prove the strong research capacity of KAIST. This will help us accomplish our vision of being a leading university that creates global impact.”
2019.12.04 View 9218
KAIST Awarded the IPBC R&D Institution Team of the Year
KAIST was awarded the R&D Institution Team of the Year during the annual IPBC (Intellectual Property Business Congress) Asia 2019 held in Tokyo October 28-30. IPBC is a conference dedicated to IP value creation strategies hosted by IAM Media, a world’s leading IP business media platform.
IPBC Asia 2019 recognized the institutions and businesses that employed innovative IP strategies and management to produce the greatest IP value in 11 categories covering automotive, electronics, healthcare and biotechnology, internet and software, R&D institutions, semiconductors, industrials, mobile and telecommunications, Asia IP deals, Asia teams, and Asia individuals. This year, KAIST was recognized as one of the most active patentees in the Asia-Pacific region by significantly increasing its IP value through licensing and tech transfers.
Associate Vice President Kyung Cheol Choi of the Office of University-Industry Cooperation remarked, “We are so delighted to prove the strong research capacity of KAIST. This will help us accomplish our vision of being a leading university that creates global impact.”
2019.12.04 View 9218 -
 KAIST and Google Jointly Develop AI Curricula
KAIST selected the two professors who will develop AI curriculum under the auspices of the KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research. The Graduate School of AI announced the two authors among the 20 applicants who will develop the curriculum next year. They will be provided 7,500 USD per subject.
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Yong-Jin Yoon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will use Google technology such as TensorFlow, Google Cloud, and Android to create the curriculum.
Professor Suh’s “TensorFlow for Information Theory and Convex Optimization “will be used for curriculum in the graduate courses and Professor Yoon’s “AI Convergence Project Based Learning (PBL)” will be used for online courses. Professor Yoon’s course will explore and define problems by utilizing AI and experiencing the process of developing products that use AI through design thinking, which involves product design, production, and verification. Professor Suh’s course will discus“information theory and convergence,” which uses basic sciences and engineering as well as AI, machine learning, and deep learning.
2019.12.04 View 16276
KAIST and Google Jointly Develop AI Curricula
KAIST selected the two professors who will develop AI curriculum under the auspices of the KAIST-Google Partnership for AI Education and Research. The Graduate School of AI announced the two authors among the 20 applicants who will develop the curriculum next year. They will be provided 7,500 USD per subject.
Professor Changho Suh from the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Yong-Jin Yoon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering will use Google technology such as TensorFlow, Google Cloud, and Android to create the curriculum.
Professor Suh’s “TensorFlow for Information Theory and Convex Optimization “will be used for curriculum in the graduate courses and Professor Yoon’s “AI Convergence Project Based Learning (PBL)” will be used for online courses. Professor Yoon’s course will explore and define problems by utilizing AI and experiencing the process of developing products that use AI through design thinking, which involves product design, production, and verification. Professor Suh’s course will discus“information theory and convergence,” which uses basic sciences and engineering as well as AI, machine learning, and deep learning.
2019.12.04 View 16276 -
 ‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 15726
‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 15726