Chemistry
-
 Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 9612
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 9612 -
 Professor Mu-Hyun Baik Honored with the POSCO TJ Park Prize
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik at the Department of Chemistry was honored to be the recipient of the 2021 POSCO TJ Park Prize in Science. The POSCO TJ Park Foundation awards every year the individual or organization which made significant contribution in science, education, community development, philanthropy, and technology.
Professor Baik, a renowned computational chemist in analyzing complicated chemical reactions to understand how molecules behave and how they change. Professor Baik was awarded in recognition of his pioneering research in designing numerous organometallic catalysts with using computational molecular modelling. In 2016, he published in Science on the catalytic borylation of methane that showed how chemical reactions can be carried out using the natural gas methane as a substrate.
In 2020, he reported in Science that electrodes can be used as functional groups with adjustable inductive effects to change the chemical reactivity of molecules that are attached to them, closely mimicking the inductive effect of conventional functional groups. This constitutes a potentially powerful new way of controlling chemical reactions, offering an alternative to preparing derivatives to install electron-withdrawing functional groups.
Joined at KAIST in 2015, Professor Baik also serves as associate director at the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalization at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) since 2015. Among the many recognitions and awards that he received include the Kavli Fellowship by the Kavli Foundation and the National Academy of Science in the US in 2019 and the 2018 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Award by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Germany.
2021.03.11 View 10719
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik Honored with the POSCO TJ Park Prize
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik at the Department of Chemistry was honored to be the recipient of the 2021 POSCO TJ Park Prize in Science. The POSCO TJ Park Foundation awards every year the individual or organization which made significant contribution in science, education, community development, philanthropy, and technology.
Professor Baik, a renowned computational chemist in analyzing complicated chemical reactions to understand how molecules behave and how they change. Professor Baik was awarded in recognition of his pioneering research in designing numerous organometallic catalysts with using computational molecular modelling. In 2016, he published in Science on the catalytic borylation of methane that showed how chemical reactions can be carried out using the natural gas methane as a substrate.
In 2020, he reported in Science that electrodes can be used as functional groups with adjustable inductive effects to change the chemical reactivity of molecules that are attached to them, closely mimicking the inductive effect of conventional functional groups. This constitutes a potentially powerful new way of controlling chemical reactions, offering an alternative to preparing derivatives to install electron-withdrawing functional groups.
Joined at KAIST in 2015, Professor Baik also serves as associate director at the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalization at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) since 2015. Among the many recognitions and awards that he received include the Kavli Fellowship by the Kavli Foundation and the National Academy of Science in the US in 2019 and the 2018 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Award by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Germany.
2021.03.11 View 10719 -
 ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 35997
ACS Nano Special Edition Highlights Innovations at KAIST
- The collective intelligence and technological innovation of KAIST was highlighted with case studies including the Post-COVID-19 New Deal R&D Initiative Project. -
KAIST’s innovative academic achievements and R&D efforts for addressing the world’s greatest challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic were featured in ACS Nano as part of its special virtual issue commemorating the 50th anniversary of KAIST. The issue consisted of 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from five departments, including two from Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who serves as an associate editor of the ACS Nano.
ACS Nano, the leading international journal in nanoscience and nanotechnology, published a special virtual issue last month, titled ‘Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues.’
This special virtual issue introduced KAIST’s vision of becoming a ‘global value-creative leading university’ and its progress toward this vision over the last 50 years. The issue explained how KAIST has served as the main hub for advanced scientific research and technological innovation in South Korea since its establishment in 1971, and how its faculty and over 69,000 graduates played a key role in propelling the nation’s rapid industrialization and economic development.
The issue also emphasized the need for KAIST to enhance global cooperation and the exchange of ideas in the years to come, especially during the post-COVID era intertwined with the Fourth Industrial Revolution (4IR). In this regard, the issue cited the first ‘KAIST Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS)’, which was held online for five days in September of last year with a global audience of over 10,000 participating live via Zoom and YouTube, as a successful example of what academic collaboration could look like in the post-COVID and 4IR eras.
In addition, the “Science & Technology New Deal Project for COVID-19 Response,” a project conducted by KAIST with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) of South Korea, was also introduced as another excellent case of KAIST’s collective intelligence and technological innovation. The issue highlighted some key achievements from this project for overcoming the pandemic-driven crisis, such as: reusable anti-virus filters, negative-pressure ambulances for integrated patient transport and hospitalization, and movable and expandable negative-pressure ward modules.
“We hold our expectations high for the outstanding achievements and progress KAIST will have made by its centennial,” said Professor Kim on the background of curating the 14 review articles contributed by KAIST faculty from the fields of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE), Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE), Nuclear and Quantum Engineering (NQE), Electrical Engineering (EE), and Chemistry (Chem).
Review articles discussing emerging materials and their properties covered photonic carbon dots (Professor Chan Beum Park, MSE), single-atom and ensemble catalysts (Professor Hyunjoo Lee, CBE), and metal/metal oxide electrocatalysts (Professor Sung-Yoon Chung, MSE).
Review articles discussing materials processing covered 2D layered materials synthesis based on interlayer engineering (Professor Kibum Kang, MSE), eco-friendly methods for solar cell production (Professor Bumjoon J. Kim, CBE), an ex-solution process for the synthesis of highly stable catalysts (Professor WooChul Jung, MSE), and 3D light-patterning synthesis of ordered nanostructures (Professor Seokwoo Jeon, MSE, and Professor Dongchan Jang, NQE).
Review articles discussing advanced analysis techniques covered operando materials analyses (Professor Jeong Yeong Park, Chem), graphene liquid cell transmission electron microscopy (Professor Jong Min Yuk, MSE), and multiscale modeling and visualization of materials systems (Professor Seungbum Hong, MSE).
Review articles discussing practical state-of-the-art devices covered chemiresistive hydrogen sensors (Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE), patient-friendly diagnostics and implantable treatment devices (Professor Steve Park, MSE), triboelectric nanogenerators (Professor Yang-Kyu Choi, EE), and next-generation lithium-air batteries (Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Chem, and Professor Il-Doo Kim, MSE).
In addition to Professor Il-Doo Kim, post-doctoral researcher Dr. Jaewan Ahn from the KAIST Applied Science Research Institute, Dean of the College of Engineering at KAIST Professor Choongsik Bae, and ACS Nano Editor-in-Chief Professor Paul S. Weiss from the University of California, Los Angeles also contributed to the publication of this ACS Nano special virtual issue.
The issue can be viewed and downloaded from the ACS Nano website at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101.
Image credit: KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image,with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Ahn, J., et al. (2021) Celebrating 50 Years of KAIST: Collective Intelligence and Innovation for Confronting Contemporary Issues. ACS Nano 15(3): 1895-1907. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c01101
Profile:
Il-Doo Kim, Ph.D
Chair Professor
idkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://advnano.kaist.ac.kr
Advanced Nanomaterials and Energy Lab.
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Membrane Innovation Center for Anti-Virus and Air-Quality Control
https://kaist.ac.kr/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.03.05 View 35997 -
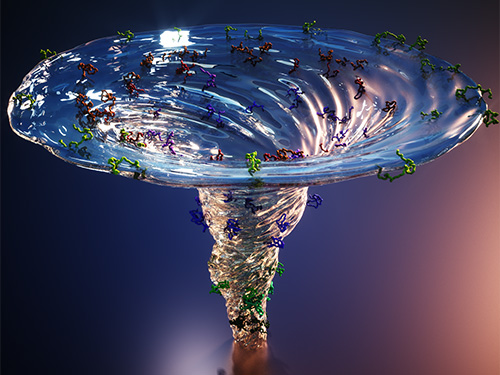 X-ray Scattering Shines Light on Protein Folding
- Multiple forms of a non-functional, unfolded protein follow different pathways and timelines to reach its folded, functional state, a study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have used an X-ray method to track how proteins fold, which could improve computer simulations of this process, with implications for understanding diseases and improving drug discovery. Their findings were reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30.
When proteins are translated from their DNA codes, they quickly transform from a non-functional, unfolded state into their folded, functional state. Problems in folding can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Protein folding is one of the most important biological processes, as it forms the functioning 3D protein structure,” explained the physical chemist Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. Dr. Tae Wu Kim, the lead author of this research from Ihee’s group, added, “Understanding the mechanisms of protein folding is important, and could pave the way for disease study and drug development.”
Ihee’s team developed an approach using an X-ray scattering technique to uncover how the protein cytochrome c folds from its initial unfolded state. This protein is composed of a chain of 104 amino acids with an iron-containing heme molecule. It is often used for protein folding studies.
The researchers placed the protein in a solution and shined ultraviolet light on it. This process provides electrons to cytochrome c, reducing the iron within it from the ferric to the ferrous form, which initiates folding. As this was happening, the researchers beamed X-rays at very short intervals onto the sample. The X-rays scattered off all the atomic pairs in the sample and a detector continuously recorded the X-ray scattering patterns. The X-ray scattering patterns provided direct information regarding the 3D protein structure and the changes made in these patterns over time showed real-time motion of the protein during the folding process.
The team found cytochrome c proteins initially exist in a wide variety of unfolded states. Once the folding process is triggered, they stop by a group of intermediates within 31.6 microseconds, and then those intermediates follow different pathways with different folding times to reach an energetically stable folded state.
“We don’t know if this diversity in folding paths can be generalized to other proteins,” Ihee confessed. He continued, “However, we believe that our approach can be used to study other protein folding systems.”
Ihee hopes this approach can improve the accuracy of models that simulate protein interactions by including information on their unstructured states. These simulations are important as they can help identify barriers to proper folding and predict a protein’s folded state given its amino acid sequence. Ultimately, the models could help clarify how some diseases develop and how drugs interact with various protein structures.
Ihee’s group collaborated with Professor Young Min Rhee at the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and this work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS).
Figure. The scientists found that non-functional unfolded forms of the protein cytochrome c follow different pathways and timelines to reach a stable functional folded state.
Publications:
Kim, T. W., et al. (2020) ‘Protein folding from heterogeneous unfolded state revealed by time-resolved X-ray solution scattering’. PNAS. Volume 117. Issue 26. Page 14996-15005. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913442117
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Young Min Rhee, Ph.D.
Professor
ymrhee@kaist.ac.kr
http://singlet.kaist.ac.kr
Rhee Research Group
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.09 View 17723
X-ray Scattering Shines Light on Protein Folding
- Multiple forms of a non-functional, unfolded protein follow different pathways and timelines to reach its folded, functional state, a study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have used an X-ray method to track how proteins fold, which could improve computer simulations of this process, with implications for understanding diseases and improving drug discovery. Their findings were reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30.
When proteins are translated from their DNA codes, they quickly transform from a non-functional, unfolded state into their folded, functional state. Problems in folding can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Protein folding is one of the most important biological processes, as it forms the functioning 3D protein structure,” explained the physical chemist Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. Dr. Tae Wu Kim, the lead author of this research from Ihee’s group, added, “Understanding the mechanisms of protein folding is important, and could pave the way for disease study and drug development.”
Ihee’s team developed an approach using an X-ray scattering technique to uncover how the protein cytochrome c folds from its initial unfolded state. This protein is composed of a chain of 104 amino acids with an iron-containing heme molecule. It is often used for protein folding studies.
The researchers placed the protein in a solution and shined ultraviolet light on it. This process provides electrons to cytochrome c, reducing the iron within it from the ferric to the ferrous form, which initiates folding. As this was happening, the researchers beamed X-rays at very short intervals onto the sample. The X-rays scattered off all the atomic pairs in the sample and a detector continuously recorded the X-ray scattering patterns. The X-ray scattering patterns provided direct information regarding the 3D protein structure and the changes made in these patterns over time showed real-time motion of the protein during the folding process.
The team found cytochrome c proteins initially exist in a wide variety of unfolded states. Once the folding process is triggered, they stop by a group of intermediates within 31.6 microseconds, and then those intermediates follow different pathways with different folding times to reach an energetically stable folded state.
“We don’t know if this diversity in folding paths can be generalized to other proteins,” Ihee confessed. He continued, “However, we believe that our approach can be used to study other protein folding systems.”
Ihee hopes this approach can improve the accuracy of models that simulate protein interactions by including information on their unstructured states. These simulations are important as they can help identify barriers to proper folding and predict a protein’s folded state given its amino acid sequence. Ultimately, the models could help clarify how some diseases develop and how drugs interact with various protein structures.
Ihee’s group collaborated with Professor Young Min Rhee at the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and this work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS).
Figure. The scientists found that non-functional unfolded forms of the protein cytochrome c follow different pathways and timelines to reach a stable functional folded state.
Publications:
Kim, T. W., et al. (2020) ‘Protein folding from heterogeneous unfolded state revealed by time-resolved X-ray solution scattering’. PNAS. Volume 117. Issue 26. Page 14996-15005. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913442117
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Young Min Rhee, Ph.D.
Professor
ymrhee@kaist.ac.kr
http://singlet.kaist.ac.kr
Rhee Research Group
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.09 View 17723 -
 Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 20807
Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 20807 -
 Simple Molecular Reagents to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
- Researchers report minimalistic principles for designing small molecules with multiple reactivities against dementia. -
Sometimes the most complex problems actually have very simple solutions. A group of South Korean researchers reported an efficient and effective redox-based strategy for incorporating multiple functions into simple molecular reagents against neurodegenerative disorders. The team developed redox-active aromatic molecular reagents with a simple structural composition that can simultaneously target and modulate various pathogenic factors in complex neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting one in ten people over the age of 65. Early-onset dementia also increasingly affects younger people.
A number of pathogenic elements such as reactive oxygen species, amyloid-beta, and metal ions have been suggested as potential causes of Alzheimer’s disease. Each element itself can lead to Alzheimer’s disease, but interactions between them may also aggravate the patient’s condition or interfere with the appropriate clinical care.
For example, when interacting with amyloid-beta, metal ions foster the aggregation and accumulation of amyloid-beta peptides that can induce oxidative stress and toxicity in the brain and lead to neurodegeneration.
Because these pathogenic factors of Alzheimer’s disease are intertwined, developing therapeutic agents that are capable of simultaneously regulating metal ion dyshomeostasis, amyloid-beta agglutination, and oxidative stress responses remains a key to halting the progression of the disease.
A research team led by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST demonstrated the feasibility of structure-mechanism-based molecular design for controlling a molecule’s chemical reactivity toward the various pathological factors of Alzheimer’s disease by tuning the redox properties of the molecule.
This study, featured as the ‘ACS Editors’ Choice’ in the May 6th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), was conducted in conjunction with KAIST Professor Mu-Hyun Baik’s group and Professor Joo-Young Lee’s group at the Asan Medical Center.
Professor Lim and her collaborators rationally designed and generated 10 compact aromatic molecules presenting a range of redox potentials by adjusting the electronic distribution of the phenyl, phenylene, or pyridyl moiety to impart redox-dependent reactivities against the multiple pathogenic factors in Alzheimer’s disease.
During the team’s biochemical and biophysical studies, these designed molecular reagents displayed redox-dependent reactivities against numerous desirable targets that are associated with Alzheimer’s disease such as free radicals, metal-free amyloid-beta, and metal-bound amyloid-beta.
Further mechanistic results revealed that the redox properties of these designed molecular reagents were essential for their function. The team demonstrated that these reagents engaged in oxidative reactions with metal-free and metal-bound amyloid-beta and led to chemical modifications. The products of such oxidative transformations were observed to form covalent adducts with amyloid-beta and alter its aggregation.
Moreover, the administration of the most promising candidate molecule significantly attenuated the amyloid pathology in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice and improved their cognitive defects.
Professor Lim said, “This strategy is straightforward, time-saving, and cost-effective, and its effect is significant. We are excited to help enable the advancement of new therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative disorders, which can improve the lives of so many patients.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and the Asan Institute for Life Sciences.
Image credit: Professor Mi Hee Lim, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of the news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kim, M. et al. (2020) ‘Minimalistic Principles for Designing Small Molecules with Multiple Reactivities against Pathological Factors in Dementia.’ Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), Volume 142, Issue 18, pp.8183-8193. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13100
Profile:
Mi Hee Lim
Professor
miheelim@kaist.ac.kr
http://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab
Lim Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Mu-Hyun Baik
Professor
mbaik2805@kaist.ac.kr
https://baik-laboratory.com/
Baik Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Joo-Yong Lee
Professor
jlee@amc.seoul.kr
Asan Institute for Life Sciences
Asan Medical Center
(END)
2020.05.11 View 18567
Simple Molecular Reagents to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
- Researchers report minimalistic principles for designing small molecules with multiple reactivities against dementia. -
Sometimes the most complex problems actually have very simple solutions. A group of South Korean researchers reported an efficient and effective redox-based strategy for incorporating multiple functions into simple molecular reagents against neurodegenerative disorders. The team developed redox-active aromatic molecular reagents with a simple structural composition that can simultaneously target and modulate various pathogenic factors in complex neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting one in ten people over the age of 65. Early-onset dementia also increasingly affects younger people.
A number of pathogenic elements such as reactive oxygen species, amyloid-beta, and metal ions have been suggested as potential causes of Alzheimer’s disease. Each element itself can lead to Alzheimer’s disease, but interactions between them may also aggravate the patient’s condition or interfere with the appropriate clinical care.
For example, when interacting with amyloid-beta, metal ions foster the aggregation and accumulation of amyloid-beta peptides that can induce oxidative stress and toxicity in the brain and lead to neurodegeneration.
Because these pathogenic factors of Alzheimer’s disease are intertwined, developing therapeutic agents that are capable of simultaneously regulating metal ion dyshomeostasis, amyloid-beta agglutination, and oxidative stress responses remains a key to halting the progression of the disease.
A research team led by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST demonstrated the feasibility of structure-mechanism-based molecular design for controlling a molecule’s chemical reactivity toward the various pathological factors of Alzheimer’s disease by tuning the redox properties of the molecule.
This study, featured as the ‘ACS Editors’ Choice’ in the May 6th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), was conducted in conjunction with KAIST Professor Mu-Hyun Baik’s group and Professor Joo-Young Lee’s group at the Asan Medical Center.
Professor Lim and her collaborators rationally designed and generated 10 compact aromatic molecules presenting a range of redox potentials by adjusting the electronic distribution of the phenyl, phenylene, or pyridyl moiety to impart redox-dependent reactivities against the multiple pathogenic factors in Alzheimer’s disease.
During the team’s biochemical and biophysical studies, these designed molecular reagents displayed redox-dependent reactivities against numerous desirable targets that are associated with Alzheimer’s disease such as free radicals, metal-free amyloid-beta, and metal-bound amyloid-beta.
Further mechanistic results revealed that the redox properties of these designed molecular reagents were essential for their function. The team demonstrated that these reagents engaged in oxidative reactions with metal-free and metal-bound amyloid-beta and led to chemical modifications. The products of such oxidative transformations were observed to form covalent adducts with amyloid-beta and alter its aggregation.
Moreover, the administration of the most promising candidate molecule significantly attenuated the amyloid pathology in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice and improved their cognitive defects.
Professor Lim said, “This strategy is straightforward, time-saving, and cost-effective, and its effect is significant. We are excited to help enable the advancement of new therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative disorders, which can improve the lives of so many patients.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and the Asan Institute for Life Sciences.
Image credit: Professor Mi Hee Lim, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of the news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kim, M. et al. (2020) ‘Minimalistic Principles for Designing Small Molecules with Multiple Reactivities against Pathological Factors in Dementia.’ Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), Volume 142, Issue 18, pp.8183-8193. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13100
Profile:
Mi Hee Lim
Professor
miheelim@kaist.ac.kr
http://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab
Lim Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Mu-Hyun Baik
Professor
mbaik2805@kaist.ac.kr
https://baik-laboratory.com/
Baik Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Joo-Yong Lee
Professor
jlee@amc.seoul.kr
Asan Institute for Life Sciences
Asan Medical Center
(END)
2020.05.11 View 18567 -
 Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 8851
Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 8851 -
 Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 14773
Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 14773 -
 Scientist of October, Professor Haeshin Lee
(Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry)
Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry received the ‘Science and Technology Award of October’ from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea for his contribution to developing an antibleeding injection needle. This novel outcome will fundamentally prevent the problem of secondary infections of AIDS, Ebola and Hepatitis viruses transmitting from patients to medical teams.
This needle’s surface is coated with hemostatic materials. Its concept is simple and the key to this technology is to make materials that are firmly coated on the needle so that they can endure frictional force when being injected into skin and blood vessels. Moreover, the materials should be adhesive to skin and the interior of blood vessels, but harmless to humans.
Professor Lee found a solution from natural polymer ingredients. Catecholamine can be found in mussels. Professor Lee conjugated catechol groups on the chitosan backbone. He applied this mussel-inspired adhesive polymer Chitosan-catechol, which immediately forms an adhesive layer with blood, as a bioadhesion for the antibleeding injection needle.
Professor Lee said, “Chitosan-catechol, which copies the adhesive mechanism of mussels, shows high solubility in physiological saline as well as great mucoadhesion. Hence, it is perfectly suitable for coating the injection needle. Combining it with proteins allows for efficient drug delivery to the heart, which is a challenging injection location, so it will be also useful for treating incurable heart disease.”
2018.10.05 View 12732
Scientist of October, Professor Haeshin Lee
(Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry)
Professor Haeshin Lee from the Department of Chemistry received the ‘Science and Technology Award of October’ from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea for his contribution to developing an antibleeding injection needle. This novel outcome will fundamentally prevent the problem of secondary infections of AIDS, Ebola and Hepatitis viruses transmitting from patients to medical teams.
This needle’s surface is coated with hemostatic materials. Its concept is simple and the key to this technology is to make materials that are firmly coated on the needle so that they can endure frictional force when being injected into skin and blood vessels. Moreover, the materials should be adhesive to skin and the interior of blood vessels, but harmless to humans.
Professor Lee found a solution from natural polymer ingredients. Catecholamine can be found in mussels. Professor Lee conjugated catechol groups on the chitosan backbone. He applied this mussel-inspired adhesive polymer Chitosan-catechol, which immediately forms an adhesive layer with blood, as a bioadhesion for the antibleeding injection needle.
Professor Lee said, “Chitosan-catechol, which copies the adhesive mechanism of mussels, shows high solubility in physiological saline as well as great mucoadhesion. Hence, it is perfectly suitable for coating the injection needle. Combining it with proteins allows for efficient drug delivery to the heart, which is a challenging injection location, so it will be also useful for treating incurable heart disease.”
2018.10.05 View 12732 -
 The 1st Korea Toray Science and Technology Awardee, Prof. Sukbok Chang
(Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
The Korea Toray Science Foundation (KTSF) awarded the first Korea Toray Science Technology Award in basic science to Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry on September 19.
KTSF was established in January 2018, and its award goes to researchers who have significantly contributed to the development of chemistry and materials research with funds to support research projects.
Distinguished Professor Chang has devoted himself in organocatalysis research; in particular, his work on catalysts for effective lactam formation, which was an intricate problem, received great attention.
The award ceremony will take place in The Federation of Korean Industries Hall on October 31. KTFS board members, judges, and the CEO of Toray Industries Akihiro Nikkaku will attend the ceremony. Also, Dr. Ryoji Noyori, the Nobel Laureate in Chemistry, will give a talk on the role of chemistry and creative challenges as a researcher.
2018.10.04 View 10774
The 1st Korea Toray Science and Technology Awardee, Prof. Sukbok Chang
(Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
The Korea Toray Science Foundation (KTSF) awarded the first Korea Toray Science Technology Award in basic science to Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry on September 19.
KTSF was established in January 2018, and its award goes to researchers who have significantly contributed to the development of chemistry and materials research with funds to support research projects.
Distinguished Professor Chang has devoted himself in organocatalysis research; in particular, his work on catalysts for effective lactam formation, which was an intricate problem, received great attention.
The award ceremony will take place in The Federation of Korean Industries Hall on October 31. KTFS board members, judges, and the CEO of Toray Industries Akihiro Nikkaku will attend the ceremony. Also, Dr. Ryoji Noyori, the Nobel Laureate in Chemistry, will give a talk on the role of chemistry and creative challenges as a researcher.
2018.10.04 View 10774 -
 Professor Hee-Sung Park Named Scientist of May
(Professor Hee-Sung Park)
Professor Hee-Sung Park from the Department of Chemistry was named ‘Scientist of May’ sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was honored in recognition of his developing a tool to engineer designer proteins via diverse chemical modifications. This approach provides a novel platform for investigating numerous diseases such as cancer and dementia.
His research focuses on the production of synthetic proteins and the generation of diverse protein functions as well as the designing and engineering of new translation machinery for genetic code expansion, and the application of synthetic biology techniques for basic cell biology and applied medical science.
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are constantly taking place during or after protein biosynthesis. PTMs play a vital role in expanding protein functional diversity and, as a result, critically affect numerous biological processes. Abnormal PTMs have been known to trigger various diseases including cancer and dementia. Therefore, this technology enables proteins to reproduce with specific modifications at selected residues and will significantly help establish experimental strategies to investigate fundamental biological mechanisms including the development of targeted cancer therapies.
Professor Park also received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2018.05.04 View 12750
Professor Hee-Sung Park Named Scientist of May
(Professor Hee-Sung Park)
Professor Hee-Sung Park from the Department of Chemistry was named ‘Scientist of May’ sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Park was honored in recognition of his developing a tool to engineer designer proteins via diverse chemical modifications. This approach provides a novel platform for investigating numerous diseases such as cancer and dementia.
His research focuses on the production of synthetic proteins and the generation of diverse protein functions as well as the designing and engineering of new translation machinery for genetic code expansion, and the application of synthetic biology techniques for basic cell biology and applied medical science.
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are constantly taking place during or after protein biosynthesis. PTMs play a vital role in expanding protein functional diversity and, as a result, critically affect numerous biological processes. Abnormal PTMs have been known to trigger various diseases including cancer and dementia. Therefore, this technology enables proteins to reproduce with specific modifications at selected residues and will significantly help establish experimental strategies to investigate fundamental biological mechanisms including the development of targeted cancer therapies.
Professor Park also received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2018.05.04 View 12750 -
 Undergrad's Paper Chosen as the Cover Article in Soft Matter
(from left: Research Professor KyuHan Kim and Undergrad Student Subeen Kim)
A KAIST undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, had his paper chosen as the cover article in an international journal during his senior year.
There have been an increasing number of undergraduate students who were published as the first author because the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation program allows more active research participation by undergraduate students.
Through URP, Kim successfully published his paper in the internationally-renowned journal, Soft Matter, which is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry, and it was chosen as the cover article of that journal in February 2018.
This publication means a lot to him because he designed the cover image himself, based on his imagination and observations.
His research is about controllable one-step double emulsion formation. Double emulsion is a system in which dispersed droplets contain additional immiscible liquid droplets.
Having great retention ability, double emulsion has been used in various applications in the food industry, in cosmetics, and for drug delivery. Nevertheless, two-step emulsification is a conventional approach to produce double emulsions that typically leads to partial destabilization of the emulsion formed during the initial stage. Hence, it does not ensure the stability of a double emulsion. On the other hand, a microfluidic approach with various flow-focusing techniques has been developed, but it has low production efficiency and thus limited industrial applications.
Kim’s results came from the process of phase inversion to solve this problem. He identified the instant formation of double emulsions during the process of phase inversion. Based on this finding, he proposed criteria to achieve high stability of double emulsion.
Through constant research, he developed a quite general method using a combination of an oil soluble poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) and hydrophobic silica nanoparticle (HDK H18). This new method enables one-step and stable production of double emersions in a stable manner. It also allows control of the number and the volume of inner oil droplets inside the outer water droplets by adjusting PMMA and HDK H18.
Kim enrolled at KAIST as a KAIST Presidential Fellowship and Presidential Science Scholarship in 2014. While studying both chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry he has been developing his hypothesis and conducting research.
He was able to begin conducting research because he has taken part in URP projects twice. In his sophomore year, he studied the formation of high internal phase double emulsions. After one year, he conducted research to produce superabsorbent resins, which are the base material for diapers, by using colloid particles. Using partial research outcomes, he published his paper in Nature Communications as a second author.
Kim said, “Double majoring the chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry has helped me producing this outcome. I hope that this research contributes to commercializing double emulsions. I will continue to identify accurate principles to produce chemicals that can be controlled exquisitely.”
Figure 1. The cover article of Soft Matter
2018.05.03 View 13020
Undergrad's Paper Chosen as the Cover Article in Soft Matter
(from left: Research Professor KyuHan Kim and Undergrad Student Subeen Kim)
A KAIST undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, had his paper chosen as the cover article in an international journal during his senior year.
There have been an increasing number of undergraduate students who were published as the first author because the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation program allows more active research participation by undergraduate students.
Through URP, Kim successfully published his paper in the internationally-renowned journal, Soft Matter, which is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry, and it was chosen as the cover article of that journal in February 2018.
This publication means a lot to him because he designed the cover image himself, based on his imagination and observations.
His research is about controllable one-step double emulsion formation. Double emulsion is a system in which dispersed droplets contain additional immiscible liquid droplets.
Having great retention ability, double emulsion has been used in various applications in the food industry, in cosmetics, and for drug delivery. Nevertheless, two-step emulsification is a conventional approach to produce double emulsions that typically leads to partial destabilization of the emulsion formed during the initial stage. Hence, it does not ensure the stability of a double emulsion. On the other hand, a microfluidic approach with various flow-focusing techniques has been developed, but it has low production efficiency and thus limited industrial applications.
Kim’s results came from the process of phase inversion to solve this problem. He identified the instant formation of double emulsions during the process of phase inversion. Based on this finding, he proposed criteria to achieve high stability of double emulsion.
Through constant research, he developed a quite general method using a combination of an oil soluble poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) and hydrophobic silica nanoparticle (HDK H18). This new method enables one-step and stable production of double emersions in a stable manner. It also allows control of the number and the volume of inner oil droplets inside the outer water droplets by adjusting PMMA and HDK H18.
Kim enrolled at KAIST as a KAIST Presidential Fellowship and Presidential Science Scholarship in 2014. While studying both chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry he has been developing his hypothesis and conducting research.
He was able to begin conducting research because he has taken part in URP projects twice. In his sophomore year, he studied the formation of high internal phase double emulsions. After one year, he conducted research to produce superabsorbent resins, which are the base material for diapers, by using colloid particles. Using partial research outcomes, he published his paper in Nature Communications as a second author.
Kim said, “Double majoring the chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry has helped me producing this outcome. I hope that this research contributes to commercializing double emulsions. I will continue to identify accurate principles to produce chemicals that can be controlled exquisitely.”
Figure 1. The cover article of Soft Matter
2018.05.03 View 13020