AT
-
 KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 16272
KAIST Honors BMW and Hyundai with the 2022 Future Mobility of the Year Award
BMW ‘iVision Circular’, Commercial Vehicle-Hyundai Motors ‘Trailer Drone’ selected as winners of the international awards for concept cars established by KAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility to honor car makers that strive to present new visions in the field of eco-friendly design of automobiles and unmanned logistics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) hosted the “2022 Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) Awards” at the Convention Hall of the BEXCO International Motor Show at Busan in the afternoon of the 14th.
The Future Mobility of the Year Awards is an award ceremony that selects a model that showcases useful transportation technology and innovative service concepts for the future society among the set of concept cars exhibited at the motor show.
As a one-of-a-kind international concept car awards established by KAIST's Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility (Headed by Professor Jang In-Gwon), the auto journalists from 11 countries were invited to be the jurors to select the winner. With the inaugural awards ceremony held in 2019, over the past three years, automakers from around the globe, including internationally renowned automakers, such as, Volvo/Toyota (2019), Honda/Hyundai (2020), and Renault (2021), even a new start-up car manufacturer like Canoo, the winner of last year’s award for commercial vehicles, were honored for their award-winning works.
At this year’s awards ceremony, the 4th of its kind, BMW's “iVision Circular” and Hyundai's “'Trailer Drone” were selected as the best concept cars of the year, the former from the Private Mobility category and the latter from the Public & Commercial Vehicles category.
The jury consisting of 16 domestic and foreign auto journalists, including BBC Top Gear's Paul Horrell and Car Magazine’s Georg Kacher, evaluated 53 concept car contestants that made their entry last year. The jurors’ general comment was that while the trend of the global automobile market flowing fast towards electric vehicles, this year's award-winning works presented a new vision in the field of eco-friendly design and unmanned logistics.
Private Mobility Categry Winner: BMW iVision Circular
BMW's 'iVision Circular', the winner of the Private Mobility category, is an eco-friendly compact car in which all parts of the vehicle are designed with recycled and/or natural materials. It has received favorable reviews for its in-depth implementation of the concept of a futuristic eco-friendly car by manufacturing the tires from natural rubber and adopting a design that made recycling of its parts very easily when the car is to be disposed of.
Public & Commercial Vehicles Categry Winner: Hyundai Trailer Drone
Hyundai Motor Company’s “Trailer Drone”, the winner of the Public & Commercial Vehicles category, is an eco-friendly autonomous driving truck that can transport large-scale logistics from a port to a destination without a human driver while two unmanned vehicles push and drag a trailer. The concept car won supports from a large number of judges for the blueprint it presented for a groundbreaking logistics service that applied both eco-friendly hydrogen fuel cell and fully autonomous driving technology.
Jurors from overseas congratulated the development team of BMW and Hyundai Motor Company via a video message for providing a new direction for the global automobile industry as it strives to transform in line with the changes in the post-pandemic era.
Professor Bo-won Kim, the Vice President for Planning and Budget of KAIST, who presented the awards, said, “It is time for the K-Mobility wave to sweep over the global mobility industry.” “KAIST will lead in the various fields of mobility technologies to support global automakers,” he added.
Splitting the center are KAIST Vice President Bo-Won Kim on the right, and Seong-Kwon Lee,
the Deputy Mayor of the City of Busan on the left. To Kim's left is the Senior VP of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, Jean-Philippe Parain, and to Lee's Right is Sangyup Lee,
the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive VP of Hyundai Motors.
At the ceremony, along with KAIST officials, including Vice President Bo-Won Kim and Professor In-Gwon Jang, the Head of Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobility, are the Deputy Mayor Seong-Kwon Lee of the City of Busan and the figures from the automobile industry, including Jean-Philippe Parain, the Senior Vice President of BMW Asia-Pacific, Eastern Europe, Middle East, Africa, who is visiting Korea to receive the '2022 Future Mobility' award, and Sangyup Lee, the Head of Hyundai Motor Design Center and the Executive Vice President of Hyundai Motor Company, were in the attendance.
More information about the awards ceremony and winning works are available at the official website of this year's Future Mobility Awards (www.fmoty.org).
Profile:In-Gwon Jang, Ph.D.Presidentthe Organizing Committeethe Future Mobility of the Year Awardshttp://www.fmoty.org/
Head ProfessorKAIST Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Mobilityhttps://gt.kaist.ac.kr
2022.07.14 View 16272 -
 An AI-based, Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated (IOI) GPS System to Bring Seismic Waves in the Terrains of Positioning Technology
KAIST breaks new grounds in positioning technology with an AI-integrated GPS board that works both indoors and out
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 8th that Professor Dong-Soo Han's research team (Intelligent Service Integration Lab) from the School of Computing has developed a GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors with quality precision regardless of the environment.
This Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated GPS System, or IOI GPS System, for short, uses the GPS signals outdoors and estimates locations indoors using signals from multiple sources like an inertial sensor, pressure sensors, geomagnetic sensors, and light sensors. To this end, the research team developed techniques to detect environmental changes such as entering a building, and methods to detect entrances, ground floors, stairs, elevators and levels of buildings by utilizing artificial intelligence techniques. Various landmark detecting techniques were also incorporated with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR), a navigation tool for pedestrians, to devise the so-called “Sensor-Fusion Positioning Algorithm”.
To date, it was common to estimate locations based on wireless LAN signals or base station signals in a space where the GPS signal could not reach. However, the IOI GPS enables positioning even in buildings without signals nor indoor maps.
The algorithm developed by the research team can provide accurate floor information within a building where even big tech companies like Google and Apple's positioning services do not provide. Unlike other positioning methods that rely on visual data, geomagnetic positioning techniques, or wireless LAN, this system also has the advantage of not requiring any prior preparation. In other words, the foundation to enable the usage of a universal GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors anywhere in the world is now ready.
The research team also produced a circuit board for the purpose of operating the IOI GPS System, mounted with chips to receive and process GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth signals, along with an inertial sensor, a barometer, a magnetometer, and a light sensor. The sensor-fusion positioning algorithm the lab has developed is also incorporated in the board.
When the accuracy of the IOI GPS board was tested in the N1 building of KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon, it achieved an accuracy of about 95% in floor estimation and an accuracy of about 3 to 6 meters in distance estimation. As for the indoor/outdoor transition, the navigational mode change was completed in about 0.3 seconds. When it was combined with the PDR technique, the estimation accuracy improved further down to a scope of one meter.
The research team is now working on assembling a tag with a built-in positioning board and applying it to location-based docent services for visitors at museums, science centers, and art galleries. The IOI GPS tag can be used for the purpose of tracking children and/or the elderly, and it can also be used to locate people or rescue workers lost in disaster-ridden or hazardous sites. On a different note, the sensor-fusion positioning algorithm and positioning board for vehicles are also under development for the tracking of vehicles entering indoor areas like underground parking lots.
When the IOI GPS board for vehicles is manufactured, the research team will work to collaborate with car manufacturers and car rental companies, and will also develop a sensor-fusion positioning algorithm for smartphones. Telecommunication companies seeking to diversify their programs in the field of location-based services will also be interested in the use the IOI GPS.
Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing, who leads the research team, said, “This is the first time to develop an indoor/outdoor integrated GPS system that can pinpoint locations in a building where there is no wireless signal or an indoor map, and there are an infinite number of areas it can be applied to. When the integration with the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS) and the Korean GPS (KPS) System that began this year, is finally completed, Korea can become the leader in the field of GPS both indoors and outdoors, and we also have plans to manufacture semi-conductor chips for the IOI GPS System to keep the tech-gap between Korea and the followers.”
He added, "The guidance services at science centers, museums, and art galleries that uses IOI GPS tags can provide a set of data that would be very helpful for analyzing the visitors’ viewing traces. It is an essential piece of information required when the time comes to decide when to organize the next exhibit. We will be working on having it applied to the National Science Museum, first.”
The projects to develop the IOI GPS system and the trace analysis system for science centers were supported through Science, Culture, Exhibits and Services Capability Enhancement Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile: Dong-Soo Han, Ph.D.Professorddsshhan@kaist.ac.krhttp://isilab.kaist.ac.kr
Intelligent Service Integration Lab.School of Computing
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 12746
An AI-based, Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated (IOI) GPS System to Bring Seismic Waves in the Terrains of Positioning Technology
KAIST breaks new grounds in positioning technology with an AI-integrated GPS board that works both indoors and out
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 8th that Professor Dong-Soo Han's research team (Intelligent Service Integration Lab) from the School of Computing has developed a GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors with quality precision regardless of the environment.
This Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated GPS System, or IOI GPS System, for short, uses the GPS signals outdoors and estimates locations indoors using signals from multiple sources like an inertial sensor, pressure sensors, geomagnetic sensors, and light sensors. To this end, the research team developed techniques to detect environmental changes such as entering a building, and methods to detect entrances, ground floors, stairs, elevators and levels of buildings by utilizing artificial intelligence techniques. Various landmark detecting techniques were also incorporated with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR), a navigation tool for pedestrians, to devise the so-called “Sensor-Fusion Positioning Algorithm”.
To date, it was common to estimate locations based on wireless LAN signals or base station signals in a space where the GPS signal could not reach. However, the IOI GPS enables positioning even in buildings without signals nor indoor maps.
The algorithm developed by the research team can provide accurate floor information within a building where even big tech companies like Google and Apple's positioning services do not provide. Unlike other positioning methods that rely on visual data, geomagnetic positioning techniques, or wireless LAN, this system also has the advantage of not requiring any prior preparation. In other words, the foundation to enable the usage of a universal GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors anywhere in the world is now ready.
The research team also produced a circuit board for the purpose of operating the IOI GPS System, mounted with chips to receive and process GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth signals, along with an inertial sensor, a barometer, a magnetometer, and a light sensor. The sensor-fusion positioning algorithm the lab has developed is also incorporated in the board.
When the accuracy of the IOI GPS board was tested in the N1 building of KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon, it achieved an accuracy of about 95% in floor estimation and an accuracy of about 3 to 6 meters in distance estimation. As for the indoor/outdoor transition, the navigational mode change was completed in about 0.3 seconds. When it was combined with the PDR technique, the estimation accuracy improved further down to a scope of one meter.
The research team is now working on assembling a tag with a built-in positioning board and applying it to location-based docent services for visitors at museums, science centers, and art galleries. The IOI GPS tag can be used for the purpose of tracking children and/or the elderly, and it can also be used to locate people or rescue workers lost in disaster-ridden or hazardous sites. On a different note, the sensor-fusion positioning algorithm and positioning board for vehicles are also under development for the tracking of vehicles entering indoor areas like underground parking lots.
When the IOI GPS board for vehicles is manufactured, the research team will work to collaborate with car manufacturers and car rental companies, and will also develop a sensor-fusion positioning algorithm for smartphones. Telecommunication companies seeking to diversify their programs in the field of location-based services will also be interested in the use the IOI GPS.
Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing, who leads the research team, said, “This is the first time to develop an indoor/outdoor integrated GPS system that can pinpoint locations in a building where there is no wireless signal or an indoor map, and there are an infinite number of areas it can be applied to. When the integration with the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS) and the Korean GPS (KPS) System that began this year, is finally completed, Korea can become the leader in the field of GPS both indoors and outdoors, and we also have plans to manufacture semi-conductor chips for the IOI GPS System to keep the tech-gap between Korea and the followers.”
He added, "The guidance services at science centers, museums, and art galleries that uses IOI GPS tags can provide a set of data that would be very helpful for analyzing the visitors’ viewing traces. It is an essential piece of information required when the time comes to decide when to organize the next exhibit. We will be working on having it applied to the National Science Museum, first.”
The projects to develop the IOI GPS system and the trace analysis system for science centers were supported through Science, Culture, Exhibits and Services Capability Enhancement Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile: Dong-Soo Han, Ph.D.Professorddsshhan@kaist.ac.krhttp://isilab.kaist.ac.kr
Intelligent Service Integration Lab.School of Computing
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 12746 -
 Atomically-Smooth Gold Crystals Help to Compress Light for Nanophotonic Applications
Highly compressed mid-infrared optical waves in a thin dielectric crystal on monocrystalline gold substrate investigated for the first time using a high-resolution scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope.
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of ultra-thin dielectric crystals in next-generation optoelectronic devices based on strong light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
Phonon-polaritons are collective oscillations of ions in polar dielectrics coupled to electromagnetic waves of light, whose electromagnetic field is much more compressed compared to the light wavelength. Recently, it was demonstrated that the phonon-polaritons in thin van der Waals crystals can be compressed even further when the material is placed on top of a highly conductive metal. In such a configuration, charges in the polaritonic crystal are “reflected” in the metal, and their coupling with light results in a new type of polariton waves called the image phonon-polaritons. Highly compressed image modes provide strong light-matter interactions, but are very sensitive to the substrate roughness, which hinders their practical application.
Challenged by these limitations, four research groups combined their efforts to develop a unique experimental platform using advanced fabrication and measurement methods. Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 13.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the hyperbolic image phonon-polaritons (HIP) propagating in a 63 nm-thick slab of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on a monocrystalline gold substrate, showing the mid-infrared light waves in dielectric crystal compressed by a hundred times.
Professor Jang and a research professor in his group, Sergey Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of HIP waves propagating for many wavelengths, and detected a signal from the ultra-compressed high-order HIP in a regular h-BN crystals for the first time. They showed that the phonon-polaritons in van der Waals crystals can be significantly more compressed without sacrificing their lifetime.
This became possible due to the atomically-smooth surfaces of the home-grown gold crystals used as a substrate for the h-BN. Practically zero surface scattering and extremely small ohmic loss in gold at mid-infrared frequencies provide a low-loss environment for the HIP propagation. The HIP mode probed by the researchers was 2.4 times more compressed and yet exhibited a similar lifetime compared to the phonon-polaritons with a low-loss dielectric substrate, resulting in a twice higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length.
The ultra-smooth monocrystalline gold flakes used in the experiment were chemically grown by the team of Professor N. Asger Mortensen from the Center for Nano Optics at the University of Southern Denmark.
Mid-infrared spectrum is particularly important for sensing applications since many important organic molecules have absorption lines in the mid-infrared. However, a large number of molecules is required by the conventional detection methods for successful operation, whereas the ultra-compressed phonon-polariton fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection limit down to a single molecule. The long lifetime of the HIP on monocrystalline gold will further improve the detection performance.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated the striking similarity between the HIP and the image graphene plasmons. Both image modes possess significantly more confined electromagnetic field, yet their lifetime remains unaffected by the shorter polariton wavelength. This observation provides a broader perspective on image polaritons in general, and highlights their superiority in terms of the nanolight waveguiding compared to the conventional low-dimensional polaritons in van der Waals crystals on a dielectric substrate.
Professor Jang said, “Our research demonstrated the advantages of image polaritons, and especially the image phonon-polaritons. These optical modes can be used in the future optoelectronic devices where both the low-loss propagation and the strong light-matter interaction are necessary. I hope that our results will pave the way for the realization of more efficient nanophotonic devices such as metasurfaces, optical switches, sensors, and other applications operating at infrared frequencies.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and The Villum Foundation, Denmark, also supported the work.
Figure. Nano-tip is used for the ultra-high-resolution imaging of the image phonon-polaritons in hBN launched by the gold crystal edge.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2022) Near-field probing of image phonon-polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride on gold crystals. Science Advances 8, Article ID: eabn0627. Available online at https://science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abn0627.
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professor
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://janglab.org/
Min Seok Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 15194
Atomically-Smooth Gold Crystals Help to Compress Light for Nanophotonic Applications
Highly compressed mid-infrared optical waves in a thin dielectric crystal on monocrystalline gold substrate investigated for the first time using a high-resolution scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscope.
KAIST researchers and their collaborators at home and abroad have successfully demonstrated a new platform for guiding the compressed light waves in very thin van der Waals crystals. Their method to guide the mid-infrared light with minimal loss will provide a breakthrough for the practical applications of ultra-thin dielectric crystals in next-generation optoelectronic devices based on strong light-matter interactions at the nanoscale.
Phonon-polaritons are collective oscillations of ions in polar dielectrics coupled to electromagnetic waves of light, whose electromagnetic field is much more compressed compared to the light wavelength. Recently, it was demonstrated that the phonon-polaritons in thin van der Waals crystals can be compressed even further when the material is placed on top of a highly conductive metal. In such a configuration, charges in the polaritonic crystal are “reflected” in the metal, and their coupling with light results in a new type of polariton waves called the image phonon-polaritons. Highly compressed image modes provide strong light-matter interactions, but are very sensitive to the substrate roughness, which hinders their practical application.
Challenged by these limitations, four research groups combined their efforts to develop a unique experimental platform using advanced fabrication and measurement methods. Their findings were published in Science Advances on July 13.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering used a highly sensitive scanning near-field optical microscope (SNOM) to directly measure the optical fields of the hyperbolic image phonon-polaritons (HIP) propagating in a 63 nm-thick slab of hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) on a monocrystalline gold substrate, showing the mid-infrared light waves in dielectric crystal compressed by a hundred times.
Professor Jang and a research professor in his group, Sergey Menabde, successfully obtained direct images of HIP waves propagating for many wavelengths, and detected a signal from the ultra-compressed high-order HIP in a regular h-BN crystals for the first time. They showed that the phonon-polaritons in van der Waals crystals can be significantly more compressed without sacrificing their lifetime.
This became possible due to the atomically-smooth surfaces of the home-grown gold crystals used as a substrate for the h-BN. Practically zero surface scattering and extremely small ohmic loss in gold at mid-infrared frequencies provide a low-loss environment for the HIP propagation. The HIP mode probed by the researchers was 2.4 times more compressed and yet exhibited a similar lifetime compared to the phonon-polaritons with a low-loss dielectric substrate, resulting in a twice higher figure of merit in terms of the normalized propagation length.
The ultra-smooth monocrystalline gold flakes used in the experiment were chemically grown by the team of Professor N. Asger Mortensen from the Center for Nano Optics at the University of Southern Denmark.
Mid-infrared spectrum is particularly important for sensing applications since many important organic molecules have absorption lines in the mid-infrared. However, a large number of molecules is required by the conventional detection methods for successful operation, whereas the ultra-compressed phonon-polariton fields can provide strong light-matter interactions at the microscopic level, thus significantly improving the detection limit down to a single molecule. The long lifetime of the HIP on monocrystalline gold will further improve the detection performance.
Furthermore, the study conducted by Professor Jang and the team demonstrated the striking similarity between the HIP and the image graphene plasmons. Both image modes possess significantly more confined electromagnetic field, yet their lifetime remains unaffected by the shorter polariton wavelength. This observation provides a broader perspective on image polaritons in general, and highlights their superiority in terms of the nanolight waveguiding compared to the conventional low-dimensional polaritons in van der Waals crystals on a dielectric substrate.
Professor Jang said, “Our research demonstrated the advantages of image polaritons, and especially the image phonon-polaritons. These optical modes can be used in the future optoelectronic devices where both the low-loss propagation and the strong light-matter interaction are necessary. I hope that our results will pave the way for the realization of more efficient nanophotonic devices such as metasurfaces, optical switches, sensors, and other applications operating at infrared frequencies.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The Korea Institute of Science and Technology, Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and The Villum Foundation, Denmark, also supported the work.
Figure. Nano-tip is used for the ultra-high-resolution imaging of the image phonon-polaritons in hBN launched by the gold crystal edge.
Publication:
Menabde, S. G., et al. (2022) Near-field probing of image phonon-polaritons in hexagonal boron nitride on gold crystals. Science Advances 8, Article ID: eabn0627. Available online at https://science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abn0627.
Profile:
Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
Associate Professor
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://janglab.org/
Min Seok Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 15194 -
 Success in Real-Time Observation of the Formation Process of Topological Solitons, a Core Technology for Next-Generation Information Transfer
< From left) Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate), Yun-Seok Choi (Ph.D.), Professor Dong Ki Yoon, and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) of the Department of Chemistry >
Professor Dong Ki Yoon's research team in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST announced on the 11th that they have succeeded in controlling the formation of topological solitons in a regular, large-area manner through the self-assembly of chiral liquid crystal materials and observing their formation process in real-time.
A soliton refers to a phenomenon where a specific wave persists without dissipating through interaction with its surroundings. In particular, even when a wave is transmitted over long distances, it retains its unique information until it reaches the desired destination. Therefore, in today's digital society, which is susceptible to hacking, solitons are highly anticipated to be the core of future communication due to their inherent high stability. Furthermore, topological solitons created using organic liquid crystal molecules are expected to be utilized as next-generation anti-counterfeiting devices and memory elements due to their unique spin directionality.
Professor Yoon's team specifically revealed the formation process of topological solitons in this study, which had not been observable in real-time under mild conditions such as room temperature until now. This was made possible by using self-assembling chiral liquid crystal materials in a confined space created by air pillars.
This research, in which Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Chemistry) and Dr. Ahram Suh participated as co-first authors, and Dr. Yun-Seok Choi and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) from the same group also participated, was published online in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on June 5th and is scheduled to be featured as the back cover of the July issue. (Paper title: "Fabrication of Arrays of Topological Solitons in Patterned Chiral Liquid Crystals for Real-Time Observation of Morphogenesis")
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research>
< Figure 2. Real-time observation of topological soliton formation using liquid crystals>
In this study, Professor Yoon's team implemented topological soliton structures at approximately 30 degrees Celsius, similar to room temperature, using chiral (asymmetric) liquid crystal materials instead of the conventional liquid crystal molecules widely used as core materials in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Generally, complex equipment is required to control the formation of topological solitons, and their formation time is very short, which has hindered research into their formation process until now.
To achieve regular formation and control of topological solitons formed by chiral liquid crystal molecules, Professor Yoon's team precisely controlled a combination of vertical alignment layers, which can orient molecules vertically, and air pillars. Specifically, they prepared concave patterns based on circular silicon material, several micrometers (one-millionth of a meter) in size, coated with a vertical alignment layer, and a glass substrate. By adjusting the gap to several micrometers and injecting chiral liquid crystal material, air pillars were spontaneously formed on the concave patterns. Subsequently, the liquid crystal molecules were vertically aligned on all substrates, inevitably causing regular distortions between the substrates, and between the substrate and the air pillars, thus developing a system where chiral molecular structures, i.e., topological solitons, could be formed.
The key to the formation and control of topological solitons lies in controlling the thermal phase transition to occur regularly as desired when cooling from the isotropic phase temperature (approximately 40 degrees Celsius) to the liquid crystal phase temperature (approximately 30 degrees Celsius), where the liquid crystal material near the air pillars is cooler than the liquid crystal material between the glass substrate and the silicon patterned parts. This is consistent with the everyday wisdom of eating steamed eggs from a 'Ttukbaegi' (earthen pot) by starting from the relatively cooler part exposed to the air (near the air pillars) rather than the hot pot part (silicon or glass substrate part).
Through real-time analysis, the research team elucidated that topological defects are formed by the naturally formed air pillars through controlled thermal phase transition, and topological solitons are formed only at the locations of these defects. This analysis technique has the potential for application in various fields, including the interpretation of topological soliton formation found in other physical phenomena such as skyrmion particles in electromagnetism.
< Figure 3. Snapshots during the formation process of regularly arranged topological solitons>
Professor Dong Ki Yoon stated, "General topological solitons are known to be highly stable, capable only of generation or annihilation. Through the results of this research, we can understand the formation process of solitons in more detail, and they can be used as spintronics application technology, considered a next-generation semiconductor device for storing and recording information."
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Ivan Smalyukh's laboratory at the University of Colorado, Department of Physics, and was supported by the Multiscale Chiral Structures Research Center and strategic projects of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2022.07.11 View 508
Success in Real-Time Observation of the Formation Process of Topological Solitons, a Core Technology for Next-Generation Information Transfer
< From left) Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate), Yun-Seok Choi (Ph.D.), Professor Dong Ki Yoon, and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) of the Department of Chemistry >
Professor Dong Ki Yoon's research team in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST announced on the 11th that they have succeeded in controlling the formation of topological solitons in a regular, large-area manner through the self-assembly of chiral liquid crystal materials and observing their formation process in real-time.
A soliton refers to a phenomenon where a specific wave persists without dissipating through interaction with its surroundings. In particular, even when a wave is transmitted over long distances, it retains its unique information until it reaches the desired destination. Therefore, in today's digital society, which is susceptible to hacking, solitons are highly anticipated to be the core of future communication due to their inherent high stability. Furthermore, topological solitons created using organic liquid crystal molecules are expected to be utilized as next-generation anti-counterfeiting devices and memory elements due to their unique spin directionality.
Professor Yoon's team specifically revealed the formation process of topological solitons in this study, which had not been observable in real-time under mild conditions such as room temperature until now. This was made possible by using self-assembling chiral liquid crystal materials in a confined space created by air pillars.
This research, in which Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Chemistry) and Dr. Ahram Suh participated as co-first authors, and Dr. Yun-Seok Choi and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) from the same group also participated, was published online in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on June 5th and is scheduled to be featured as the back cover of the July issue. (Paper title: "Fabrication of Arrays of Topological Solitons in Patterned Chiral Liquid Crystals for Real-Time Observation of Morphogenesis")
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research>
< Figure 2. Real-time observation of topological soliton formation using liquid crystals>
In this study, Professor Yoon's team implemented topological soliton structures at approximately 30 degrees Celsius, similar to room temperature, using chiral (asymmetric) liquid crystal materials instead of the conventional liquid crystal molecules widely used as core materials in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Generally, complex equipment is required to control the formation of topological solitons, and their formation time is very short, which has hindered research into their formation process until now.
To achieve regular formation and control of topological solitons formed by chiral liquid crystal molecules, Professor Yoon's team precisely controlled a combination of vertical alignment layers, which can orient molecules vertically, and air pillars. Specifically, they prepared concave patterns based on circular silicon material, several micrometers (one-millionth of a meter) in size, coated with a vertical alignment layer, and a glass substrate. By adjusting the gap to several micrometers and injecting chiral liquid crystal material, air pillars were spontaneously formed on the concave patterns. Subsequently, the liquid crystal molecules were vertically aligned on all substrates, inevitably causing regular distortions between the substrates, and between the substrate and the air pillars, thus developing a system where chiral molecular structures, i.e., topological solitons, could be formed.
The key to the formation and control of topological solitons lies in controlling the thermal phase transition to occur regularly as desired when cooling from the isotropic phase temperature (approximately 40 degrees Celsius) to the liquid crystal phase temperature (approximately 30 degrees Celsius), where the liquid crystal material near the air pillars is cooler than the liquid crystal material between the glass substrate and the silicon patterned parts. This is consistent with the everyday wisdom of eating steamed eggs from a 'Ttukbaegi' (earthen pot) by starting from the relatively cooler part exposed to the air (near the air pillars) rather than the hot pot part (silicon or glass substrate part).
Through real-time analysis, the research team elucidated that topological defects are formed by the naturally formed air pillars through controlled thermal phase transition, and topological solitons are formed only at the locations of these defects. This analysis technique has the potential for application in various fields, including the interpretation of topological soliton formation found in other physical phenomena such as skyrmion particles in electromagnetism.
< Figure 3. Snapshots during the formation process of regularly arranged topological solitons>
Professor Dong Ki Yoon stated, "General topological solitons are known to be highly stable, capable only of generation or annihilation. Through the results of this research, we can understand the formation process of solitons in more detail, and they can be used as spintronics application technology, considered a next-generation semiconductor device for storing and recording information."
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Ivan Smalyukh's laboratory at the University of Colorado, Department of Physics, and was supported by the Multiscale Chiral Structures Research Center and strategic projects of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2022.07.11 View 508 -
 The 1st Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp bridges KAIST and Silicon Valley, US
Twenty KAIST students gave a go at selling their business ideas to investors at Silicon Valley on the “Pitch Day” at 2022 Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp.
From Tuesday, June 21 to Monday, July 4, 2022, KAIST held the first Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp (GESC).
The 2022 GESC, which was organized in collaboration with Stanford Technology Ventures Program (STVP), KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, and KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, was a pilot program that offered opportunities of experiencing and learning about the cases of startup companies in Silicon Valley and a chance to expand businesses to Silicon Valley through networking.
Twenty KAIST students, including pre-startup entrepreneurs and students interested in global entrepreneurship with less than one year of business experience were selected. The first week of the program was organized by Startup KAIST while the second week program was organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) at KAIST in collaboration with the Stanford Technology Venture Program (STVP), KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, and KOTRA at Silicon Valley.
Dr. Mo-Yun Lei Fong, the Executive Director of STVP, said, “The program offered an opportunity for us to realize our vision of empowering aspiring entrepreneurs to become global citizens who create and scale responsible innovation. By collaborating with KAIST and offering entrepreneurial insights to Korean students, we are able to have a positive impact on a global scale.” Mo added, “The program also enabled STVP to build bridges, learn from the students, and refine our culturally relevant curriculum by understanding Korean culture and ideas.”
On the “Pitch Day” on July 1, following a special talk by Dr. Chong-Moon Lee, the Chairman of AmBex Venture Partners, the students presented their team business ideas such as an AI-assisted, noise-canceling pillow devised for better sleep, a metaverse dating application, an XR virtual conferencing system, and an AI language tutoring application to the entice global investors’ curiosity. The invited investors, majorly based in Silicon Valley, commented that all the presentation was very exciting, and the level of pitches was beyond the expectation considering that the students have given only two weeks.
Ms. Seunghee Lee of the team “Bored KAIST Yacht Club”, which was awarded the first prize, explained, “our item, called ‘Meta-Everland’, is a service that offers real-time dating experiences similar to off-line dates. The GESC taught me that anybody can launch a startup as long as they are willing. Developing a business model from ideation and taking it to the actual pitching was challenging, but it was a very thrilling experience at the same time.” Lee added, “Most importantly, over the course of the program and the final pitch, I found out that an interesting idea can attract investors interest even at a very early stage of the launching.”
Mr. Byunghoon Hwang, a student who attended the program said, “Having learned the thoughts and attitudes the people at the front line of Silicon Valley, my views on career and launching of a start-up have been expanded a lot.”
Ms. Marina Mondragon, another attendee at the program, also said that the program was very meaningful because she was able to learn the difference between the ecosystem for the new start-up businesses at Korea and at Silicon Valley through her talks with the CEOs at Silicon Valley.
The program was co-organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST International Office and Startup of KAIST. Dr. Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President for KAIST International Office, who guided students in Silicon Valley, said, “I believe the GESC program broadened the views and entrepreneurial mindset of students. After joining this program, students stepped forward to become a founder of startups.” In addition, Dr. Young-Tae Kim, the Associate Vice President of the Institute for Startup KAIST, addressed “Startup KAIST will support business items founded via the program through various other programs in order to enhance their competitiveness in the global market.”
The GSP and Startup KAIST will continuously revamp the program by selecting distinguished fellows to join the program and coming up with innovative startup items.
Profile:
Sooa Lee, Ph.D.
Research Assistant Professor
slee900@kaist.ac.kr
Center for Global Strategies and Planning
Office of Global Initiatives
KAIST International Office
https://io.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.05 View 13672
The 1st Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp bridges KAIST and Silicon Valley, US
Twenty KAIST students gave a go at selling their business ideas to investors at Silicon Valley on the “Pitch Day” at 2022 Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp.
From Tuesday, June 21 to Monday, July 4, 2022, KAIST held the first Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp (GESC).
The 2022 GESC, which was organized in collaboration with Stanford Technology Ventures Program (STVP), KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, and KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, was a pilot program that offered opportunities of experiencing and learning about the cases of startup companies in Silicon Valley and a chance to expand businesses to Silicon Valley through networking.
Twenty KAIST students, including pre-startup entrepreneurs and students interested in global entrepreneurship with less than one year of business experience were selected. The first week of the program was organized by Startup KAIST while the second week program was organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) at KAIST in collaboration with the Stanford Technology Venture Program (STVP), KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, and KOTRA at Silicon Valley.
Dr. Mo-Yun Lei Fong, the Executive Director of STVP, said, “The program offered an opportunity for us to realize our vision of empowering aspiring entrepreneurs to become global citizens who create and scale responsible innovation. By collaborating with KAIST and offering entrepreneurial insights to Korean students, we are able to have a positive impact on a global scale.” Mo added, “The program also enabled STVP to build bridges, learn from the students, and refine our culturally relevant curriculum by understanding Korean culture and ideas.”
On the “Pitch Day” on July 1, following a special talk by Dr. Chong-Moon Lee, the Chairman of AmBex Venture Partners, the students presented their team business ideas such as an AI-assisted, noise-canceling pillow devised for better sleep, a metaverse dating application, an XR virtual conferencing system, and an AI language tutoring application to the entice global investors’ curiosity. The invited investors, majorly based in Silicon Valley, commented that all the presentation was very exciting, and the level of pitches was beyond the expectation considering that the students have given only two weeks.
Ms. Seunghee Lee of the team “Bored KAIST Yacht Club”, which was awarded the first prize, explained, “our item, called ‘Meta-Everland’, is a service that offers real-time dating experiences similar to off-line dates. The GESC taught me that anybody can launch a startup as long as they are willing. Developing a business model from ideation and taking it to the actual pitching was challenging, but it was a very thrilling experience at the same time.” Lee added, “Most importantly, over the course of the program and the final pitch, I found out that an interesting idea can attract investors interest even at a very early stage of the launching.”
Mr. Byunghoon Hwang, a student who attended the program said, “Having learned the thoughts and attitudes the people at the front line of Silicon Valley, my views on career and launching of a start-up have been expanded a lot.”
Ms. Marina Mondragon, another attendee at the program, also said that the program was very meaningful because she was able to learn the difference between the ecosystem for the new start-up businesses at Korea and at Silicon Valley through her talks with the CEOs at Silicon Valley.
The program was co-organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST International Office and Startup of KAIST. Dr. Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President for KAIST International Office, who guided students in Silicon Valley, said, “I believe the GESC program broadened the views and entrepreneurial mindset of students. After joining this program, students stepped forward to become a founder of startups.” In addition, Dr. Young-Tae Kim, the Associate Vice President of the Institute for Startup KAIST, addressed “Startup KAIST will support business items founded via the program through various other programs in order to enhance their competitiveness in the global market.”
The GSP and Startup KAIST will continuously revamp the program by selecting distinguished fellows to join the program and coming up with innovative startup items.
Profile:
Sooa Lee, Ph.D.
Research Assistant Professor
slee900@kaist.ac.kr
Center for Global Strategies and Planning
Office of Global Initiatives
KAIST International Office
https://io.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.05 View 13672 -
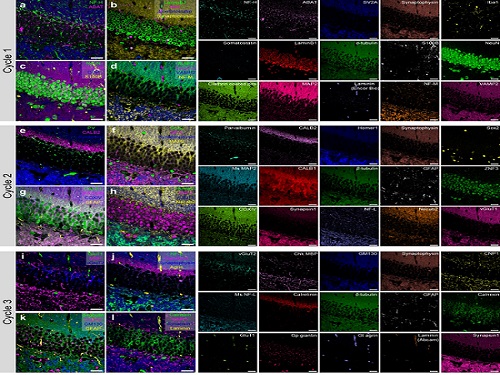 PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 11414
PICASSO Technique Drives Biological Molecules into Technicolor
The new imaging approach brings current imaging colors from four to more than 15 for mapping overlapping proteins
Pablo Picasso’s surreal cubist artistic style shifted common features into unrecognizable scenes, but a new imaging approach bearing his namesake may elucidate the most complicated subject: the brain. Employing artificial intelligence to clarify spectral color blending of tiny molecules used to stain specific proteins and other items of research interest, the PICASSO technique, allows researchers to use more than 15 colors to image and parse our overlapping proteins.
The PICASSO developers, based in Korea, published their approach on May 5 in Nature Communications.
Fluorophores — the staining molecules — emit specific colors when excited by a light, but if more than four fluorophores are used, their emitted colors overlap and blend. Researchers previously developed techniques to correct this spectral overlap by precisely defining the matrix of mixed and unmixed images. This measurement depends on reference spectra, found by identifying clear images of only one fluorophore-stained specimen or of multiple, identically prepared specimens that only contain a single fluorophore each.
“Such reference spectra measurement could be complicated to perform in highly heterogeneous specimens, such as the brain, due to the highly varied emission spectra of fluorophores depending on the subregions from which the spectra were measured,” said co-corresponding author Young-Gyu Yoon, professor in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST. He explained that the subregions would each need their own spectra reference measurements, making for an inefficient, time-consuming process. “To address this problem, we developed an approach that does not require reference spectra measurements.”
The approach is the “Process of ultra-multiplexed Imaging of biomolecules viA the unmixing of the Signals of Spectrally Overlapping fluorophores,” also known as PICASSO. Ultra-multiplexed imaging refers to visualizing the numerous individual components of a unit. Like a cinema multiplex in which each theater plays a different movie, each protein in a cell has a different role. By staining with fluorophores, researchers can begin to understand those roles.
“We devised a strategy based on information theory; unmixing is performed by iteratively minimizing the mutual information between mixed images,” said co-corresponding author Jae-Byum Chang, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST. “This allows us to get away with the assumption that the spatial distribution of different proteins is mutually exclusive and enables accurate information unmixing.”
To demonstrate PICASSO’s capabilities, the researchers applied the technique to imaging a mouse brain. With a single round of staining, they performed 15-color multiplexed imaging of a mouse brain. Although small, mouse brains are still complex, multifaceted organs that can take significant resources to map. According to the researchers, PICASSO can improve the capabilities of other imaging techniques and allow for the use of even more fluorophore colors.
Using one such imaging technique in combination with PICASSO, the team achieved 45-color multiplexed imaging of the mouse brain in only three staining and imaging cycles, according to Yoon.
“PICASSO is a versatile tool for the multiplexed biomolecule imaging of cultured cells, tissue slices and clinical specimens,” Chang said. “We anticipate that PICASSO will be useful for a broad range of applications for which biomolecules’ spatial information is important. One such application the tool would be useful for is revealing the cellular heterogeneities of tumor microenvironments, especially the heterogeneous populations of immune cells, which are closely related to cancer prognoses and the efficacy of cancer therapies.”
The Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology supported this work. Spectral imaging was performed at the Korea Basic Science Institute Western Seoul Center.
-PublicationJunyoung Seo, Yeonbo Sim, Jeewon Kim, Hyunwoo Kim, In Cho, Hoyeon Nam, Yong-Gyu Yoon, Jae-Byum Chang, “PICASSO allows ultra-multiplexed fluorescence imaging of spatiallyoverlapping proteins without reference spectra measurements,” May 5, Nature Communications (doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30168-z)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Byum ChangDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
Professor Young-Gyu YoonSchool of Electrical EngineeringCollege of EngineeringKAIST
2022.06.22 View 11414 -
 KAIST & LG U+ Team Up for Quantum Computing Solution for Ultra-Space 6G Satellite Networking
KAIST quantum computer scientists have optimized ultra-space 6G Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite networking, finding the shortest path to transfer data from a city to another place via multi-satellite hops.
The research team led by Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Dongsu Han in partnership with LG U+ verified the possibility of ultra-performance and precision communication with satellite networks using D-Wave, the first commercialized quantum computer.
Satellite network optimization has remained challenging since the network needs to be reconfigured whenever satellites approach other satellites within the connection range in a three-dimensional space. Moreover, LEO satellites orbiting at 200~2000 km above the Earth change their positions dynamically, whereas Geo-Stationary Orbit (GSO) satellites do not change their positions. Thus, LEO satellite network optimization needs to be solved in real time.
The research groups formulated the problem as a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) problem and managed to solve the problem, incorporating the connectivity and link distance limits as the constraints.
The proposed optimization algorithm is reported to be much more efficient in terms of hop counts and path length than previously reported studies using classical solutions. These results verify that a satellite network can provide ultra-performance (over 1Gbps user-perceived speed), and ultra-precision (less than 5ms end-to-end latency) network services, which are comparable to terrestrial communication.
Once QUBO is applied, “ultra-space networking” is expected to be realized with 6G. Researchers said that an ultra-space network provides communication services for an object moving at up to 10 km altitude with an extreme speed (~ 1000 km/h). Optimized LEO satellite networks can provide 6G communication services to currently unavailable areas such as air flights and deserts.
Professor Rhee, who is also the CEO of Qunova Computing, noted, “Collaboration with LG U+ was meaningful as we were able to find an industrial application for a quantum computer. We look forward to more quantum application research on real problems such as in communications, drug and material discovery, logistics, and fintech industries.”
2022.06.17 View 10236
KAIST & LG U+ Team Up for Quantum Computing Solution for Ultra-Space 6G Satellite Networking
KAIST quantum computer scientists have optimized ultra-space 6G Low-Earth Orbit (LEO) satellite networking, finding the shortest path to transfer data from a city to another place via multi-satellite hops.
The research team led by Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Dongsu Han in partnership with LG U+ verified the possibility of ultra-performance and precision communication with satellite networks using D-Wave, the first commercialized quantum computer.
Satellite network optimization has remained challenging since the network needs to be reconfigured whenever satellites approach other satellites within the connection range in a three-dimensional space. Moreover, LEO satellites orbiting at 200~2000 km above the Earth change their positions dynamically, whereas Geo-Stationary Orbit (GSO) satellites do not change their positions. Thus, LEO satellite network optimization needs to be solved in real time.
The research groups formulated the problem as a Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO) problem and managed to solve the problem, incorporating the connectivity and link distance limits as the constraints.
The proposed optimization algorithm is reported to be much more efficient in terms of hop counts and path length than previously reported studies using classical solutions. These results verify that a satellite network can provide ultra-performance (over 1Gbps user-perceived speed), and ultra-precision (less than 5ms end-to-end latency) network services, which are comparable to terrestrial communication.
Once QUBO is applied, “ultra-space networking” is expected to be realized with 6G. Researchers said that an ultra-space network provides communication services for an object moving at up to 10 km altitude with an extreme speed (~ 1000 km/h). Optimized LEO satellite networks can provide 6G communication services to currently unavailable areas such as air flights and deserts.
Professor Rhee, who is also the CEO of Qunova Computing, noted, “Collaboration with LG U+ was meaningful as we were able to find an industrial application for a quantum computer. We look forward to more quantum application research on real problems such as in communications, drug and material discovery, logistics, and fintech industries.”
2022.06.17 View 10236 -
 New Polymer Mesophase Structure Discovered
Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymer sequence
Polymers, large molecules made up of repeating smaller molecules called monomers, are found in nearly everything we use in our day-to-day lives. Polymers can be natural or created synthetically. Natural polymers, also called biopolymers, include DNA, proteins, and materials like silk, gelatin, and collagen. Synthetic polymers make up many different kinds of materials, including plastic, that are used in constructing everything from toys to industrial fiber cables to brake pads.
As polymers are formed through a process called polymerization, the monomers are connected through a chain. As the chain develops, the structure of the polymer determines its unique physical and chemical properties. Researchers are continually studying polymers, how they form, how they are structured, and how they develop these unique properties. By understanding this information, scientists can develop new uses for polymers and create new materials that can be used in a wide variety of industries.
In a paper published in Nature Communications on May 4, researchers describe a new structure found in an aqueous solution of an amphiphilic copolymer, called a bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase, that has been discovered through a random copolymer sequence.
“A new mesophase is an important discovery as it shows a new way for molecules to self-organize,” said Professor Myungeun Seo at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. “We were particularly thrilled to identify this bilayer-folded lamellar phase because pure bilayer membranes are difficult to fold thermodynamically.”
Researchers think that this mesophase structure comes from the sequence of the monomers within the copolymer. The way the different monomers arrange themselves in the chain that makes up a copolymer is important and can have implications for what the copolymer can do. Many copolymers are random, which means that their structure relies on how the monomers interact with each other. In this case, the interaction between the hydrophobic monomers associates the copolymer chains to conceal the hydrophobic domain from water. As the structure gets more complex, researchers have found that a visible order develops so that monomers can be matched up with the right pair.
“While we tend to think random means disorder, here we showed that a periodic order can spontaneously arise from the random copolymer sequence based on their collective behavior,” said Professor Seo. “We believe this comes from the sequence matching problem: finding a perfectly complementary pair for a long sequence is nearly impossible.”
This is what creates the unique structure of this newly discovered mesophase. The copolymer spontaneously folds and creates a multilamellar structure that is separated by water. A multilamellar structure refers to plate-like folds and the folded layers stack on top of each other. The resulting mesophase is birefringent, meaning light refracts through it, it is similar to liquid crystalline, and viscoelastic, which means that it is both viscous and elastic at the same time.
Looking ahead, researchers hope to learn more about this new mesophase and figure out how to control the outcome. Once more is understood about the mesophase and how it is formed, it’s possible that new mesophases could be discovered as more sequences are researched. “One of the obvious questions for us is how to control the folding frequency and adjust the folded height, which we are currently working to address. Ultimately, we want to understand how different multinary sequences can associate with another to create order and apply the knowledge to develop new materials,” said Professor Seo. The National Research Foundation, the Ministry of Education, and the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea funded this research.
-PublicationMinjoong Shin, Hayeon Kim, Geonhyeong Park, Jongmin Park, Hyungju Ahn, Dong Ki Yoon, Eunji Lee, Myungeun Seo, “Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymersequence,” May 4, 2022, Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30122-z)
-ProfileProfessor Myungeun SeoMacromolecular Materials Chemistry Lab (https://nanopsg.kaist.ac.kr/)Department of ChemistryCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.06.17 View 9868
New Polymer Mesophase Structure Discovered
Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymer sequence
Polymers, large molecules made up of repeating smaller molecules called monomers, are found in nearly everything we use in our day-to-day lives. Polymers can be natural or created synthetically. Natural polymers, also called biopolymers, include DNA, proteins, and materials like silk, gelatin, and collagen. Synthetic polymers make up many different kinds of materials, including plastic, that are used in constructing everything from toys to industrial fiber cables to brake pads.
As polymers are formed through a process called polymerization, the monomers are connected through a chain. As the chain develops, the structure of the polymer determines its unique physical and chemical properties. Researchers are continually studying polymers, how they form, how they are structured, and how they develop these unique properties. By understanding this information, scientists can develop new uses for polymers and create new materials that can be used in a wide variety of industries.
In a paper published in Nature Communications on May 4, researchers describe a new structure found in an aqueous solution of an amphiphilic copolymer, called a bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase, that has been discovered through a random copolymer sequence.
“A new mesophase is an important discovery as it shows a new way for molecules to self-organize,” said Professor Myungeun Seo at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. “We were particularly thrilled to identify this bilayer-folded lamellar phase because pure bilayer membranes are difficult to fold thermodynamically.”
Researchers think that this mesophase structure comes from the sequence of the monomers within the copolymer. The way the different monomers arrange themselves in the chain that makes up a copolymer is important and can have implications for what the copolymer can do. Many copolymers are random, which means that their structure relies on how the monomers interact with each other. In this case, the interaction between the hydrophobic monomers associates the copolymer chains to conceal the hydrophobic domain from water. As the structure gets more complex, researchers have found that a visible order develops so that monomers can be matched up with the right pair.
“While we tend to think random means disorder, here we showed that a periodic order can spontaneously arise from the random copolymer sequence based on their collective behavior,” said Professor Seo. “We believe this comes from the sequence matching problem: finding a perfectly complementary pair for a long sequence is nearly impossible.”
This is what creates the unique structure of this newly discovered mesophase. The copolymer spontaneously folds and creates a multilamellar structure that is separated by water. A multilamellar structure refers to plate-like folds and the folded layers stack on top of each other. The resulting mesophase is birefringent, meaning light refracts through it, it is similar to liquid crystalline, and viscoelastic, which means that it is both viscous and elastic at the same time.
Looking ahead, researchers hope to learn more about this new mesophase and figure out how to control the outcome. Once more is understood about the mesophase and how it is formed, it’s possible that new mesophases could be discovered as more sequences are researched. “One of the obvious questions for us is how to control the folding frequency and adjust the folded height, which we are currently working to address. Ultimately, we want to understand how different multinary sequences can associate with another to create order and apply the knowledge to develop new materials,” said Professor Seo. The National Research Foundation, the Ministry of Education, and the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea funded this research.
-PublicationMinjoong Shin, Hayeon Kim, Geonhyeong Park, Jongmin Park, Hyungju Ahn, Dong Ki Yoon, Eunji Lee, Myungeun Seo, “Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymersequence,” May 4, 2022, Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30122-z)
-ProfileProfessor Myungeun SeoMacromolecular Materials Chemistry Lab (https://nanopsg.kaist.ac.kr/)Department of ChemistryCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.06.17 View 9868 -
 Professor Juho Kim’s Team Wins Best Paper Award at ACM CHI 2022
The research team led by Professor Juho Kim from the KAIST School of Computing won a Best Paper Award and an Honorable Mention Award at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI) held between April 30 and May 6.
ACM CHI is the world’s most recognized conference in the field of human computer interactions (HCI), and is ranked number one out of all HCI-related journals and conferences based on Google Scholar’s h-5 index. Best paper awards are given to works that rank in the top one percent, and honorable mention awards are given to the top five percent of the papers accepted by the conference.
Professor Juho Kim presented a total of seven papers at ACM CHI 2022, and tied for the largest number of papers. A total of 19 papers were affiliated with KAIST, putting it fifth out of all participating institutes and thereby proving KAIST’s competence in research.
One of Professor Kim’s research teams composed of Jeongyeon Kim (first author, MS graduate) from the School of Computing, MS candidate Yubin Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Dr. Meng Xia (post-doctoral associate in the School of Computing, currently a post-doctoral associate at Carnegie Mellon University) received a best paper award for their paper, “Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design Opportunities”.
The study analyzed the difficulties experienced by learners watching video-based educational content in a mobile environment and suggests guidelines for solutions. The research team analyzed 134 survey responses and 21 interviews, and revealed that texts that are too small or overcrowded are what mainly brings down the legibility of video contents. Additionally, lighting, noise, and surrounding environments that change frequently are also important factors that may disturb a learning experience.
Based on these findings, the team analyzed the aptness of 41,722 frames from 101 video lectures for mobile environments, and confirmed that they generally show low levels of adequacy. For instance, in the case of text sizes, only 24.5% of the frames were shown to be adequate for learning in mobile environments. To overcome this issue, the research team suggested a guideline that may improve the legibility of video contents and help overcome the difficulties arising from mobile learning environments.
The importance of and dependency on video-based learning continue to rise, especially in the wake of the pandemic, and it is meaningful that this research suggested a means to analyze and tackle the difficulties of users that learn from the small screens of mobile devices. Furthermore, the paper also suggested technology that can solve problems related to video-based learning through human-AI collaborations, enhancing existing video lectures and improving learning experiences. This technology can be applied to various video-based platforms and content creation.
Meanwhile, a research team composed of Ph.D. candidate Tae Soo Kim (first author), MS candidate DaEun Choi, and Ph.D. candidate Yoonseo Choi from the School of Computing received an honorable mention award for their paper, “Stylette: styling the Web with Natural Language”.
The research team developed a novel interface technology that allows nonexperts who are unfamiliar with technical jargon to edit website features through speech. People often find it difficult to use or find the information they need from various websites due to accessibility issues, device-related constraints, inconvenient design, style preferences, etc. However, it is not easy for laymen to edit website features without expertise in programming or design, and most end up just putting up with the inconveniences. But what if the system could read the intentions of its users from their everyday language like “emphasize this part a little more”, or “I want a more modern design”, and edit the features automatically?
Based on this question, Professor Kim’s research team developed ‘Stylette’, a system in which AI analyses its users’ speech expressed in their natural language and automatically recommends a new style that best fits their intentions. The research team created a new system by putting together language AI, visual AI, and user interface technologies. On the linguistic side, a large-scale language model AI converts the intentions of the users expressed through their everyday language into adequate style elements. On the visual side, computer vision AI compares 1.7 million existing web design features and recommends a style adequate for the current website. In an experiment where 40 nonexperts were asked to edit a website design, the subjects that used this system showed double the success rate in a time span that was 35% shorter compared to the control group.
It is meaningful that this research proposed a practical case in which AI technology constructs intuitive interactions with users. The developed technology can be applied to existing design applications and web browsers in a plug-in format, and can be utilized to improve websites or for advertisements by collecting the natural intention data of users on a large scale.
2022.06.13 View 9718
Professor Juho Kim’s Team Wins Best Paper Award at ACM CHI 2022
The research team led by Professor Juho Kim from the KAIST School of Computing won a Best Paper Award and an Honorable Mention Award at the Association for Computing Machinery Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (ACM CHI) held between April 30 and May 6.
ACM CHI is the world’s most recognized conference in the field of human computer interactions (HCI), and is ranked number one out of all HCI-related journals and conferences based on Google Scholar’s h-5 index. Best paper awards are given to works that rank in the top one percent, and honorable mention awards are given to the top five percent of the papers accepted by the conference.
Professor Juho Kim presented a total of seven papers at ACM CHI 2022, and tied for the largest number of papers. A total of 19 papers were affiliated with KAIST, putting it fifth out of all participating institutes and thereby proving KAIST’s competence in research.
One of Professor Kim’s research teams composed of Jeongyeon Kim (first author, MS graduate) from the School of Computing, MS candidate Yubin Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, and Dr. Meng Xia (post-doctoral associate in the School of Computing, currently a post-doctoral associate at Carnegie Mellon University) received a best paper award for their paper, “Mobile-Friendly Content Design for MOOCs: Challenges, Requirements, and Design Opportunities”.
The study analyzed the difficulties experienced by learners watching video-based educational content in a mobile environment and suggests guidelines for solutions. The research team analyzed 134 survey responses and 21 interviews, and revealed that texts that are too small or overcrowded are what mainly brings down the legibility of video contents. Additionally, lighting, noise, and surrounding environments that change frequently are also important factors that may disturb a learning experience.
Based on these findings, the team analyzed the aptness of 41,722 frames from 101 video lectures for mobile environments, and confirmed that they generally show low levels of adequacy. For instance, in the case of text sizes, only 24.5% of the frames were shown to be adequate for learning in mobile environments. To overcome this issue, the research team suggested a guideline that may improve the legibility of video contents and help overcome the difficulties arising from mobile learning environments.
The importance of and dependency on video-based learning continue to rise, especially in the wake of the pandemic, and it is meaningful that this research suggested a means to analyze and tackle the difficulties of users that learn from the small screens of mobile devices. Furthermore, the paper also suggested technology that can solve problems related to video-based learning through human-AI collaborations, enhancing existing video lectures and improving learning experiences. This technology can be applied to various video-based platforms and content creation.
Meanwhile, a research team composed of Ph.D. candidate Tae Soo Kim (first author), MS candidate DaEun Choi, and Ph.D. candidate Yoonseo Choi from the School of Computing received an honorable mention award for their paper, “Stylette: styling the Web with Natural Language”.
The research team developed a novel interface technology that allows nonexperts who are unfamiliar with technical jargon to edit website features through speech. People often find it difficult to use or find the information they need from various websites due to accessibility issues, device-related constraints, inconvenient design, style preferences, etc. However, it is not easy for laymen to edit website features without expertise in programming or design, and most end up just putting up with the inconveniences. But what if the system could read the intentions of its users from their everyday language like “emphasize this part a little more”, or “I want a more modern design”, and edit the features automatically?
Based on this question, Professor Kim’s research team developed ‘Stylette’, a system in which AI analyses its users’ speech expressed in their natural language and automatically recommends a new style that best fits their intentions. The research team created a new system by putting together language AI, visual AI, and user interface technologies. On the linguistic side, a large-scale language model AI converts the intentions of the users expressed through their everyday language into adequate style elements. On the visual side, computer vision AI compares 1.7 million existing web design features and recommends a style adequate for the current website. In an experiment where 40 nonexperts were asked to edit a website design, the subjects that used this system showed double the success rate in a time span that was 35% shorter compared to the control group.
It is meaningful that this research proposed a practical case in which AI technology constructs intuitive interactions with users. The developed technology can be applied to existing design applications and web browsers in a plug-in format, and can be utilized to improve websites or for advertisements by collecting the natural intention data of users on a large scale.
2022.06.13 View 9718 -
 Professor Sang Kil Cha Receives IEEE Test-of-Time Award
Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security (GSIS) in the School of Computing received the Test-of-Time Award from IEEE Security & Privacy, a top conference in the field of information security.
The Test-of-Time Award recognizes the research papers that have influenced the field of information security the most over the past decade. Three papers were selected this year, and Professor Cha is the first Korean winner of the award.
The paper by Professor Cha was published in 2012 under the title, “Unleashing Mayhem on Binary Code”. It was the first to ever suggest an algorithm that automatically finds bugs in binary code and creates exploits that links them to an attack code.
The developed algorithm is a core technique used for world-class cyber security hacking competitions like the Cyber Grand Challenge, an AI hacking contest.
Starting with this research, Professor Cha has carried out various studies to develop technologies that can find bugs and vulnerabilities through binary analyses, and is currently developing B2R2, a Korean platform that can analyze various binary codes.
2022.06.13 View 6308
Professor Sang Kil Cha Receives IEEE Test-of-Time Award
Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security (GSIS) in the School of Computing received the Test-of-Time Award from IEEE Security & Privacy, a top conference in the field of information security.
The Test-of-Time Award recognizes the research papers that have influenced the field of information security the most over the past decade. Three papers were selected this year, and Professor Cha is the first Korean winner of the award.
The paper by Professor Cha was published in 2012 under the title, “Unleashing Mayhem on Binary Code”. It was the first to ever suggest an algorithm that automatically finds bugs in binary code and creates exploits that links them to an attack code.
The developed algorithm is a core technique used for world-class cyber security hacking competitions like the Cyber Grand Challenge, an AI hacking contest.
Starting with this research, Professor Cha has carried out various studies to develop technologies that can find bugs and vulnerabilities through binary analyses, and is currently developing B2R2, a Korean platform that can analyze various binary codes.
2022.06.13 View 6308 -
 Now You Can See Floral Scents!
Optical interferometry visualizes how often lilies emit volatile organic compounds
Have you ever thought about when flowers emit their scents?
KAIST mechanical engineers and biological scientists directly visualized how often a lily releases a floral scent using a laser interferometry method. These measurement results can provide new insights for understanding and further exploring the biosynthesis and emission mechanisms of floral volatiles.
Why is it important to know this? It is well known that the fragrance of flowers affects their interactions with pollinators, microorganisms, and florivores. For instance, many flowering plants can tune their scent emission rates when pollinators are active for pollination. Petunias and the wild tobacco Nicotiana attenuata emit floral scents at night to attract night-active pollinators. Thus, visualizing scent emissions can help us understand the ecological evolution of plant-pollinator interactions.
Many groups have been trying to develop methods for scent analysis. Mass spectrometry has been one widely used method for investigating the fragrance of flowers. Although mass spectrometry reveals the quality and quantity of floral scents, it is impossible to directly measure the releasing frequency. A laser-based gas detection system and a smartphone-based detection system using chemo-responsive dyes have also been used to measure volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in real-time, but it is still hard to measure the time-dependent emission rate of floral scents.
However, the KAIST research team co-led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Sang-Gyu Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences measured a refractive index difference between the vapor of the VOCs of lilies and the air to measure the emission frequency. The floral scent vapor was detected and the refractive index of air was 1.0 while that of the major floral scent of a linalool lily was 1.46.
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “We expect this technology to be further applicable to various industrial sectors such as developing it to detect hazardous substances in a space.” The research team also plans to identify the DNA mechanism that controls floral scent secretion.
The current work entitled “Real-time visualization of scent accumulation reveals the frequency of floral scent emissions” was published in ‘Frontiers in Plant Science’ on April 18, 2022. (https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.835305).
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2021R1A2C2007835), the Rural Development Administration (PJ016403), and the KAIST-funded Global Singularity Research PREP-Program.
-Publication:H. Kim, G. Lee, J. Song, and S.-G. Kim, "Real-time visualization of scent accumulation reveals the frequency of floral scent emissions," Frontiers in Plant Science 18, 835305 (2022) (https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.835305)
-Profile:Professor Hyoungsoo Kimhttp://fil.kaist.ac.kr
@MadeInH on TwitterDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sang-Gyu Kimhttps://sites.google.com/view/kimlab/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
2022.05.25 View 10778
Now You Can See Floral Scents!
Optical interferometry visualizes how often lilies emit volatile organic compounds
Have you ever thought about when flowers emit their scents?
KAIST mechanical engineers and biological scientists directly visualized how often a lily releases a floral scent using a laser interferometry method. These measurement results can provide new insights for understanding and further exploring the biosynthesis and emission mechanisms of floral volatiles.
Why is it important to know this? It is well known that the fragrance of flowers affects their interactions with pollinators, microorganisms, and florivores. For instance, many flowering plants can tune their scent emission rates when pollinators are active for pollination. Petunias and the wild tobacco Nicotiana attenuata emit floral scents at night to attract night-active pollinators. Thus, visualizing scent emissions can help us understand the ecological evolution of plant-pollinator interactions.
Many groups have been trying to develop methods for scent analysis. Mass spectrometry has been one widely used method for investigating the fragrance of flowers. Although mass spectrometry reveals the quality and quantity of floral scents, it is impossible to directly measure the releasing frequency. A laser-based gas detection system and a smartphone-based detection system using chemo-responsive dyes have also been used to measure volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in real-time, but it is still hard to measure the time-dependent emission rate of floral scents.
However, the KAIST research team co-led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Sang-Gyu Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences measured a refractive index difference between the vapor of the VOCs of lilies and the air to measure the emission frequency. The floral scent vapor was detected and the refractive index of air was 1.0 while that of the major floral scent of a linalool lily was 1.46.
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “We expect this technology to be further applicable to various industrial sectors such as developing it to detect hazardous substances in a space.” The research team also plans to identify the DNA mechanism that controls floral scent secretion.
The current work entitled “Real-time visualization of scent accumulation reveals the frequency of floral scent emissions” was published in ‘Frontiers in Plant Science’ on April 18, 2022. (https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.835305).
This research was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2021R1A2C2007835), the Rural Development Administration (PJ016403), and the KAIST-funded Global Singularity Research PREP-Program.
-Publication:H. Kim, G. Lee, J. Song, and S.-G. Kim, "Real-time visualization of scent accumulation reveals the frequency of floral scent emissions," Frontiers in Plant Science 18, 835305 (2022) (https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.835305)
-Profile:Professor Hyoungsoo Kimhttp://fil.kaist.ac.kr
@MadeInH on TwitterDepartment of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sang-Gyu Kimhttps://sites.google.com/view/kimlab/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
2022.05.25 View 10778 -
 Energy-Efficient AI Hardware Technology Via a Brain-Inspired Stashing System
Researchers demonstrate neuromodulation-inspired stashing system for the energy-efficient learning of a spiking neural network using a self-rectifying memristor array
Researchers have proposed a novel system inspired by the neuromodulation of the brain, referred to as a ‘stashing system,’ that requires less energy consumption. The research group led by Professor Kyung Min Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a technology that can efficiently handle mathematical operations for artificial intelligence by imitating the continuous changes in the topology of the neural network according to the situation. The human brain changes its neural topology in real time, learning to store or recall memories as needed. The research group presented a new artificial intelligence learning method that directly implements these neural coordination circuit configurations.
Research on artificial intelligence is becoming very active, and the development of artificial intelligence-based electronic devices and product releases are accelerating, especially in the Fourth Industrial Revolution age. To implement artificial intelligence in electronic devices, customized hardware development should also be supported. However most electronic devices for artificial intelligence require high power consumption and highly integrated memory arrays for large-scale tasks. It has been challenging to solve these power consumption and integration limitations, and efforts have been made to find out how the human brain solves problems.
To prove the efficiency of the developed technology, the research group created artificial neural network hardware equipped with a self-rectifying synaptic array and algorithm called a ‘stashing system’ that was developed to conduct artificial intelligence learning. As a result, it was able to reduce energy by 37% within the stashing system without any accuracy degradation. This result proves that emulating the neuromodulation in humans is possible.
Professor Kim said, "In this study, we implemented the learning method of the human brain with only a simple circuit composition and through this we were able to reduce the energy needed by nearly 40 percent.”
This neuromodulation-inspired stashing system that mimics the brain’s neural activity is compatible with existing electronic devices and commercialized semiconductor hardware. It is expected to be used in the design of next-generation semiconductor chips for artificial intelligence.
This study was published in Advanced Functional Materials in March 2022 and supported by KAIST, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National NanoFab Center, and SK Hynix.
-Publication:
Woon Hyung Cheong, Jae Bum Jeon†, Jae Hyun In, Geunyoung Kim, Hanchan Song, Janho An, Juseong Park, Young Seok Kim, Cheol Seong Hwang, and Kyung Min Kim (2022)
“Demonstration of Neuromodulation-inspired Stashing System for Energy-efficient Learning of Spiking Neural Network using a Self-Rectifying Memristor Array,” Advanced FunctionalMaterials March 31, 2022 (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202200337)
-Profile:
Professor Kyung Min Kimhttp://semi.kaist.ac.kr https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=BGw8yDYAAAAJ&hl=ko
Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.18 View 12283
Energy-Efficient AI Hardware Technology Via a Brain-Inspired Stashing System
Researchers demonstrate neuromodulation-inspired stashing system for the energy-efficient learning of a spiking neural network using a self-rectifying memristor array
Researchers have proposed a novel system inspired by the neuromodulation of the brain, referred to as a ‘stashing system,’ that requires less energy consumption. The research group led by Professor Kyung Min Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a technology that can efficiently handle mathematical operations for artificial intelligence by imitating the continuous changes in the topology of the neural network according to the situation. The human brain changes its neural topology in real time, learning to store or recall memories as needed. The research group presented a new artificial intelligence learning method that directly implements these neural coordination circuit configurations.
Research on artificial intelligence is becoming very active, and the development of artificial intelligence-based electronic devices and product releases are accelerating, especially in the Fourth Industrial Revolution age. To implement artificial intelligence in electronic devices, customized hardware development should also be supported. However most electronic devices for artificial intelligence require high power consumption and highly integrated memory arrays for large-scale tasks. It has been challenging to solve these power consumption and integration limitations, and efforts have been made to find out how the human brain solves problems.
To prove the efficiency of the developed technology, the research group created artificial neural network hardware equipped with a self-rectifying synaptic array and algorithm called a ‘stashing system’ that was developed to conduct artificial intelligence learning. As a result, it was able to reduce energy by 37% within the stashing system without any accuracy degradation. This result proves that emulating the neuromodulation in humans is possible.
Professor Kim said, "In this study, we implemented the learning method of the human brain with only a simple circuit composition and through this we were able to reduce the energy needed by nearly 40 percent.”
This neuromodulation-inspired stashing system that mimics the brain’s neural activity is compatible with existing electronic devices and commercialized semiconductor hardware. It is expected to be used in the design of next-generation semiconductor chips for artificial intelligence.
This study was published in Advanced Functional Materials in March 2022 and supported by KAIST, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National NanoFab Center, and SK Hynix.
-Publication:
Woon Hyung Cheong, Jae Bum Jeon†, Jae Hyun In, Geunyoung Kim, Hanchan Song, Janho An, Juseong Park, Young Seok Kim, Cheol Seong Hwang, and Kyung Min Kim (2022)
“Demonstration of Neuromodulation-inspired Stashing System for Energy-efficient Learning of Spiking Neural Network using a Self-Rectifying Memristor Array,” Advanced FunctionalMaterials March 31, 2022 (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202200337)
-Profile:
Professor Kyung Min Kimhttp://semi.kaist.ac.kr https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=BGw8yDYAAAAJ&hl=ko
Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.18 View 12283