college+of+e
-
 Researchers Report Longest-lived Aqueous Flow Batteries
New technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries
A research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed water-based zinc/bromine redox flow batteries (ZBBs) with the best life expectancy among all the redox flow batteries reported by identifying and solving the deterioration issue with zinc electrodes.
Professor Kim, head of the Advanced Battery Center at KAIST's Nano-fusion Research Institute, said, "We presented a new technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries. Not only is it cheaper than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but it can contribute to the expansion of renewable energy and the safe supply of energy storage systems that can run with more than 80 percent energy efficiency."
ZBBs were found to have stable life spans of more than 5,000 cycles, even at a high current density of 100 mA/cm2. It was also confirmed that it represented the highest output and life expectancy compared to Redox flow batteries (RFBs) reported worldwide, which use other redox couples such as zinc-bromine, zinc-iodine, zinc-iron, and vanadium.
Recently, more attention has been focused on energy storage system (ESS) that can improve energy utilization efficiency by storing new and late-night power in large quantities and supplying it to the grid if necessary to supplement the intermittent nature of renewable energy and meet peak power demand.
However, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are currently the core technology of ESSs, have been criticized for not being suitable for ESSs, which store large amounts of electricity due to their inherent risk of ignition and fire. In fact, a total of 33 cases of ESSs using LIBs in Korea had fire accidents, and 35% of all ESS facilities were shut down. This is estimated to have resulted in more than 700 billion won in losses.
As a result, water-based RFBs have drawn great attention. In particular, ZBBs that use ultra-low-cost bromide (ZnBr2) as an active material have been developed for ESSs since the 1970s, with their advantages of high cell voltage, high energy density, and low price compared to other RFBs. Until now, however, the commercialization of ZBBs has been delayed due to the short life span caused by the zinc electrodes. In particular, the uneven "dendrite" growth behavior of zinc metals during the charging and discharging process leads to internal short circuits in the battery which shorten its life.
The research team noted that self-aggregation occurs through the surface diffusion of zinc nuclei on the carbon electrode surface with low surface energy, and determined that self-aggregation was the main cause of zinc dendrite formation through quantum mechanics-based computer simulations and transmission electron microscopy. Furthermore, it was found that the surface diffusion of the zinc nuclei was inhibited in certain carbon fault structures so that dendrites were not produced.
Single vacancy defect, where one carbon atom is removed, exchanges zinc nuclei and electrons, and is strongly coupled, thus inhibiting surface diffusion and enabling uniform nuclear production/growth. The research team applied carbon electrodes with high density fault structure to ZBBs, achieving life characteristics of more than 5,000 cycles at a high charge current density (100 mA/cm2), which is 30 times that of LIBs.
This ESS technology, which can supply eco-friendly electric energy such as renewable energy to the private sector through technology that can drive safe and cheap redox flow batteries for long life, is expected to draw attention once again.
Publication:
Ju-Hyuk Lee, Riyul Kim, Soohyun Kim, Jiyun Heo, Hyeokjin Kwon, Jung Hoon Yang, and Hee-Tak Kim. 2020. Dendrite-free Zn electrodeposition triggered by interatomic orbital hybridization of Zn and single vacancy carbon defects for aqueous Zn-based flow batteries. Energy and Environmental Science, 2020, 13, 2839-2848.
Link to download the full-text paper:http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D0EE00723D
Profile: Prof. Hee-Tak Kimheetak.kim@kaist.ac.krhttp://eed.kaist.ac.krAssociate ProfessorDepartment of Chemical & Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.16 View 13122
Researchers Report Longest-lived Aqueous Flow Batteries
New technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries
A research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed water-based zinc/bromine redox flow batteries (ZBBs) with the best life expectancy among all the redox flow batteries reported by identifying and solving the deterioration issue with zinc electrodes.
Professor Kim, head of the Advanced Battery Center at KAIST's Nano-fusion Research Institute, said, "We presented a new technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries. Not only is it cheaper than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but it can contribute to the expansion of renewable energy and the safe supply of energy storage systems that can run with more than 80 percent energy efficiency."
ZBBs were found to have stable life spans of more than 5,000 cycles, even at a high current density of 100 mA/cm2. It was also confirmed that it represented the highest output and life expectancy compared to Redox flow batteries (RFBs) reported worldwide, which use other redox couples such as zinc-bromine, zinc-iodine, zinc-iron, and vanadium.
Recently, more attention has been focused on energy storage system (ESS) that can improve energy utilization efficiency by storing new and late-night power in large quantities and supplying it to the grid if necessary to supplement the intermittent nature of renewable energy and meet peak power demand.
However, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are currently the core technology of ESSs, have been criticized for not being suitable for ESSs, which store large amounts of electricity due to their inherent risk of ignition and fire. In fact, a total of 33 cases of ESSs using LIBs in Korea had fire accidents, and 35% of all ESS facilities were shut down. This is estimated to have resulted in more than 700 billion won in losses.
As a result, water-based RFBs have drawn great attention. In particular, ZBBs that use ultra-low-cost bromide (ZnBr2) as an active material have been developed for ESSs since the 1970s, with their advantages of high cell voltage, high energy density, and low price compared to other RFBs. Until now, however, the commercialization of ZBBs has been delayed due to the short life span caused by the zinc electrodes. In particular, the uneven "dendrite" growth behavior of zinc metals during the charging and discharging process leads to internal short circuits in the battery which shorten its life.
The research team noted that self-aggregation occurs through the surface diffusion of zinc nuclei on the carbon electrode surface with low surface energy, and determined that self-aggregation was the main cause of zinc dendrite formation through quantum mechanics-based computer simulations and transmission electron microscopy. Furthermore, it was found that the surface diffusion of the zinc nuclei was inhibited in certain carbon fault structures so that dendrites were not produced.
Single vacancy defect, where one carbon atom is removed, exchanges zinc nuclei and electrons, and is strongly coupled, thus inhibiting surface diffusion and enabling uniform nuclear production/growth. The research team applied carbon electrodes with high density fault structure to ZBBs, achieving life characteristics of more than 5,000 cycles at a high charge current density (100 mA/cm2), which is 30 times that of LIBs.
This ESS technology, which can supply eco-friendly electric energy such as renewable energy to the private sector through technology that can drive safe and cheap redox flow batteries for long life, is expected to draw attention once again.
Publication:
Ju-Hyuk Lee, Riyul Kim, Soohyun Kim, Jiyun Heo, Hyeokjin Kwon, Jung Hoon Yang, and Hee-Tak Kim. 2020. Dendrite-free Zn electrodeposition triggered by interatomic orbital hybridization of Zn and single vacancy carbon defects for aqueous Zn-based flow batteries. Energy and Environmental Science, 2020, 13, 2839-2848.
Link to download the full-text paper:http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D0EE00723D
Profile: Prof. Hee-Tak Kimheetak.kim@kaist.ac.krhttp://eed.kaist.ac.krAssociate ProfessorDepartment of Chemical & Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.16 View 13122 -
 KAIST and Google Partner to Develop AI Curriculum
Two KAIST professors, Hyun Wook Ka from the School of Transdisciplinary Studies and Young Jae Jang from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, were recipients of Google Education Grants that will support the development of new AI courses integrating the latest industrial technology. This collaboration is part of the KAIST-Google Partnership, which was established in July 2019 with the goal of nurturing AI talent at KAIST.
The two proposals -- Professor Ka’s ‘Cloud AI-Empowered Multimodal Data Analysis for Human Affect Detection and Recognition’ and Professor Jang’s ‘Learning Smart Factory with AI’-- were selected by the KAIST Graduate School of AI through a school-wide competition held in July. The proposals then went through a final review by Google and were accepted. The two professors will receive $7,500 each for developing AI courses using Google technology for one year.
Professor Ka’s curriculum aims to provide a rich learning experience for students by providing basic knowledge on data science and AI and helping them obtain better problem solving and application skills using practical and interdisciplinary data science and AI technology.
Professor Jang’s curriculum is designed to solve real-world manufacturing problems using AI and it will be field-oriented. Professor Jang has been managing three industry-academic collaboration centers in manufacturing and smart factories within KAIST and plans to develop his courses to go beyond theory and be centered on case studies for solving real-world manufacturing problems using AI.
Professor Jang said, “Data is at the core of smart factories and AI education, but there is often not enough of it for the education to be effective. The KAIST Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory has a testbed for directly acquiring data generated from real semiconductor automation equipment, analyzing it, and applying algorithms, which enables truly effective smart factory and AI education.”
KAIST signed a partnership with Google in July 2019 to foster global AI talent and is operating various programs to train AI experts and support excellent AI research for two years.
The Google AI Focused Research Award supports world-class faculty performing cutting-edge research and was previously awarded to professors Sung Ju Hwang from the Graduate School of AI and Steven Whang from the School of Electrical Engineering along with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) credits. These two professors have been collaborating with Google teams since October 2018 and recently extended their projects to continue through 2021.
In addition, a Google Ph.D. Fellowship was awarded to Taesik Gong from the School of Computing in October this year, and three Student Travel Grants were awarded to Sejun Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, Chulhyung Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, and Sangyun Lee from the School of Computing earlier in March. Five students were also recommended for the Google Internship program in March.
(END)
2020.12.11 View 12070
KAIST and Google Partner to Develop AI Curriculum
Two KAIST professors, Hyun Wook Ka from the School of Transdisciplinary Studies and Young Jae Jang from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, were recipients of Google Education Grants that will support the development of new AI courses integrating the latest industrial technology. This collaboration is part of the KAIST-Google Partnership, which was established in July 2019 with the goal of nurturing AI talent at KAIST.
The two proposals -- Professor Ka’s ‘Cloud AI-Empowered Multimodal Data Analysis for Human Affect Detection and Recognition’ and Professor Jang’s ‘Learning Smart Factory with AI’-- were selected by the KAIST Graduate School of AI through a school-wide competition held in July. The proposals then went through a final review by Google and were accepted. The two professors will receive $7,500 each for developing AI courses using Google technology for one year.
Professor Ka’s curriculum aims to provide a rich learning experience for students by providing basic knowledge on data science and AI and helping them obtain better problem solving and application skills using practical and interdisciplinary data science and AI technology.
Professor Jang’s curriculum is designed to solve real-world manufacturing problems using AI and it will be field-oriented. Professor Jang has been managing three industry-academic collaboration centers in manufacturing and smart factories within KAIST and plans to develop his courses to go beyond theory and be centered on case studies for solving real-world manufacturing problems using AI.
Professor Jang said, “Data is at the core of smart factories and AI education, but there is often not enough of it for the education to be effective. The KAIST Advanced Manufacturing Laboratory has a testbed for directly acquiring data generated from real semiconductor automation equipment, analyzing it, and applying algorithms, which enables truly effective smart factory and AI education.”
KAIST signed a partnership with Google in July 2019 to foster global AI talent and is operating various programs to train AI experts and support excellent AI research for two years.
The Google AI Focused Research Award supports world-class faculty performing cutting-edge research and was previously awarded to professors Sung Ju Hwang from the Graduate School of AI and Steven Whang from the School of Electrical Engineering along with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) credits. These two professors have been collaborating with Google teams since October 2018 and recently extended their projects to continue through 2021.
In addition, a Google Ph.D. Fellowship was awarded to Taesik Gong from the School of Computing in October this year, and three Student Travel Grants were awarded to Sejun Park from the School of Electrical Engineering, Chulhyung Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, and Sangyun Lee from the School of Computing earlier in March. Five students were also recommended for the Google Internship program in March.
(END)
2020.12.11 View 12070 -
 A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 10783
A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 10783 -
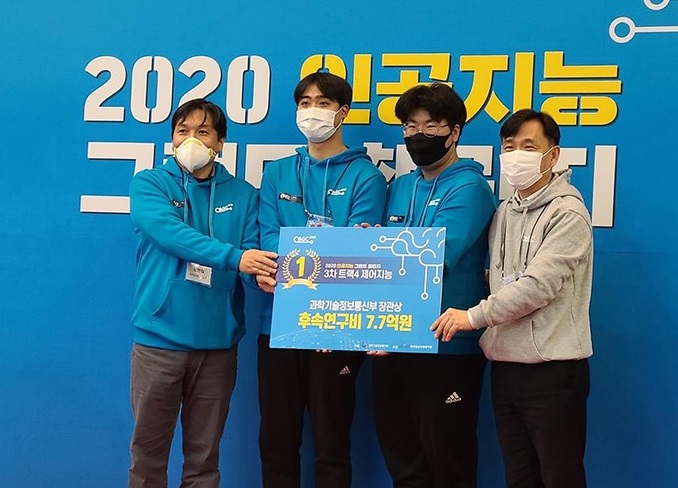 Team USRG’s Winning Streak Continues at the AI Grand Challenge
Team USRG (Unmanned Systems Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering has won the AI Grand Challenge 2020 held on Nov. 23 at Kintex in Ilsan, Kyonggi-do for the second consecutive year. The team received 7.7 million KRW in research funding from the Ministry of Science and ICT, the organizer of the challenge.
The team took a little over two minutes to complete the rescue operation mission of the challenge. The mission included swerving around seven obstacles, airdropping an aid package, and safely landing after identifying the landing spot. Their drone is the only one that successfully passed through a 10-meter tunnel out of five pre-qualified teams: three from universities and two from companies.
The AI Grand Challenge, which began in 2017, was designed to promote AI technology and its applications for addressing high-risk technical challenges, especially for conducting complex disaster relief operations.
For autonomous flying drones, swerving to avoid objects has always been an essential skill and a big challenge. For their flawless performance in the rescue operation, the team loaded an AI algorithm and upgraded their drone by improving the LiDAR-based localization system and a stronger propulsion system to carry more sensors. The drone weighs 2.4 kg and carries a small yet powerful computer with a GPU.
This AI-powered drone can complete rescue missions more efficiently in complicated and disastrous environments by precisely comprehending where the drone should go without needing GPS. The team also designed an all-in-one prop guard and installed a gripper onto the bottom of the drone to hold the aid package securely.
“We tried hard to improve our localization system better to resolve issues we had in the previous event,” said Professor Shim. Two PhD candidates, Han-Sob Lee and Bo-Sung Kim played a critical role in developing this drone.
After their two-year winning streak, their prize money now totals 2.4 billion KRW, equivalent to the winning prize of the DARPA Challenge. As the winning team, they will collaborate with other champions at the AI track challenge to develop rescue mission technology for a more complex environment.
“The importance of AI technology is continuing to grow and the government is providing large amounts of funding for research in this field. We would like to develop very competitive technology that will work in the real world,” Professor Shim added.
His group is investigating a wide array of AI technologies applicable to unmanned vehicles including indoor flying drones, self-driving cars, delivery robots, and a tram that circles the campus.
2020.12.01 View 8731
Team USRG’s Winning Streak Continues at the AI Grand Challenge
Team USRG (Unmanned Systems Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering has won the AI Grand Challenge 2020 held on Nov. 23 at Kintex in Ilsan, Kyonggi-do for the second consecutive year. The team received 7.7 million KRW in research funding from the Ministry of Science and ICT, the organizer of the challenge.
The team took a little over two minutes to complete the rescue operation mission of the challenge. The mission included swerving around seven obstacles, airdropping an aid package, and safely landing after identifying the landing spot. Their drone is the only one that successfully passed through a 10-meter tunnel out of five pre-qualified teams: three from universities and two from companies.
The AI Grand Challenge, which began in 2017, was designed to promote AI technology and its applications for addressing high-risk technical challenges, especially for conducting complex disaster relief operations.
For autonomous flying drones, swerving to avoid objects has always been an essential skill and a big challenge. For their flawless performance in the rescue operation, the team loaded an AI algorithm and upgraded their drone by improving the LiDAR-based localization system and a stronger propulsion system to carry more sensors. The drone weighs 2.4 kg and carries a small yet powerful computer with a GPU.
This AI-powered drone can complete rescue missions more efficiently in complicated and disastrous environments by precisely comprehending where the drone should go without needing GPS. The team also designed an all-in-one prop guard and installed a gripper onto the bottom of the drone to hold the aid package securely.
“We tried hard to improve our localization system better to resolve issues we had in the previous event,” said Professor Shim. Two PhD candidates, Han-Sob Lee and Bo-Sung Kim played a critical role in developing this drone.
After their two-year winning streak, their prize money now totals 2.4 billion KRW, equivalent to the winning prize of the DARPA Challenge. As the winning team, they will collaborate with other champions at the AI track challenge to develop rescue mission technology for a more complex environment.
“The importance of AI technology is continuing to grow and the government is providing large amounts of funding for research in this field. We would like to develop very competitive technology that will work in the real world,” Professor Shim added.
His group is investigating a wide array of AI technologies applicable to unmanned vehicles including indoor flying drones, self-driving cars, delivery robots, and a tram that circles the campus.
2020.12.01 View 8731 -
 Simulations Open a New Way to Reverse Cell Aging
Turning off a newly identified enzyme could reverse a natural aging process in cells.
Research findings by a KAIST team provide insight into the complex mechanism of cellular senescence and present a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing age-related diseases associated with the accumulation of senescent cells.
Simulations that model molecular interactions have identified an enzyme that could be targeted to reverse a natural aging process called cellular senescence. The findings were validated with laboratory experiments on skin cells and skin equivalent tissues, and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Our research opens the door for a new generation that perceives aging as a reversible biological phenomenon,” says Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), who led the research with colleagues from KAIST and Amorepacific Corporation in Korea.
Cells respond to a variety of factors, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, and shortening of the telomeres capping the ends of chromosomes, by entering a stable and persistent exit from the cell cycle. This process, called cellular senescence, is important, as it prevents damaged cells from proliferating and turning into cancer cells. But it is also a natural process that contributes to aging and age-related diseases. Recent research has shown that cellular senescence can be reversed. But the laboratory approaches used thus far also impair tissue regeneration or have the potential to trigger malignant transformations.
Professor Cho and his colleagues used an innovative strategy to identify molecules that could be targeted for reversing cellular senescence. The team pooled together information from the literature and databases about the molecular processes involved in cellular senescence. To this, they added results from their own research on the molecular processes involved in the proliferation, quiescence (a non-dividing cell that can re-enter the cell cycle) and senescence of skin fibroblasts, a cell type well known for repairing wounds. Using algorithms, they developed a model that simulates the interactions between these molecules. Their analyses allowed them to predict which molecules could be targeted to reverse cell senescence.
They then investigated one of the molecules, an enzyme called PDK1, in incubated senescent skin fibroblasts and three-dimensional skin equivalent tissue models. They found that blocking PDK1 led to the inhibition of two downstream signalling molecules, which in turn restored the cells’ ability to enter back into the cell cycle. Notably, the cells retained their capacity to regenerate wounded skin without proliferating in a way that could lead to malignant transformation.
The scientists recommend investigations are next done in organs and organisms to determine the full effect of PDK1 inhibition. Since the gene that codes for PDK1 is overexpressed in some cancers, the scientists expect that inhibiting it will have both anti-aging and anti-cancer effects.
-Profile
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
Laboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired Engineering
http://sbie.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.26 View 12805
Simulations Open a New Way to Reverse Cell Aging
Turning off a newly identified enzyme could reverse a natural aging process in cells.
Research findings by a KAIST team provide insight into the complex mechanism of cellular senescence and present a potential therapeutic strategy for reducing age-related diseases associated with the accumulation of senescent cells.
Simulations that model molecular interactions have identified an enzyme that could be targeted to reverse a natural aging process called cellular senescence. The findings were validated with laboratory experiments on skin cells and skin equivalent tissues, and published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
“Our research opens the door for a new generation that perceives aging as a reversible biological phenomenon,” says Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), who led the research with colleagues from KAIST and Amorepacific Corporation in Korea.
Cells respond to a variety of factors, such as oxidative stress, DNA damage, and shortening of the telomeres capping the ends of chromosomes, by entering a stable and persistent exit from the cell cycle. This process, called cellular senescence, is important, as it prevents damaged cells from proliferating and turning into cancer cells. But it is also a natural process that contributes to aging and age-related diseases. Recent research has shown that cellular senescence can be reversed. But the laboratory approaches used thus far also impair tissue regeneration or have the potential to trigger malignant transformations.
Professor Cho and his colleagues used an innovative strategy to identify molecules that could be targeted for reversing cellular senescence. The team pooled together information from the literature and databases about the molecular processes involved in cellular senescence. To this, they added results from their own research on the molecular processes involved in the proliferation, quiescence (a non-dividing cell that can re-enter the cell cycle) and senescence of skin fibroblasts, a cell type well known for repairing wounds. Using algorithms, they developed a model that simulates the interactions between these molecules. Their analyses allowed them to predict which molecules could be targeted to reverse cell senescence.
They then investigated one of the molecules, an enzyme called PDK1, in incubated senescent skin fibroblasts and three-dimensional skin equivalent tissue models. They found that blocking PDK1 led to the inhibition of two downstream signalling molecules, which in turn restored the cells’ ability to enter back into the cell cycle. Notably, the cells retained their capacity to regenerate wounded skin without proliferating in a way that could lead to malignant transformation.
The scientists recommend investigations are next done in organs and organisms to determine the full effect of PDK1 inhibition. Since the gene that codes for PDK1 is overexpressed in some cancers, the scientists expect that inhibiting it will have both anti-aging and anti-cancer effects.
-Profile
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
Laboratory for Systems Biology and Bio-Inspired Engineering
http://sbie.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.26 View 12805 -
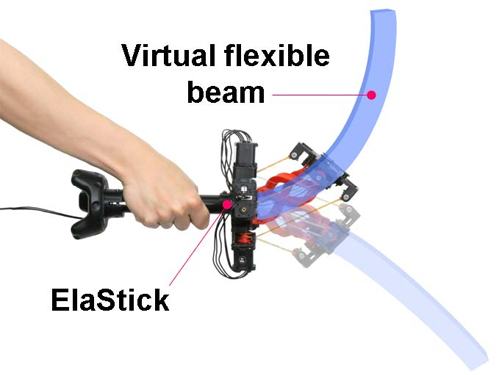 Feel the Force with ElaStick
ElaStick, a handheld variable stiffness display, renders the dynamic haptic response of a flexible object
Haptic controllers play an important role in providing rich and immersive virtual reality experiences. Professor Andrea Bianchi’s team in the Department of Industrial Design recreated the haptic response of flexible objects made of different materials and with different shapes by changing the stiffness of a custom-controller – ElaStick.
ElaStick is a portable hand-held force-feedback controller that is capable of rendering the illusion of how flexible and deformable objects feel when held in the hand. This VR haptic controller can change its stiffness in two directions independently and continuously. Since providing haptic feedback enhances the VR experience, researchers have suggested numerous approaches for rendering the physical properties of virtual objects - such as weights, the movement of mass, impacts, and damped oscillations.
The research team designed a new mechanism based on a quaternion joint and four variable-stiffness tendons. The quaternion joint is a two-DoF bending joint that enables ElaStick to bend and oscillate in any direction using a pair of tendons with varying stiffness. In fact, each tendon around the joint is made of a series of elastic rubber bands and inelastic fishing lines and can vary its stiffness by changing the proportion of the two materials. Thanks to these structures, each pair of tendons can behave independently, controlling the anisotropic characteristics of the entire device.
“The main challenge was to implement the mechanism to control the stiffness while maintaining independence between deformations in two perpendicular directions,” said Professor Bianchi.
The research team successfully measured the relative threshold of human perception on the stiffness of a handheld object. The results showed that the just-noticeable difference (JND) of human perception of stiffness is at most about 30% of the change from the initial value. It also found that appropriate haptic responses significantly enhance the quality of the VR experience. The research team surveyed the perceived realism, immersion, and enjoyment of participants after they played with various flexible objects in VR.
“It is meaningful that the haptic feedback of a flexible object was mechanically reproduced and its effectiveness in VR was proven. ElaStick has succeeded in implementing a novel mechanism to recreate the dynamic response of flexible objects that mimic real ones, suggesting a new category of haptic feedback that can be provided in VR,” explained Professor Bianchi.
The team plans to extend the ElaStick’s applications, from being used merely as a game controller to driving simulations, medical training, and many other digital contexts. This research, led by MS candidate Neung Ryu, won the Best Paper Award at the ACM UIST 2020 (the ACM Symposium on User Interface Software & Technology) last month.
-ProfileProfessor Andrea BianchiMakinteract.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Industrial DesignKAIST
2020.11.23 View 6526
Feel the Force with ElaStick
ElaStick, a handheld variable stiffness display, renders the dynamic haptic response of a flexible object
Haptic controllers play an important role in providing rich and immersive virtual reality experiences. Professor Andrea Bianchi’s team in the Department of Industrial Design recreated the haptic response of flexible objects made of different materials and with different shapes by changing the stiffness of a custom-controller – ElaStick.
ElaStick is a portable hand-held force-feedback controller that is capable of rendering the illusion of how flexible and deformable objects feel when held in the hand. This VR haptic controller can change its stiffness in two directions independently and continuously. Since providing haptic feedback enhances the VR experience, researchers have suggested numerous approaches for rendering the physical properties of virtual objects - such as weights, the movement of mass, impacts, and damped oscillations.
The research team designed a new mechanism based on a quaternion joint and four variable-stiffness tendons. The quaternion joint is a two-DoF bending joint that enables ElaStick to bend and oscillate in any direction using a pair of tendons with varying stiffness. In fact, each tendon around the joint is made of a series of elastic rubber bands and inelastic fishing lines and can vary its stiffness by changing the proportion of the two materials. Thanks to these structures, each pair of tendons can behave independently, controlling the anisotropic characteristics of the entire device.
“The main challenge was to implement the mechanism to control the stiffness while maintaining independence between deformations in two perpendicular directions,” said Professor Bianchi.
The research team successfully measured the relative threshold of human perception on the stiffness of a handheld object. The results showed that the just-noticeable difference (JND) of human perception of stiffness is at most about 30% of the change from the initial value. It also found that appropriate haptic responses significantly enhance the quality of the VR experience. The research team surveyed the perceived realism, immersion, and enjoyment of participants after they played with various flexible objects in VR.
“It is meaningful that the haptic feedback of a flexible object was mechanically reproduced and its effectiveness in VR was proven. ElaStick has succeeded in implementing a novel mechanism to recreate the dynamic response of flexible objects that mimic real ones, suggesting a new category of haptic feedback that can be provided in VR,” explained Professor Bianchi.
The team plans to extend the ElaStick’s applications, from being used merely as a game controller to driving simulations, medical training, and many other digital contexts. This research, led by MS candidate Neung Ryu, won the Best Paper Award at the ACM UIST 2020 (the ACM Symposium on User Interface Software & Technology) last month.
-ProfileProfessor Andrea BianchiMakinteract.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Industrial DesignKAIST
2020.11.23 View 6526 -
 Researchers Control Multiple Wavelengths of Light from a Single Source
KAIST researchers have synthesized a collection of nanoparticles, known as carbon dots, capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of light from a single particle. Additionally, the team discovered that the dispersion of the carbon dots, or the interparticle distance between each dot, influences the properties of the light the carbon dots emit. The discovery will allow researchers to understand how to control these carbon dots and create new, environmentally responsible displays, lighting, and sensing technology.
Research into nanoparticles capable of emitting light, such as quantum dots, has been an active area of interest for the last decade and a half. These particles, or phosphors, are nanoparticles made out of various materials that are capable of emitting light at specific wavelengths by leveraging quantum mechanical properties of the materials. This provides new ways to develop lighting and display solutions as well as more precise detection and sensing in instruments.
As technology becomes smaller and more sophisticated, the usage of fluorescent nanoparticles has seen a dramatic increase in many applications due to the purity of the colors emitting from the dots as well as their tunability to meet desired optical properties.
Carbon dots, a type of fluorescent nanoparticles, have seen an increase in interest from researchers as a candidate to replace non-carbon dots, the construction of which requires heavy metals that are toxic to the environment. Since they are made up of mostly carbon, the low toxicity is an extremely attractive quality when coupled with the tunability of their inherent optical properties.
Another striking feature of carbon dots is their capability to emit multiple wavelengths of light from a single nanoparticle. This multi-wavelength emission can be stimulated under a single excitation source, enabling the simple and robust generation of white light from a single particle by emitting multiple wavelengths simultaneously.
Carbon dots also exhibit a concentration-dependent photoluminescence. In other words, the distance between individual carbon dots affects the light that the carbon dots subsequently emit under an excitation source. These combined properties make carbon dots a unique source that will result in extremely accurate detection and sensing.
This concentration-dependency, however, had not been fully understood. In order to fully utilize the capabilities of carbon dots, the mechanisms that govern the seemingly variable optical properties must first be uncovered. It was previously theorized that the concentration-dependency of carbon dots was due to a hydrogen bonding effect.
Now, a KAIST research team, led by Professor Do Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has posited and demonstrated that the dual-color-emissiveness is instead due to the interparticle distances between each carbon dot. This study was made available online in June 2020 ahead of final publication in the 36th Issue of Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics on September 28, 2020.
First author of the paper, PhD candidate Hyo Jeong Yoo, along with Professor Kim and researcher Byeong Eun Kwak, examined how the relative light intensity of the red and blue colors changed when varying the interparticle distances, or concentration, of the carbon dots. They found that as the concentration was adjusted, the light emitted from the carbon dots would transform. By varying the concentration, the team was able to control the relative intensity of the colors, as well as emit them simultaneously to generate a white light from a single source (See Figure).
“The concentration-dependence of the photoluminescence of carbon dots on the change of the emissive origins for different interparticle distances has been overlooked in previous research. With the analysis of the dual-color-emission phenomenon of carbon dots, we believe that this result may provide a new perspective to investigate their photoluminescence mechanism,” Yoo explained.
The newly analyzed ability to control the photoluminescence of carbon dots will likely be heavily utilized in the continued development of solid-state lighting applications and sensing.
Publication:
Yoo, H. J., Kwak, B. E., and Kim. D. H. (2020) Interparticle distance as a key factor for controlling the dual-emission properties of carbon dots. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Issue 36, Pages 20227-20237. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp02120b
Profile:
Do Hyun Kim, Sc.D.
Professor
dokim@kaist.ac.kr
http://procal.kaist.ac.kr/
Process Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.23 View 10690
Researchers Control Multiple Wavelengths of Light from a Single Source
KAIST researchers have synthesized a collection of nanoparticles, known as carbon dots, capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of light from a single particle. Additionally, the team discovered that the dispersion of the carbon dots, or the interparticle distance between each dot, influences the properties of the light the carbon dots emit. The discovery will allow researchers to understand how to control these carbon dots and create new, environmentally responsible displays, lighting, and sensing technology.
Research into nanoparticles capable of emitting light, such as quantum dots, has been an active area of interest for the last decade and a half. These particles, or phosphors, are nanoparticles made out of various materials that are capable of emitting light at specific wavelengths by leveraging quantum mechanical properties of the materials. This provides new ways to develop lighting and display solutions as well as more precise detection and sensing in instruments.
As technology becomes smaller and more sophisticated, the usage of fluorescent nanoparticles has seen a dramatic increase in many applications due to the purity of the colors emitting from the dots as well as their tunability to meet desired optical properties.
Carbon dots, a type of fluorescent nanoparticles, have seen an increase in interest from researchers as a candidate to replace non-carbon dots, the construction of which requires heavy metals that are toxic to the environment. Since they are made up of mostly carbon, the low toxicity is an extremely attractive quality when coupled with the tunability of their inherent optical properties.
Another striking feature of carbon dots is their capability to emit multiple wavelengths of light from a single nanoparticle. This multi-wavelength emission can be stimulated under a single excitation source, enabling the simple and robust generation of white light from a single particle by emitting multiple wavelengths simultaneously.
Carbon dots also exhibit a concentration-dependent photoluminescence. In other words, the distance between individual carbon dots affects the light that the carbon dots subsequently emit under an excitation source. These combined properties make carbon dots a unique source that will result in extremely accurate detection and sensing.
This concentration-dependency, however, had not been fully understood. In order to fully utilize the capabilities of carbon dots, the mechanisms that govern the seemingly variable optical properties must first be uncovered. It was previously theorized that the concentration-dependency of carbon dots was due to a hydrogen bonding effect.
Now, a KAIST research team, led by Professor Do Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has posited and demonstrated that the dual-color-emissiveness is instead due to the interparticle distances between each carbon dot. This study was made available online in June 2020 ahead of final publication in the 36th Issue of Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics on September 28, 2020.
First author of the paper, PhD candidate Hyo Jeong Yoo, along with Professor Kim and researcher Byeong Eun Kwak, examined how the relative light intensity of the red and blue colors changed when varying the interparticle distances, or concentration, of the carbon dots. They found that as the concentration was adjusted, the light emitted from the carbon dots would transform. By varying the concentration, the team was able to control the relative intensity of the colors, as well as emit them simultaneously to generate a white light from a single source (See Figure).
“The concentration-dependence of the photoluminescence of carbon dots on the change of the emissive origins for different interparticle distances has been overlooked in previous research. With the analysis of the dual-color-emission phenomenon of carbon dots, we believe that this result may provide a new perspective to investigate their photoluminescence mechanism,” Yoo explained.
The newly analyzed ability to control the photoluminescence of carbon dots will likely be heavily utilized in the continued development of solid-state lighting applications and sensing.
Publication:
Yoo, H. J., Kwak, B. E., and Kim. D. H. (2020) Interparticle distance as a key factor for controlling the dual-emission properties of carbon dots. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Issue 36, Pages 20227-20237. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp02120b
Profile:
Do Hyun Kim, Sc.D.
Professor
dokim@kaist.ac.kr
http://procal.kaist.ac.kr/
Process Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.23 View 10690 -
 ‘WalkON Suit 4’ Releases Paraplegics from Wheelchairs
- KAIST Athletes in ‘WalkON Suit 4’ Dominated the Cybathlon 2020 Global Edition. -
Paraplegic athletes Byeong-Uk Kim and Joohyun Lee from KAIST’s Team Angel Robotics won a gold and a bronze medal respectively at the Cybathlon 2020 Global Edition last week. ‘WalkON Suit 4,’ a wearable robot developed by the Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering topped the standings at the event with double medal success.
Kim, the former bronze medallist, clinched his gold medal by finishing all six tasks in 3 minutes and 47 seconds, whereas Lee came in third with a time of 5 minutes and 51 seconds. TWIICE, a Swiss team, lagged 53 seconds behind Kim’s winning time to be the runner-up.
Cybathlon is a global championship, organized by ETH Zurich, which brings together people with physical disabilities to compete using state-of-the-art assistive technologies to perform everyday tasks. The first championship was held in 2016 in Zurich, Switzerland.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the second championship was postponed twice and held in a new format in a decentralized setting. A total of 51 teams from 20 countries across the world performed the events in their home bases in different time zones instead of traveling to Zurich. Under the supervision of a referee and timekeeper, all races were filmed and then reviewed by judges.
KAIST’s Team Angel Robotics participated in the Powered Exoskeleton Race category, where nine pilots representing five nations including Korea, Switzerland, the US, Russia, and France competed against each other.
The team installed their own arena and raced at the KAIST Main Campus in Daejeon according to the framework, tasks, and rules defined by the competition committee. The two paraplegic pilots were each equipped with exoskeletal devices, the WalkON Suit 4, and undertook six tasks related to daily activities.
The WalkON Suit 4 recorded the fastest walking speed for a complete paraplegic ever reported. For a continuous walk, it achieved a maximum speed of 40 meters per minute. This is comparable to the average walking pace of a non-disabled person, which is around two to four kilometers per hour.
The research team raised the functionality of the robot by adding technology that can observe the user’s level of anxiety and external factors like the state of the walking surface, so it can control itself intelligently. The assistive functions a robot should provide vary greatly with the environment, and the WalkON Suit 4 made it possible to analyze the pace of the user within 30 steps and provide a personally optimized walking pattern, enabling a high walking speed.
The six tasks that Kim and Lee had to complete were:1) sitting and standing back up, 2) navigating around obstacles while avoiding collisions, 3) stepping over obstacles on the ground, 4) going up and down stairs, 5) walking across a tilted path, and 6) climbing a steep slope, opening and closing a door, and descending a steep slope.
Points were given based on the accuracy of each completed task, and the final scores were calculated by adding all of the points that were gained in each attempt, which lasted 10 minutes. Each pilot was given three opportunities and used his/her highest score. Should pilots have the same final score, the pilot who completed the race in the shortest amount of time would win.
Kim said in his victory speech that he was so thrilled to see all his and fellow researchers’ years of hard work paying off. “This will be a good opportunity to show how outstanding Korean wearable robot technologies are,” he added.
Lee, who participated in the competition for the first time, said, “By showing that I can overcome my physical disabilities with robot technology, I’d like to send out a message of hope to everyone who is tired because of COVID-19”.
Professor Kong’s team collaborated in technology development and pilot training with their colleagues from Angel Robotics Co., Ltd., Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, Yeungnam University, Stalks, and the Institute of Rehabilitation Technology.
Footage from the competition is available at the Cybathlon’s official website.
(END)
2020.11.20 View 9604
‘WalkON Suit 4’ Releases Paraplegics from Wheelchairs
- KAIST Athletes in ‘WalkON Suit 4’ Dominated the Cybathlon 2020 Global Edition. -
Paraplegic athletes Byeong-Uk Kim and Joohyun Lee from KAIST’s Team Angel Robotics won a gold and a bronze medal respectively at the Cybathlon 2020 Global Edition last week. ‘WalkON Suit 4,’ a wearable robot developed by the Professor Kyoungchul Kong’s team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering topped the standings at the event with double medal success.
Kim, the former bronze medallist, clinched his gold medal by finishing all six tasks in 3 minutes and 47 seconds, whereas Lee came in third with a time of 5 minutes and 51 seconds. TWIICE, a Swiss team, lagged 53 seconds behind Kim’s winning time to be the runner-up.
Cybathlon is a global championship, organized by ETH Zurich, which brings together people with physical disabilities to compete using state-of-the-art assistive technologies to perform everyday tasks. The first championship was held in 2016 in Zurich, Switzerland.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the second championship was postponed twice and held in a new format in a decentralized setting. A total of 51 teams from 20 countries across the world performed the events in their home bases in different time zones instead of traveling to Zurich. Under the supervision of a referee and timekeeper, all races were filmed and then reviewed by judges.
KAIST’s Team Angel Robotics participated in the Powered Exoskeleton Race category, where nine pilots representing five nations including Korea, Switzerland, the US, Russia, and France competed against each other.
The team installed their own arena and raced at the KAIST Main Campus in Daejeon according to the framework, tasks, and rules defined by the competition committee. The two paraplegic pilots were each equipped with exoskeletal devices, the WalkON Suit 4, and undertook six tasks related to daily activities.
The WalkON Suit 4 recorded the fastest walking speed for a complete paraplegic ever reported. For a continuous walk, it achieved a maximum speed of 40 meters per minute. This is comparable to the average walking pace of a non-disabled person, which is around two to four kilometers per hour.
The research team raised the functionality of the robot by adding technology that can observe the user’s level of anxiety and external factors like the state of the walking surface, so it can control itself intelligently. The assistive functions a robot should provide vary greatly with the environment, and the WalkON Suit 4 made it possible to analyze the pace of the user within 30 steps and provide a personally optimized walking pattern, enabling a high walking speed.
The six tasks that Kim and Lee had to complete were:1) sitting and standing back up, 2) navigating around obstacles while avoiding collisions, 3) stepping over obstacles on the ground, 4) going up and down stairs, 5) walking across a tilted path, and 6) climbing a steep slope, opening and closing a door, and descending a steep slope.
Points were given based on the accuracy of each completed task, and the final scores were calculated by adding all of the points that were gained in each attempt, which lasted 10 minutes. Each pilot was given three opportunities and used his/her highest score. Should pilots have the same final score, the pilot who completed the race in the shortest amount of time would win.
Kim said in his victory speech that he was so thrilled to see all his and fellow researchers’ years of hard work paying off. “This will be a good opportunity to show how outstanding Korean wearable robot technologies are,” he added.
Lee, who participated in the competition for the first time, said, “By showing that I can overcome my physical disabilities with robot technology, I’d like to send out a message of hope to everyone who is tired because of COVID-19”.
Professor Kong’s team collaborated in technology development and pilot training with their colleagues from Angel Robotics Co., Ltd., Severance Rehabilitation Hospital, Yeungnam University, Stalks, and the Institute of Rehabilitation Technology.
Footage from the competition is available at the Cybathlon’s official website.
(END)
2020.11.20 View 9604 -
 In Memory of Professor Dong-Soo Kim
Pioneering geotechnical engineer Dong-Soo Kim dies at 59
The Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering lost a pioneering scholar in geotechnical engineering, Professor Dong-Soo Kim. Professor Kim died on November 3, after a one-and-a-half-year battle with a brain tumor. He was 59.
Known for his piercing insight and infectious enthusiasm for the deepest questions in geotechnical science and engineering, Professor Kim built an extraordinary academic career while working at KAIST for 26 years. Professor Kim paved the way for establishing the geo-centrifuge experiment facilities at KAIST as part of the KOCED (Korea Construction Engineering Development Collaboratory Management Institute) Projects funded by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. He also served as director of the KOCED Geo-Centrifuge Center.
“He made significant contributions to the growth of the department since his joining and he was at the forefront of the globalization of the department. He passed away so early leaving behind so many projects,” lamented Professor Emeritus Chung-Bang Yun.
“Professor Kim insisted on lecturing despite his serious illness. He wanted to play his part so gracefully for his students until his last days,” said Professor Hyo-Gyong Kwak, the head of the department who was also a close colleague of 25 years. “His captivating warm smile and unwavering mentorship and guidance will be missed by students and faculty alike. We lost an exemplary leader, mentor, colleague, and friend.” One of his colleagues, Professor Gye-Chun Cho said, “We have lost a great professor and colleague in civil engineering worldwide. His impact and legacy will be remembered forever.”
Joining the KAIST faculty in 1994, he began his academic career at the Polytechnique University, New York for three years after earning his PhD at the University of Texas at Austin in 1991. He finished his BS and MS at Seoul National University in 1983 and 1985 respectively.
While at KAIST, he led the Soil Dynamics Lab in 1994 and researched on site characterization via field and lab tests. He also conducted geotechnical centrifuge tests on earthquake and offshore geotechnical problems. His research team studied the seismic design of geotechnical structures and explored the non-destructive testing and evaluation of civil structures.
Professor Kim made profound contributions to understanding fundamental geotechnical engineering problems. More recently, his lab investigated physical modeling using the geo-centrifuge testing machine that could simulate field geotechnical problems on small-scale models. Professor Kim’s perseverance, deep curiosity, and enthusiasm for discovery served him well in his roles as a teacher, mentor, and colleague in the department and beyond. “I thought of him as an elder brother who fully understand everything with generous mind,” said Professor Haeng-Ki Lee, former head of the department.
“I will never forget the hiking trip to Halla Mountain in Jeju last summer. He continuously cheered on the junior professors. Without him, we could not have made it to the summit. His support and encouragement always led us to produce good results and achievement in the labs,” remembered Professor Youngchul Kim. Taking great delight in helping young scientists, he inspired colleagues and students to find their own eureka moments. To professors like Jong-In Han and Ayoung Kim, he was the role model they hope to be due to his rigorous scholarship and generous character. Upon his passing, Professor Jaewook Myung reviewed all the emails he and Professor Kim has sent starting from his undergraduate days at KAIST. “He was my guiding light. He always listened attentively to my struggles from my undergraduate days and advised me very warmly.”
Professor Kim was also known for his key role in the Korean Geotechnical Society. His unmatched leadership led him to serve as the Chair of the Organizing Committee for the 19th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering in Seoul in 2017. He was the General Secretary of the 5th International Symposium on Deformation Characteristics of Geomaterials. He also served as a chair of the ISSSMGE TC 104 committee.
Professor Kim successfully carried out numerous projects with his research team and supervised more than 60 graduate students. For current students under his supervision, it is still tough to acknowledge the loss of their professor.
Master candidate Yeonjun Kim feels lost moving forward. PhD candidate Junsik Bae said that it is like a bad dream and he feels Professor Kim will still be in his lab whenever he goes inside. One of the staff members who worked with him, Byeol-Nim Cha, remembered that Professor Kim always entered the office with a big smile. “He always asked me how I am doing,” Cha added.
Professor Kim’s trailblazing research was recognized with several awards and honors. Cited as a Top 100 Scientist by the International Biographical Center (IBC) in 2008, Professor Kim received the Young Presidential Research Award from the Korean Academy of Science and Technology in 2002, the Korean Presidential Award on Civil Engineer’s Day in 2011, and the Telford Premium Rewards in 2018. Throughout his career, he authored or co-authored 321 papers in international journals and conference proceedings, and 278 papers in domestic journals and conferences.
President of the Korean Geotechnical Society Choong-gi Chung also eulogized him, “Above his impressive professional contributions, Professor Kim will be remembered forever for his generosity, simplicity, playfulness, and his smile.”
Professor Kim is survived by his wife, son, and daughter.
2020.11.19 View 7849
In Memory of Professor Dong-Soo Kim
Pioneering geotechnical engineer Dong-Soo Kim dies at 59
The Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering lost a pioneering scholar in geotechnical engineering, Professor Dong-Soo Kim. Professor Kim died on November 3, after a one-and-a-half-year battle with a brain tumor. He was 59.
Known for his piercing insight and infectious enthusiasm for the deepest questions in geotechnical science and engineering, Professor Kim built an extraordinary academic career while working at KAIST for 26 years. Professor Kim paved the way for establishing the geo-centrifuge experiment facilities at KAIST as part of the KOCED (Korea Construction Engineering Development Collaboratory Management Institute) Projects funded by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. He also served as director of the KOCED Geo-Centrifuge Center.
“He made significant contributions to the growth of the department since his joining and he was at the forefront of the globalization of the department. He passed away so early leaving behind so many projects,” lamented Professor Emeritus Chung-Bang Yun.
“Professor Kim insisted on lecturing despite his serious illness. He wanted to play his part so gracefully for his students until his last days,” said Professor Hyo-Gyong Kwak, the head of the department who was also a close colleague of 25 years. “His captivating warm smile and unwavering mentorship and guidance will be missed by students and faculty alike. We lost an exemplary leader, mentor, colleague, and friend.” One of his colleagues, Professor Gye-Chun Cho said, “We have lost a great professor and colleague in civil engineering worldwide. His impact and legacy will be remembered forever.”
Joining the KAIST faculty in 1994, he began his academic career at the Polytechnique University, New York for three years after earning his PhD at the University of Texas at Austin in 1991. He finished his BS and MS at Seoul National University in 1983 and 1985 respectively.
While at KAIST, he led the Soil Dynamics Lab in 1994 and researched on site characterization via field and lab tests. He also conducted geotechnical centrifuge tests on earthquake and offshore geotechnical problems. His research team studied the seismic design of geotechnical structures and explored the non-destructive testing and evaluation of civil structures.
Professor Kim made profound contributions to understanding fundamental geotechnical engineering problems. More recently, his lab investigated physical modeling using the geo-centrifuge testing machine that could simulate field geotechnical problems on small-scale models. Professor Kim’s perseverance, deep curiosity, and enthusiasm for discovery served him well in his roles as a teacher, mentor, and colleague in the department and beyond. “I thought of him as an elder brother who fully understand everything with generous mind,” said Professor Haeng-Ki Lee, former head of the department.
“I will never forget the hiking trip to Halla Mountain in Jeju last summer. He continuously cheered on the junior professors. Without him, we could not have made it to the summit. His support and encouragement always led us to produce good results and achievement in the labs,” remembered Professor Youngchul Kim. Taking great delight in helping young scientists, he inspired colleagues and students to find their own eureka moments. To professors like Jong-In Han and Ayoung Kim, he was the role model they hope to be due to his rigorous scholarship and generous character. Upon his passing, Professor Jaewook Myung reviewed all the emails he and Professor Kim has sent starting from his undergraduate days at KAIST. “He was my guiding light. He always listened attentively to my struggles from my undergraduate days and advised me very warmly.”
Professor Kim was also known for his key role in the Korean Geotechnical Society. His unmatched leadership led him to serve as the Chair of the Organizing Committee for the 19th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering in Seoul in 2017. He was the General Secretary of the 5th International Symposium on Deformation Characteristics of Geomaterials. He also served as a chair of the ISSSMGE TC 104 committee.
Professor Kim successfully carried out numerous projects with his research team and supervised more than 60 graduate students. For current students under his supervision, it is still tough to acknowledge the loss of their professor.
Master candidate Yeonjun Kim feels lost moving forward. PhD candidate Junsik Bae said that it is like a bad dream and he feels Professor Kim will still be in his lab whenever he goes inside. One of the staff members who worked with him, Byeol-Nim Cha, remembered that Professor Kim always entered the office with a big smile. “He always asked me how I am doing,” Cha added.
Professor Kim’s trailblazing research was recognized with several awards and honors. Cited as a Top 100 Scientist by the International Biographical Center (IBC) in 2008, Professor Kim received the Young Presidential Research Award from the Korean Academy of Science and Technology in 2002, the Korean Presidential Award on Civil Engineer’s Day in 2011, and the Telford Premium Rewards in 2018. Throughout his career, he authored or co-authored 321 papers in international journals and conference proceedings, and 278 papers in domestic journals and conferences.
President of the Korean Geotechnical Society Choong-gi Chung also eulogized him, “Above his impressive professional contributions, Professor Kim will be remembered forever for his generosity, simplicity, playfulness, and his smile.”
Professor Kim is survived by his wife, son, and daughter.
2020.11.19 View 7849 -
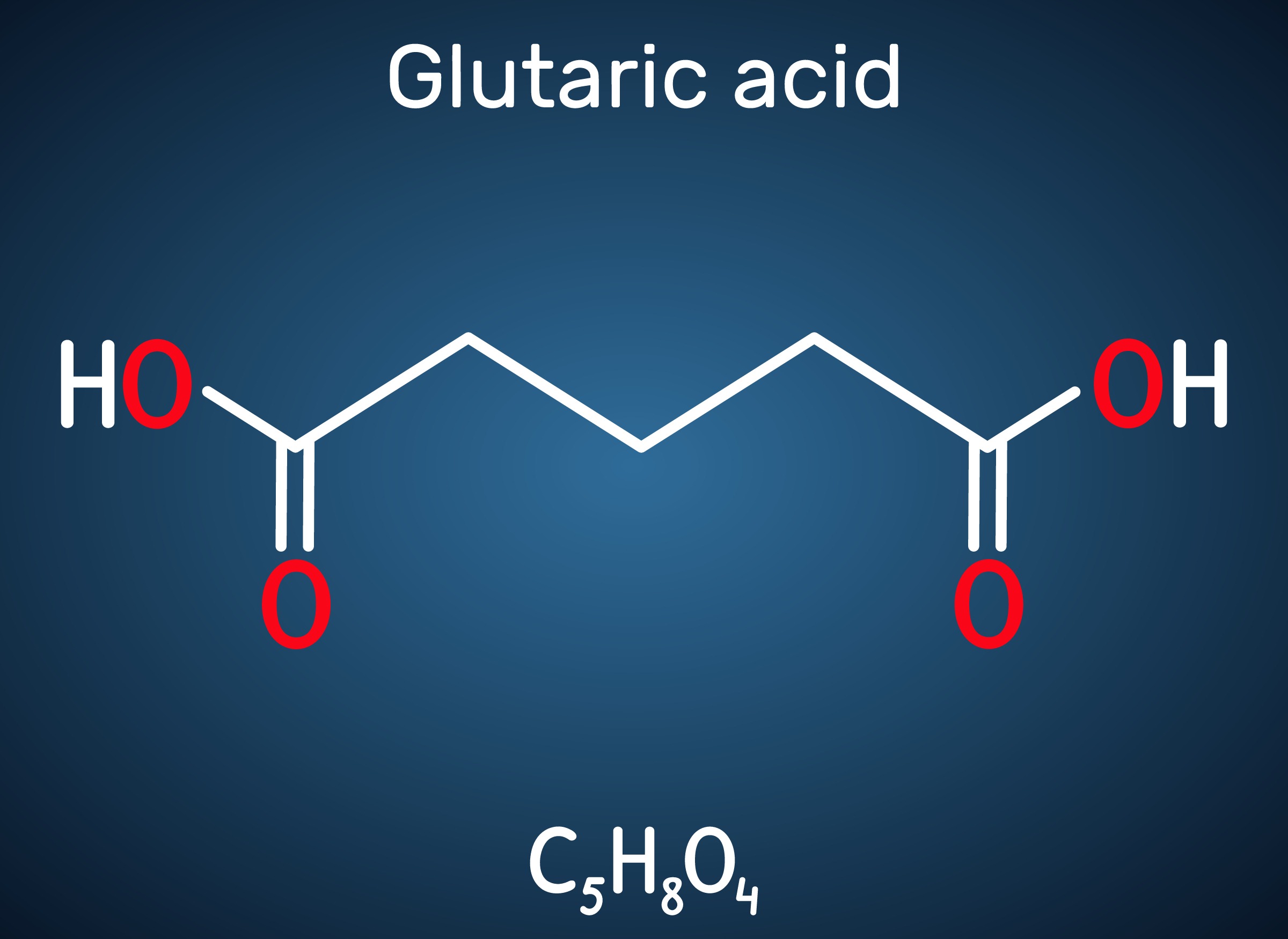 Engineered C. glutamicum Strain Capable of Producing High-Level Glutaric Acid from Glucose
An engineered C. glutamicum strain that can produce the world’s highest titer of glutaric acid was developed by employing systems metabolic engineering strategies
A metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid without byproducts from glucose. This new strategy will be useful for developing engineered micro-organisms for the bio-based production of value-added chemicals.
Glutaric acid, also known as pentanedioic acid, is a carboxylic acid that is widely used for various applications including the production of polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, glutaric anhydride, 1,5-pentanediol, and 5-hydroxyvaleric acid. Glutaric acid has been produced using various petroleum-based chemical methods, relying on non-renewable and toxic starting materials. Thus, various approaches have been taken to biologically produce glutaric acid from renewable resources. Previously, the development of the first glutaric acid producing Escherichia coli by introducing Pseudomonas putida genes was reported by a research group from KAIST, but the titer was low. Glutaric acid production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum has also been reported in several studies, but further improvements in glutaric acid production seemed possible since C. glutamicum has the capability of producing more than 130 g/L of L-lysine.
A research group comprised of Taehee Han, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. Their research paper “Glutaric acid production by systems metabolic engineering of an L-lysine-overproducing Corynebacterium glutamicum” was published online in PNAS on November 16, 2020.
This research reports the development of a metabolically engineered C. glutamicum strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid, starting from an L-lysine overproducer. The following novel strategies and approaches to achieve high-level glutaric acid production were employed. First, metabolic pathways in C. glutamicum were reconstituted for glutaric acid production by introducing P. putida genes. Then, multi-omics analyses including genome, transcriptome, and fluxome were conducted to understand the phenotype of the L-lysine overproducer strain. In addition to systematic understanding of the host strain, gene manipulation targets were predicted by omics analyses and applied for engineering C. glutamicum, which resulted in the development of an engineered strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid. Furthermore, the new glutaric acid exporter was discovered for the first time, which was used to further increase glutaric acid production through enhancing product excretion. Last but not least, culture conditions were optimized for high-level glutaric acid production. As a result, the final engineered strain was able to produce 105.3 g/L glutaric acid, the highest titer ever reported, in 69 hours by fed-batch fermentation.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is meaningful that we were able to develop a highly efficient glutaric acid producer capable of producing glutaric acid at the world’s highest titer without any byproducts from renewable carbon sources. This will further accelerate the bio-based production of valuable chemicals in pharmaceutical/medical/chemical industries.” This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.17 View 7314
Engineered C. glutamicum Strain Capable of Producing High-Level Glutaric Acid from Glucose
An engineered C. glutamicum strain that can produce the world’s highest titer of glutaric acid was developed by employing systems metabolic engineering strategies
A metabolic engineering research group at KAIST has developed an engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum strain capable of producing high-level glutaric acid without byproducts from glucose. This new strategy will be useful for developing engineered micro-organisms for the bio-based production of value-added chemicals.
Glutaric acid, also known as pentanedioic acid, is a carboxylic acid that is widely used for various applications including the production of polyesters, polyamides, polyurethanes, glutaric anhydride, 1,5-pentanediol, and 5-hydroxyvaleric acid. Glutaric acid has been produced using various petroleum-based chemical methods, relying on non-renewable and toxic starting materials. Thus, various approaches have been taken to biologically produce glutaric acid from renewable resources. Previously, the development of the first glutaric acid producing Escherichia coli by introducing Pseudomonas putida genes was reported by a research group from KAIST, but the titer was low. Glutaric acid production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum has also been reported in several studies, but further improvements in glutaric acid production seemed possible since C. glutamicum has the capability of producing more than 130 g/L of L-lysine.
A research group comprised of Taehee Han, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering addressed this issue. Their research paper “Glutaric acid production by systems metabolic engineering of an L-lysine-overproducing Corynebacterium glutamicum” was published online in PNAS on November 16, 2020.
This research reports the development of a metabolically engineered C. glutamicum strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid, starting from an L-lysine overproducer. The following novel strategies and approaches to achieve high-level glutaric acid production were employed. First, metabolic pathways in C. glutamicum were reconstituted for glutaric acid production by introducing P. putida genes. Then, multi-omics analyses including genome, transcriptome, and fluxome were conducted to understand the phenotype of the L-lysine overproducer strain. In addition to systematic understanding of the host strain, gene manipulation targets were predicted by omics analyses and applied for engineering C. glutamicum, which resulted in the development of an engineered strain capable of efficiently producing glutaric acid. Furthermore, the new glutaric acid exporter was discovered for the first time, which was used to further increase glutaric acid production through enhancing product excretion. Last but not least, culture conditions were optimized for high-level glutaric acid production. As a result, the final engineered strain was able to produce 105.3 g/L glutaric acid, the highest titer ever reported, in 69 hours by fed-batch fermentation.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is meaningful that we were able to develop a highly efficient glutaric acid producer capable of producing glutaric acid at the world’s highest titer without any byproducts from renewable carbon sources. This will further accelerate the bio-based production of valuable chemicals in pharmaceutical/medical/chemical industries.” This research was supported by the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
-Profile
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee
leesy@kaist.ac.kr
http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
2020.11.17 View 7314 -
 To Talk or Not to Talk: Smart Speaker Determines Optimal Timing to Talk
A KAIST research team has developed a new context-awareness technology that enables AI assistants to determine when to talk to their users based on user circumstances. This technology can contribute to developing advanced AI assistants that can offer pre-emptive services such as reminding users to take medication on time or modifying schedules based on the actual progress of planned tasks.
Unlike conventional AI assistants that used to act passively upon users’ commands, today’s AI assistants are evolving to provide more proactive services through self-reasoning of user circumstances. This opens up new opportunities for AI assistants to better support users in their daily lives. However, if AI assistants do not talk at the right time, they could rather interrupt their users instead of helping them.
The right time for talking is more difficult for AI assistants to determine than it appears. This is because the context can differ depending on the state of the user or the surrounding environment.
A group of researchers led by Professor Uichin Lee from the KAIST School of Computing identified key contextual factors in user circumstances that determine when the AI assistant should start, stop, or resume engaging in voice services in smart home environments. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT) in September.
The group conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Jae-Gil Lee’s group in the KAIST School of Computing, Professor Sangsu Lee’s group in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, and Professor Auk Kim’s group at Kangwon National University.
After developing smart speakers equipped with AI assistant function for experimental use, the researchers installed them in the rooms of 40 students who live in double-occupancy campus dormitories and collected a total of 3,500 in-situ user response data records over a period of a week.
The smart speakers repeatedly asked the students a question, “Is now a good time to talk?” at random intervals or whenever a student’s movement was detected. Students answered with either “yes” or “no” and then explained why, describing what they had been doing before being questioned by the smart speakers.
Data analysis revealed that 47% of user responses were “no” indicating they did not want to be interrupted. The research team then created 19 home activity categories to cross-analyze the key contextual factors that determine opportune moments for AI assistants to talk, and classified these factors into ‘personal,’ ‘movement,’ and ‘social’ factors respectively.
Personal factors, for instance, include:
1. the degree of concentration on or engagement in activities,
2. the degree urgency and busyness,
3. the state of user’s mental or physical condition, and
4. the state of being able to talk or listen while multitasking.
While users were busy concentrating on studying, tired, or drying hair, they found it difficult to engage in conversational interactions with the smart speakers.
Some representative movement factors include departure, entrance, and physical activity transitions. Interestingly, in movement scenarios, the team found that the communication range was an important factor. Departure is an outbound movement from the smart speaker, and entrance is an inbound movement. Users were much more available during inbound movement scenarios as opposed to outbound movement scenarios.
In general, smart speakers are located in a shared place at home, such as a living room, where multiple family members gather at the same time. In Professor Lee’s group’s experiment, almost half of the in-situ user responses were collected when both roommates were present. The group found social presence also influenced interruptibility. Roommates often wanted to minimize possible interpersonal conflicts, such as disturbing their roommates' sleep or work.
Narae Cha, the lead author of this study, explained, “By considering personal, movement, and social factors, we can envision a smart speaker that can intelligently manage the timing of conversations with users.”
She believes that this work lays the foundation for the future of AI assistants, adding, “Multi-modal sensory data can be used for context sensing, and this context information will help smart speakers proactively determine when it is a good time to start, stop, or resume conversations with their users.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Cha, N, et al. (2020) “Hello There! Is Now a Good Time to Talk?”: Opportune Moments for Proactive Interactions with Smart Speakers. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), Vol. 4, No. 3, Article No. 74, pp. 1-28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1145/3411810
Link to Introductory Video:
https://youtu.be/AA8CTi2hEf0
Profile:
Uichin Lee
Associate Professor
uclee@kaist.ac.kr
http://ic.kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Computing Lab.
School of Computing
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.05 View 11840
To Talk or Not to Talk: Smart Speaker Determines Optimal Timing to Talk
A KAIST research team has developed a new context-awareness technology that enables AI assistants to determine when to talk to their users based on user circumstances. This technology can contribute to developing advanced AI assistants that can offer pre-emptive services such as reminding users to take medication on time or modifying schedules based on the actual progress of planned tasks.
Unlike conventional AI assistants that used to act passively upon users’ commands, today’s AI assistants are evolving to provide more proactive services through self-reasoning of user circumstances. This opens up new opportunities for AI assistants to better support users in their daily lives. However, if AI assistants do not talk at the right time, they could rather interrupt their users instead of helping them.
The right time for talking is more difficult for AI assistants to determine than it appears. This is because the context can differ depending on the state of the user or the surrounding environment.
A group of researchers led by Professor Uichin Lee from the KAIST School of Computing identified key contextual factors in user circumstances that determine when the AI assistant should start, stop, or resume engaging in voice services in smart home environments. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT) in September.
The group conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Jae-Gil Lee’s group in the KAIST School of Computing, Professor Sangsu Lee’s group in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, and Professor Auk Kim’s group at Kangwon National University.
After developing smart speakers equipped with AI assistant function for experimental use, the researchers installed them in the rooms of 40 students who live in double-occupancy campus dormitories and collected a total of 3,500 in-situ user response data records over a period of a week.
The smart speakers repeatedly asked the students a question, “Is now a good time to talk?” at random intervals or whenever a student’s movement was detected. Students answered with either “yes” or “no” and then explained why, describing what they had been doing before being questioned by the smart speakers.
Data analysis revealed that 47% of user responses were “no” indicating they did not want to be interrupted. The research team then created 19 home activity categories to cross-analyze the key contextual factors that determine opportune moments for AI assistants to talk, and classified these factors into ‘personal,’ ‘movement,’ and ‘social’ factors respectively.
Personal factors, for instance, include:
1. the degree of concentration on or engagement in activities,
2. the degree urgency and busyness,
3. the state of user’s mental or physical condition, and
4. the state of being able to talk or listen while multitasking.
While users were busy concentrating on studying, tired, or drying hair, they found it difficult to engage in conversational interactions with the smart speakers.
Some representative movement factors include departure, entrance, and physical activity transitions. Interestingly, in movement scenarios, the team found that the communication range was an important factor. Departure is an outbound movement from the smart speaker, and entrance is an inbound movement. Users were much more available during inbound movement scenarios as opposed to outbound movement scenarios.
In general, smart speakers are located in a shared place at home, such as a living room, where multiple family members gather at the same time. In Professor Lee’s group’s experiment, almost half of the in-situ user responses were collected when both roommates were present. The group found social presence also influenced interruptibility. Roommates often wanted to minimize possible interpersonal conflicts, such as disturbing their roommates' sleep or work.
Narae Cha, the lead author of this study, explained, “By considering personal, movement, and social factors, we can envision a smart speaker that can intelligently manage the timing of conversations with users.”
She believes that this work lays the foundation for the future of AI assistants, adding, “Multi-modal sensory data can be used for context sensing, and this context information will help smart speakers proactively determine when it is a good time to start, stop, or resume conversations with their users.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Cha, N, et al. (2020) “Hello There! Is Now a Good Time to Talk?”: Opportune Moments for Proactive Interactions with Smart Speakers. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), Vol. 4, No. 3, Article No. 74, pp. 1-28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1145/3411810
Link to Introductory Video:
https://youtu.be/AA8CTi2hEf0
Profile:
Uichin Lee
Associate Professor
uclee@kaist.ac.kr
http://ic.kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Computing Lab.
School of Computing
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.05 View 11840 -
 Chemical Scissors Snip 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenides into Nanoribbon
New ‘nanoribbon’ catalyst should slash cost of hydrogen production for clean fuels
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative – and an innovative way to produce them using chemical ‘scissors’ – that could make hydrogen production more economical.
The research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering published their work in Nature Communications.
Hydrogen is likely to play a key role in the clean transition away from fossil fuels and other processes that produce greenhouse gas emissions. There is a raft of transportation sectors such as long-haul shipping and aviation that are difficult to electrify and so will require cleanly produced hydrogen as a fuel or as a feedstock for other carbon-neutral synthetic fuels. Likewise, fertilizer production and the steel sector are unlikely to be “de-carbonized” without cheap and clean hydrogen.
The problem is that the cheapest methods by far of producing hydrogen gas is currently from natural gas, a process that itself produces the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide–which defeats the purpose.
Alternative techniques of hydrogen production, such as electrolysis using an electric current between two electrodes plunged into water to overcome the chemical bonds holding water together, thereby splitting it into its constituent elements, oxygen and hydrogen are very well established. But one of the factors contributing to the high cost, beyond being extremely energy-intensive, is the need for the very expensive precious and relatively rare metal platinum. The platinum is used as a catalyst–a substance that kicks off or speeds up a chemical reaction–in the hydrogen production process.
As a result, researchers have long been on the hunt for a substitution for platinum -- another catalyst that is abundant in the earth and thus much cheaper.
Transition metal dichalcogenides, or TMDs, in a nanomaterial form, have for some time been considered a good candidate as a catalyst replacement for platinum. These are substances composed of one atom of a transition metal (the elements in the middle part of the periodic table) and two atoms of a chalcogen element (the elements in the third-to-last column in the periodic table, specifically sulfur, selenium and tellurium).
What makes TMDs a good bet as a platinum replacement is not just that they are much more abundant, but also their electrons are structured in a way that gives the electrodes a boost.
In addition, a TMD that is a nanomaterial is essentially a two-dimensional super-thin sheet only a few atoms thick, just like graphene. The ultrathin nature of a 2-D TMD nanosheet allows for a great many more TMD molecules to be exposed during the catalysis process than would be the case in a block of the stuff, thus kicking off and speeding up the hydrogen-making chemical reaction that much more.
However, even here the TMD molecules are only reactive at the four edges of a nanosheet. In the flat interior, not much is going on. In order to increase the chemical reaction rate in the production of hydrogen, the nanosheet would need to be cut into very thin – almost one-dimensional strips, thereby creating many edges.
In response, the research team developed what are in essence a pair of chemical scissors that can snip TMD into tiny strips.
“Up to now, the only substances that anyone has been able to turn into these ‘nano-ribbons’ are graphene and phosphorene,” said Sang Professor Kim, one of the researchers involved in devising the process.
“But they’re both made up of just one element, so it’s pretty straightforward. Figuring out how to do it for TMD, which is made of two elements was going to be much harder.”
The ‘scissors’ involve a two-step process involving first inserting lithium ions into the layered structure of the TMD sheets, and then using ultrasound to cause a spontaneous ‘unzipping’ in straight lines.
“It works sort of like how when you split a plank of plywood: it breaks easily in one direction along the grain,” Professor Kim continued. “It’s actually really simple.”
The researchers then tried it with various types of TMDs, including those made of molybdenum, selenium, sulfur, tellurium and tungsten. All worked just as well, with a catalytic efficiency as effective as platinum’s.
Because of the simplicity of the procedure, this method should be able to be used not just in the large-scale production of TMD nanoribbons, but also to make similar nanoribbons from other multi-elemental 2D materials for purposes beyond just hydrogen production.
-ProfileProfessor Sang Ouk KimSoft Nanomaterials Laboratory (http://snml.kaist.ac.kr)Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.29 View 8306
Chemical Scissors Snip 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenides into Nanoribbon
New ‘nanoribbon’ catalyst should slash cost of hydrogen production for clean fuels
Researchers have identified a potential catalyst alternative – and an innovative way to produce them using chemical ‘scissors’ – that could make hydrogen production more economical.
The research team led by Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering published their work in Nature Communications.
Hydrogen is likely to play a key role in the clean transition away from fossil fuels and other processes that produce greenhouse gas emissions. There is a raft of transportation sectors such as long-haul shipping and aviation that are difficult to electrify and so will require cleanly produced hydrogen as a fuel or as a feedstock for other carbon-neutral synthetic fuels. Likewise, fertilizer production and the steel sector are unlikely to be “de-carbonized” without cheap and clean hydrogen.
The problem is that the cheapest methods by far of producing hydrogen gas is currently from natural gas, a process that itself produces the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide–which defeats the purpose.
Alternative techniques of hydrogen production, such as electrolysis using an electric current between two electrodes plunged into water to overcome the chemical bonds holding water together, thereby splitting it into its constituent elements, oxygen and hydrogen are very well established. But one of the factors contributing to the high cost, beyond being extremely energy-intensive, is the need for the very expensive precious and relatively rare metal platinum. The platinum is used as a catalyst–a substance that kicks off or speeds up a chemical reaction–in the hydrogen production process.
As a result, researchers have long been on the hunt for a substitution for platinum -- another catalyst that is abundant in the earth and thus much cheaper.
Transition metal dichalcogenides, or TMDs, in a nanomaterial form, have for some time been considered a good candidate as a catalyst replacement for platinum. These are substances composed of one atom of a transition metal (the elements in the middle part of the periodic table) and two atoms of a chalcogen element (the elements in the third-to-last column in the periodic table, specifically sulfur, selenium and tellurium).
What makes TMDs a good bet as a platinum replacement is not just that they are much more abundant, but also their electrons are structured in a way that gives the electrodes a boost.
In addition, a TMD that is a nanomaterial is essentially a two-dimensional super-thin sheet only a few atoms thick, just like graphene. The ultrathin nature of a 2-D TMD nanosheet allows for a great many more TMD molecules to be exposed during the catalysis process than would be the case in a block of the stuff, thus kicking off and speeding up the hydrogen-making chemical reaction that much more.
However, even here the TMD molecules are only reactive at the four edges of a nanosheet. In the flat interior, not much is going on. In order to increase the chemical reaction rate in the production of hydrogen, the nanosheet would need to be cut into very thin – almost one-dimensional strips, thereby creating many edges.
In response, the research team developed what are in essence a pair of chemical scissors that can snip TMD into tiny strips.
“Up to now, the only substances that anyone has been able to turn into these ‘nano-ribbons’ are graphene and phosphorene,” said Sang Professor Kim, one of the researchers involved in devising the process.
“But they’re both made up of just one element, so it’s pretty straightforward. Figuring out how to do it for TMD, which is made of two elements was going to be much harder.”
The ‘scissors’ involve a two-step process involving first inserting lithium ions into the layered structure of the TMD sheets, and then using ultrasound to cause a spontaneous ‘unzipping’ in straight lines.
“It works sort of like how when you split a plank of plywood: it breaks easily in one direction along the grain,” Professor Kim continued. “It’s actually really simple.”
The researchers then tried it with various types of TMDs, including those made of molybdenum, selenium, sulfur, tellurium and tungsten. All worked just as well, with a catalytic efficiency as effective as platinum’s.
Because of the simplicity of the procedure, this method should be able to be used not just in the large-scale production of TMD nanoribbons, but also to make similar nanoribbons from other multi-elemental 2D materials for purposes beyond just hydrogen production.
-ProfileProfessor Sang Ouk KimSoft Nanomaterials Laboratory (http://snml.kaist.ac.kr)Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2020.10.29 View 8306