ICT
-
 Professor Byungha Shin Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering won the Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on May 4. Professor Shin was recognized for his research in the field of next-generation perovskite solar cells and received 10 million won in prize money.
To achieve ‘carbon neutrality,’ which many countries across the globe including Korea hope to realize, the efficiency of converting renewable energies to electricity must be improved. Solar cells convert solar energy to electricity. Since single solar cells show lower efficiency, the development of ‘tandem solar cells’ that connect two or more cells together has been popular in recent years.
However, although ‘perovskite’ received attention as a next-generation material for tandem solar cells, it is sensitive to the external environment including light and moisture, making it difficult to maintain stability.
Professor Shin discovered that, theoretically, adding certain anion additives to perovskite solar cells would allow the control of the electrical and structural properties of the two-dimensional stabilization layer that forms inside the film. He confirmed this through high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Controlling the amount of anions in the additives allowed the preservation of over 80% of the initial stability even after 1000 hours of continuous exposure to sunlight.
Based on this discovery, Professor Shin combined silicon with solar cells to create a tandem solar cell with 26.7% energy convergence efficiency. Considering that the highest-efficiency tandem solar cell in existence showed 29.5% efficiency, this figure is quite high. Professor Shin’s perovskite solar cell is also combinable with the CIGS (Cu(In,Ga)Se2) thin-film solar cell composed of copper (Cu), indium (In), gallium (Ga), and selenium (Se2).
Professor Shin’s research results were published in the online edition of the journal Science in April of last year.
“This research is meaningful for having suggested a direction for solar cell material stabilization using additives,” said Professor Shin. “I look forward to this technique being applied to a wide range of photoelectrical devices including solar cells, LEDs, and photodetectors,” he added.
(END)
2021.05.07 View 11448
Professor Byungha Shin Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Byungha Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering won the Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on May 4. Professor Shin was recognized for his research in the field of next-generation perovskite solar cells and received 10 million won in prize money.
To achieve ‘carbon neutrality,’ which many countries across the globe including Korea hope to realize, the efficiency of converting renewable energies to electricity must be improved. Solar cells convert solar energy to electricity. Since single solar cells show lower efficiency, the development of ‘tandem solar cells’ that connect two or more cells together has been popular in recent years.
However, although ‘perovskite’ received attention as a next-generation material for tandem solar cells, it is sensitive to the external environment including light and moisture, making it difficult to maintain stability.
Professor Shin discovered that, theoretically, adding certain anion additives to perovskite solar cells would allow the control of the electrical and structural properties of the two-dimensional stabilization layer that forms inside the film. He confirmed this through high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Controlling the amount of anions in the additives allowed the preservation of over 80% of the initial stability even after 1000 hours of continuous exposure to sunlight.
Based on this discovery, Professor Shin combined silicon with solar cells to create a tandem solar cell with 26.7% energy convergence efficiency. Considering that the highest-efficiency tandem solar cell in existence showed 29.5% efficiency, this figure is quite high. Professor Shin’s perovskite solar cell is also combinable with the CIGS (Cu(In,Ga)Se2) thin-film solar cell composed of copper (Cu), indium (In), gallium (Ga), and selenium (Se2).
Professor Shin’s research results were published in the online edition of the journal Science in April of last year.
“This research is meaningful for having suggested a direction for solar cell material stabilization using additives,” said Professor Shin. “I look forward to this technique being applied to a wide range of photoelectrical devices including solar cells, LEDs, and photodetectors,” he added.
(END)
2021.05.07 View 11448 -
 ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 34333
ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 34333 -
 Professor Bumjoon Kim Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won January’s Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on January 6. Professor Kim also received 10 million won in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his research in the field of fuel cells. Since the first paper on fuel cells was published in 1839 by the German chemist Friedrich Schonbein, there has been an increase in the number of fields in which fuel cells are used, including national defense, aerospace engineering, and autonomous vehicles.
Professor Kim developed carbonized block copolymer particles with high durability and a high-performance fuel cell. Block copolymers are two different polymers cross-linked into a chain structure. Various nanostructures can be made effectively by using the attractive and repulsive forces between the chains.
Professor Kim used the membrane emulsification technique, employing a high-performance separation membrane to develop a platform that makes the mass production of highly durable carbonized particles possible, which he then used to develop high-performance energy devices like fuel cells.
The carbonized particles designed by Professor Kim and his research team were used to create the world’s more durable fuel cells that boast outstanding performance while using only five percent of the costly platinum needed for existing commercialized products.
The team’s research results were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and Energy Environmental Science in May and July of last year.
“We have developed a fuel cell that ticks all the boxes including performance, durability, and cost,” said Professor Kim. “Related techniques will not be limited to fuel cells, but could also be applied to the development of various energy devices like solar cells and secondary cells,” he added.
(END)
2021.01.22 View 13708
Professor Bumjoon Kim Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won January’s Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on January 6. Professor Kim also received 10 million won in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his research in the field of fuel cells. Since the first paper on fuel cells was published in 1839 by the German chemist Friedrich Schonbein, there has been an increase in the number of fields in which fuel cells are used, including national defense, aerospace engineering, and autonomous vehicles.
Professor Kim developed carbonized block copolymer particles with high durability and a high-performance fuel cell. Block copolymers are two different polymers cross-linked into a chain structure. Various nanostructures can be made effectively by using the attractive and repulsive forces between the chains.
Professor Kim used the membrane emulsification technique, employing a high-performance separation membrane to develop a platform that makes the mass production of highly durable carbonized particles possible, which he then used to develop high-performance energy devices like fuel cells.
The carbonized particles designed by Professor Kim and his research team were used to create the world’s more durable fuel cells that boast outstanding performance while using only five percent of the costly platinum needed for existing commercialized products.
The team’s research results were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and Energy Environmental Science in May and July of last year.
“We have developed a fuel cell that ticks all the boxes including performance, durability, and cost,” said Professor Kim. “Related techniques will not be limited to fuel cells, but could also be applied to the development of various energy devices like solar cells and secondary cells,” he added.
(END)
2021.01.22 View 13708 -
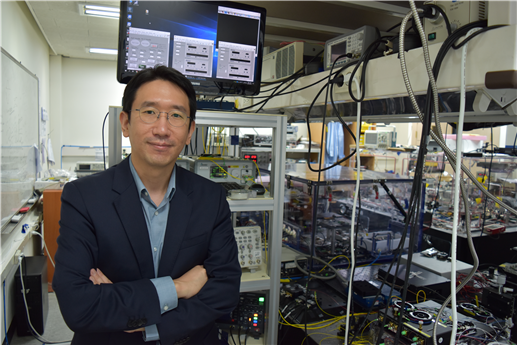 Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 13711
Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 13711 -
 Slippery When Wet: Fish and Seaweed Inspire Ships to Reduce Fluid Friction
Faster ships could be on the horizon after KAIST scientists develop a slippery surface inspired by fish and seaweed to reduce the hull's drag through the water.
Long-distance cargo ships lose a significant amount of energy due to fluid friction. Looking to the drag reduction mechanisms employed by aquatic life can provide inspiration on how to improve efficiency.
Fish and seaweed secrete a layer of mucus to create a slippery surface, reducing their friction as they travel through water. A potential way to mimic this is by creating lubricant-infused surfaces covered with cavities. As the cavities are continuously filled with the lubricant, a layer is formed over the surface.
Though this method has previously been shown to work, reducing drag by up to 18%, the underlying physics is not fully understood. KAIST researchers in collaboration with a team of researchers from POSTECH conducted simulations of this process to help explain the effects, and their findings were published in the journal Physics of Fluids on September 15.
The group looked at the average speed of a cargo ship with realistic material properties and simulated how it behaves under various lubrication setups. Specifically, they monitored the effects of the open area of the lubricant-filled cavities, as well as the thickness of the cavity lids.
They found that for larger open areas, the lubricant spreads more than it does with smaller open areas, leading to a slipperier surface. On the other hand, the lid thickness does not have much of an effect on the slip, though a thicker lid does create a thicker lubricant buildup layer.
Professor Emeritus Hyung Jin Sung from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering who led this study said, “Our investigation of the hydrodynamics of a lubricant layer and how it results in drag reduction with a slippery surface in a basic configuration has provided significant insight into the benefits of a lubricant-infused surface.”
Now that they have worked on optimizing the lubricant secretion design, the authors hope it can be implemented in real-life marine vehicles.
“If the present design parameters are adopted, the drag reduction rate will increase significantly,” Professor Sung added.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Source:
Materials provided by American Institute of Physics.
Publication:
Kim, Seung Joong, et al. (2020). A lubricant-infused slip surface for drag reduction. Physics of Fluids. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0018460
Profile:
Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Emeritus
hyungjin@kaist.ac.kr
http://flow.kaist.ac.kr/index.php
Flow Control Lab. (FCL)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.10.12 View 8467
Slippery When Wet: Fish and Seaweed Inspire Ships to Reduce Fluid Friction
Faster ships could be on the horizon after KAIST scientists develop a slippery surface inspired by fish and seaweed to reduce the hull's drag through the water.
Long-distance cargo ships lose a significant amount of energy due to fluid friction. Looking to the drag reduction mechanisms employed by aquatic life can provide inspiration on how to improve efficiency.
Fish and seaweed secrete a layer of mucus to create a slippery surface, reducing their friction as they travel through water. A potential way to mimic this is by creating lubricant-infused surfaces covered with cavities. As the cavities are continuously filled with the lubricant, a layer is formed over the surface.
Though this method has previously been shown to work, reducing drag by up to 18%, the underlying physics is not fully understood. KAIST researchers in collaboration with a team of researchers from POSTECH conducted simulations of this process to help explain the effects, and their findings were published in the journal Physics of Fluids on September 15.
The group looked at the average speed of a cargo ship with realistic material properties and simulated how it behaves under various lubrication setups. Specifically, they monitored the effects of the open area of the lubricant-filled cavities, as well as the thickness of the cavity lids.
They found that for larger open areas, the lubricant spreads more than it does with smaller open areas, leading to a slipperier surface. On the other hand, the lid thickness does not have much of an effect on the slip, though a thicker lid does create a thicker lubricant buildup layer.
Professor Emeritus Hyung Jin Sung from the KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering who led this study said, “Our investigation of the hydrodynamics of a lubricant layer and how it results in drag reduction with a slippery surface in a basic configuration has provided significant insight into the benefits of a lubricant-infused surface.”
Now that they have worked on optimizing the lubricant secretion design, the authors hope it can be implemented in real-life marine vehicles.
“If the present design parameters are adopted, the drag reduction rate will increase significantly,” Professor Sung added.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Source:
Materials provided by American Institute of Physics.
Publication:
Kim, Seung Joong, et al. (2020). A lubricant-infused slip surface for drag reduction. Physics of Fluids. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0018460
Profile:
Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Emeritus
hyungjin@kaist.ac.kr
http://flow.kaist.ac.kr/index.php
Flow Control Lab. (FCL)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.10.12 View 8467 -
 Long Economic Depressions and Disparities Loom in the Wake of the COVID-19
"Global Cooperation for Managing Data Key to Mitigating the Impacts Around the World"
<Full recorded video of the GSI-IF2020>
The COVID-19 pandemic will lead to long economic depressions around the entire world. Experts predicted that the prevalent inequities among the countries, regions, and individuals will aggravate the economic crisis. However, crises always come with new opportunities and international cooperation and solidarity will help creating a new normal in the post-coronavirus era.
In a very basic but urgent step, global cooperation for managing data is the key to respond to COVID-19 since medicine and healthcare are intertwined with data science, said experts during an online international forum hosted by the Global Strategy Institute at KAIST on April 22.
KAIST launched its think-tank, the Global Strategy Institute (GSI), in February. The GSI aims to identify global issues proactively and help make breakthroughs well aligned with solid science-based policies.
The inaugural forum of the GSI focused on how the COVID-19 pandemic would impact socio-economic, scientific, and political landscapes, under the theme “Global Cooperation in the Coronavirus Era.”
In his opening remarks, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that future global governance will be dominated by the power of science and technology. “If we can implement efficient policies together with troubleshooting technology for responding to future crises, we will emerge stronger than before,” he said.
President Shin said ‘the Korean model’, which is being recognized as a shining example for dealing with the pandemic, is the result of collaborations combining the creativity of the private sector, the public sector’s strong infrastructure, and the full support of the citizens. He added, “Without the technological prowess coming from the competent R&D power of Korea, we could not achieve these impressive results.”
“Creative collaboration among the private and public sectors, along with research universities from around the world, will help shore up global resilience against the epidemic. We should work together to build a world of growing prosperity,” President Shin said.
Prime Minister Sye-Kyun Chung, who is in charge of the Central Disaster and Safety Countermeasures Headquarters in Korea, stressed global solidarity in his welcoming remarks, saying that “We need to share information and rely on the strength of our connections, rather than retreating into nationalistic isolation.”
Peter Lee, Vice President of the Microsoft Healthcare, pointed out in his welcoming remarks three critical sectors for global cooperation: medicine and healthcare, public health and prevention, and life and the economy. He emphasized the rule of thumb for managing data, saying that data in these fields should be open, standardized, and shared among countries to combat this global pandemic.
During a keynote session, Director General of the International Vaccine Institute (IVI) Jerome Kim described the challenges that go along with developing a vaccine. Dr. Kim said that only 7% of vaccine candidates go through the clinical trial stages, and it will take five to 10 years to completely prove a new vaccine’s safety after completing three stages of clinical tests.
“It’s very challenging to develop the vaccine for COVID-19 within 12 to 15 months,” said Dr. Kim. He added that 78 out of 115 candidates are currently undergoing clinical trials around the world.
There are five groups, including Moderna, Inovio, Jenner Institute, CanSino, and the Beijing Institute of Biological Products, who are doing clinical trials in phases 1 and 2. “Given the fact that COVID-19 is a totally new type of virus, various stakeholders’ participation, such as the National Immunization Technical Advisory Groups, the WHO, and UNICEF, is needed to work together to benefit the entire world,” he pointed out.
Professor Edward Yoonjae Choi from the Graduate School of AI at KAIST shared how AI and data sciences are being utilized to interpret the major trends of the epidemic. His group mainly focuses on deep learning to model electronic health records (EHR) for disease predictions. Professor Choi said AI and machine learning would be crucial solutions and collaborative research projects will surely accelerate how quickly we can overcome the pandemic.
In addition, Dr. Kijung Shin’s group is interpreting the SIR (Susceptible, Infected, and Recovered) model in Korea to predict the number of infections and when people were infected. However, researchers noticed that they could not see the typical modeling in Korea for predicting the number of infections since the model disregarded the new variable of humans’ efforts to stop the spread the virus.
According to research by Professor Steven Whang’s group on social distancing and face mask distribution among vulnerable age groups, people in their 20s, 60s, and 70s followed the social distancing guidelines the most strictly. The research team analyzed the data provided by SK Telecom in the Gangnam district of Seoul. The data provided on people in their 70s, a group that accounted for half of all fatalities, showed that masks were generally well distributed nationwide.
Dr. Alexandros Papaspyrids, Tertiary Education Industry Director of the Asia region of Microsoft, said that despite all the disadvantages and problems related to remote education, we shouldn’t expect to return to the days before the COVID-19 any time soon. “We should accept the new normal and explore new opportunities in the new educational environment,” he said.
Hongtaek Yong, Deputy Minister at the Office of R&D Policy at the Ministry of Science and ICT presented the Korean government’s disease prevention and response policy and how they tried to mitigate the economic and social impact.
He stressed the government’s fast testing, tracing, and openness for successfully flattening the curve, adding that the government used an ICT-based approach in all aspects of their response. From early this year when the first patient was reported, the government aggressively encouraged the biotech industry to develop diagnostic kits and novel therapeutic medications.
As a result, five companies were able to produce genetic diagnostic reagents through the emergency approval. More notably, four of them are conducting massive R&D projects sponsored by the government and this is the result of the government’s continuous investment in R&D. Korea is the leader in R&D investment among the OECD countries.
According to Yong, the government’s big data project that was launched in 2017 continuously traces the trends of epidemics in Korea. The epidemiological studies based on the paths taken by suspected patients using credit card transaction made the difference in predicting the spread of the coronavirus and implementing countermeasures. The data has been provided to the Korea’s Center for Disease Control (CDC).
“In addition to the epidemics, we have so many other pending issues arising from digital and social equities, un-contact services, and job security. We are very open to collaborate and cooperate with other countries to deal with this global crisis,” Yong said.
During the subsequent panel discussions, David Dollar, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, said, “The global economy in the coronavirus era will not have a rapid V-shaped recovery, but rather will fall into a long depression for at least two years.” He pointed out that if countries practice protectionism like they did during the Great Depression, the recession will be even worse. Hence, he urged the international community, especially developed nations, to avoid protectionism, consider the economic difficulties of developing countries, and provide them with financial support.
Co-Director of the Center for Universal Education at the Brookings Institution Rebecca Winthrop raised concerns over the recent shift to online teaching and learning, claiming that insufficient infrastructures in low-income families in developing nations are already causing added educational disparities and provoking the inequity issue around the world. “The ways to provide quality education equally through faster and more effective means should be studied,” she said.
Professor Joungho Kim, the director of the KAIST GSI and the forum’s organizer, concluded the event by saying that this forum will be a valuable resource for everyone who is providing assistance to those in need, both during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
(END)
2020.04.22 View 24200
Long Economic Depressions and Disparities Loom in the Wake of the COVID-19
"Global Cooperation for Managing Data Key to Mitigating the Impacts Around the World"
<Full recorded video of the GSI-IF2020>
The COVID-19 pandemic will lead to long economic depressions around the entire world. Experts predicted that the prevalent inequities among the countries, regions, and individuals will aggravate the economic crisis. However, crises always come with new opportunities and international cooperation and solidarity will help creating a new normal in the post-coronavirus era.
In a very basic but urgent step, global cooperation for managing data is the key to respond to COVID-19 since medicine and healthcare are intertwined with data science, said experts during an online international forum hosted by the Global Strategy Institute at KAIST on April 22.
KAIST launched its think-tank, the Global Strategy Institute (GSI), in February. The GSI aims to identify global issues proactively and help make breakthroughs well aligned with solid science-based policies.
The inaugural forum of the GSI focused on how the COVID-19 pandemic would impact socio-economic, scientific, and political landscapes, under the theme “Global Cooperation in the Coronavirus Era.”
In his opening remarks, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that future global governance will be dominated by the power of science and technology. “If we can implement efficient policies together with troubleshooting technology for responding to future crises, we will emerge stronger than before,” he said.
President Shin said ‘the Korean model’, which is being recognized as a shining example for dealing with the pandemic, is the result of collaborations combining the creativity of the private sector, the public sector’s strong infrastructure, and the full support of the citizens. He added, “Without the technological prowess coming from the competent R&D power of Korea, we could not achieve these impressive results.”
“Creative collaboration among the private and public sectors, along with research universities from around the world, will help shore up global resilience against the epidemic. We should work together to build a world of growing prosperity,” President Shin said.
Prime Minister Sye-Kyun Chung, who is in charge of the Central Disaster and Safety Countermeasures Headquarters in Korea, stressed global solidarity in his welcoming remarks, saying that “We need to share information and rely on the strength of our connections, rather than retreating into nationalistic isolation.”
Peter Lee, Vice President of the Microsoft Healthcare, pointed out in his welcoming remarks three critical sectors for global cooperation: medicine and healthcare, public health and prevention, and life and the economy. He emphasized the rule of thumb for managing data, saying that data in these fields should be open, standardized, and shared among countries to combat this global pandemic.
During a keynote session, Director General of the International Vaccine Institute (IVI) Jerome Kim described the challenges that go along with developing a vaccine. Dr. Kim said that only 7% of vaccine candidates go through the clinical trial stages, and it will take five to 10 years to completely prove a new vaccine’s safety after completing three stages of clinical tests.
“It’s very challenging to develop the vaccine for COVID-19 within 12 to 15 months,” said Dr. Kim. He added that 78 out of 115 candidates are currently undergoing clinical trials around the world.
There are five groups, including Moderna, Inovio, Jenner Institute, CanSino, and the Beijing Institute of Biological Products, who are doing clinical trials in phases 1 and 2. “Given the fact that COVID-19 is a totally new type of virus, various stakeholders’ participation, such as the National Immunization Technical Advisory Groups, the WHO, and UNICEF, is needed to work together to benefit the entire world,” he pointed out.
Professor Edward Yoonjae Choi from the Graduate School of AI at KAIST shared how AI and data sciences are being utilized to interpret the major trends of the epidemic. His group mainly focuses on deep learning to model electronic health records (EHR) for disease predictions. Professor Choi said AI and machine learning would be crucial solutions and collaborative research projects will surely accelerate how quickly we can overcome the pandemic.
In addition, Dr. Kijung Shin’s group is interpreting the SIR (Susceptible, Infected, and Recovered) model in Korea to predict the number of infections and when people were infected. However, researchers noticed that they could not see the typical modeling in Korea for predicting the number of infections since the model disregarded the new variable of humans’ efforts to stop the spread the virus.
According to research by Professor Steven Whang’s group on social distancing and face mask distribution among vulnerable age groups, people in their 20s, 60s, and 70s followed the social distancing guidelines the most strictly. The research team analyzed the data provided by SK Telecom in the Gangnam district of Seoul. The data provided on people in their 70s, a group that accounted for half of all fatalities, showed that masks were generally well distributed nationwide.
Dr. Alexandros Papaspyrids, Tertiary Education Industry Director of the Asia region of Microsoft, said that despite all the disadvantages and problems related to remote education, we shouldn’t expect to return to the days before the COVID-19 any time soon. “We should accept the new normal and explore new opportunities in the new educational environment,” he said.
Hongtaek Yong, Deputy Minister at the Office of R&D Policy at the Ministry of Science and ICT presented the Korean government’s disease prevention and response policy and how they tried to mitigate the economic and social impact.
He stressed the government’s fast testing, tracing, and openness for successfully flattening the curve, adding that the government used an ICT-based approach in all aspects of their response. From early this year when the first patient was reported, the government aggressively encouraged the biotech industry to develop diagnostic kits and novel therapeutic medications.
As a result, five companies were able to produce genetic diagnostic reagents through the emergency approval. More notably, four of them are conducting massive R&D projects sponsored by the government and this is the result of the government’s continuous investment in R&D. Korea is the leader in R&D investment among the OECD countries.
According to Yong, the government’s big data project that was launched in 2017 continuously traces the trends of epidemics in Korea. The epidemiological studies based on the paths taken by suspected patients using credit card transaction made the difference in predicting the spread of the coronavirus and implementing countermeasures. The data has been provided to the Korea’s Center for Disease Control (CDC).
“In addition to the epidemics, we have so many other pending issues arising from digital and social equities, un-contact services, and job security. We are very open to collaborate and cooperate with other countries to deal with this global crisis,” Yong said.
During the subsequent panel discussions, David Dollar, a senior fellow at the Brookings Institution, said, “The global economy in the coronavirus era will not have a rapid V-shaped recovery, but rather will fall into a long depression for at least two years.” He pointed out that if countries practice protectionism like they did during the Great Depression, the recession will be even worse. Hence, he urged the international community, especially developed nations, to avoid protectionism, consider the economic difficulties of developing countries, and provide them with financial support.
Co-Director of the Center for Universal Education at the Brookings Institution Rebecca Winthrop raised concerns over the recent shift to online teaching and learning, claiming that insufficient infrastructures in low-income families in developing nations are already causing added educational disparities and provoking the inequity issue around the world. “The ways to provide quality education equally through faster and more effective means should be studied,” she said.
Professor Joungho Kim, the director of the KAIST GSI and the forum’s organizer, concluded the event by saying that this forum will be a valuable resource for everyone who is providing assistance to those in need, both during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
(END)
2020.04.22 View 24200 -
 Professor Sungyeol Choi Receives Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Sungyeol Choi >
Professor Sungyeol Choi from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering received the Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation on the 9th Annual Nuclear Safety and Promotion Day last month, in recognition of his contributions to the promotion of nuclear energy through the safe management of spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste.
Professor Choi developed high-precision, multi-physics codes that can predict and prevent abnormal power fluctuations caused by boron hideout within nuclear fuel in a pressurized water reactor, solving the problem that has caused economic losses of tens of billions of won every year from industrial sites.
He is now developing a new technology that can reduce high-level waste by recycling spent nuclear fuel, while preventing nuclear material from being used for nuclear weapons, which is one of the biggest challenges faced by the nuclear industry.
In 2017, his first year in office as a KAIST professor, Professor Choi was selected as the youngest and the only member under 50 of the Standing Scientific Advisory Committee at the Information Exchange Meeting on Partitioning and Transmutation (IEMPT), an authoritative association on the disposal of high-level nuclear waste.
The following year, he became the first Korean to receive the Early Career Award, which is given to one person every two years by the International Youth Nuclear Congress.
2020.01.15 View 6102
Professor Sungyeol Choi Receives Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Sungyeol Choi >
Professor Sungyeol Choi from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering received the Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation on the 9th Annual Nuclear Safety and Promotion Day last month, in recognition of his contributions to the promotion of nuclear energy through the safe management of spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste.
Professor Choi developed high-precision, multi-physics codes that can predict and prevent abnormal power fluctuations caused by boron hideout within nuclear fuel in a pressurized water reactor, solving the problem that has caused economic losses of tens of billions of won every year from industrial sites.
He is now developing a new technology that can reduce high-level waste by recycling spent nuclear fuel, while preventing nuclear material from being used for nuclear weapons, which is one of the biggest challenges faced by the nuclear industry.
In 2017, his first year in office as a KAIST professor, Professor Choi was selected as the youngest and the only member under 50 of the Standing Scientific Advisory Committee at the Information Exchange Meeting on Partitioning and Transmutation (IEMPT), an authoritative association on the disposal of high-level nuclear waste.
The following year, he became the first Korean to receive the Early Career Award, which is given to one person every two years by the International Youth Nuclear Congress.
2020.01.15 View 6102 -
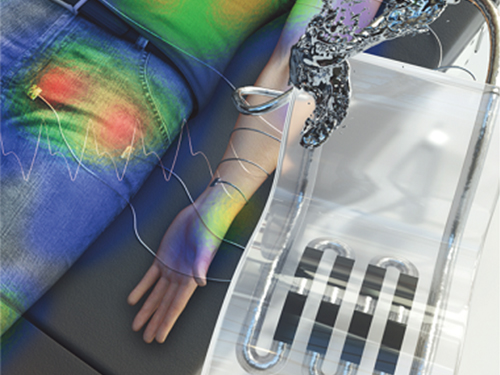 New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 16301
New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 16301 -
 Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 11506
Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 11506 -
 AI to Determine When to Intervene with Your Driving
(Professor Uichin Lee (left) and PhD candidate Auk Kim)
Can your AI agent judge when to talk to you while you are driving? According to a KAIST research team, their in-vehicle conservation service technology will judge when it is appropriate to contact you to ensure your safety.
Professor Uichin Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST and his research team have developed AI technology that automatically detects safe moments for AI agents to provide conversation services to drivers.
Their research focuses on solving the potential problems of distraction created by in-vehicle conversation services. If an AI agent talks to a driver at an inopportune moment, such as while making a turn, a car accident will be more likely to occur.
In-vehicle conversation services need to be convenient as well as safe. However, the cognitive burden of multitasking negatively influences the quality of the service. Users tend to be more distracted during certain traffic conditions. To address this long-standing challenge of the in-vehicle conversation services, the team introduced a composite cognitive model that considers both safe driving and auditory-verbal service performance and used a machine-learning model for all collected data.
The combination of these individual measures is able to determine the appropriate moments for conversation and most appropriate types of conversational services. For instance, in the case of delivering simple-context information, such as a weather forecast, driver safety alone would be the most appropriate consideration. Meanwhile, when delivering information that requires a driver response, such as a “Yes” or “No,” the combination of driver safety and auditory-verbal performance should be considered.
The research team developed a prototype of an in-vehicle conversation service based on a navigation app that can be used in real driving environments. The app was also connected to the vehicle to collect in-vehicle OBD-II/CAN data, such as the steering wheel angle and brake pedal position, and mobility and environmental data such as the distance between successive cars and traffic flow.
Using pseudo-conversation services, the research team collected a real-world driving dataset consisting of 1,388 interactions and sensor data from 29 drivers who interacted with AI conversational agents. Machine learning analysis based on the dataset demonstrated that the opportune moments for driver interruption could be correctly inferred with 87% accuracy.
The safety enhancement technology developed by the team is expected to minimize driver distractions caused by in-vehicle conversation services. This technology can be directly applied to current in-vehicle systems that provide conversation services. It can also be extended and applied to the real-time detection of driver distraction problems caused by the use of a smartphone while driving.
Professor Lee said, “In the near future, cars will proactively deliver various in-vehicle conversation services. This technology will certainly help vehicles interact with their drivers safely as it can fairly accurately determine when to provide conversation services using only basic sensor data generated by cars.”
The researchers presented their findings at the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Ubicomp’19) in London, UK. This research was supported in part by Hyundai NGV and by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Visual description of safe enhancement technology for in-vehicle conversation services)
2019.11.13 View 19682
AI to Determine When to Intervene with Your Driving
(Professor Uichin Lee (left) and PhD candidate Auk Kim)
Can your AI agent judge when to talk to you while you are driving? According to a KAIST research team, their in-vehicle conservation service technology will judge when it is appropriate to contact you to ensure your safety.
Professor Uichin Lee from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering at KAIST and his research team have developed AI technology that automatically detects safe moments for AI agents to provide conversation services to drivers.
Their research focuses on solving the potential problems of distraction created by in-vehicle conversation services. If an AI agent talks to a driver at an inopportune moment, such as while making a turn, a car accident will be more likely to occur.
In-vehicle conversation services need to be convenient as well as safe. However, the cognitive burden of multitasking negatively influences the quality of the service. Users tend to be more distracted during certain traffic conditions. To address this long-standing challenge of the in-vehicle conversation services, the team introduced a composite cognitive model that considers both safe driving and auditory-verbal service performance and used a machine-learning model for all collected data.
The combination of these individual measures is able to determine the appropriate moments for conversation and most appropriate types of conversational services. For instance, in the case of delivering simple-context information, such as a weather forecast, driver safety alone would be the most appropriate consideration. Meanwhile, when delivering information that requires a driver response, such as a “Yes” or “No,” the combination of driver safety and auditory-verbal performance should be considered.
The research team developed a prototype of an in-vehicle conversation service based on a navigation app that can be used in real driving environments. The app was also connected to the vehicle to collect in-vehicle OBD-II/CAN data, such as the steering wheel angle and brake pedal position, and mobility and environmental data such as the distance between successive cars and traffic flow.
Using pseudo-conversation services, the research team collected a real-world driving dataset consisting of 1,388 interactions and sensor data from 29 drivers who interacted with AI conversational agents. Machine learning analysis based on the dataset demonstrated that the opportune moments for driver interruption could be correctly inferred with 87% accuracy.
The safety enhancement technology developed by the team is expected to minimize driver distractions caused by in-vehicle conversation services. This technology can be directly applied to current in-vehicle systems that provide conversation services. It can also be extended and applied to the real-time detection of driver distraction problems caused by the use of a smartphone while driving.
Professor Lee said, “In the near future, cars will proactively deliver various in-vehicle conversation services. This technology will certainly help vehicles interact with their drivers safely as it can fairly accurately determine when to provide conversation services using only basic sensor data generated by cars.”
The researchers presented their findings at the ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (Ubicomp’19) in London, UK. This research was supported in part by Hyundai NGV and by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Visual description of safe enhancement technology for in-vehicle conversation services)
2019.11.13 View 19682 -
 Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 23026
Tungsten Suboxide Improves the Efficiency of Platinum in Hydrogen Production
< PhD Candidate Jinkyu Park and Professor Jinwoo Lee >
Researchers presented a new strategy for enhancing catalytic activity using tungsten suboxide as a single-atom catalyst (SAC). This strategy, which significantly improves hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in metal platinum (pt) by 16.3 times, sheds light on the development of new electrochemical catalyst technologies.
Hydrogen has been touted as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. However, most of the conventional industrial hydrogen production methods come with environmental issues, releasing significant amounts of carbon dioxide and greenhouse gases.
Electrochemical water splitting is considered a potential approach for clean hydrogen production. Pt is one of the most commonly used catalysts to improve HER performance in electrochemical water splitting, but the high cost and scarcity of Pt remain key obstacles to mass commercial applications.
SACs, where all metal species are individually dispersed on a desired support material, have been identified as one way to reduce the amount of Pt usage, as they offer the maximum number of surface exposed Pt atoms.
Inspired by earlier studies, which mainly focused on SACs supported by carbon-based materials, a KAIST research team led by Professor Jinwoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering investigated the influence of support materials on the performance of SACs.
Professor Lee and his researchers suggested mesoporous tungsten suboxide as a new support material for atomically dispersed Pt, as this was expected to provide high electronic conductivity and have a synergetic effect with Pt.
They compared the performance of single-atom Pt supported by carbon and tungsten suboxide respectively. The results revealed that the support effect occurred with tungsten suboxide, in which the mass activity of a single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide was 2.1 times greater than that of single-atom Pt supported by carbon, and 16.3 times higher than that of Pt nanoparticles supported by carbon.
The team indicated a change in the electronic structure of Pt via charge transfer from tungsten suboxide to Pt. This phenomenon was reported as a result of strong metal-support interaction between Pt and tungsten suboxide.
HER performance can be improved not only by changing the electronic structure of the supported metal, but also by inducing another support effect, the spillover effect, the research group reported. Hydrogen spillover is a phenomenon where adsorbed hydrogen migrates from one surface to another, and it occurs more easily as the Pt size becomes smaller.
The researchers compared the performance of single-atom Pt and Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide. The single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide exhibited a higher degree of hydrogen spillover phenomenon, which enhanced the Pt mass activity for hydrogen evolution up to 10.7 times compared to Pt nanoparticles supported by tungsten suboxide.
Professor Lee said, “Choosing the right support material is important for improving electrocatalysis in hydrogen production. The tungsten suboxide catalyst we used to support Pt in our study implies that interactions between the well-matched metal and support can drastically enhance the efficiency of the process.”
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and introduced in the International Edition of the German journal Angewandte Chemie.
Figure. Schematic representation of hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) of pseudo single-atom Pt supported by tungsten suboxide
-Publication
Jinkyu Park, Dr. Seonggyu Lee, Hee-Eun Kim, Ara Cho, Seongbeen Kim, Dr. Youngjin Ye, Prof. Jeong Woo Han, Prof. Hyunjoo Lee, Dr. Jong Hyun Jang, and Prof. Jinwoo Lee. 2019. Investigation of the Support Effect in Atomically Dispersed Pt on WO3−x for Utilization of Pt in the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. International Edition of Angewandte Chemie. Volume No. 58. Issue No. 45. 6 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201908122
-ProfileProfessor Jinwoo LeeConvergence of Energy and Nano Science Laboratoryhttp://cens.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2019.10.28 View 23026 -
 Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 13811
Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 13811