ES
-
 Three Professors Named to Highly Cited Researchers 2020 List
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry, Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor Jiyong Eom from the College of Business were named to Clarivate’s Highly Cited Researchers 2020 list.
Clarivate announced the researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. A total of 6,167 researchers from more than 60 countries were listed this year and 37 Korean scholars made the list.
The methodology that determines the “Who’s Who” of influential researchers draws on data and analyses performed by bibliometric experts and data scientists at the Institute for Scientific Information at Clarivate. It also uses the tallies to identify the countries and research institutions where these scientific elite are based. More than 6,000 researchers from 21 fields in the sciences, social sciences, and cross field categories were selected based on the number of highly cited papers they produced over an 11-year period from January 2009 to December 2019.
Professor Chang made the list six years in a row, while Professor Lee made it for four consecutive years, and Professor Eom for the last two years. Professor Chang’s group (http://sbchang.kaist.ac.kr) investigates catalytic hydrocarbon functionalization. Professor Lee (http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr) is a pioneering scholar in the field of metabolic engineering, systems, and synthetic biology. Professor Eom’s (https://kaistceps.quv.kr) research extends to energy and environmental economics and management, energy big data, and green information systems.
2020.11.30 View 9327
Three Professors Named to Highly Cited Researchers 2020 List
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry, Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor Jiyong Eom from the College of Business were named to Clarivate’s Highly Cited Researchers 2020 list.
Clarivate announced the researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. A total of 6,167 researchers from more than 60 countries were listed this year and 37 Korean scholars made the list.
The methodology that determines the “Who’s Who” of influential researchers draws on data and analyses performed by bibliometric experts and data scientists at the Institute for Scientific Information at Clarivate. It also uses the tallies to identify the countries and research institutions where these scientific elite are based. More than 6,000 researchers from 21 fields in the sciences, social sciences, and cross field categories were selected based on the number of highly cited papers they produced over an 11-year period from January 2009 to December 2019.
Professor Chang made the list six years in a row, while Professor Lee made it for four consecutive years, and Professor Eom for the last two years. Professor Chang’s group (http://sbchang.kaist.ac.kr) investigates catalytic hydrocarbon functionalization. Professor Lee (http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr) is a pioneering scholar in the field of metabolic engineering, systems, and synthetic biology. Professor Eom’s (https://kaistceps.quv.kr) research extends to energy and environmental economics and management, energy big data, and green information systems.
2020.11.30 View 9327 -
 Simulations Open a New Way to Reverse Cell Aging
Turning off a newly identified enzyme could reverse a natural aging process in cells.
Research findings by a KAIST team provide insight into the complex mechanism of cellular senescence and present a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing age-related diseases associated with the accumulation of senescent cells.
Simulations that model molecular interactions have identified an enzyme that could be targeted to reverse a natural aging process called cellular senescence. The findings were validated with laboratory experiments on skin cells and skin equivalent tissues, and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Our research opens the door for a new generation that perceives aging as a reversible biological phenomenon,” says Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), who led the research with colleagues from KAIST and Amorepacific Corporation in Korea.
Cells respond to a variety of factors, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, and shortening of the telomeres capping the ends of chromosomes, by entering a stable and persistent exit from the cell cycle. This process, called cellular senescence, is important, as it prevents damaged cells from proliferating and turning into cancer cells. But it is also a natural process that contributes to aging and age-related diseases. Recent research has shown that cellular senescence can be reversed. But the laboratory approaches used thus far also impair tissue regeneration or have the potential to trigger malignant transformations.
Professor Cho and his colleagues used an innovative strategy to identify molecules that could be targeted for reversing cellular senescence. The team pooled together information from the literature and databases about the molecular processes involved in cellular senescence. To this, they added results from their own research on the molecular processes involved in the proliferation, quiescence (a non-dividing cell that can re-enter the cell cycle) and senescence of skin fibroblasts, a cell type well known for repairing wounds. Using algorithms, they developed a model that simulates the interactions between these molecules. Their analyses allowed them to predict which molecules could be targeted to reverse cell senescence.
They then investigated one of the molecules, an enzyme called PDK1, in incubated senescent skin fibroblasts and three-dimensional skin equivalent tissue models. They found that blocking PDK1 led to the inhibition of two downstream signalling molecules, which in turn restored the cells’ ability to enter back into the cell cycle. Notably, the cells retained their capacity to regenerate wounded skin without proliferating in a way that could lead to malignant transformation.
The scientists recommend investigations are next done in organs and organisms to determine the full effect of PDK1 inhibition. Since the gene that codes for PDK1 is overexpressed in some cancers, the scientists expect that inhibiting it will have both anti-aging and anti-cancer effects.
-Profile
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
Laboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired Engineering
http://sbie.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.26 View 12632
Simulations Open a New Way to Reverse Cell Aging
Turning off a newly identified enzyme could reverse a natural aging process in cells.
Research findings by a KAIST team provide insight into the complex mechanism of cellular senescence and present a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing age-related diseases associated with the accumulation of senescent cells.
Simulations that model molecular interactions have identified an enzyme that could be targeted to reverse a natural aging process called cellular senescence. The findings were validated with laboratory experiments on skin cells and skin equivalent tissues, and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Our research opens the door for a new generation that perceives aging as a reversible biological phenomenon,” says Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), who led the research with colleagues from KAIST and Amorepacific Corporation in Korea.
Cells respond to a variety of factors, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, and shortening of the telomeres capping the ends of chromosomes, by entering a stable and persistent exit from the cell cycle. This process, called cellular senescence, is important, as it prevents damaged cells from proliferating and turning into cancer cells. But it is also a natural process that contributes to aging and age-related diseases. Recent research has shown that cellular senescence can be reversed. But the laboratory approaches used thus far also impair tissue regeneration or have the potential to trigger malignant transformations.
Professor Cho and his colleagues used an innovative strategy to identify molecules that could be targeted for reversing cellular senescence. The team pooled together information from the literature and databases about the molecular processes involved in cellular senescence. To this, they added results from their own research on the molecular processes involved in the proliferation, quiescence (a non-dividing cell that can re-enter the cell cycle) and senescence of skin fibroblasts, a cell type well known for repairing wounds. Using algorithms, they developed a model that simulates the interactions between these molecules. Their analyses allowed them to predict which molecules could be targeted to reverse cell senescence.
They then investigated one of the molecules, an enzyme called PDK1, in incubated senescent skin fibroblasts and three-dimensional skin equivalent tissue models. They found that blocking PDK1 led to the inhibition of two downstream signalling molecules, which in turn restored the cells’ ability to enter back into the cell cycle. Notably, the cells retained their capacity to regenerate wounded skin without proliferating in a way that could lead to malignant transformation.
The scientists recommend investigations are next done in organs and organisms to determine the full effect of PDK1 inhibition. Since the gene that codes for PDK1 is overexpressed in some cancers, the scientists expect that inhibiting it will have both anti-aging and anti-cancer effects.
-Profile
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
Laboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired Engineering
http://sbie.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.26 View 12632 -
 Chairman Soo-Young Lee Named Among the Heroes of Philanthropy in Asia
Chairman Soo-Young Lee from the KAIST Development Foundation was named one of 15 philanthropists who made the biggest donations in the Asia-Pacific region by Forbes Asia on November 11.
The annual Heroes of Philanthropy list features the 15 the most generous individual philanthropists who are donating from their personal fortunes, not through companies. This year, the biggest philanthropies donated to make a difference in wide arrays of sectors such as Covid-19 relief to education and the arts.
Chairman Lee donated totaling 68 billion KRW to KAIST in July. Her donation marked the largest donation KAIST has ever received. She is one of two Korean philanthropists that Forbes selected. Honorary Chairman of GS Caltex Dong-Soo Huh also made the list.
Her donation will establish the Soo-Young Lee Science Education Foundation to support ‘the Singularity Professor program’ that KAIST is launching. She expressed confidence that her donation will fund KAIST researchers to make breakthroughs that will lead to a Nobel Prize.
“Without the advancement of science and technology, Korea cannot be one of the top countries in the world. I believe KAIST can make it with our all supports,” she frequently said when asked why she selected KAIST for her donation.
Chairman Lee previously made generous donations in 2012 and 2016 and said she plans to make another gift to KAIST in the very near future.
2020.11.13 View 6471
Chairman Soo-Young Lee Named Among the Heroes of Philanthropy in Asia
Chairman Soo-Young Lee from the KAIST Development Foundation was named one of 15 philanthropists who made the biggest donations in the Asia-Pacific region by Forbes Asia on November 11.
The annual Heroes of Philanthropy list features the 15 the most generous individual philanthropists who are donating from their personal fortunes, not through companies. This year, the biggest philanthropies donated to make a difference in wide arrays of sectors such as Covid-19 relief to education and the arts.
Chairman Lee donated totaling 68 billion KRW to KAIST in July. Her donation marked the largest donation KAIST has ever received. She is one of two Korean philanthropists that Forbes selected. Honorary Chairman of GS Caltex Dong-Soo Huh also made the list.
Her donation will establish the Soo-Young Lee Science Education Foundation to support ‘the Singularity Professor program’ that KAIST is launching. She expressed confidence that her donation will fund KAIST researchers to make breakthroughs that will lead to a Nobel Prize.
“Without the advancement of science and technology, Korea cannot be one of the top countries in the world. I believe KAIST can make it with our all supports,” she frequently said when asked why she selected KAIST for her donation.
Chairman Lee previously made generous donations in 2012 and 2016 and said she plans to make another gift to KAIST in the very near future.
2020.11.13 View 6471 -
 Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 10996
Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 10996 -
 To Talk or Not to Talk: Smart Speaker Determines Optimal Timing to Talk
A KAIST research team has developed a new context-awareness technology that enables AI assistants to determine when to talk to their users based on user circumstances. This technology can contribute to developing advanced AI assistants that can offer pre-emptive services such as reminding users to take medication on time or modifying schedules based on the actual progress of planned tasks.
Unlike conventional AI assistants that used to act passively upon users’ commands, today’s AI assistants are evolving to provide more proactive services through self-reasoning of user circumstances. This opens up new opportunities for AI assistants to better support users in their daily lives. However, if AI assistants do not talk at the right time, they could rather interrupt their users instead of helping them.
The right time for talking is more difficult for AI assistants to determine than it appears. This is because the context can differ depending on the state of the user or the surrounding environment.
A group of researchers led by Professor Uichin Lee from the KAIST School of Computing identified key contextual factors in user circumstances that determine when the AI assistant should start, stop, or resume engaging in voice services in smart home environments. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT) in September.
The group conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Jae-Gil Lee’s group in the KAIST School of Computing, Professor Sangsu Lee’s group in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, and Professor Auk Kim’s group at Kangwon National University.
After developing smart speakers equipped with AI assistant function for experimental use, the researchers installed them in the rooms of 40 students who live in double-occupancy campus dormitories and collected a total of 3,500 in-situ user response data records over a period of a week.
The smart speakers repeatedly asked the students a question, “Is now a good time to talk?” at random intervals or whenever a student’s movement was detected. Students answered with either “yes” or “no” and then explained why, describing what they had been doing before being questioned by the smart speakers.
Data analysis revealed that 47% of user responses were “no” indicating they did not want to be interrupted. The research team then created 19 home activity categories to cross-analyze the key contextual factors that determine opportune moments for AI assistants to talk, and classified these factors into ‘personal,’ ‘movement,’ and ‘social’ factors respectively.
Personal factors, for instance, include:
1. the degree of concentration on or engagement in activities,
2. the degree urgency and busyness,
3. the state of user’s mental or physical condition, and
4. the state of being able to talk or listen while multitasking.
While users were busy concentrating on studying, tired, or drying hair, they found it difficult to engage in conversational interactions with the smart speakers.
Some representative movement factors include departure, entrance, and physical activity transitions. Interestingly, in movement scenarios, the team found that the communication range was an important factor. Departure is an outbound movement from the smart speaker, and entrance is an inbound movement. Users were much more available during inbound movement scenarios as opposed to outbound movement scenarios.
In general, smart speakers are located in a shared place at home, such as a living room, where multiple family members gather at the same time. In Professor Lee’s group’s experiment, almost half of the in-situ user responses were collected when both roommates were present. The group found social presence also influenced interruptibility. Roommates often wanted to minimize possible interpersonal conflicts, such as disturbing their roommates' sleep or work.
Narae Cha, the lead author of this study, explained, “By considering personal, movement, and social factors, we can envision a smart speaker that can intelligently manage the timing of conversations with users.”
She believes that this work lays the foundation for the future of AI assistants, adding, “Multi-modal sensory data can be used for context sensing, and this context information will help smart speakers proactively determine when it is a good time to start, stop, or resume conversations with their users.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Cha, N, et al. (2020) “Hello There! Is Now a Good Time to Talk?”: Opportune Moments for Proactive Interactions with Smart Speakers. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), Vol. 4, No. 3, Article No. 74, pp. 1-28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1145/3411810
Link to Introductory Video:
https://youtu.be/AA8CTi2hEf0
Profile:
Uichin Lee
Associate Professor
uclee@kaist.ac.kr
http://ic.kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Computing Lab.
School of Computing
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.05 View 11706
To Talk or Not to Talk: Smart Speaker Determines Optimal Timing to Talk
A KAIST research team has developed a new context-awareness technology that enables AI assistants to determine when to talk to their users based on user circumstances. This technology can contribute to developing advanced AI assistants that can offer pre-emptive services such as reminding users to take medication on time or modifying schedules based on the actual progress of planned tasks.
Unlike conventional AI assistants that used to act passively upon users’ commands, today’s AI assistants are evolving to provide more proactive services through self-reasoning of user circumstances. This opens up new opportunities for AI assistants to better support users in their daily lives. However, if AI assistants do not talk at the right time, they could rather interrupt their users instead of helping them.
The right time for talking is more difficult for AI assistants to determine than it appears. This is because the context can differ depending on the state of the user or the surrounding environment.
A group of researchers led by Professor Uichin Lee from the KAIST School of Computing identified key contextual factors in user circumstances that determine when the AI assistant should start, stop, or resume engaging in voice services in smart home environments. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT) in September.
The group conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Jae-Gil Lee’s group in the KAIST School of Computing, Professor Sangsu Lee’s group in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, and Professor Auk Kim’s group at Kangwon National University.
After developing smart speakers equipped with AI assistant function for experimental use, the researchers installed them in the rooms of 40 students who live in double-occupancy campus dormitories and collected a total of 3,500 in-situ user response data records over a period of a week.
The smart speakers repeatedly asked the students a question, “Is now a good time to talk?” at random intervals or whenever a student’s movement was detected. Students answered with either “yes” or “no” and then explained why, describing what they had been doing before being questioned by the smart speakers.
Data analysis revealed that 47% of user responses were “no” indicating they did not want to be interrupted. The research team then created 19 home activity categories to cross-analyze the key contextual factors that determine opportune moments for AI assistants to talk, and classified these factors into ‘personal,’ ‘movement,’ and ‘social’ factors respectively.
Personal factors, for instance, include:
1. the degree of concentration on or engagement in activities,
2. the degree urgency and busyness,
3. the state of user’s mental or physical condition, and
4. the state of being able to talk or listen while multitasking.
While users were busy concentrating on studying, tired, or drying hair, they found it difficult to engage in conversational interactions with the smart speakers.
Some representative movement factors include departure, entrance, and physical activity transitions. Interestingly, in movement scenarios, the team found that the communication range was an important factor. Departure is an outbound movement from the smart speaker, and entrance is an inbound movement. Users were much more available during inbound movement scenarios as opposed to outbound movement scenarios.
In general, smart speakers are located in a shared place at home, such as a living room, where multiple family members gather at the same time. In Professor Lee’s group’s experiment, almost half of the in-situ user responses were collected when both roommates were present. The group found social presence also influenced interruptibility. Roommates often wanted to minimize possible interpersonal conflicts, such as disturbing their roommates' sleep or work.
Narae Cha, the lead author of this study, explained, “By considering personal, movement, and social factors, we can envision a smart speaker that can intelligently manage the timing of conversations with users.”
She believes that this work lays the foundation for the future of AI assistants, adding, “Multi-modal sensory data can be used for context sensing, and this context information will help smart speakers proactively determine when it is a good time to start, stop, or resume conversations with their users.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Cha, N, et al. (2020) “Hello There! Is Now a Good Time to Talk?”: Opportune Moments for Proactive Interactions with Smart Speakers. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), Vol. 4, No. 3, Article No. 74, pp. 1-28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1145/3411810
Link to Introductory Video:
https://youtu.be/AA8CTi2hEf0
Profile:
Uichin Lee
Associate Professor
uclee@kaist.ac.kr
http://ic.kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Computing Lab.
School of Computing
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.05 View 11706 -
 Chemical Scissors Snip 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenides into Nanoribbon
New ‘nanoribbon’ catalyst should slash cost of hydrogen production for clean fuels
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative – and an innovative way to produce them using chemical ‘scissors’ – that could make hydrogen production more economical.
The research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering published their work in Nature Communications.
Hydrogen is likely to play a key role in the clean transition away from fossil fuels and other processes that produce greenhouse gas emissions. There is a raft of transportation sectors such as long-haul shipping and aviation that are difficult to electrify and so will require cleanly produced hydrogen as a fuel or as a feedstock for other carbon-neutral synthetic fuels. Likewise, fertilizer production and the steel sector are unlikely to be “de-carbonized” without cheap and clean hydrogen.
The problem is that the cheapest methods by far of producing hydrogen gas is currently from natural gas, a process that itself produces the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide–which defeats the purpose.
Alternative techniques of hydrogen production, such as electrolysis using an electric current between two electrodes plunged into water to overcome the chemical bonds holding water together, thereby splitting it into its constituent elements, oxygen and hydrogen are very well established. But one of the factors contributing to the high cost, beyond being extremely energy-intensive, is the need for the very expensive precious and relatively rare metal platinum. The platinum is used as a catalyst–a substance that kicks off or speeds up a chemical reaction–in the hydrogen production process.
As a result, researchers have long been on the hunt for a substitution for platinum -- another catalyst that is abundant in the earth and thus much cheaper.
Transition metal dichalcogenides, or TMDs, in a nanomaterial form, have for some time been considered a good candidate as a catalyst replacement for platinum. These are substances composed of one atom of a transition metal (the elements in the middle part of the periodic table) and two atoms of a chalcogen element (the elements in the third-to-last column in the periodic table, specifically sulfur, selenium and tellurium).
What makes TMDs a good bet as a platinum replacement is not just that they are much more abundant, but also their electrons are structured in a way that gives the electrodes a boost.
In addition, a TMD that is a nanomaterial is essentially a two-dimensional super-thin sheet only a few atoms thick, just like graphene. The ultrathin nature of a 2-D TMD nanosheet allows for a great many more TMD molecules to be exposed during the catalysis process than would be the case in a block of the stuff, thus kicking off and speeding up the hydrogen-making chemical reaction that much more.
However, even here the TMD molecules are only reactive at the four edges of a nanosheet. In the flat interior, not much is going on. In order to increase the chemical reaction rate in the production of hydrogen, the nanosheet would need to be cut into very thin – almost one-dimensional strips, thereby creating many edges.
In response, the research team developed what are in essence a pair of chemical scissors that can snip TMD into tiny strips.
“Up to now, the only substances that anyone has been able to turn into these ‘nano-ribbons’ are graphene and phosphorene,” said Sang Professor Kim, one of the researchers involved in devising the process.
“But they’re both made up of just one element, so it’s pretty straightforward. Figuring out how to do it for TMD, which is made of two elements was going to be much harder.”
The ‘scissors’ involve a two-step process involving first inserting lithium ions into the layered structure of the TMD sheets, and then using ultrasound to cause a spontaneous ‘unzipping’ in straight lines.
“It works sort of like how when you split a plank of plywood: it breaks easily in one direction along the grain,” Professor Kim continued. “It’s actually really simple.”
The researchers then tried it with various types of TMDs, including those made of molybdenum, selenium, sulfur, tellurium and tungsten. All worked just as well, with a catalytic efficiency as effective as platinum’s.
Because of the simplicity of the procedure, this method should be able to be used not just in the large-scale production of TMD nanoribbons, but also to make similar nanoribbons from other multi-elemental 2D materials for purposes beyond just hydrogen production.
-ProfileProfessor Sang Ouk KimSoft Nanomaterials Laboratory (http://snml.kaist.ac.kr)Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.29 View 8170
Chemical Scissors Snip 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenides into Nanoribbon
New ‘nanoribbon’ catalyst should slash cost of hydrogen production for clean fuels
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative – and an innovative way to produce them using chemical ‘scissors’ – that could make hydrogen production more economical.
The research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering published their work in Nature Communications.
Hydrogen is likely to play a key role in the clean transition away from fossil fuels and other processes that produce greenhouse gas emissions. There is a raft of transportation sectors such as long-haul shipping and aviation that are difficult to electrify and so will require cleanly produced hydrogen as a fuel or as a feedstock for other carbon-neutral synthetic fuels. Likewise, fertilizer production and the steel sector are unlikely to be “de-carbonized” without cheap and clean hydrogen.
The problem is that the cheapest methods by far of producing hydrogen gas is currently from natural gas, a process that itself produces the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide–which defeats the purpose.
Alternative techniques of hydrogen production, such as electrolysis using an electric current between two electrodes plunged into water to overcome the chemical bonds holding water together, thereby splitting it into its constituent elements, oxygen and hydrogen are very well established. But one of the factors contributing to the high cost, beyond being extremely energy-intensive, is the need for the very expensive precious and relatively rare metal platinum. The platinum is used as a catalyst–a substance that kicks off or speeds up a chemical reaction–in the hydrogen production process.
As a result, researchers have long been on the hunt for a substitution for platinum -- another catalyst that is abundant in the earth and thus much cheaper.
Transition metal dichalcogenides, or TMDs, in a nanomaterial form, have for some time been considered a good candidate as a catalyst replacement for platinum. These are substances composed of one atom of a transition metal (the elements in the middle part of the periodic table) and two atoms of a chalcogen element (the elements in the third-to-last column in the periodic table, specifically sulfur, selenium and tellurium).
What makes TMDs a good bet as a platinum replacement is not just that they are much more abundant, but also their electrons are structured in a way that gives the electrodes a boost.
In addition, a TMD that is a nanomaterial is essentially a two-dimensional super-thin sheet only a few atoms thick, just like graphene. The ultrathin nature of a 2-D TMD nanosheet allows for a great many more TMD molecules to be exposed during the catalysis process than would be the case in a block of the stuff, thus kicking off and speeding up the hydrogen-making chemical reaction that much more.
However, even here the TMD molecules are only reactive at the four edges of a nanosheet. In the flat interior, not much is going on. In order to increase the chemical reaction rate in the production of hydrogen, the nanosheet would need to be cut into very thin – almost one-dimensional strips, thereby creating many edges.
In response, the research team developed what are in essence a pair of chemical scissors that can snip TMD into tiny strips.
“Up to now, the only substances that anyone has been able to turn into these ‘nano-ribbons’ are graphene and phosphorene,” said Sang Professor Kim, one of the researchers involved in devising the process.
“But they’re both made up of just one element, so it’s pretty straightforward. Figuring out how to do it for TMD, which is made of two elements was going to be much harder.”
The ‘scissors’ involve a two-step process involving first inserting lithium ions into the layered structure of the TMD sheets, and then using ultrasound to cause a spontaneous ‘unzipping’ in straight lines.
“It works sort of like how when you split a plank of plywood: it breaks easily in one direction along the grain,” Professor Kim continued. “It’s actually really simple.”
The researchers then tried it with various types of TMDs, including those made of molybdenum, selenium, sulfur, tellurium and tungsten. All worked just as well, with a catalytic efficiency as effective as platinum’s.
Because of the simplicity of the procedure, this method should be able to be used not just in the large-scale production of TMD nanoribbons, but also to make similar nanoribbons from other multi-elemental 2D materials for purposes beyond just hydrogen production.
-ProfileProfessor Sang Ouk KimSoft Nanomaterials Laboratory (http://snml.kaist.ac.kr)Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.29 View 8170 -
 'Mini-Lungs' Reveal Early Stages of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Researchers in Korea and the UK have successfully grown miniature models of critical lung structures called alveoli, and used them to study how the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 infects the lungs.
To date, there have been more than 40 million cases of COVID-19 and almost 1.13 million deaths worldwide. The main target tissues of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, especially in patients that develop pneumonia, appear to be alveoli – tiny air sacs in the lungs that take up the oxygen we breathe and exchange it with carbon dioxide to exhale.
To better understand how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease, a team of Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST in collaboration with the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute at the University of Cambridge turned to organoids – ‘mini-organs’ grown in three dimensions to mimic the behaviour of tissue and organs.
The team used tissue donated to tissue banks at the Royal Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge University NHS Foundations Trust, UK, and Seoul National University Hospital to extract a type of lung cell known as human lung alveolar type 2 cells. By reprogramming these cells back to their earlier ‘stem cell’ stage, they were able to grow self-organizing alveolar-like 3D structures that mimic the behaviour of key lung tissue.
“The research community now has a powerful new platform to study precisely how the virus infects the lungs, as well as explore possible treatments,” said Professor Ju, co-senior author of the research.
Dr. Joo-Hyeon Lee, another co-senior author at the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute, said: “We still know surprisingly little about how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease. Our approach has allowed us to grow 3D models of key lung tissue – in a sense, ‘mini-lungs’ – in the lab and study what happens when they become infected.”
The team infected the organoids with a strain of SARS-CoV-2 taken from a patient in Korea who was diagnosed with COVID-19 on January 26 after traveling to Wuhan, China. Using a combination of fluorescence imaging and single cell genetic analysis, they were able to study how the cells responded to the virus.
When the 3D models were exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus began to replicate rapidly, reaching full cellular infection just six hours after infection. Replication enables the virus to spread throughout the body, infecting other cells and tissue.
Around the same time, the cells began to produce interferons – proteins that act as warning signals to neighbouring cells, telling them to activate their antiviral defences. After 48 hours, the interferons triggered the innate immune response – its first line of defence – and the cells started fighting back against infection.
Sixty hours after infection, a subset of alveolar cells began to disintegrate, leading to cell death and damage to the lung tissue.
Although the researchers observed changes to the lung cells within three days of infection, clinical symptoms of COVID-19 rarely occur so quickly and can sometimes take more than ten days after exposure to appear. The team say there are several possible reasons for this. It may take several days from the virus first infiltrating the upper respiratory tract to it reaching the alveoli. It may also require a substantial proportion of alveolar cells to be infected or for further interactions with immune cells resulting in inflammation before a patient displays symptoms.
“Based on our model we can tackle many unanswered key questions, such as understanding genetic susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, assessing relative infectivity of viral mutants, and revealing the damage processes of the virus in human alveolar cells,” said Professor Ju. “Most importantly, it provides the opportunity to develop and screen potential therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
“We hope to use our technique to grow these 3D models from cells of patients who are particularly vulnerable to infection, such as the elderly or people with diseased lungs, and find out what happens to their tissue,” added Dr. Lee.
The research was a collaboration involving scientists from KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Korea National Institute of Health, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Seoul National University Hospital and Genome Insight in Korea.
- ProfileProfessor Young Seok JuLaboratory of Cancer Genomics https://julab.kaist.ac.kr the Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.26 View 11407
'Mini-Lungs' Reveal Early Stages of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Researchers in Korea and the UK have successfully grown miniature models of critical lung structures called alveoli, and used them to study how the coronavirus that causes COVID-19 infects the lungs.
To date, there have been more than 40 million cases of COVID-19 and almost 1.13 million deaths worldwide. The main target tissues of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, especially in patients that develop pneumonia, appear to be alveoli – tiny air sacs in the lungs that take up the oxygen we breathe and exchange it with carbon dioxide to exhale.
To better understand how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease, a team of Professor Young Seok Ju from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST in collaboration with the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute at the University of Cambridge turned to organoids – ‘mini-organs’ grown in three dimensions to mimic the behaviour of tissue and organs.
The team used tissue donated to tissue banks at the Royal Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust and Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge University NHS Foundations Trust, UK, and Seoul National University Hospital to extract a type of lung cell known as human lung alveolar type 2 cells. By reprogramming these cells back to their earlier ‘stem cell’ stage, they were able to grow self-organizing alveolar-like 3D structures that mimic the behaviour of key lung tissue.
“The research community now has a powerful new platform to study precisely how the virus infects the lungs, as well as explore possible treatments,” said Professor Ju, co-senior author of the research.
Dr. Joo-Hyeon Lee, another co-senior author at the Wellcome-MRC Cambridge Stem Cell Institute, said: “We still know surprisingly little about how SARS-CoV-2 infects the lungs and causes disease. Our approach has allowed us to grow 3D models of key lung tissue – in a sense, ‘mini-lungs’ – in the lab and study what happens when they become infected.”
The team infected the organoids with a strain of SARS-CoV-2 taken from a patient in Korea who was diagnosed with COVID-19 on January 26 after traveling to Wuhan, China. Using a combination of fluorescence imaging and single cell genetic analysis, they were able to study how the cells responded to the virus.
When the 3D models were exposed to SARS-CoV-2, the virus began to replicate rapidly, reaching full cellular infection just six hours after infection. Replication enables the virus to spread throughout the body, infecting other cells and tissue.
Around the same time, the cells began to produce interferons – proteins that act as warning signals to neighbouring cells, telling them to activate their antiviral defences. After 48 hours, the interferons triggered the innate immune response – its first line of defence – and the cells started fighting back against infection.
Sixty hours after infection, a subset of alveolar cells began to disintegrate, leading to cell death and damage to the lung tissue.
Although the researchers observed changes to the lung cells within three days of infection, clinical symptoms of COVID-19 rarely occur so quickly and can sometimes take more than ten days after exposure to appear. The team say there are several possible reasons for this. It may take several days from the virus first infiltrating the upper respiratory tract to it reaching the alveoli. It may also require a substantial proportion of alveolar cells to be infected or for further interactions with immune cells resulting in inflammation before a patient displays symptoms.
“Based on our model we can tackle many unanswered key questions, such as understanding genetic susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2, assessing relative infectivity of viral mutants, and revealing the damage processes of the virus in human alveolar cells,” said Professor Ju. “Most importantly, it provides the opportunity to develop and screen potential therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
“We hope to use our technique to grow these 3D models from cells of patients who are particularly vulnerable to infection, such as the elderly or people with diseased lungs, and find out what happens to their tissue,” added Dr. Lee.
The research was a collaboration involving scientists from KAIST, the University of Cambridge, Korea National Institute of Health, Institute for Basic Science (IBS), Seoul National University Hospital and Genome Insight in Korea.
- ProfileProfessor Young Seok JuLaboratory of Cancer Genomics https://julab.kaist.ac.kr the Graduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.26 View 11407 -
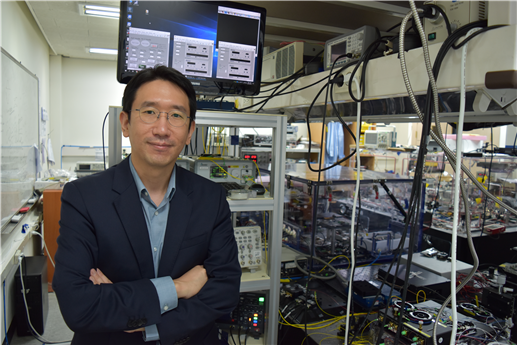 Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11400
Scientist of October: Professor Jungwon Kim
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was selected as the ‘Scientist of the Month’ for October 2020 by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea. Professor Kim was recognized for his contributions to expanding the horizons of the basics of precision engineering through his research on multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution sensors. He received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was selected as the recipient of this award in celebration of “Measurement Day”, which commemorates October 26 as the day in which King Sejong the Great established a volume measurement system.
Professor Kim discovered that the time difference between the pulse of light created by a laser and the pulse of the current produced by a light-emitting diode was as small as 100 attoseconds (10-16 seconds). He then developed a unique multifunctional ultrahigh-speed, high-resolution Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensor that could take measurements of multiple points at the same time by sampling electric light. The sensor, with a measurement speed of 100 megahertz (100 million vibrations per second), a resolution of 180 picometers (1/5.5 billion meters), and a dynamic range of 150 decibels, overcame the limitations of both existing TOF techniques and laser interferometric techniques at the same time. The results of this research were published in Nature Photonics on February 10, 2020.
Professor Kim said, “I’d like to thank the graduate students who worked passionately with me, and KAIST for providing an environment in which I could fully focus on research. I am looking forward to the new and diverse applications in the field of machine manufacturing, such as studying the dynamic phenomena in microdevices, or taking ultraprecision measurement of shapes for advanced manufacturing.”
(END)
2020.10.15 View 11400 -
 Professor Won-Ki Cho Selected as the 2020 SUHF Young Investigator
Professor Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of three recipients of the 2020 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Award.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 67 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the three recipients.
Professor Cho proposed research on how to observe the interactions between nuclear structures and constantly-changing chromatin monomers in four dimensions through ultra-high-resolution imaging of single living cells. This proposal was recognized as one that could help us better understand the process of transcription regulation, which remains a long-standing question in biology.
The other awards were given to Professor Soung-hun Roh of Seoul National University and Professor Joo-Hyeon Lee of the University of Cambridge.
With these three new awardees, a total of 17 scientists have been named SUHF Young Investigators to date, and the funding to support these scientists now totals 42.5 billion KRW.
Professor Inkyung Jung and Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences, and Professor Young Seok Ju and Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering are the four previous winners from KAIST in the years 2017 through 2019.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 12839
Professor Won-Ki Cho Selected as the 2020 SUHF Young Investigator
Professor Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of three recipients of the 2020 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Award.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 67 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the three recipients.
Professor Cho proposed research on how to observe the interactions between nuclear structures and constantly-changing chromatin monomers in four dimensions through ultra-high-resolution imaging of single living cells. This proposal was recognized as one that could help us better understand the process of transcription regulation, which remains a long-standing question in biology.
The other awards were given to Professor Soung-hun Roh of Seoul National University and Professor Joo-Hyeon Lee of the University of Cambridge.
With these three new awardees, a total of 17 scientists have been named SUHF Young Investigators to date, and the funding to support these scientists now totals 42.5 billion KRW.
Professor Inkyung Jung and Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences, and Professor Young Seok Ju and Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering are the four previous winners from KAIST in the years 2017 through 2019.
(END)
2020.10.15 View 12839 -
 Fundraising for the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building Kicks Off
KAIST started the fundraising campaign to construct the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building. This is one of the projects and events the 50th Anniversary Commemorative Committee established to celebrate the anniversary.
The ground will be broken in 2022 after raising approximately 50 billion KRW through 2021. The five-story building will be the latest addition to the KAIST campus. To highlight the campus’s history, the new building will connect the N5 (Basic Experiment & Research) and N2 (Administration Branch) buildings, the first buildings on the main Daejeon campus after its main campus moved from Seoul in 1987. Currently, the College of Business remains at the Seoul campus.
The 50th Anniversary Memorial Building will connect the two buildings in the shape of C, and represent KAIST’s C3 core value of Challenging, Creating, and Caring. The concept of this building was designed by Professor Sang-Min Bae from the Department of Industrial Design.
The 50th Anniversary Commemorative Committee said the Memorial Building will reflect the spirit of its core values. The first floor will accommodate the auditorium and exhibition hall, showcasing the latest achievements in KAIST innovation and convergence research as well as alumni startups and companies. The second floor will be an education space for entrepreneurship and video studios. An area for delivering creative education platforms such as Education 4.0 will be prepared on the third floor. The fourth floor will be used for global leadership education. The fifth floor will house the KAIST Club, a lounge for alumni and the Global Strategy Institute.
Co-Chair of the Fundraising & PR Sub-Committee of the KAIST 50th Anniversary Commemorative Committee and Former Vice President for Planning and Budget Seung-Bin Park and current Vice President for Planning and Budget Suchan Chae reiterated the importance of extending the infrastructure of the campus, saying that investments in the infrastructure will expand the university’s future growth potential. In a letter to kick off the fundraising efforts last month, they called for support from the entire KAIST community to help construct the new memorial building that will produce global talents and help young scientists make their dreams come true.
To donate, click here
2020.10.07 View 7922
Fundraising for the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building Kicks Off
KAIST started the fundraising campaign to construct the 50th Anniversary Memorial Building. This is one of the projects and events the 50th Anniversary Commemorative Committee established to celebrate the anniversary.
The ground will be broken in 2022 after raising approximately 50 billion KRW through 2021. The five-story building will be the latest addition to the KAIST campus. To highlight the campus’s history, the new building will connect the N5 (Basic Experiment & Research) and N2 (Administration Branch) buildings, the first buildings on the main Daejeon campus after its main campus moved from Seoul in 1987. Currently, the College of Business remains at the Seoul campus.
The 50th Anniversary Memorial Building will connect the two buildings in the shape of C, and represent KAIST’s C3 core value of Challenging, Creating, and Caring. The concept of this building was designed by Professor Sang-Min Bae from the Department of Industrial Design.
The 50th Anniversary Commemorative Committee said the Memorial Building will reflect the spirit of its core values. The first floor will accommodate the auditorium and exhibition hall, showcasing the latest achievements in KAIST innovation and convergence research as well as alumni startups and companies. The second floor will be an education space for entrepreneurship and video studios. An area for delivering creative education platforms such as Education 4.0 will be prepared on the third floor. The fourth floor will be used for global leadership education. The fifth floor will house the KAIST Club, a lounge for alumni and the Global Strategy Institute.
Co-Chair of the Fundraising & PR Sub-Committee of the KAIST 50th Anniversary Commemorative Committee and Former Vice President for Planning and Budget Seung-Bin Park and current Vice President for Planning and Budget Suchan Chae reiterated the importance of extending the infrastructure of the campus, saying that investments in the infrastructure will expand the university’s future growth potential. In a letter to kick off the fundraising efforts last month, they called for support from the entire KAIST community to help construct the new memorial building that will produce global talents and help young scientists make their dreams come true.
To donate, click here
2020.10.07 View 7922 -
 Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 14480
Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 14480 -
 Biomarker Predicts Who Will Have Severe COVID-19
- Airway cell analyses showing an activated immune axis could pinpoint the COVID-19 patients who will most benefit from targeted therapies.-
KAIST researchers have identified key markers that could help pinpoint patients who are bound to get a severe reaction to COVID-19 infection. This would help doctors provide the right treatments at the right time, potentially saving lives. The findings were published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology on August 28.
People’s immune systems react differently to infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, ranging from mild to severe, life-threatening responses.
To understand the differences in responses, Professor Heung Kyu Lee and PhD candidate Jang Hyun Park from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST analysed ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequencing data extracted from individual airway cells of healthy controls and of mildly and severely ill patients with COVID-19. The data was available in a public database previously published by a group of Chinese researchers.
“Our analyses identified an association between immune cells called neutrophils and special cell receptors that bind to the steroid hormone glucocorticoid,” Professor Lee explained. “This finding could be used as a biomarker for predicting disease severity in patients and thus selecting a targeted therapy that can help treat them at an appropriate time,” he added.
Severe illness in COVID-19 is associated with an exaggerated immune response that leads to excessive airway-damaging inflammation. This condition, known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), accounts for 70% of deaths in fatal COVID-19 infections.
Scientists already know that this excessive inflammation involves heightened neutrophil recruitment to the airways, but the detailed mechanisms of this reaction are still unclear.
Lee and Park’s analyses found that a group of immune cells called myeloid cells produced excess amounts of neutrophil-recruiting chemicals in severely ill patients, including a cytokine called tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and a chemokine called CXCL8.
Further RNA analyses of neutrophils in severely ill patients showed they were less able to recruit very important T cells needed for attacking the virus. At the same time, the neutrophils produced too many extracellular molecules that normally trap pathogens, but damage airway cells when produced in excess.
The researchers additionally found that the airway cells in severely ill patients were not expressing enough glucocorticoid receptors. This was correlated with increased CXCL8 expression and neutrophil recruitment.
Glucocorticoids, like the well-known drug dexamethasone, are anti-inflammatory agents that could play a role in treating COVID-19. However, using them in early or mild forms of the infection could suppress the necessary immune reactions to combat the virus. But if airway damage has already happened in more severe cases, glucocorticoid treatment would be ineffective.
Knowing who to give this treatment to and when is really important. COVID-19 patients showing reduced glucocorticoid receptor expression, increased CXCL8 expression, and excess neutrophil recruitment to the airways could benefit from treatment with glucocorticoids to prevent airway damage. Further research is needed, however, to confirm the relationship between glucocorticoids and neutrophil inflammation at the protein level.
“Our study could serve as a springboard towards more accurate and reliable COVID-19 treatments,” Professor Lee said.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, and Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by KAIST.
Figure. Low glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression led to excessive inflammation and lung damage by neutrophils through enhancing the expression of CXCL8 and other cytokines.
Image credit: Professor Heung Kyu Lee, KAIST. Created with Biorender.com.
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
-Publication:
Jang Hyun Park, and Heung Kyu Lee. (2020). Re-analysis of Single Cell Transcriptome Reveals That the NR3C1-CXCL8-Neutrophil Axis Determines the Severity of COVID-19. Frontiers in Immunology, Available online at https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.02145
-Profile: Heung Kyu Lee
Associate Professor
heungkyu.lee@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.heungkyulee.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory of Host Defenses
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE)
The Center for Epidemic Preparedness at KAIST Institute
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Jang Hyun Park
PhD Candidate
janghyun.park@kaist.ac.kr
GSMSE, KAIST
2020.09.17 View 15552
Biomarker Predicts Who Will Have Severe COVID-19
- Airway cell analyses showing an activated immune axis could pinpoint the COVID-19 patients who will most benefit from targeted therapies.-
KAIST researchers have identified key markers that could help pinpoint patients who are bound to get a severe reaction to COVID-19 infection. This would help doctors provide the right treatments at the right time, potentially saving lives. The findings were published in the journal Frontiers in Immunology on August 28.
People’s immune systems react differently to infection with SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, ranging from mild to severe, life-threatening responses.
To understand the differences in responses, Professor Heung Kyu Lee and PhD candidate Jang Hyun Park from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST analysed ribonucleic acid (RNA) sequencing data extracted from individual airway cells of healthy controls and of mildly and severely ill patients with COVID-19. The data was available in a public database previously published by a group of Chinese researchers.
“Our analyses identified an association between immune cells called neutrophils and special cell receptors that bind to the steroid hormone glucocorticoid,” Professor Lee explained. “This finding could be used as a biomarker for predicting disease severity in patients and thus selecting a targeted therapy that can help treat them at an appropriate time,” he added.
Severe illness in COVID-19 is associated with an exaggerated immune response that leads to excessive airway-damaging inflammation. This condition, known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), accounts for 70% of deaths in fatal COVID-19 infections.
Scientists already know that this excessive inflammation involves heightened neutrophil recruitment to the airways, but the detailed mechanisms of this reaction are still unclear.
Lee and Park’s analyses found that a group of immune cells called myeloid cells produced excess amounts of neutrophil-recruiting chemicals in severely ill patients, including a cytokine called tumour necrosis factor (TNF) and a chemokine called CXCL8.
Further RNA analyses of neutrophils in severely ill patients showed they were less able to recruit very important T cells needed for attacking the virus. At the same time, the neutrophils produced too many extracellular molecules that normally trap pathogens, but damage airway cells when produced in excess.
The researchers additionally found that the airway cells in severely ill patients were not expressing enough glucocorticoid receptors. This was correlated with increased CXCL8 expression and neutrophil recruitment.
Glucocorticoids, like the well-known drug dexamethasone, are anti-inflammatory agents that could play a role in treating COVID-19. However, using them in early or mild forms of the infection could suppress the necessary immune reactions to combat the virus. But if airway damage has already happened in more severe cases, glucocorticoid treatment would be ineffective.
Knowing who to give this treatment to and when is really important. COVID-19 patients showing reduced glucocorticoid receptor expression, increased CXCL8 expression, and excess neutrophil recruitment to the airways could benefit from treatment with glucocorticoids to prevent airway damage. Further research is needed, however, to confirm the relationship between glucocorticoids and neutrophil inflammation at the protein level.
“Our study could serve as a springboard towards more accurate and reliable COVID-19 treatments,” Professor Lee said.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, and Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by KAIST.
Figure. Low glucocorticoid receptor (GR) expression led to excessive inflammation and lung damage by neutrophils through enhancing the expression of CXCL8 and other cytokines.
Image credit: Professor Heung Kyu Lee, KAIST. Created with Biorender.com.
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute these figures and image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
-Publication:
Jang Hyun Park, and Heung Kyu Lee. (2020). Re-analysis of Single Cell Transcriptome Reveals That the NR3C1-CXCL8-Neutrophil Axis Determines the Severity of COVID-19. Frontiers in Immunology, Available online at https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.02145
-Profile: Heung Kyu Lee
Associate Professor
heungkyu.lee@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.heungkyulee.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory of Host Defenses
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE)
The Center for Epidemic Preparedness at KAIST Institute
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Jang Hyun Park
PhD Candidate
janghyun.park@kaist.ac.kr
GSMSE, KAIST
2020.09.17 View 15552